Lab 4 final
1/531
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
532 Terms
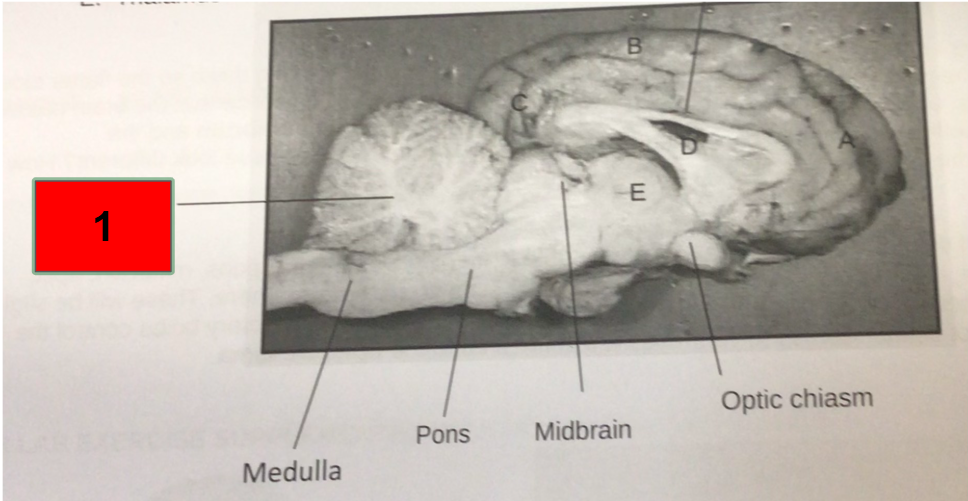
What is this?
Cerebellum
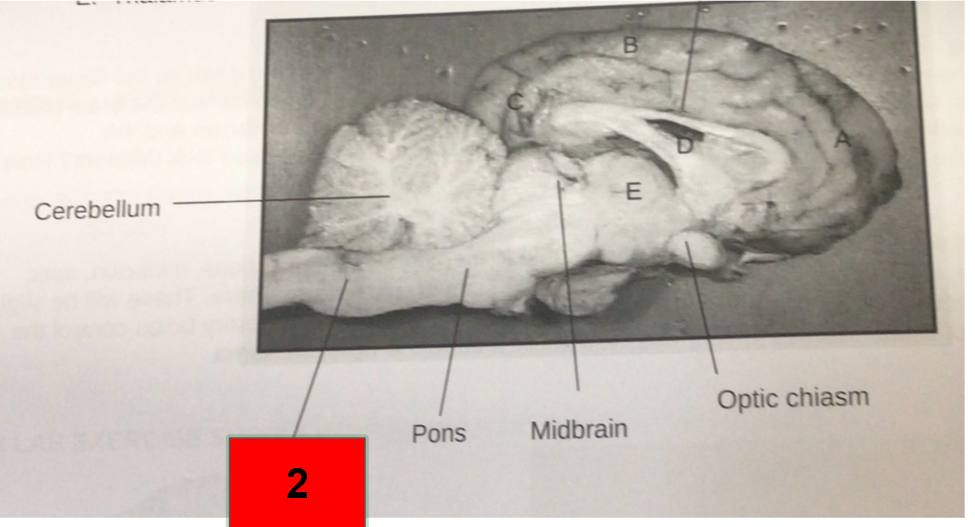
What is this?
Medulla

What is this?
Pons

What is this?
