Skull Osteology
1/56
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
57 Terms
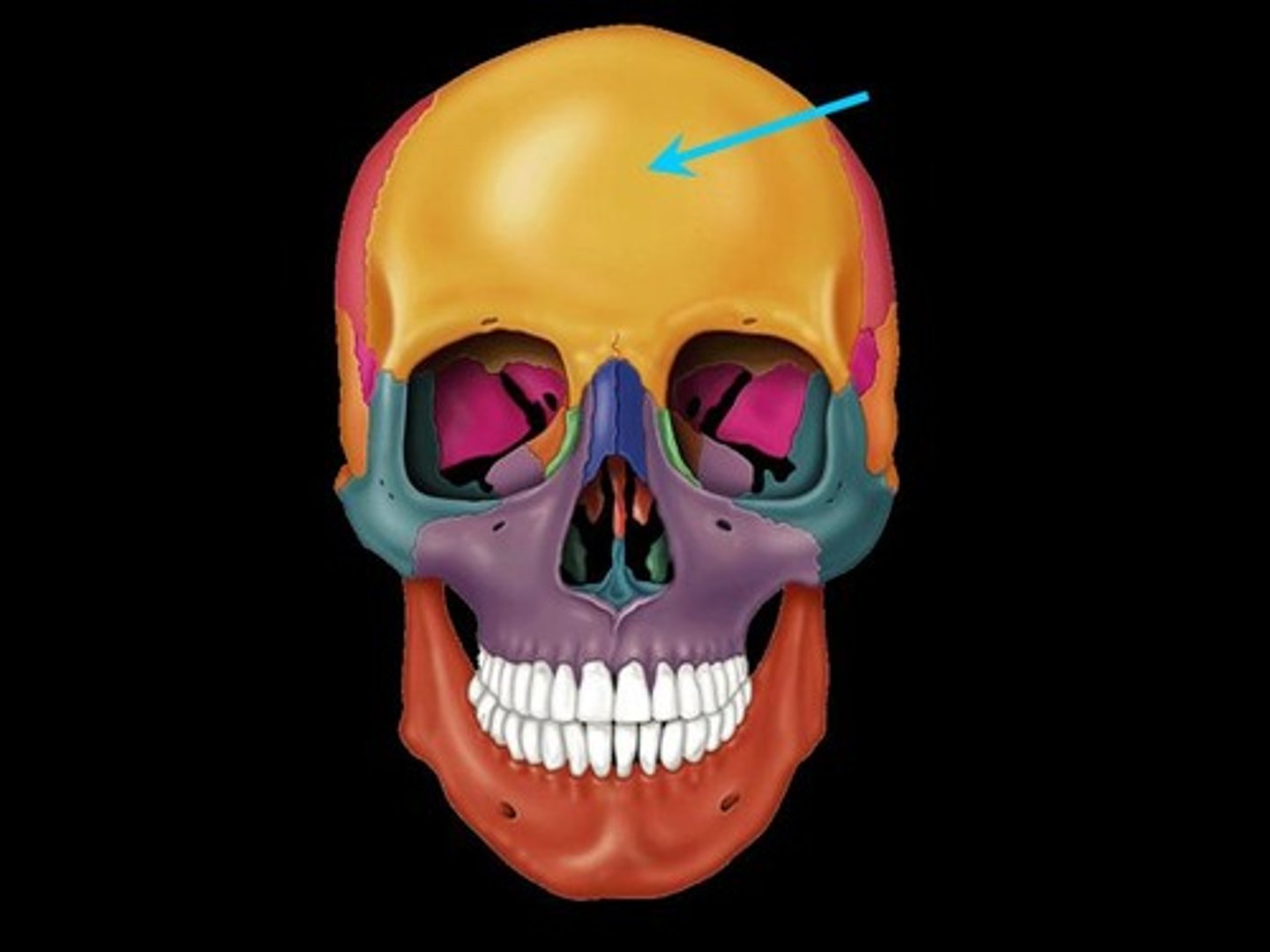
frontal bone
bone that makes up forehead and extends beyond eyebrows
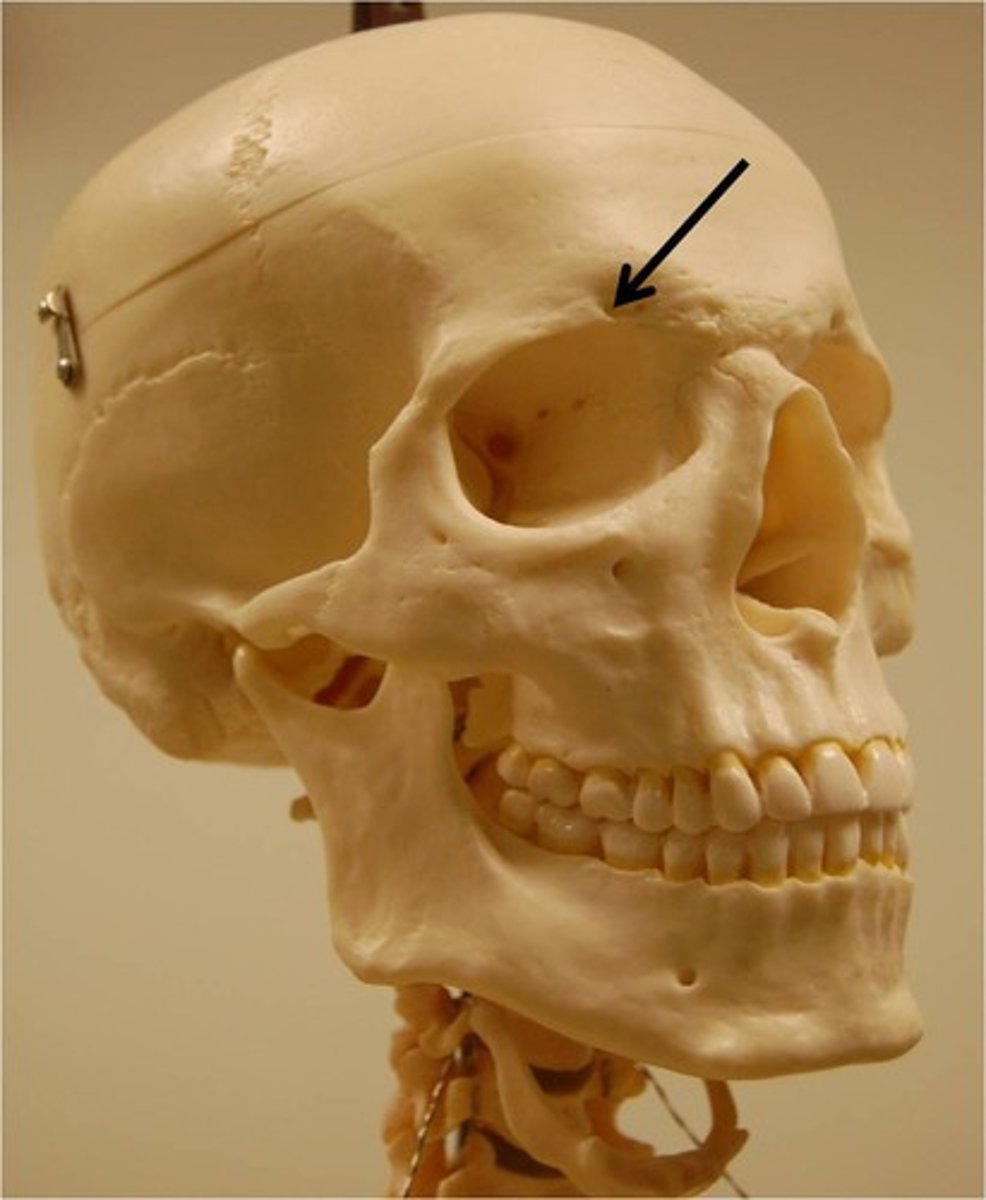
supraorbital foramen
opthalmic branch of trigeminal nerve emerges from this
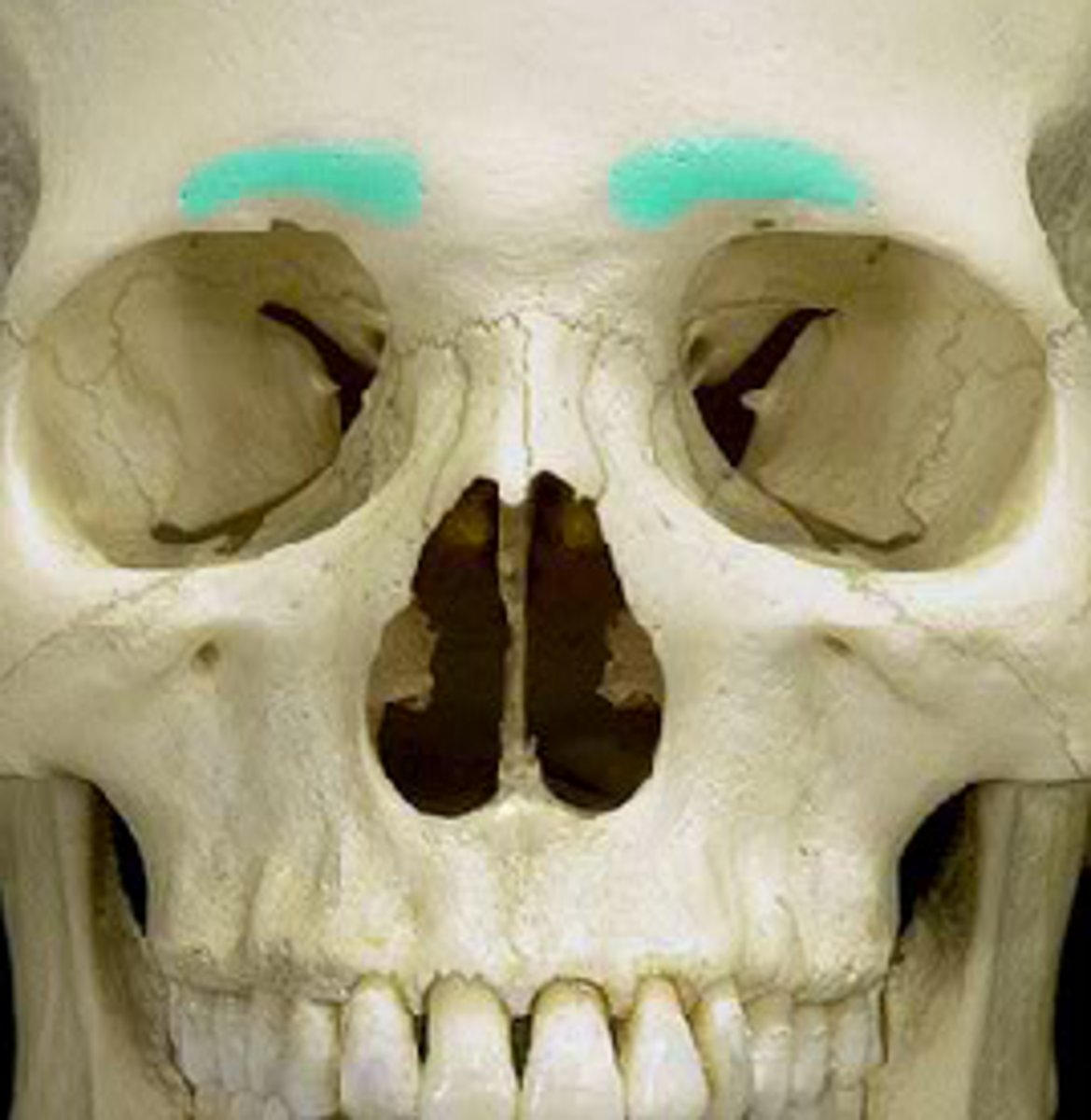
supraorbital ridge
- supraorbital margin
- superciliary ridge
glabella
area b/w supraorbital ridges & above nose
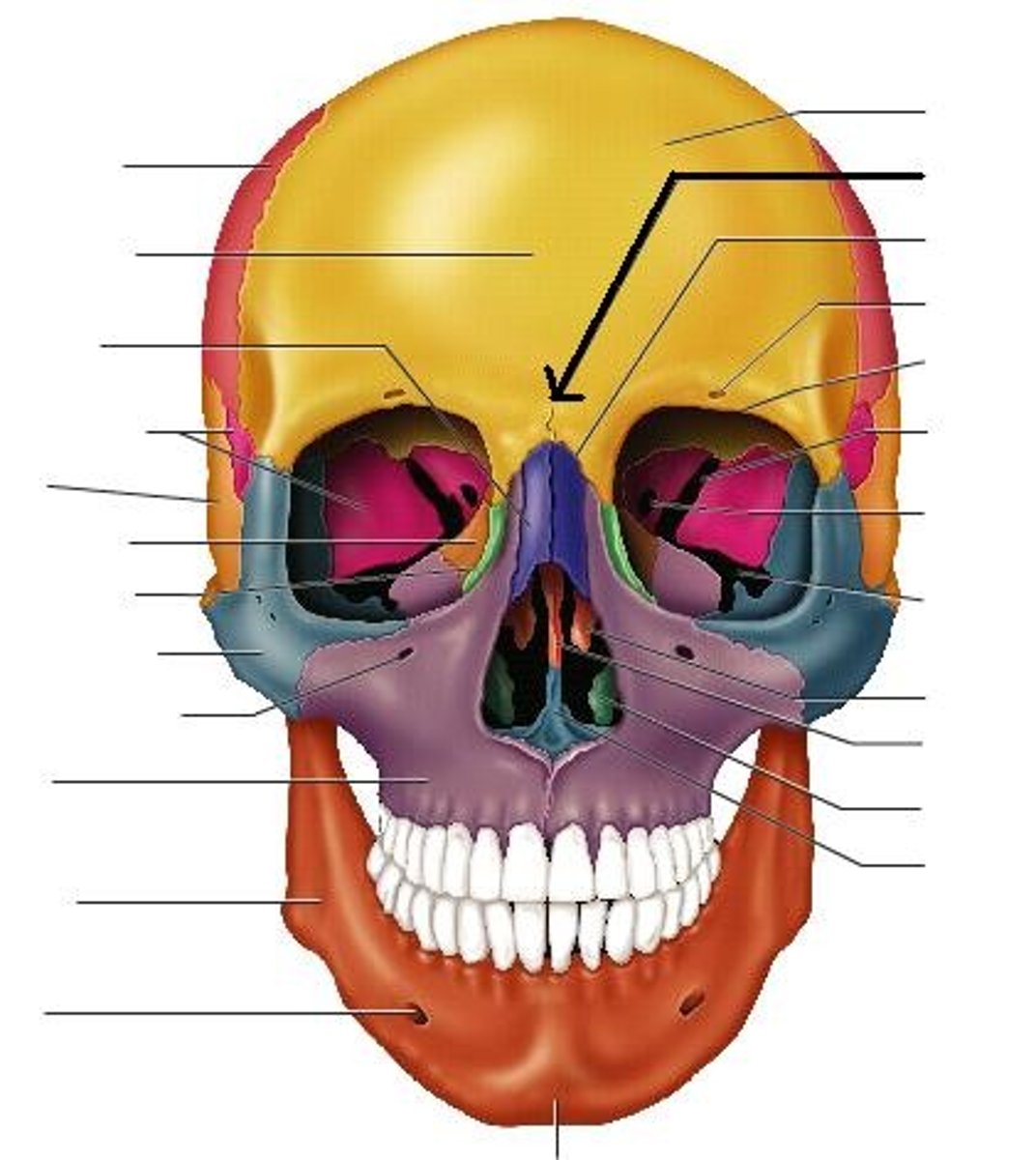
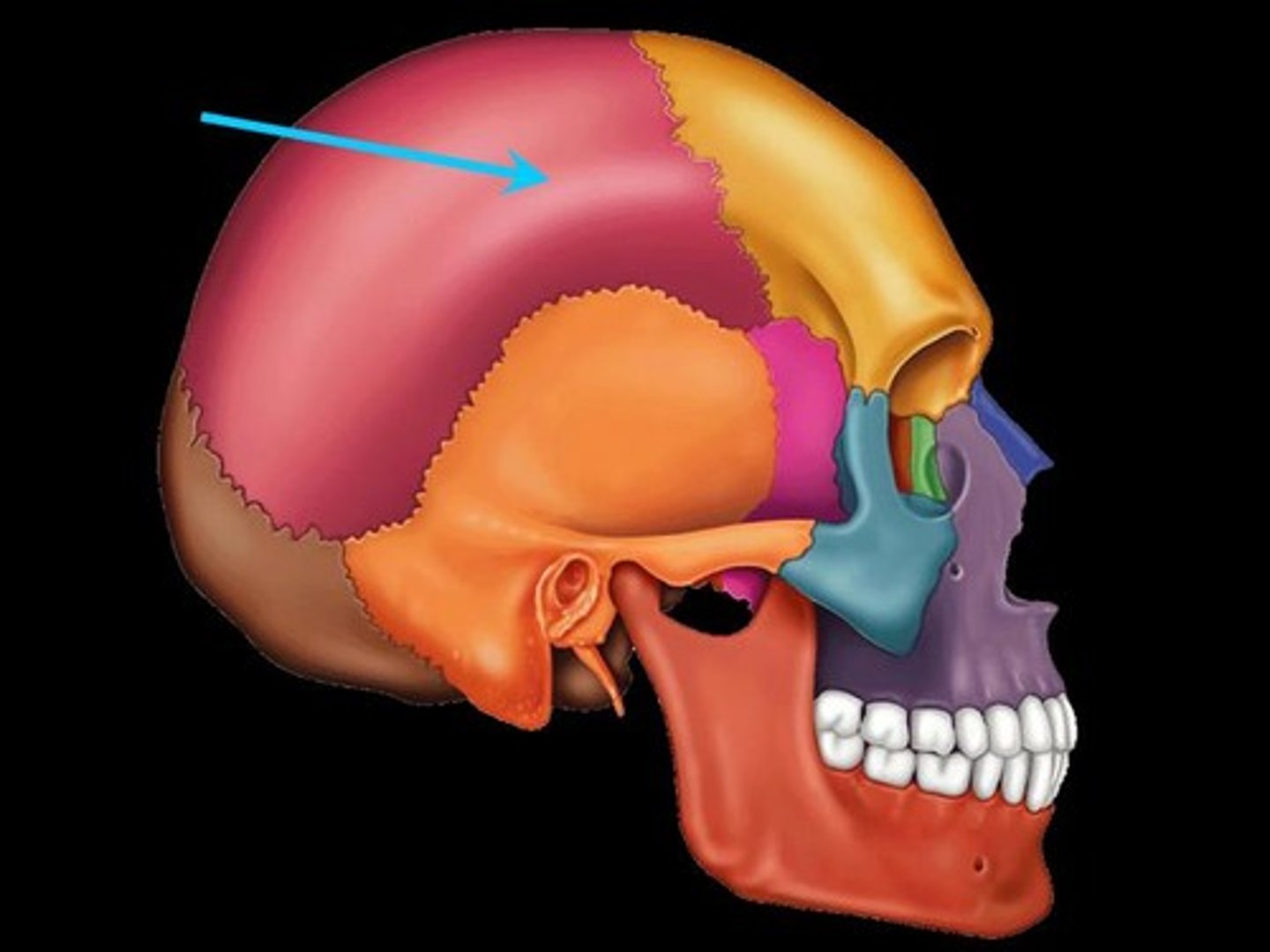
parietal bone
two bones in the human skull which, when joined together, form the sides and roof of the cranium
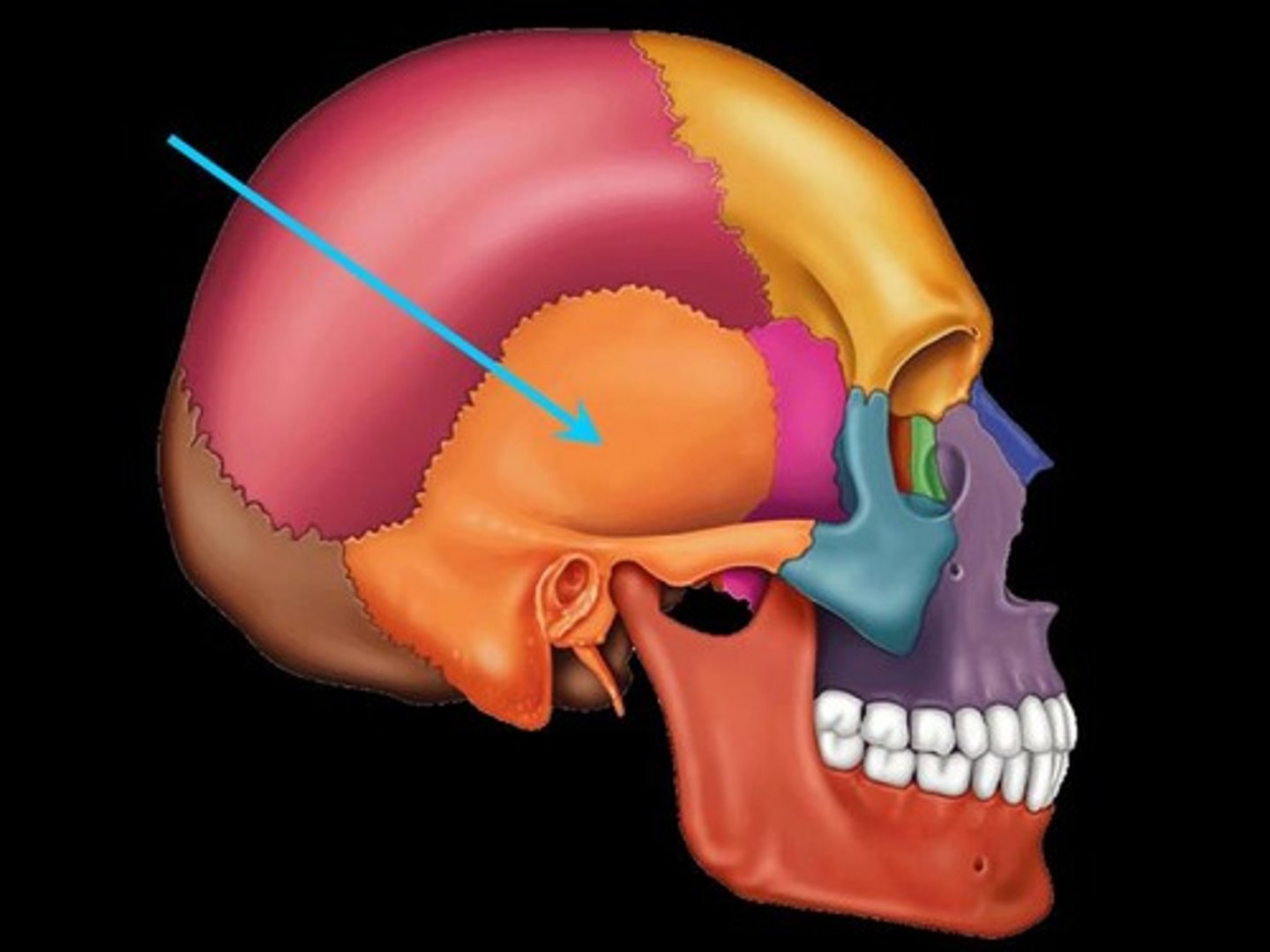
temporal bone
pair of bones that form part of the side of the skull on each side and enclose the middle and inner ear
