3.2.5 and 3.3.5 - Maxwell-Boltzmann Distribution and Rate of reaction
1/10
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
11 Terms
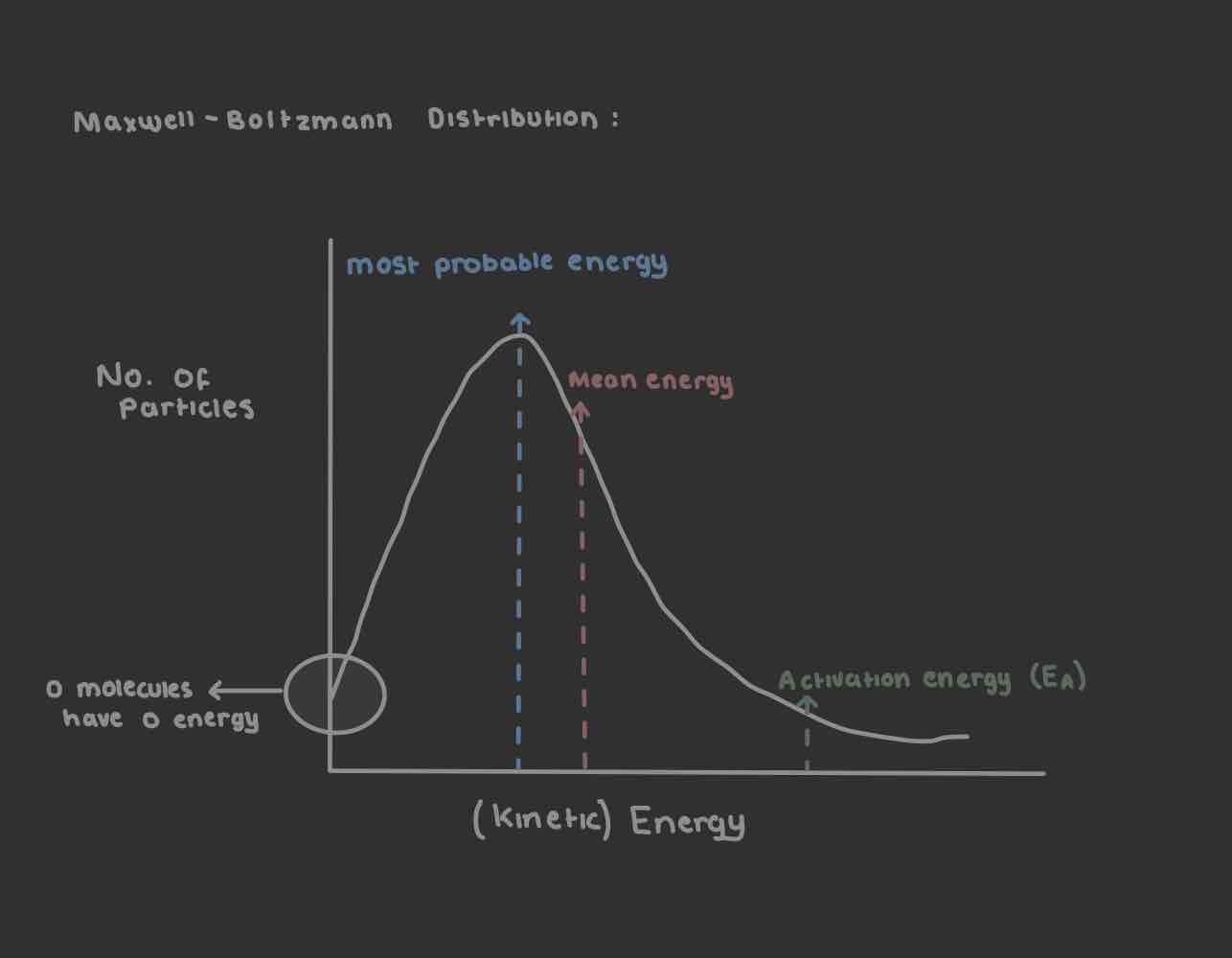
Maxwell - Boltzmann Distribution Graph
Rate of reaction
Change in amount of concentration of a reactant or product over time (speed at which reactants get used up and reactants start to form)
Factors affecting rate of reaction
temperature
Concentration
Pressure
Catalysts
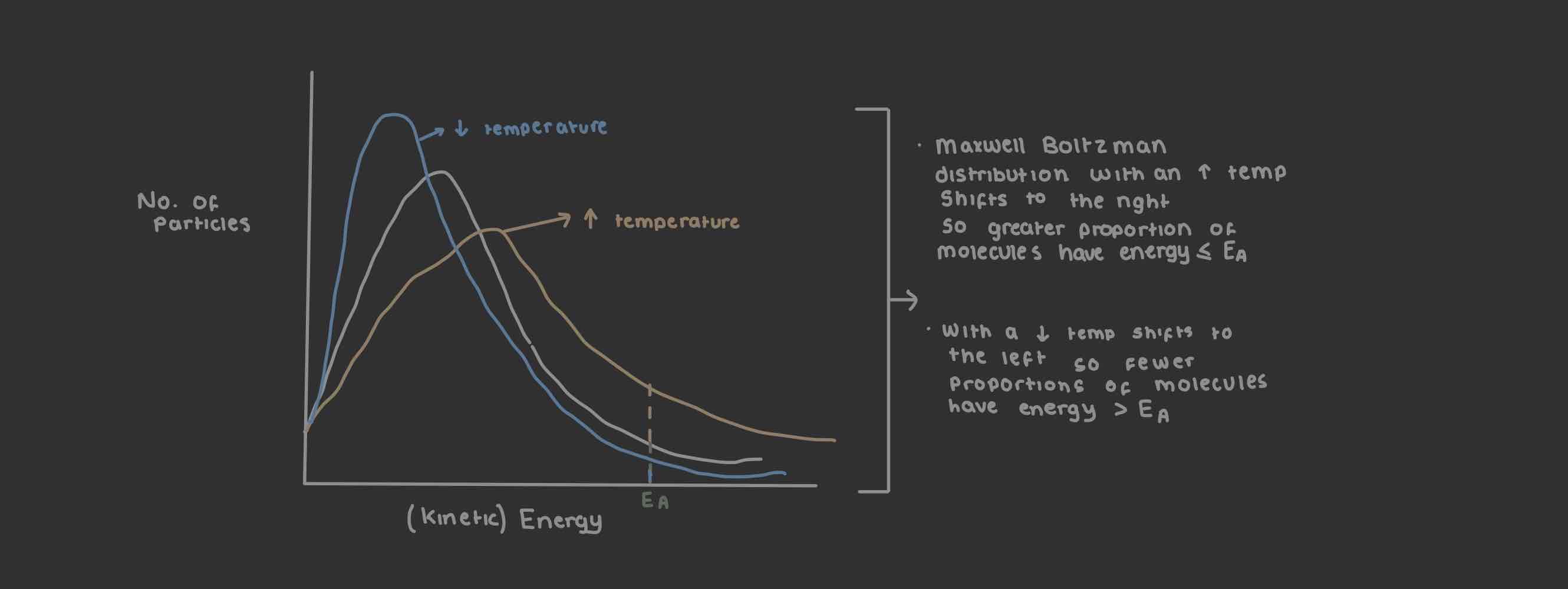
Temperatures affect on rate of reaction
Heat substance → thermal energy transferred to it → thermal energy converted to kinetic energy → ∴ molecules move faster → ↑ movement ↑ frequency of collisions with energy ≤ to Ea in a given time → ∴ ROR ↑
Cool substance → thermal energy ↓ → ∴ molecules have less kinetic energy → so molecules move slower → ↓ movement → ↓ frequency of collisions with energy ≤ to Ea in a given time → ∴ ROR ↓
Concentration affect on rate of reaction
when conc of sample ↑ the no. of molecules within a fixed volume ↑ → particles more packed closer together → because of smaller distance between particles they collide more frequently → ↑ ROR as there’s an ↑ in no. of successful collisions
Pressure affect on rate of reaction
↑ pressure ↑ no. of particles within fixed volume → particles packed closer together ∴ distance between molecules is small → ↑ frequency of collisions → ↑ ROR as there’s an ↑ in no. of successful collisions
Catalyst affect on rate of reaction
↑ ROR without being used up → works by providing alternative reaction pathway which requires a lower Ea for reaction to occur
Heterogeneous Catalyst
usually solid catalysts and gaseous reactants
Heterogeneous (diff state / phase from reactant)
Reactants adsorb (sticks onto surface) onto surface onto active site
weakens bonds
Brings molecules closer → more frequent collision