Midbrain
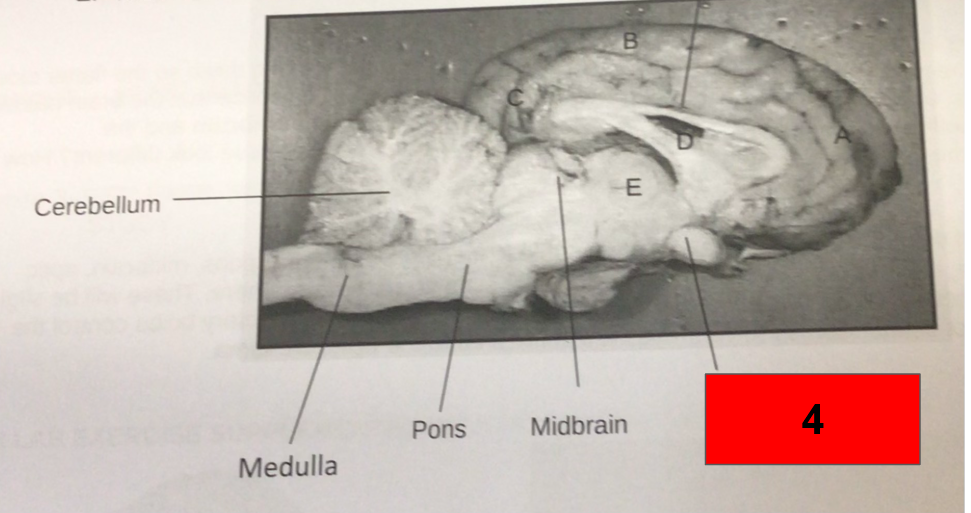
What is this?
Optic Chiasm
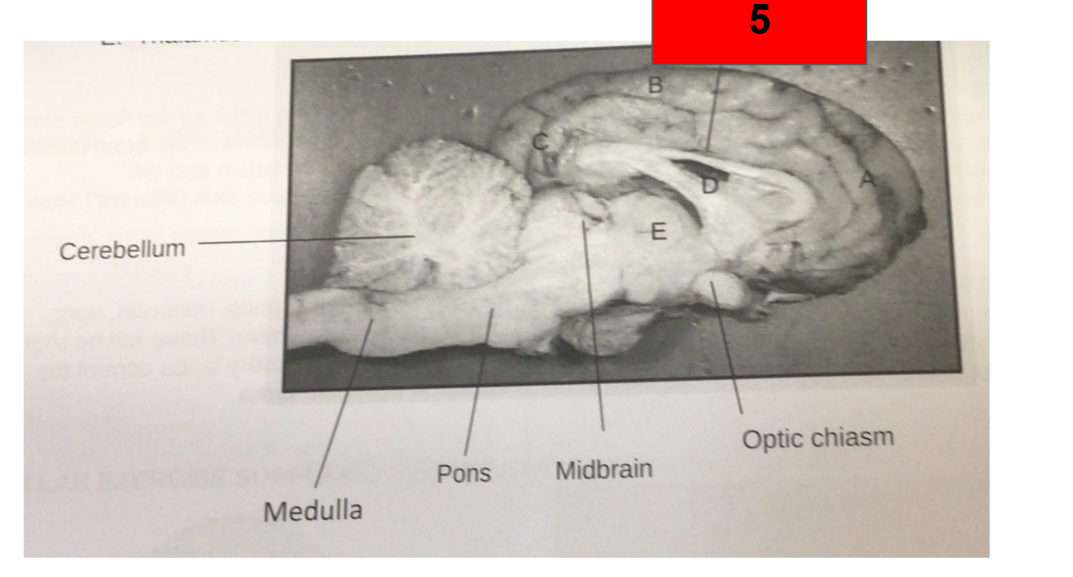
What is this?
Corpus callosum
What is the corpus callosum?
A bundle of white fibers that connects the 2 hemispheres of the brain, Providing coordination between the 2
What does the medulla oblongata control?
Vital functions like heartbeat and respiration.
What is the function of the pons?
Relay messages between the cerebrum and the cerebellum
What gland produces the important hormones?
Pituitary gland
What is gray matter?
Collection of nerve cell bodies
What is white mater made up of?
nerve axons
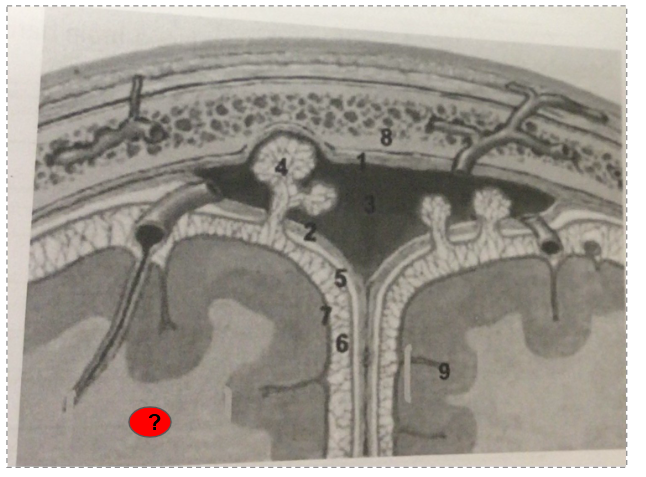
What is this?
