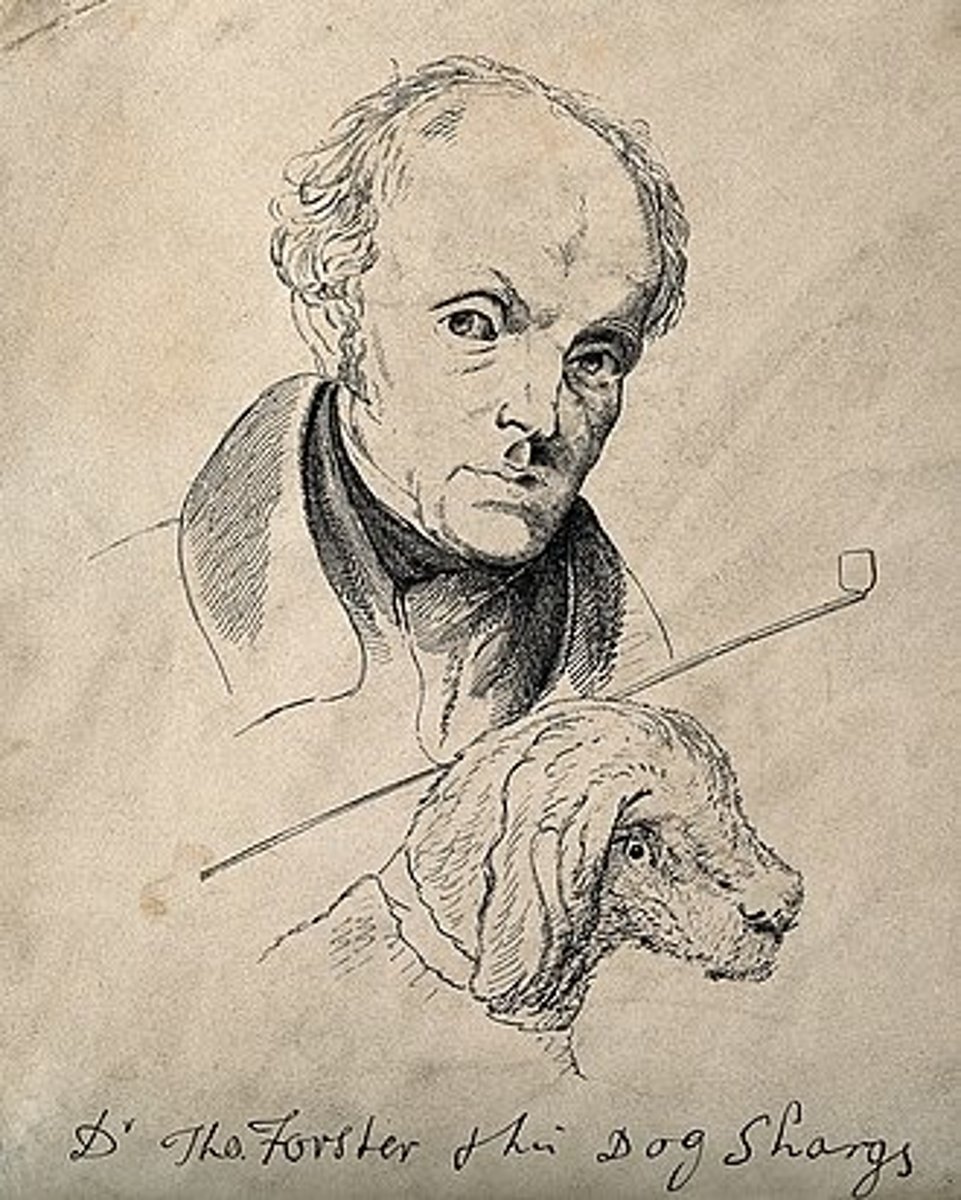Famous British Astronomers
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
37 Terms
(Theoretical Physicist - First to Set Out a Theory of Cosmology)
Birthdate: January 8, 1942
Sun Sign: Capricorn
Birthplace: Oxford, England
Died: March 14, 2018
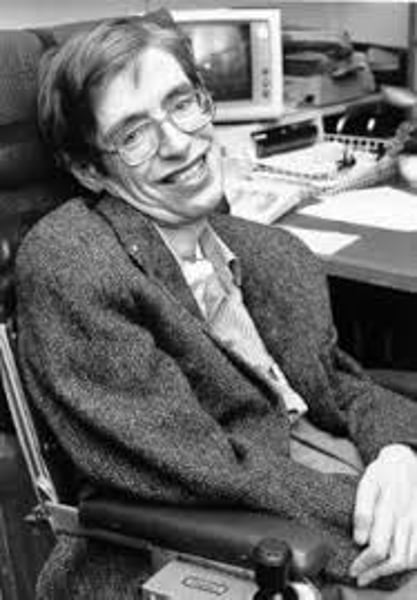
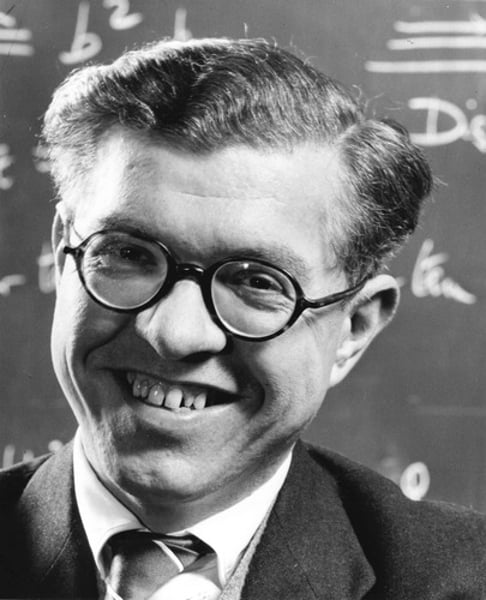
Stephen Hawking was an English theoretical physicist and cosmologist, who despite being afflicted motor neurone disease that severely limited his physical abilities, was able to build a phenomenally successful career. He was the first to set out a theory of cosmology explained by a union of the general theory of relativity and quantum mechanics. Hawking was ranked 25 in the BBC's poll of the 100 Greatest Britons, in 2002.
Stephen Hawking

(Astronomer Known for His Discovery of 'Uranus' and 'Infrared Radiation')
Birthdate: November 15, 1738
Sun Sign: Scorpio
Birthplace: Hanover, Germany
Died: August 23, 1822
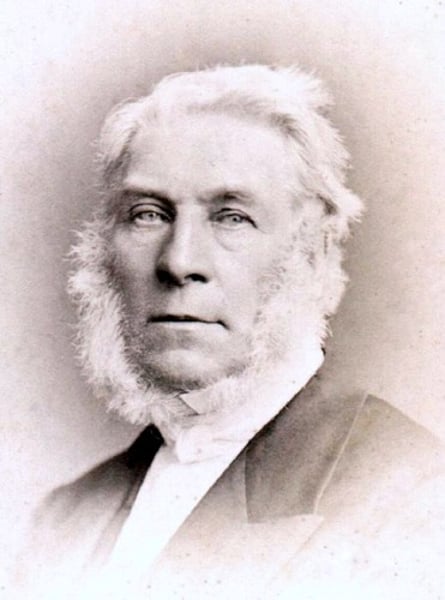
William Herschel was a German-born British astronomer and composer. He pioneered the use of astronomical spectrophotometry and discovered infrared radiation. Impressed by his work, King George III appointed him the Court Astronomer. Herschel often collaborated with his sister, Caroline Lucretia Herschel, a fellow astronomer. In 1816, he was made a Knight of the Royal Guelphic Order.
William Herschel
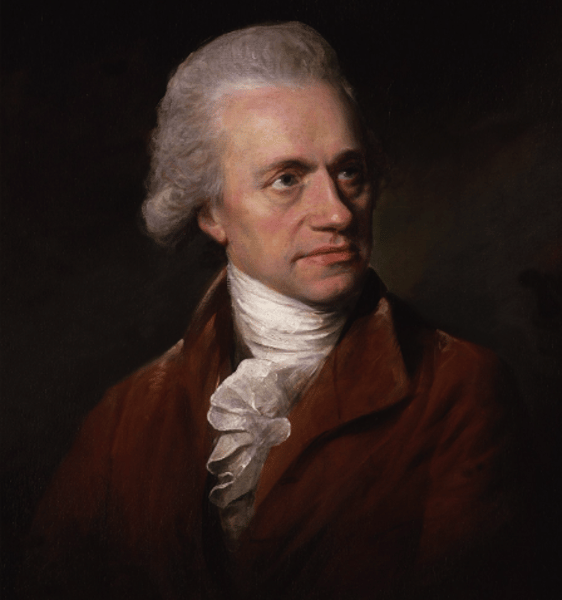
(Philosopher)
Birthdate: July 28, 1635
Sun Sign: Leo
Birthplace: Freshwater, Isle of Wight
Died: March 3, 1703
Scientist Robert Hooke, also called England's Leonardo, initially gained recognition as an architect, conducting surveys following the Great Fire of London. He also taught geometry and was part of the Royal Society. He assisted Robert Boyle and eventually developed his own microscope, thus becoming the first to visualize micro-organisms.
Robert Hooke

(Mathematician known for Calculating the Orbit of a Comet & Was the Second Astronomer Royal in Britain)
Birthdate: November 8, 1656
Sun Sign: Scorpio
Birthplace: Haggerston, London, England
Died: January 14, 1742
Edmond Halley was an English astronomer and mathematician who was mainly concerned with practical applications of science. He abandoned college education to travel to St. Helena. He published catalogue of 341 southern stars with telescopically determined locations. Known for his wide range of interest, he helped Newton to publish his magnum opus, Philosophiæ Naturalis Principia Mathematica. He used Newton's Law of Motion to compute periodicty of Halley’s Comet.
Edmond Halley

(Astronomer)
Birthdate: December 28, 1882
Sun Sign: Capricorn
Birthplace: Kendal
Died: November 22, 1944
Arthur Eddington was an English physicist, astronomer, and mathematician. He wrote numerous articles that explained Albert Einstein's theory of general relativity to the English-speaking world. He began his career in academics and eventually shifted to astronomy, becoming the chief assistant to the Astronomer Royal at the Royal Greenwich Observatory. He was a recipient of the Henry Draper Medal.
Arthur Eddington

(Astronomer, Astrophysicist)
Birthdate: May 10, 1900
Sun Sign: Taurus
Birthplace: Wendover, Buckinghamshire, England
Died: December 7, 1979
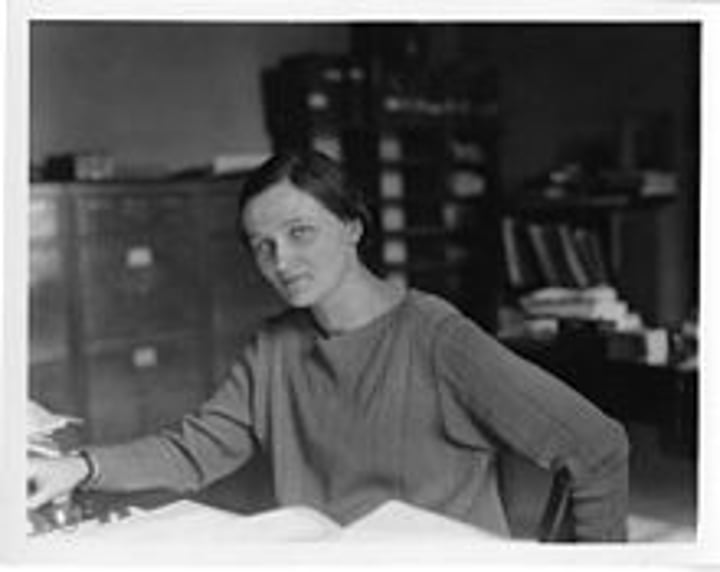
After losing her father at 4, Cecilia Payne-Gaposchkin was raised singlehandedly by her mother. The incredibly talented Cecilia studied at Cambridge but failed to secure a degree because of her gender. She later joined Harvard and opposing prevalent beliefs, proposed that stars were mainly made of hydrogen and helium.
Cecilia Payne-Gaposchkin