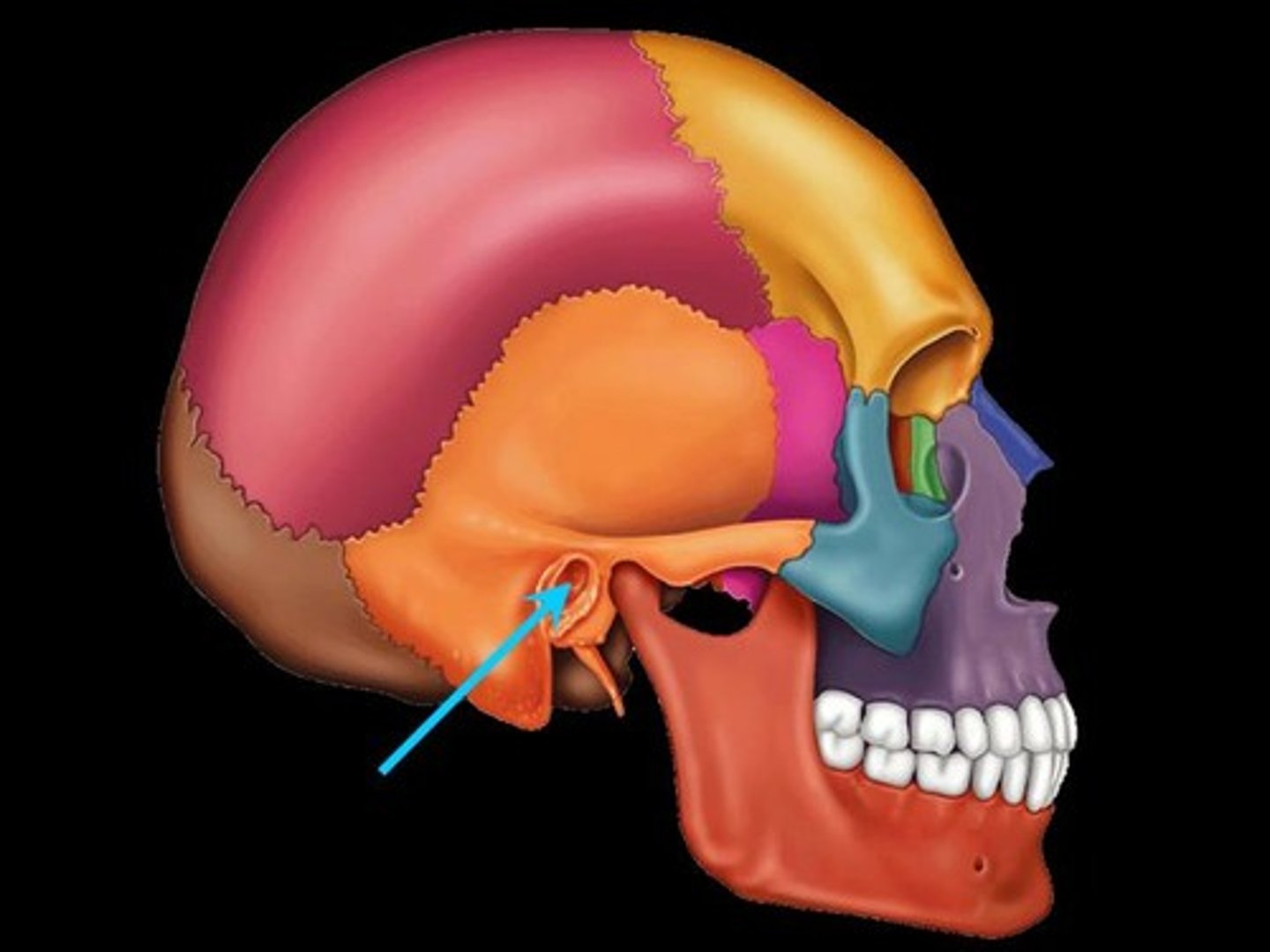
external auditory meatus
opening into the ear canal
mastoid process
large process located just posterior to ext. auditory meatus
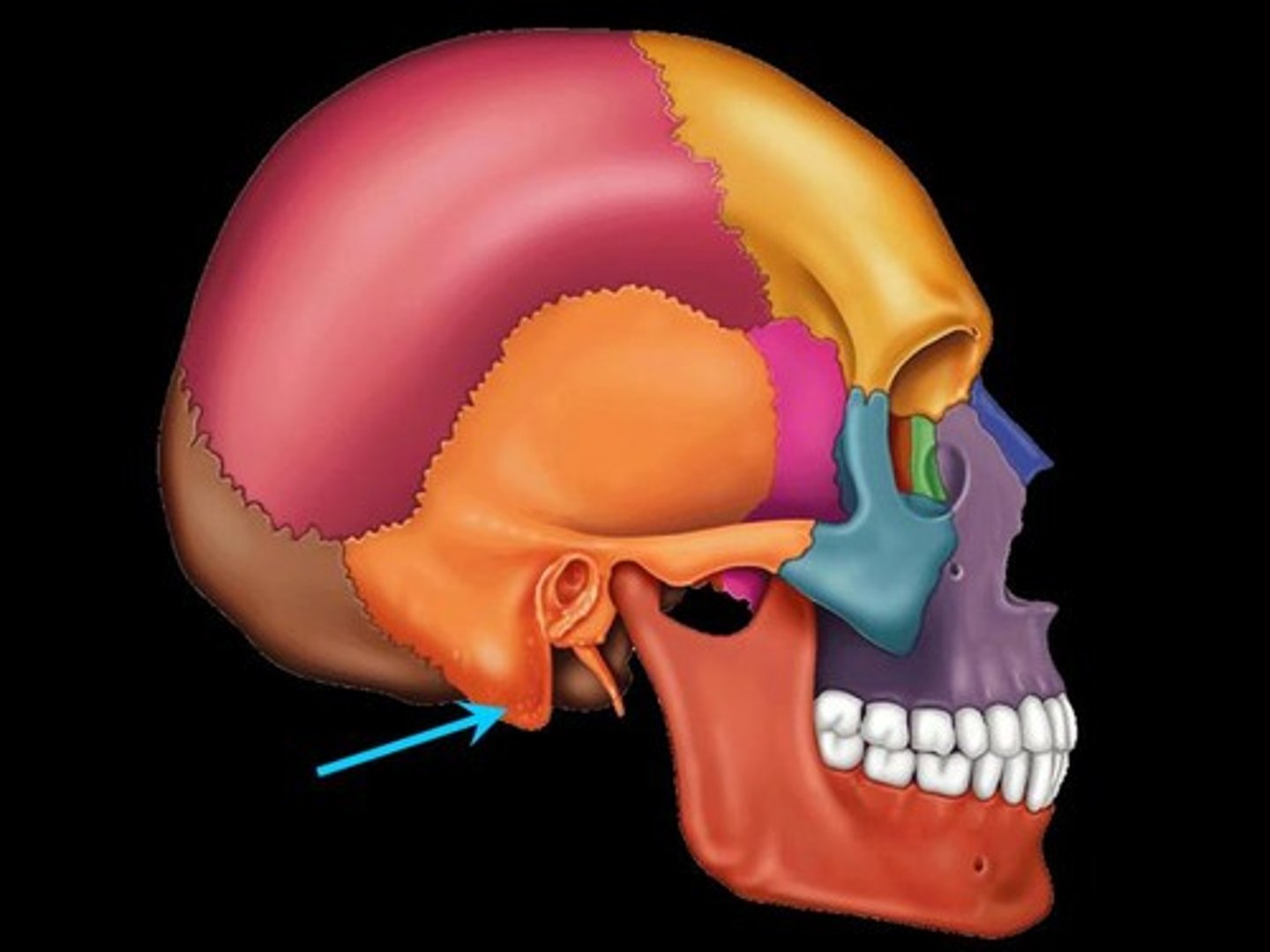
styloid process
small delicate process located just anterior & medial to the ext. auditory meatus
carotid canal
contains internal carotid artery and nerves
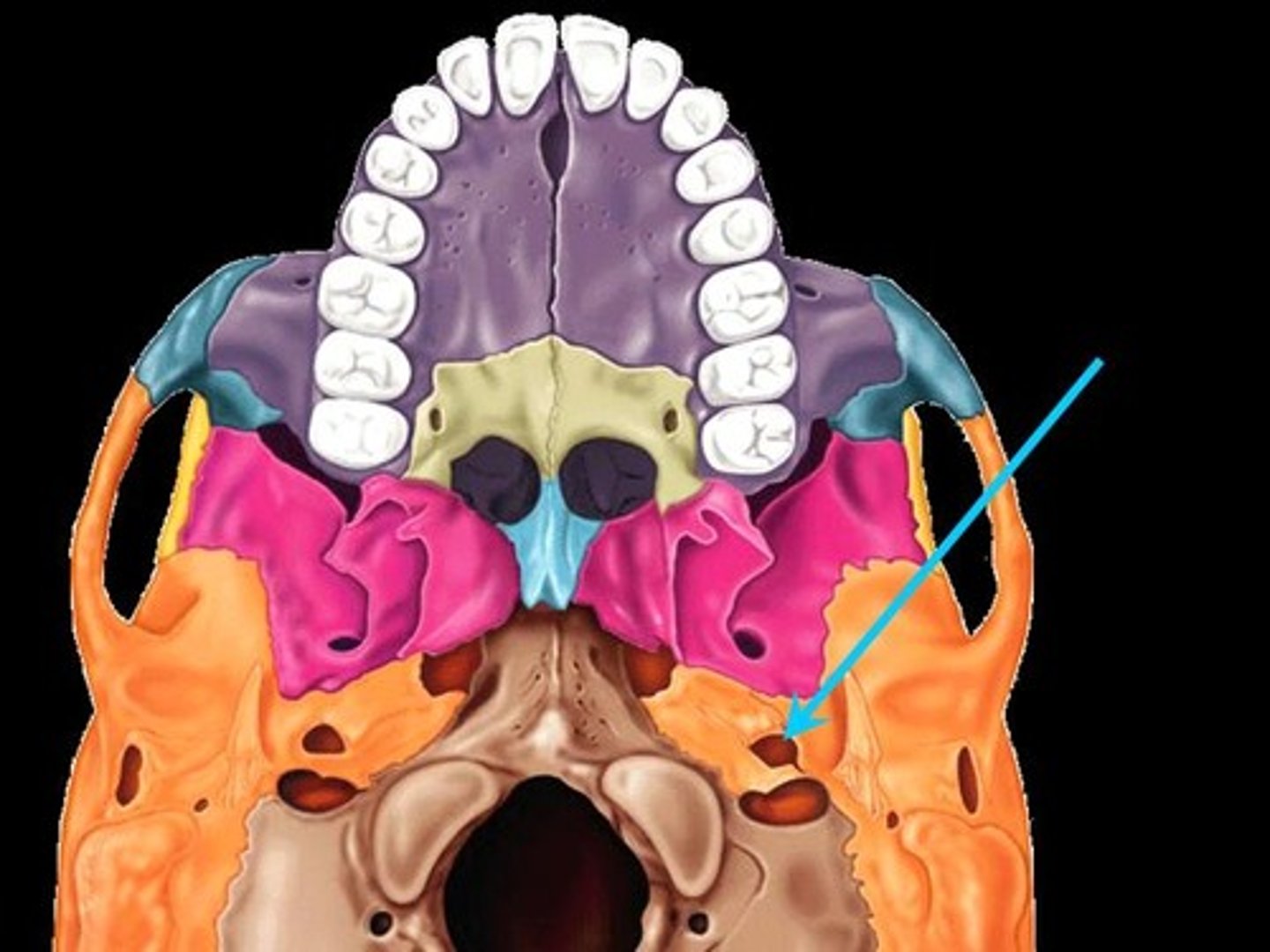
jugular fossa
contains int. jugular vein, CNIX, CNX, and CNXI
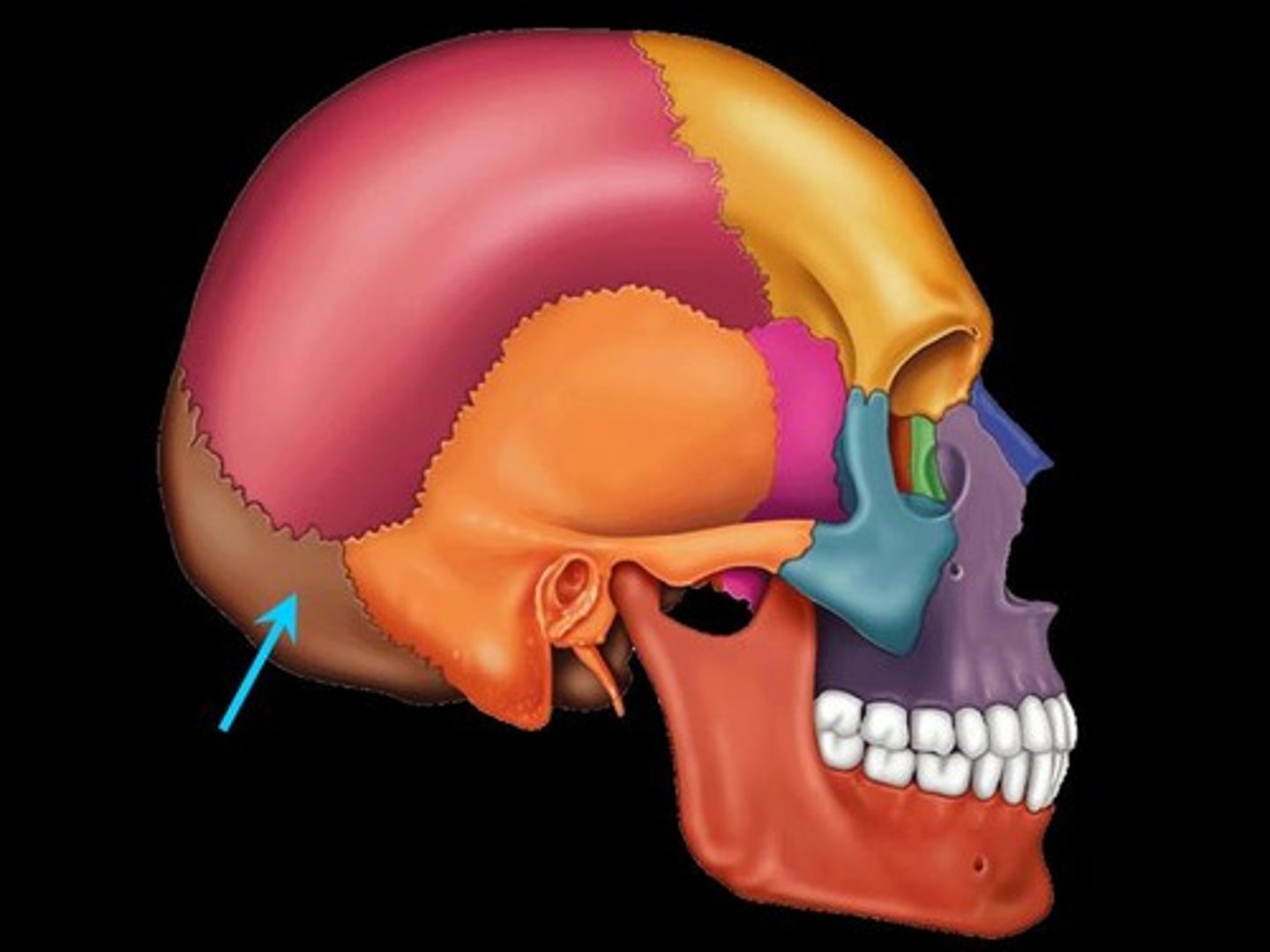
zygomatic ramus of temporal bone
joins w/ the temporal ramus of zygomatic bone to form zygomatic arch
occipital bone
situated in back and lower part of skull
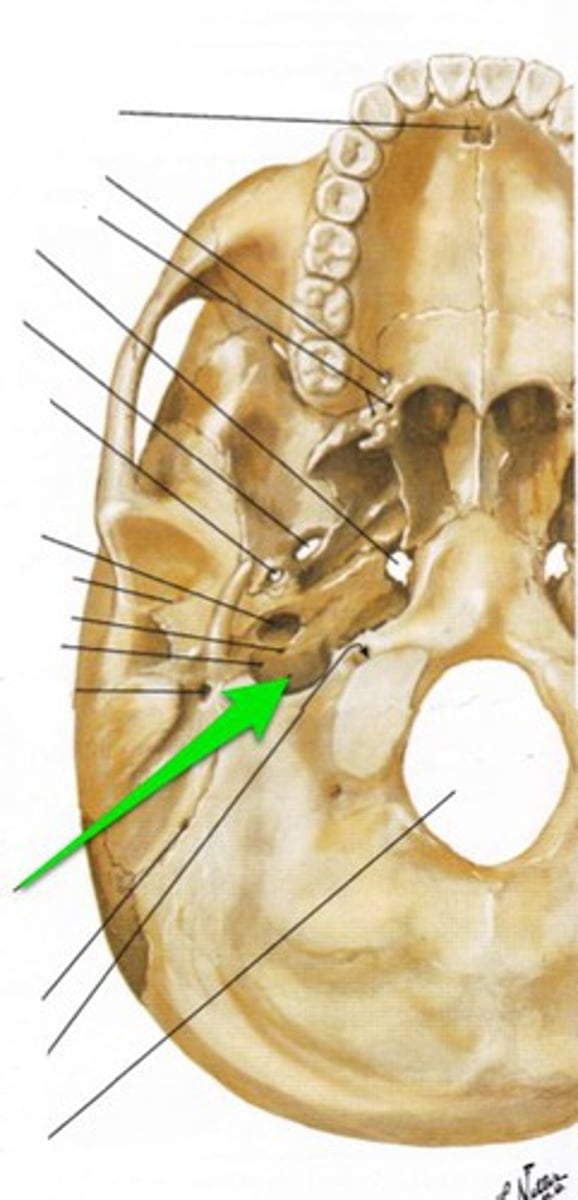
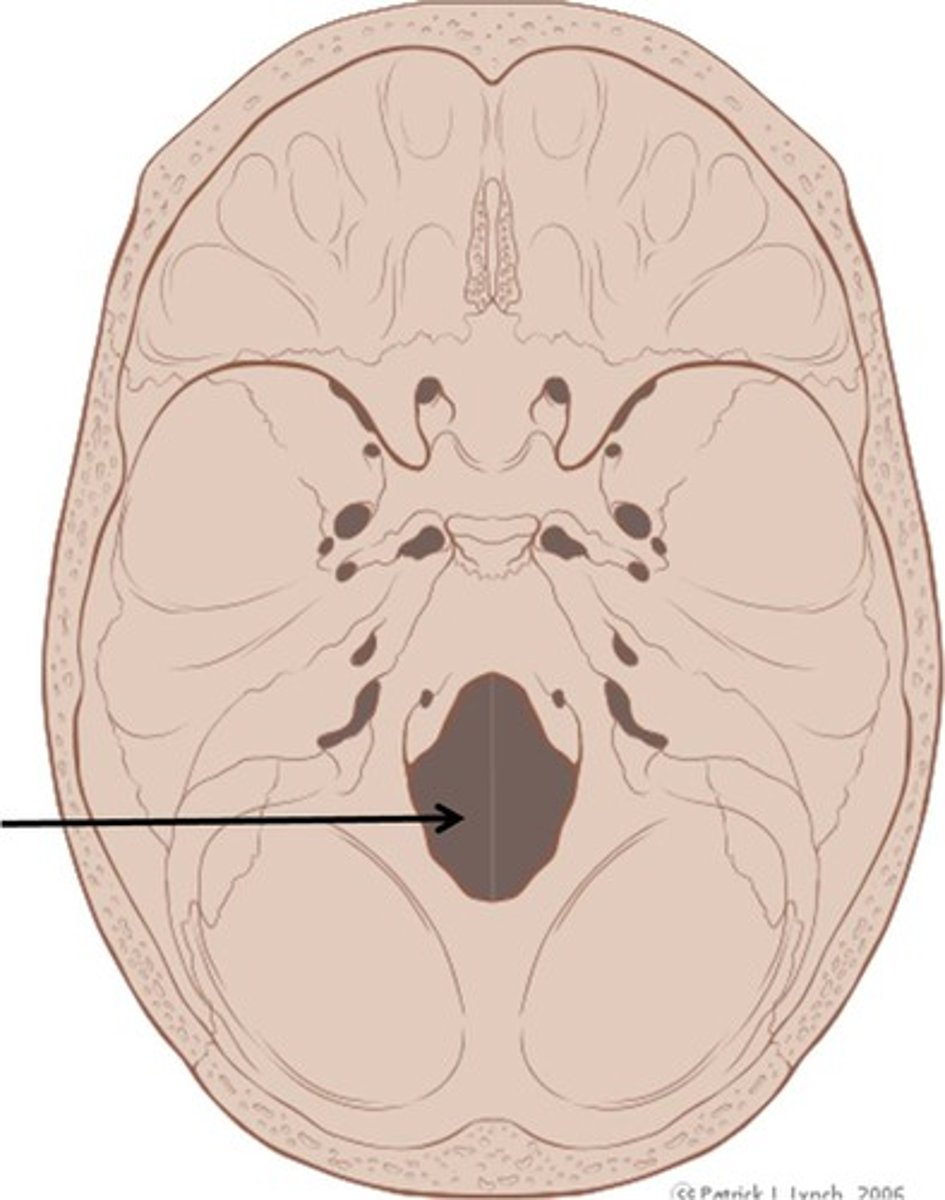
foramen magnum
contains spinal cord, vertebral artery and CNXI
