Chemistry - C2 Chemical patterns
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/19
Earn XP
Last updated 10:37 AM on 4/4/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
20 Terms
1
New cards
Ancient Greeks
Most people believed that there were four basic elements; fire, water, earth and air but others (Leucippus and Democritus) believed in something smaller than the elements that couldn’t be broken up smaller - The atom
2
New cards
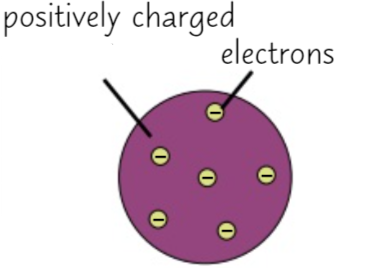
Plum Pudding Model
At the beginning of the 19th century, John Dalton claimed that atoms were solid spheres that made up the elements However in 1904 JJ Thompson concluded that they weren’t solid spheres and in fact, his experiments of charge and mass proved that there were electrons but the main body was positively charged
3
New cards
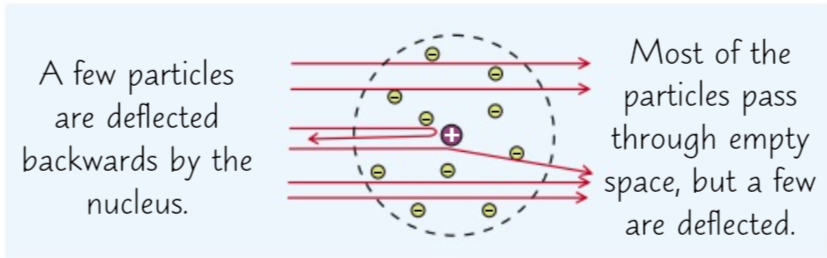
Rutherford Model
In 1911 Rutherford published the results of his alpha scattering experiment. He fired positively charged alpha particles at a thin sheet of gold and most went straight through (as expected from the plum pudding model) but more than expected deflected backwards so from this he created the nuclear model.
4
New cards
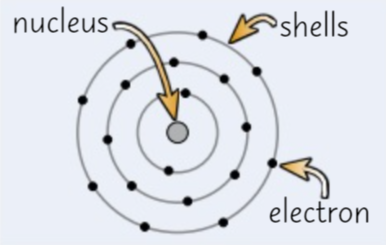
Bohr Model
Scientists realised that the ‘cloud’ of electrons around the nucleus would attract and cause the atom to collapse. Bohr suggested that the electrons orbit around the nucleus in fixed shells at a fixed distance form the nucleus.
5
New cards
Proton
A subatomic particle with a relative mass of 1 and a positive (+1) charge
6
New cards
Neutron
A subatomic particle with a relative mass of 1 and a neutral (0) charge
7
New cards
Electron
A subatomic particle with a relative mass of 0.0005 and a negative (-1) charge
8
New cards
Atomic number
The number of protons in an atom
9
New cards
Mass number
The total number of protons and neutrons
10
New cards
Isotope
Two atoms that are the same except for their number of neutrons
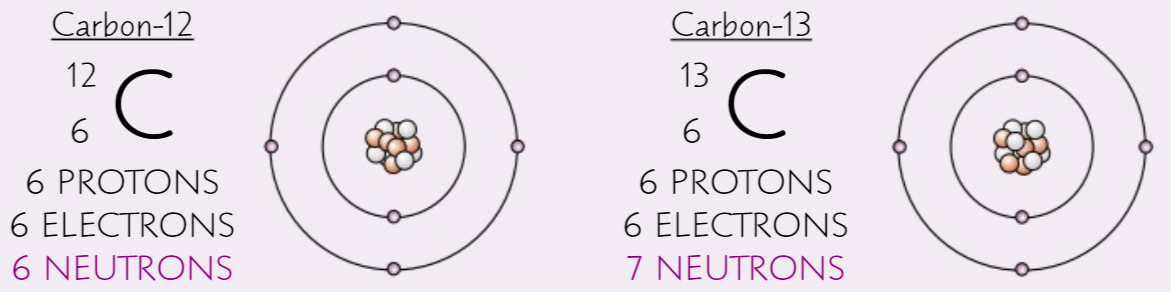
11
New cards
Ion
These form when an atom loses or gains electrons. Negative ---- are when an atom gains electrons because they have more electrons than protons. Positive ---- are when the opposite occurs, they lose electrons causing there to be more protons than electrons.
12
New cards
Mendeleev
He created the first periodic table of elements in 1869 by keeping elements with similar properties in vertical groups. He left gaps in his table for undiscovered elements. He was able to predict the properties of these undiscovered elements. These ideas were proven as the modern periodic table slowly developed.