(Architect)
Birthdate: October 20, 1632
Sun Sign: Libra
Birthplace: East Knoyle
Died: February 25, 1723
Architect Sir Christopher Wren had built over 50 churches in London, the most popular of them being the St. Paul’s Cathedral. He was a major force behind the formation of the Royal Society and was also knighted for his achievements. He was also a member of the English Parliament.
Sir Christopher Wren

(Meteorologists)
Birthdate: April 7, 1809
Sun Sign: Aries
Birthplace: Rotherhithe, London, England
Died: February 7, 1903
Renowned meteorologist and aeronaut James Glaisher was a pioneer of balloon flights and had penned the iconic book Travels in the Air. He had also contributed to the formation of the Meteorological Society and the Aeronautical Society of Britain. The 2019 movie The Aeronauts depicts his exploits as a balloonist.
James Glaisher

(English Astronomer Who Formulated the Theory of 'Stellar Nucleosynthesis')
Birthdate: June 24, 1915
Sun Sign: Cancer
Birthplace: Bingley, England
Died: August 20, 2001
Fred Hoyle was an English astronomer known for his theory of stellar nucleosynthesis. He spent most of his career at the Institute of Astronomy at Cambridge, serving as its director for six years. He was also an author of science fiction novels, short stories, and plays and appeared in a series of radio talks on astronomy for the BBC.
Fred Hoyle

(British Polymath Known for His Invention of 'Blueprint')
Birthdate: March 7, 1792
Sun Sign: Pisces
Birthplace: Slough, Buckinghamshire, England
Died: May 11, 1871
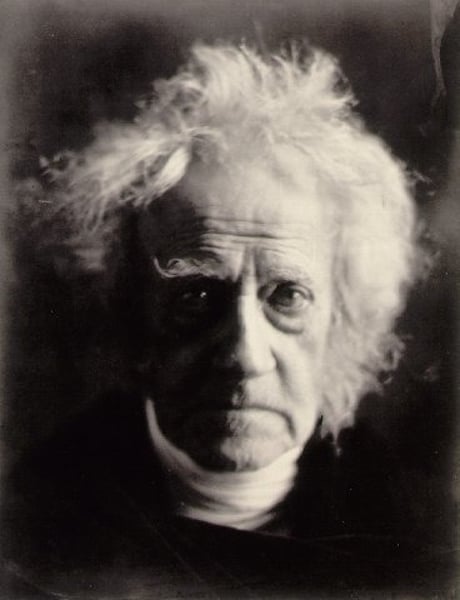
The son of renowned astronomer William Herschel, John Herschel was educated at Eton and Cambridge and grew up to be a polymath. Apart from contributing to the field of photography, he was known for cataloguing and naming stars and satellites. He briefly also served as the Master of the Royal Mint.
John Herschel

(Mathematician, Linguist, Translator, Astronomer, Scientist)
Birthdate: December 26, 1780
Sun Sign: Capricorn
Birthplace: Jedburgh
Died: November 28, 1872
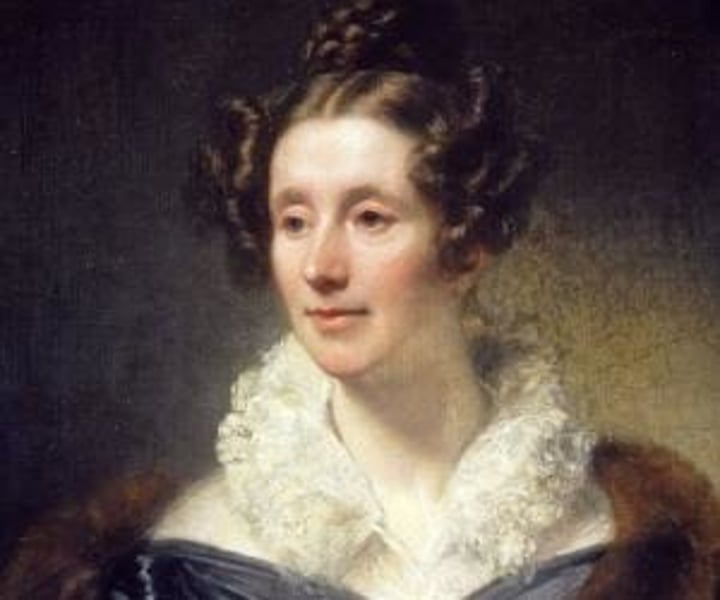
One of the two pioneering female honorary members of the Royal Astronomical Society, Mary Somerville was a 19th-century polymath and science writer. Though she specialized in math and astronomy, she was also well-versed in botany and geology. The Connection of the Physical Sciences remains her most notable work.
Mary Somerville

(Scientist)
Birthdate: December 11, 1781
Sun Sign: Sagittarius
Birthplace: Jedburgh, Scotland
Died: February 10, 1868
David Brewster was a British scientist, inventor, and author. He conducted many experiments in physical optics, especially concerned with the study of the polarization of light. Fellow scientist William Whewell dubbed him the "father of modern experimental optics." He was also a pioneer in photography and invented an improved stereoscope. He wrote numerous works of popular science as well.
David Brewster

(Nobleman)
Birthdate: April 27, 1564
Sun Sign: Taurus
Birthplace: Tynemouth Castle, Northumberland, England
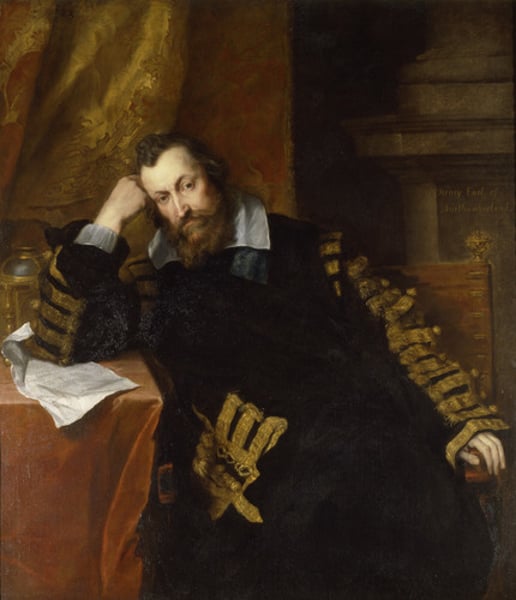
English nobleman. He was a grandee and one of the wealthiest peers of the court of Elizabeth I. Under James I, Northumberland was a long-term prisoner in the Tower of London, due to the suspicion that he was complicit in the Gunpowder Plot. He is known for the circles he moved in as well as for his own achievements. He acquired the sobriquet The Wizard Earl (also given to Gerald FitzGerald, 11th Earl of Kildare), from his scientific and alchemical experiments, his passion for cartography, and his large library.
Henry Percy, 9th Earl of Northumberland

(Radio Astronomer)
Birthdate: May 11, 1924
Sun Sign: Taurus
Birthplace: Fowey, Cornwall, England
Died: September 13, 2021
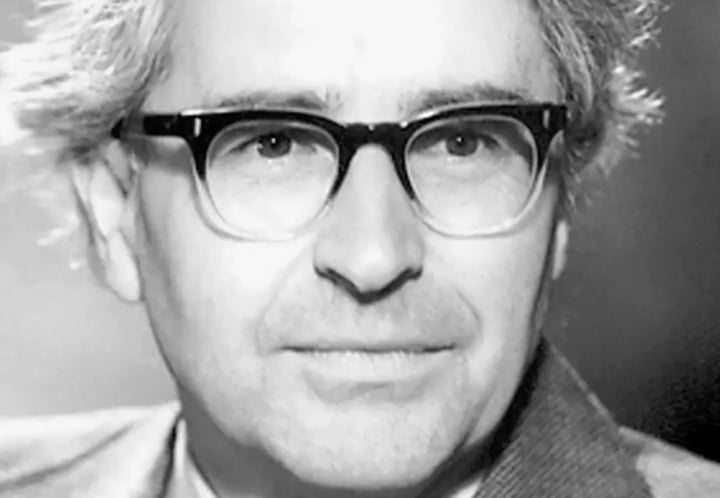
Radio astronomer and physicist Antony Hewish is best known for his Nobel Prize-winning research on pulsars. Apart from teaching at Cavendish Laboratory, Cambridge, he has also served as an advisory council member for the Campaign for Science and Engineering. He also has six honorary degrees to his credit.
Antony Hewish

(British Mathematician and Astronomer)
Birthdate: July 27, 1801
Sun Sign: Leo
Birthplace: Alnwick, Northumberland, England
Died: January 2, 1892
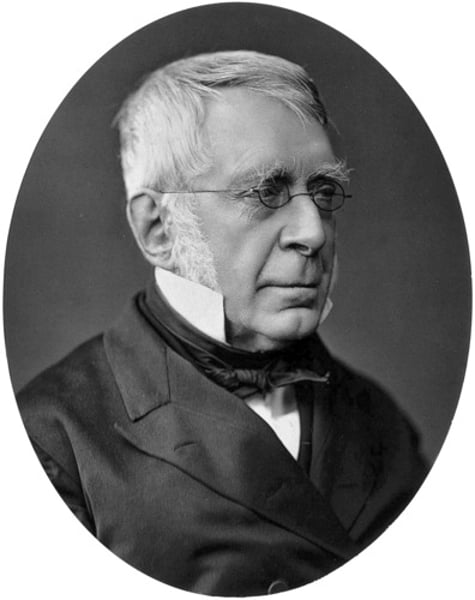
English astronomer George Biddell Airy is best known for locating Greenwich as the prime meridian. He was ripped apart by critics for allegedly failing to help British astronomer John Couch Adams to discover Neptune. The Astronomer Royal was also the first to cure astigmatism by using cylindrical lenses.
George Biddell Airy