Pia mater

What is this?
Skull bones
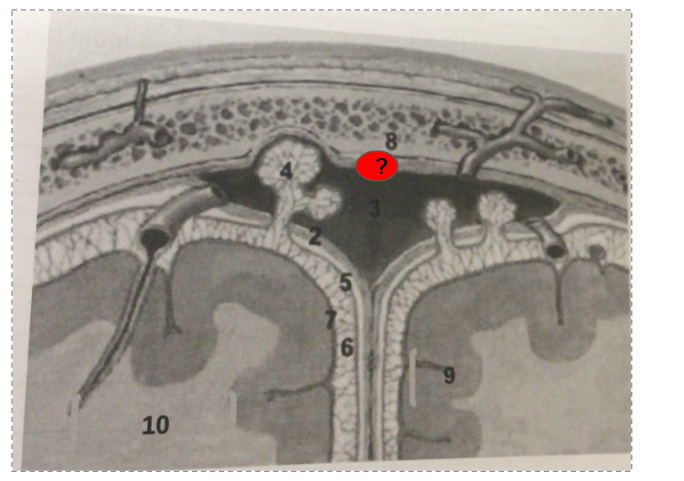
What is this?
Superior sagittal sinus
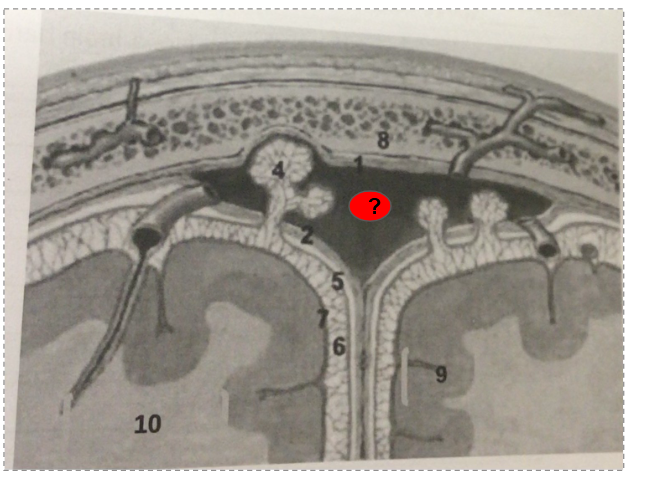
What is this?
Gray matter of cerebral cortex
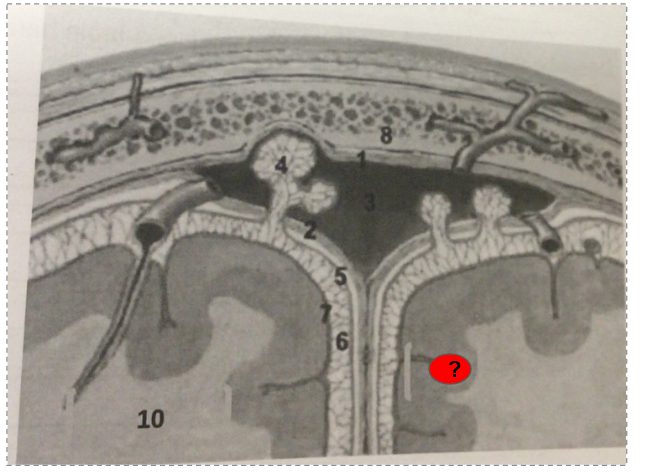
What is this?
