Unit 1 - Intro to Economics
1/64
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
65 Terms
Scarcity
Supplies are not unlimited, so we must make choices on how we use them.
Choice
The way you choose to allocate your supply.
Economics
A social science that studies how individuals, institutions, and society make the best choices under scarcity.→ How society deals with scarcity
Economic Problem
We have unlimited wants but limited resources to satisfy them.
Microeconomics
The study of individual units such as people, firms, and industries.
Individual, measurable factors in specific industries (S&D, Production Cost, Labour Markets)
Macroeconomics
The study of the economy as a whole.
Economic growth, government spending, Inflation, unemployment, trade, etc
Positive Statements
Statements that are factual and objective.
BC has a higher unemployment than Alberta
Normative Statements
Statements focused on value judgements.
BC SHOULD increase revenue by increasing tax
Key Economic Principals (5)
Society has unlimited wants and limited resources
Due to scarcity, choices must be made - Every choice has a cost (trade-off)
Everyone’s goal is to make choices that maximizes satisfaction → Act in Self-Interest
Everyone makes decisions by comparing marginal costs and benefits of every choice
If the benefit exceeds cost people are more likely to do it
Real-life situations can be explained and analyzed through models and graphs
Self-Interest
Everyone's goal is to make choices that maximize their satisfaction.
Ceteris Paribus (Give Example)
Ceteris Paribus: Focusing on only 2 factors but ignoring other interests
Latin for “other things being equal” or “other things remaining the same
There are so many variables and its too complicated so they change one variable at a time
If you change too many variables there can be a lot of errors
EXAMPLE: Study ONLY the price and quantity purchased, while ignoring other factors like income, or like other global factors
Opportunity Cost & Give an Example
The value you could have gained by choosing the next-best alternative.
It can be money, time, product, etc
Eg. How many cars do I give up if I choose to manufacture planes?
Explicit Cost
Traditional, direct costs associated with making a decision, typically "out of pocket" money.
Implicit Cost
The opportunity costs of making a decision, or the things you give up.
Eg. Time lost if I go to movies instead of studying
Cost-Benefit Analysis
A method of economic thinking where decisions are made by comparing total benefits and total costs (both explicit and implicit).
Economic decisions are made by comparing total benefits and total costs (Explicit and Implicit)
Marginal Analysis (Marg. Benefit and Cost) - Provide an Example
Comparing the additional benefit of an activity with its additional cost.
Should I spend another hour studying? What do I give up?
Marg. Benefit: Improved grades/ learning
Marg. Cost:Lost time on other activities
Optimal Quantity
The ideal amount of an activity or product that maximizes benefit and minimizes cost.
Resource
Anything used to produce something else, primarily goods or services
FACTOR OF PRODUCTION
Land
All natural resources used in the production process.
Labour
The physical and mental talent/effort of workers used in production.
Capital
Manufactured goods used to make other goods and services, such as tools and machinery. Capital does NOT refer to money.
Entrepreneurial Ability
The special human resource of organizing resources, taking risks, and innovating to create new products and processes.
3 Economic Questions
What goods and services should be produced?
How should they be produced?
For whom should they be produced?
Utility
Satisfaction or usefulness.
Marginal
Additional.
Allocate
The distribution of resources.
Price
The amount a buyer or consumer pays.
Cost
The amount a seller pays to produce goods.
Investments
Money spent by businesses to improve production.
Consumer Goods
Goods created for direct consumption.
Capital Goods
Goods created for indirect consumption, used to make consumer goods.
Net Benefits
(Total Benefit- Total Cost) are maximized at the optimal choice
What are the different categories if resources?
Land
Labour
Capital
Entrepreneurial Ability
A measure of efficiency that shows the number of outputs per unit of input.
