MICRO LAB [Inoculation, Morphology, Hemolysis]
1/42
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
43 Terms
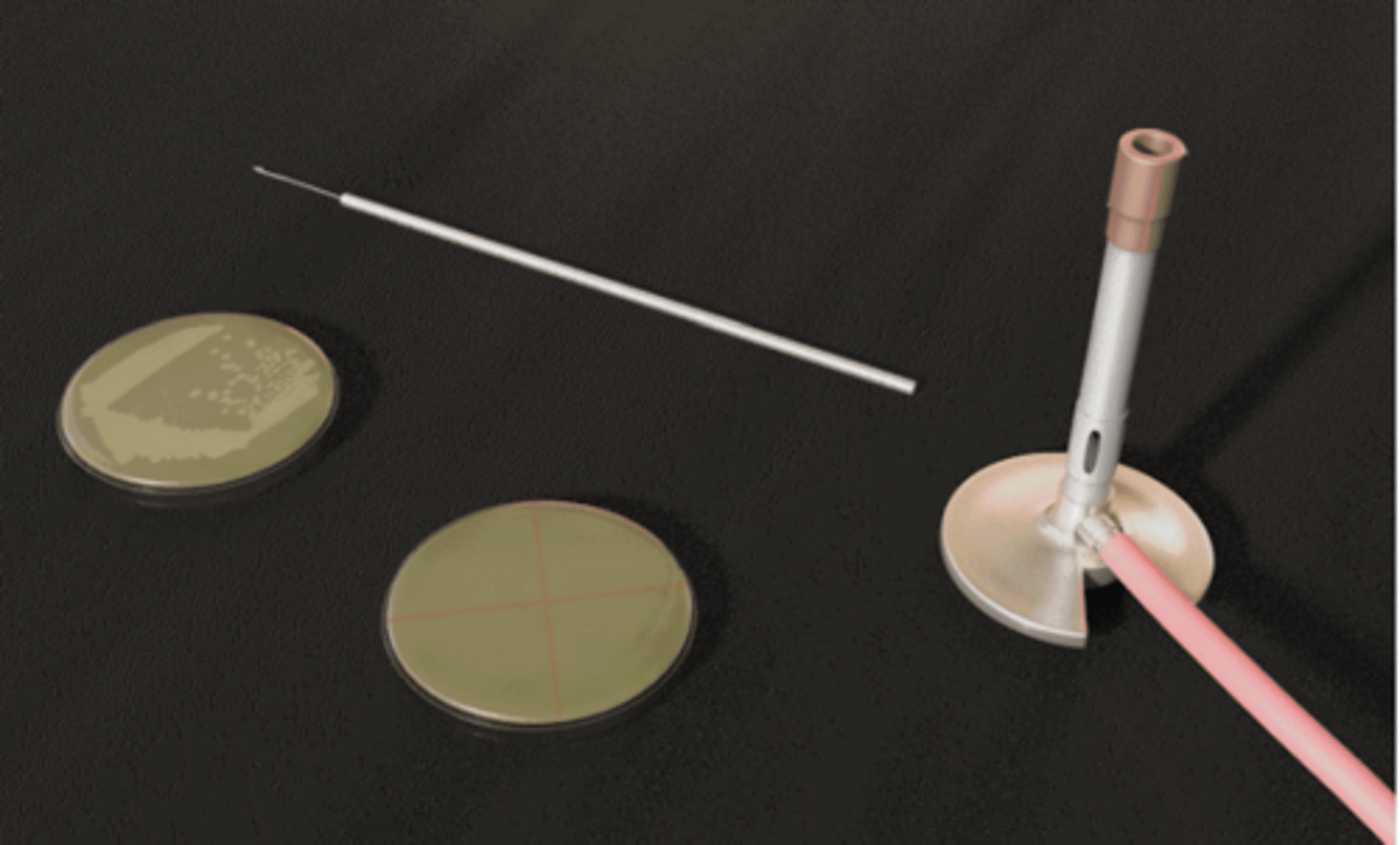
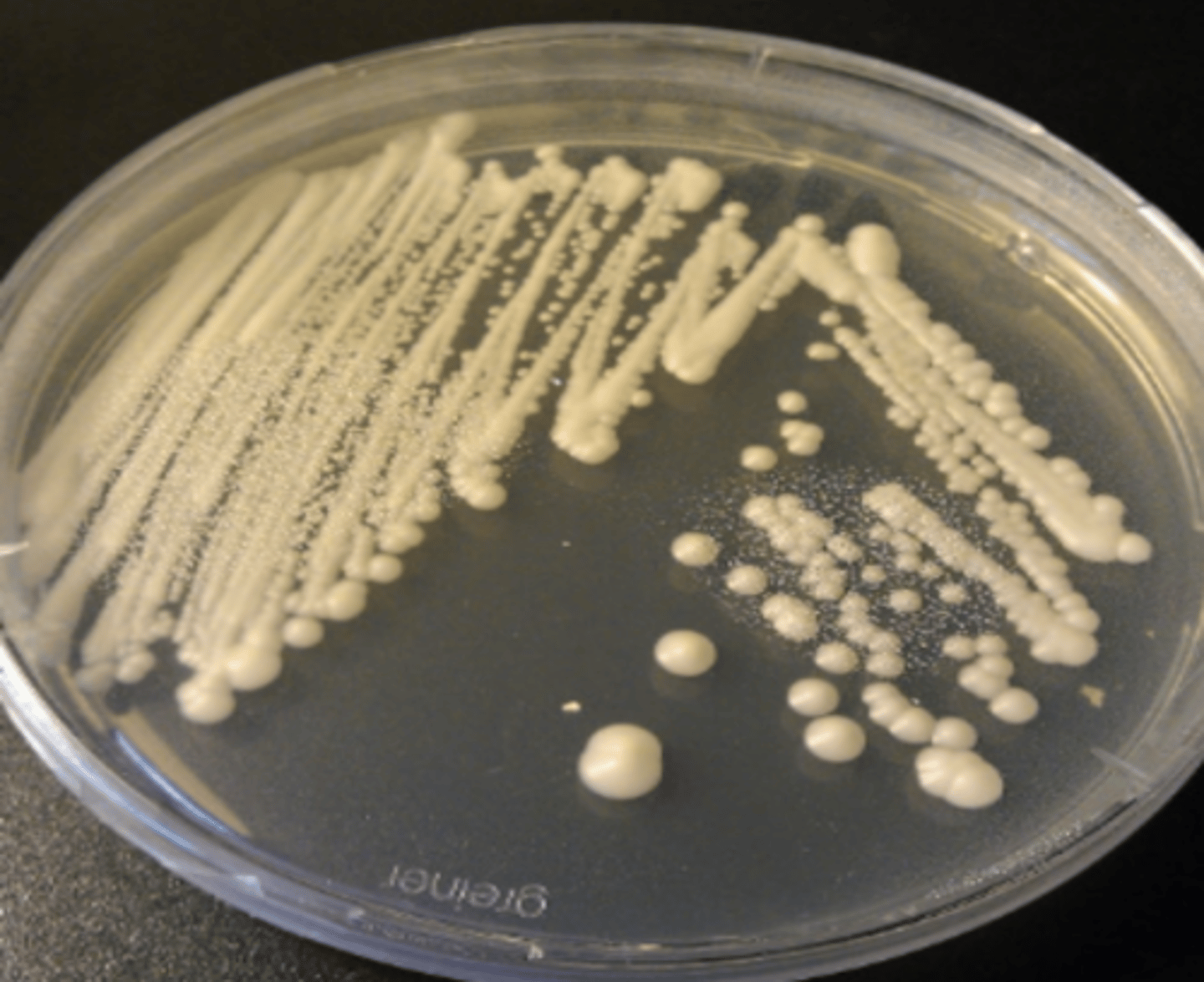
Streak plate method
What set-up?
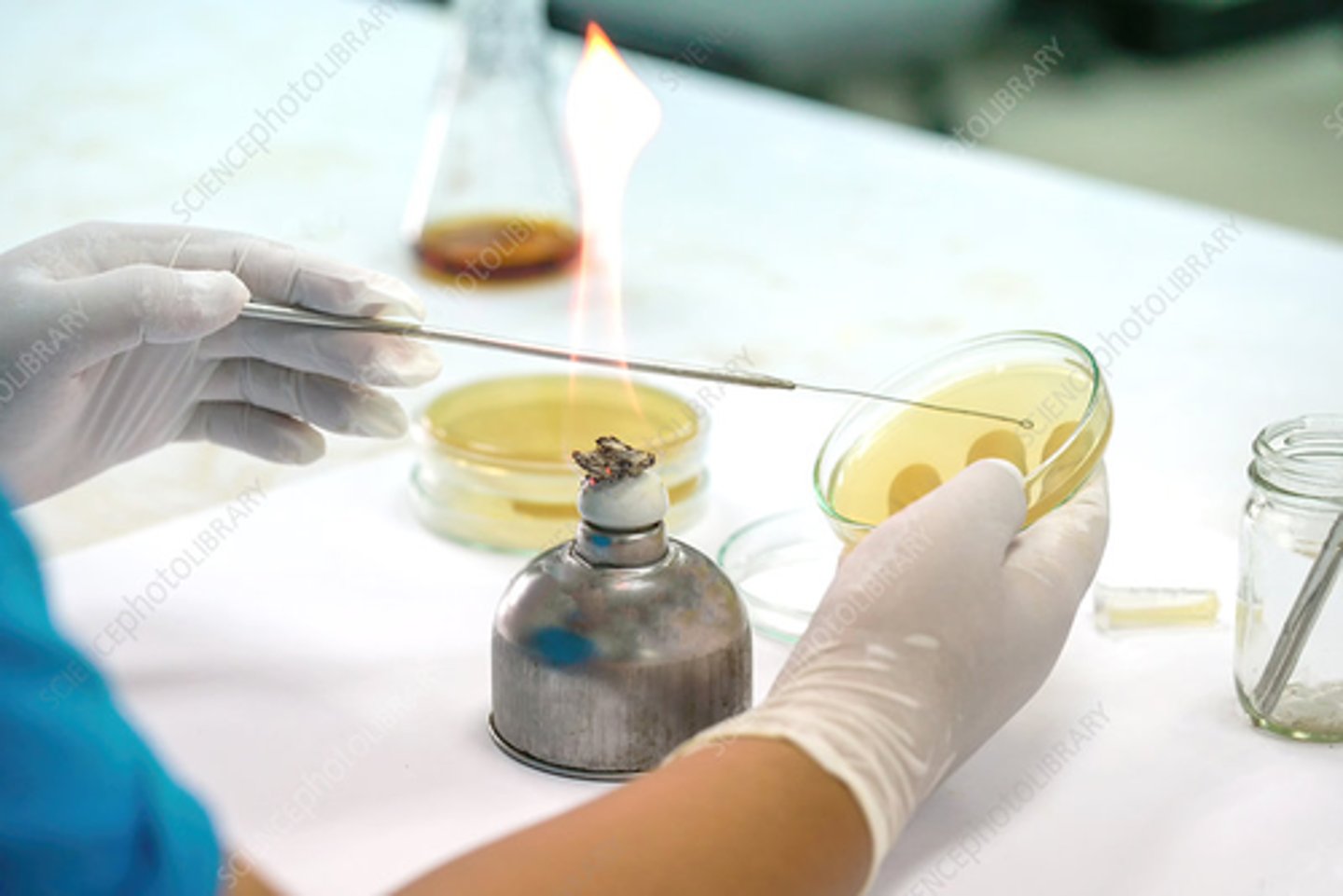

To isolate single colonies /
To isolate the organism in pure culture
What is the rationale or purpose for this set-up?
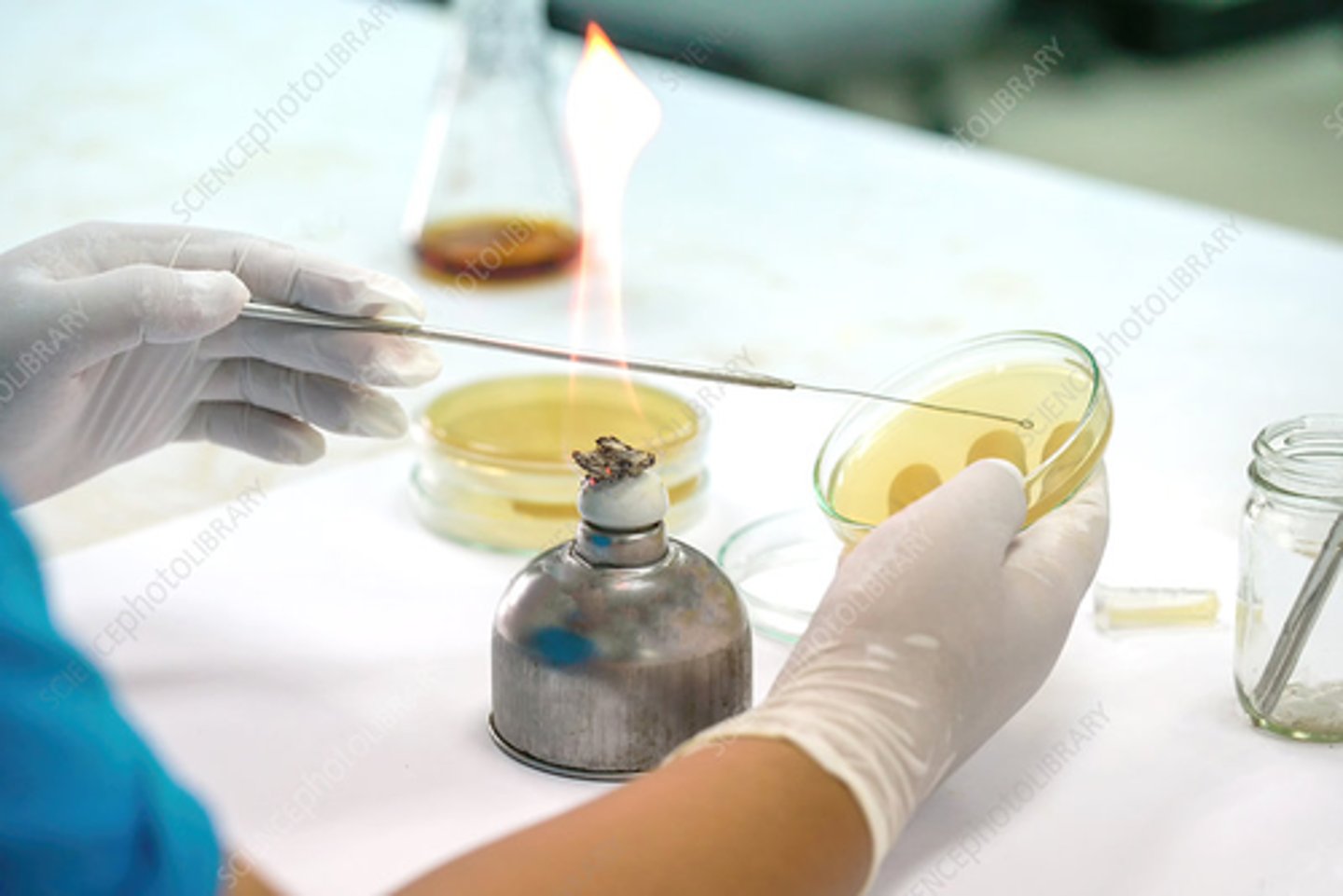

Streak plate method
What set-up?