White mater of cerebrum
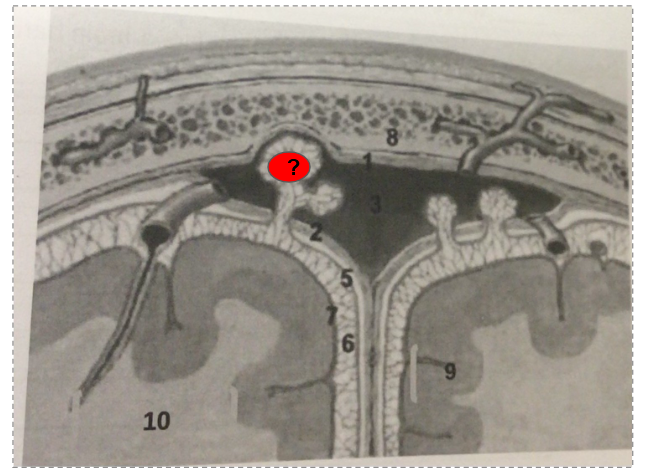
What is this?
arachnoid vili
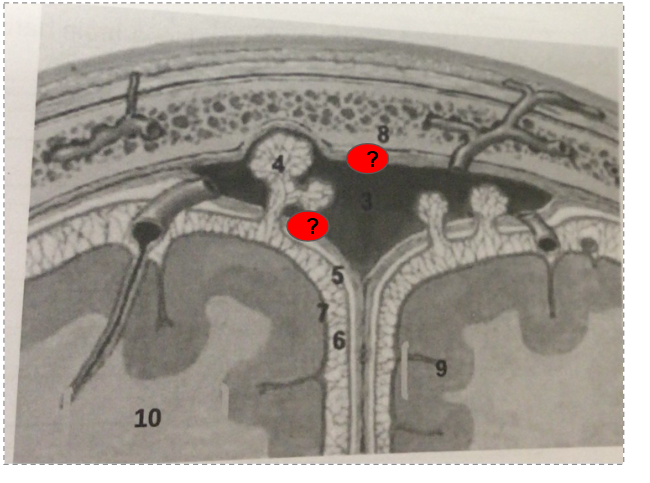
What is this?
Dura mater
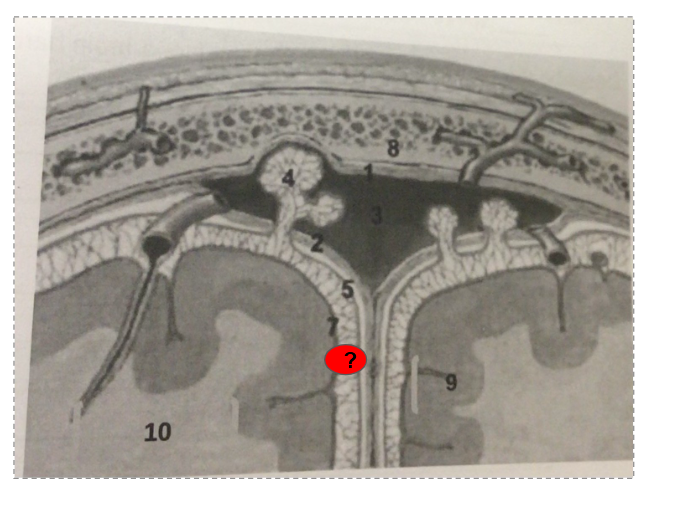
What is this?
Subarachnoid space
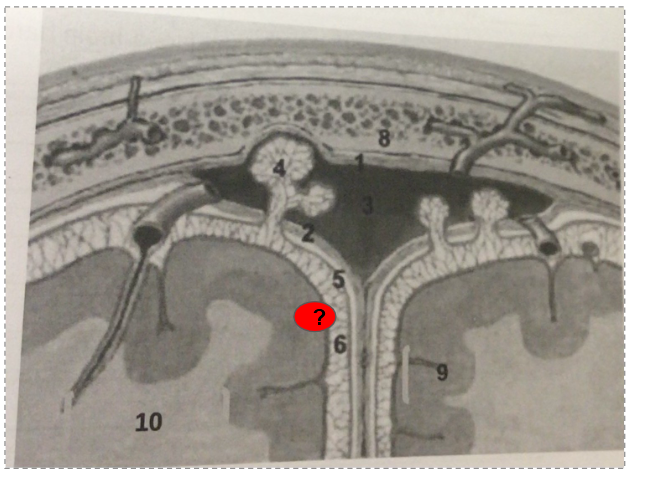
What is this?
