Inorganic Compounds and Solutions
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
37 Terms
Mixture
a combo of elements or compounds that are physically blended together but are not bound by chemical bonds
Solution
a substance called a solvent dissolved another substance called the solute, Usually more solvent than solute (i.e. sweat)
Colloid
a solution with larger particles which are large enough to scatter light (i.e. milk)
Suspension
larger particles that are usually visible to the naked eye, mixed into a liquid or a suspending medium for some time, but will eventually settles out (i.e. blood, paint)
Water
all living organisms are made of it, 65% body mass, 70-90% of cell composition, most important and abundant inorganic compound in all living systems.
What is a universal solvent and an ideal medium for most chemical reactions, that can dissolved sugar (hydrophilic) and cannot dissolve veggie oil (hydrophobic) ?
water
what is used to flush dissolved water and eliminate it from the body
water
Hydrolisis
breaks large molecules down to simpler ones by adding a molecule of water, breaks down nutrients
Dehydration Synthesis
occurs when two simple molecules join together, eliminating a molecule of water in the process
What is a lubricant, a major part of mucus and other lubricating fluids (synovial fluid, serous membranes), found wherever friction needs to be reduced or particles eliminated?
water
Cohesion of Water
when the H bonds that link water molecules to one another, the tendency of like particles to stay together
Adhesion of water
creates high surface tension, a measure of difficulty of stretching or breaking the surface of a liquid. (i.e. water droplets on a leaf)
Acid
any solute that dissociates in solution and releases H+ ions
Base
any solute that dissociates in solution and releases OH- ions
pH
negative logarithm of the H+ concentration in a solution, the human body usually remains at a neutral pH=7
Buffers
compounds that stabilize the pH of a solution by removing or replacing H+ ions
Inorganic Compounds
lack C and are simple molecules
Organic Compounds
always contain C and H, usually O, have covalent bonds, 40% body mass and carry out complex functions, a good source of energy
Carbon
can react with several hundred other C atoms to form large molecules, some don't dissolve easy in water, C compounds are mostly or entirely held together by covalent bonds and tend to decompose easily
