Acids and Bases (Chem I + Chem HL II)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/96
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 11:43 PM on 9/12/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
97 Terms
1
New cards
a substance that contains hydrogen and ionizes to produce hydrogen ions in an aqueous solution.
Arrhenius definition of an acid:
2
New cards
a substance that contains a hydroxide group, and, when dissociated in water, yields hydroxide ions.
Arrhenius definition of a base:
3
New cards
properties of an acid:
- sour taste
- produces stinging sensation on skin
- reacts with certain metals to produce hydrogen gas
- reacts with limestone (CaCO3) and baking soda to produce CO2
- turns blue litmus paper red
- produces stinging sensation on skin
- reacts with certain metals to produce hydrogen gas
- reacts with limestone (CaCO3) and baking soda to produce CO2
- turns blue litmus paper red
4
New cards
properties of a base:
- bitter taste
- feels slippery on skin
- reacts with acids to produce salt and water (neutralization reaction)
- turns red litmus paper blue
- feels slippery on skin
- reacts with acids to produce salt and water (neutralization reaction)
- turns red litmus paper blue
5
New cards
common acids
hydrochloric acid (HCl), sulfuric acid (H2SO4), acetic/ethanoic acid (CH3COOH), nitric acid (HNO3)
6
New cards
common bases
ammonium hydroxide (NH4OH), sodium hydroxide (NaOH), magnesium hydroxide (Mg(OH)2)
7
New cards
pH
the negative logarithm of the hydrogen/hydronium ion concentration
8
New cards
pH=-log[H+]
formula for pH (H+)
9
New cards
pH=-log[H3O+]
formula for pH (H3O+)
10
New cards
10^-pH
[H+] = ? or [H3O+] = ?
11
New cards
0 to 14
pH scale ranges from
12
New cards
acidic, larger
the more acidic a solution is, the _________ (larger, smaller) the concentration of H+ ions.
13
New cards
10^x
An increase or decrease of one pH unit x means an increase in [H+] of
14
New cards
poH
the negative logarithm of the hydroxide ion concentration
15
New cards
pOH = -log[OH-]
formula for poH:
16
New cards
10^-poH
[OH-] =
17
New cards
14
pH + pOH =
18
New cards
A proton donor
Bronsted-Lowry acid:
19
New cards
A proton acceptor
Bronsted-Lowry base
20
New cards
conjugate acid-base pair
two substances that are related by the loss or gain of a single hydrogen ion
21
New cards
Change "ate" (in polyatomic ion) to "ic" and end with "acid"
how to name an acid that consists of hydrogen and a polyatomic ion
22
New cards
add prefix "hydro," change ending to "ic," and add "acid"
how to name an acid that consists of hydrogen in an element
23
New cards
name the cation, name the anion, change the suffix to '-ide,' or use the polyatomic anion name.
how to name a base/ionic compound
24
New cards
Strong acids
acids that dissociate completely in water and are therefore strong electrolytes
25
New cards
electrolyte
a solution that conducts electricity
26
New cards
examples of strong acids:
HCl, HBr, HI, H2SO4, HNO3, HClO4
27
New cards
weak acid
acids that ionize or dissociate partially in water, and therefore are poor electrolytes
28
New cards
reversible
partial dissociations/reactions with weak acids or bases will always be ____________
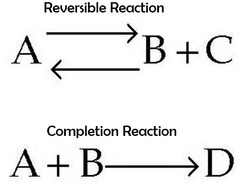
29
New cards
strong bases
bases that dissociate completely into metal ions and hydroxide ions. also strong electrolytes
30
New cards
examples of strong bases
NaOH, KOH
31
New cards
weak base
bases that dissociate partially in dilute aqueous solutions. also weak electrolytes
32
New cards
autoionization
the transfer of a proton from one molecule to another of the same substance. (In a sample of pure water, a very small number of water molecules ionizes, producing equal concentration of both hydrogen and hydroxide ions.)
33
New cards
Neutralization
a rxn in which an acid and a base react in an aqueous solution to produce sale and water. DOUBLE REPLACEMENT rxn.
34
New cards
acid-base titration
a method for determining the concentration of a solution by reacting a known volume of the solution with a solution of unknown concentration.
35
New cards
lone pair acceptor
lewis acid
36
New cards
lone pair donor
Lewis base
37
New cards
nucleophile
an electron-rich species that donates a lone pair to form a covalent bond in a reaction. another term for an electron pair donor or lewis base
38
New cards
examples of nucleophiles
OH-, NH3, Cl-
39
New cards
electrophile
an electron-deficient species that accepts a lone pair from another reactant to form a new covalent bond. another term for electron pair acceptor or lewis acid
40
New cards
examples of electrophiles
BF3, CU(2+), Br+, NO2(+)
41
New cards
Coordinate bond
the shared pair of electrons that come from the lewis base.
42
New cards
kw
ionic product for water
43
New cards
1x10^-14
at 25C or 298K, kw =
44
New cards
endothermic
The dissociation of water is ___________.
45
New cards
increases
kw value ____________ (increases, decreases, stays the same) with an increase in temperature.
46
New cards
Ka
acid dissociation constant
47
New cards
kb
base dissociation constant
48
New cards
strength of acid
as ka increases, what also increases?
49
New cards
strength of base
as kb increases, what also increases?
50
New cards
negligible
if ka or kb is less than 10^-3, dissociation is considered ________________. in other words, initial [acid/base] = equilibrium [acid/base]
51
New cards
pKa = -logKa
formula of pka
52
New cards
pKb = -logKb
formula for pkb
53
New cards
Ka = 10^-pKa
ka formula in terms of pka
54
New cards
Kb = 10^-pKb
kb formula in terms of pkb
55
New cards
inversely
ka/kb and pka/pkb (respectively) are ___________ related.