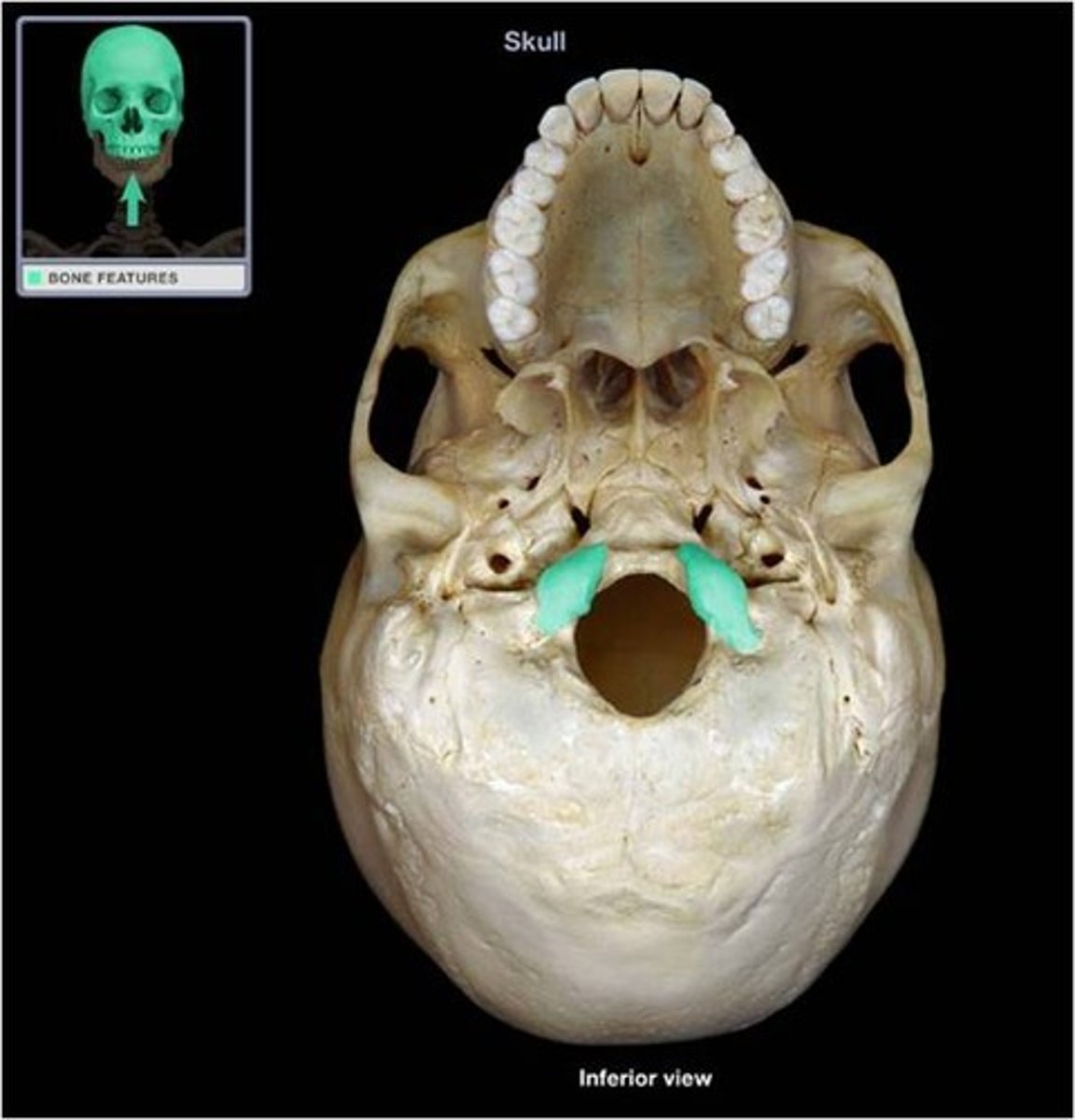
occipital condyles
main articulation b/w skull and C1 (atlas)
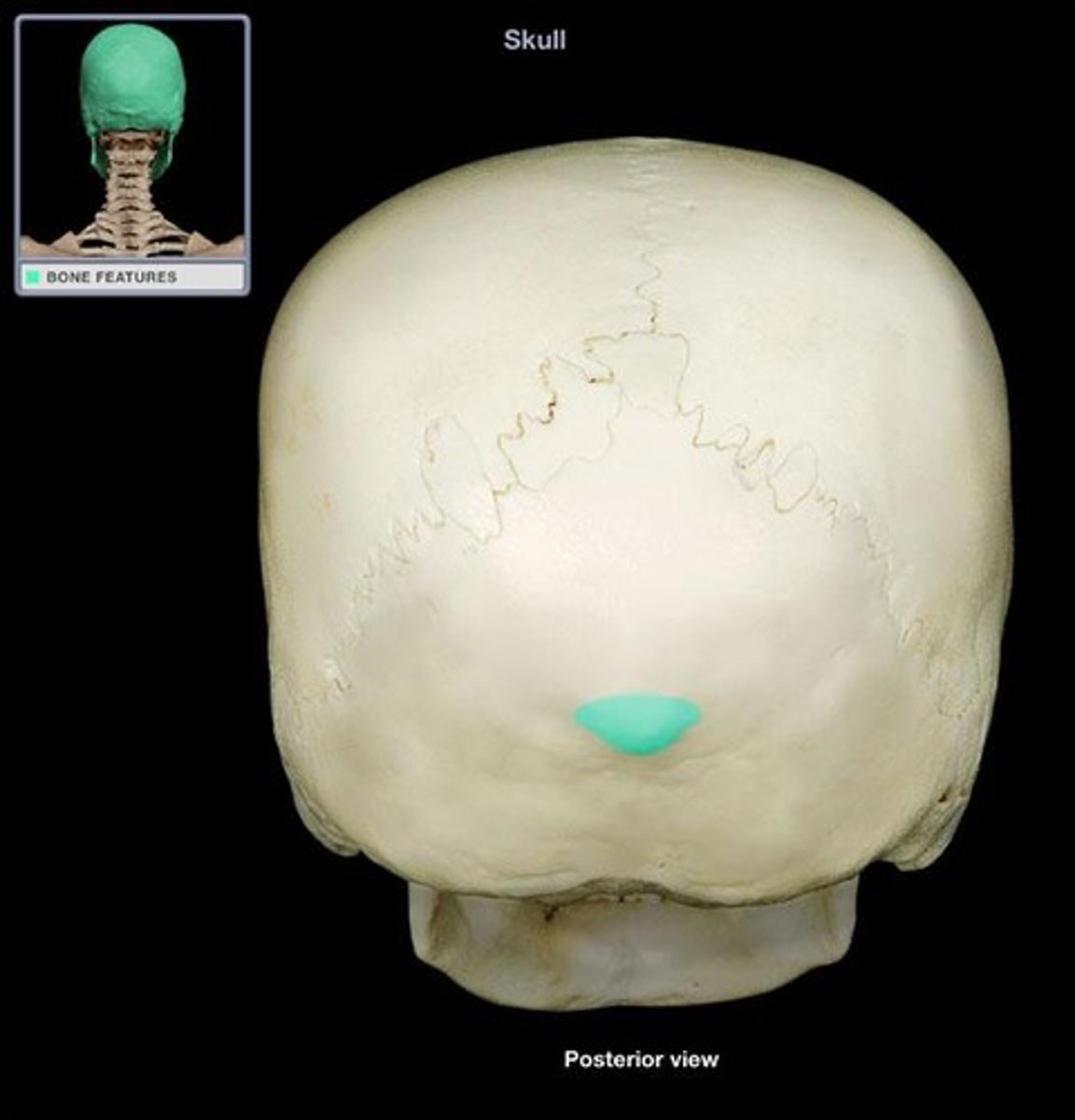
external occipital protuberance
supraspinous (nuchal) ligament attaches here
superior nuchal line
muscles of the head & neck do not cross this line
inferior nuchal line
deeper neck muscles attach here
coronal suture
located b/w frontal & parietal bones
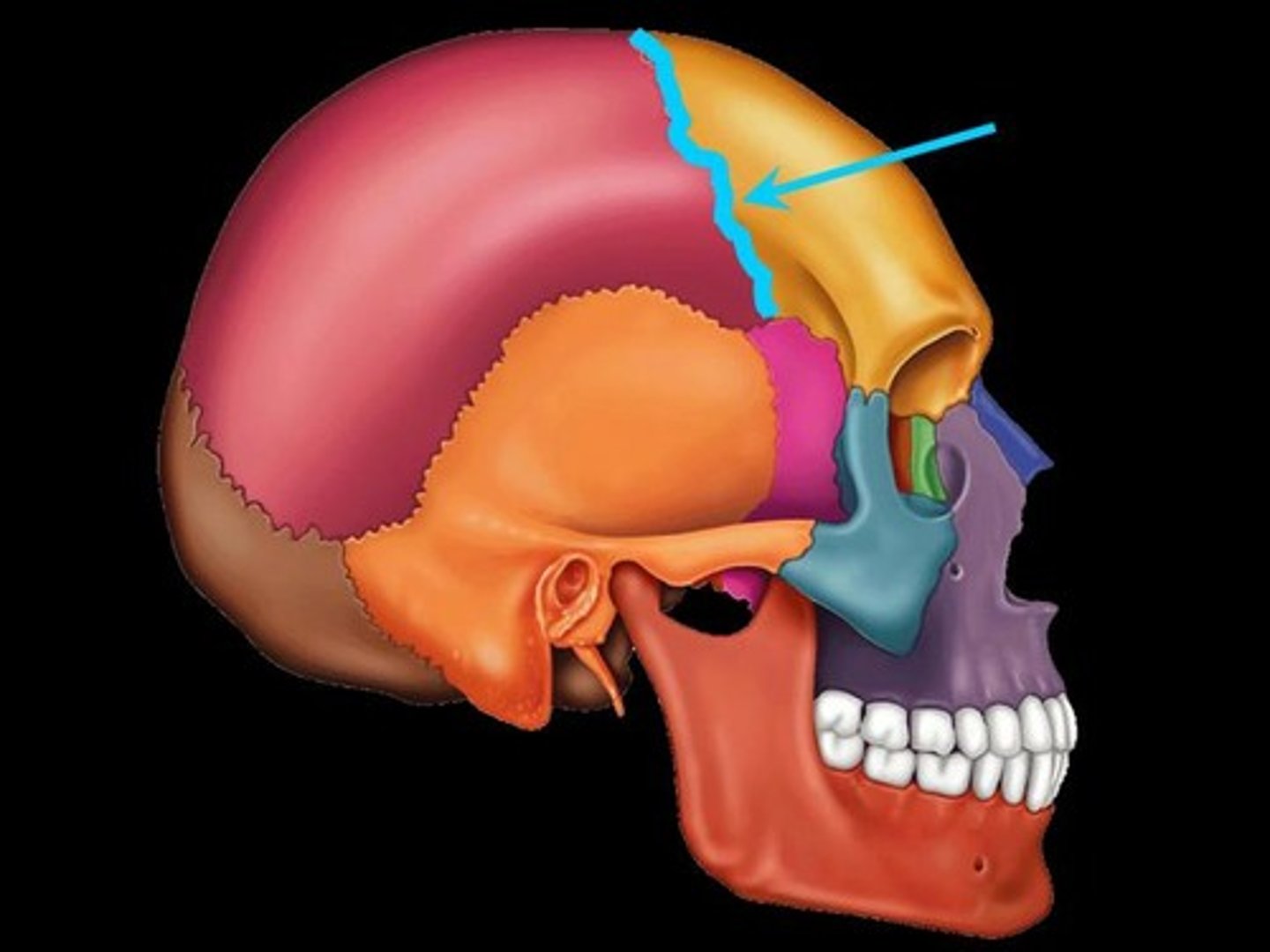
sagittal suture
located b/w parietal bones
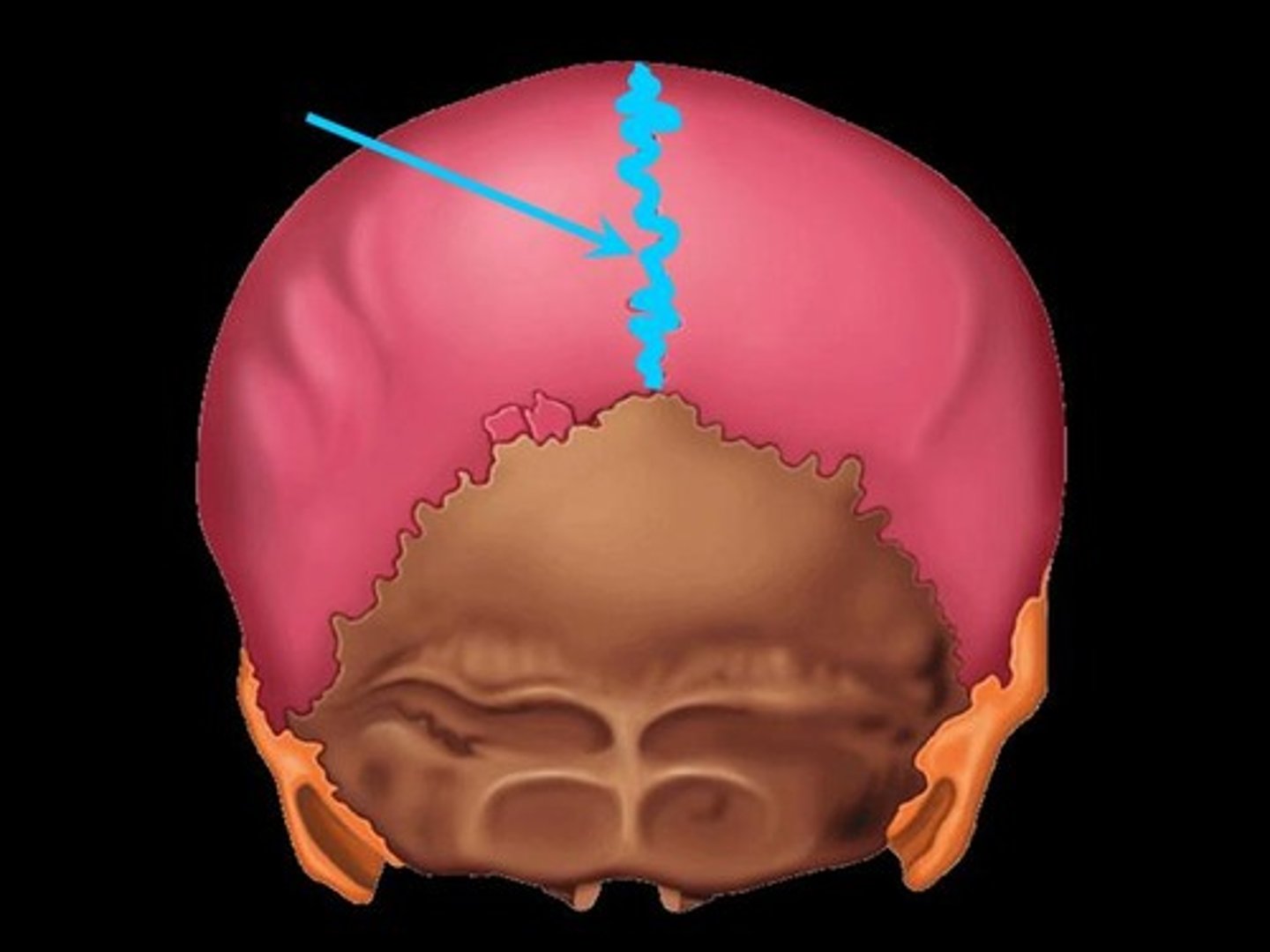
lambdoidal suture
located b/w parietal & occipital bones
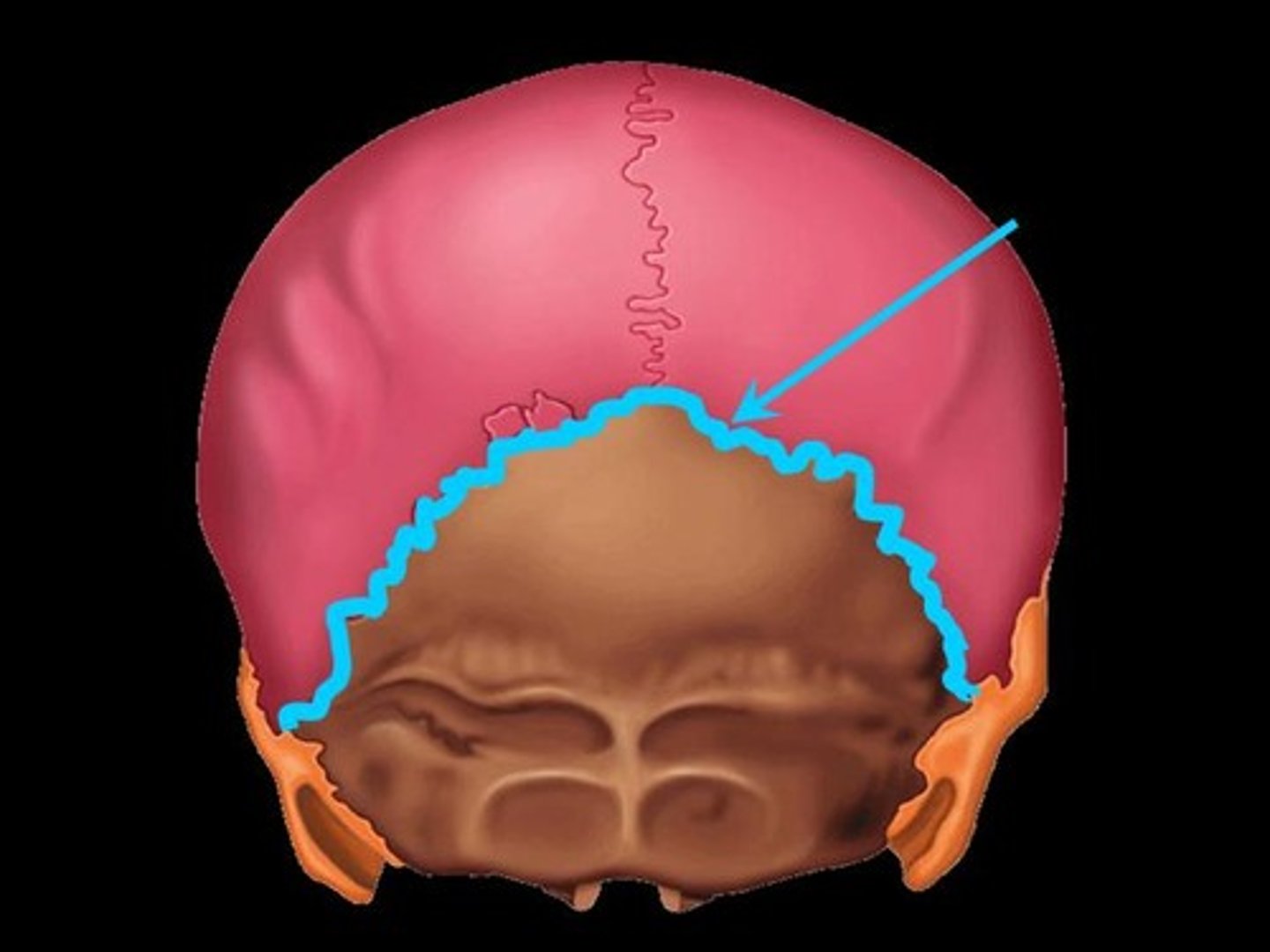
squamous suture
located b/w the temporal and parietal bones
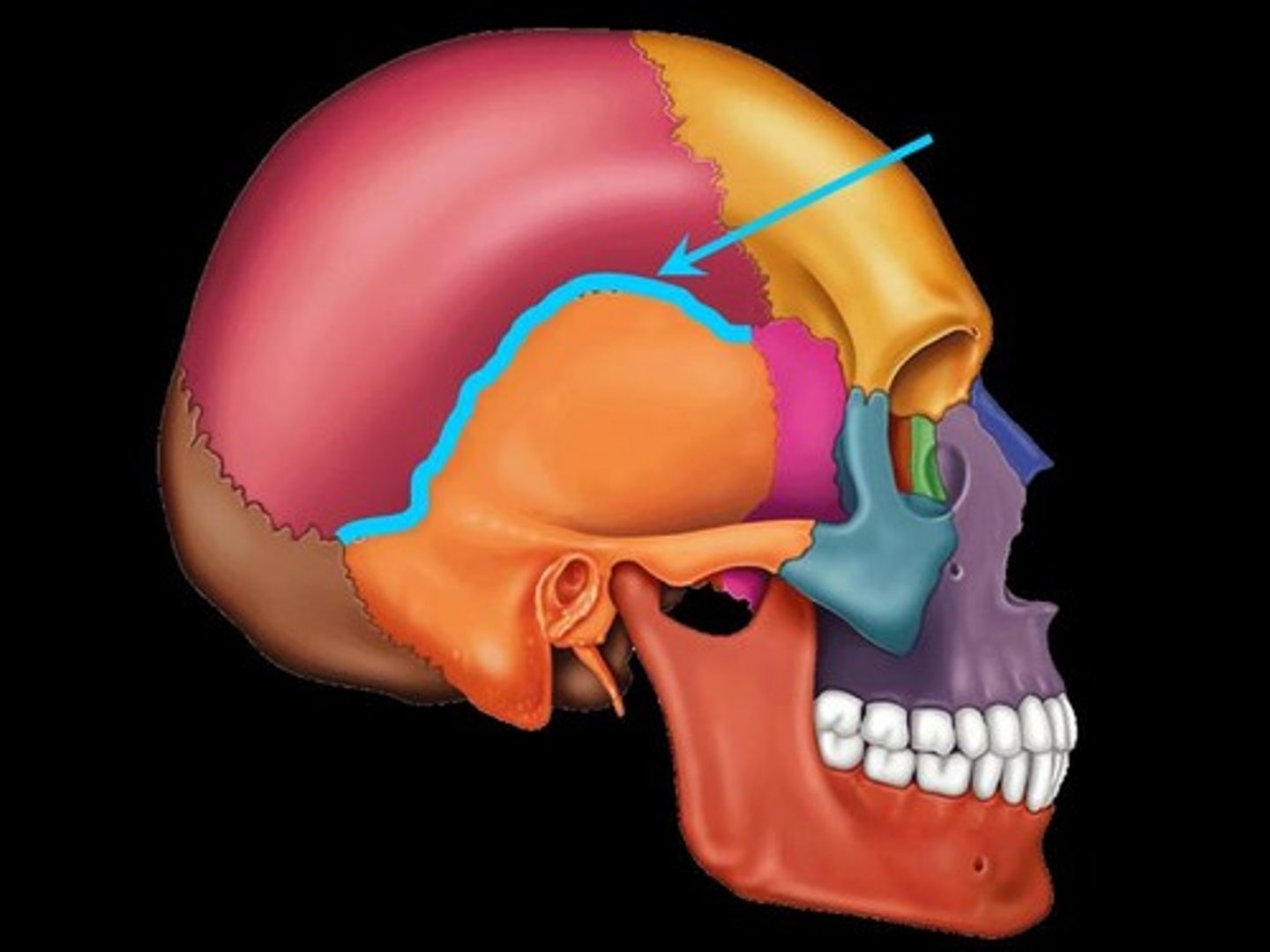
cranial fossa
any of the three large depressions in the posterior, middle, and anterior aspects of the floor of the cranial cavity
