AP Psychology: Topic 2.2 - Thinking, Problem-Solving, Judgments, and Decision Making
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
17 Terms
Prototypes
a mental image or best example that incorporates all the features we associate with a category

Assimilation
making new information fit in with an existing understanding of the world (existing schema)

Accommodation
adapting our current understandings (schemas) to incorporate new information

Algorithms
a methodical problem-solving routine that attempts all possible solutions until the correct one is found
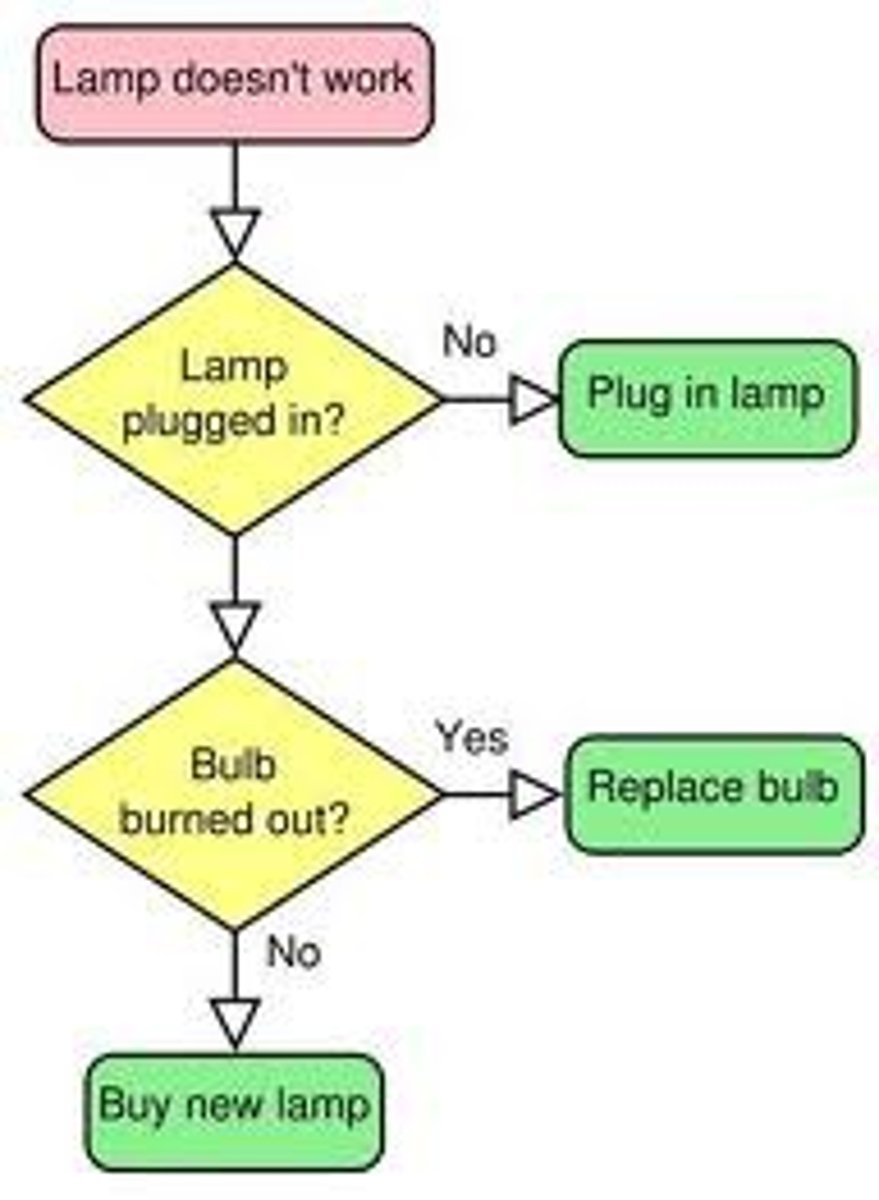
Heuristics
tools of thinking that address problems by using mental shortcuts to make judgments

Representativeness heuristic
a mental shortcut whereby people classify something according to how similar it is to a stereotypical case or prior expectation

Availability heuristic
a mental shortcut that bases a decision on the first or most vivid example that comes to mind

Mental set
a tendency to approach a problem in a particular way that has been successful in the past

Priming
a technique in which the introduction of one stimulus influences how people respond to a subsequent stimulus

