chemistry midterm #4
1/98
Earn XP
Description and Tags
el question y la respuesta correcta (99.9% sure)
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
99 Terms
1. Double and triple form bonds because…
b. single covalent bonds do not give all eight valence electrons
2. Which of the following is the correct electron dot structure for CS₂?
b.
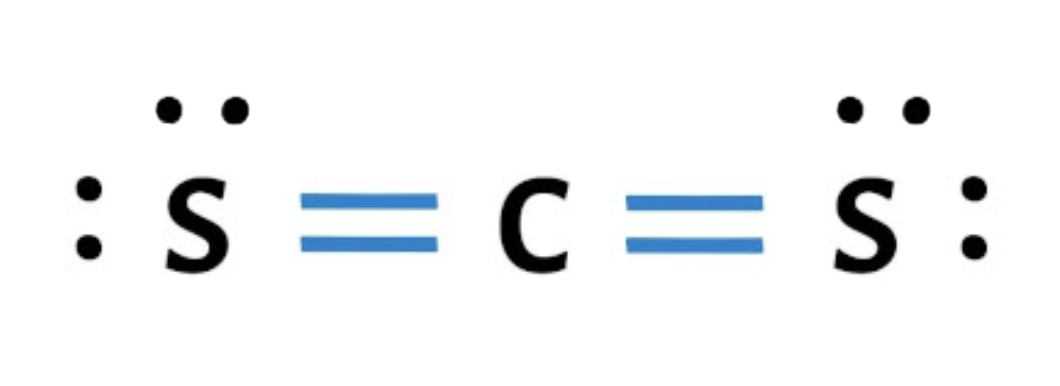
3. The number of lone pairs in the water molecule is…
e. 2
4. The lone pair of ammonia molecules is located in…
d. nitrogen atom
5. How many covalent bonds will a hydrogen atom usually make?
a. 1
6. The NO₃⁻ ion is an example of a polyatomic ion with…
a. resonance structure
7. The shape of a polyatomic ammonium ion NH₄⁺ is…
d. tetrahedral
8. The VSEPR theory allows us to determine the…
a. shape of a molecule
9. The shape of the ammonia molecule is…
c. trigonal pyramidal
10. H₂S, has a shape similar to…
d. water
11. A molecule that has a central atom and three identical bonds to other atoms, with no lone pairs. The shape of this molecule is…
c. trigonal planar
12. A molecule contains a central atom with two identical bonds to other atoms and two lone pairs. The shape of this molecule is…
b. bent
13. The ability of an atom to attract the shared electrons in a covalent bond is its…
a. electronegativity
14. Which of the following substances contains a nonpolar bond?
e. N₂
15. Which of the following elements has the lowest electronegativity?
a. Li
16. Which of the following compounds contains an ionic bond?
c. CaO
17. If the electronegativity difference between elements X and Y is 2.1, the bond between the elements X-Y is…
a. ionic
18. The water molecule has a dipole with the negative portion(head of the arrow)...
b. pointing towards the oxygen atom
19. The element in the following list with the lowest electronegativity is…
d. cesium
20. The dipole in the nitrogen-hydrogen bond points…
c. from the hydrogen to the nitrogen
21. The difference in electronegativity between hydrogen and sulfur is 0.4. What type of bond is found in the molecule H₂S?
c. nonpolar covalent
22. In the following list, which is the nonpolar molecule?
b. CCl₄
23. In the following list, which is the polar molecule?
a. H₂O
24. In water, the melting point is unusually high because of…
c. hydrogen bonding between molecules
25. Water has a boiling point of 100°C, and alcohol has a boiling point of 78°C, even though water is a smaller molecule. This large difference in boiling points is due to…
d. more hydrogen bonds between water molecules
26. When a solid is converted directly to a gas, the state is called…
e. sublimation
27. A heating curve illustrates…
d. the changes in temperature and physical state as it is heated
28. The O-H bond in water is polar because…
e. oxygen is much more electronegative than hydrogen
29. A hydrogen bond is…
a. an attraction between a hydrogen atom attached to N, O, or F and a N, O, or F atom attached to another molecule
30. Which of the following molecules can form hydrogen bonds
c. H₂O
31. A solution is prepared by dissolving 2g of KCl in 100g of H₂O. In this solution, H₂O is the…
b. solvent
32. Oil does NOT dissolve in water because…
b. oil is nonpolar and water is polar
33. When KCl dissolves in water…
d. the K⁺ ions are attracted to the partially negative oxygen atoms of water molecules
34. When C₁₂H₂₂O₁₁ is dissolved in water it classifies as…
a. solute
35. Vinegar is a solution of acetic acid with a melting point of 16.5°C in water, while at room temperature it is 25°C. This is an example of…
a. liquid-liquid
36. A solution containing a large concentration of dissolved ions can be classified as a(n)...
c. electrolyte
37. A solution of an electrolyte in water will…
a. carry an electric current
38. In water, a substance that ionizes completely in a solution is called a…
e. strong electrolyte
39. When the weak electrolyte HF is dissolved in water, the solution contains…
d. mostly HF molecules and a few H⁺ and F⁻ ions
40. When the electrolyte glucose is dissolved in water, the solution contains…
a. all glucose molecules
41. When some of the sugar added to the iced tea remains undissolved at the bottom of the glass, the solution is…
d. saturated
42. At 26°C, the solubility of sodium chloride is 36/100mL of solution. How would you describe a solution of 10g of sodium chloride in 100mL of solution at room temperature?