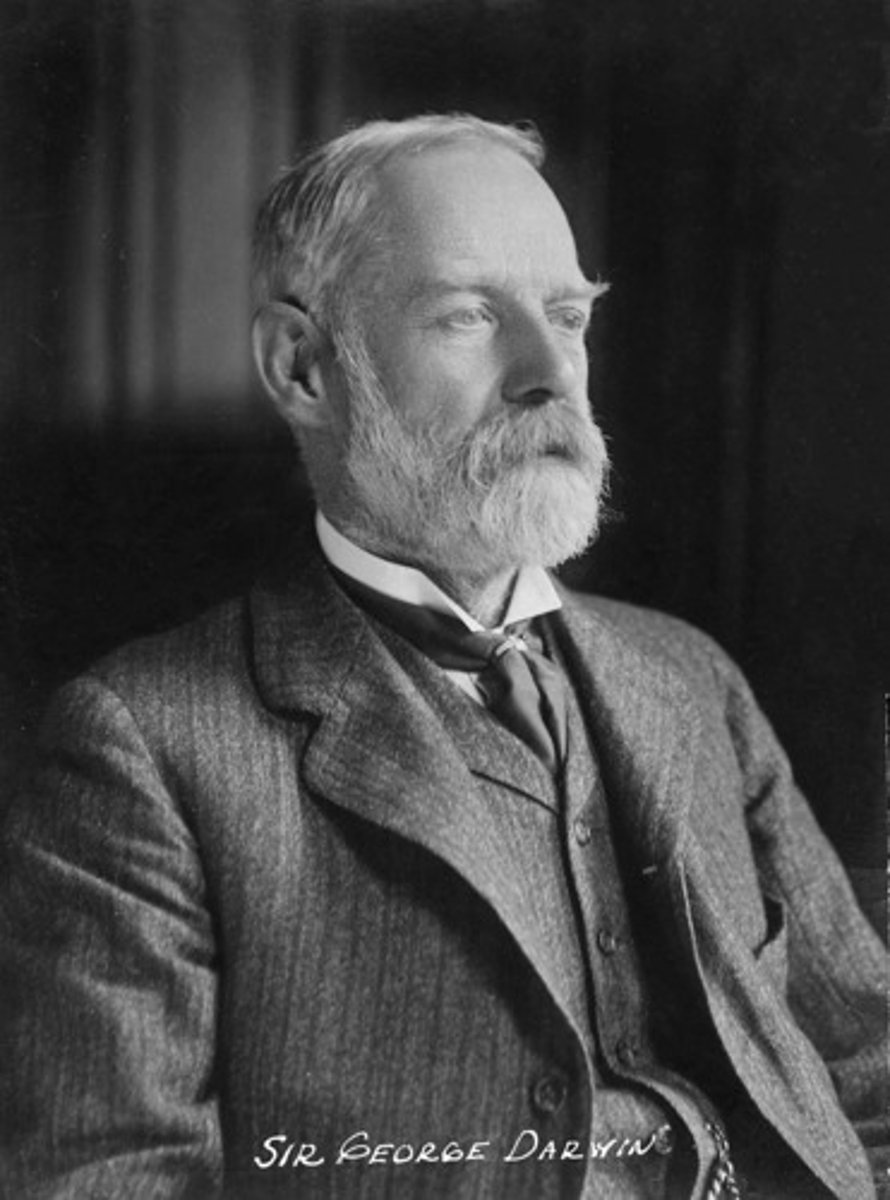
(British Barrister, Astronomer and the Second Son of Naturalist Charles Darwin)
Birthdate: July 9, 1845
Sun Sign: Cancer
Birthplace: Down House, Downe, Kent, England
Died: December 7, 1912
Born to legendary biologist Charles Darwin, George Darwin initially studied law and became a barrister. However, his interest in science made him deviate to astronomy. He believed the Moon was one part of the Earth. He later also taught at Cambridge and was made a Fellow of The Royal Society.
George Darwin

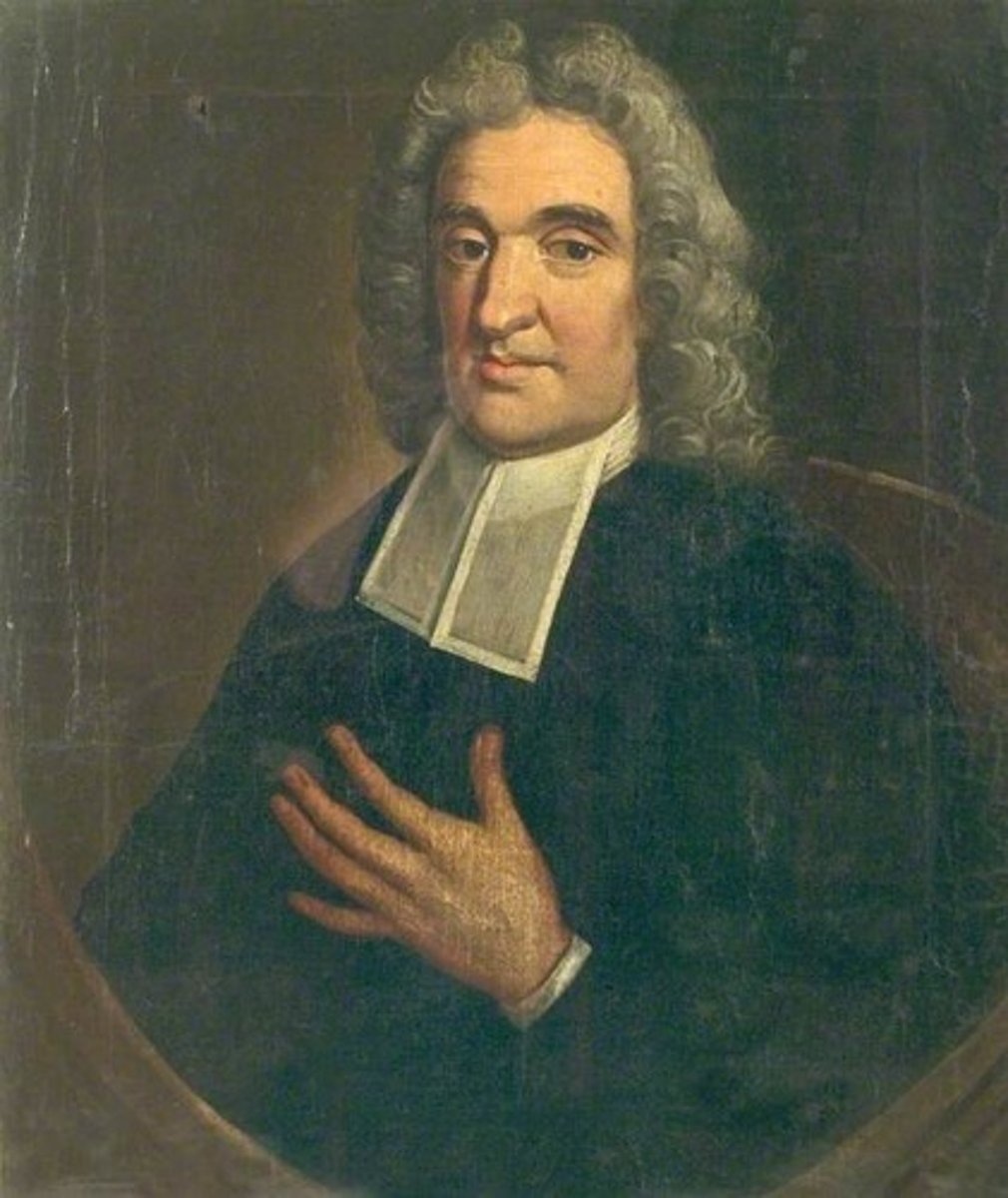
(Astronomer and the first Astronomer Royal)
Birthdate: August 19, 1646
Sun Sign: Leo
Birthplace: Denby, Derbyshire, England
Died: December 31, 1719
an English astronomer and the first Astronomer Royal. His main achievements were the preparation of a 3,000-star catalogue, Catalogus Britannicus, and a star atlas called Atlas Coelestis, both published posthumously. He also made the first recorded observations of Uranus, although he mistakenly catalogued it as a star, and he laid the foundation stone for the Royal Greenwich Observatory.
John Flamsteed

(British Physicist and Radio Astronomer Known for Developing the 76m Radio Telescope at Jodrell Bank)
Birthdate: August 31, 1913
Sun Sign: Virgo
Birthplace: Oldland Common, Bristol, England
Died: August 6, 2012
Bernard Lovell was a British physicist and radio astronomer who served as the first director of Jodrell Bank Observatory, holding this position from 1945 to 1980. He studied at the University of Bristol and embarked on an academic career. During World War II, he worked for the Telecommunications Research Establishment (TRE). He was awarded the Benjamin Franklin Medal in 1980.
Bernard Lovell
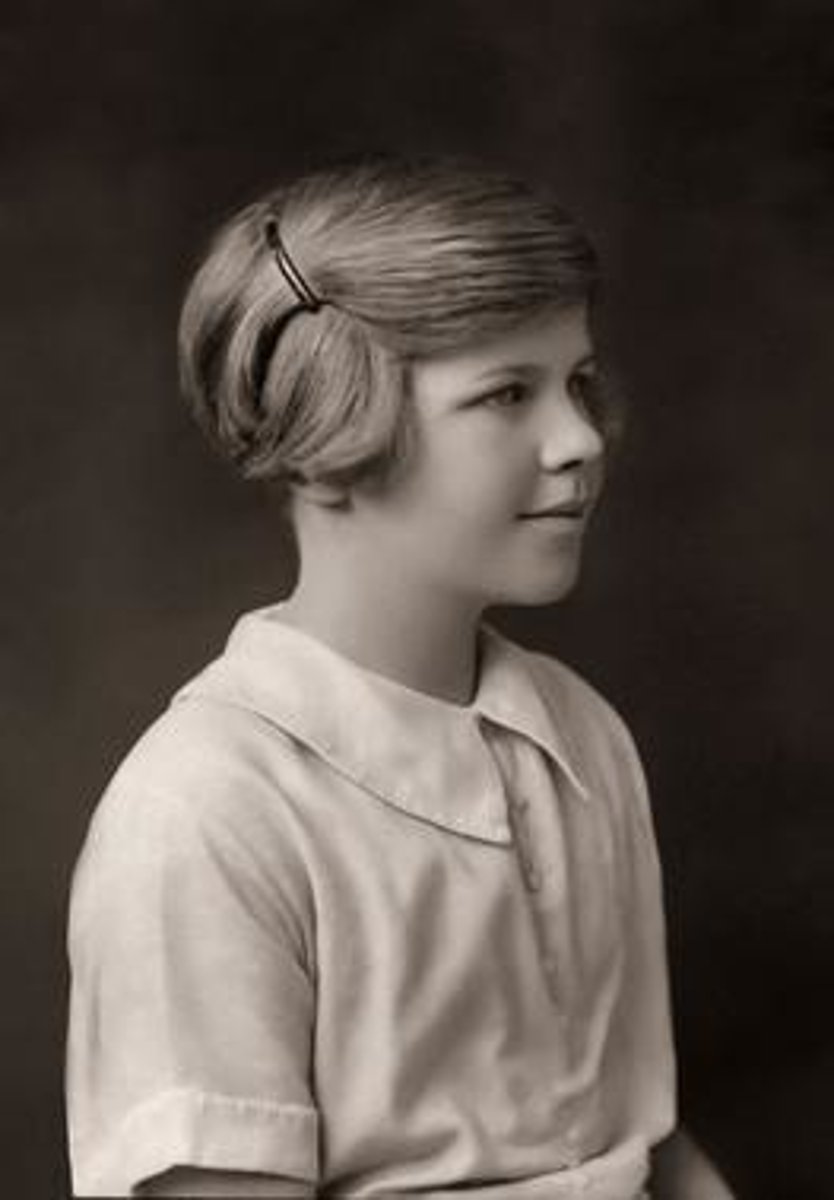
(Amateur astronomer)
Birthdate: July 11, 1918
Sun Sign: Cancer
Birthplace: Oxford, England
Died: April 30, 2009
an English accountant and teacher. She is remembered as the first person to suggest the name Pluto for the dwarf planet discovered by Clyde Tombaugh in 1930. At the time, she was 11 years old.
Venetia Phair