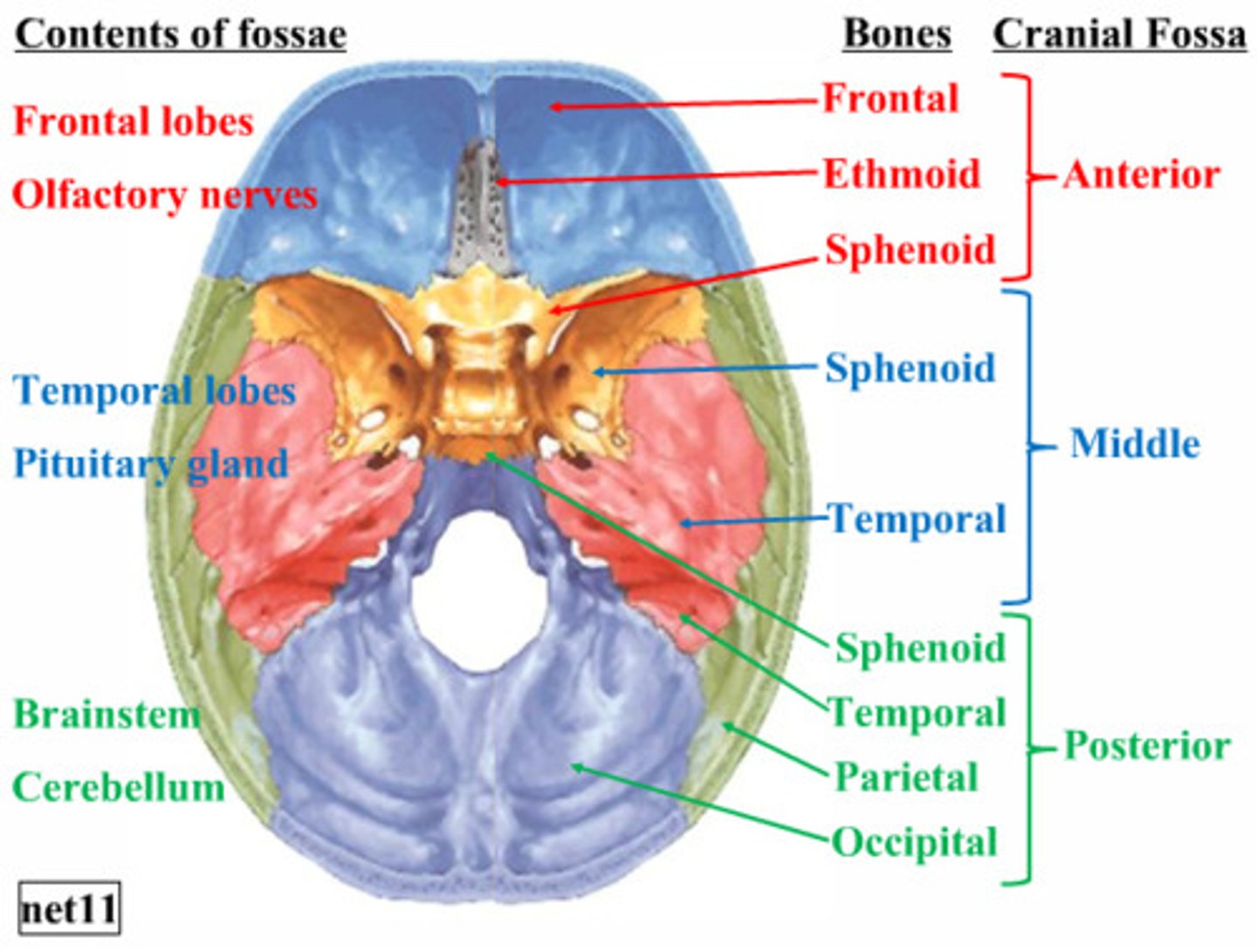
anterior cranial fossa
bounded by the frontal bone anteriorly and the lesser wing of sphenoid bone posteriorly
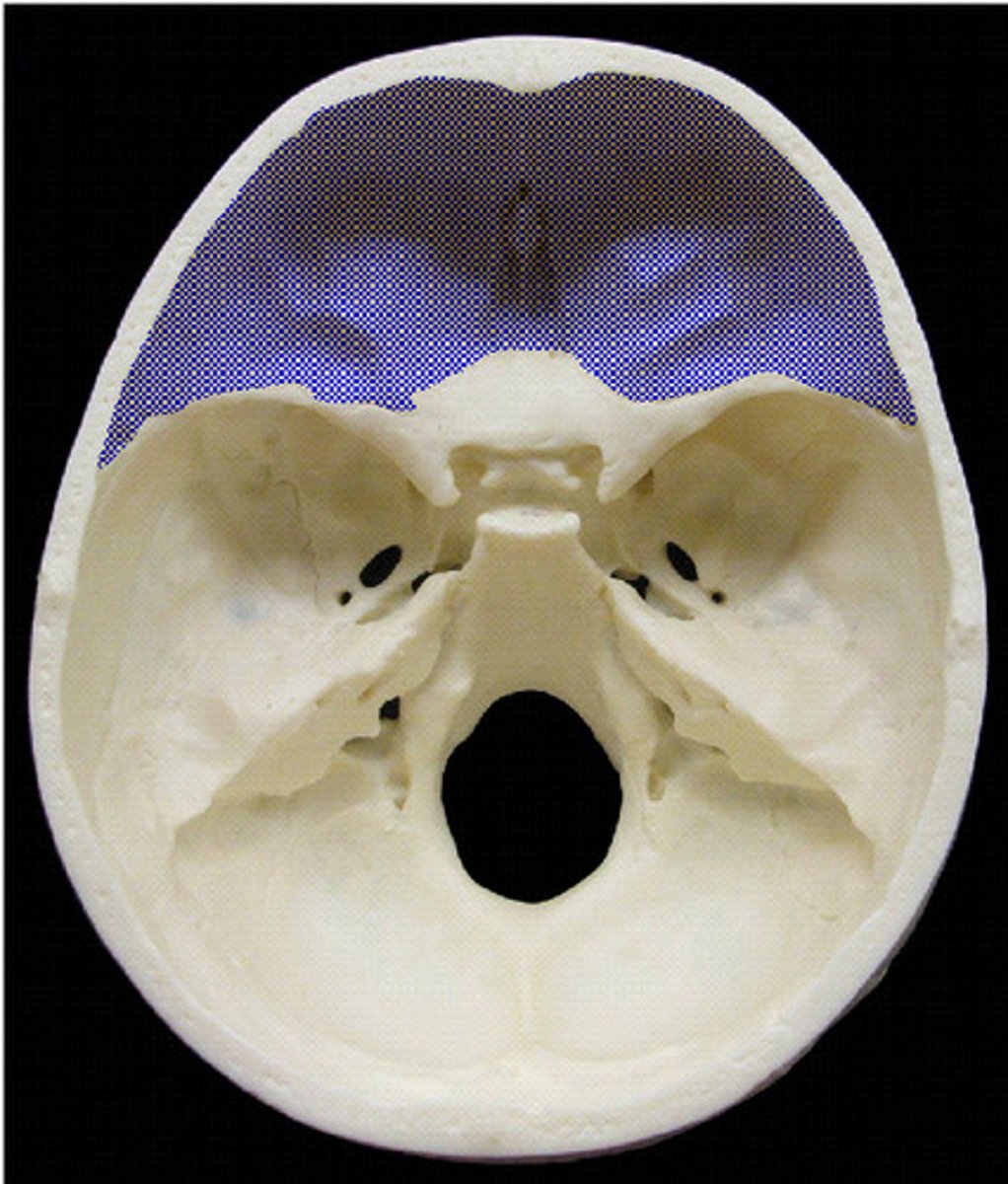
middle cranial fossa
bounded by the lesser wing of sphenoid bone anteriorly and the ridge along the
petrous part of the temporal bone posteriorly
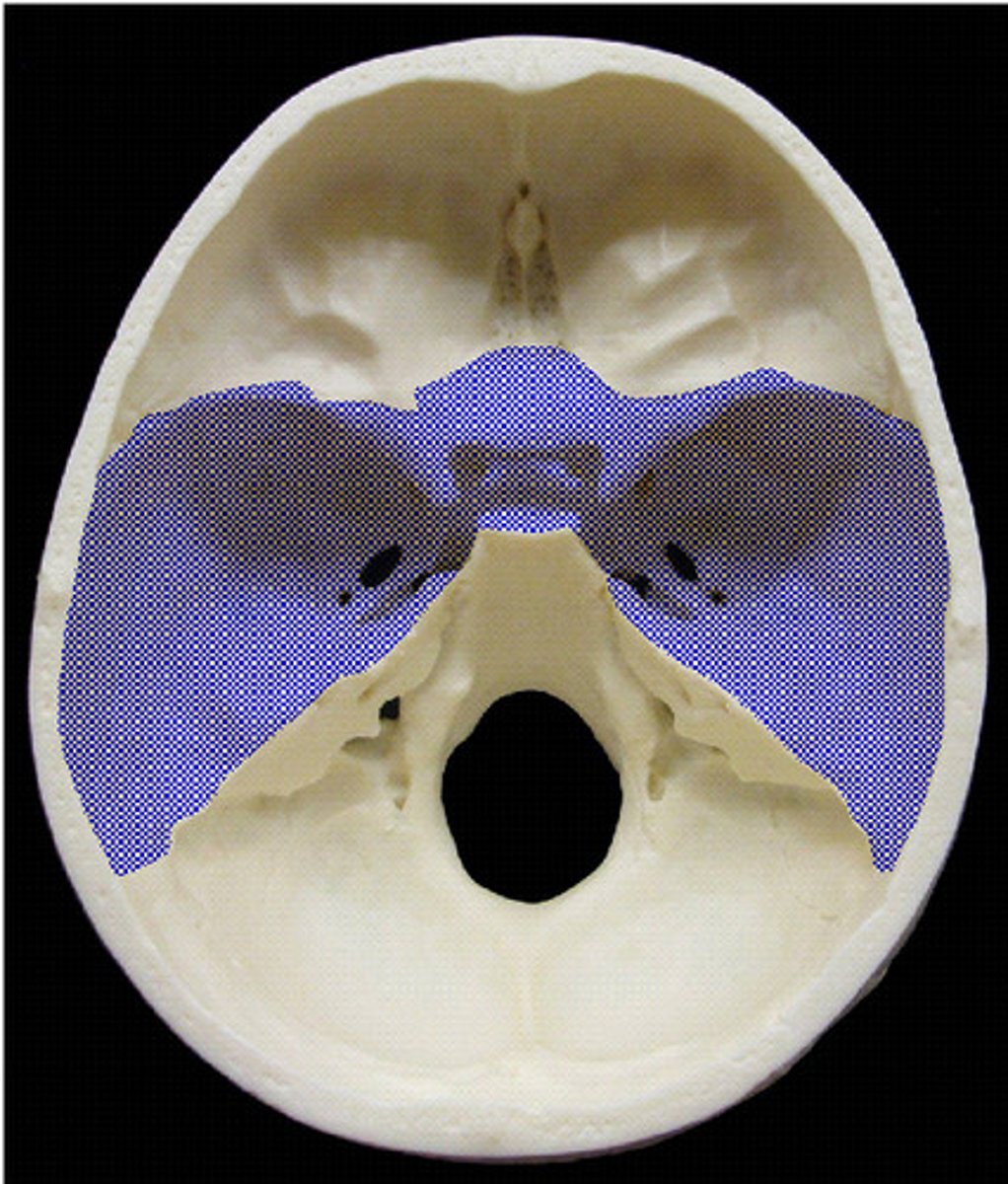
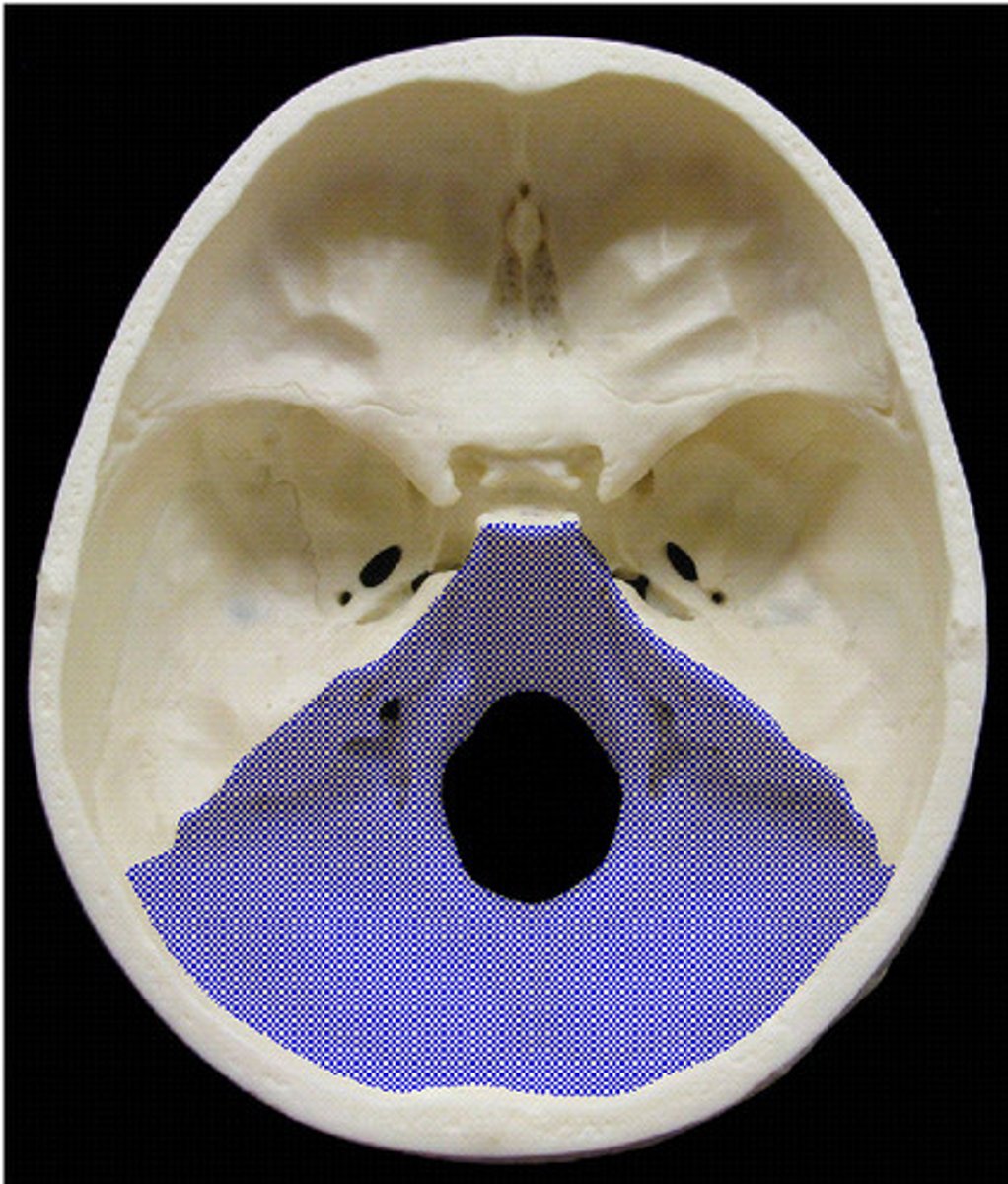
posterior cranial fossa
- bounded by the ridge along the petrous part of the temporal bone anteriorly and the occipital bone posteriorly
- located inferior to the tentorium cerebelli
sphenoid bone
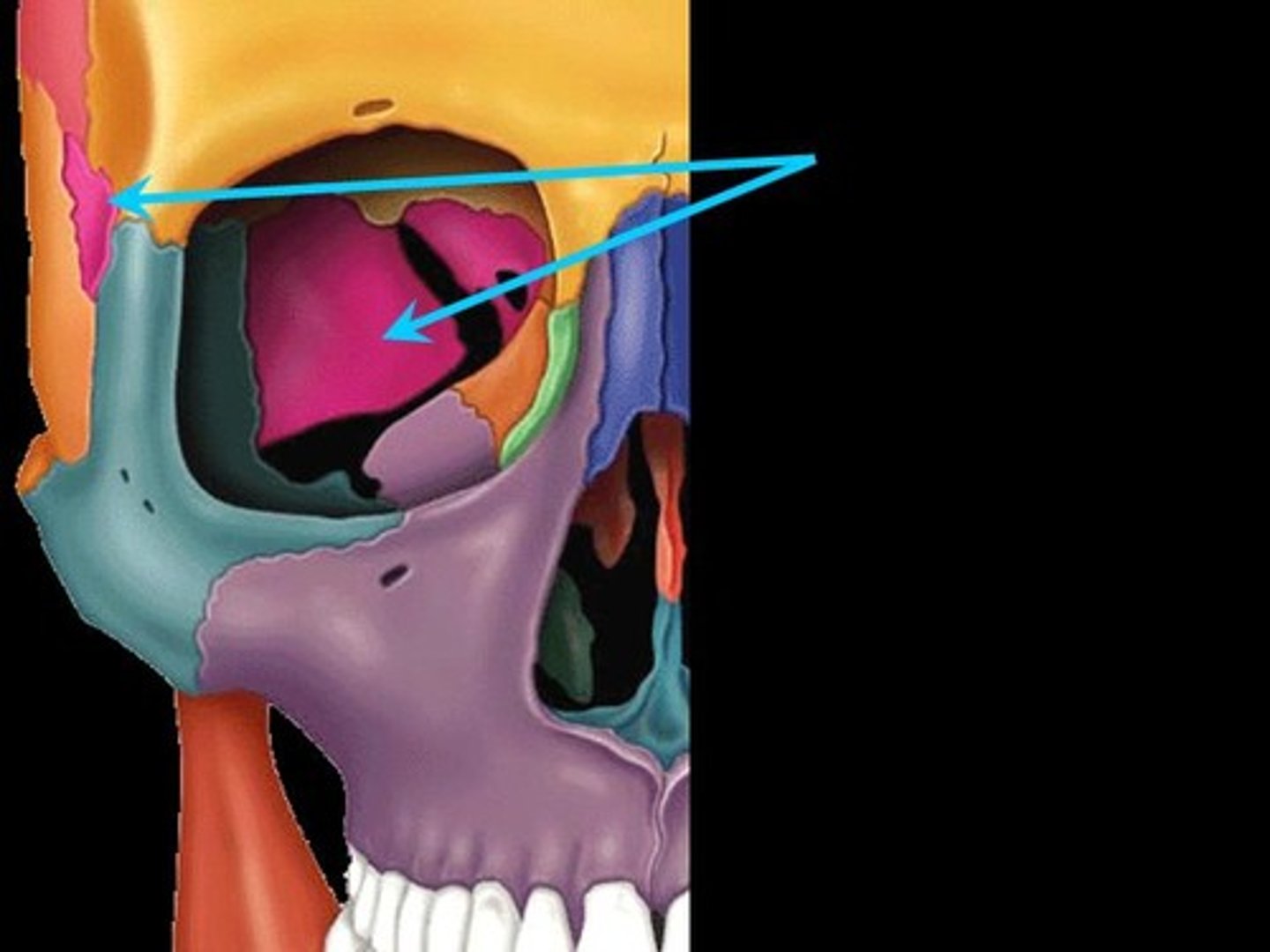
sella tursica
from anterior to posterior contains - Tuberculum sellae, hypophyseal (pituitary) fossa, dorsum sellae