Pia mater
What structure is responsible for returning CSF back to the blood?
Arachnoid villi
In which space is CSF found?
Subarachnoid space
What is the condition where there is elevated levels of CSF in the brain?
Hydrocephalus
What are the 3 functions of CSF
How does the needle flow during a spinal tap procedure?
Epidermis
Dermis
Hypodermis
epidural space
dura mater
subdural space
arachnoid mater
subarachnoid space
Describe the structure of the blood brain barrier?
The blood brain barrier is composed of a capillary basement membrane and three cellular elements: endothelial cells, pericytes, and astrocyte end-feet
What is the function of the blood brain barrier?
The blood–brain barrier permits passage of essential substances while excluding unwanted materials
The blood–brain barrier prevents many drugs from entering the brain
What is the normal color of CSF?
Clear/Colorless
What is the normal pressure of CSF in the lumbar area?
70-180
What are the normal amount of cells in the CSF in the lumbar area, and what type of cells?
0-5 lymphocytes
What is the normal amount of protein for CSF in the lumbar area?
< 50 mg/dl
What is the normal glucose amount in CSF for the lumbar region?
50-75 mg/dl
What is the normal amount of protein for CSF in the ventricular area?
5-15mg/dl
What are the normal amount of cells in the CSF in the Ventricular area, and what type of cells?
0-5 lymphocytes
What is the normal pressure of CSF in the Ventricular area?
70-190
What is the function for the occipital lobe?
Visual sensory images
What is the function of the temporal lobe?
Hearing
What is the function of the Frontal lobe?
Motor function
What is the function of the Parietal lobe?
Sensory( not associated with special senses)
What is the function of the Thalamus?
Relay station
What is are the functions of the medulla ?
The medulla has several critical functions including:
Cardiovascular center:
Regulates the force and rate of the heartbeat.
Controls the diameter of blood vessels.
Respiratory center:
The medullary rhythmicity area sets the basic rhythm of breathing.
Information transmission:
Facilitates communication in and out of the cerebellum.
Reflex centers:
Coordinates reflex actions of the autonomic nervous system, such as coughing, sneezing, and swallowing.
What are the functions of the pons?
Controls breathing:
The pneumotaxic and apneustic areas play key roles in regulating the breathing cycle.
Carries sensory information:
The middle cerebellar peduncles transport sensory information to the cerebellum for processing.
Connects cranial nerves:
Associated with cranial nerves V through VII, which are involved in various sensory and motor functions
What are the functions of the midbrain?
What are the functions of the thalamus?
Relay station for sensory information on way to cortex
Crude perception of some sensations
What are the functions of the Hypothalamus?
The hypothalamus regulates autonomic nervous system activities, synthesizes hormones for the anterior pituitary, secretes hormones through the posterior pituitary, manages emotions (rage, aggression, pain, pleasure, arousal), controls feeding, thirst, and satiety, regulates body temperature, and oversees daily sleep patterns.
What are the functions of the cerebellum?
The cerebellum coordinates movements of limbs, trunk, head, larynx, and eyes; processes feedback from muscles, tendons, and joints for smooth movements; compares intended and actual movements, sending corrective signals; and maintains equilibrium and coordination.
The _____ is the part of the brain that helps maintain posture and balance. It also coordinates actual with intended movements.
Cerebellum
The ___ plays a major role in maintaining homeostasis by controlling the autonomic nervous system, secreting hormones that control the pituitary gland and regulating behaviors such a feeding ,thirst and sexual arousal.
Hypothalamus
The___ is a raised area or convoluting on the surface of the cerebrum
Gyrus
The ___ is a collection of structures that are collectively called the emotional brain
Limbic system
___area is the primary motor area associated with speech and is found predominantly in the left cerebral hemisphere.
Frontal lobe
The disorder of ___ is associated with parkinson’s disease
Midbrain Substantia Nigra
Impaired blood flow to the brain causing temporary impairment of function is called a ____
Transient Ischemic Attack (TMI)
The ____ regulates vital functions such as heart and respiration rate was well as nonvital functions functions such as hiccupping and sneezing
Medulla
What is a type of conventional radiograph?
x-rays
In x-rays what absorbs most of the radiation?
