Windows Active Directory
1/8
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
9 Terms
Windows domain
a grouping of users and computers under the administration of a given business.
Active Directory
a directory service developed for Windows domain networks. It stores information about network objects such as computers, users, and groups. It provides authentication and authorization services, and allows administrators to manage network resources centrally.
Domain Controller
a server that manages security authentication requests in a Windows Server network. It stores user account information and controls access to resources.
Security Principals
Users
Users are one of the most common object types in Active Directory.
Users can be used to represent two types of entities:
People: users will generally represent persons in your organization that need to access the network, like employees.
Services: you can also define users to be used by services like IIS or MSSQL.
Machines
Machines are another type of object within Active Directory; for every computer that joins the Active Directory domain, a machine object will be created. Machines are also considered "security principals" and are assigned an account just as any regular user.
Security Groups
Used to assign access rights to files or other resources to entire groups instead of single users.
Default Security Groups
Security Group | Description |
Domain Admins | Users of this group have administrative privileges over the entire domain. By default, they can administer any computer on the domain, including the DCs. |
Server Operators | Users in this group can administer Domain Controllers. They cannot change any administrative group memberships. |
Backup Operators | Users in this group are allowed to access any file, ignoring their permissions. They are used to perform backups of data on computers. |
Account Operators | Users in this group can create or modify other accounts in the domain. |
Domain Users | Includes all existing user accounts in the domain. |
Domain Computers | Includes all existing computers in the domain. |
Domain Controllers | Includes all existing DCs on the domain. |
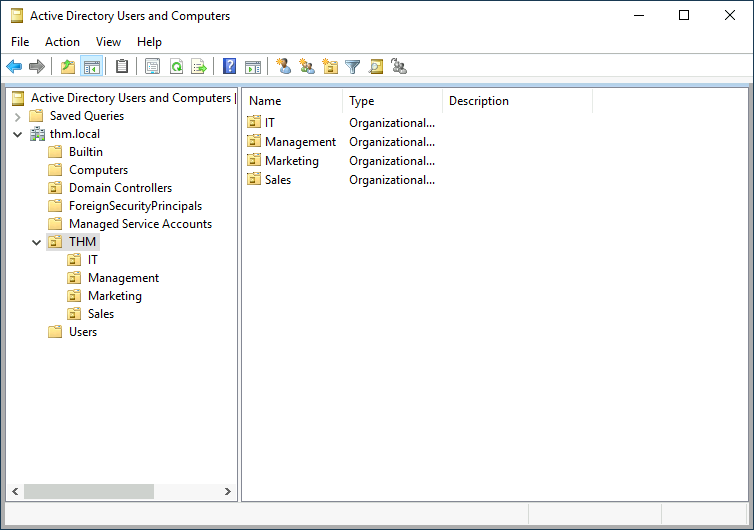
Organizational Units (OUs)
Container objects that allow you to classify users and machines. OUs are mainly used to define sets of users with similar policing requirements.
It is very typical to see the OUs mimic the business' structure. ie IT, Management, Sales, etc.
Group Policy Objects (GPO)
a collection of settings that can be applied to OUs. GPOs can contain policies aimed at either users or computers, allowing you to set a baseline on specific machines and identities.
To configure GPOs, you can use the Group Policy Management
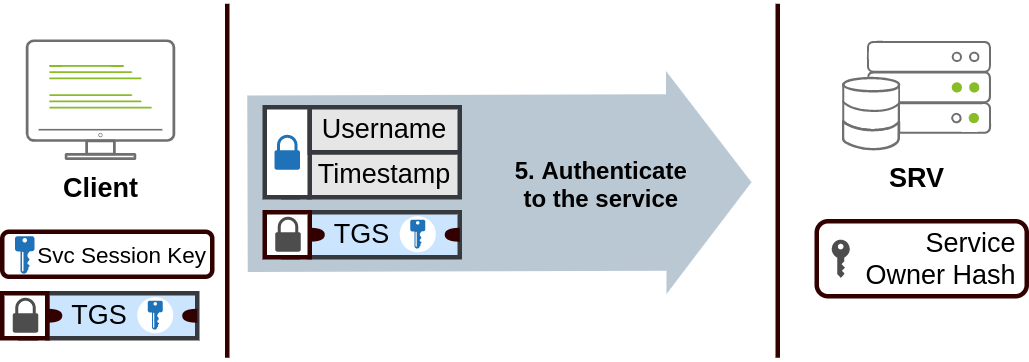
Kerberos Authentication
This authentication is the default authentication protocol. Users who log into a service using Kerberos will be assigned tickets. Think of tickets as proof of a previous authentication. Users with tickets can present them to a service to demonstrate they have already authenticated into the network before and are therefore enabled to use it.