More favourable orientation will hit the correct angle = more successful collisions
Reactions take place
Products are described (leave the surface)
Conditions for heterogenous catalysts
large surface area
Spread thinly over ceramic honeycomb
In catalytic converter ceramic honeycomb structure counted with with rhodium and platinum
Poisoned catalyst
some substances block the active site (they adsorb and don’t come off)
Required Practical 3 - Measuring Rate Of Reaction
• Measure 10cm3 of sodium thiosulfate using a pipette or measuring cylinder and transfer it to the tube labelled sodium thiosulfate
• Measure 2cm3 of 1 mol Hydrochloric Acid using a pipette or measuring cylinder and transfer it to the tube labelled hydrochloric acid
• When using water baths begin from the coldest temperature to the hottest allowing the water baths to heat up
• using a 400 ml beaker fill it (using the tap) with cold water and place the tubes in leave them in
• after min 5 mins use the thermometer to see if both tubes are at the same temperature if not place them back into their water baths
• Once temperatures are the same record the starting temperature on your graph drawn
• Then proceed to add the HCL into the sodium thiosulfate tube and begin the timer swirl it with cap on then remove the cap to observe when the cross disappears
• Once the black cross disappears stop the stopwatch and record the time it took for the cross to disappear
• Using the thermometer measure the ending temp and record it on your table with results
• Repeat this with the 3 water baths and room temperature tubes
• Once you have recorded the starting and ending temp you calculate the mean temperature (this is going to be the x axis on the graph you have drawn)
• You then use the time taken for the cross to disappear you calculate the rate of reaction by using 1000/Time (this is going to be your y axis)