Bone
What type of radiation are x-rays?
Ionizing radiation
What spectrum is ionizing radiation apart of?
Electromagnetic spectrum
How will bones appear on x-rays and why?
Bones will appear more white in color because of high calcium levels in bones.
What can x-rays detect?
Detects bone fractures, certain tumors and other abnormal masses, pneumonia, and some type of injuries, classification, foreign objects, dental problems, etc
What is a CT (computed tomography)?
The combination of traditional x-ray technology with no computer processing to generate a series of cross-sectional images of the body that can later be combined to form a three-dimensional x-ray image
Why might someone use a CT scan rather than plain radiographs?
CT images are more detailed than plain radiographs
What is an MRI (Magneti Resonance Imaging) based on?
Physical principle that certain atomic nuclei when places in a strong magnetic field resonate and emit a radiofrquency signal
When may you use a MRI?
When examining bones, joints, and soft tissues for injuries or the presence of structural abnormalities or certain other conditions such as tumors, inflammatory disease, congenital abnormalities
What is an fMRI (functional magnetic resonance imaging)?
A noninvasive test that uses a strong magnetic field and radio waves to create detailed images of the body?
What makes an fMri diffrent from a MRI?
Instead of an fMRI, which creates images of organs and tissues like an MRI, fMRI looks at blood flow in the brain to detect the areas of activity.
What is a PET (Positron emission tomography) scan?
A scan that combines the principle of CT scan with radioactive tracer imaging to study the structure and function of an organ.
How may the tracer be inserted for a PET scan?
It can be injected, swallowed, or inhaled depending on which organ or tissue is being studied by the PET scan
What is the most commonly used radiotracer in a clinical PET scan?
Glucose-PET
In a PET scan, neuron activity is directly related to ____ use
Glucose
Why would a PET scan be used for locating a tumor?
A PET scan would be best for this because cancer cells take up or absorb sugar more avidly than other tissues in the body
What is a SPECT (single photon emission computed tomography)?
A test similar to a PET scan, it uses radioactive tracers and a scanner to record data that a computer constructs into 2 or 3-dimensional images.
How is the procedure for a SPECT done?
A small amount of a radioactive drug is injected into a vein, and a scanner is used to make detailed images of areas inside the body where the radioactive material is taken up by cells.
What can a SPECT test give you information about?
Blood flow to tissues and chemical reactions in your bloodstream.
What imaging test is best for examining longer-lasting brain functions?
SPECT
What is a Cerebral Angiogram?
An invasive diagnostic test that uses x-rays to take pictures of your blood vessels.
What is another name for Cerebral Angiogram?
Arteriogram
How is a cerebral Angiogram performed?
A long, flexible catheter is inserted through the bloodstream to deliver dye into the arteries, making them visible on the X-ray.
What can a cerebral angiogram help diagnose?
Stroke, aneurysm, arteriovenous malformation, tumor clots, and arterial stenosis.
What is fluoroscopy?
A study of moving body structures.
What imaging technique uses X-rays passed through the body part to be examined to obtain real-time moving images of the internal structures of a patient through the use of a fluoroscope
Fluoroscopy
When is a fluoroscopy study mainly used?
When viewing the upper GI tract and lower GI tract.
What is a nerve?
A group of neurons
Cranial nerves emerge from ____
Brain
Spinal nerves emerge from___
Spinal cord
Sensory nerves are made from ___ neurons
sensory
What is an example of a sensory nerve?
Optic nerve
What are motor nerves made of?
Motor neurons
What is an example of a motor nerve?
