Reflex Physiology and General Senses Overview
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
23 Terms
Reflex
comparatively simple automatic response to a stimulus
Reflex Arc
The pathway that a reflex follows, including receptor, sensory relay, integration, motor command relay, and effector.
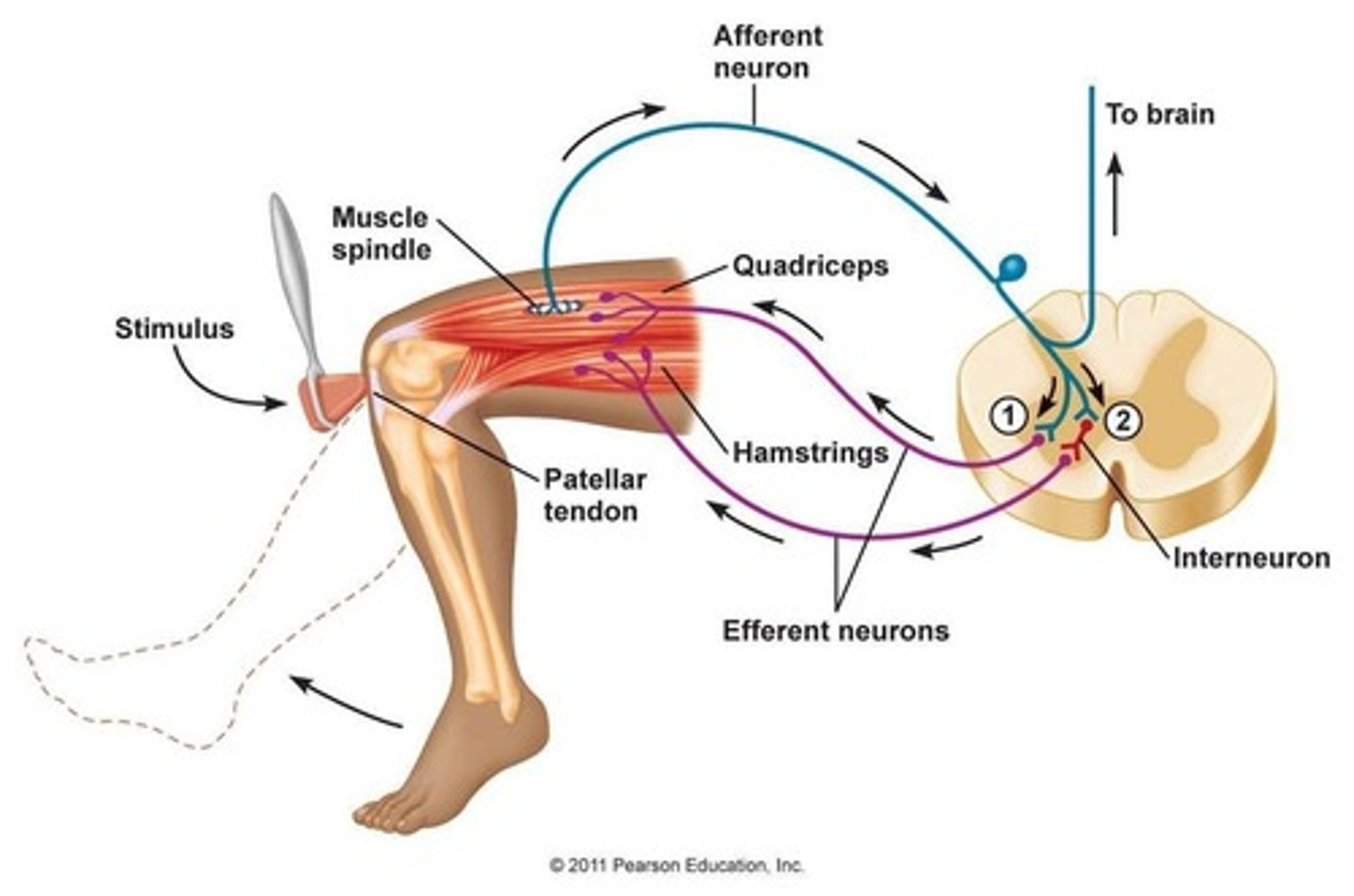
Monosynaptic Reflex
Reflexes that are faster and are integrated in the spinal cord, involving only one synapse.
Polysynaptic Reflex
Reflexes that contain at least one interneuron and involve multiple synapses.
Somatic Reflex
Voluntary reflexes that involve skeletal muscles.
Autonomic Reflex
Involuntary reflexes that involve smooth muscles, glands, or visceral organs.