(Mathematician, Astronomer, University teacher)
Birthdate: June 5, 1819
Sun Sign: Gemini
Birthplace: Laneast
Died: January 21, 1892
His most famous achievement was predicting the existence and position of Neptune, using only mathematics. The calculations were made to explain discrepancies with Uranus's orbit and the laws of Kepler and Newton. At the same time, but unknown to each other, the same calculations were made by Urbain Le Verrier. Le Verrier would send his coordinates to Berlin Observatory astronomer Johann Gottfried Galle, who confirmed the existence of the planet on 23 September 1846, finding it within 1° of Le Verrier's predicted location. (There was, and to some extent still is, some controversy over the apportionment of credit for the discovery; see Discovery of Neptune.)
Adams was Lowndean Professor in the University of Cambridge from 1859 until his death. He won the Gold Medal of the Royal Astronomical Society in 1866. In 1884, he attended the International Meridian Conference as a delegate for Britain.
John Couch Adams
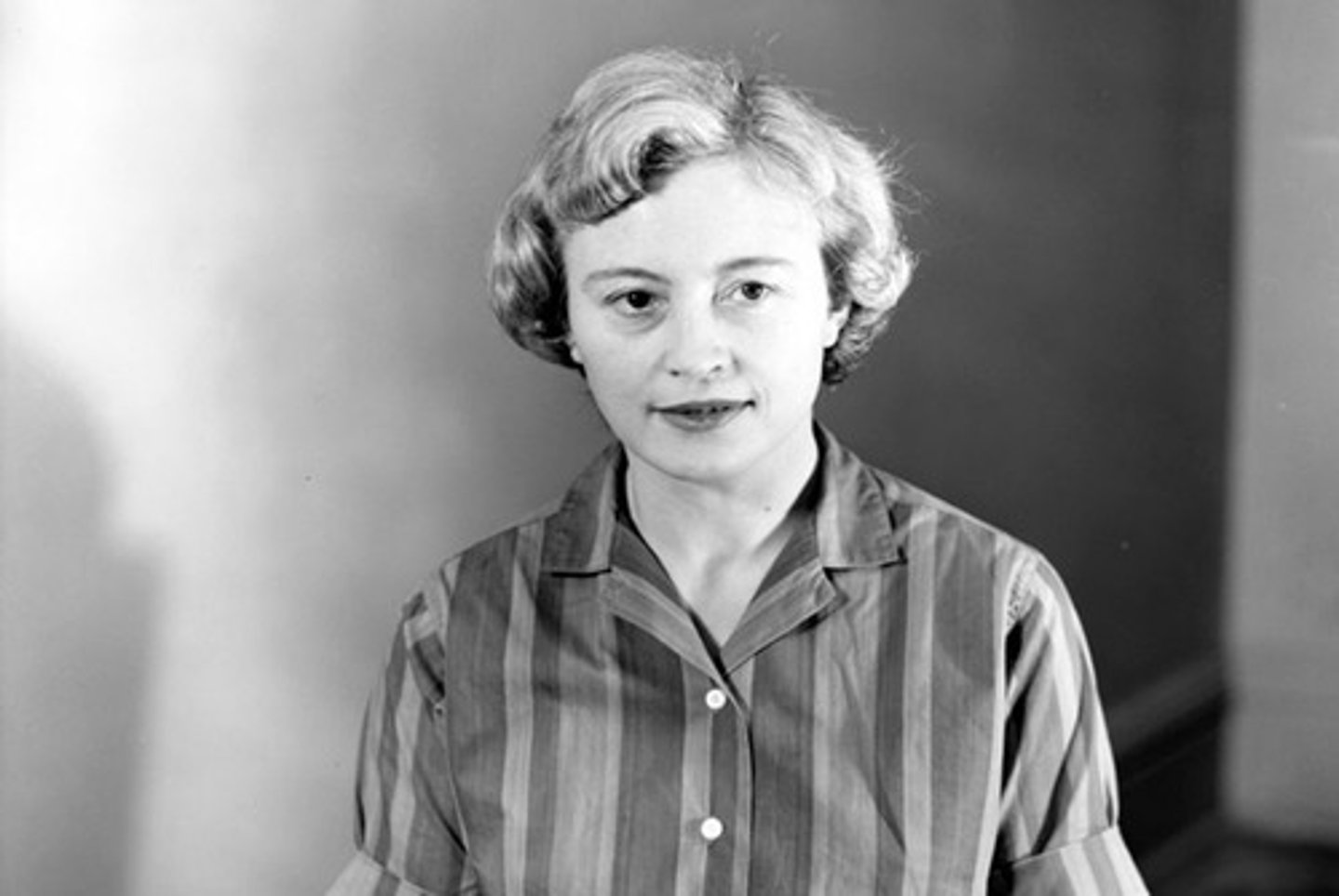
(British-American Observational Astronomer and Astrophysicist Known for Her Contributions to the Theory of ‘Quasars')
Birthdate: August 12, 1919
Sun Sign: Leo
Birthplace: Davenport, Stockport, England
Died: April 5, 2020
Margaret Burbidge was a British-American observational astronomer and astrophysicist. She was the first author of the influential B2FH paper and one of the founders of stellar nucleosynthesis. She held several leadership and administrative posts and was well known for her work opposing discrimination against women in astronomy. In 1988, she was awarded the Albert Einstein World Award of Science.
Margaret Burbidge

(Astronomer)
Birthdate: 1693
Sun Sign: Pisces
Birthplace: Sherborne, Gloucestershire, England
Died: July 13, 1762
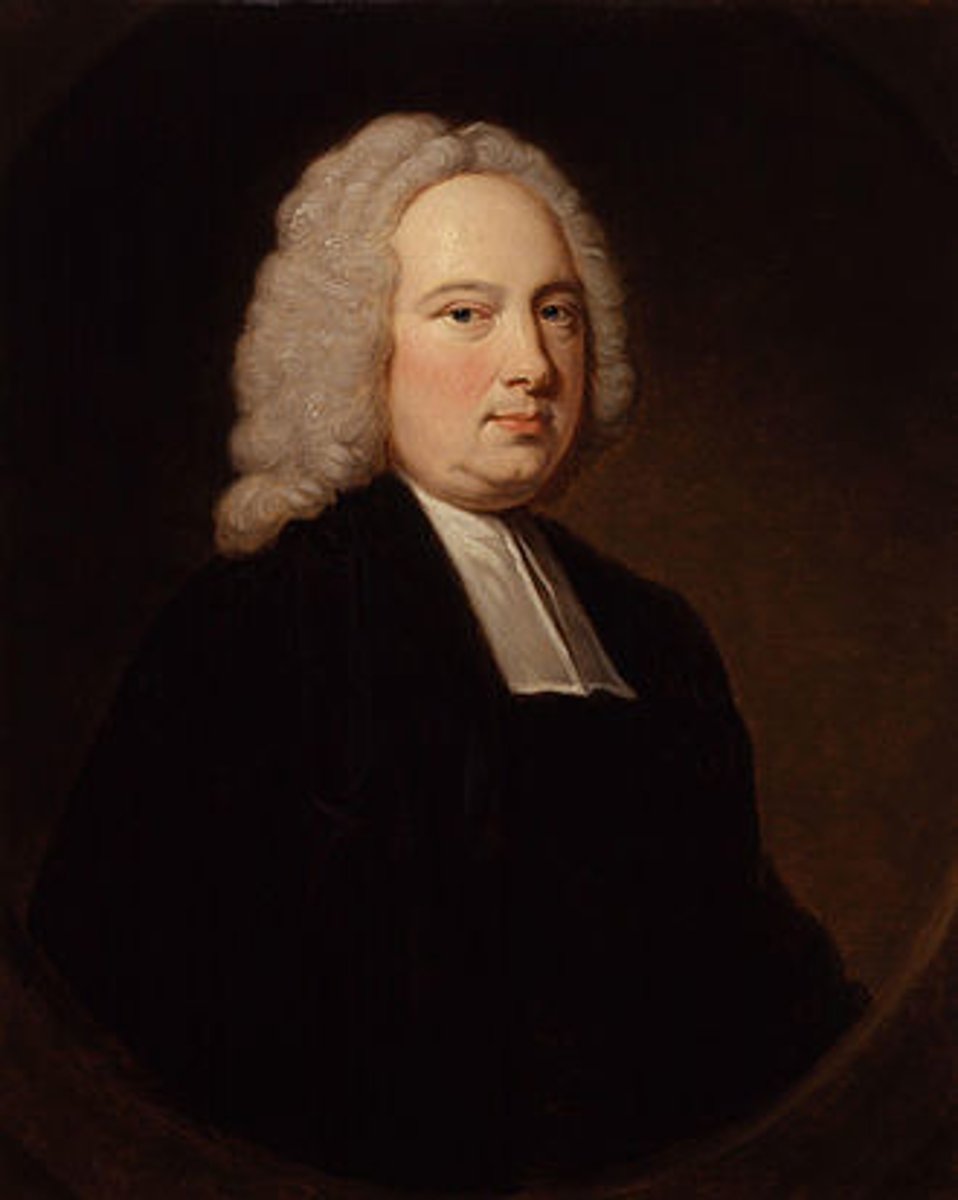
was an English astronomer and priest who served as the third Astronomer Royal from 1742. He is best known for two fundamental discoveries in astronomy, the aberration of light (1725–1728), and the nutation of the Earth's axis (1728–1748).
These two discoveries were called "the most brilliant and useful of the century" by Jean Baptiste Joseph Delambre, historian of astronomy, mathematical astronomer and director of the Paris Observatory. In his History of astronomy in the 18th century (1821), Delambre stated:[1]
"It is to these two discoveries by Bradley that we owe the exactness of modern astronomy. ... This double service assures to their discoverer the most distinguished place (after Hipparchus and Kepler) above the greatest astronomers of all ages and all countries."
James Bradley