Oculomotor nerve
Mixed nerve is composed of ___& ___
Sensory and motor neurons
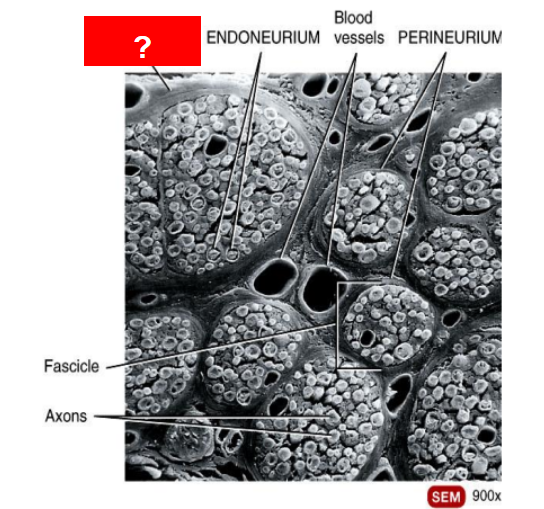
What is this?
Epineurium
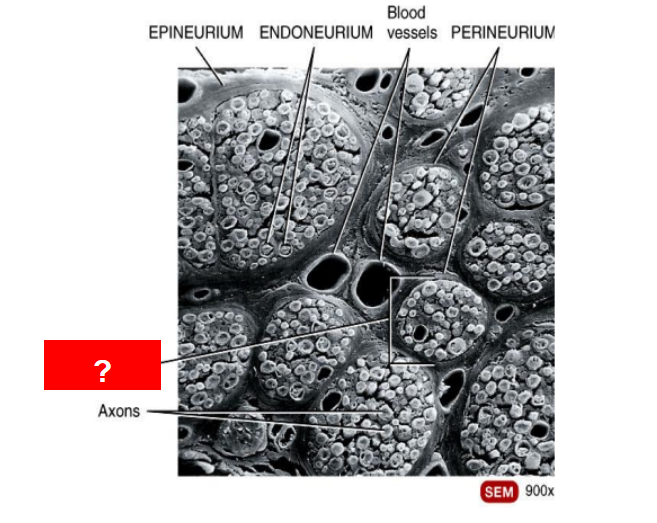
What is this?
Fascicle
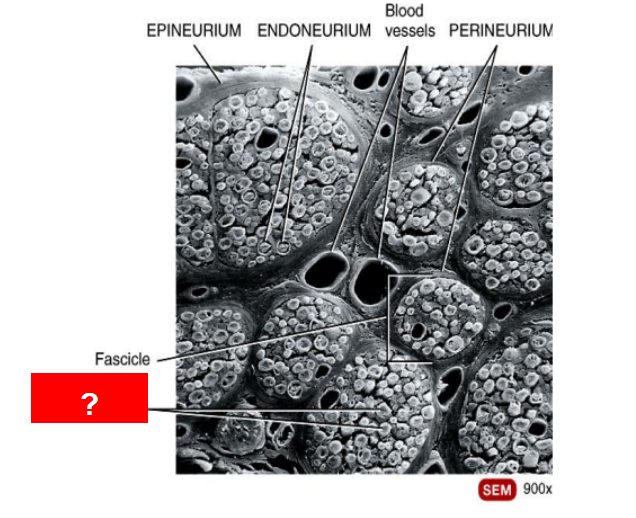
What is this?
Axons
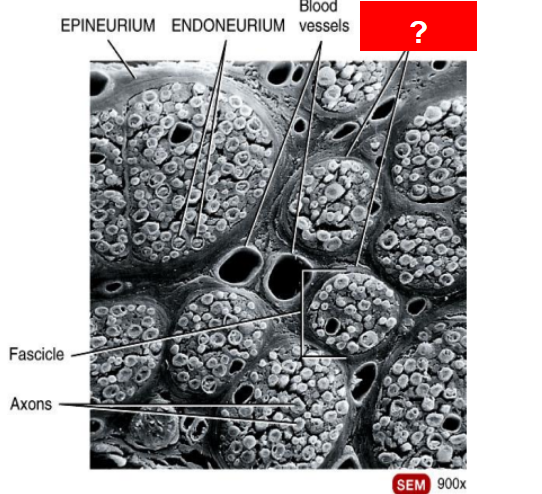
What is this?