Acquired Reflexes
Reflexes that are learned through experience, such as driving or skiing.
Exteroceptors
Sensory receptors that monitor external conditions such as heat, cold, touch, pain, and pressure.
Interoceptors
Sensory receptors that monitor internal conditions, such as blood pH.
Chemoreceptors
Receptors that monitor chemical changes, like blood pH.
Visceral Stretch Receptors
Receptors that detect distension of visceral organs.
Proprioceptors
Receptors that provide postural information and monitor muscle position.
Free Nerve Endings
Nerve endings that detect pain and extreme temperature, located in the epidermis/dermis junction.
Merkel Cells
Cells associated with free nerve endings that detect light touch and sustained pressure.
Meissner's Corpuscles
Encapsulated receptors that detect light touch and are located more superficially.
Pacinian Corpuscle
Encapsulated receptors that detect forceful pressure and vibrations, located deeper in the skin.
Muscle Spindle
Proprioceptors that monitor muscle position and ensure muscles are not overstretched.
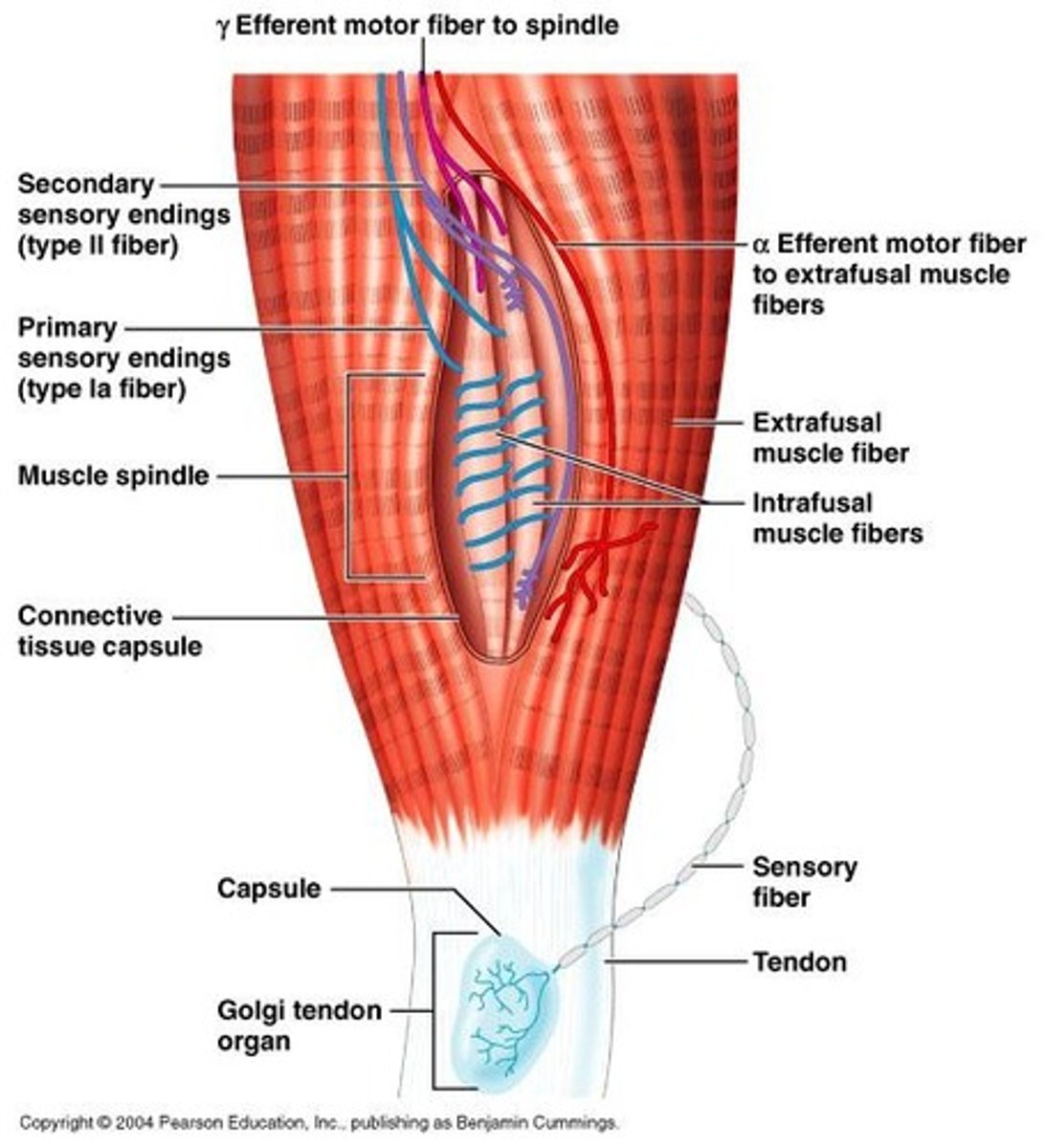
α-motor Neurons
Neurons that innervate the contractile region of extrafusal fibers.