4th quadrant
Which quadrant should have isolated colonies?
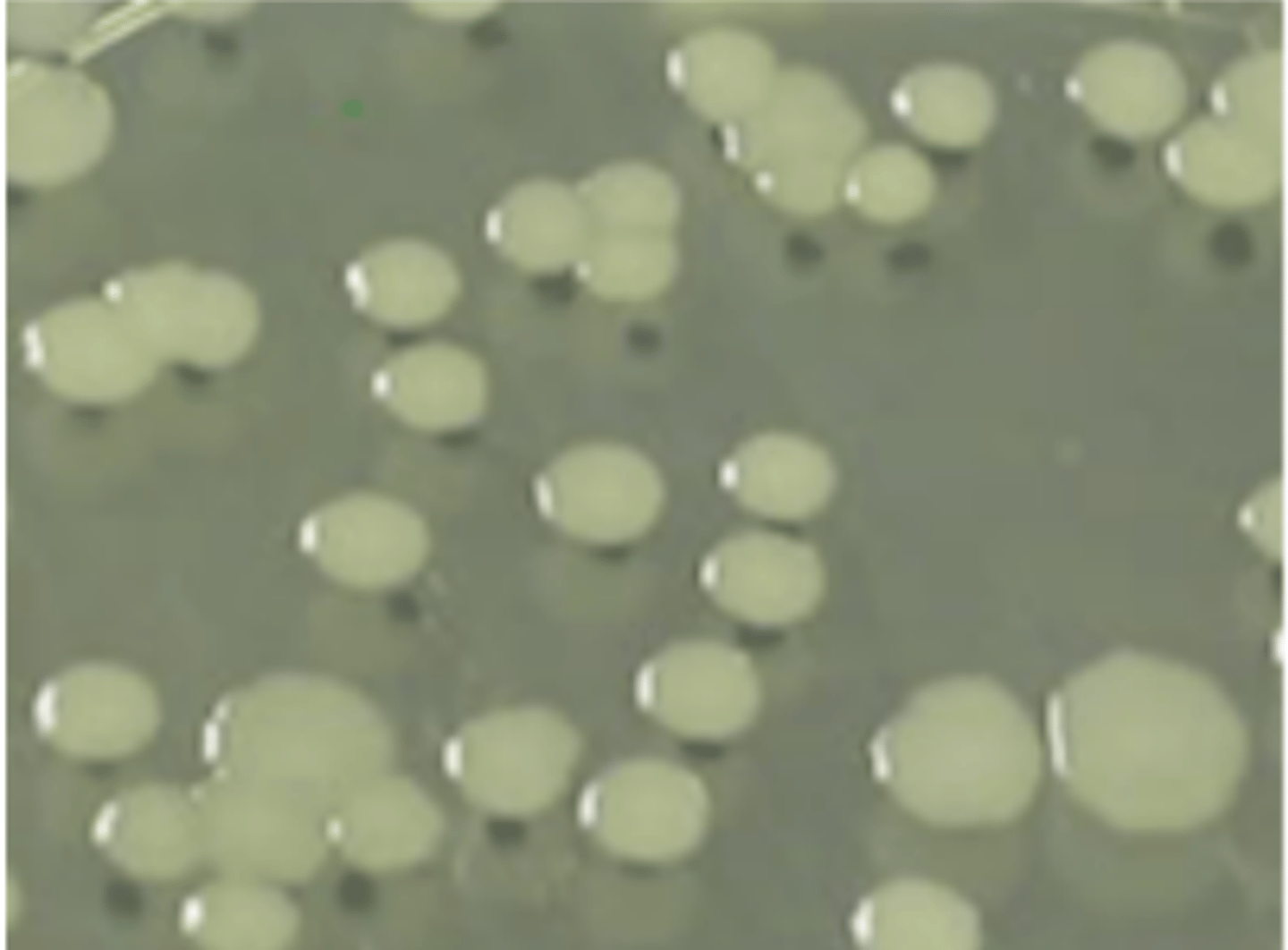
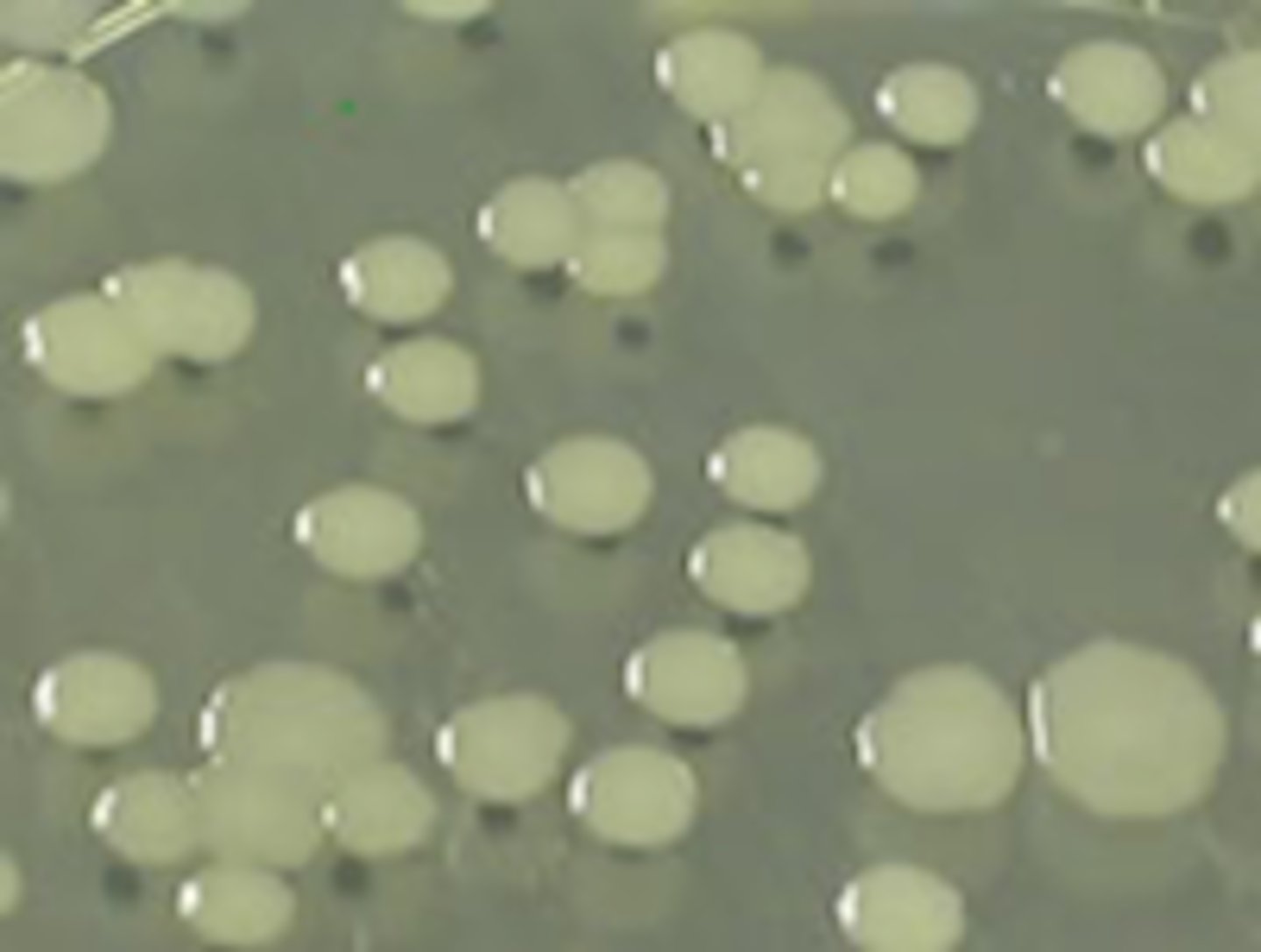
Punctiform (tiny)
Identify the SHAPE
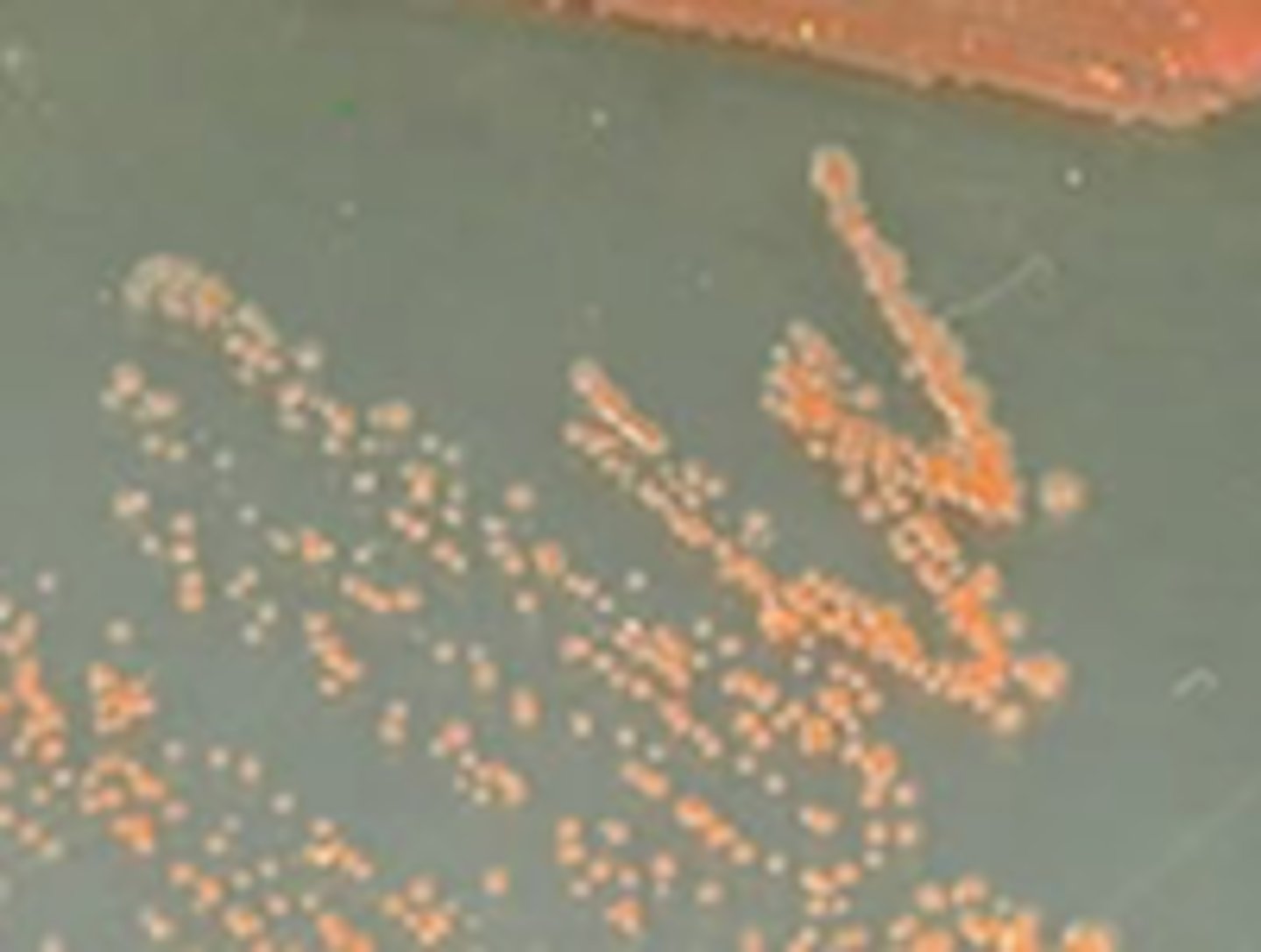

Circular
Identify the SHAPE
Irregular
Identify the SHAPE
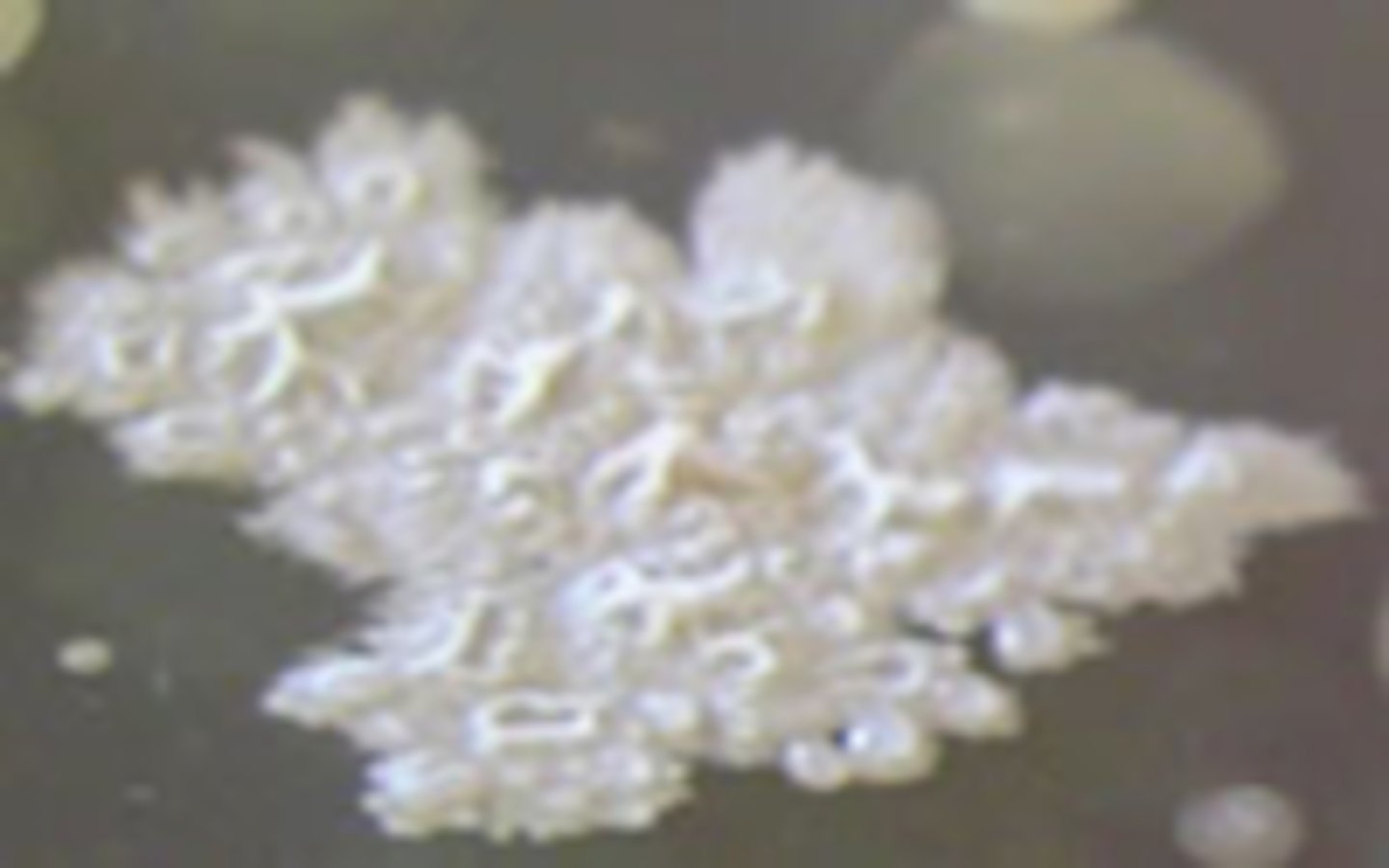

Entire (smooth)
Identify the MARGIN
Undulate (wavy)
Identify the MARGIN
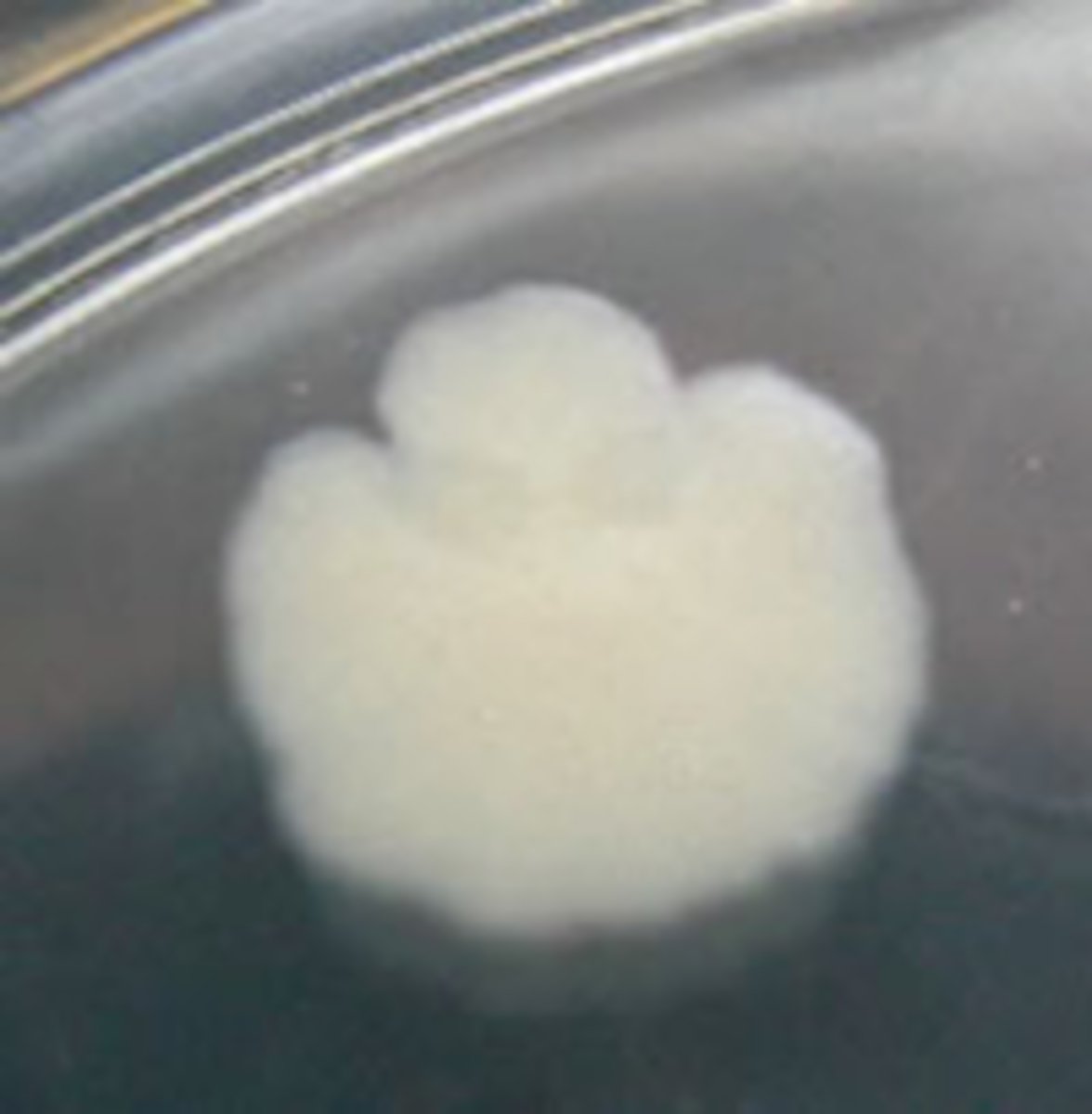

Rhizoid