(Astronomer, Engineer)
Birthdate: August 19, 1808
Sun Sign: Leo
Birthplace: Edinburgh
Die May 7, 1890
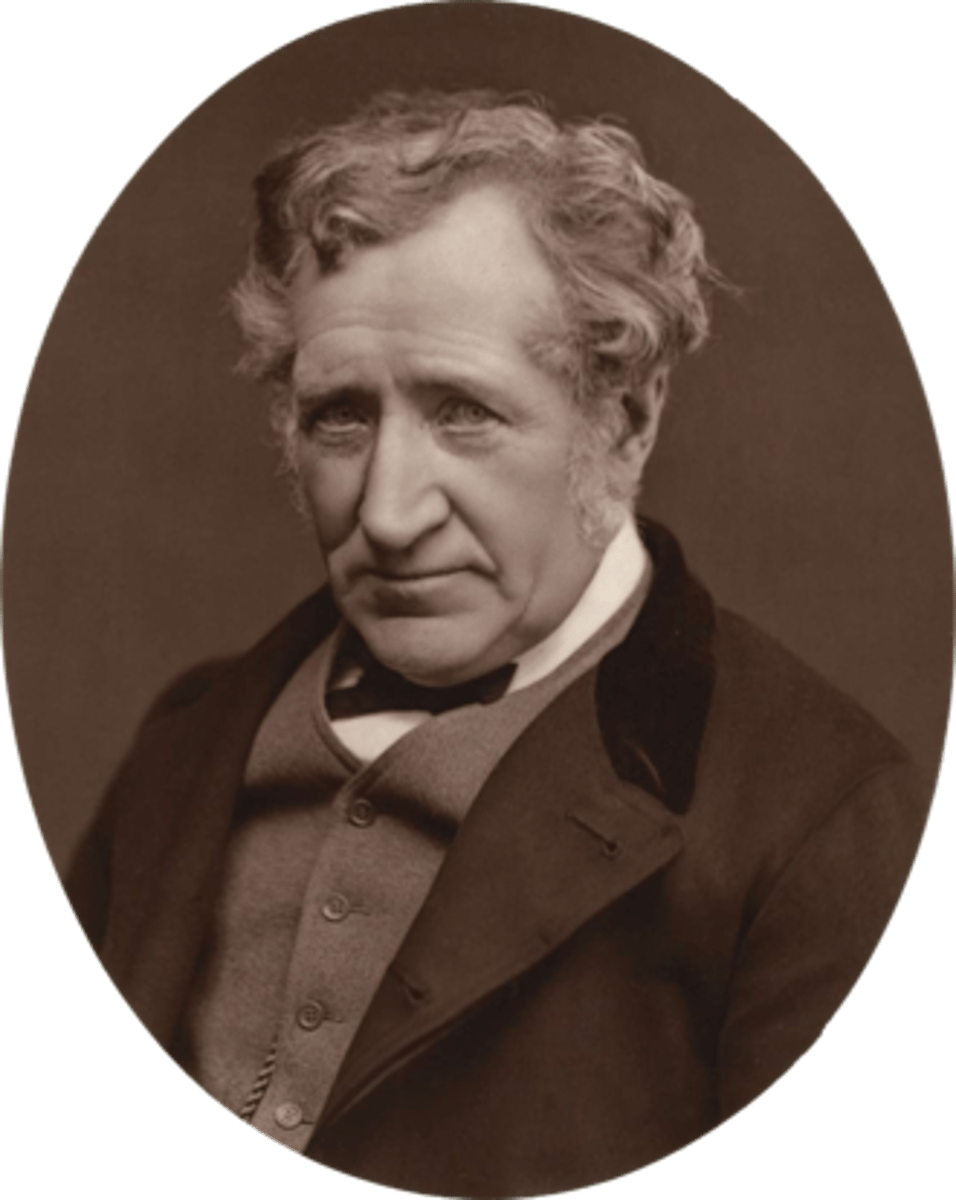
was a Scottish engineer, philosopher, artist and inventor famous for his development of the steam hammer. He was the co-founder of Nasmyth, Gaskell and Company manufacturers of machine tools. He retired at the age of 48, and moved to Penshurst, Kent where he developed his hobbies of astronomy and photography.
James Nasmyth

(British Scientist and Astronomer Known for Discovering the Gas Helium and Was the Founder of the Journal 'Nature')
Birthdate: May 17, 1836
Sun Sign: Taurus
Birthplace: Rugby, Warwickshire, England
Died: August 16, 1920
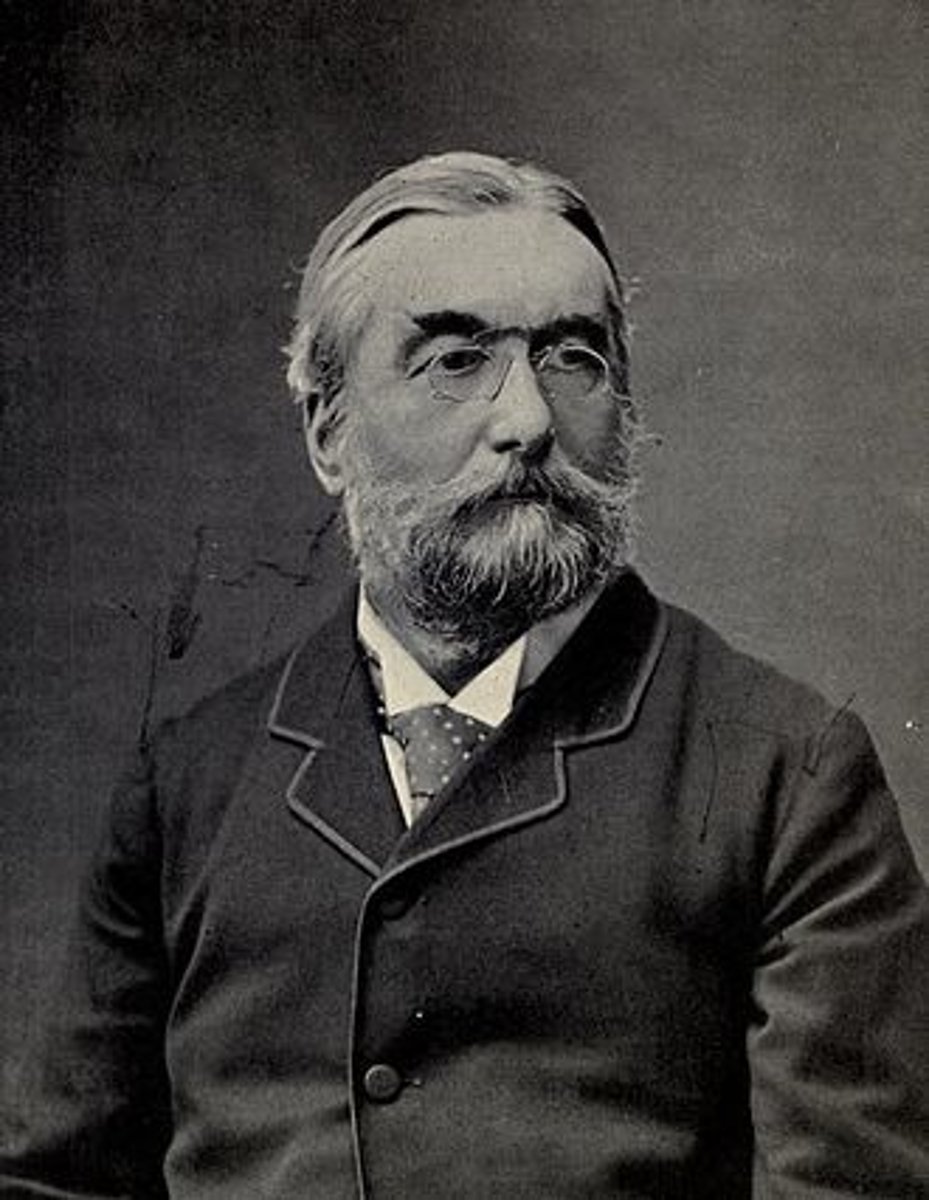
British astronomer Norman Lockyer is known for his discovery of the gas helium, along with French astronomer Pierre Janssen, though both worked independently. A talented author, too, he established the periodical Nature and remained associated with it till death. He was knighted for his achievements.
Norman Lockyer

(Astronomer Who Predicted the Transit of Venus of 1639)
Birthdate: 1618 AD
Birthplace: Toxteth Park, Liverpool, Lancashire, England
Died: January 3, 1641
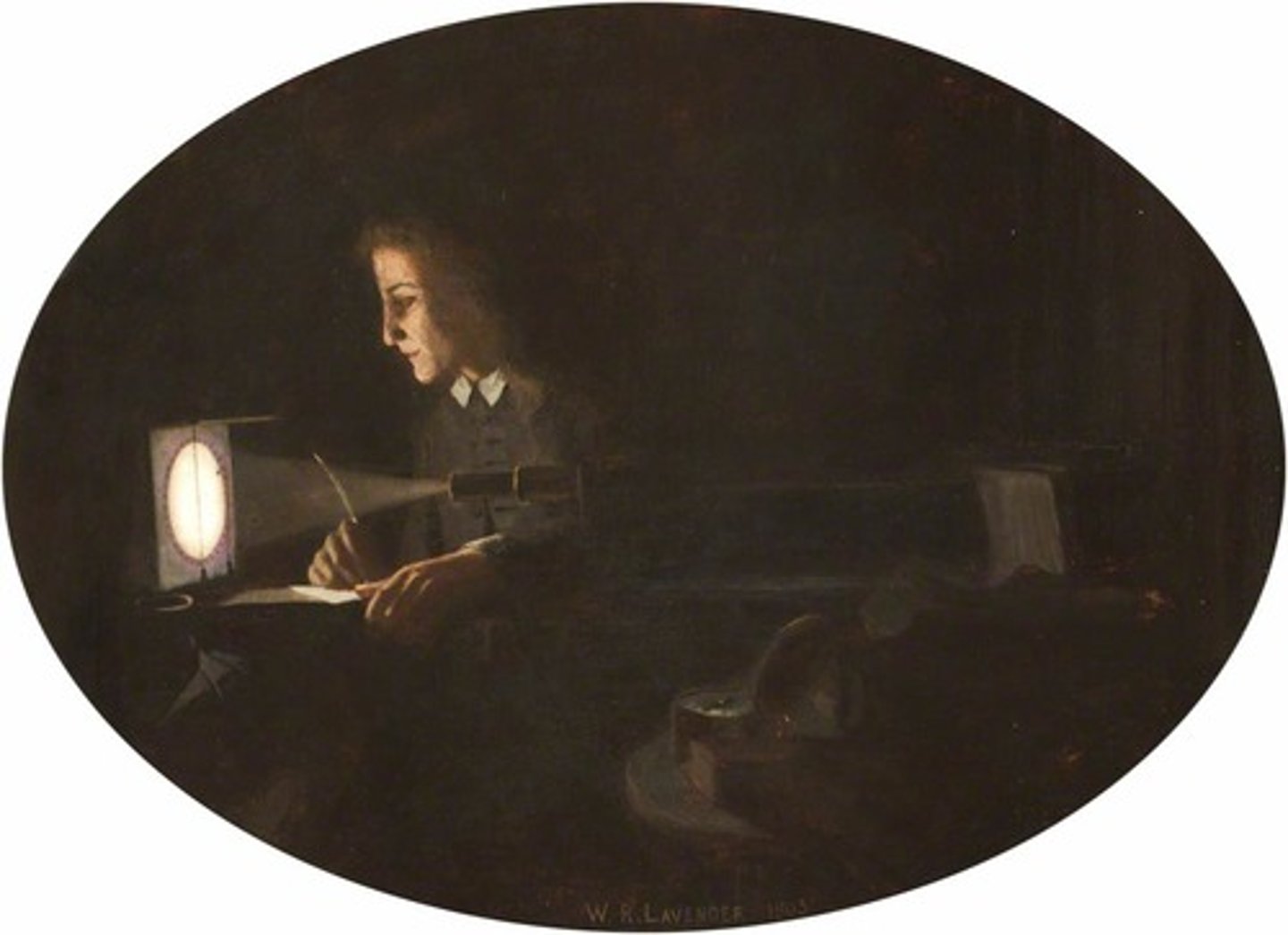
He was the first person to demonstrate that the Moon moved around the Earth in an elliptical orbit; and he was the only person to predict the transit of Venus of 1639, an event which he and his friend William Crabtree were the only two people to observe and record. Most remarkably, Horrocks (correctly) asserted that Jupiter was accelerating in its orbit while Saturn was slowing and interpreted this as due to mutual gravitational interaction, thereby demonstrating that gravity's actions were not limited to the Earth, Sun, and Moon.[3]
His early death and the chaos of the English Civil War nearly resulted in the loss to science of his treatise on the transit, Venus in sole visa; but for this and his other work he is acknowledged as one of the founding fathers of British astronomy.
Jeremiah Horrocks

