AP Bio: Cellular Energetics
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/27
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
28 Terms
1
New cards
ADP
Lower-energy molecule that can be converted into ATP by the addition of a phosphate
2
New cards
Aerobic
Process that requires oxygen
3
New cards
Endergonic
the process of building up larger molecules from smaller ones (energy added)
4
New cards
Anaerobic
Process that does not require oxygen
5
New cards
ATP
main energy source that cells use for most of their work
6
New cards
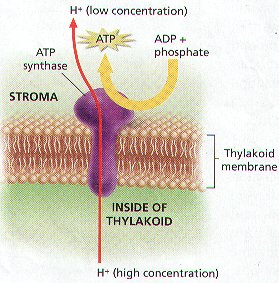
Chemiosmosis
A process for synthesizing ATP using the energy of an electrochemical gradient and the ATP synthase enzyme.
7
New cards
Chlorophyll
Green pigment in plants that absorbs light energy used to carry out photosynthesis
8
New cards
Chloroplasts
organelles that capture the energy from sunlight and convert it into chemical energy in a process called photosynthesis
9
New cards
Electron
a negatively charged subatomic particle
10
New cards
Enzymes
Proteins that speed up chemical reactions
11
New cards
FAD
acts as hydrogen acceptors when hydrogen atoms are present and accept the hydrogen atoms during the process
12
New cards
Lactic acid
Produced in muscle cells from the reduction of pyruvate (under anaerobic conditions) to regenerate NAD+ so that glycolysis can continue
13
New cards
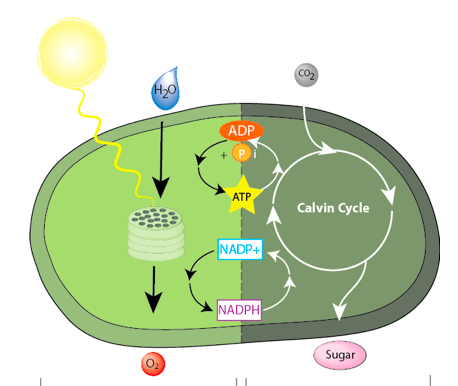
Light-dependent reactions
reactions of photosynthesis that use energy from light to produce ATP and NADPH
14
New cards
Mitochondria
An organelle in where respiration and energy production occur
15
New cards
NAD
electron carrier involved in glycolysis and Krebs cycle
16
New cards
NADPH
Electron carrier in photosynthesis; provides the high-energy electrons for the reduction of carbon dioxide to sugar in the Calvin cycle
17
New cards
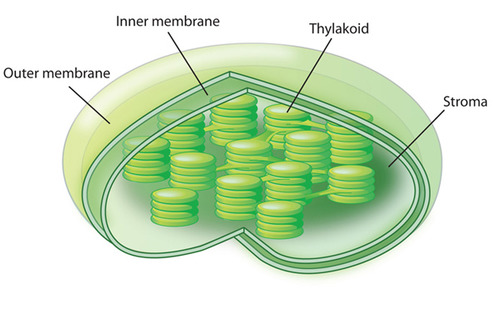
Stroma
Fluid of the chloroplast surrounding the thylakoid membrane; involved in the synthesis of organic molecules from carbon dioxide and water (Calvin Cycle)
18
New cards
Thylakoid membrane
Photosynthetic membrane within a chloroplast that contains light gathering pigment molecules and electron transport chains (PS II and PS I)
19
New cards
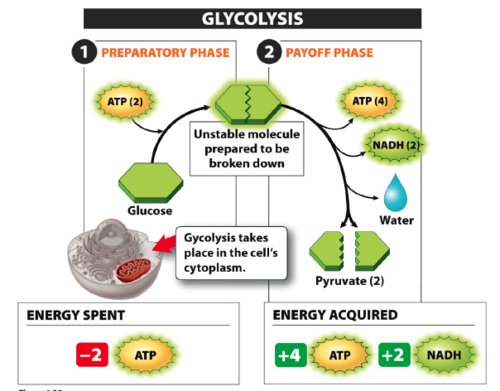
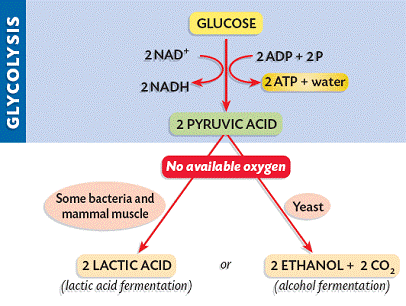
Glycolysis
Breakdown of glucose by enzymes, releasing energy and pyruvates
20
New cards
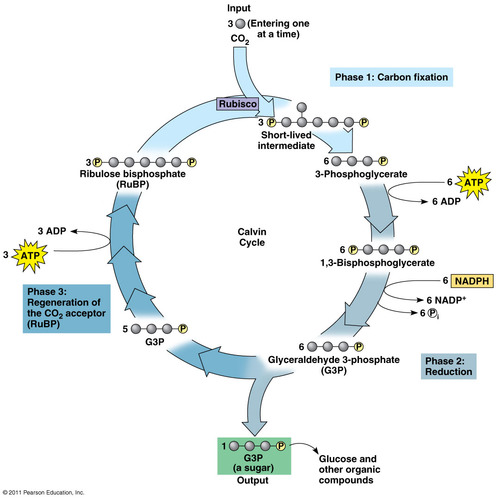
Calvin Cycle
Reactions of photosynthesis in which energy from ATP and NADPH is used to build high-energy compounds such as sugars (occurs in stroma)
21
New cards
Electron Transport Chain
series of electron carrier proteins that shuttle high-energy electrons during ATP-generating reactions
22
New cards
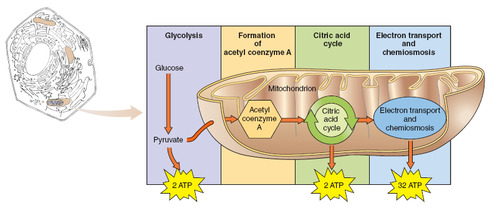
stages of aerobic respiration
glycolysis, krebs cycle, electron transport chain
23
New cards
stages of anaerobic respiration
glycolysis and fermentation
24
New cards
ATP synthase
Large protein that uses energy from H+ ions to bind ADP and a phosphate group together to produce ATP
25
New cards
Pyruvate
Organic compound with a backbone of three carbon atoms; two molecules form as end products of glycolysis
26
New cards
Krebs cycle
Third stage of cellular respiration, pyruvic acid is broken down into carbon dioxide in a series of energy-extracting reactions
27
New cards
PS II
Consists of chlorophyll, oxidized by sun energy
Regains electrons from the splitting of water; Oxygen released
Regains electrons from the splitting of water; Oxygen released
28
New cards
PS I
Consists of chlorophyll, oxidized by sun energy to reduce NADP+ to NADPH; regains electrons from PS II