Identify the MARGIN
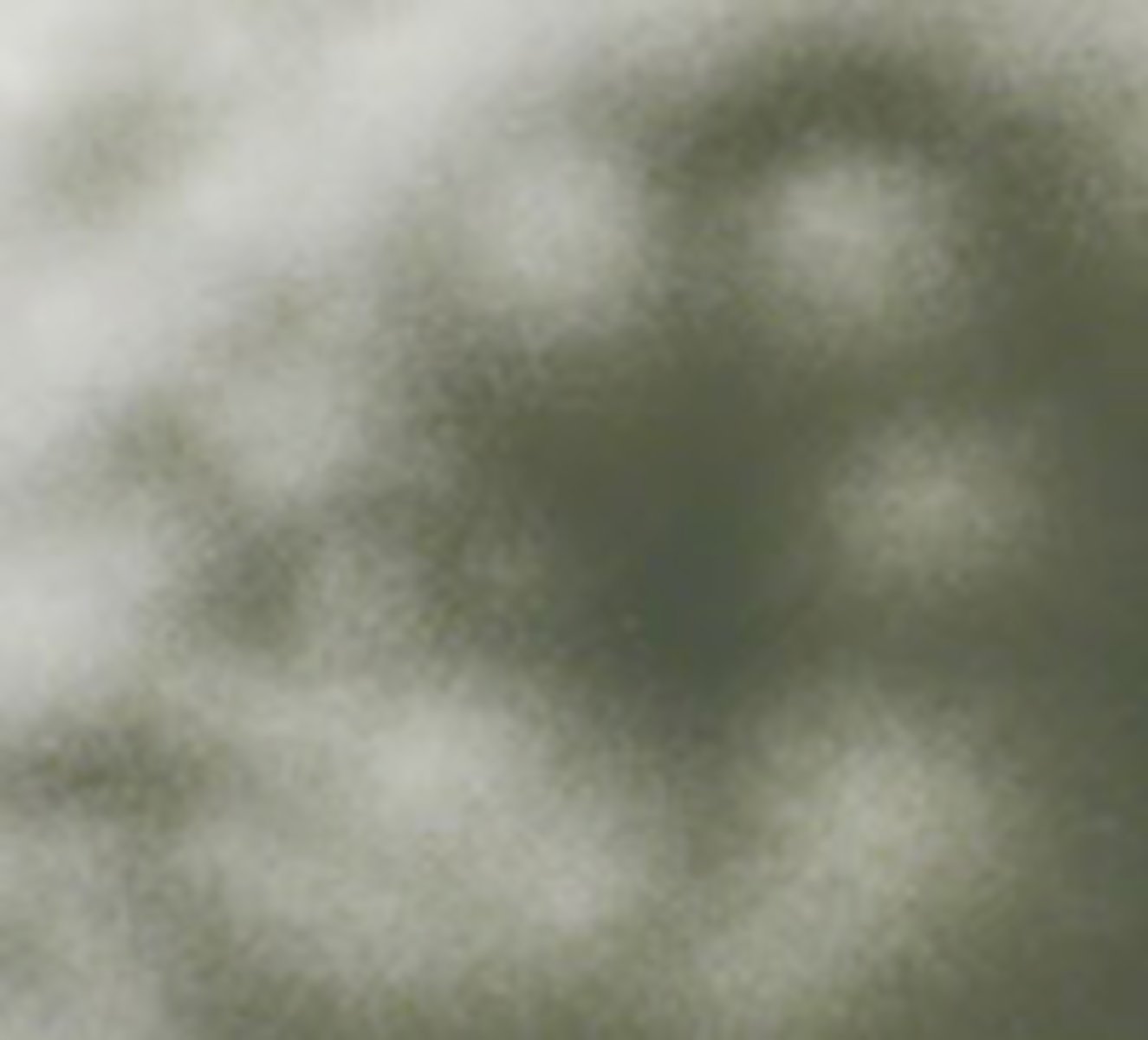

Lobate
Identify the MARGIN
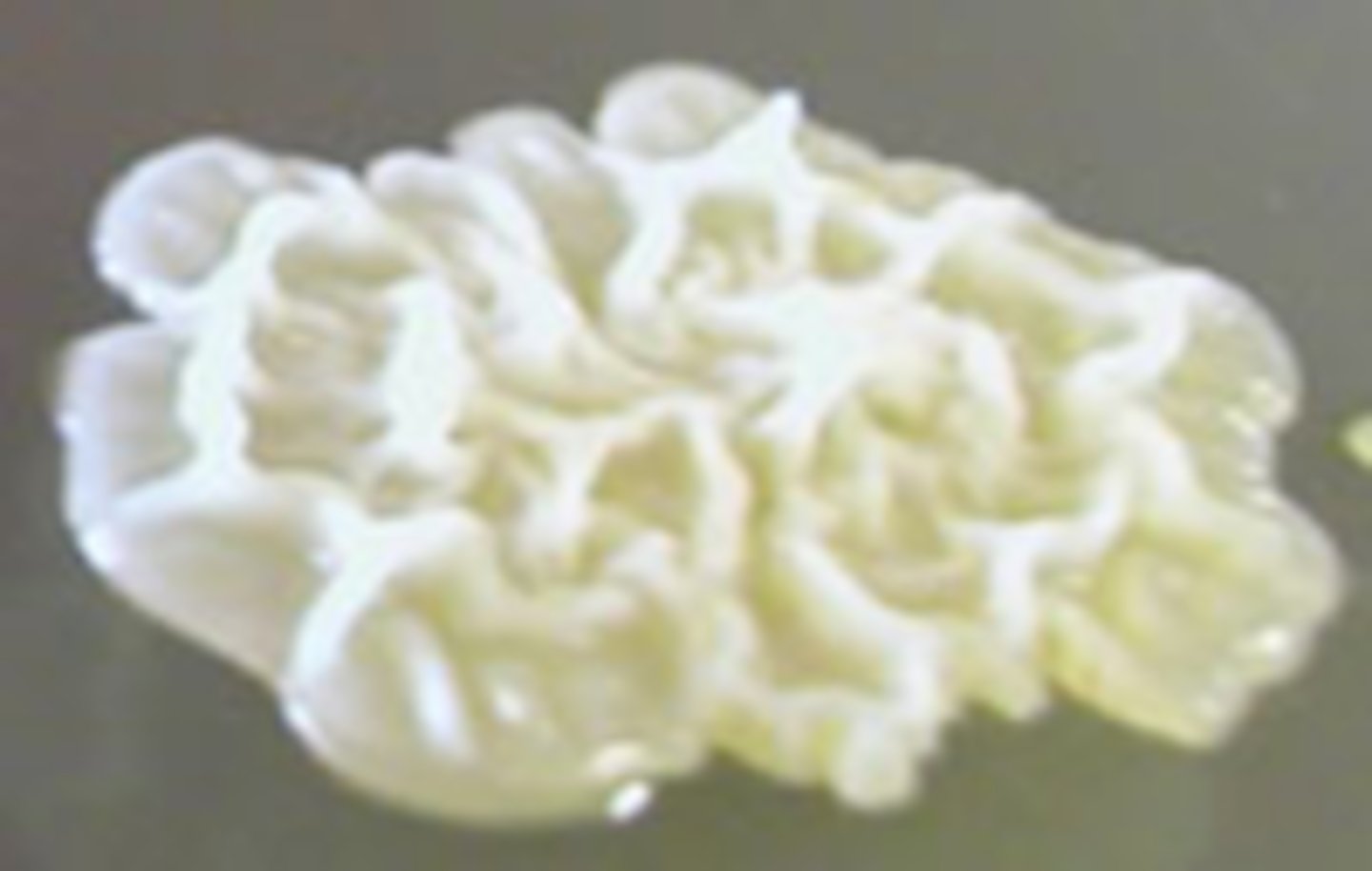

Filamentous
Identify the MARGIN
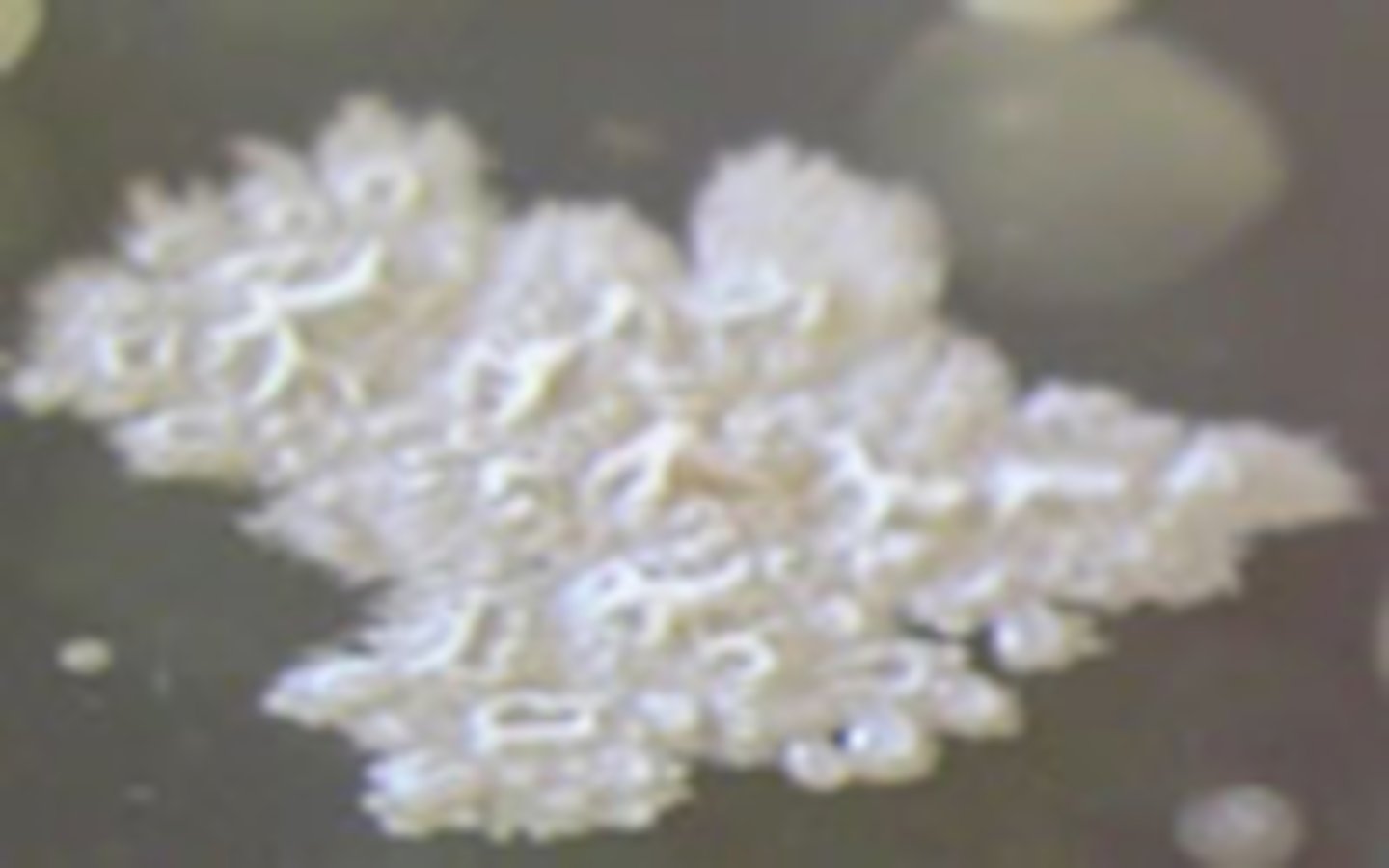

Flat
Identify the ELEVATION
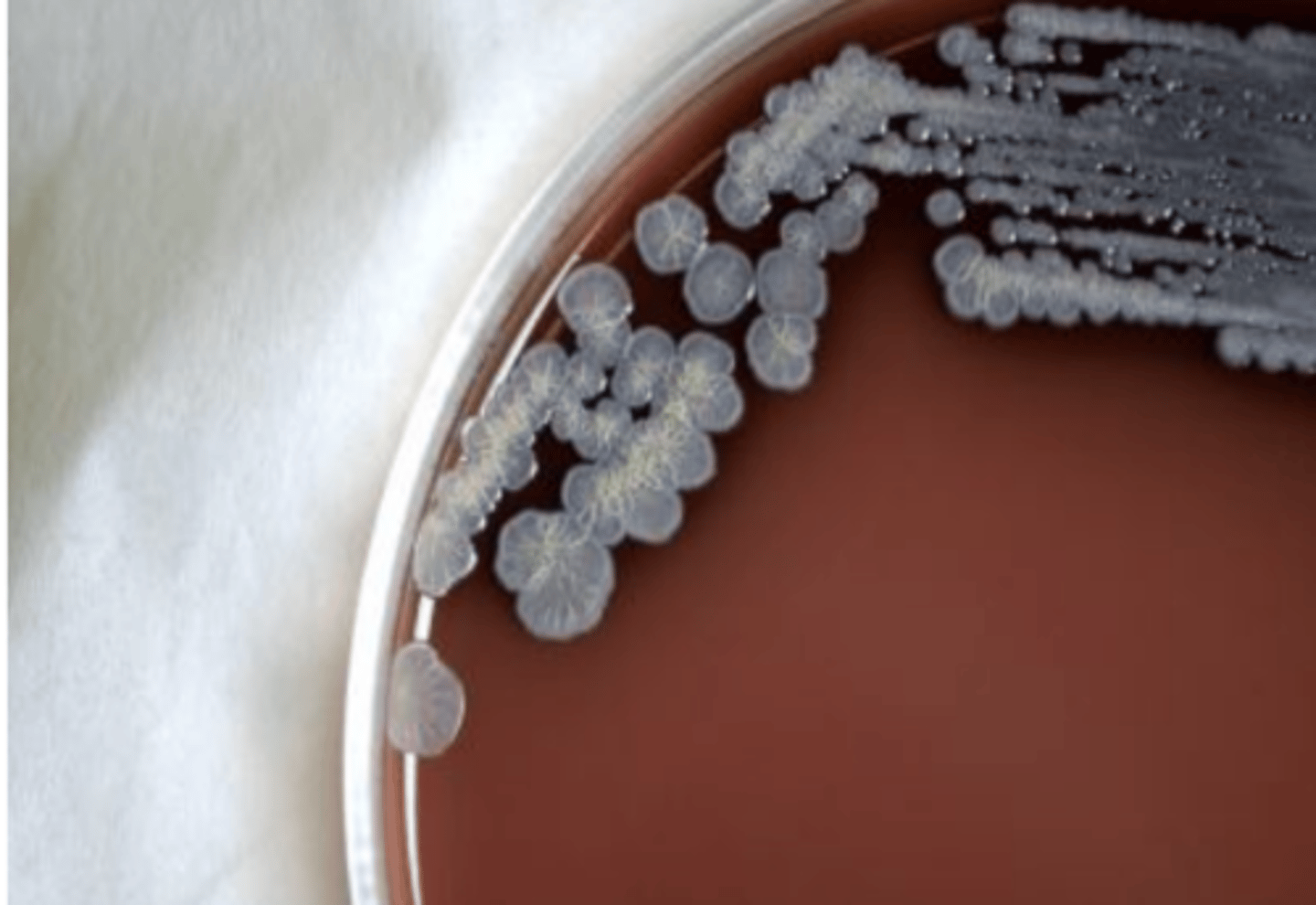
Convex
Identify the ELEVATION
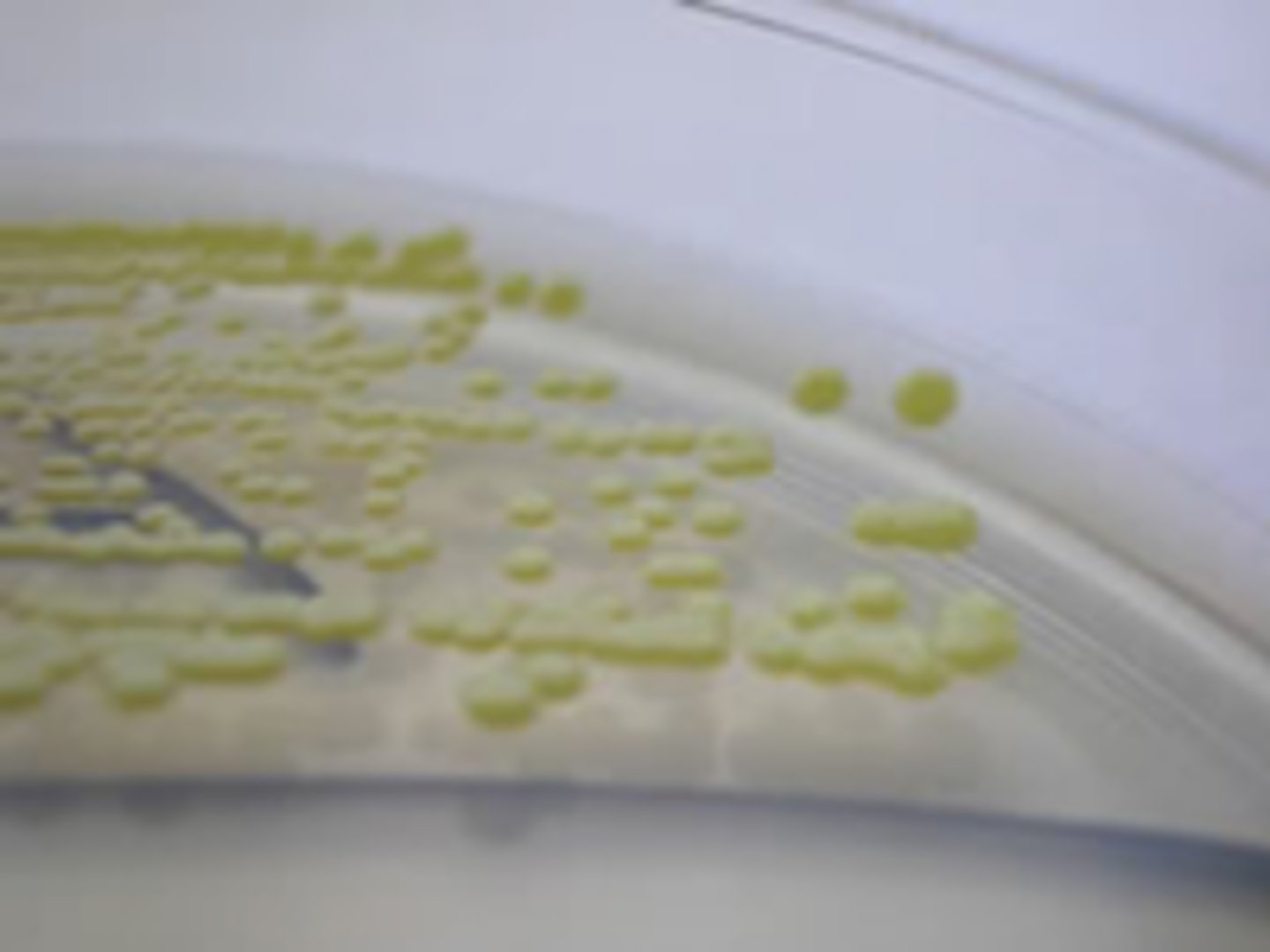

Umbonate
Identify the ELEVATION
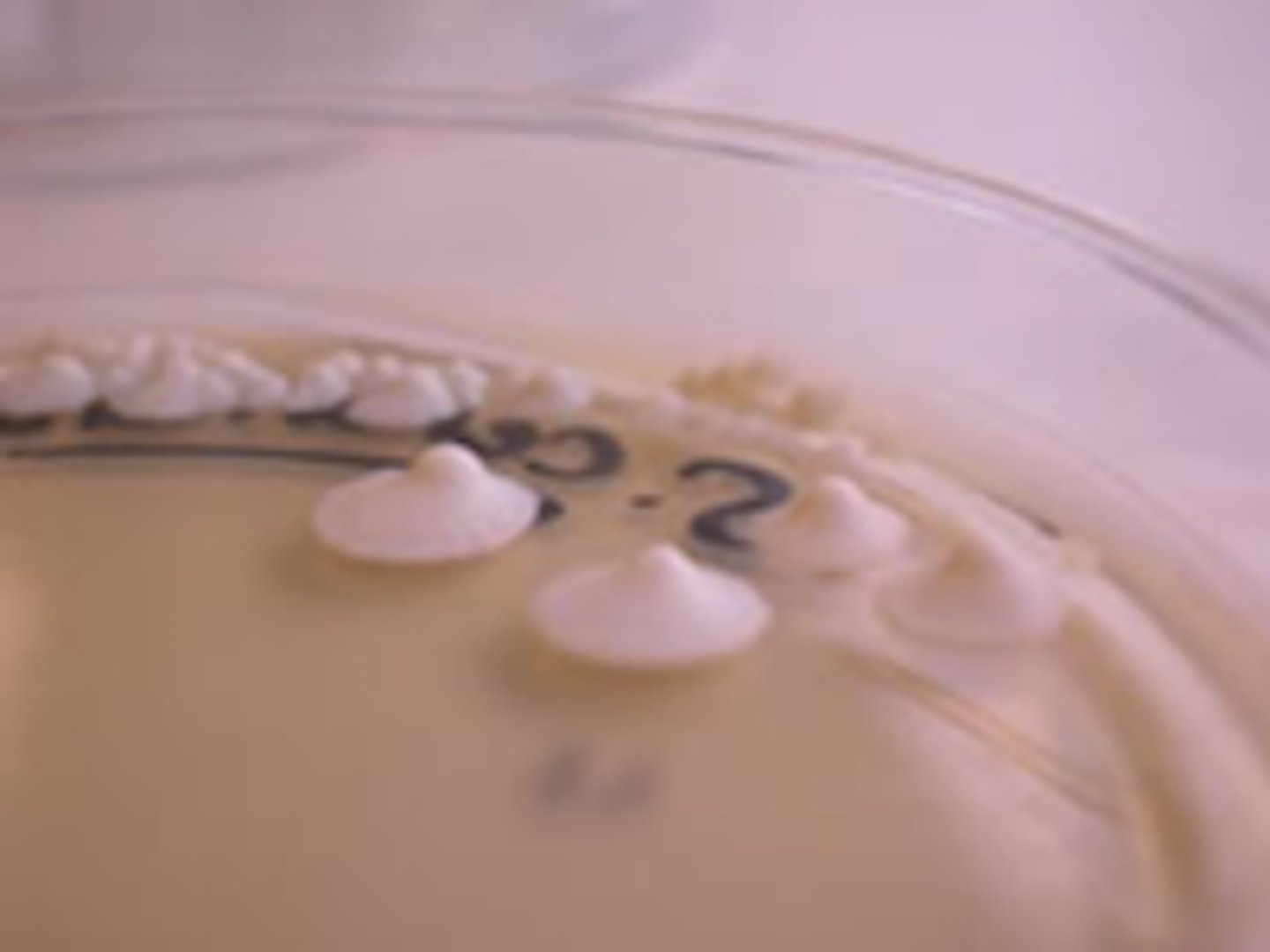
Raised
Identify the ELEVATION