13
New cards
Metals
These generally have a shiny appearance; they can easily conduct heat and electricity; they usually have high densities; They have high melting and boiling points so are generally solid at room temperature; reactivity increases down the periodic table and they form compounds with ionic or metallic bonds.
14
New cards
Non-metals
These are usually dull; they are poor conductors of heat and electricity; They often have a low density; They are more likely to be gases or liquids at room temperature so have a lower melting and boiling point; reactivity decreases down the periodic tale and they form compounds with ionic or covalent bonds.
15
New cards
Alkali metals
Also known as group 1 elements, this group of elements are all soft, reactive metals including lithium, sodium, potassium and rubidium. As you go down the group, boiling points decrease but reactivity increases. They are shiny when freshly cut but they quickly react with oxygen in moist air and tarnish quickly. Lithium, sodium and potassium are stored in oil to prevent reaction with the air but rubidium and caesium are much more reactive so are stored in sealed glass tubes under special conditions. When they react with cold water they produce a hydroxide and hydrogen gas and when reacted with chlorine they produce a chloride salt.
16
New cards
Halogens
Also known as the group 7 elements include fluorine, chlorine, bromine, iodine and astatine with similar chemical properties. Melting and boiling points increase as you go down the group meaning at room temperature they are at different states (shown in the image) but reactivity decreases going down. They react with alkali metals (group 1 elements) to form salts like sodium chloride or potassium bromide. A more reactive group 7 element (one higher up the group) will displace a lesser reactive one.

17
New cards
Noble Gases
Also known as group 0 or group 8 elements, these elements are all inert, colourless gases including helium, neon, argon, krypton and xenon. They are all non-flammable and the melting and boiling points increase as you go down the table.
18
New cards
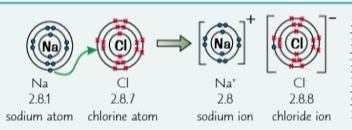
Ionic bonding
this is when a metal and non-metal react together and the metal loses electrons, becoming a cation, and the non-meta gains them, becoming an anion. These compounds always have giant ionic lattice structures meaning that they have very strong electrostatic forces of attraction in all directions. They also have high melting and boiling points, they don’t conduct electricity and many easily dissolve in water.
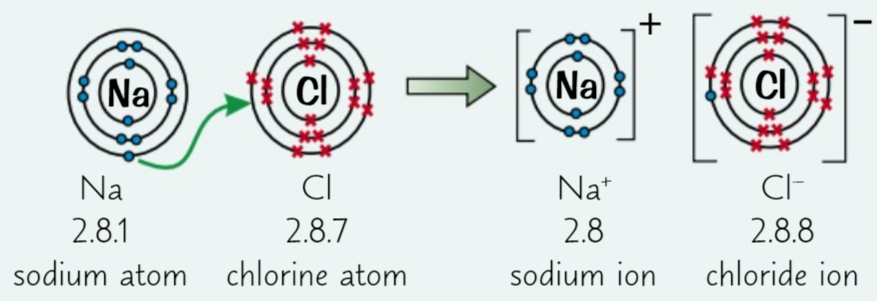
19
New cards
The reactivity series
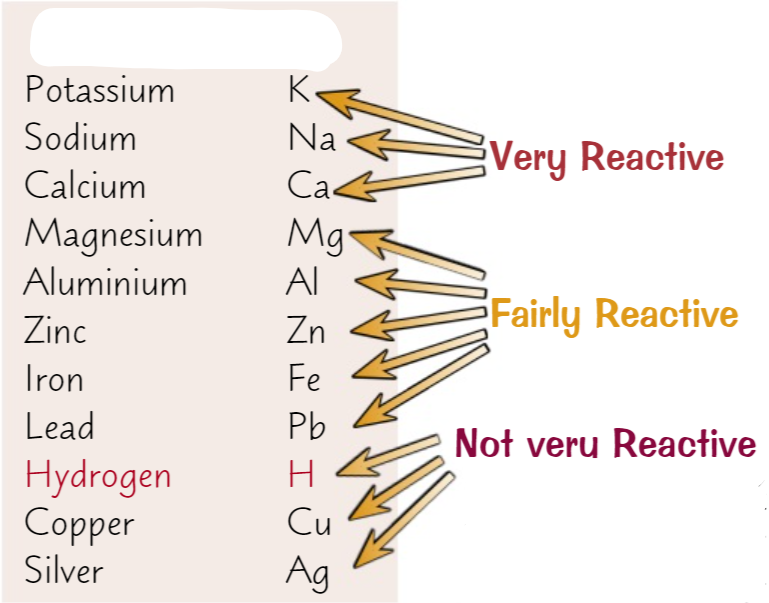
20
New cards
dot cross diagram