optic chiasmic groove
optic nerve (chiasm) sits in this groove
greater wing
larger wing located posterior to orbital sockets
lesser wing
smaller wing located superior to orbital sockets
zygomatic bone
bone that forms the prominent part of the cheek and the outer side of the eye socket
temporal ramus of zygomatic bone
joins with the zygomatic ramus of temporal bone to form the zygomatic arch
zygomatic arch
see temporal ramus of zygomatic bone and zygomatic ramus of temporal bone
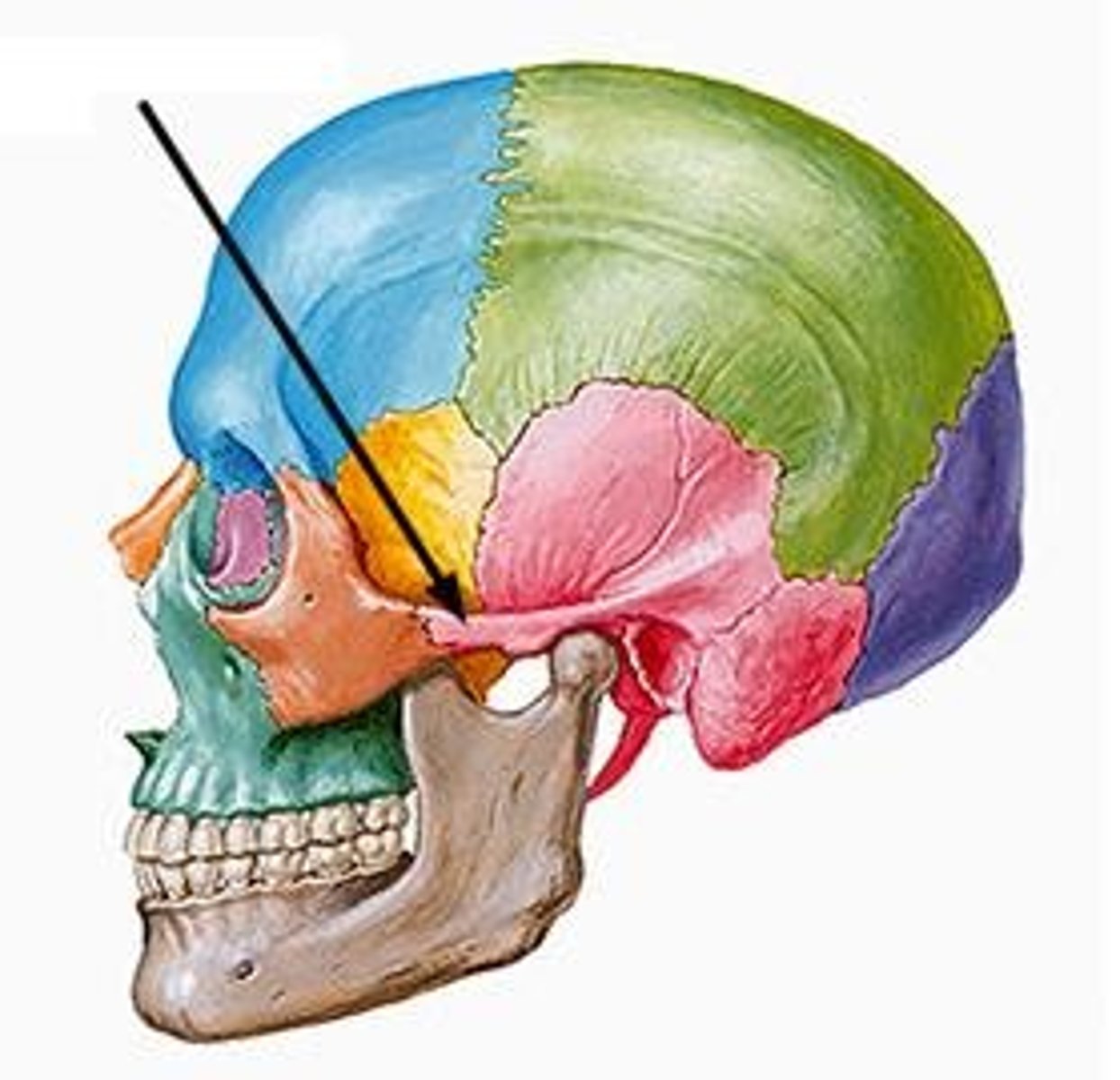
lacrimal bones
bones forming part of the eye socket
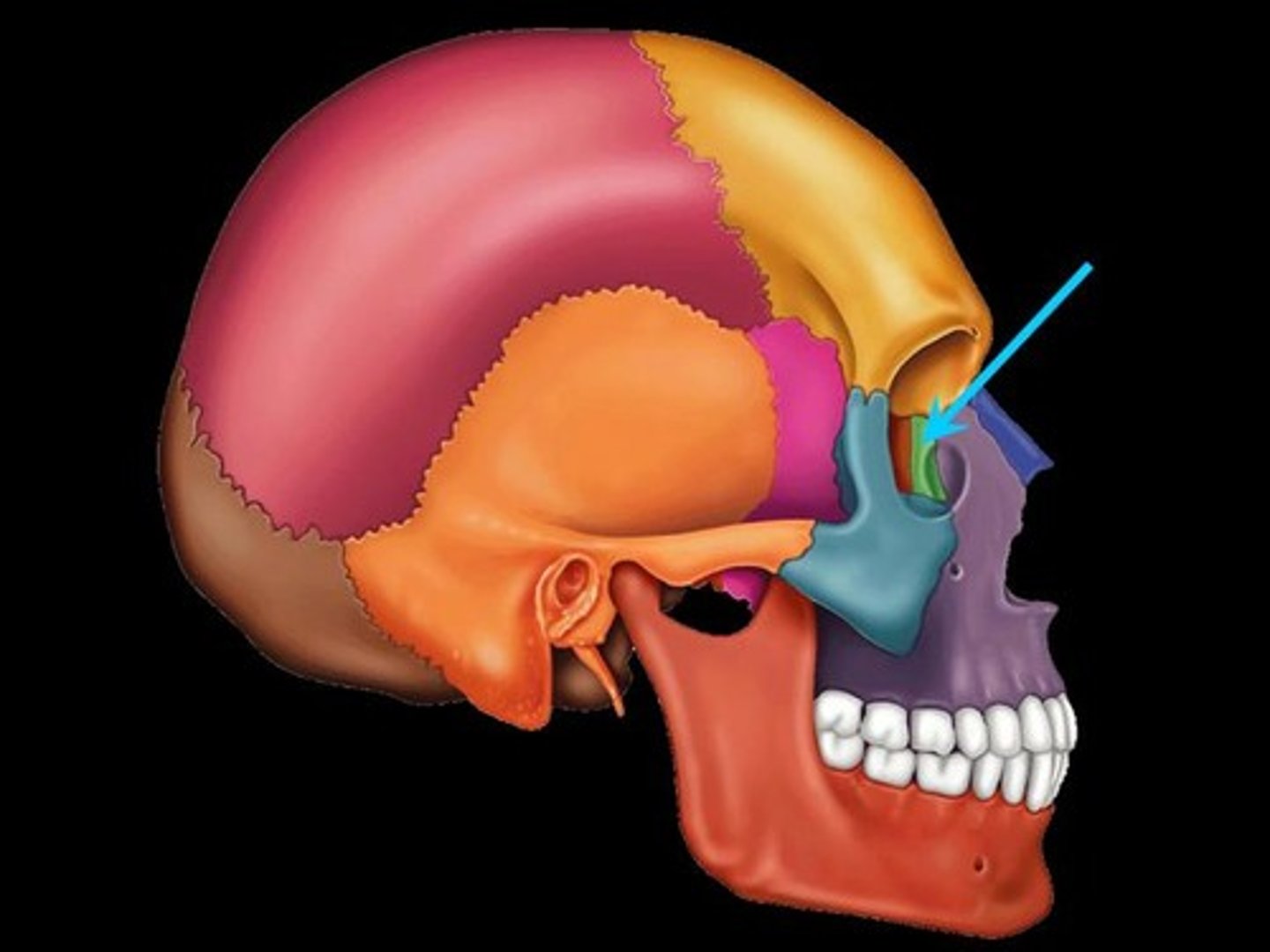
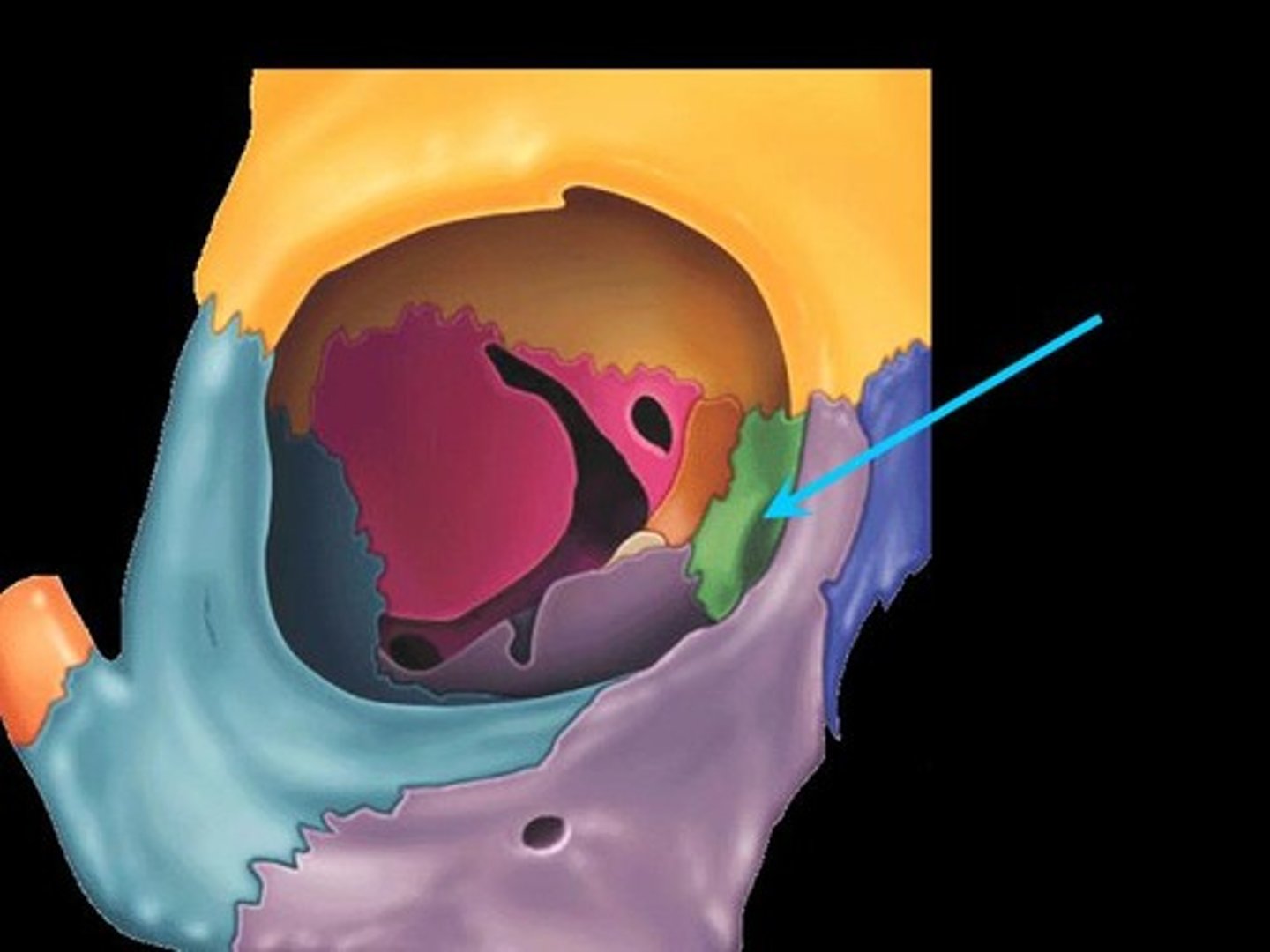
lacrimal fossa
contains nasolacrimal (tear) duct
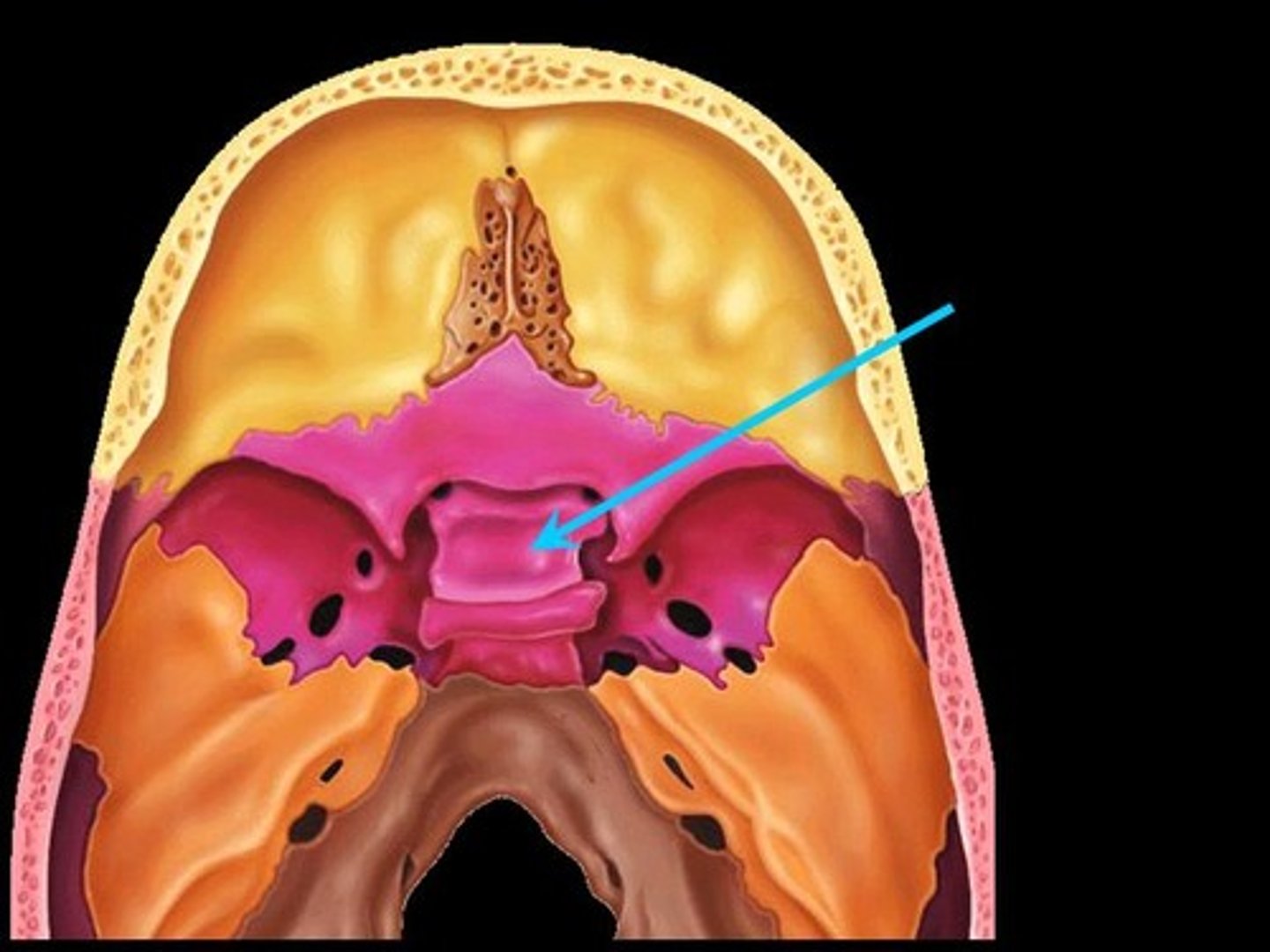
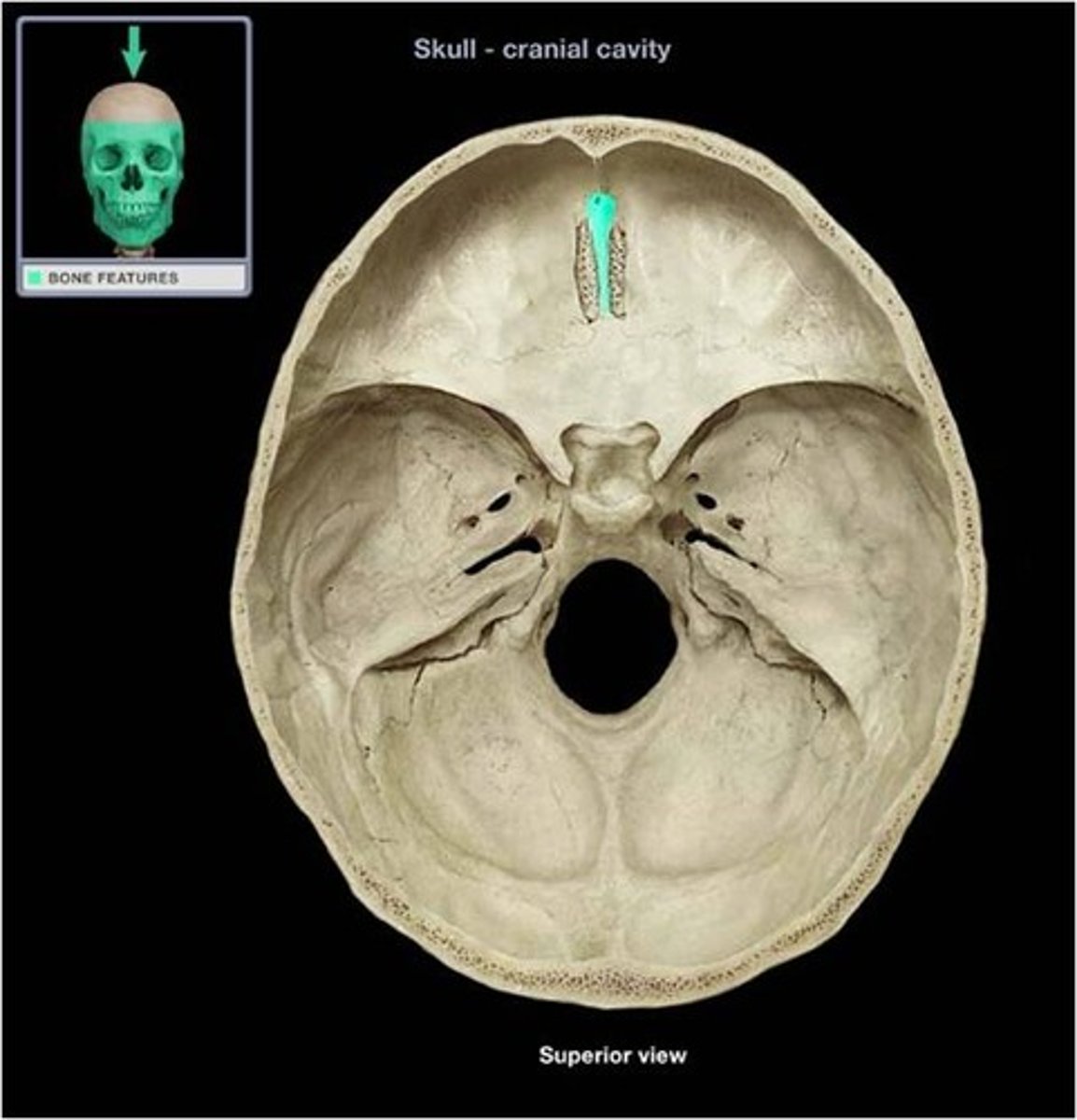
ethmoid bone