γ-motor Neurons
Neurons that innervate the contractile region of intrafusal fibers.
Receptors
Transducers that convert stimuli to action potentials.
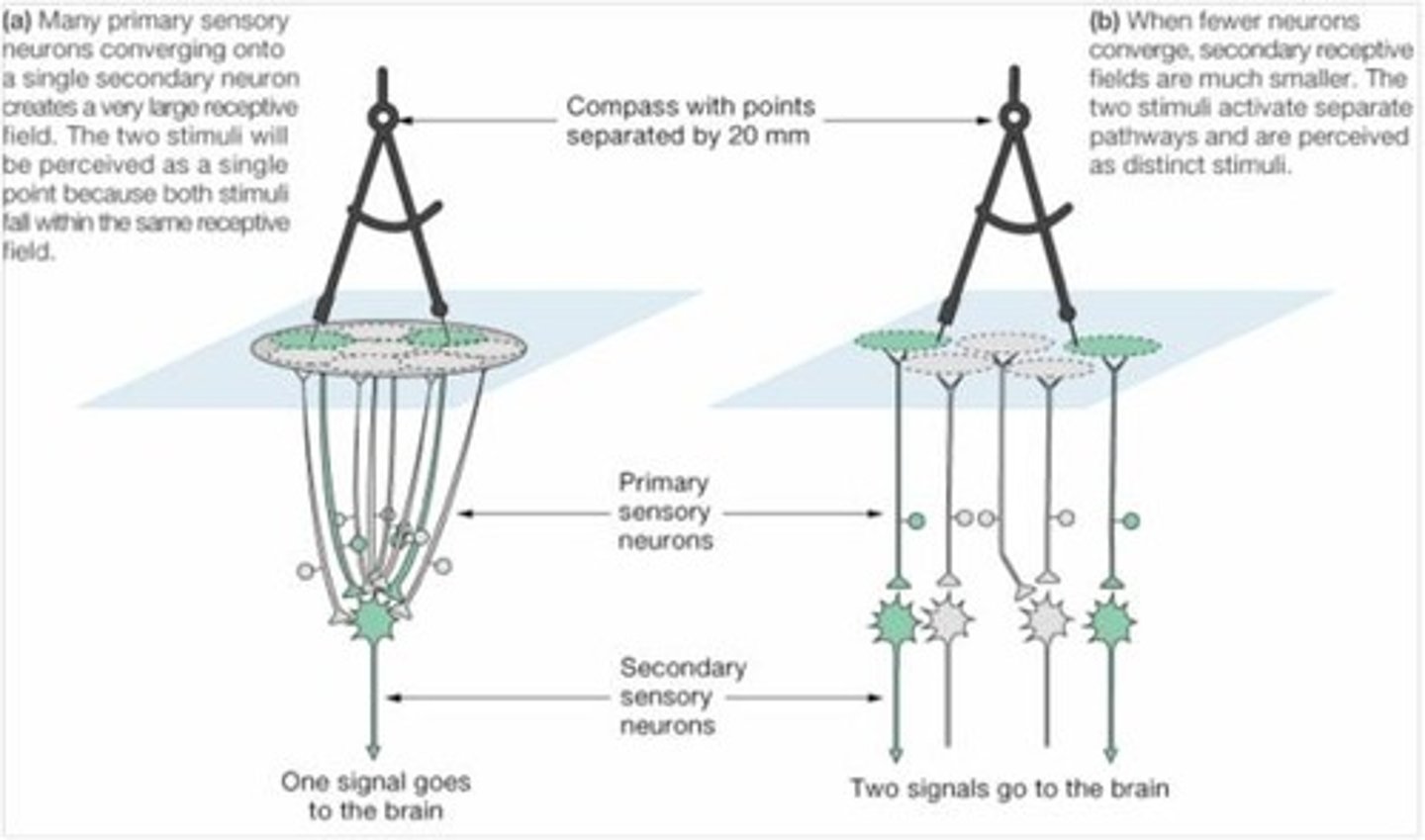
Receptor Fields
The area monitored by a receptor; smaller and denser fields indicate higher sensitivity.
Adaptation
Desensitization to constant stimuli.
2 Point Discrimination Test
A test used to measure the ability to distinguish two points of contact on the skin.