carbohydrates and lipids
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
What are the unique chemical properties that carbon has to make it so special?
can form single, double and triple covalent bonds.
covalent bonds are the strongest type of bond between atoms. Stable molecules can be formed.
Carbon atoms contain four electrons in their outer shell allowing them to form four covalent bonds with other atoms.
carbon can form molecules with many different elements (metallic and non-metallic).
carbon can form long chains or rings of molecules.
what are the carbon containing macromolecules?
carbohydrates - polysaccharides, disaccharides, monosaccharides
lipids - triglycerides/ composed of fatty acids and glycerol
proteins - composed of peptides/ which are composed of amino acids
nucleic acids. - include RNA and DNA composed of nucleotides.
what are the words for three-carbon sugars/ five carbon sugars and six-carbon sugars.
three-carbon sugars: trioses
five carbon sugars: Pentoses
six carbon sugars: hexoses
what monosaccharides come in hexoses and pentose shapes
hexoses: glucose, fructose, gelectose
pentose: deoxibase + ribose
describe the features of monosaccharides
mostly ring structures
one c- atom is usually outside the ring
they are all attached to OH groups
the atoms C,H,O are in a ratio 1:2:1
what are the two isomers that glucose has.
alpha D-Glucose and beta D-glucose
what are the functions of monosaccharides
Solubility: Glucose is polar and hydrophilic, and therefore soluble in aqueous solutions (like blood or plant sap). It therefore can be easily transported around
chemical stability: Monosaccharides have strong covalent bonds and therefore are very stable. This property is useful for food storage.
energy: Glucose gives out energy when oxidized during cellular respiration.
what are Disaccharides?
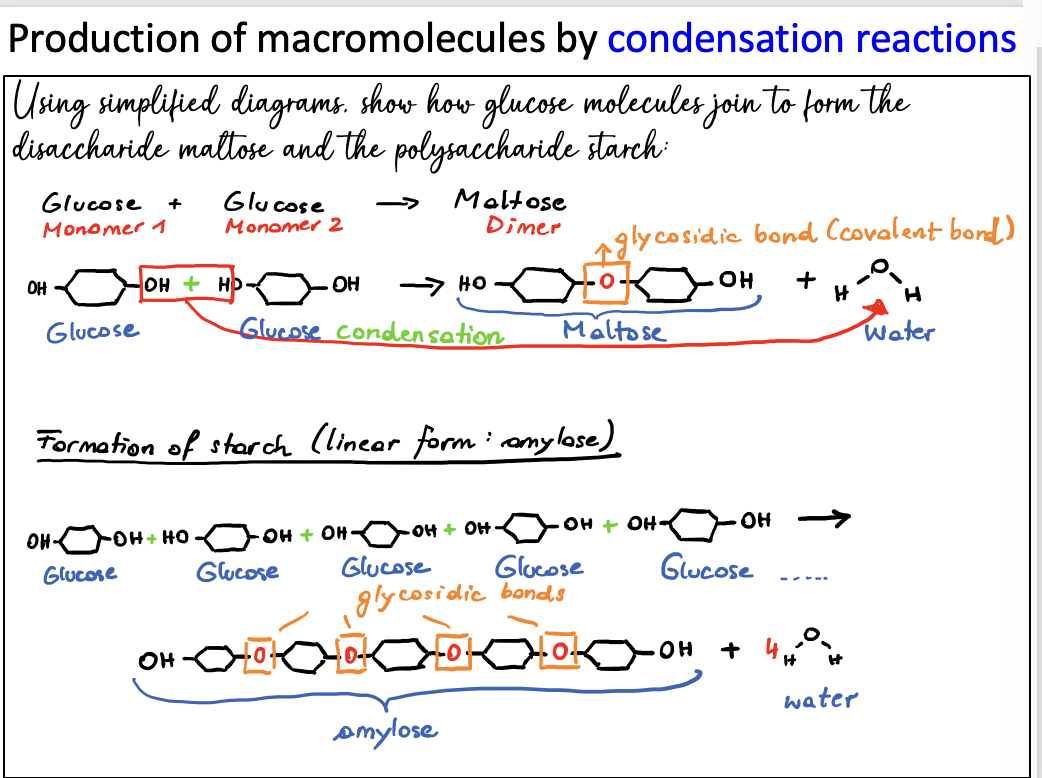
they are formed when two monosaccharide monomers join together in a condensation reaction. (glycosidic bond) is formed between the monomers and a molecule of water is formed.
what are polysaccharides?