d. unsaturated
43. A solid that forms when its solubility is
d. precipitate
44. What is the mass percent (m/m) concentration of a solution of 10.0g of sodium chloride in 100g of solution?
e. 10.0%
45. What is the mass percent (m/m) concentration of a solution prepared from 50.0g of NaCl and 150.0g of water?
d. 25.0%
46. The mass percent (m/m) concentration of
e. 331 mL
47. The mass percent (m/m) concentration refers to the number of g of solute in…
d. 100 g of solution
48. What is the mass percent (m/m), of a solution prepared from 50.0g NaCl and 150.0g of water?
d. 25.0%
49. Rubbing alcohol is 70.0% alcohol by volume. How many mL of alcohol are in a full 1 pint (473 mL) container?
e. 331 mL
50. What is the molarity (M) of a solution that has 2.35g of NH3 in 0.0500L of solution?
b. 2.76 M
51. The molarity (M) of a solution refers to…
a. moles of solute/L of solution
52. What is the molarity of a solution containing 5.00 moles of KCl in 2.00L of solution?
2.50 M
53. How many moles of CaCl₂ are in 250.0mL of a 3.00 M of CaCl₂ solution?
d. 0.750 mol
54. During the process of diluting a solution to a lower concentration…
a. the amount of solute does not change
55. When 100.0mL OF 6.00 HCl is diluted to 300.0mL the final concentration is…
c. 2.00 M
56. How many mL of 1.24 M H2SO4 reacts with 1.26g of Al?
2Al + 3H₂SO₄ → Al₂(SO₄)₃ + 3H₂
b. 56.5mL
57. Calculate the molality of the solution formed when 50.0g of the nonelectrolyte glucose (Molar Mass: 180.2) is dissolved in 0.250kg of water.
b. 1.11 molal
58. Calculate the freezing point of a 2.00 molal solution of the nonelectrolyte glucose. The freezing point constant for water is 1.86°C/molal.
e. -3.72°C
59. What happens to an animal cell placed in a hypotonic solution?
c. it bursts due to water intake
60. Which of the following describes an isotonic solution relative to the cell?
d. has equal concentration of solutes as the cell
61. Crenation occurs when a red blood cell is placed in which type of solution?
d. hypertonic
62. In the process of dialysis, what primarily passes through the membrane?
c. small solute molecules and water
63. Which statement correctly explains osmosis?
b. the movement of solvent from a low to a high solute concentration across a membrane
64. According to the Arrhenius concept, if HNO3 were dissolved in water, it would act as…
b. an acid
65. The name given to the aqueous solution of HBr is…
b. hydrobromic acid
66. The name of HClO is…
e. hypochlorous acid
67. The name of H₂CO₃ is…
a. carbonic acid
68. An example of an Arrhenius base is…
b. KOH
69. Water is an example of a ____ compound.
a. amphoteric
70. In a water solution, the conjugate base of HF is…
a. F⁻
71. The conjugate acid of NO₂⁻ is…
b. HNO₂
72. The conjugate base of H₂CO₃ is…
b. HCO₃⁻
73. The conjugate base of H₂S is…
c. HS⁻
74. According to the Bronsted-Lowry definition…
d. a base is a proton acceptor
75. Identify the Bronsted-Lowry acid in the reaction:
H₂O(l) + CO₃²⁻(aq) → HCO₃⁻(aq) + OH⁻(aq)
a. H₂O
76. The conjugate acid of NH₃ is…
d. NH₄⁺
77. Which of the following is the strongest acid?
e. HCl
78. Which of the following is correctly identified?
b. NaOH, strong base
79. Ammonia is a weak base because…
d. it produced few hydroxide ions in water
80. The Ka for hydrofluoric acid is 7.2×10⁻⁴. This means that HF is…
c. a weak acid
81. A solution with a pH of 4 is…
b. moderately acidic
82. In which of the following are the pH values arranged from the most basic to most acidic?
c. 14,10,7,4,3,1
83. In a hydrochloric acid solution where the [HCl] is 0.010 M, what is the pH?
b. pH=2.0
84. The ph of a 0.5 M solution of potassium hydroxide, KOH is…
b. 13.5
85. When hydrochloric acid reacts with sodium carbonate, what are the results?
c. CO₂
86. When potassium hydroxide reacts with sulfuric acid, one product is…
c. H₂O
87. When Zinc metal reacts with hydrochloric acid, one product is…
c. H₂
88. An acid and a base react to form salt and water in a ____ reaction.
d. neutralization
89. Which of the following is a neutralization reaction?
b. HNO₃ + KOH → H₂O + KNO₃
90. Which of the following substances increases the concentration of OH⁻ in an aqueous solution?
c. KOH
91. What is the correct name for H₂SO₄ when dissolved in water?
b. sulfuric acid
92. Which of the following is a weak acid?
b. H₂CO₃
93. According to Arrhenius, a base is defined as a substance that ____ in water.
d. increases [OH⁻]
94. The conjugate base of HSO₄⁻ is…
a. SO₄²⁻
95. Which of the following is amphoteric?
c. H₂O
96. Identify the Bronsted-Lowry base:
NH₃ + H₂O ⇌ NH₄⁺ + OH⁻
b. NH₃
97. The name for HNO₂ is…
b. nitrous acid
98. Which is a product when NaOH reacts with HCl?
c. NaCl and H₂O
99. A solution with [H₃O⁺]=1x10²⁻ M has a pH of…
b. 2