Framing
a cognitive bias in which people decide between options based on whether the options are presented with positive or negative connotations

Gambler's fallacy
the belief that the chances of something happening with a fixed probability become higher or lower as the process is repeated

Sunk-cost fallacy
the tendency to continue with a decision we've invested resources into even if the costs outweigh the benefits

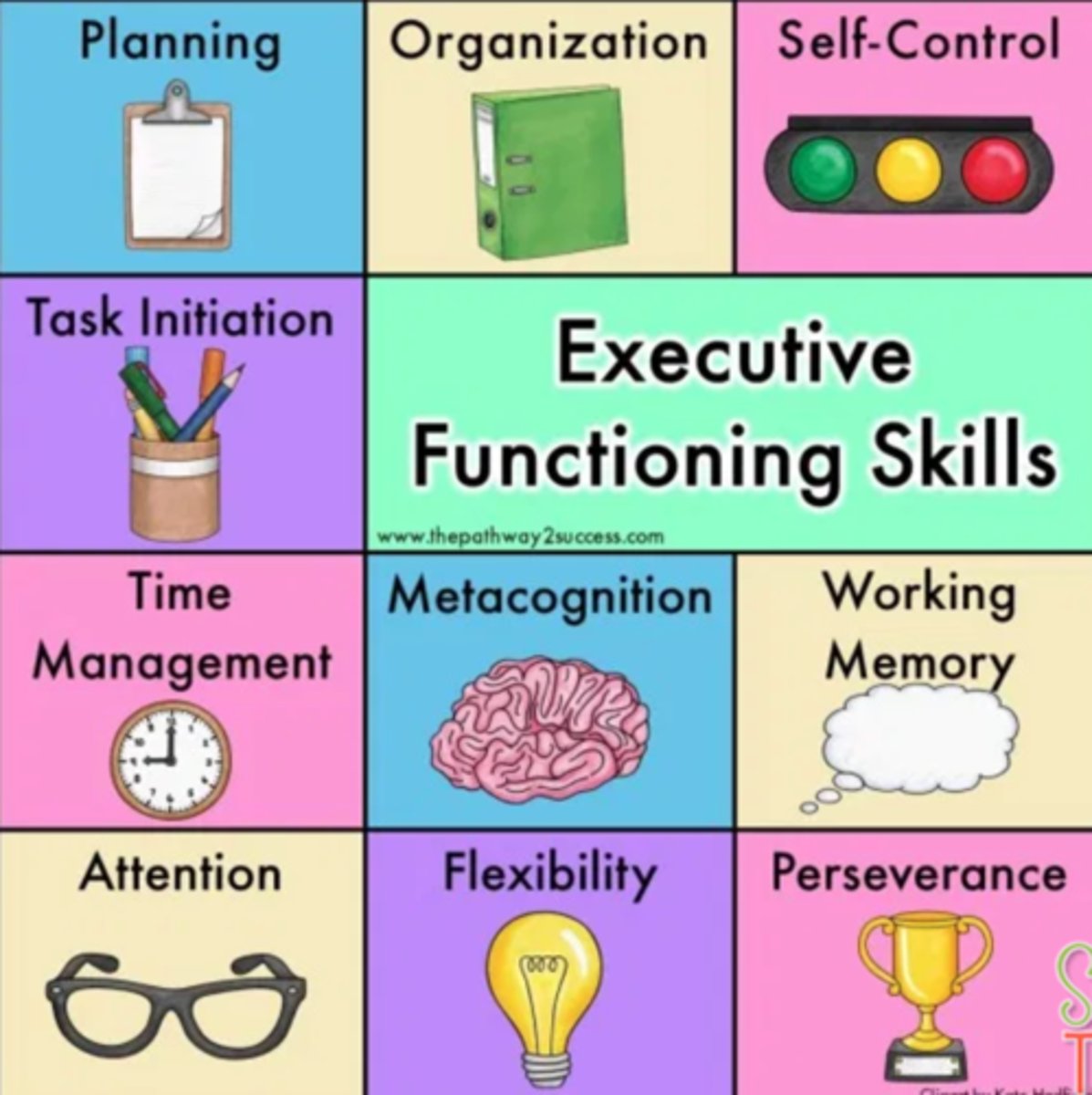
Executive functions
higher order mental processes that allow individuals to generate, organize, plan, and carry out goal-directed behaviors and experience critical thinking
Creativity
a way of thinking that includes generating novel ideas and engaging in divergent thinking