unpaired bone in the skull that separates the nasal cavity from the brain
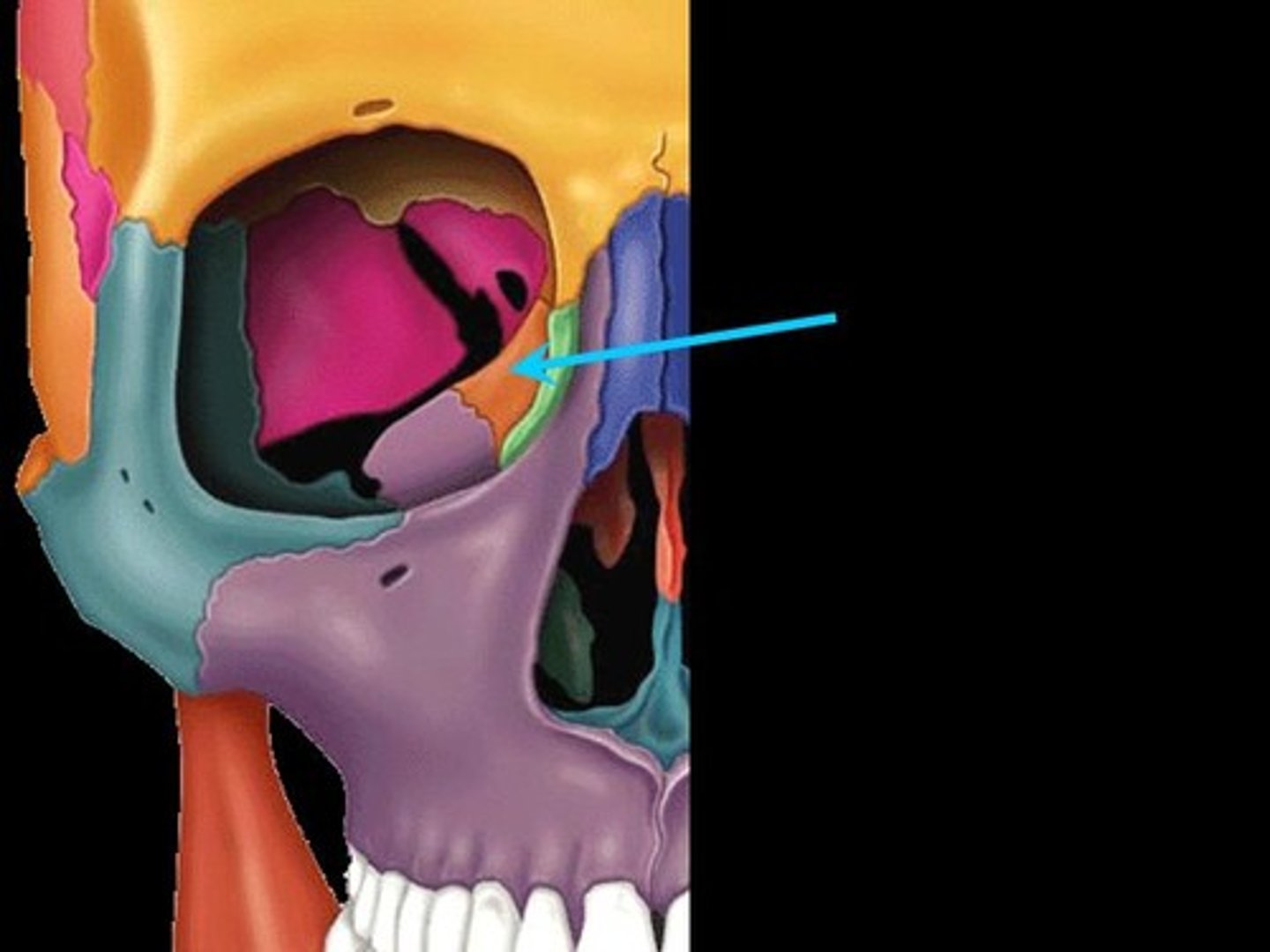
crista galli
ridge that serves as attachment point for falx cerebri
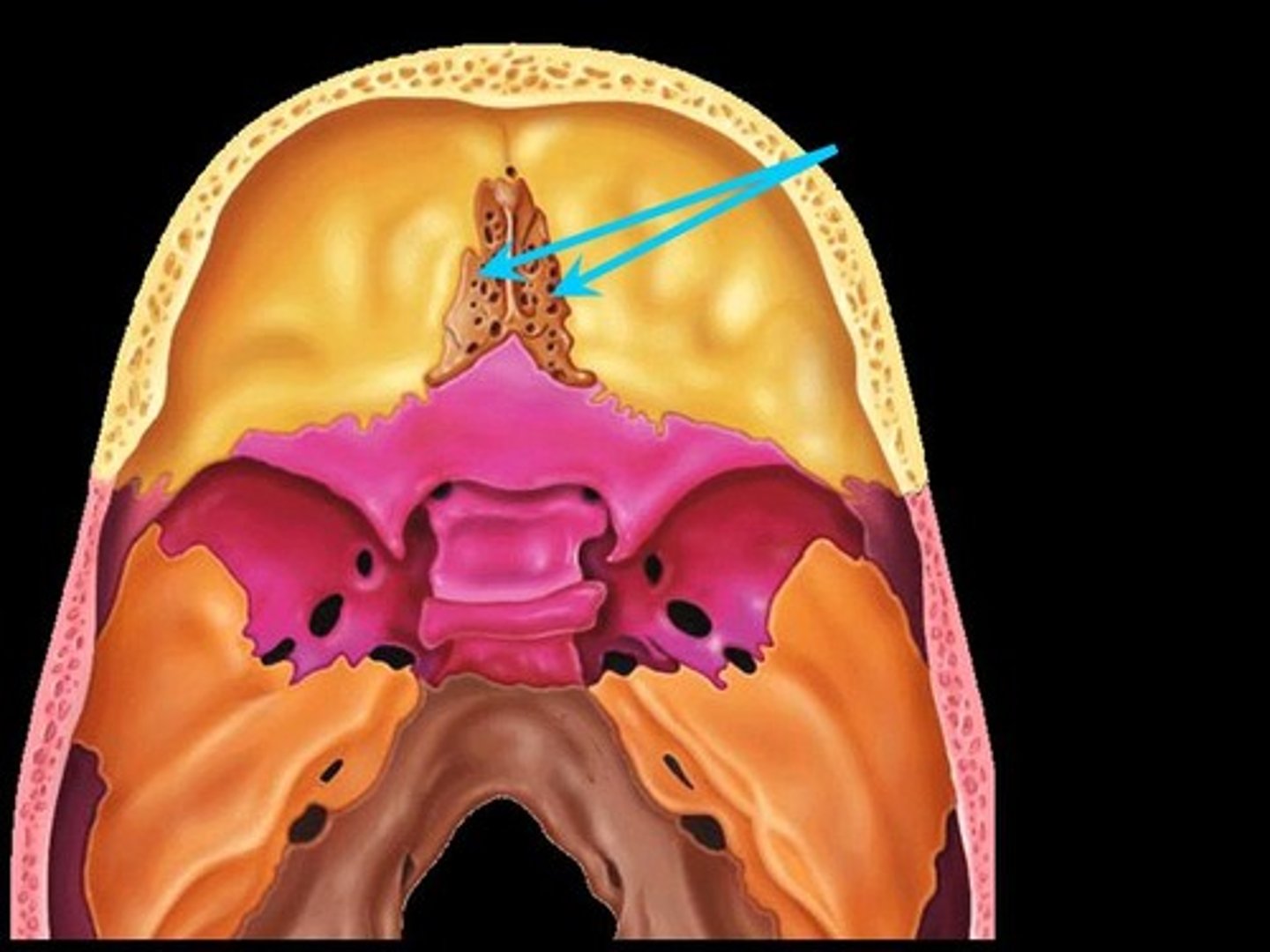
cribiform plate
perforated bone located lateral to the crista galli; allows olfactory nerve (CNI) to penetrate into nasal cavity
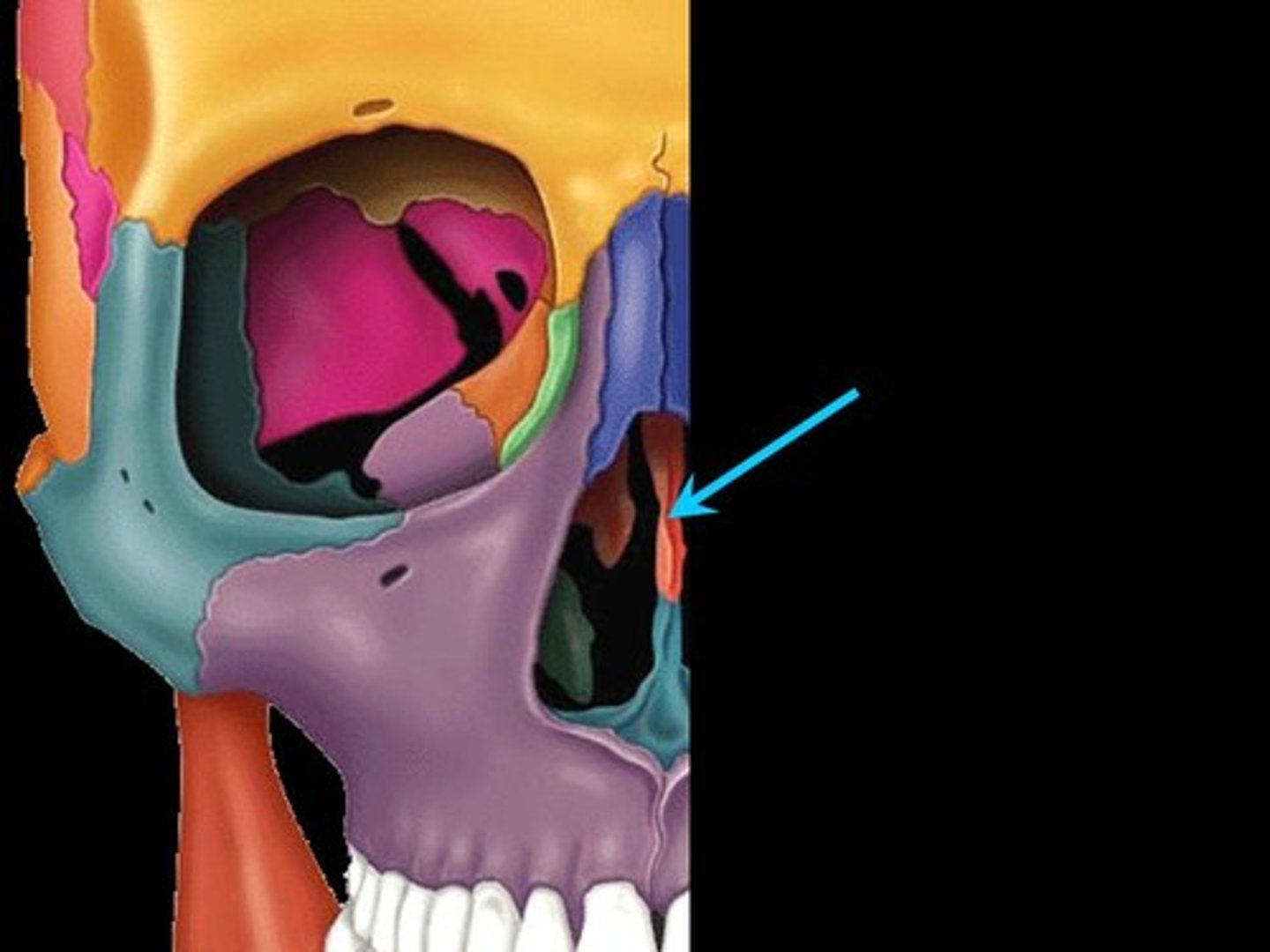
perpendicular plate
separates the two halves of the nasal cavity (superior portion)
vomer
separates two halves of the nasal cavity (inferior portion)
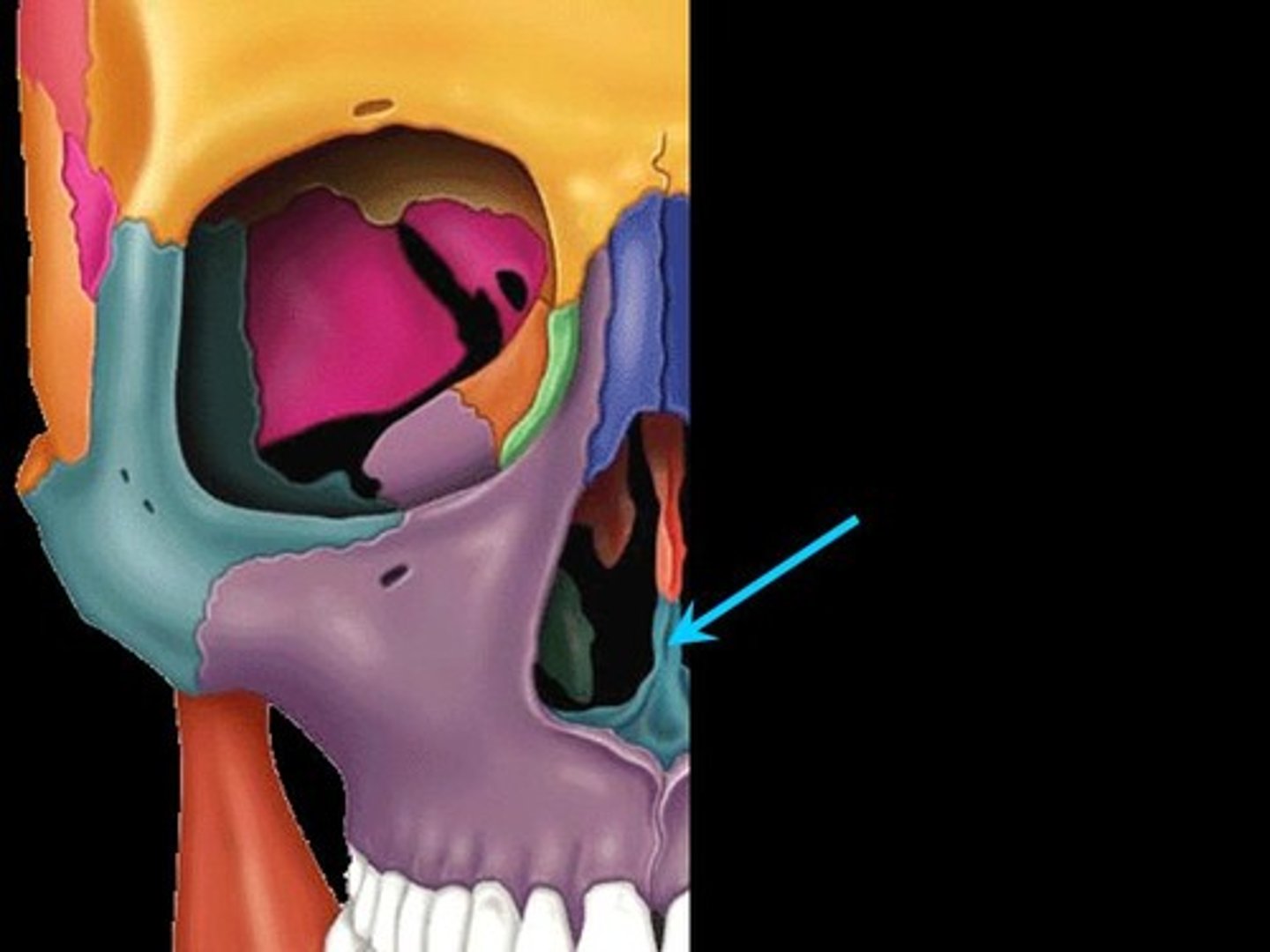
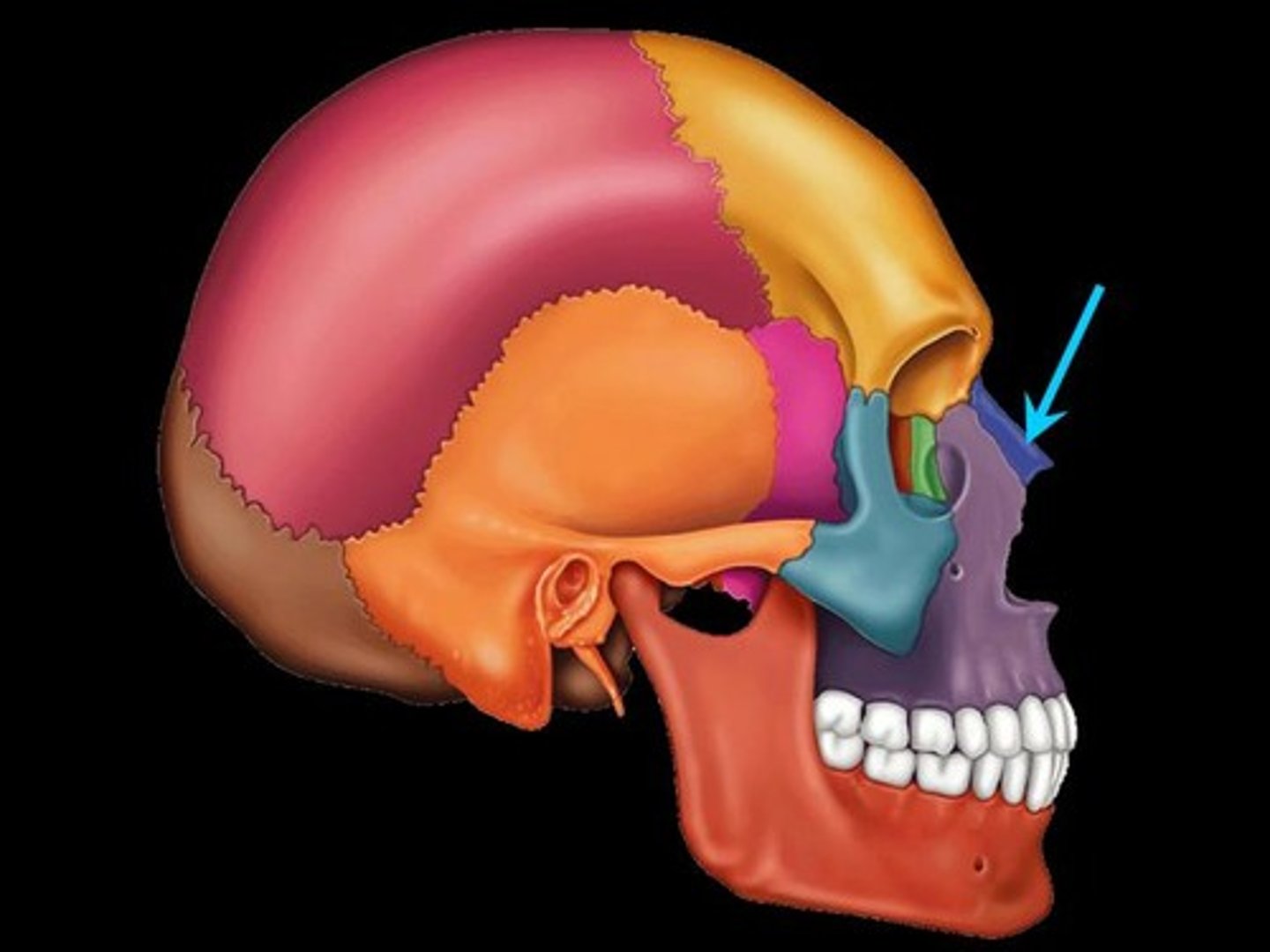
nasal bones
two small oblong bones, varying in size and form in different individuals; they are placed side by side at the middle and upper part of the face, and form, by their junction, "the bridge" of the nose.