Perineurium
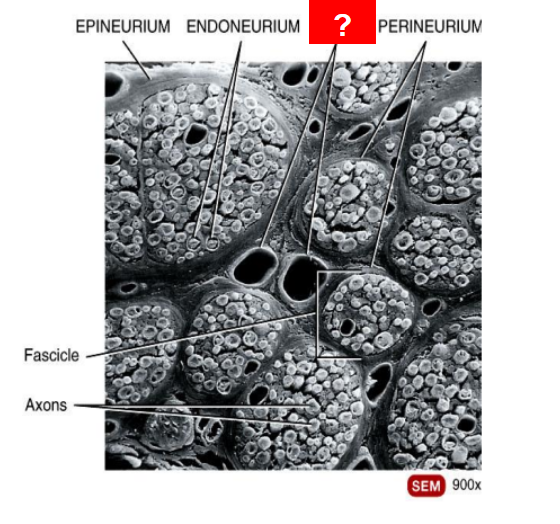
What is this?
Blood vessels
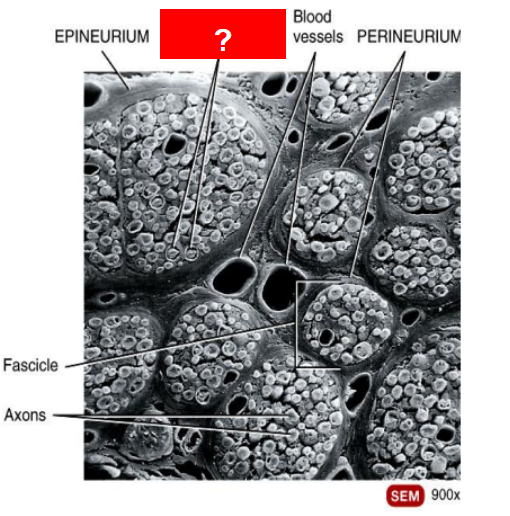
What is this?
Endoneurium
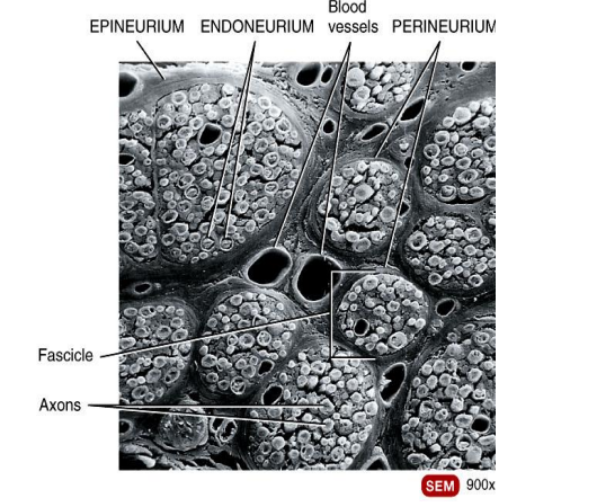
What is this structure?
Spinal nerve structure
What are the functional regions of the neuron?
▪ Dendrites
▪ Cell body (soma)
▪ Axon hillock
▪ Axon
▪ Axon terminals
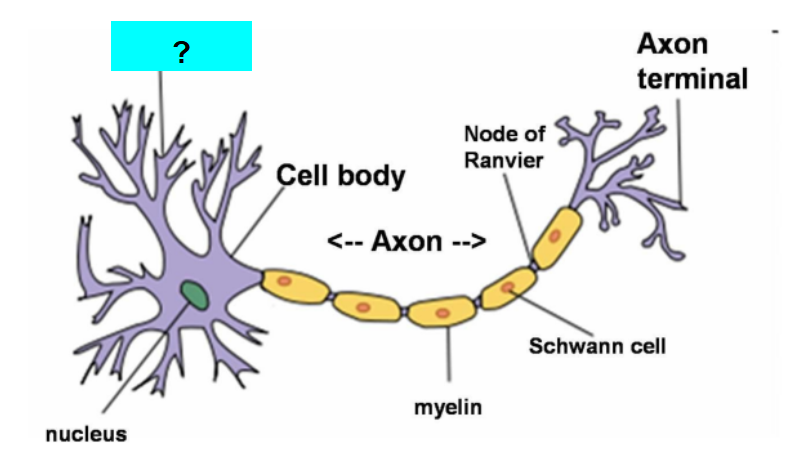
What is this?
Dendrite