(Mathematician)
Birthdate: 1546 AD
Birthplace: Wootton, Kent, England
Died: August 24, 1595
was an English mathematician and astronomer. He was the first to expound the Copernican system in English but discarded the notion of a fixed shell of immoveable stars to postulate infinitely many stars at varying distances.[1] He was also first to postulate the "dark night sky paradox".[2]
Thomas Digges
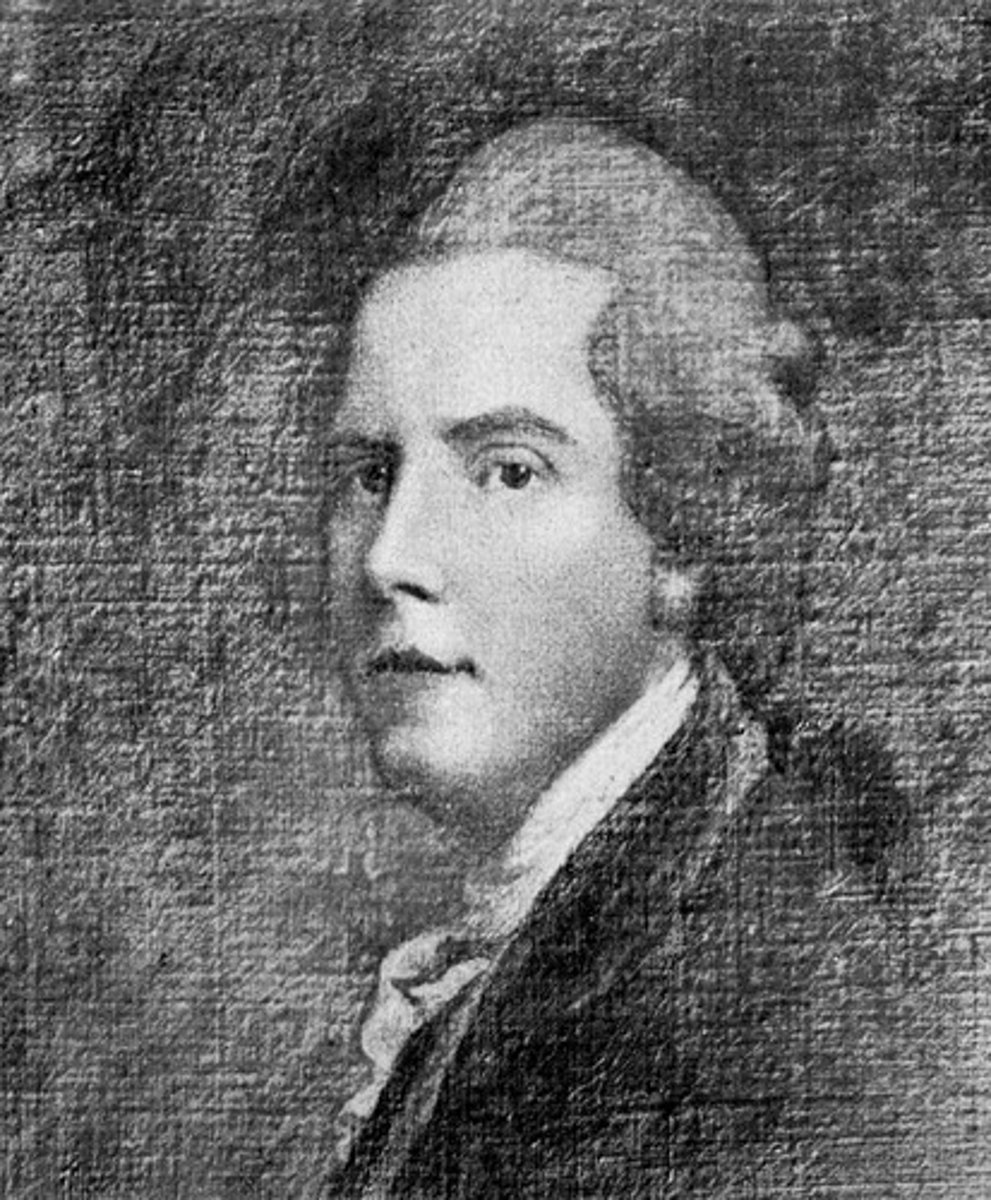

(Merchant ,Astronomer)
Birthdate: June 18, 1799
Sun Sign: Gemini
Birthplace: Bolton
Died: October 5, 1880
He is remembered for his improvements to the reflecting telescope and his ensuing discoveries of four planetary satellites.
William Lassell
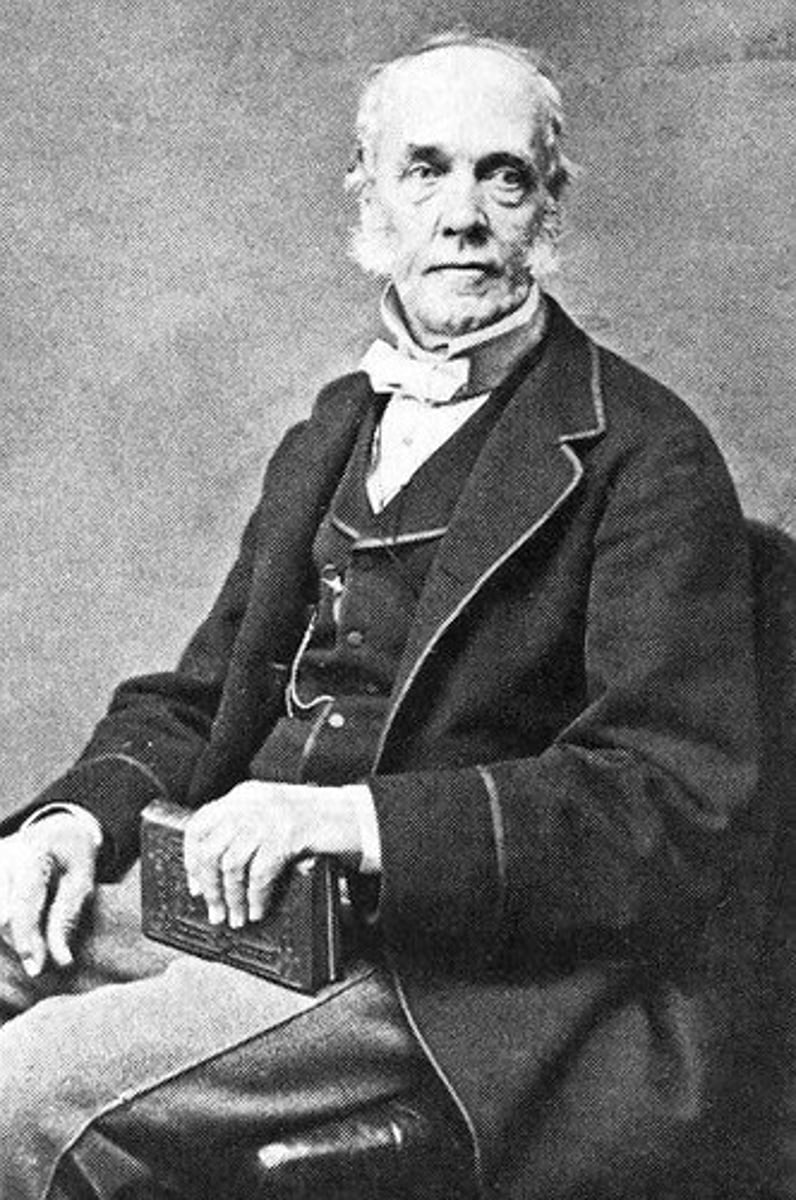

(Astronomer)
Birthdate: January 8, 1868
Sun Sign: Capricorn
Birthplace: Measham, Leicestershire, England
Died: May 25, 1939
was an English astronomer and the ninth Astronomer Royal who is remembered today largely for introducing time signals ("pips") from Greenwich, England, and for the role he played in proving Einstein's theory of general relativity.
Frank Watson Dyson
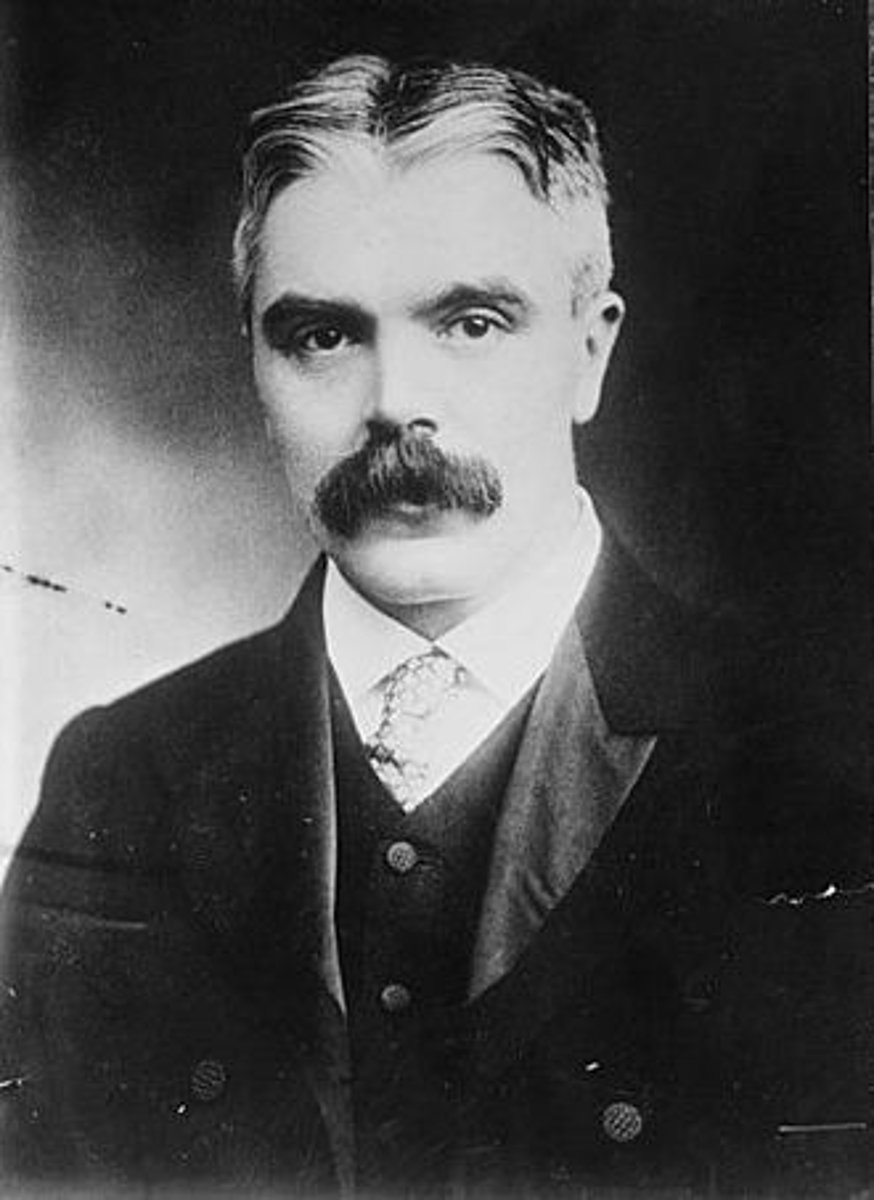

