Agri 22 Lecture Ideal Parameters and Pastures
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
32 Terms
305 days
Lactation period
Milking cows in entire herd
40-48%
Milking cows in adult herd
60-74%
Dry period
50-60 days
Age at 1st breeding
14-15 months
Weight at 1st breeding
250-300 kg
Age at 1st calving
24 months
Calving interval
12-13 months
Average days open (animal is not pregnant)
85-110 days
Average days open to 1st breeding (VWP) - for uterine involution
45-60 days
<10%
number of wows open more than 120 days
<10%
Culling rate due to reproductive problems
<1.7
Number of services per conception
>50%
Ideal conception rate
<5%
Abortion rate
<5%
Calf mortality
<2%
Cow mortality
<5%
Incidence of clinical mastitis
Pasture
used by dairy farmers with native grasses and improved grass species
- i.e. cogon, talahib
Pasture Establishment
sequences of seed germination and seedling development that normally permit the persistence of the introduced species in the longer-term
Improved grasses
napier grass
guinea grass
para grass
star grass
pangola grass
signal grass
mulato
mulato II
Legumes
centrosema
kudzu
ipil-ipil
kakawate
dapdap
katuray
stylo
flemingia
Systems of farm operation (production systems)
extensive - grazing
intensive - cut and carry
semi-intensive - combination
Cut and carry
Animals rely on feed to be cut and carried to them daily
Less wastage of grasses due to trampling
grasses are cut at constant level resulting to efficient use of all available feed
as the grass matures, yield increases while quality decreases
Grazing
animals are in the pastures day and night
loss in pasture yield due to trampling
animals have the opportunity to select the more nutritious parts of the forage
Continuous grazing
Rotational grazing
Strip grazing

Leader-follower grazing system
Night grazing
animal can eat more at night because of cooler temperature
Tethering
Individual animals tied with a rope
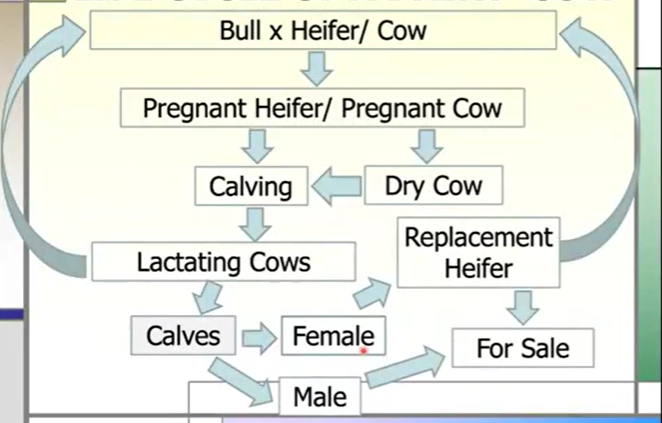
Life Cycle of a Dairy Cow