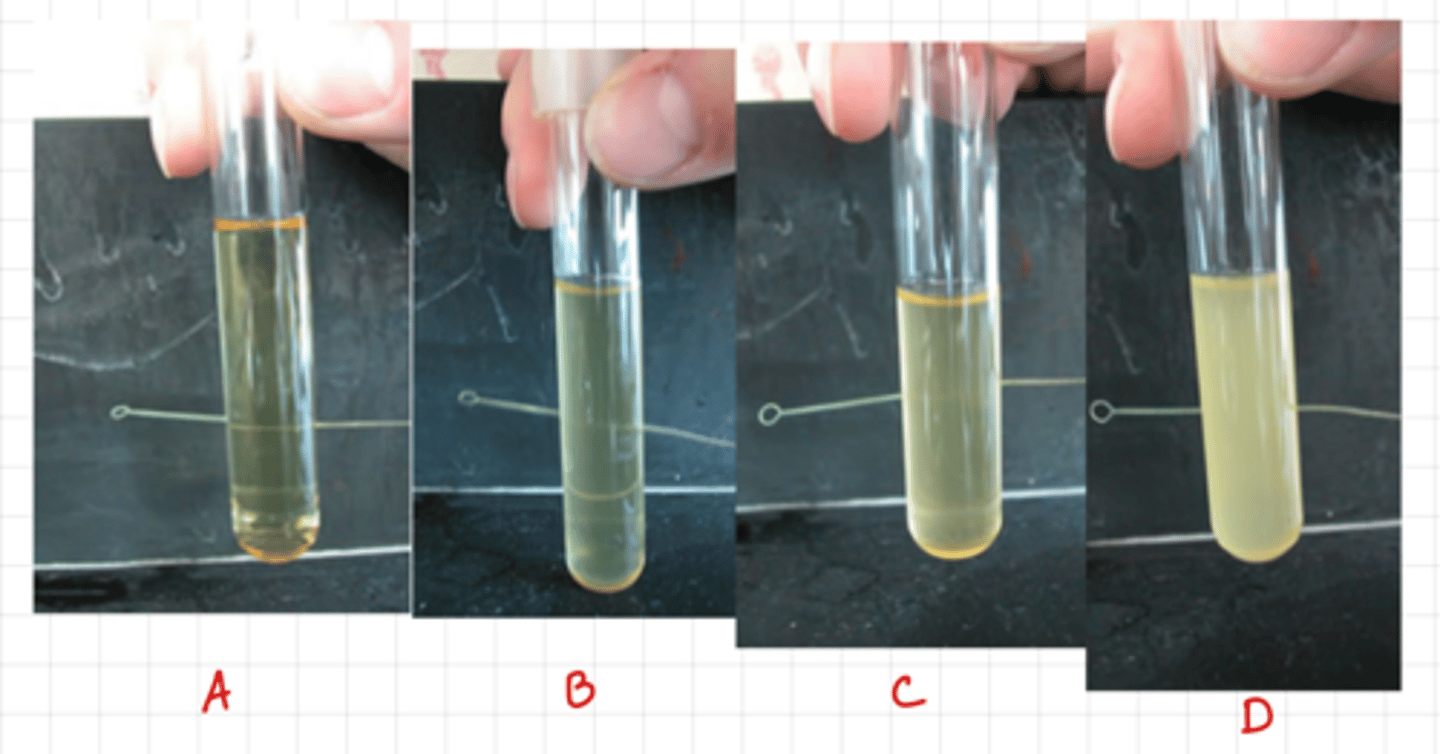
Turbidity
The cloudy appearance of a liquid medium due to the presence of bacteria
A = None
B = Light
C = Moderate
D = Heavy
Identify the TURBIDITY
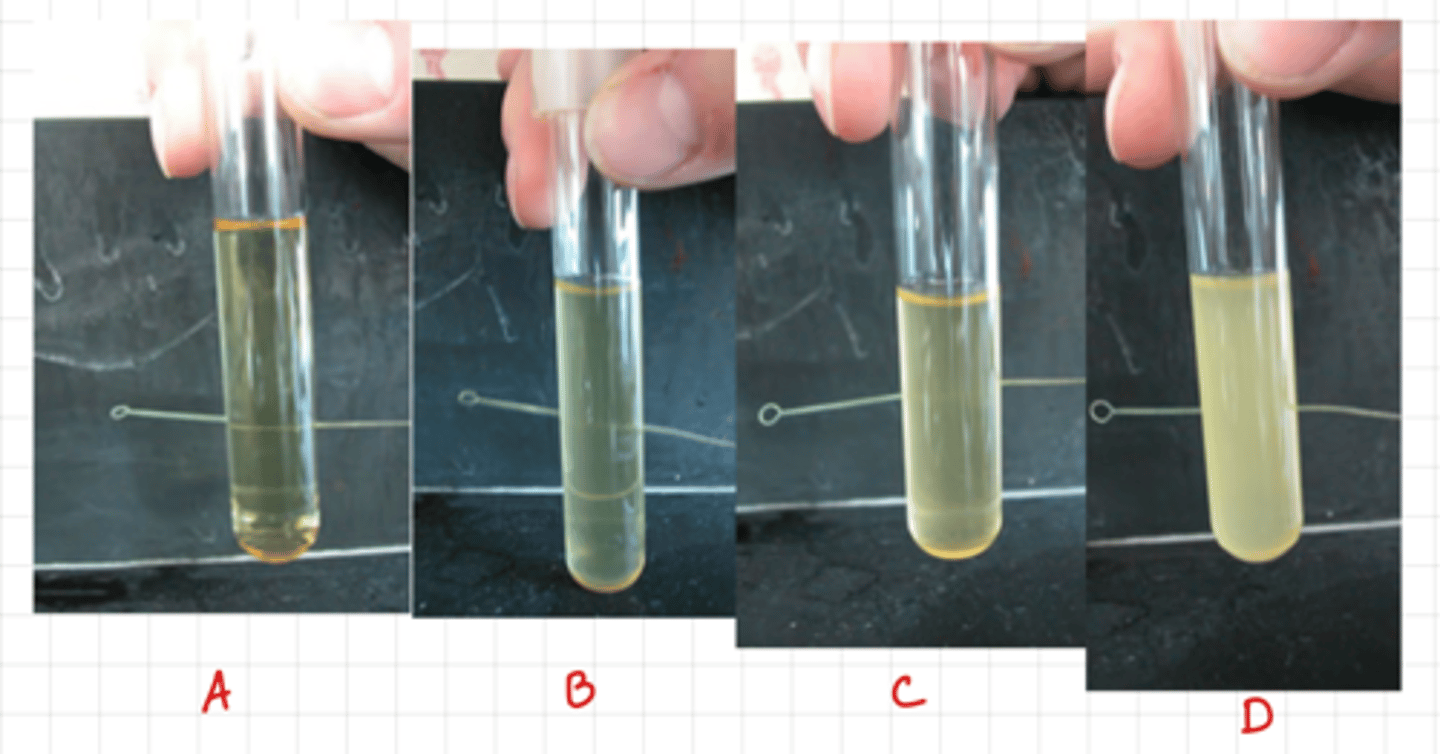
A = 0-16^6
B = 10^7
C = 10^8
D = 10^9
Identify the estimated # Bacteria per mL
3 x 10^9
Usually bacterial populations do not exceed ________ bacteria/mL when grown in liquid media.
Blood Agar Plate
a rich, complex medium that contains 5% sheep red blood cells