nasal septum
cartilage connected to anterior side of vomer and perpendicular plate of ethmoid bone
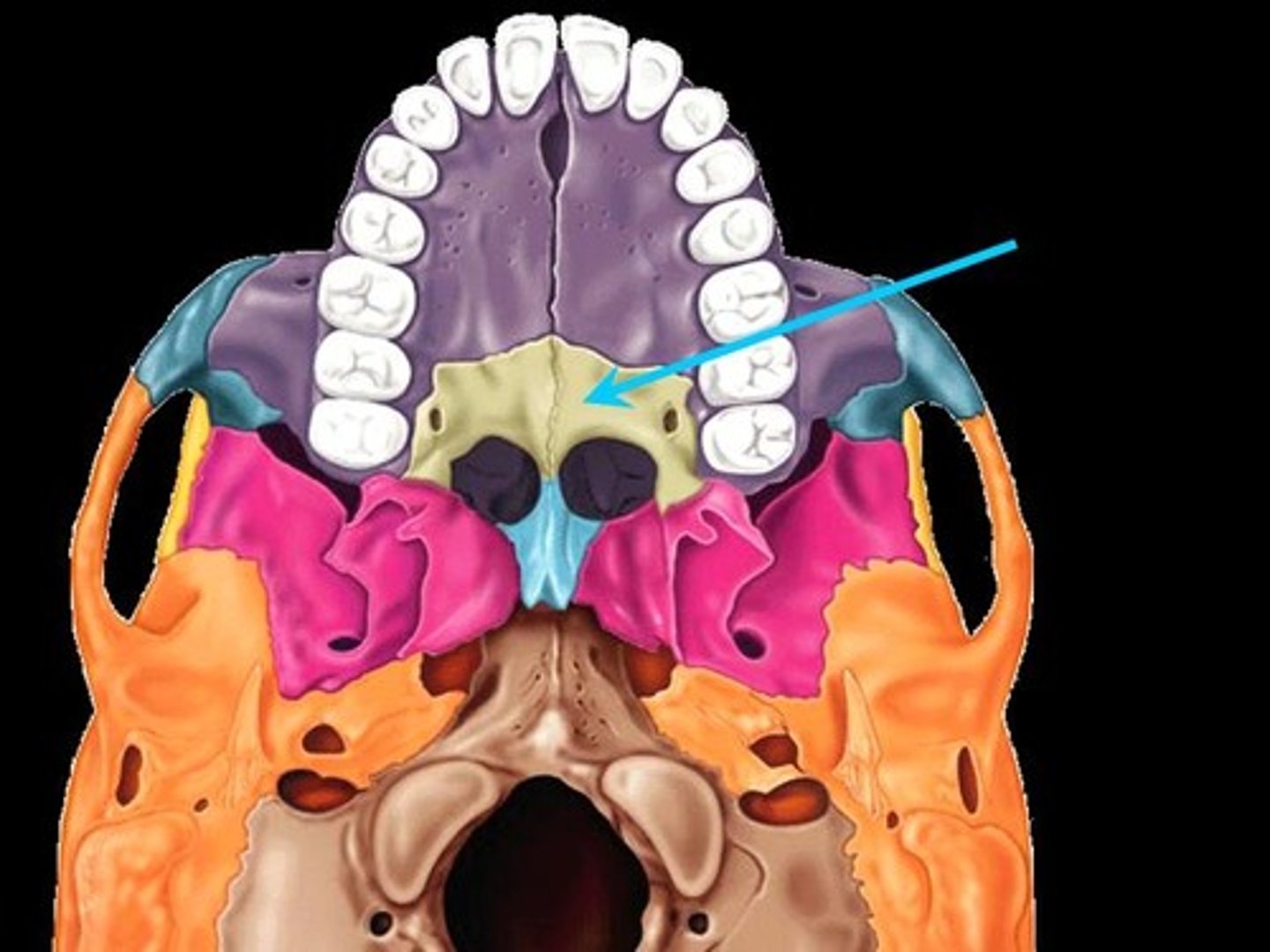
maxilla
jaw or jaw bone
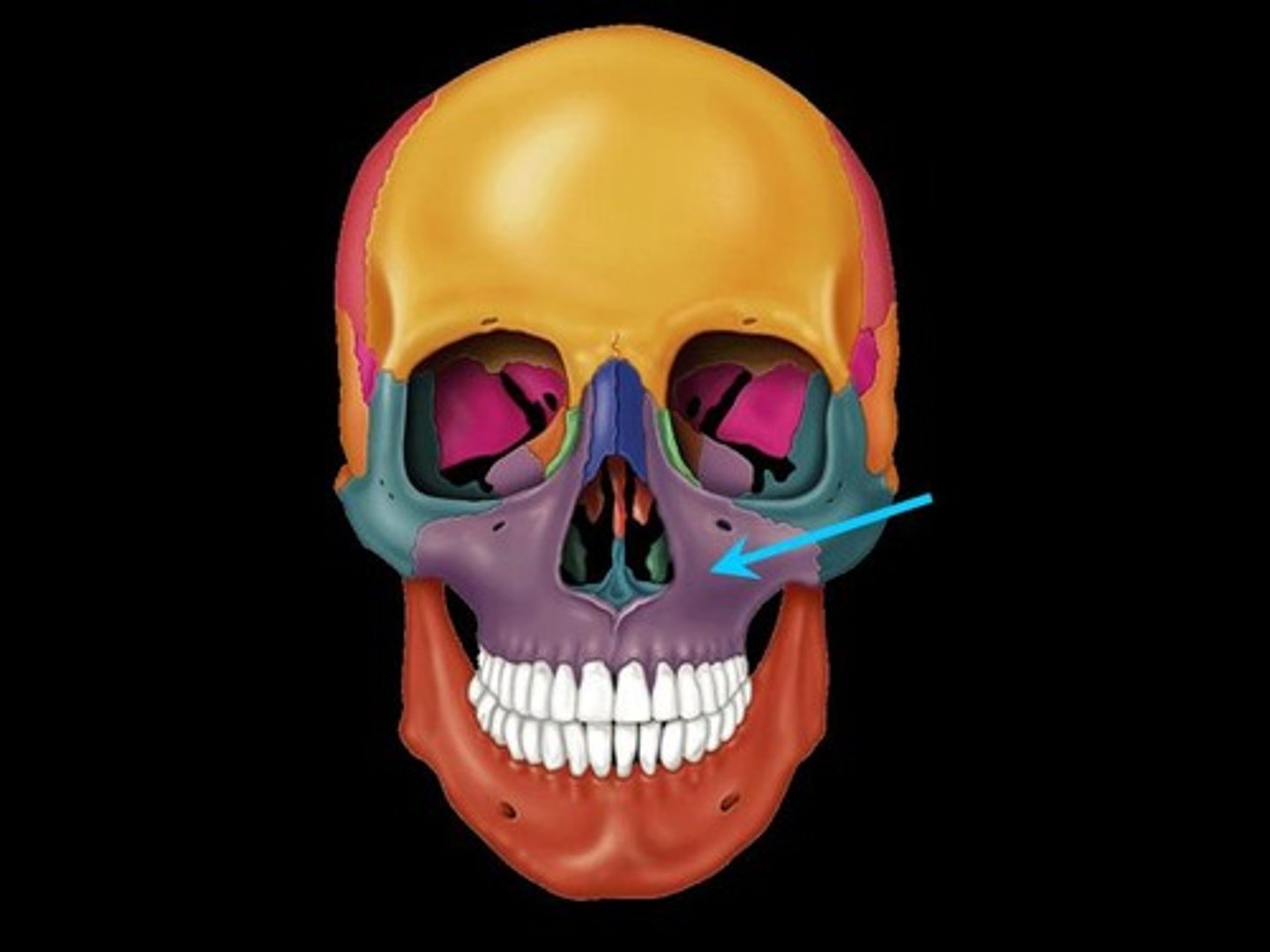
infraorbital foramen
maxillary branch of trigeminal nerve emerges from this opening
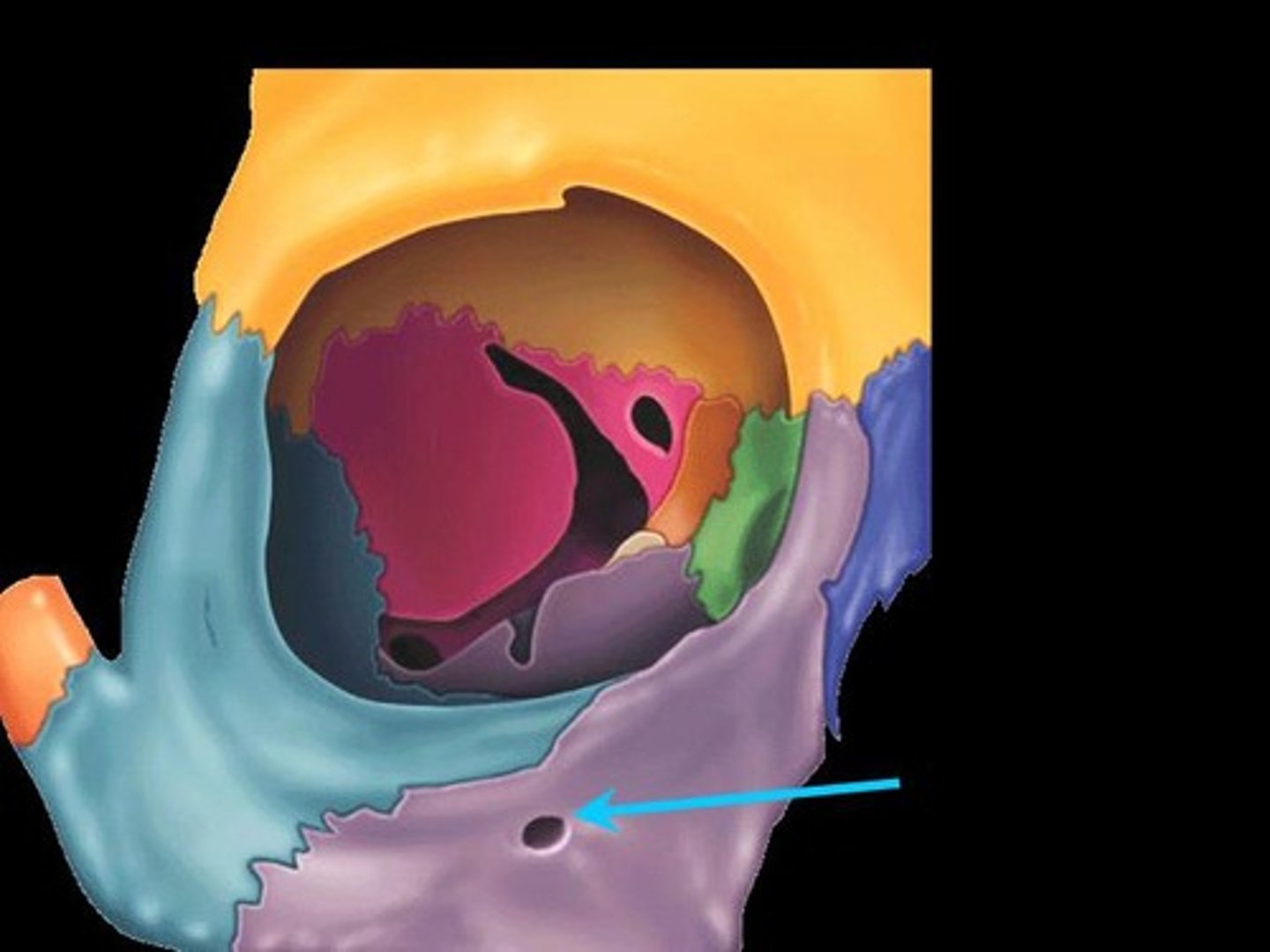
palatine process
- forms the roof of the mouth (posterior portion)
- "hard palate"
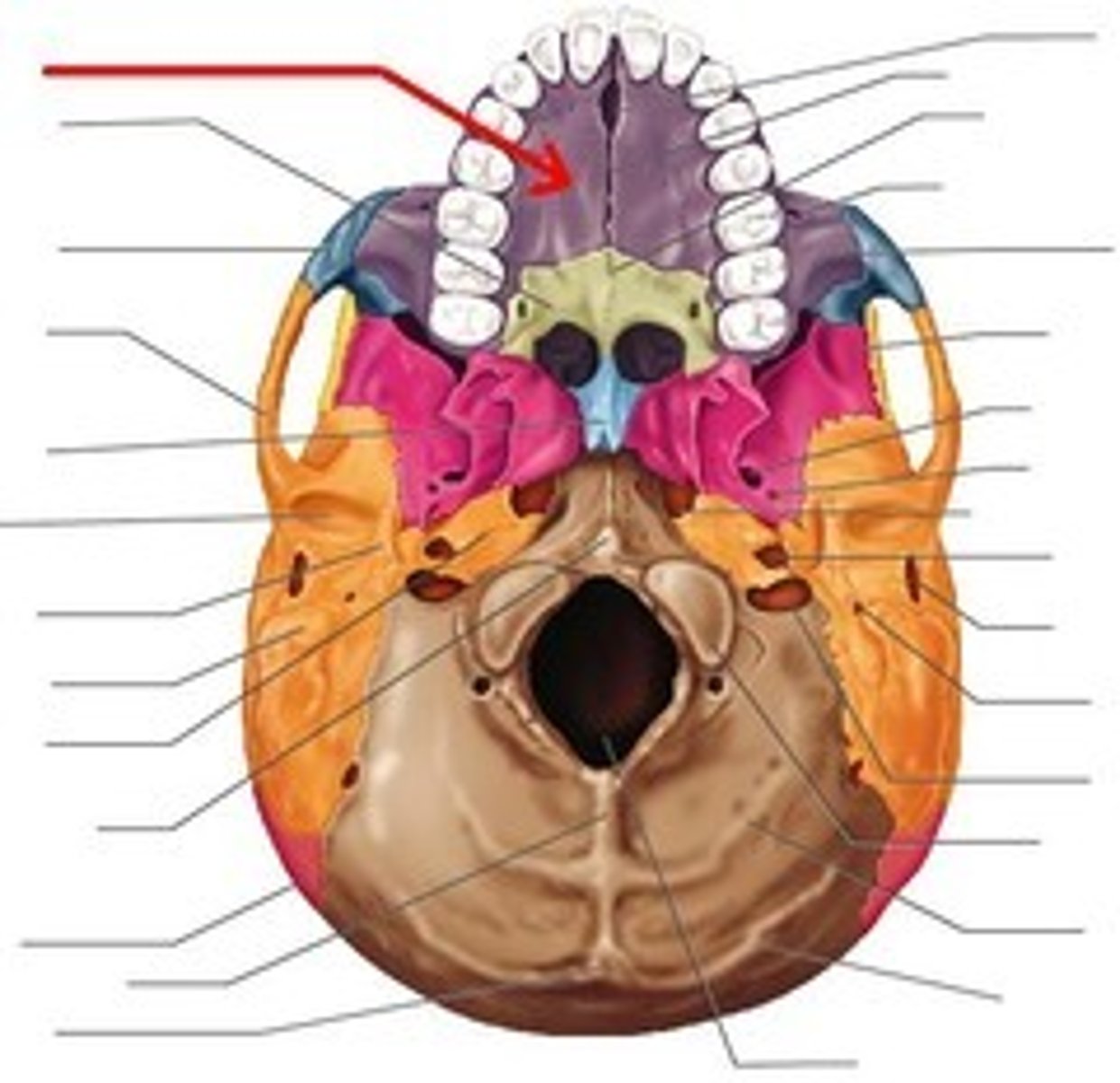
alveolar process (maxilla)
terminates in an alveolus (tooth socket)
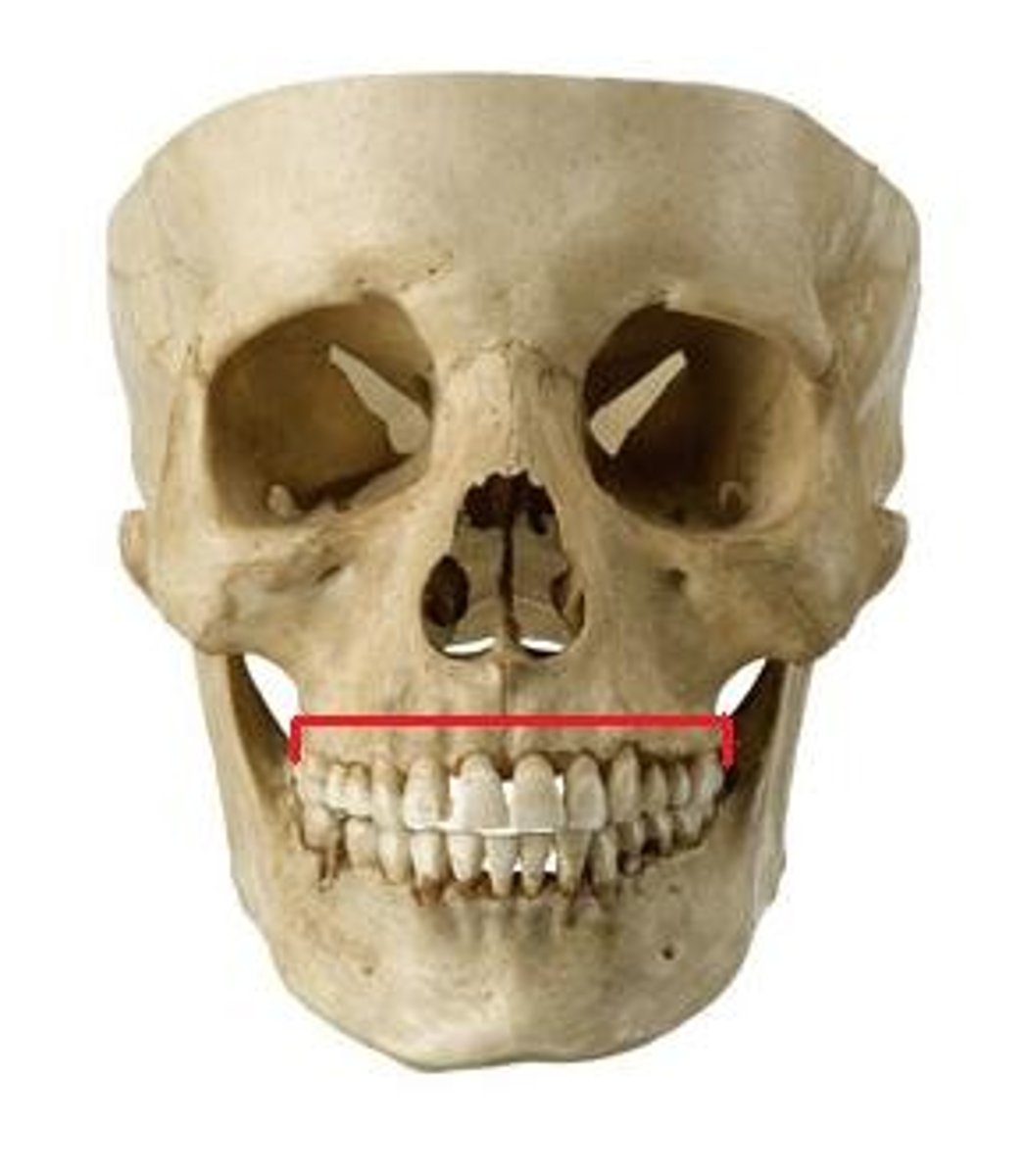
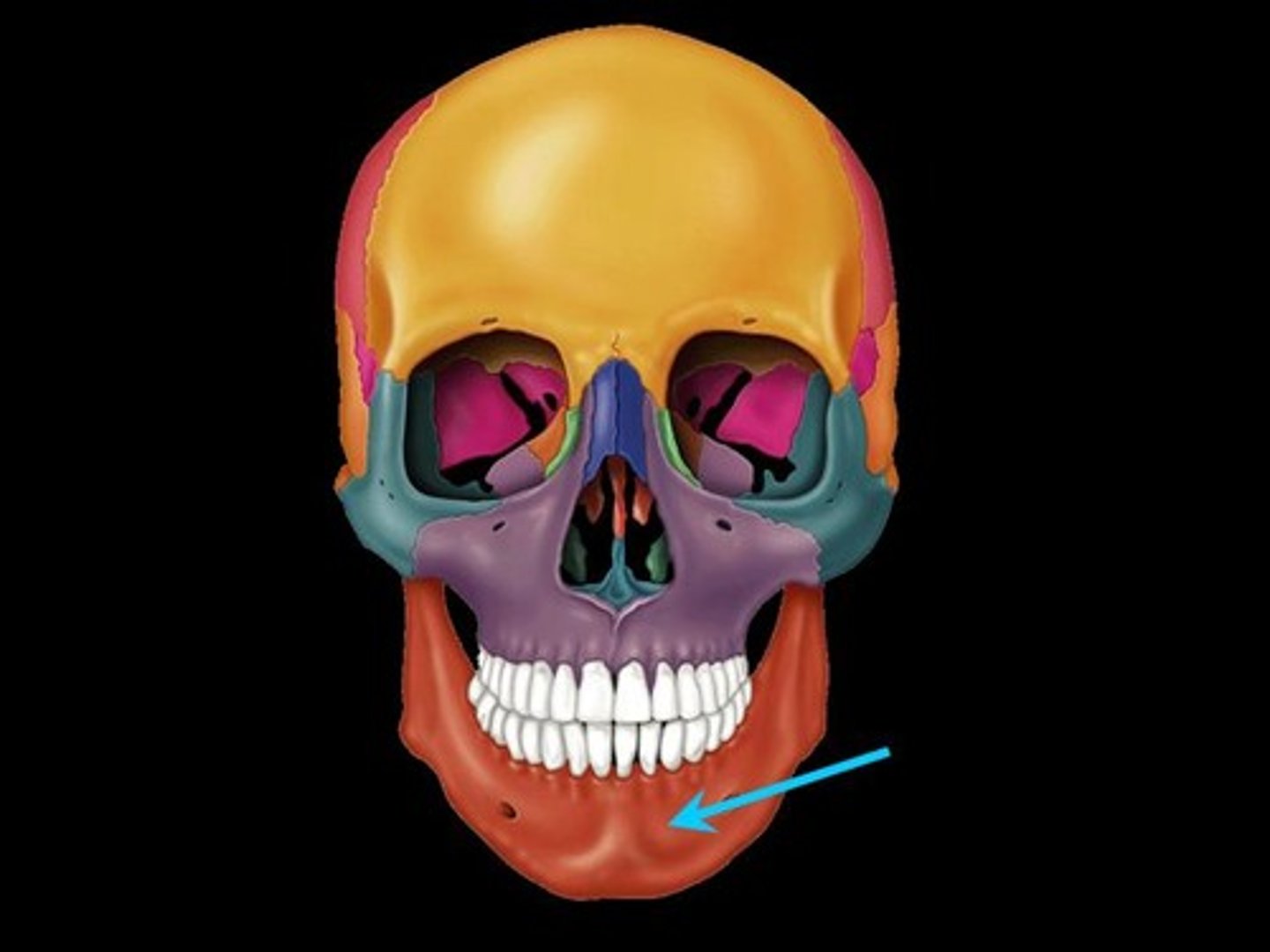
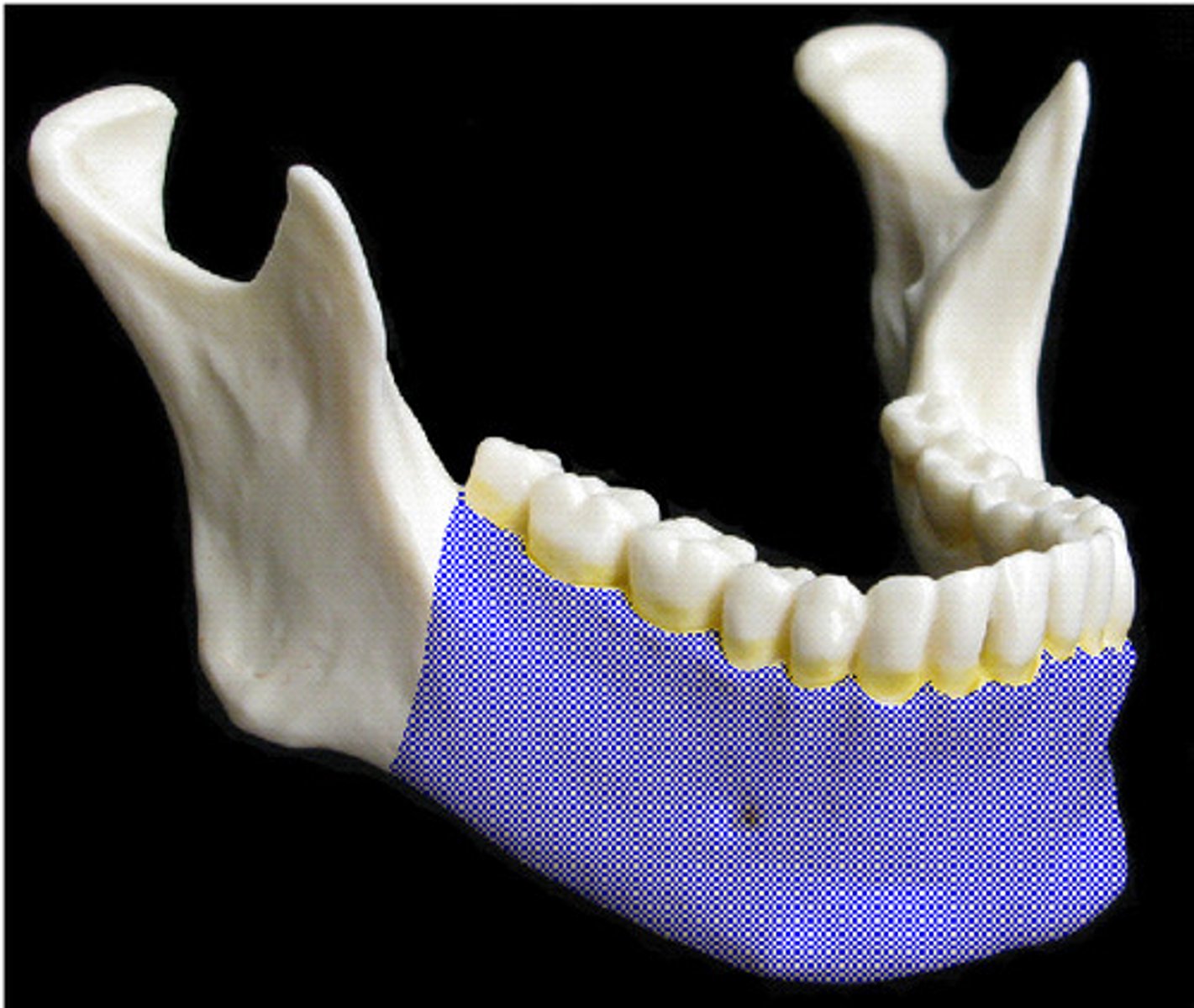
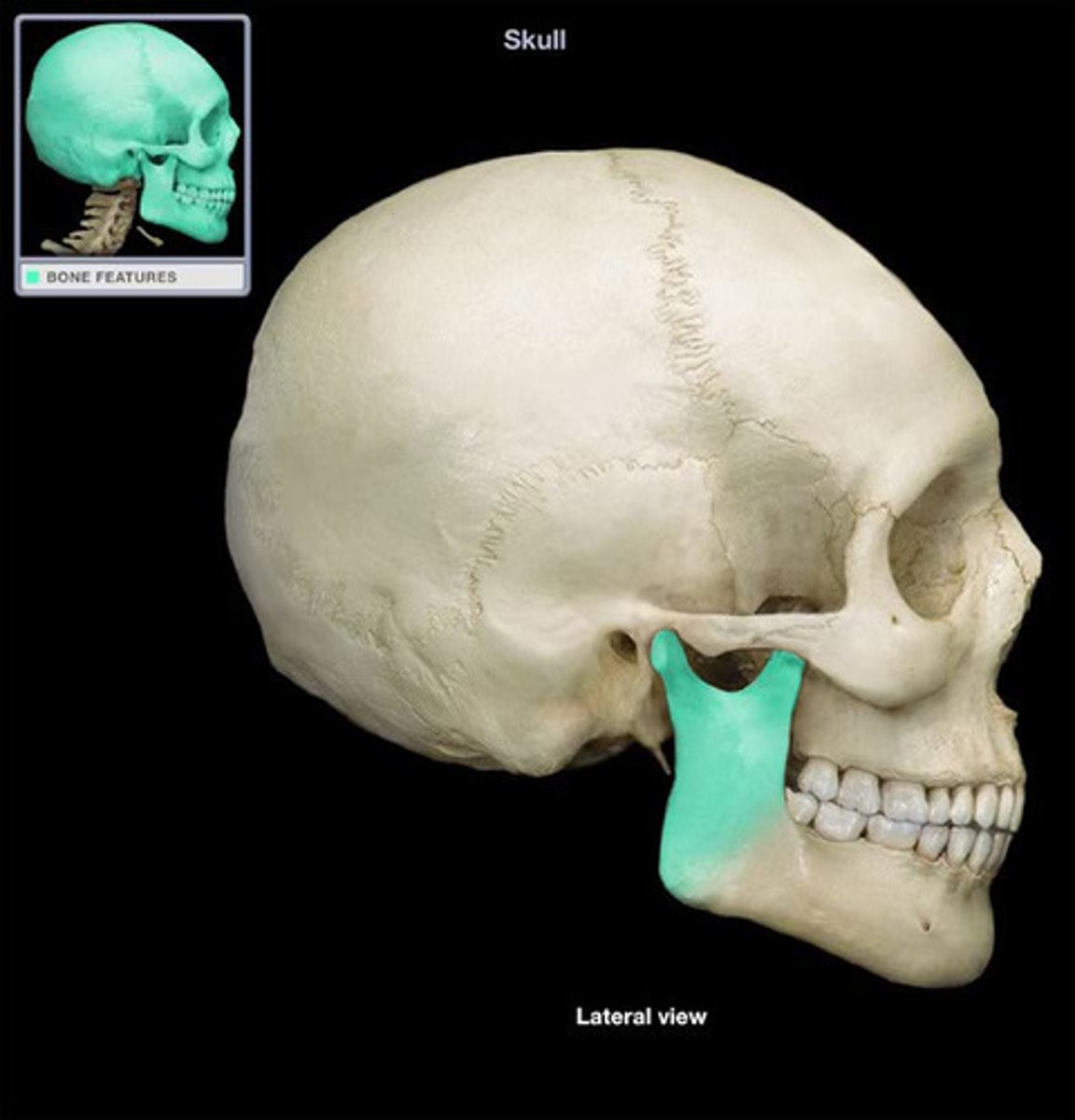
mandible
body
main (anterior) portion of the mandible