Higher productivity = Make more with less
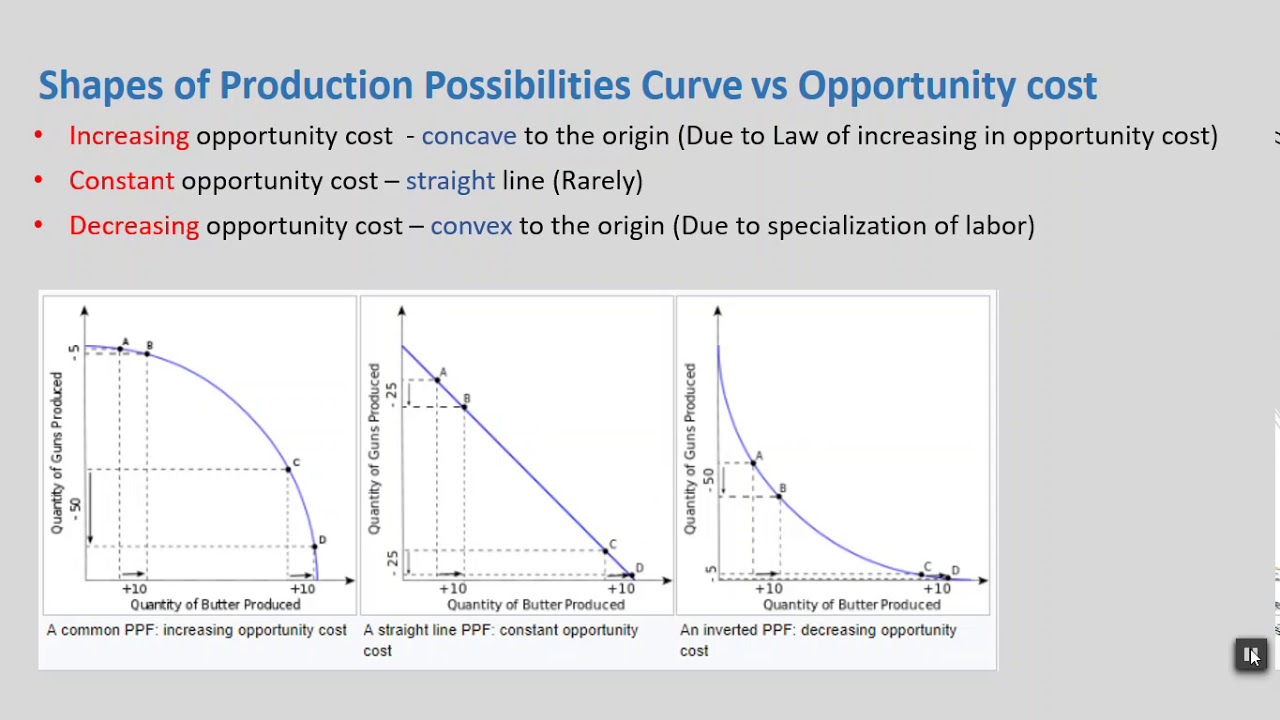
As you produce more of a good, the opportunity cost of producing an additional unit gets bigger.
Resources are not easily adaptable to produce both goods. (Cherry Example)
The optimal point on the PPC where the products being produced are the most desirable for society.
Country with no electricity example
An increase in resource quality, quantity, or technology causes the PPC to grow bigger, representing economic growth and high productive potential.
A decrease in resource quality, quantity, or technology causes the PPC to shrink. (eg. a Drought)
What is the main concept of the PPC?
MAIN CONCEPT: Producing more of one good means producing less of the other
You can not always produce all of everything → Scarcity
You must allocate resources efficiently to reach maximum means of production
What are the 4 main assumptions in the PPC?
Only 2 goods can be produced
Full employment of available resources (full utilization of resources)
Fixed Resources and Technology
What are the 3 different types of PPC Opportunity Costs?
See Photo
What is Economics Used For?
Produce models to make generalizations and abstraction to develop theories
The theories are applied to solve problems and meet economic goals
What are 4 types of Resources?
Land
Labor
Capital
Entrepreneurial Ability
Constant Opportunity Cost
Opportunity cost stays the same, results in a straight line PPC
Resources are easily adaptable to produce both products (eg. Bread, Muffins)
What Causes the PPC to shift?
PPC is shifted by a change in quality, quantity of resources and technology
NOT SHIFTED BY DEMMAND
The ability to produce more of a given product with a specific amount of resources.
MOST OUTPUT FOR LEAST INPUT
The agreed-upon conditions that would benefit both trading countries, which must fall between the two countries' opportunity costs.
BOTH COUNTRIES BENEFIT
Why do countries trade?
Countries trade so they can specialize in what they produce most efficiently then trade with other people and get goods for a lower opportunity cost
TV | Salsa | |
Canda | 4 (1TV = ⅓ S) | 12 (1S = 3TV) |
Japan | 1 (1TV = ⅕ S) | 5 (1S = 5TV) |
For the given INPUT question, who has the comparative advantage? Identify Terms of Trade
Canada has advantage in salsa
Japan has the comparative advantage in TVs
1 Salsa for 4 TV
OUTPUT: Who has comparative advantage? Identify terms of trade
Wheat | Sugar | |
USA | 40 (1W = ½ S) | 20 (1S = 2W) |
Brazil | 10 (1W = 2S) | 20 (1S = ½ W) |
USA had advantage in Wheat
Brazil has advantage in Sugar
1 Wheat for between 0.5 and 2 sugar
Law of Diminishing Marginal Utility
As you consume something, the additional utility/ satisfaction you receive will decrease
The more you eat, the less you feel satisfied the more you eat it
Helps understand why demand curve slopes downward
Marginal Utility
Change in utility generated by consuming one-additional unit of a good or service
Like how much ADDITIONAL satisfaction you gain from eating one more
Utility Maximizing Rule
As you move down, buy the product with the highest marginal utility per dollar
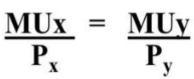
Total Utility
SUM of all utility gained after calculating maximized utility
What are some guidelines for utility maximization?
Know how much money you have and keep track
Pick the choice with Highest MU/P until you use up all money - ONE AT A TIME
If the MU/P is the same → Choose either one → Both lead to optimal combination
Determine total utils from combination of two choices → ONLY DETERMINE TOTAL UTILS AT THE END