Blood Agar Plate
What plate?
Blood Agar Plate
- tests the ability of an organism to produce hemolysins, enzymes that damage/lyse red blood cells (erythrocytes).
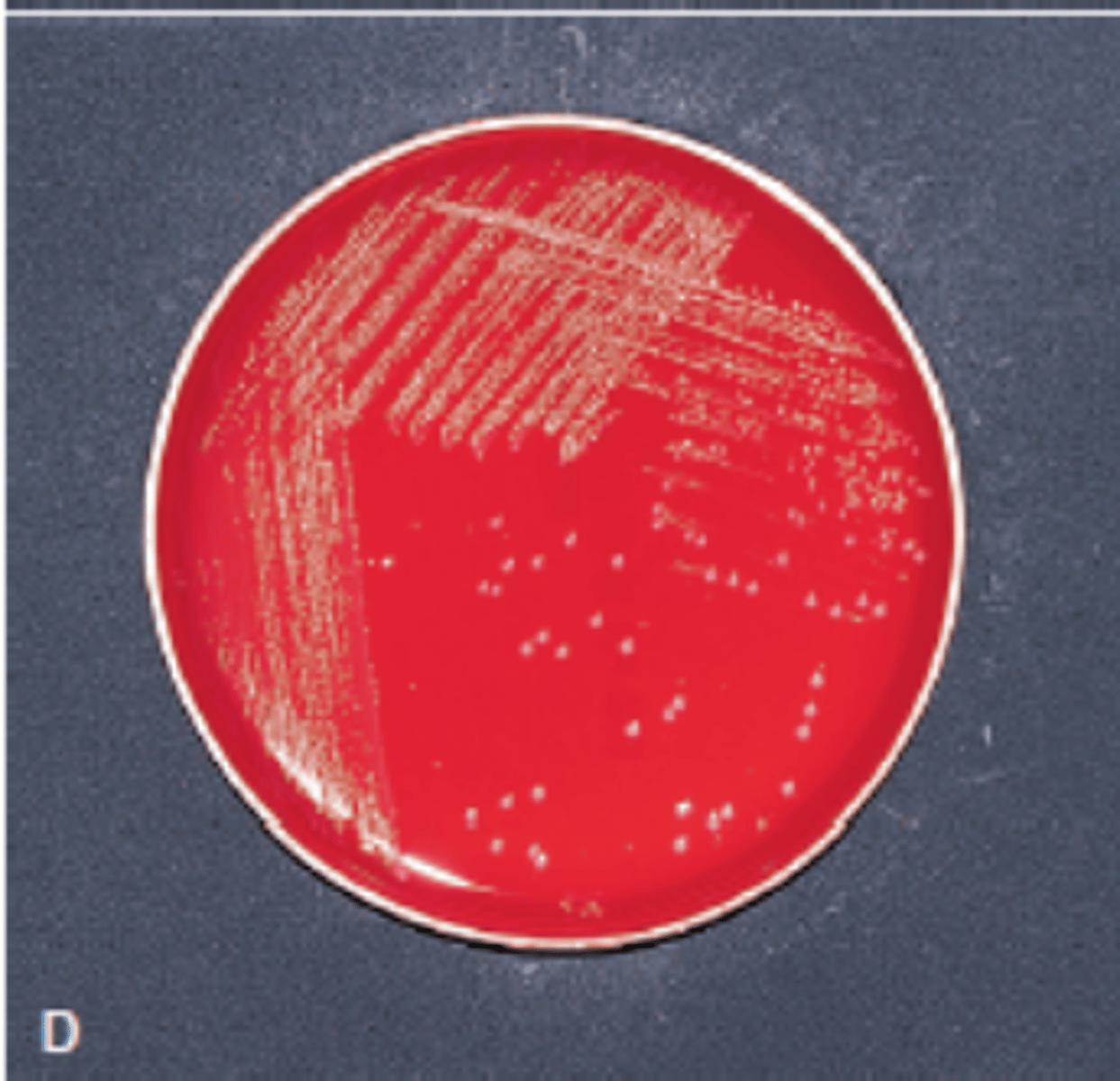
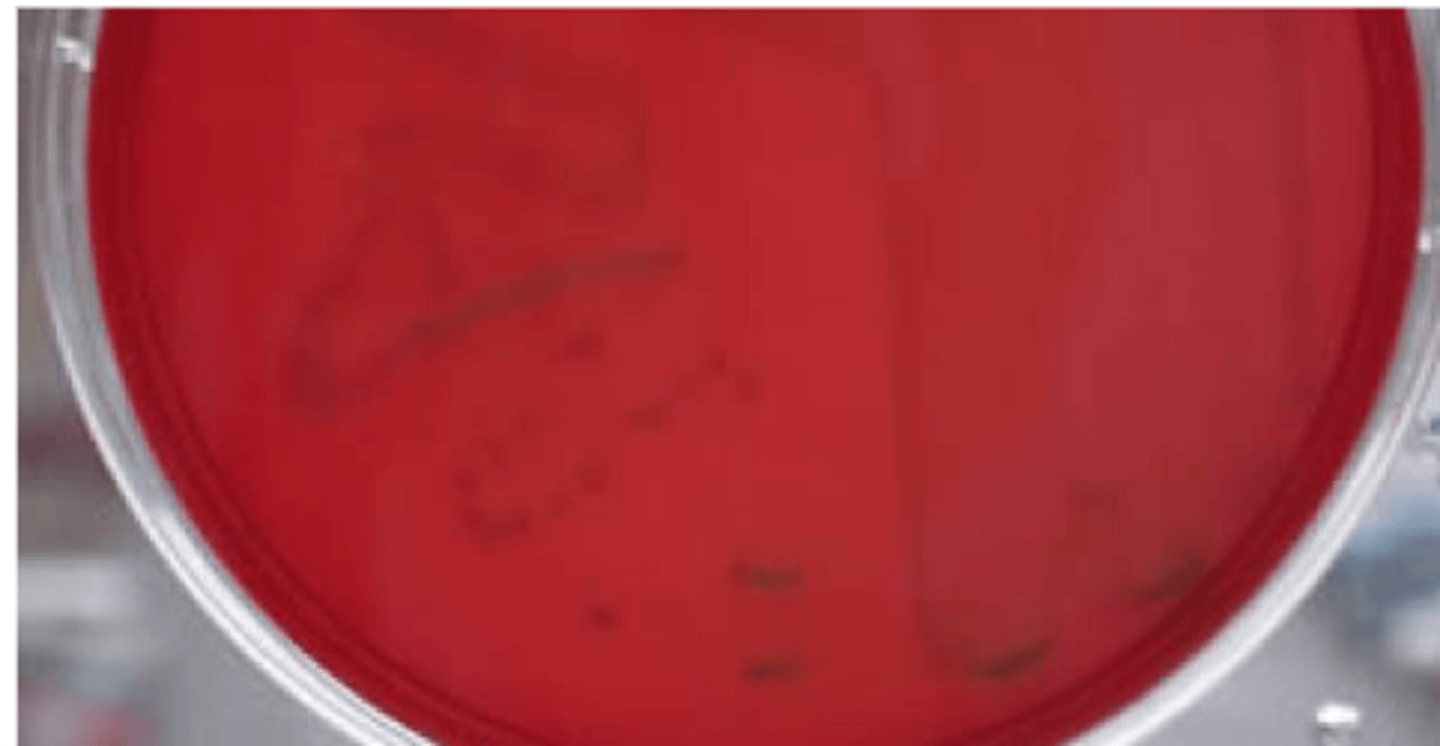
Beta-hemolysis
_________ is complete hemolysis
Beta-hemolysis
It is characterized by a clear (transparent) zone surrounding the colonies
Beta-hemolysis
What type of Hemolysis?