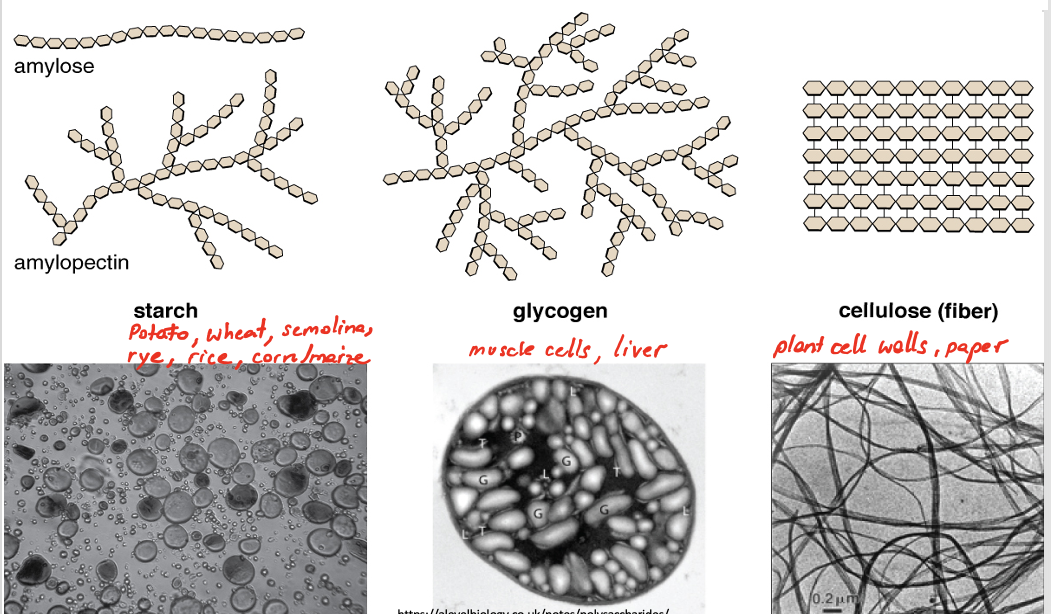
consists of many monosaccharides linked together. Starch, glycogen and cellulose are polysaccharides.
all made from glucose but with different bonding.
examples of polysaccharides
Using simplified diagrams show how glucose molecules join to form the disaccharide maltose and the polysaccharide starch.
Define the term hydrolysis
breaking a glycosidic bond to release monomers. This requires the input of water making it the opposite reaction to the condensation reaction.
compare and contrast condensation and hydrolysis

where does digestion occur in the natural world and how is it benifical?
can take place in the digestive track
can also take place in decomposers - releasing digestive enzymes to break down polymers.
the products of hydrolysis can be absorbed and used as monomers
Name three different polysaccharides that are all made uop of the same monosaccharide (glucose)
starch
Glycogen
cellulose
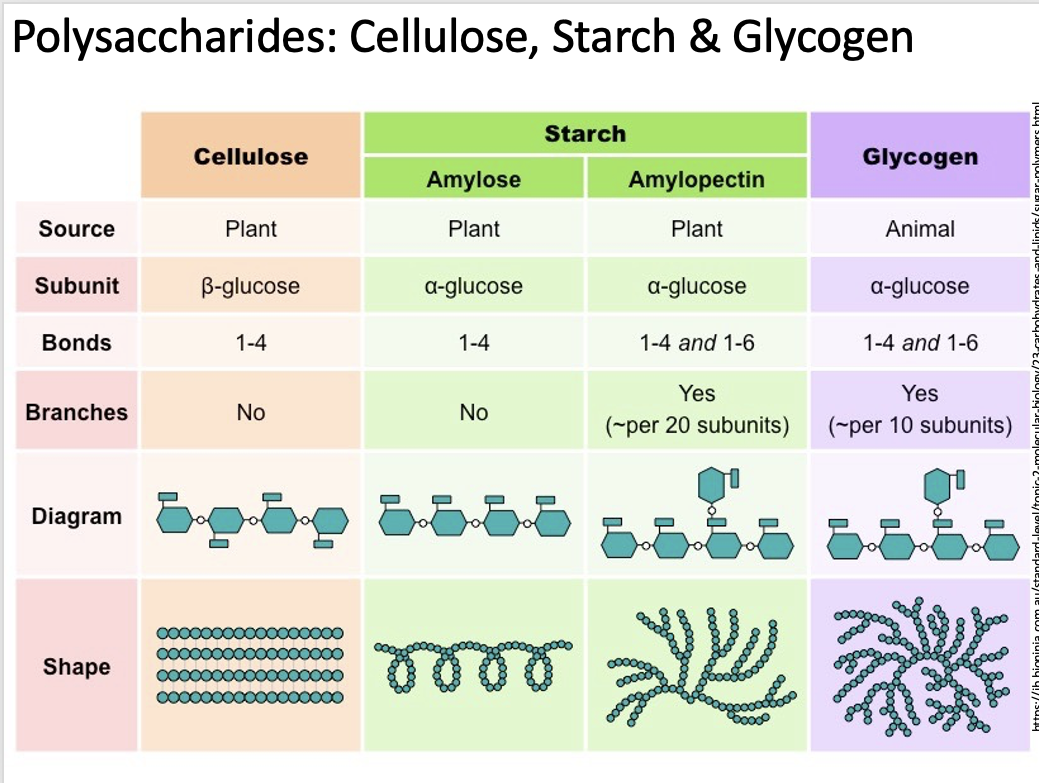
what is the structure and function of starch as a polysaccharide. (found in plant)
function
good energy source as glucose can be removed from the amylose and amylopectin and transported into a cell.