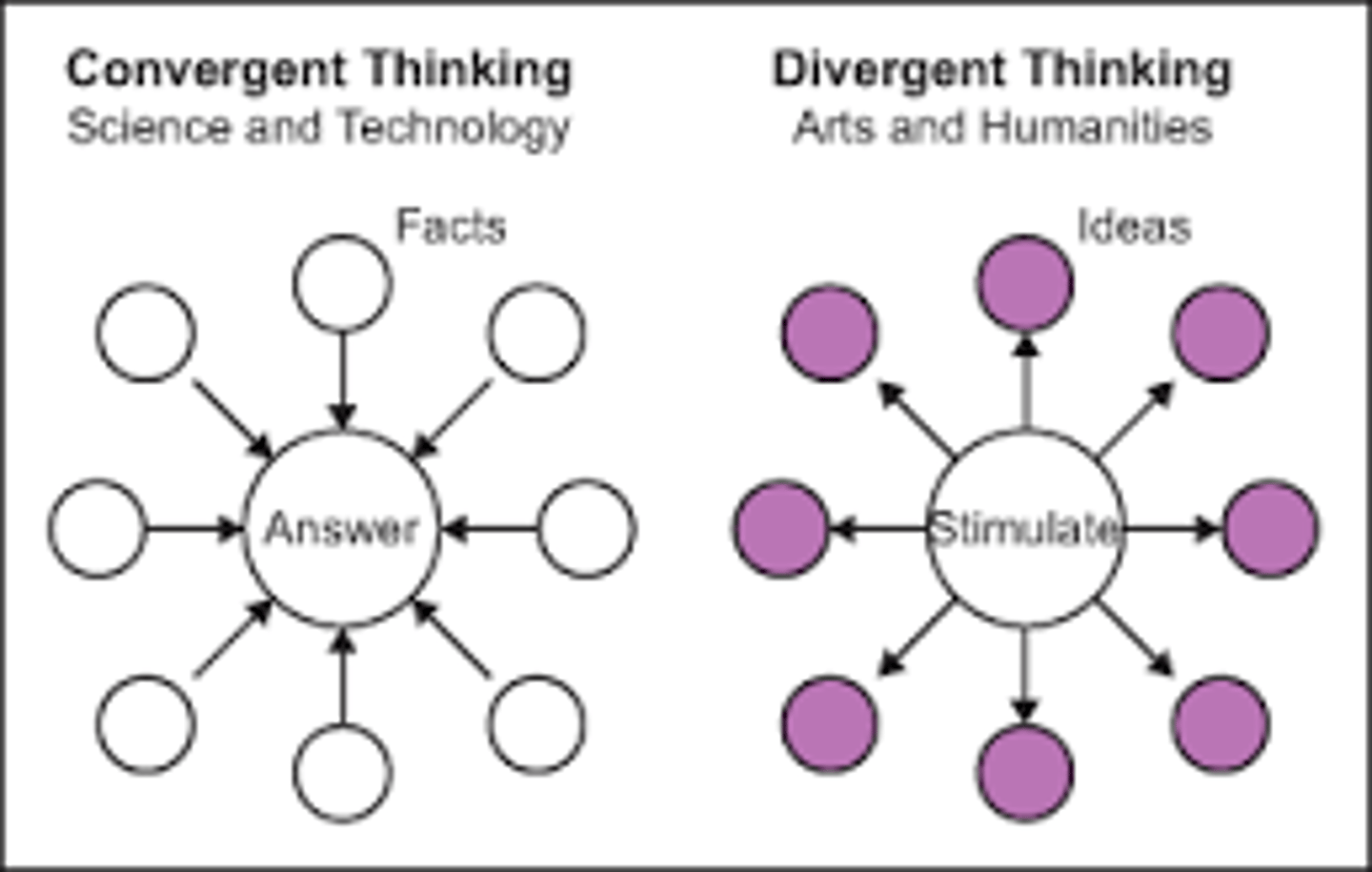
Divergent thinking
expanding the number of possible problem solutions; thinking that flows in different directions

Convergent thinking
reapplying prior learning to quickly and accurately solve problems that do not require novel thinking
Functional fixedness
a block to problem solving that comes from thinking about objects in terms of only their typical functions