angle
located b/w body and ramus
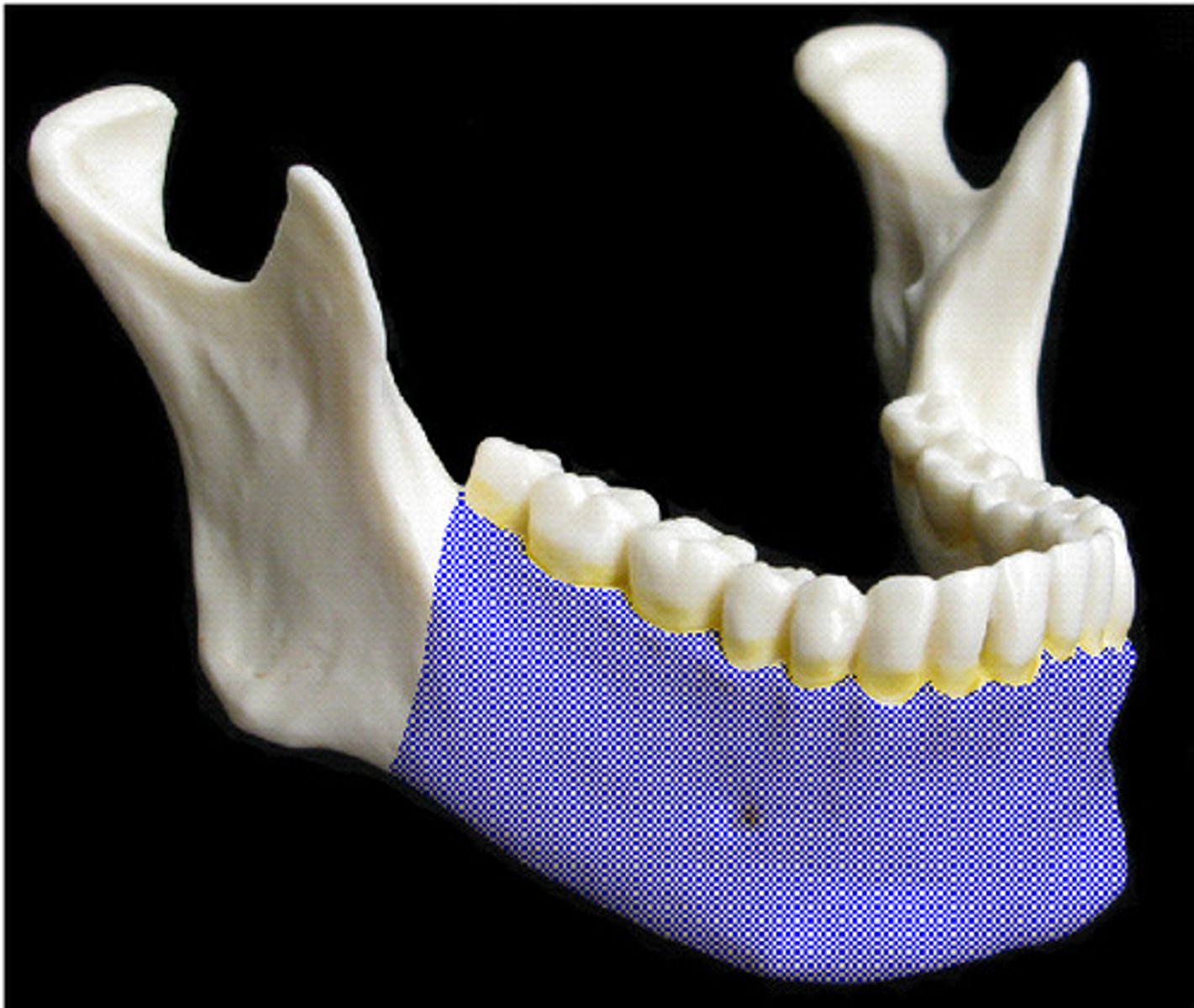
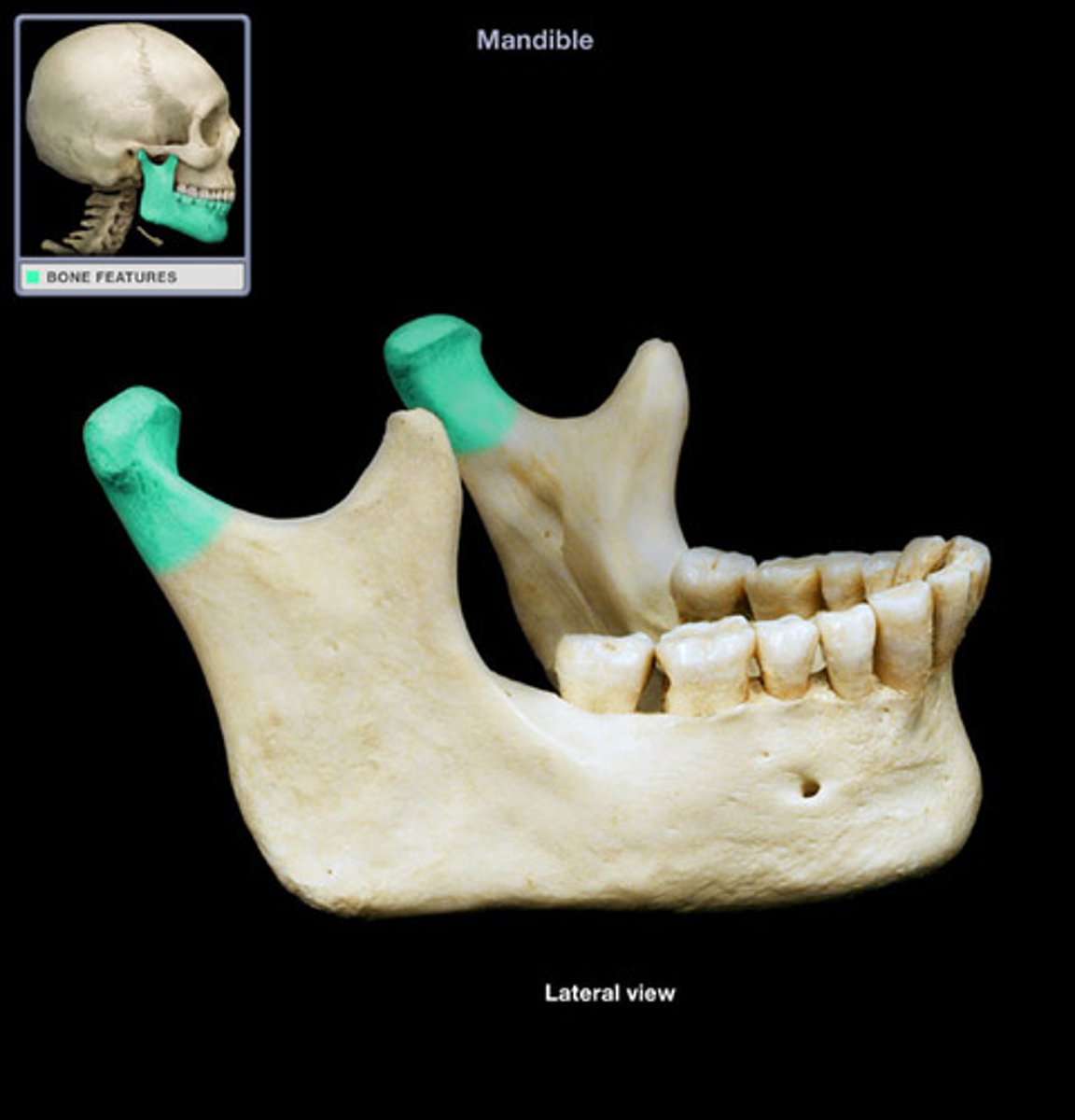
ramus
terminates in condyloid and coronoid process
condyloid process
more posterior process that articulates w/ temporal bone
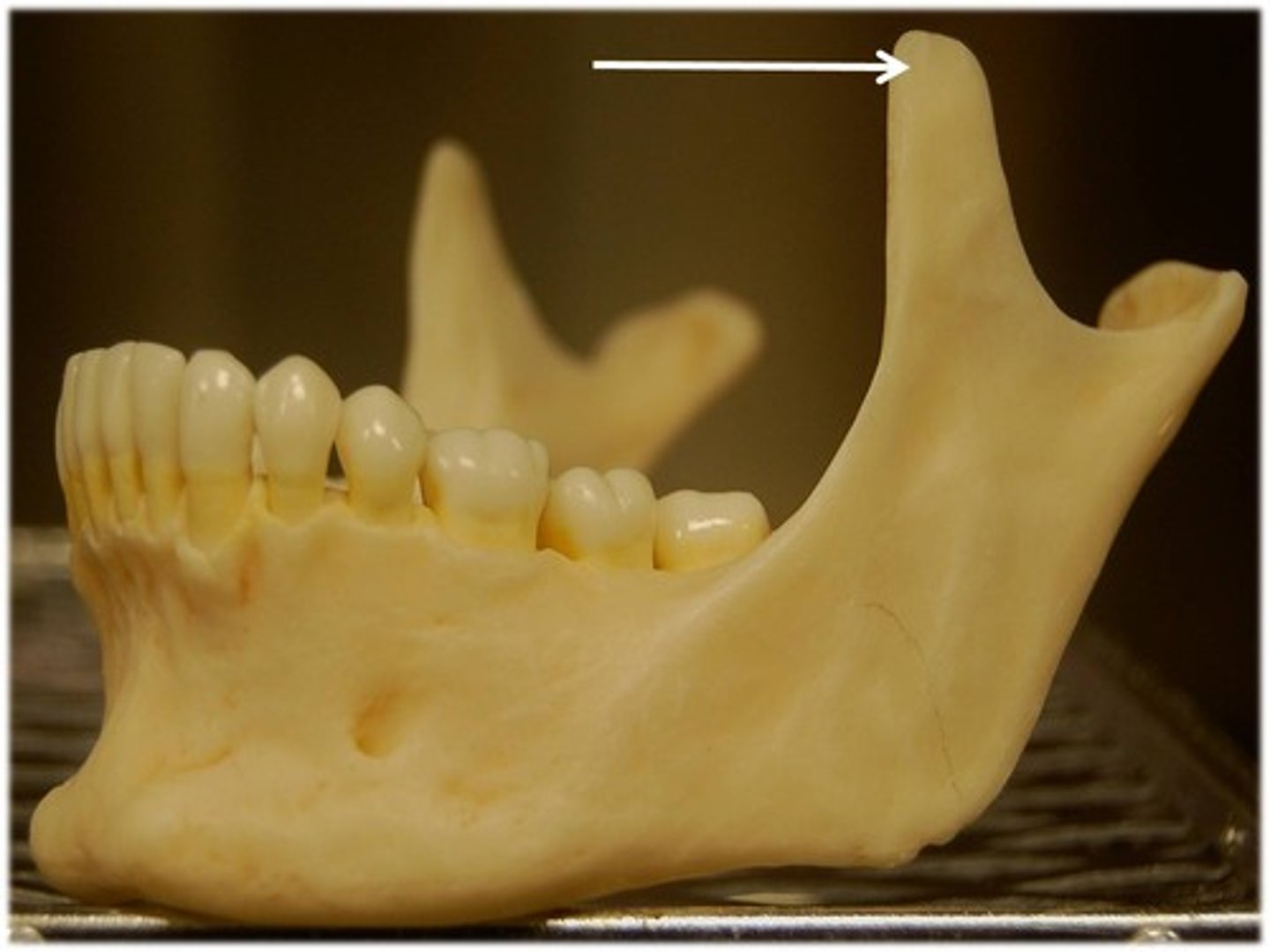
coronoid process
more anterior process that serves as an attachment for temporalis mm.
mental protuberance
most anterior point of the mandible (tip of chin)
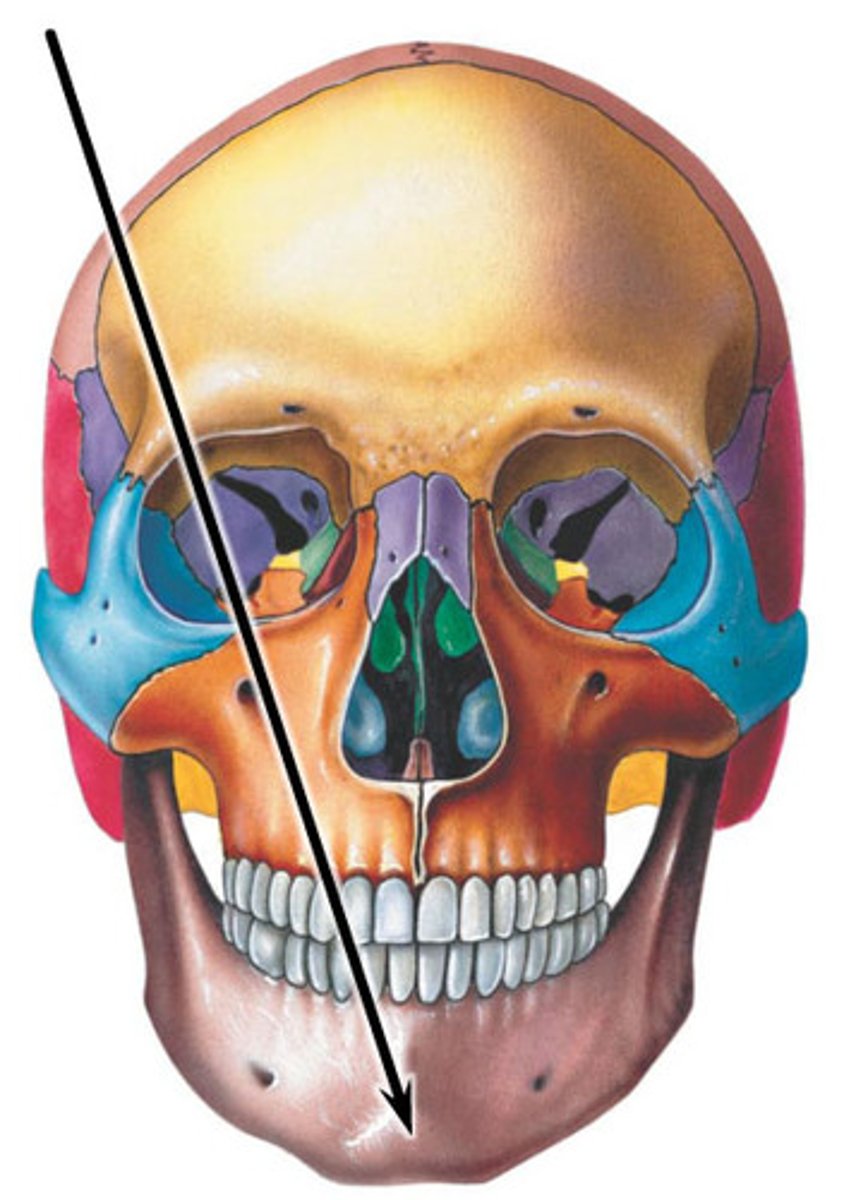
mental foramen
mental branch of trigeminal nerve emerges from this opening
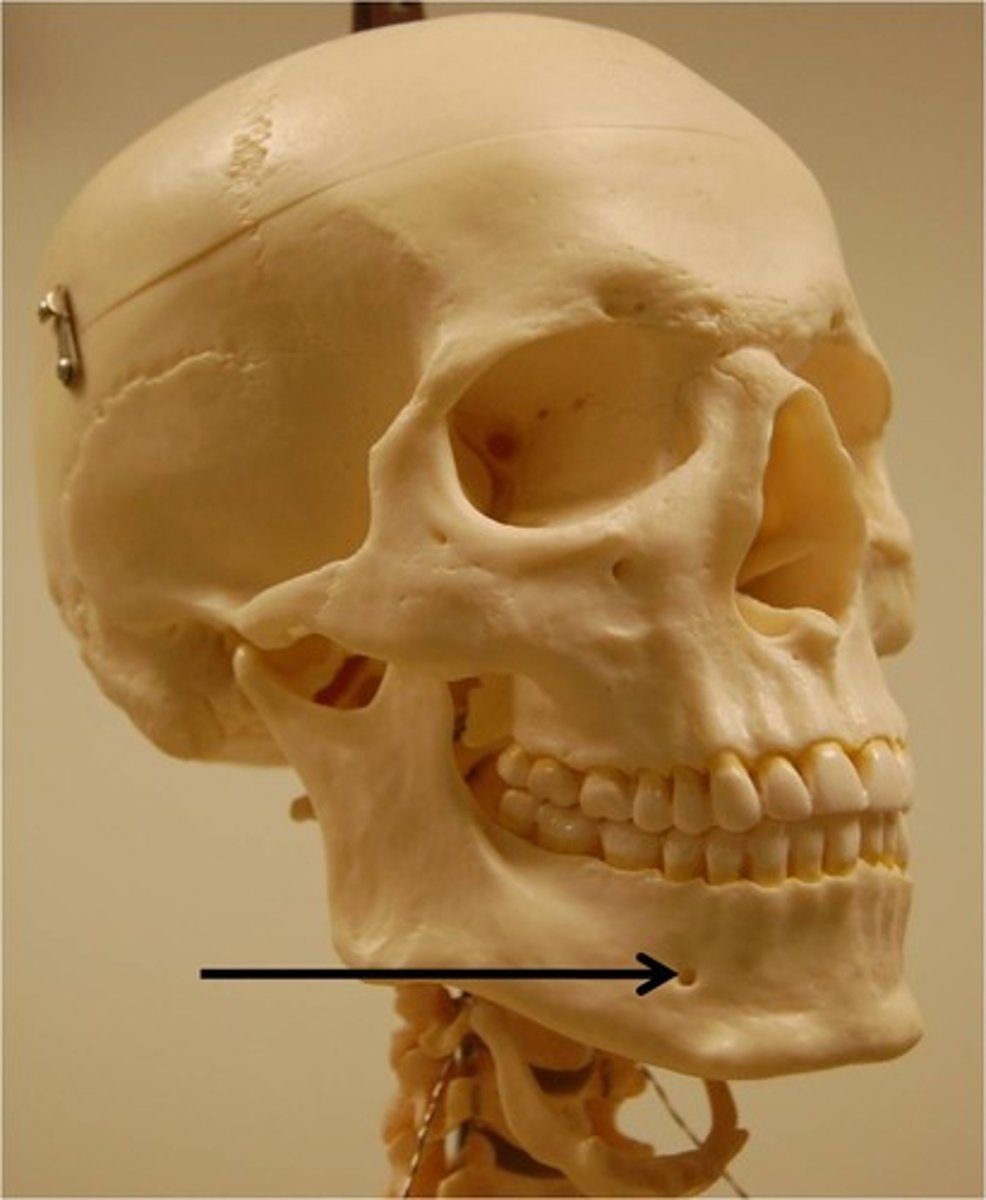
alveolar process (mandible)
terminates in an alveolus (tooth socket)
palatine bone
- forms the roof of the mouth (posterior portion)
- "hard palate"