Lecture 1: Introduction to Immunology
1/48
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
49 Terms
prevent, eradicate
The most important physiologic function of the immune system is to ________ or _________ infections
Immunity
the ability to respond to pathogens and non-infectious substances
-environmental molecules, tumors, and unaltered host components
-clears damaged tissue
Immune System
the molecules, cells, tissues, and organs that collectively function to provide immunity, or protection, against foreign pathogens and cancers
-think of it like a symphony
Immune Response
a collective and coordinated response to the introduction of foreign substances in an individual mediated by the cells and molecules of the immune system
infections, tumors, self, regeneration, injure
The roles of the immune system include:
Defense against _________, which is the biggest and most principle role. This is why we give vaccines.
Defense against ________
Differentiate ____ from foreign, important for organ transplants
Control of tissue _________ and scarring, repairing/clearing damaged tissue
Immune system can ______ cells and induce pathologic inflammation, auto-immune disorders / allergies
Innate Immunity
initial protection, immediate and present in all healthy individuals
-natural/native, phylogenetically older than adaptive
-mediates inflammatory response
-non-specific
-no memory
Adaptive Immunity
develops more slowly, specific and has memory
-can recognize unique antigens on invading pathogens
-subdivided into humoral (extracellular infections) and cell-mediated immunity (intracellular microbes)
First
The innate immune system is the ____ line of defense. Has physical and biochemical barriers
-physical = skin, mucosa
-biochemical = secretions, saliva, GI tract
Second
Inflammation is the ______ line of defense, mediated by cellular influences
Third
Adaptive immunity is the ______ line of defense. It has a specialized response and memory for future infections
recognition, innate, adaptive, antibody, memory
The components of innate and adaptive immunity are:
Innate microbial _______
Induction of the _____ immune response
Activation of the ______ immune response
______ production
Production of _________
Not
The innate immune response does ____ stop when the adaptive immune response is activated
Specificity
one of the characteristics of the adaptive immune system
out of millions of microbes, the immune system can recognize one single one
Clonal Selection Hypothesis
-tons of clones are derived from a common lymphocyte precursor cell
-the body selects one clone based on what it needs and makes tons of copies
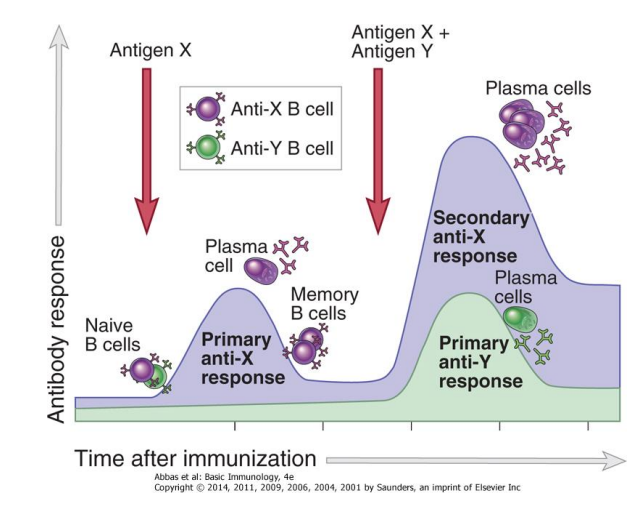
Primary Response
the phase of the immune response where the naive lymphocytes are seeing an antigen for the first time
-leads to the production of plasma cells and memory B cells
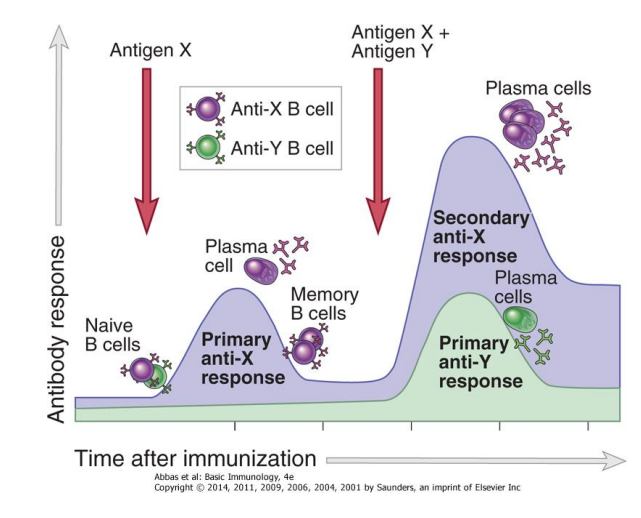
Secondary Response
the phase of the immune response where memory lymphocytes recognize the antigen and is able to mount a larger, more specific attack
Lymphocytes
specific recognition of antigens and generation of adaptive immune responses
-B Lymphocytes = mediators of humoral immunity
-T lymphocytes = mediators of cell-mediated immunity
Antigen Presenting Cells