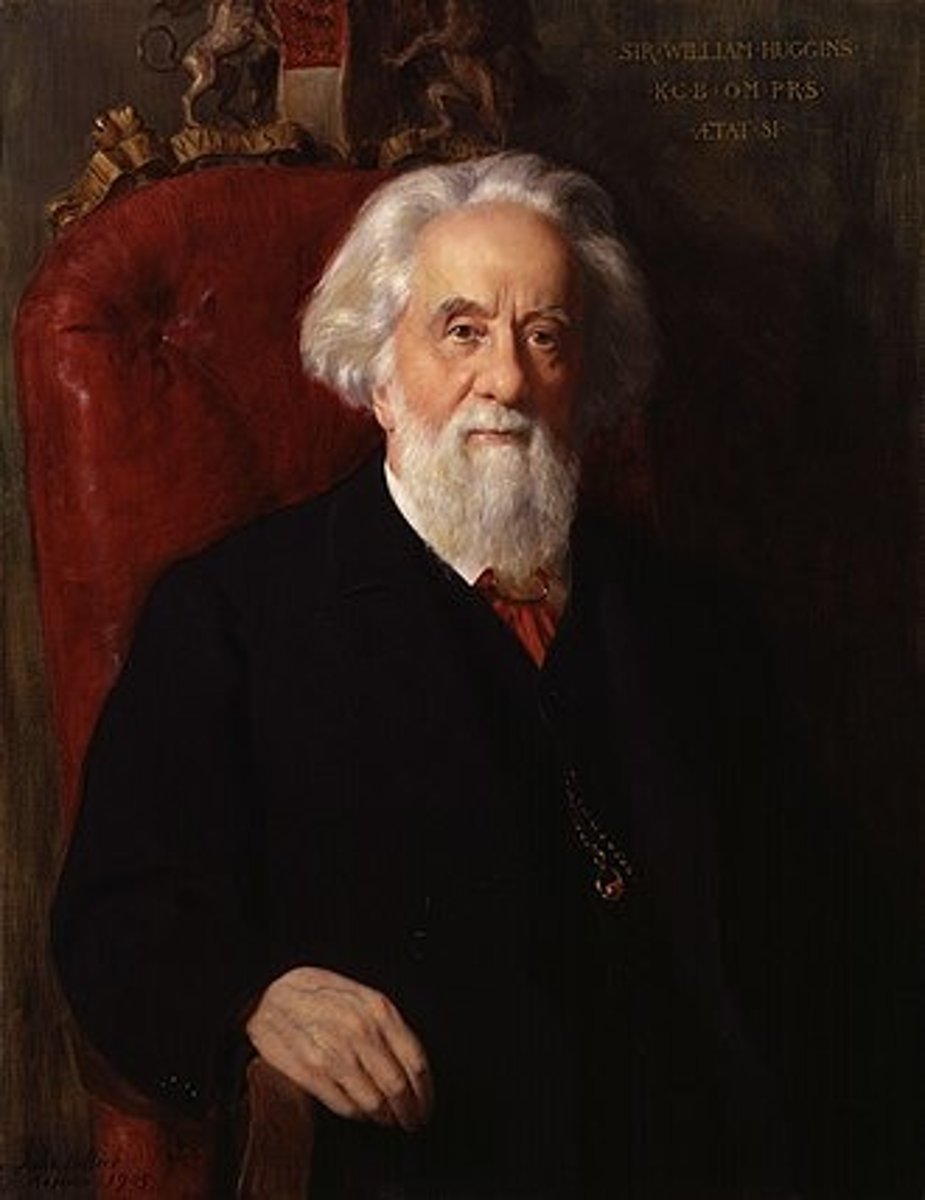
(Astronomer)
Birthdate: February 7, 1824
Sun Sign: Aquarius
Birthplace: Cornhill, Middlesex, England
Died: May 12, 1910
was an English astronomer best known for his pioneering work in astronomical spectroscopy together with his wife, Margaret.[1]
William Huggins

(Astronomer)
Birthdate: July 24, 1843
Sun Sign: Leo
Birthplace: Derby, England
Died: December 3, 1920
Sir William de Wiveleslie Abney was an English photographer, chemist, and astronomer. A pioneer of many technical facets of photography, Abney's work in the chemistry of photography led to developments in astronomy apart from producing useful photographic products. Sir William de Wiveleslie Abney also wrote several books on photography that went on to become standard texts at that time.
Sir William de Wiveleslie Abney
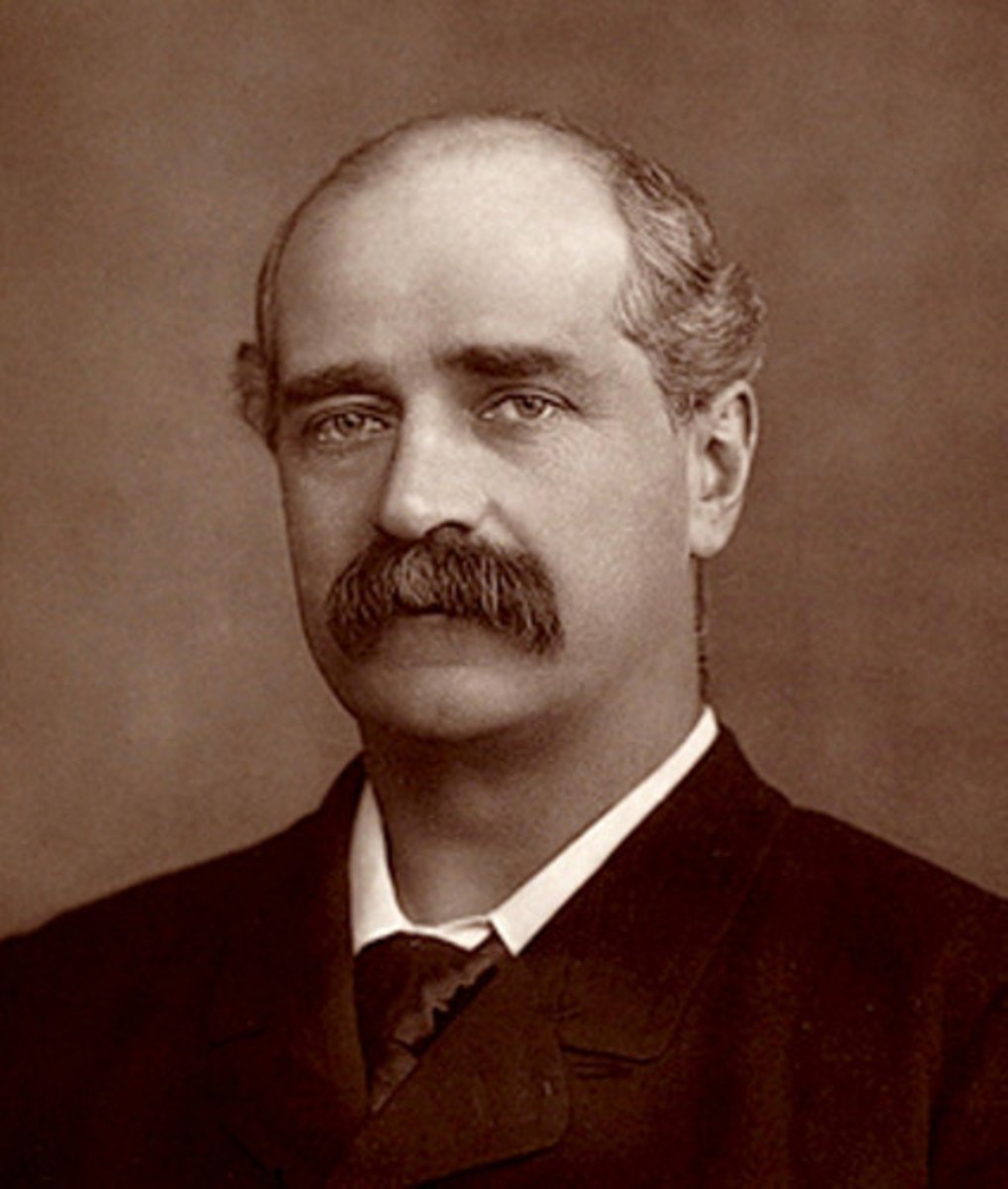

(Mathematician)
Birthdate: April 16, 1682
Sun Sign: Aries
Birthplace: Bloomsbury, London, England
Died: February 14, 1744
was an English mathematician, and laid claim to the invention of the octant, two years after Thomas Godfrey claimed the same.[1]
John Hadley
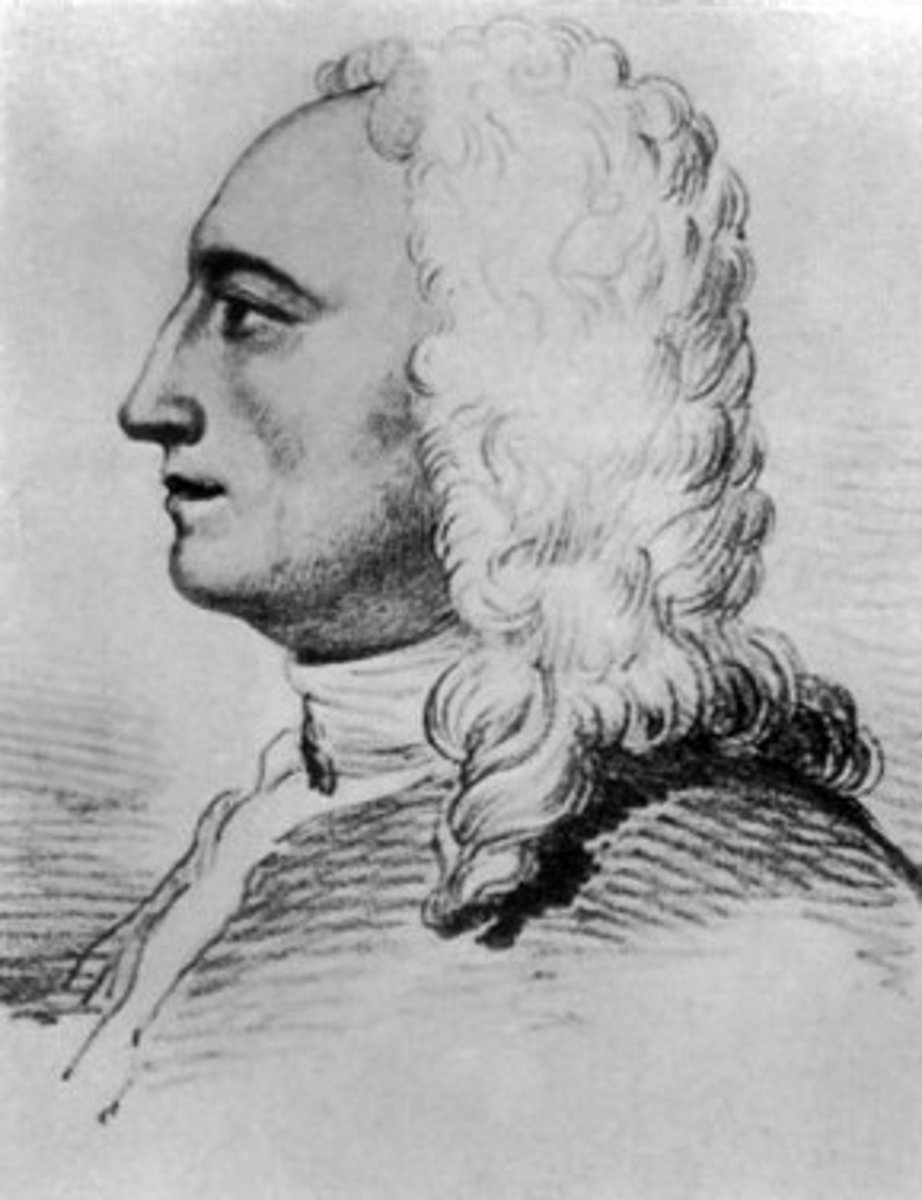