Carbohydrates
C,H,O, most of the energy for life, can be converted to other substances, metabolic primer, primary fuel for CNS and red blood cells, have three major groups; monosaccharides, disaccharides, polysaccharides,
Monosaccharides
the main energy supplying compound of the body (glucose, fructose and galactose)
Glucose
C6H12O6, dextrose or blood sugar, used directly by cells for energy, primary component of corn syrup
Galactose
C6H12O6, liver can convert it to glucose
Fructose
liver can convert it to glucose, abundant in fruits and root veggies
Disaccharide
A double sugar, consisting of two monosaccharides joined by dehydration synthesis.
Disaccharide: Maltose
glucose + glucose
Disaccharide: Sucrose
glucose + fructose
Disaccharide: Lactose
glucose + galactose
Polysaccharides
glycogen, starch, fiber
Lipids
C,H,O, fewer covalent bonds, insoluble in polar solvents, i.e. water, triglycerides, phospholipids, steroids, eicosanoids (prostaglandins, leukotrienes) protect vital organs, insulate from cold, transport fat soluble vitamins (A,D,E,K)
Triglycerides
glycerol backbone, 3 fatty acids, protection, insulation, energy, room temp=solid(fats) or liquid (oil), 2x energy as CHO's or PRO's, type of covalent bond decides of trigly. is saturated, monounsaturated or polyunsaturated
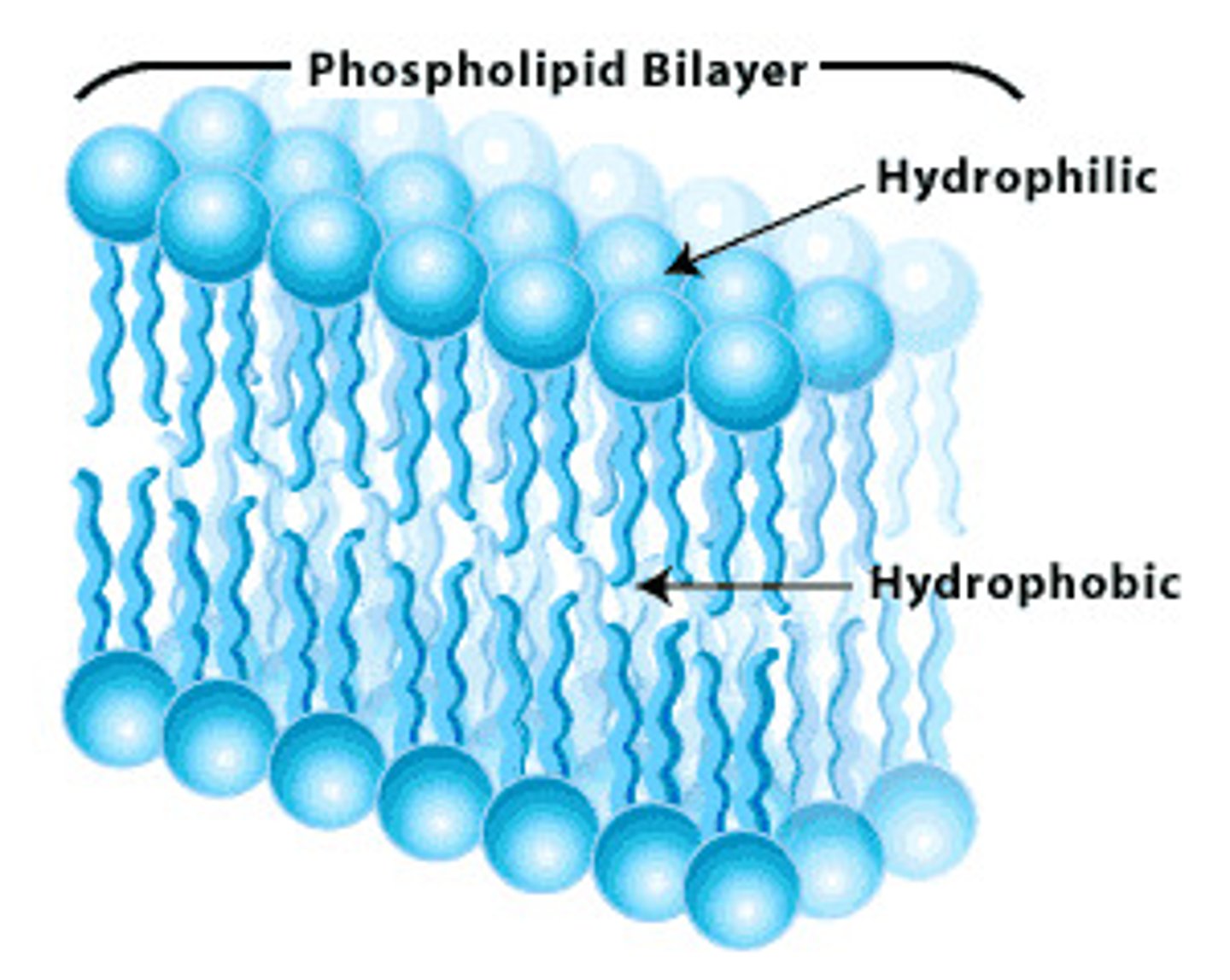
Phospholipids
important membrane components, amphipathic, w both polar and non-polar regions, hydrophilic outer layer, hydrophobic inner layer, phospholipid bilayer
Steriods
include sex hormones, and cholesterol, w cholesterol serving as important component of cell membranes and as starting material for synthesizing other steroids
Prostaglandins
modify responses to hormones, contribute to inflammatory responses, prevent stomach ulcers, dilate airways to lungs, regulate body temp, influence blood clots
Leukotrienes
participate in allergic and inflammatory responses
Proteins
give structure to body, regulate processes, provide protection (immune system) help muscles to contract (contractile) transport substances and serve as enzymes (catalytic)
Amino acids and polypeptides
building blocks of body that contain C, N, H, O, joined together with polypeptide bonds; resulting polypeptide chains may contain 10-2000 AA's