capture antigens for display to lymphocytes, function in innate immunity and as a bridge to adaptive immunity
-dedritic cells, macrophages, B lymphocytes
Neutrophils (PMN)
most abundant leukocyte in the blood
-phagocytic, acute inflammatory response to bacterial infection
Natural Killer Cells
target infected, stressed, or dying cells
-secrete interferon gamma
Mast Cells
derived from bone marrow, found in skin and mucosa
-involved in complement (innate immunity) and helminth infection or allergies (adaptive immunity)
B Lymphocytes
required for humoral immunity, produces antibodies
key mediators: promote phagocytosis, complement activation
T Lymphocytes
required for cell-mediated immunity
-broken up into CD4+, CD8+, and regulatory T cells
CD4+ T-Cells
recognize peptide fragments, help body produce antibodies, help eat microbes, and help with inflammation
CD8+ T Cells
also known as cytotoxic T cells
-identify and kill cells
Regulatory T Cells
help limit and prevent the activation of the immune response once infection has been cleared, helps prevent auto-immunity development
Humoral Immunity
Microbe: extracellular microbes
Responding Lymphocytes: B lymphocytes
Effector Mechanism: secreted antibody
Functions: block infections and eliminate extracellular microbes
Cell-Mediated Immunity
Microbe: phagocytosed microbes in macrophages or intracellular microbes replicating within infected cell
Responding Lymphocytes: Helper T lymphocytes or Cytotoxic T lymphocyte
Effector mechanism: activated macrophage or killing infected cell
Function: eliminate phagocytosed microbes, kill infected cells and eliminate reservoirs of infection
Cytokines
cell signaling molecules, important for communication
-interleukins, interferons, or tumor necrosis factor
Interleukins
secreted primarily by macrophages and lymphocytes, action varies depending on target cell
-plays a role in inflammation or anti-inflammatory, depending on target cell
Interferons
modulate inflammatory response, activate innate immune cells
-interfere with viral infections
Tumor Necrosis Factor
secreted by macrophages and T-cells
-helps with proliferation, differentiation, apoptosis
Chemokines
family of low molecular weight peptides that function primarily in leukocyte chemotaxis, which is the movement of leukocytes from blood into tissues and maintain cell organization
Bone marrow
What generative lymphoid organ houses B lymphocytes?
Thymus
What generative lymphoid organ houses T lymphocytes?
Peripheral Lymphoid Organ
spleen, lymph nodes, and mucosal/cutaneous lymphoid tissues
-encounter antigens, recognize, receive signals to proliferate/mature/differentiate
Precursor, organ, circulation, organs
T and B Cells mature following this path:
Common lymphoid ________
Move to the generative lymphoid ______. The immature B lymphocytes are in the bone marrow, and the mature naive T lymphocytes are in the thymus.
The cells then move into _______.
Cells can go to the peripheral lymphoid _______, like the spleen and lymph nodes.
They then become mature and can recirculate between the organ and blood.
Memory, naive
At a young age, humans have more naive T cells than _________ T cells. This shifts as you age and encounter antigens, eventually the production of memory T cells compensates for the decline in ____ T cells.