less soluble then glucose and therefore water wont swell the cells through osmosis.
structure:
amylose:
unbranched chains linked by only alpha D-glucose.
1-4 glycosidic bonds between glucose forming a curved helix shape
Amylopectin:
branched chains only made by alpha D - glucose
1-6 glycosidic bonds forming a straight chain
Starch is made up of 25-30% amylose and 70-75% amylopectin.
Both amylose and amylopectin are hydrophilic but are too large to be soluble in water.
What is statch used for in plants?
it is overall used as a storage system in case glucose is short supplied and is a the main storage source for seeds in plants
Does addition or removal of glucose happen faster in amylose or in amylopectin? why?
amylopectin has more points form which the glucose molecules can be broken off.
what is the structure and function of glycogen as a polysaccharide. (found in animal cells)
function:
Molecules of glucose can easily hydrolysed and used.
It is made in muscle and liver cells of animals
mostly insoluble in water preventing swelling of cells through osmosis
structure:
branched polysaccharide of only alpha D-glucose
there are more 1-6 glycosidic bonds
because of the higher number of branches it is more complex.
what is the structure and function of cellulose as a polysaccharide. (found in plant)
structure:
only beta D-glucose
1-4 glycosidic bonds
each beta glucose added to the chain needs to be positioned 180 degrees to the previous one forming a straight chain.
parallel bonds become cross linked with hydrogen binds forming bundles of microfibrils.
Function:
microfibrils are strong and rigid and give tensile strength to the plant cell preventing cells from bursting from high pressures.
use the table to remind you of what you just learned.
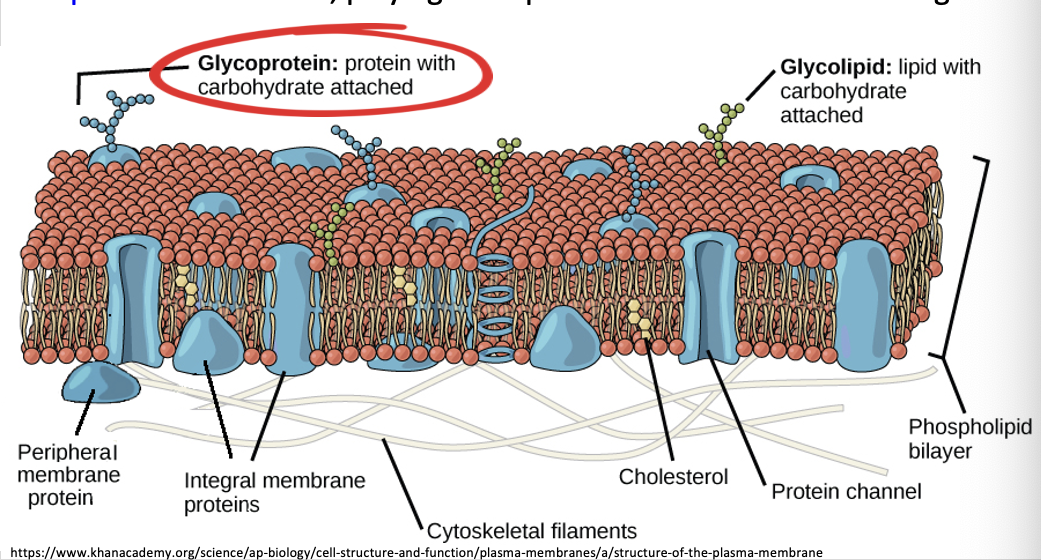
whats the role of glycoproteins in cell - cell recognition
glycoproteins are membrane proteins with carbohydrates attached to them.
this is important on the animal cell wall as the carbohydrate is able to be recognised by other receptors on other cells.