Basic Atomic Structure
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
15 Terms
Atom
The basic building block of matter, made up of protons, neutrons, and electrons.
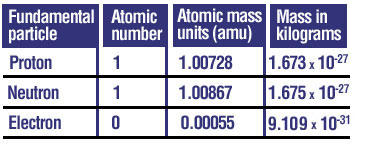
Proton
A positively charged particle found in the nucleus of an atom, with a mass of approximately 1.673 x 10-27 kg.
Neutron
A neutral particle found in the nucleus of an atom, with a mass of approximately 1.675 x 10-27 kg.
Electron
A negatively charged particle that orbits the nucleus of an atom, with a very small mass of approximately 9.109 x 10-31 kg.
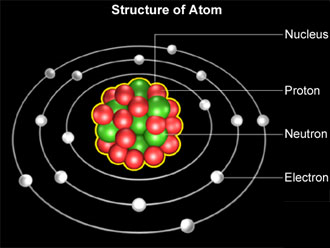
Nucleus
The dense, central part of an atom, made up of protons and neutrons.
Atomic Theory
A scientific theory describing the nature of matter, with atoms as the fundamental units.
Dalton's Theory
The early atomic theory proposed by John Dalton that elements are made of identical atoms.
Periodic Table
A tabular arrangement of the chemical elements organized by their atomic number and properties, developed by Dimitri Mendeleev.
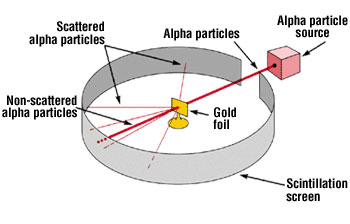
Rutherford Model
The atomic model presented by Ernest Rutherford, which describes the atom as having a nucleus surrounded by a cloud of electrons.
Bohr Model
An atomic model proposed by Neils Bohr, where electrons orbit the nucleus similar to planets around the sun.
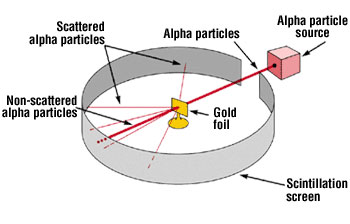
Alpha Particles
A type of particulate radiation used in Rutherford's gold foil experiment, consisting of two protons and two neutrons.
Empty Space in Atom
The majority of an atom's volume is empty space, with electrons orbiting around the nucleus.
The Fundamental Particles
The components of an atom, namely protons, neutrons, and electrons.
Scintillation Screen
A substance that emits light when struck by ionizing radiation, used to detect alpha particles in Rutherford's experiments.
Chemical Properties
Character traits that can be observed in how substances react with others, often shown in the periodic table.