Bone marrow, thymus
Central lymphoid organs
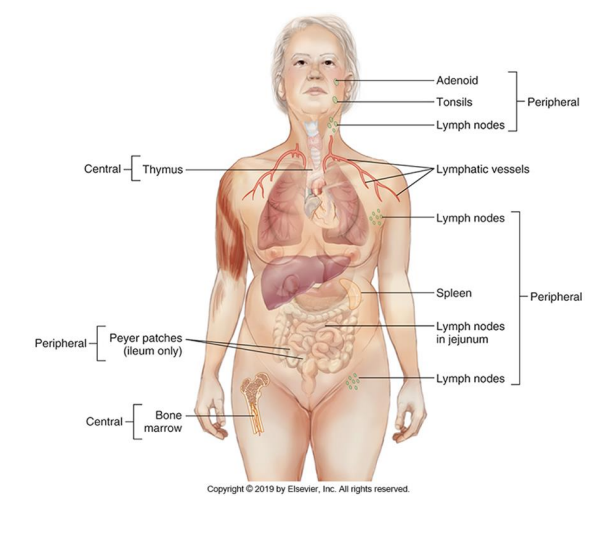
lymph nodes, spleen, cutaneous and mucosal systems
Peripheral lymphoid organs
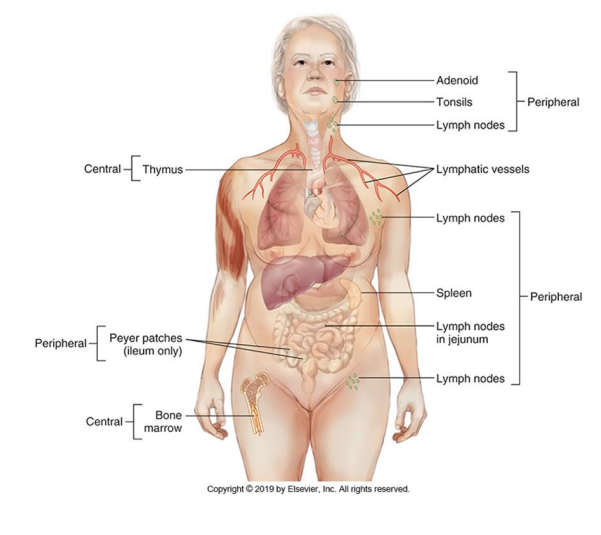
Lymph Nodes
collection of lymph tissues along lymphatic channels throughout the body
-drains lymph
-B-Cells arranged into follicles along the exterior
-T cells localized to central portion
Expert filters
Lymph nodes are _____ _____. This process is really slow, APCs sample fluid for microbes that may have entered the lymph.
Lymph nodes
Which peripheral lymphoid organ has the most lymphocytes?
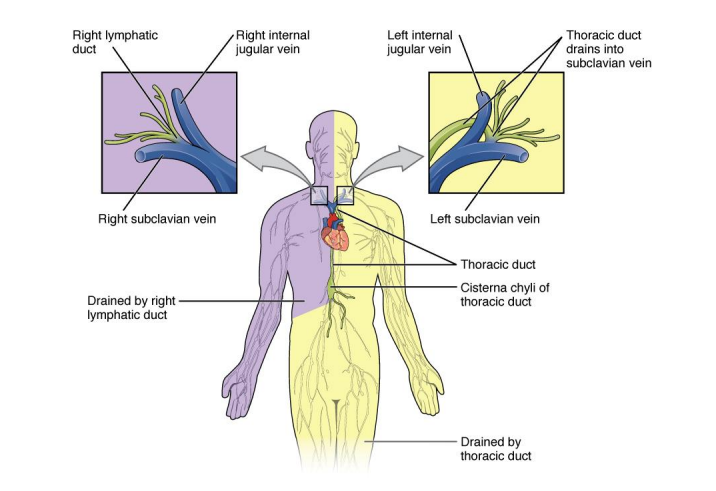
Right Lymphatic Duct
drains the right side of the head, right arm, and right side above the diaphragm