56
New cards
Kw = Ka x Kb
kw formula in terms of ka and kb
57
New cards
pKw = pKa + pKb = 14
pkw formula
58
New cards
buffer solutions
solutions that resist change in their pH when limited amounts of acid or base are added
59
New cards
Composition of an acid buffer
aqueous solution of weak acid + salt of strong base
60
New cards
The H+ ions combine with the base, therefore removing most of the acid.
How do acid buffers respond to added acid?
61
New cards
the OH- ions combine with the acid, therefore removing most of the base.
How do acid buffers respond to added base?
62
New cards
Composition of basic buffer
aqueous solution of weak base + strong acid
63
New cards
- start with an acid or base with a pKa or pKb value as close as possible to the required pH of the buffer
- mix in either (a) a solution containing a salt and its conjugate or (b) partially neutralized by a strong acid or strong base
- after the reaction mixture will contain unreacted acid or base in an equimolar amount
- mix in either (a) a solution containing a salt and its conjugate or (b) partially neutralized by a strong acid or strong base
- after the reaction mixture will contain unreacted acid or base in an equimolar amount
How to make a buffer solution
64
New cards
No; no effect on pH, just increased volume
Does dilution affect buffer solutions?
65
New cards
Yes; buffer solutions must be kept at certain temperatures
Does temperature change affect buffer solutions?
66
New cards
salt hydrolysis
the process by which salt reacts with water. the ions contained in salt can act as acids or bases in aqueous solution
67
New cards
cations, anions
in salt hydrolysis, _______ act as acids and __________ act as bases.
68
New cards
True
Strong acids/bases do NOT undergo hydrolysis (true/false).
69
New cards
Titration curve: strong acid and strong base
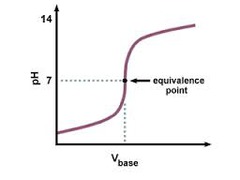
70
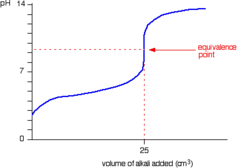
New cards
Titration curve: weak acid and strong base
71
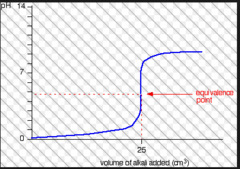
New cards
Titration curve: strong acid and weak base
72
New cards
Titration curve: weak acid and weak base

73
New cards
equivalence point
the point at which the two solutions used in a titration are present in chemically equivalent amounts
74
New cards
half equivalence point
The point in a titration at which exactly half the molar equivalence of reactant is consumed by the titrant being added. At this point in an acid-base titration, the pKa of the unknown solution is revealed. pH = pKa
75
New cards
Indicator
A compound that changes color in the presence of an acid or a base.
76
New cards
carbonic acid
A weak acid formed naturally when rain falls and absorbs carbon dioxide in the atmosphere.
77
New cards
5.6
acid rain has a pH less than ______.
78
New cards
sulfurous acid
H2SO3
79
New cards
sulfuric acid
H2SO4
80
New cards
nitrous acid
HNO2
81
New cards
nitric acid
HNO3
82
New cards
natural causes of SO2
volcanic eruptions
83
New cards
anthropogenic causes of SO2
sulfur-containing fuels, smelting of sulfide ore
84
New cards
S + O2 -> SO2; SO2 + H2O -> H2SO3
chemical reaction for the formation of sulfurous acid; chemical reaction for the formation of acid rain from sulfurous acid
85
New cards
2SO2 + O2 -> (UV light) 2SO3; SO3 + H2O -> H2SO4
chemical reaction for the formation of sulfuric acid; chemical reaction for the formation of acid rain from sulfuric acid
86
New cards
natural causes of nitrogen oxides
lightning, actions of some bacteria
87
New cards
anthropogenic causes of nitrogen oxides
internal combustion engines and jets
88
New cards
N2 + O2 -> 2NO; 2NO + H2O + O2 -> 4HNO2
chemical reaction for the formation of nitrous acid; chemical reaction for the formation of acid rain from nitrous acid
89
New cards
NO + O2 -> 2NO2; 2NO2 + H2O -> HNO3 + HNO2
chemical reaction for the formation of 2NO2; chemical reaction for the formation of acid rain from nitrous AND nitric acid
90
New cards
4NO + 2H2O + O2 -> 4HNO3
chemical reaction for the formation of acid rain from nitric acid
91
New cards
- affects statues or buildings made out of limestone and marble
- kills fish and other forms of aquatic life
- increases the risk of respiratory illness in humans
- kills fish and other forms of aquatic life
- increases the risk of respiratory illness in humans
Effects of acid rain:
92
New cards
CaCO3
calcium carbonate / limestone / marble
93
New cards
CaCO3 + H2SO3 -> CaSO4 + CO2 + H2O
CHEMICAL equation for the degradation of limestone/marble because of acid rain
94
New cards
CO3(2-) + 2H(+) -> CO2 + H2O
IONIC equation for the degradation of limestone/marble because of acid rain
95
New cards
- carpooling
- public transport
- hydro sulfurization
- floatation method for coal
- public transport
- hydro sulfurization
- floatation method for coal
pre-combustion methods of reduction for sulfur oxides
96
New cards
scrubbing method (desulfurization)
post-combustion method of reduction for sulfur oxides
97
New cards
CaO + SO2 -> CaSO3
chemical equation for desulfurization