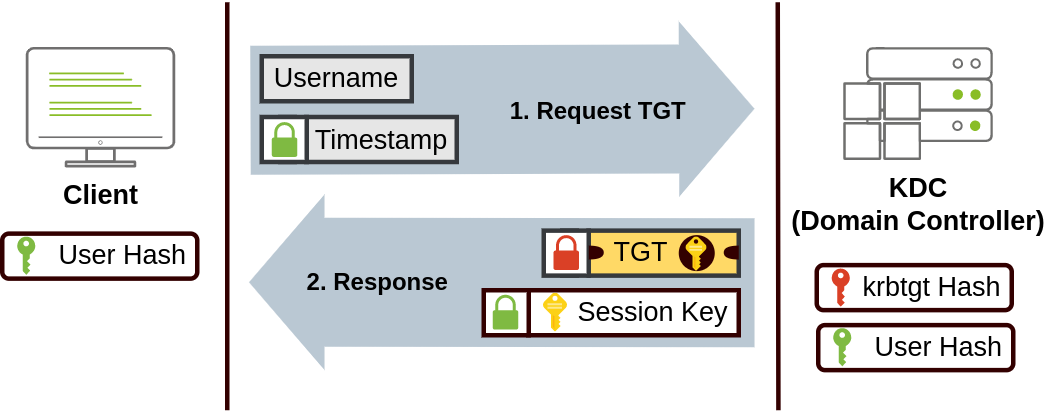
Key Distribution Center (KDC), a service usually installed on the Domain Controller in charge of creating Kerberos tickets
KDC will create and send back a Ticket Granting Ticket (TGT)
Then they will use their TGT to ask the KDC for a Ticket Granting Service (TGS).
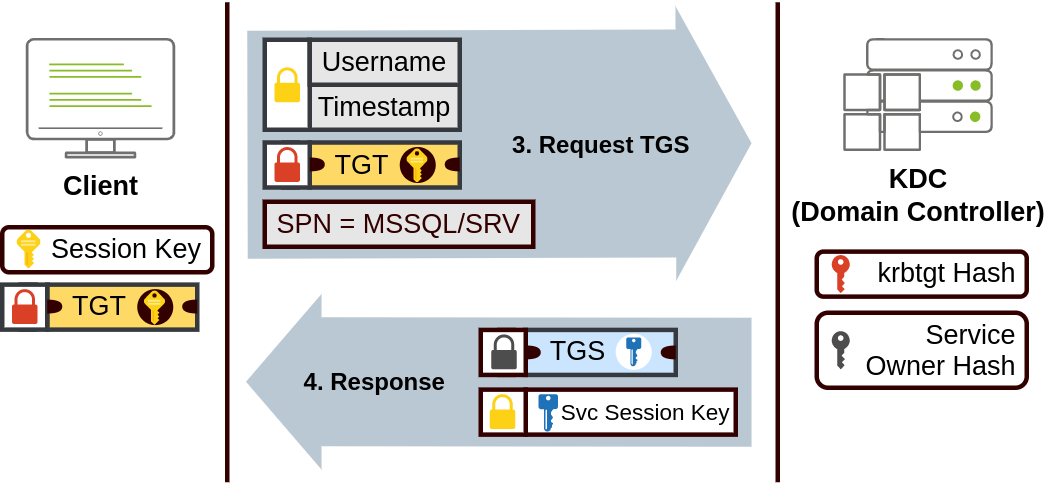
The TGS can then be sent to the desired service to authenticate and establish a connection.
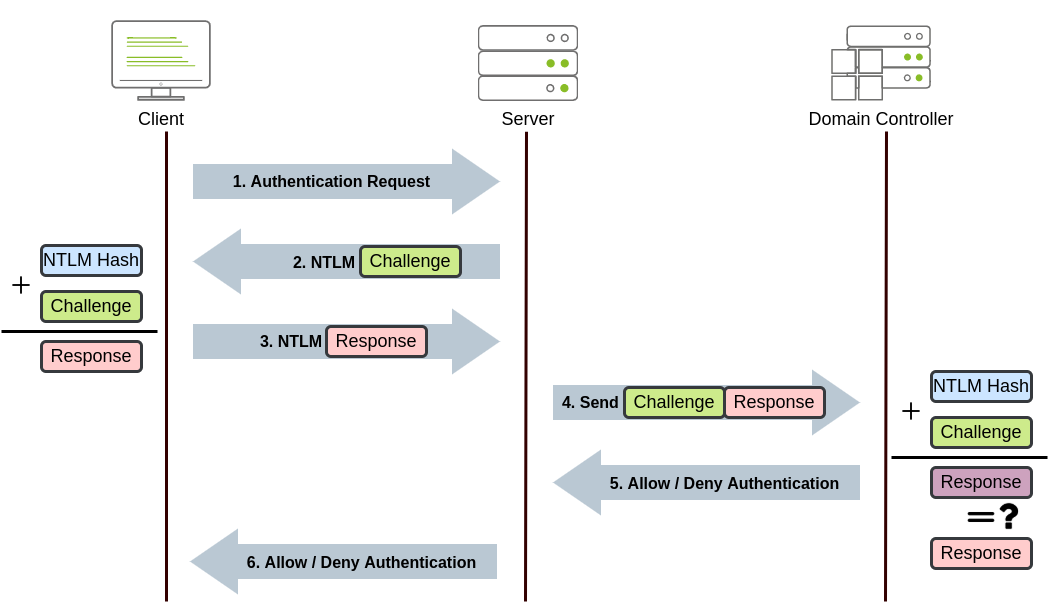
NetNTLM Authentication