-located below the right subclavian vein
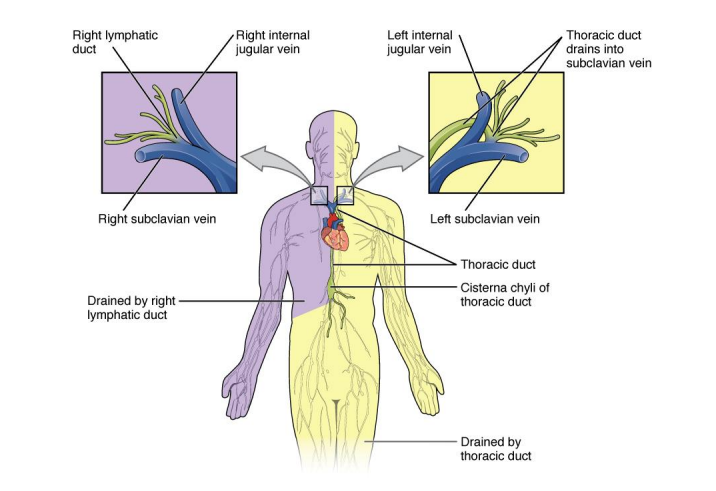
Thoracic Duct
drains the entire left side of the body, also the right side below the diaphragm
-located below the left subclavian vein
Spleen
peripheral lymphoid organ that helps clear old red blood cells, provide immune responses to blood borne pathogens, and are lined with phagocytes
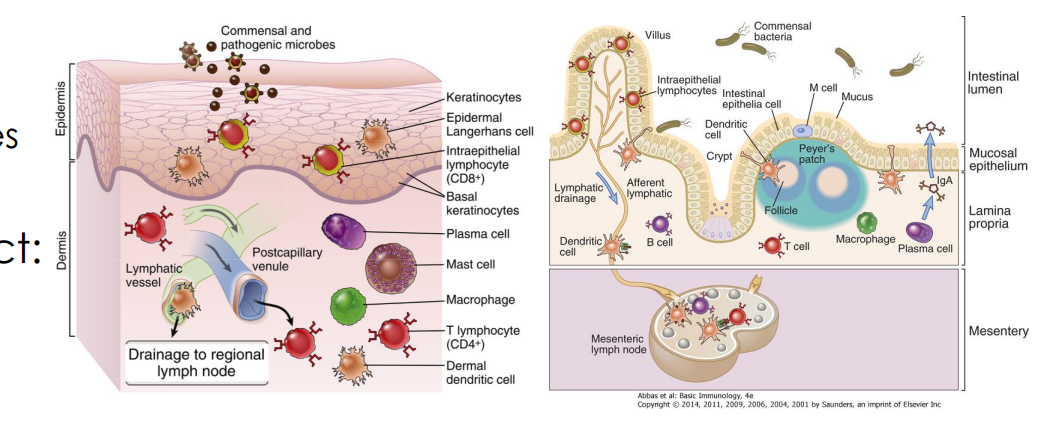
Cutaneous and Mucosal Systems
specialized collections of lymphoid tissues
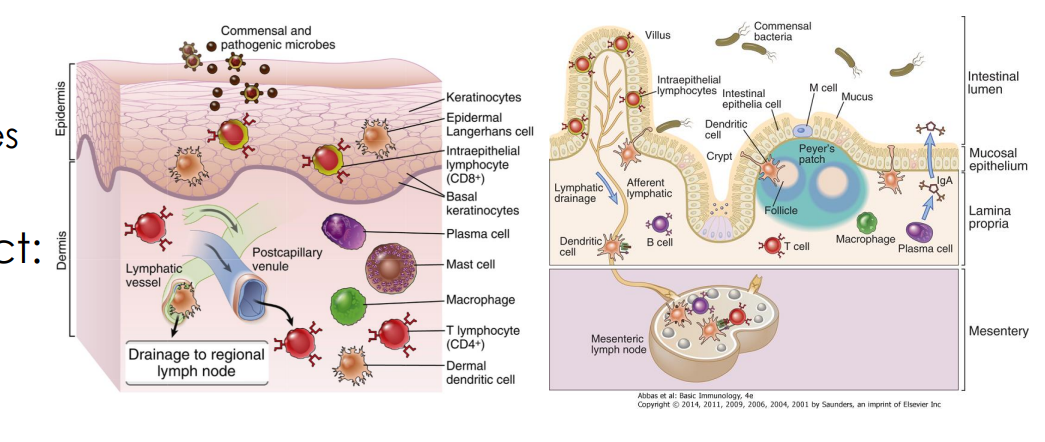
Peyer’s Patches
found in the GI tract
-specialized collection of lymphoid tissue that resembles a lymph node, contains APCs and other cells
Tonsils
found in respiratory tract
-specialized collection of immune cells found in the respiratory tract