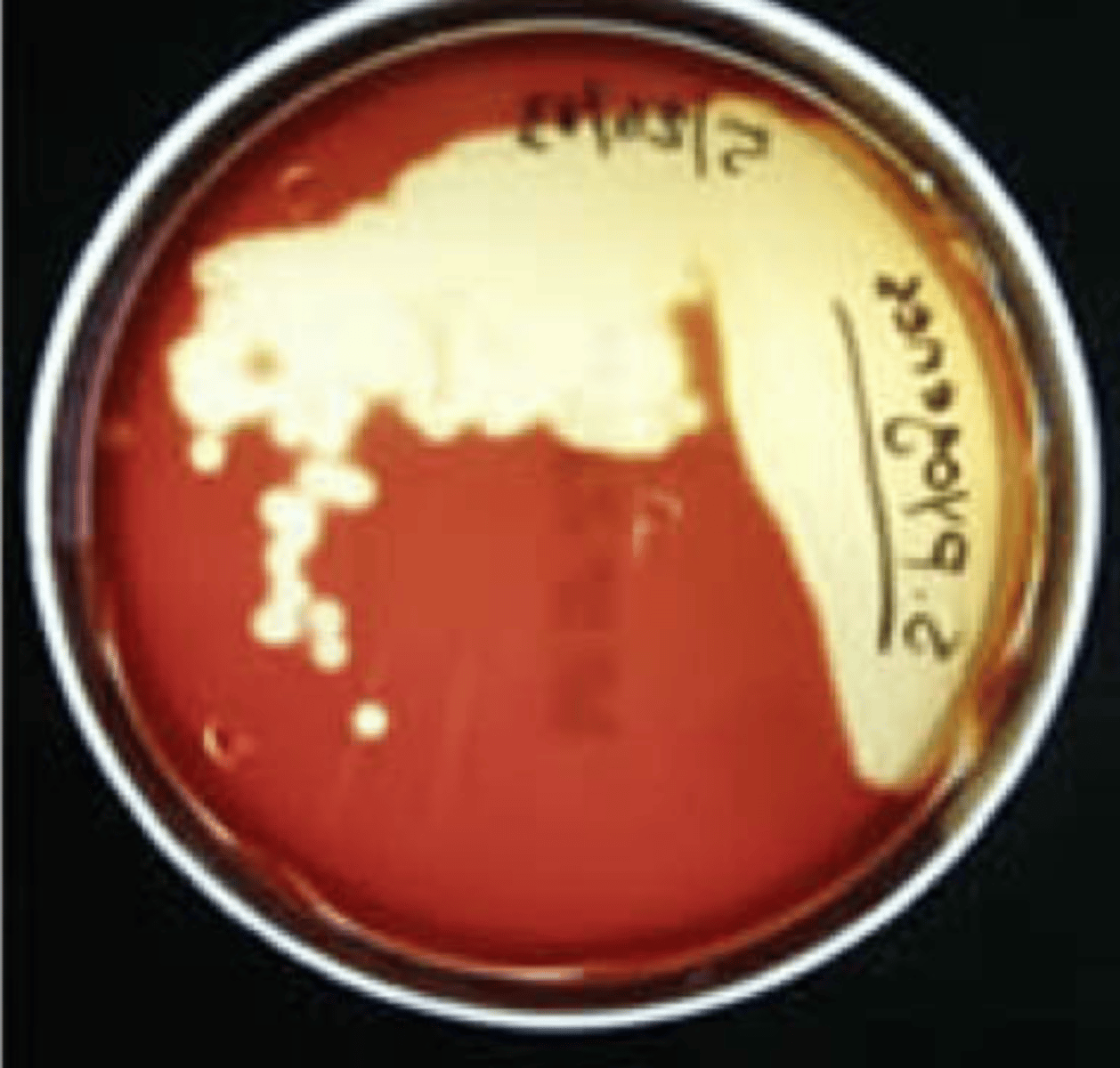
Beta-hemolysis
Staphylococcus aureus
Streptococcus pyogenes
Streptococcus agalactiae
What type of Hemolysis? Give example of organism w/ this type
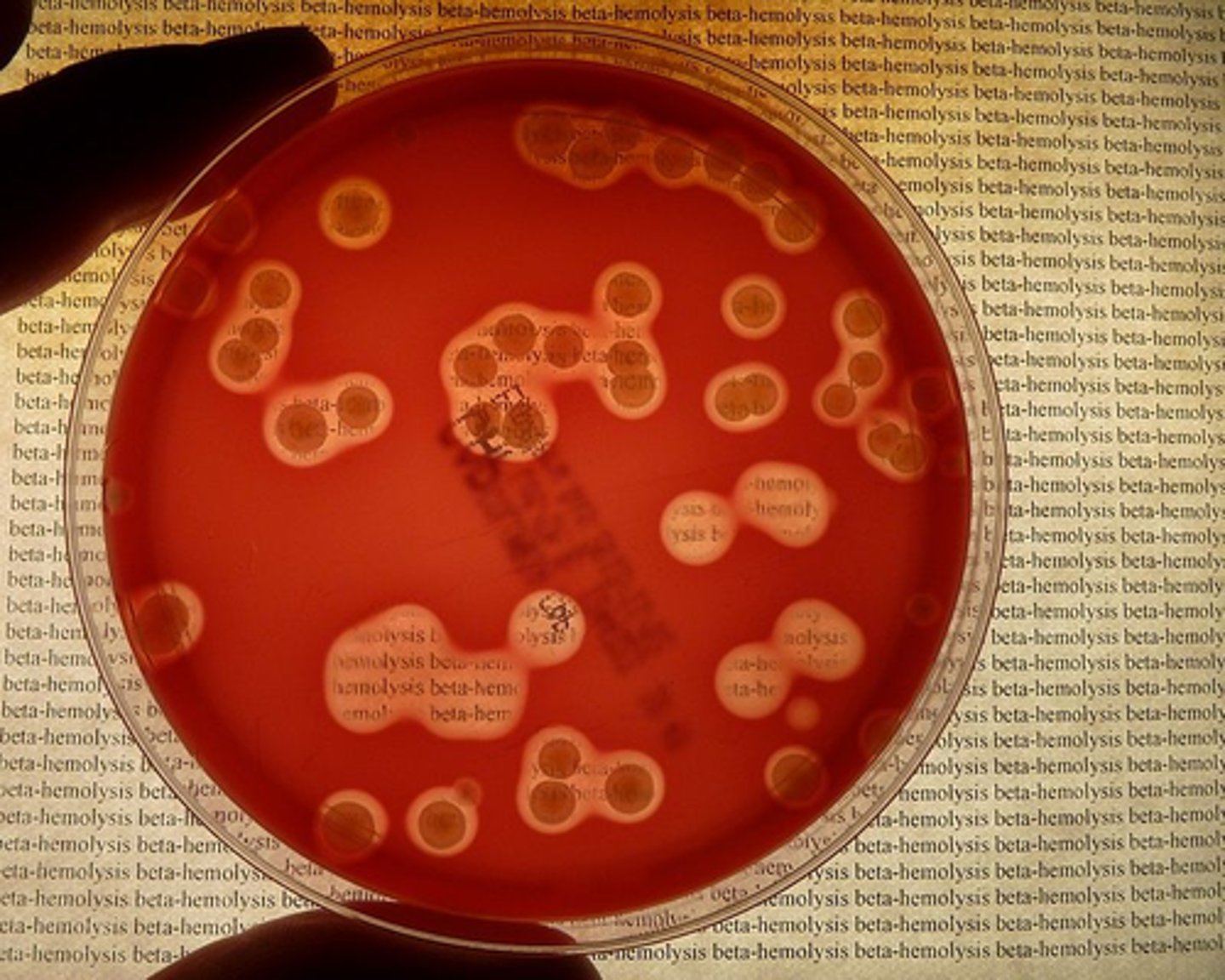
Alpha-hemolysis
Partial hemolysis is termed _________
Alpha-hemolysis
Colonies typically are surrounded by a green, opaque zone
Alpha-hemolysis
What type of hemolysis?
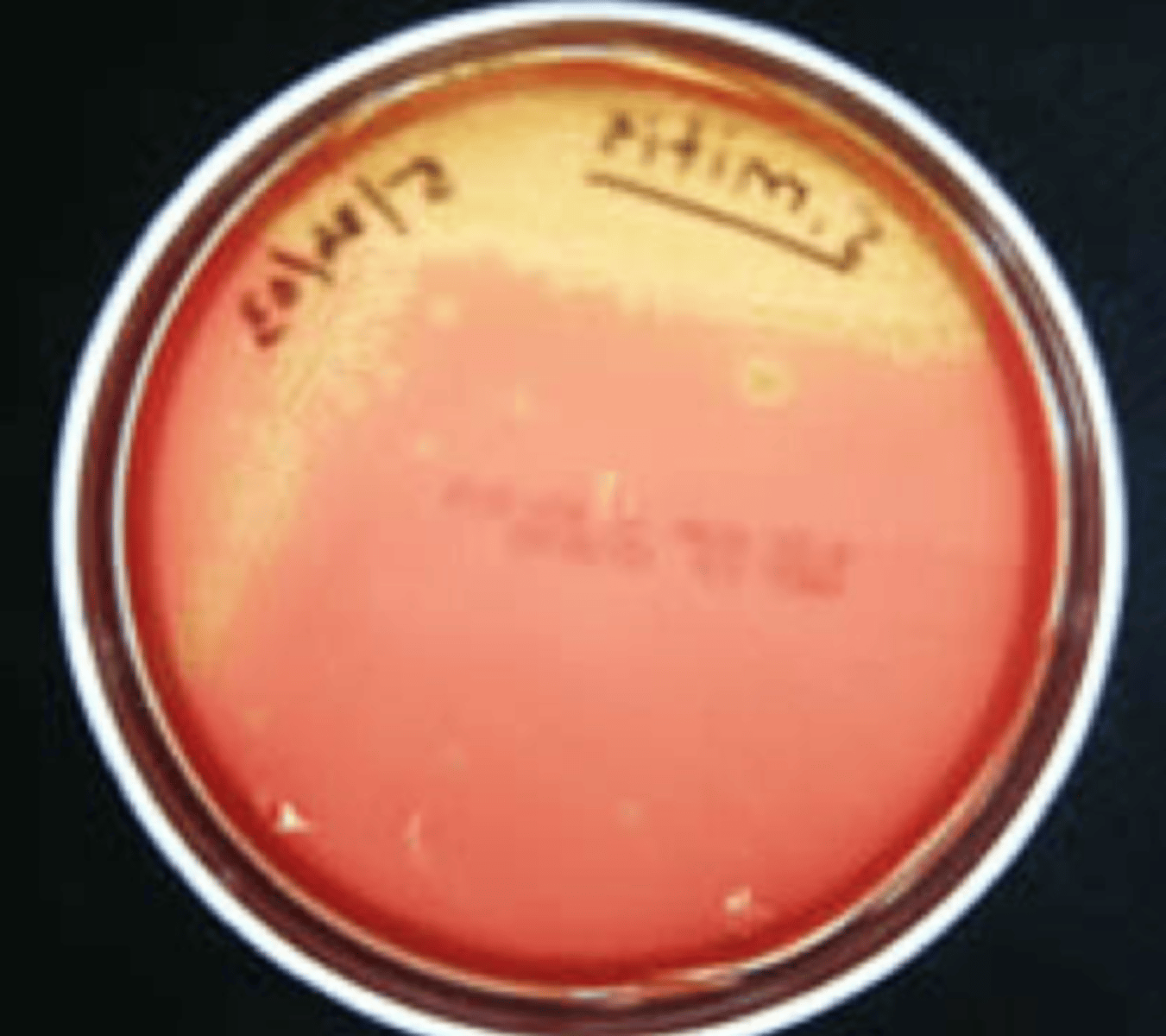
Alpha-hemolysis
Streptococcus pneumoniae
Streptococcus mitis
What type of hemolysis?
Give example of organism
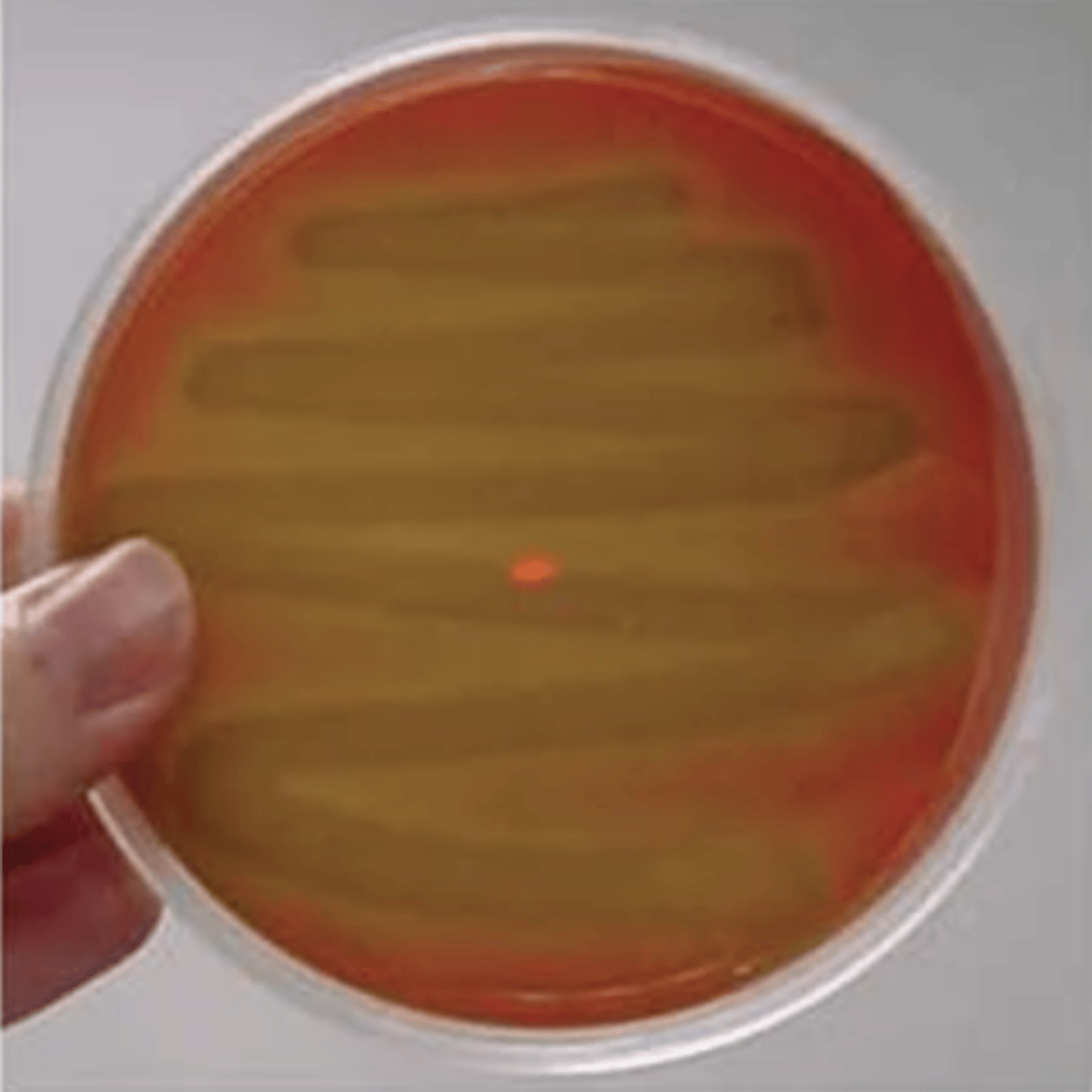
Gamma-hemolysis
What type of hemolysis?