(Astronomer)
Birthdate: April 28, 1774
Sun Sign: Taurus
Birthplace: Newbury, England
Died: August 30, 1844
was an English astronomer. He is most famous for his observations of "Baily's beads" during a total eclipse of the Sun. Baily was also a major figure in the early history of the Royal Astronomical Society, as one of the founders and as the president four times.
Francis Baily
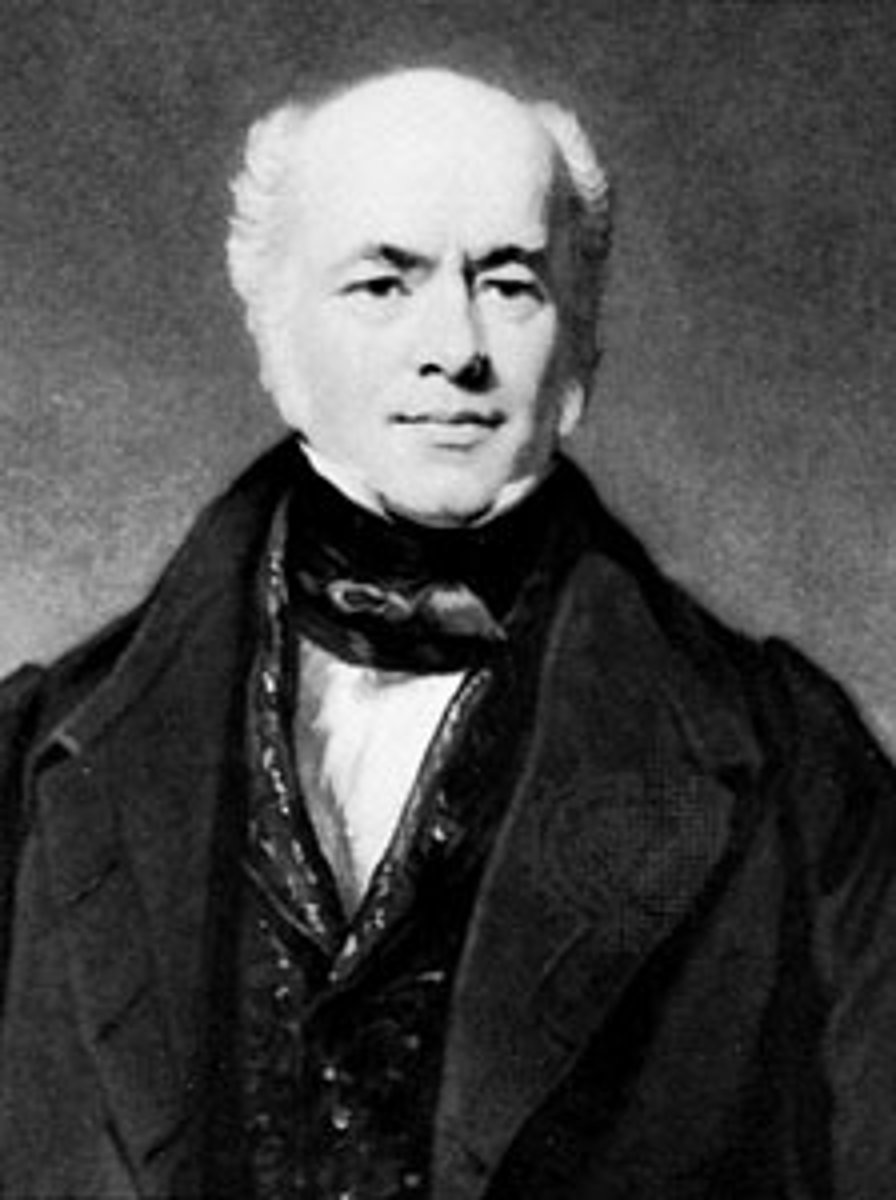

(Astronomer)
Birthdate: January 15, 1815
Sun Sign: Capricorn
Birthplace: Guernsey, Guernsey
Died: April 19, 1889
Warren De la Rue was an astronomer, inventor, and chemist remembered for his work in astronomical photography. In 1840, Warren created one of the first electric light bulbs in the world when he transferred an electric current through a vacuum tube with a platinum coil enclosed. Over the course of his career, he received many awards like the Lalande Prize.
Warren De la Rue
Astronomer Royal is a senior post in the Royal Households of the United Kingdom. There are two officers, the senior being the Astronomer Royal dating from 22 June 1675; the second is the Astronomer Royal for Scotland dating from 1834.
The post was created by King Charles II in 1675, at the same time as he founded the Royal Observatory Greenwich. He appointed John Flamsteed, instructing him "forthwith to apply himself with the most exact care and diligence to the rectifying the tables of the motions of the heavens, and the places of the fixed stars, so as to find out the so-much desired longitude of places, for the perfecting the art of navigation
1st - John Flamsteed (1675 - 1719),
latest - Martin Rees, Baron Rees of Ludlow (from 1995)
Astronomer Royal
(Astronomer)
Birthdate: 1714 AD
Died: October 16, 1786
Apart from being a renowned astronomer, Alexander Wilson was also a qualified surgeon and once co-owned a type-founding business, too. He pioneered the use of kites in meteorological research and also co-founded the Royal Society of Edinburgh. He has a lunar crater named after him.
Alexander Wilson
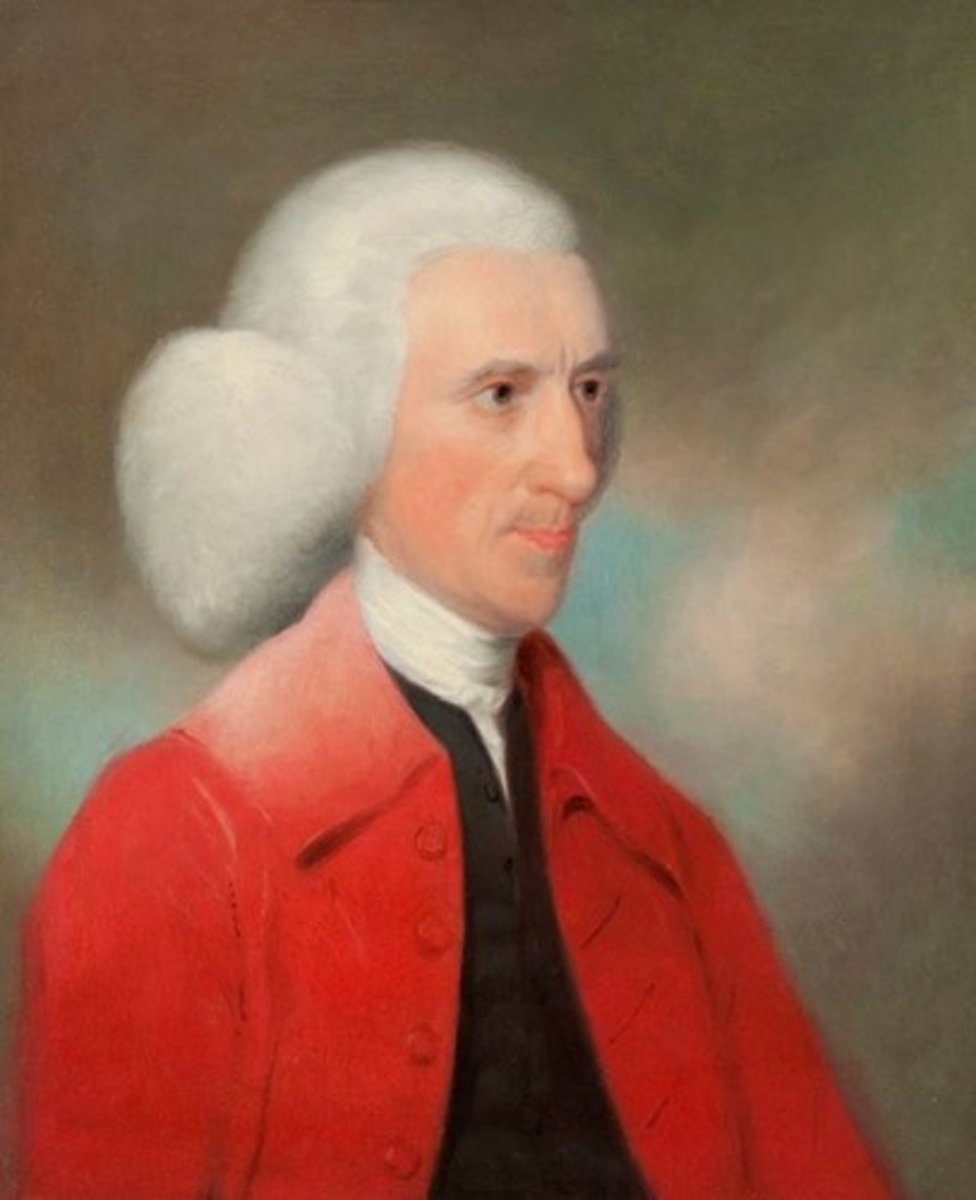

(Instrument maker)
Birthdate: 1753 AD
Birthplace: Corney, England
Died: June 12, 1835
was a British instrument maker who was notable for making telescopes and other astronomical instruments.[1]
Edward Troughton
(Astronomer, Naturalist, Physician)
Birthdate: November 9, 1789
Sun Sign: Scorpio
Birthplace: London, England
Died: February 2, 1860
was an English astronomer, physician, naturalist and philosopher. An early animal rights activist, he promoted vegetarianism and founded the Animals' Friend Society with Lewis Gompertz. He published pamphlets on a wide variety of subjects, including morality, Pythagorean philosophy, bird migration, Sati, and "phrenology", a term that he coined in 1815.
Thomas Ignatius Maria Forster