Gamma-hemolysis
Staphylococcus epidermidis
What type of hemolysis?
Give example
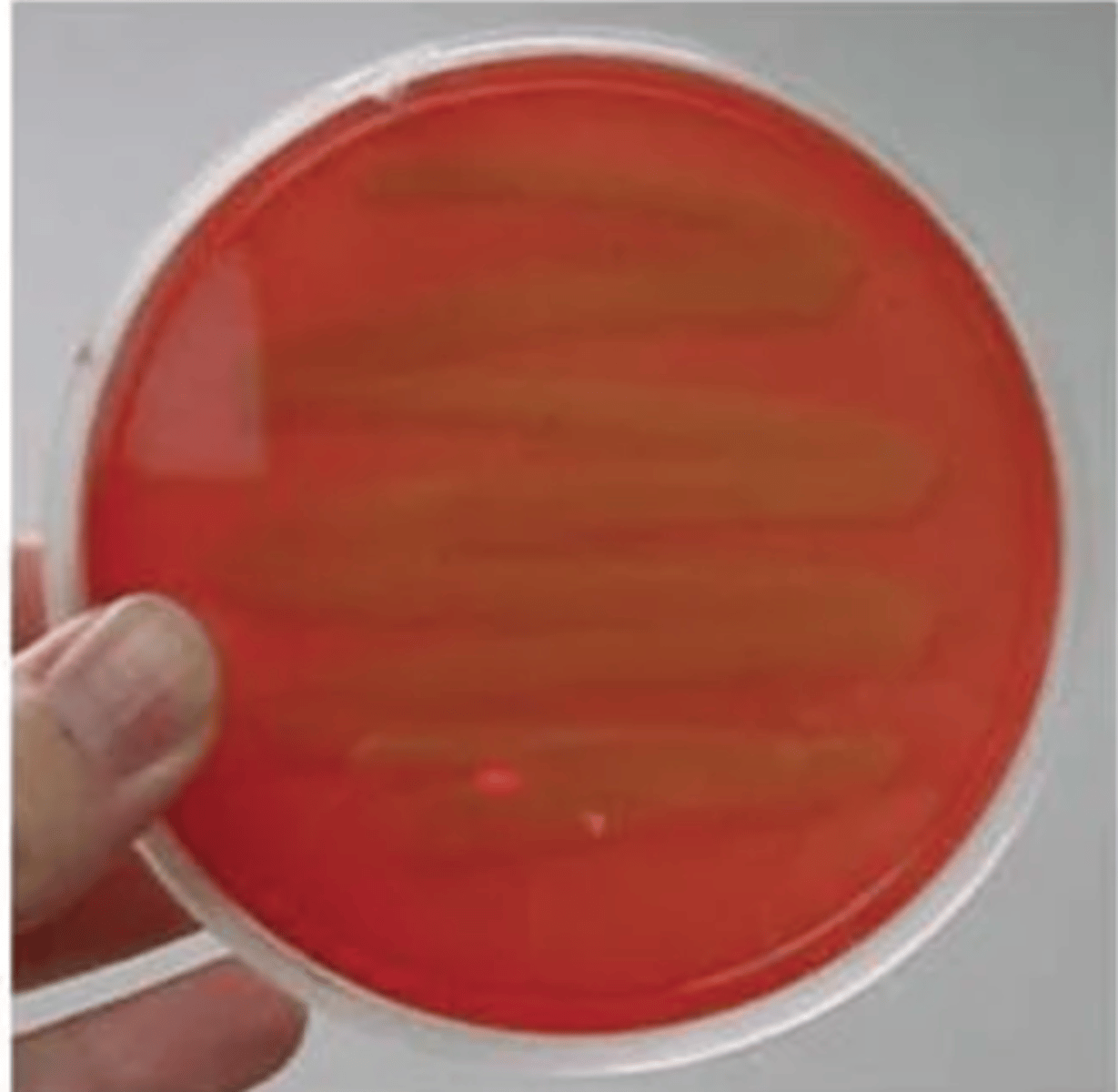
Gamma-hemolysis
- no hemolysis
- no notable zones around the colonies
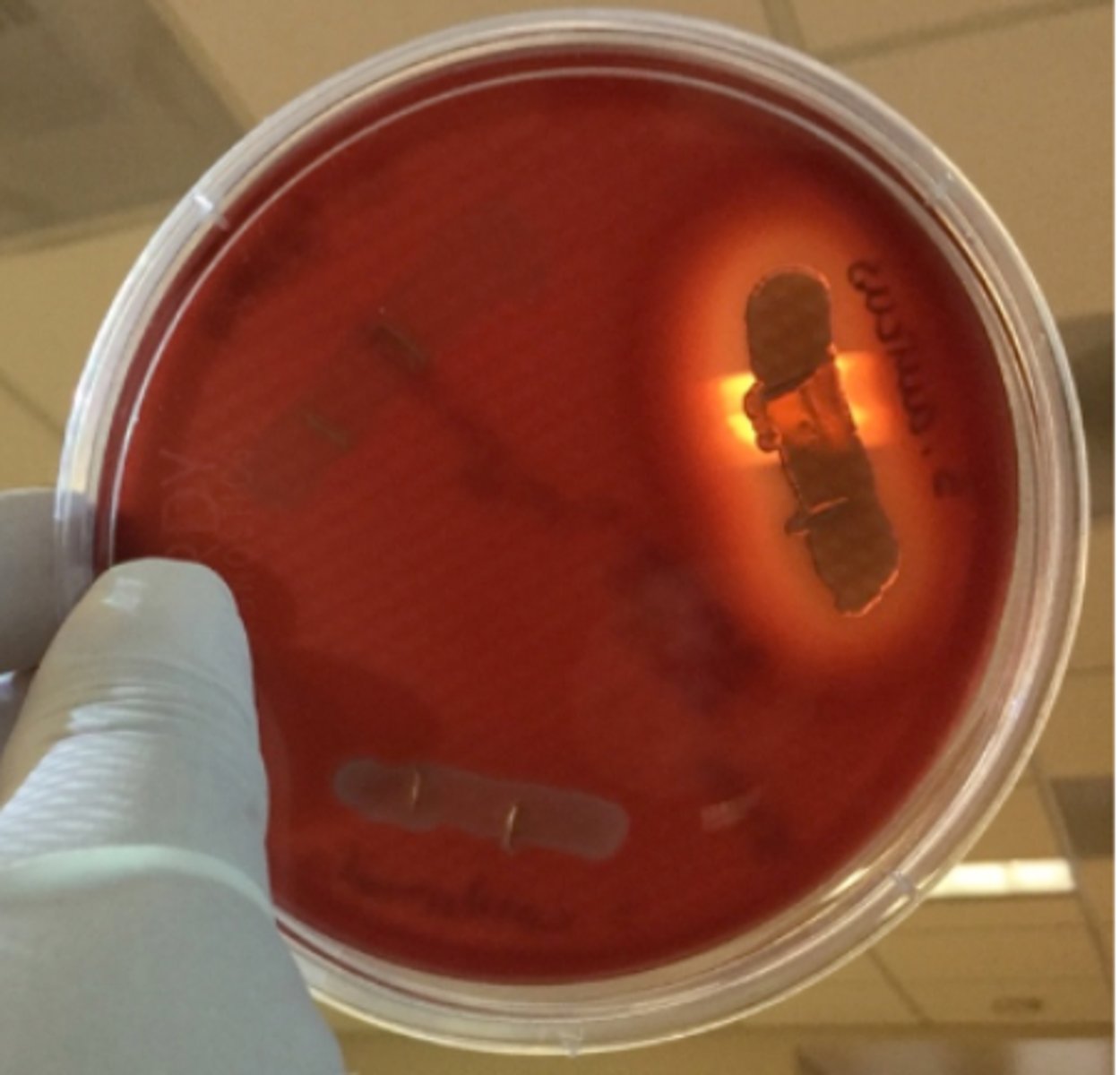
Streak-stab technique
Often when inoculating a BAP to observe hemoloysis patterns, investigators will also stab several times through the agar using an inoculating loop. What do you call this technique?
streptolysin O
This stab allows for the detection of ___________, a specific hemolysin produced by Streptococcus pyogenes.
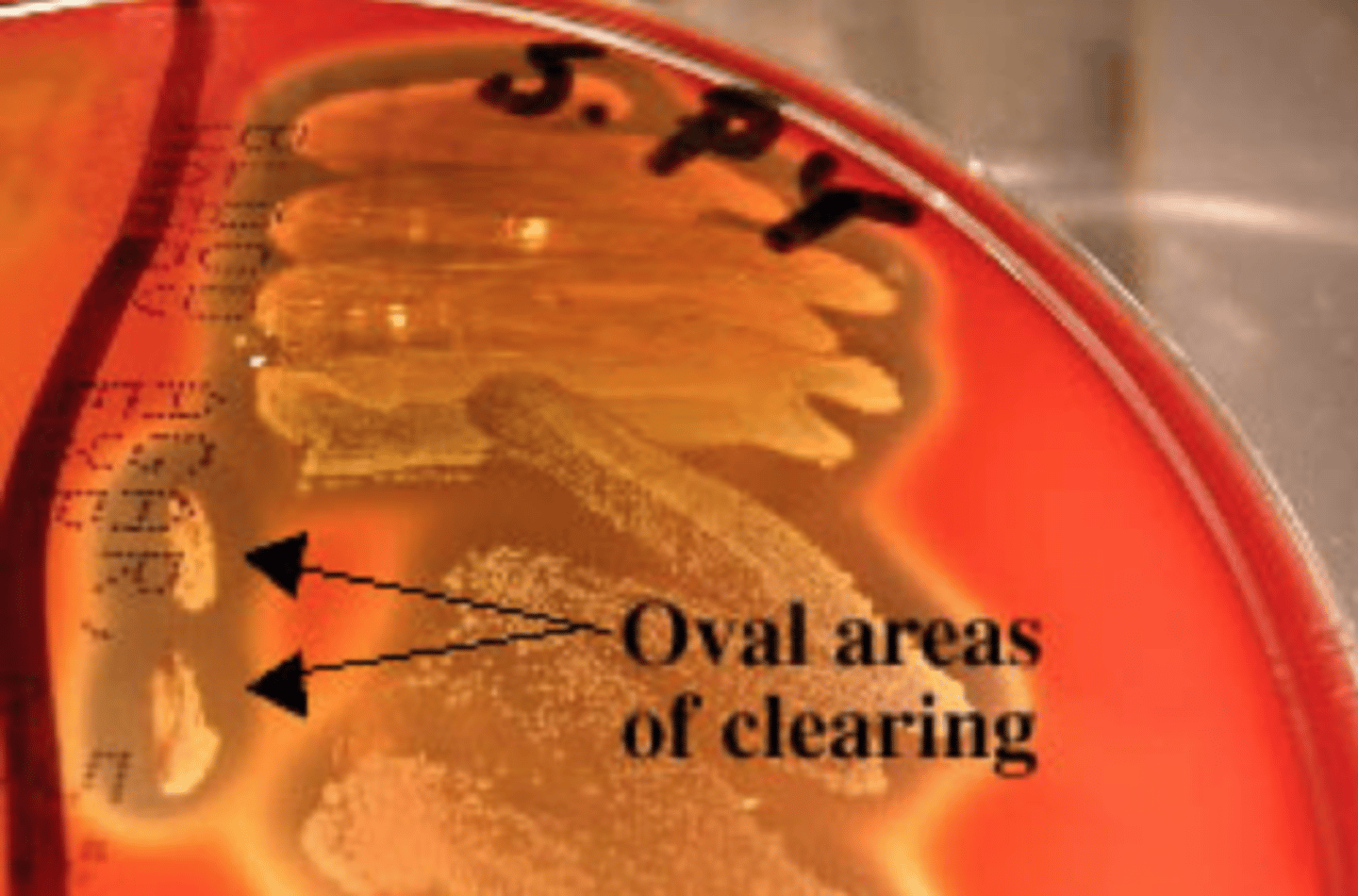
Streak-stab technique
What technique is this?
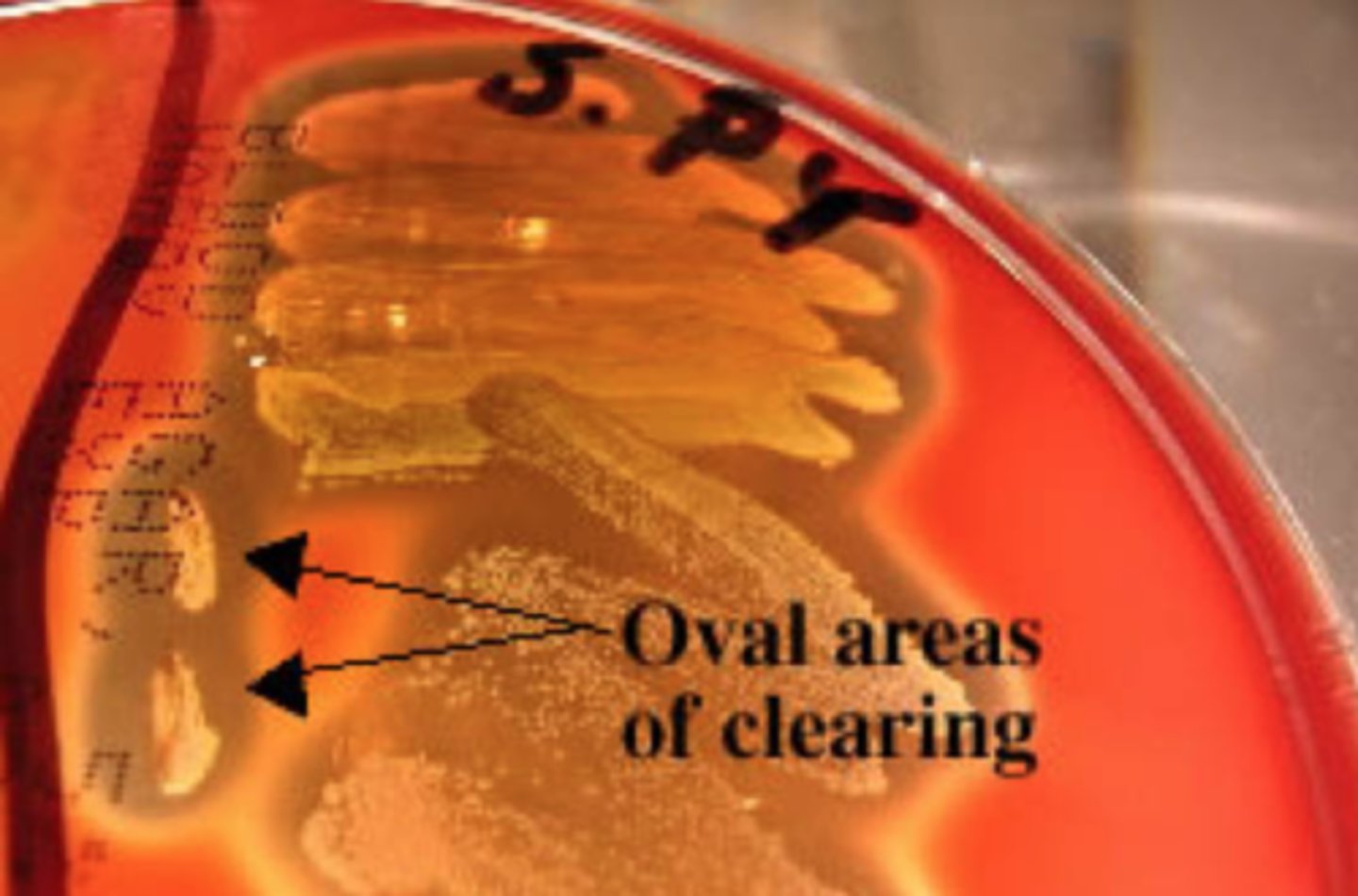
streptolysin O
What is detected in this technique?
Note the oval-shaped areas of clearing around the stab marks in the picture; these are caused by __________
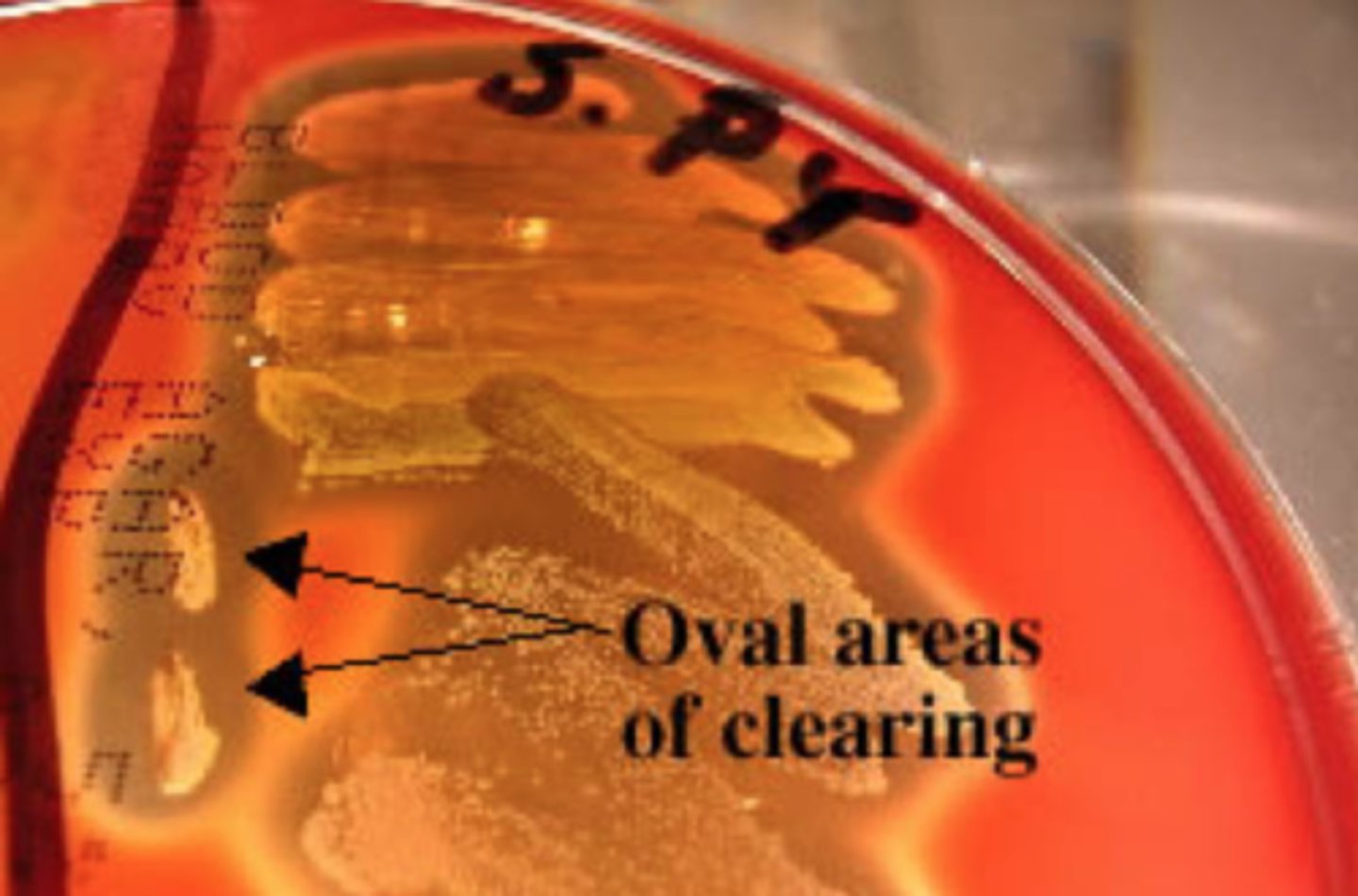
Streptococcus pyogenes
streptolysin O is a specific hemolysin produced by ___________
Aseptic technique
What do you call this technique?
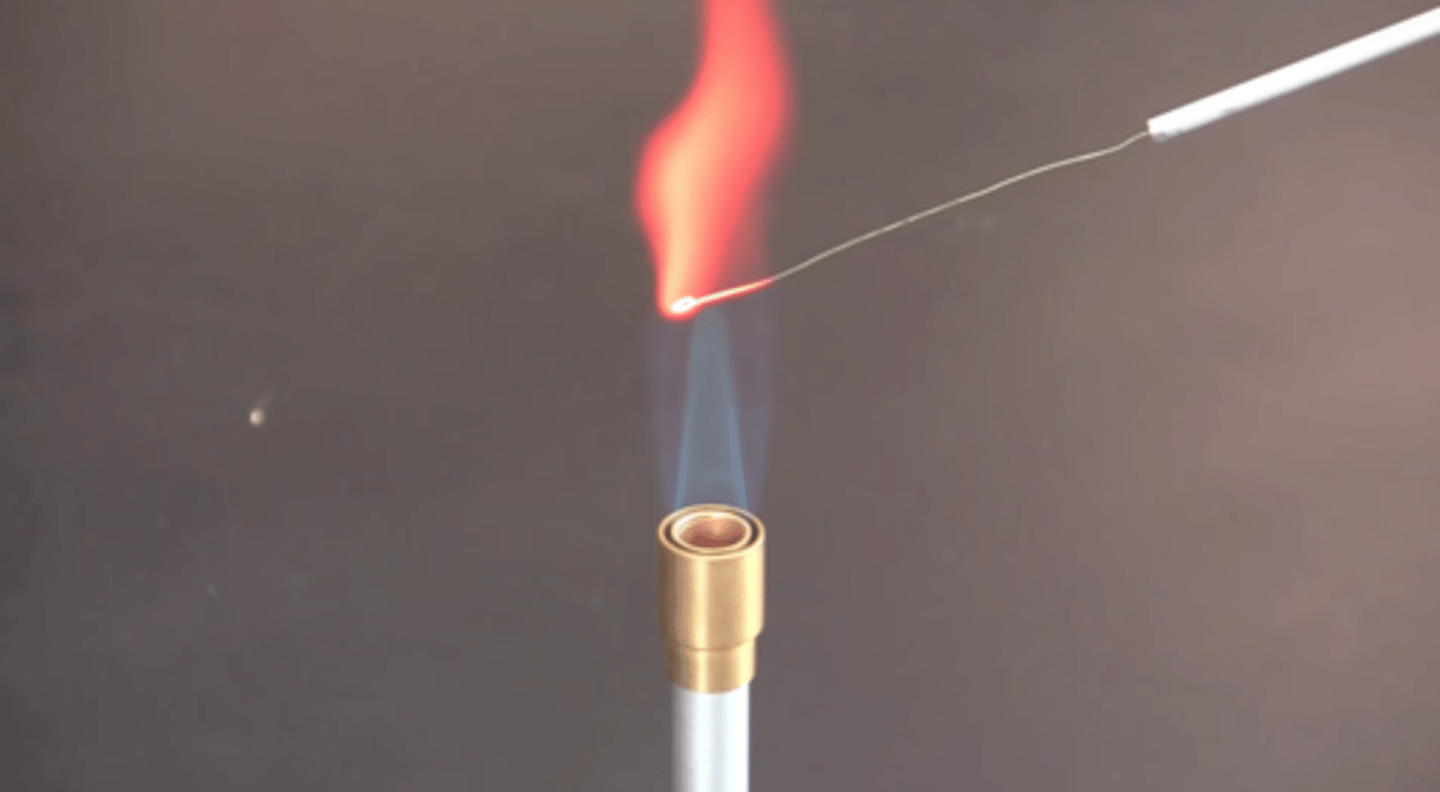

Aseptic technique
For sterilization
What do you call this technique?
What is it's purpose?
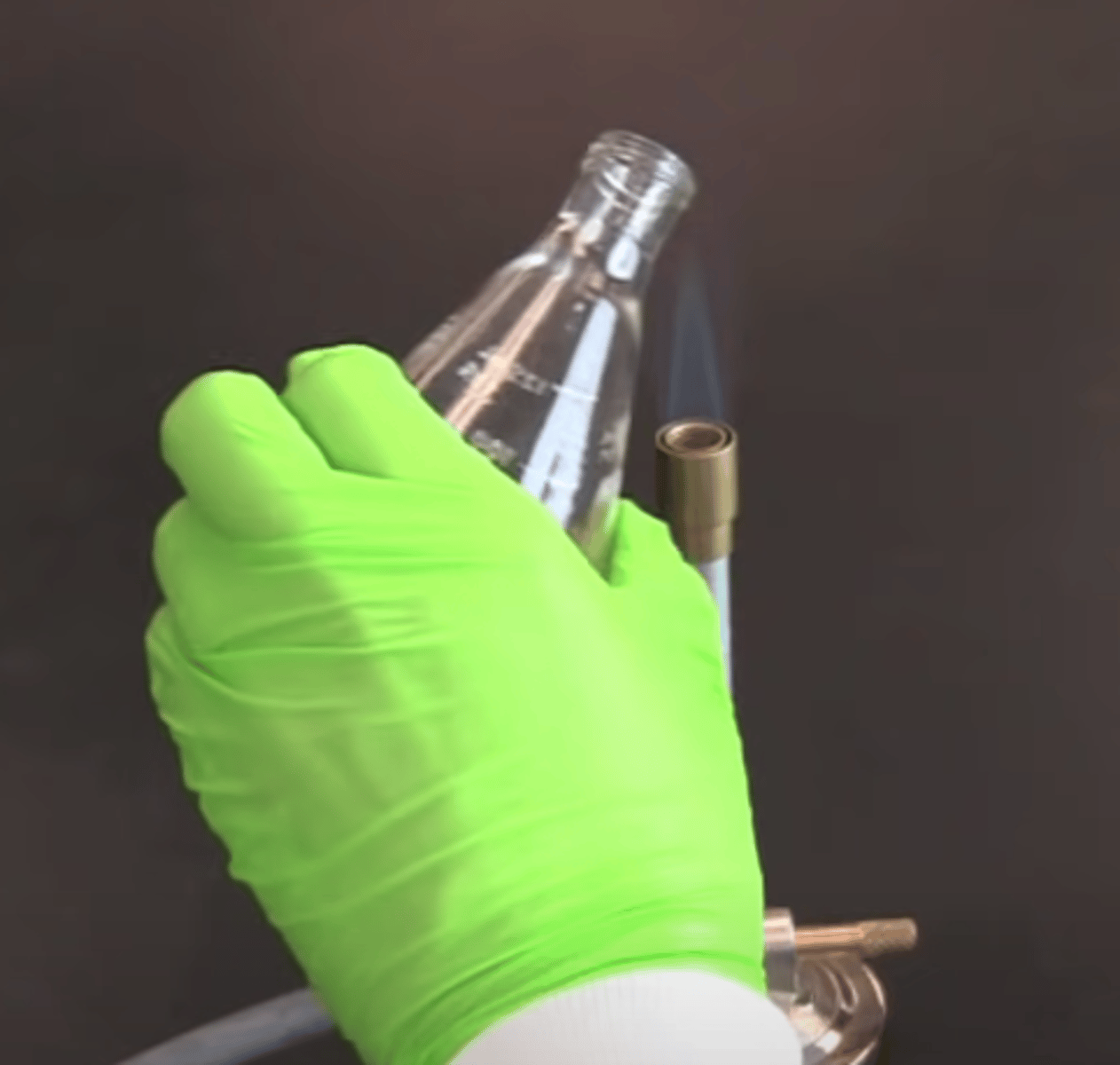

Broth culturing
What type of culture?

35-37C @ 24-48hours
How many minutes/hours and at what temperature is the incubation of culture media?