a&p 2 lab microscope and blood
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
19 Terms
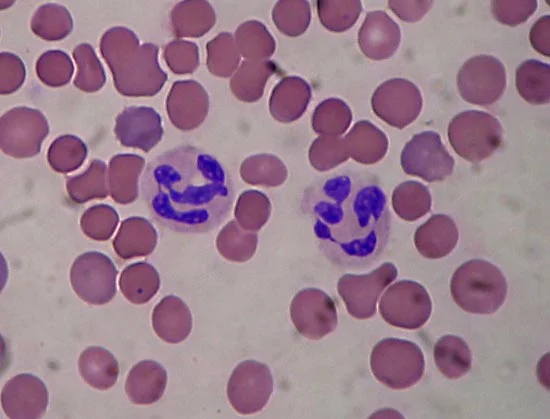
50-70%
gran
increased numbers with acute stress
neutrophil
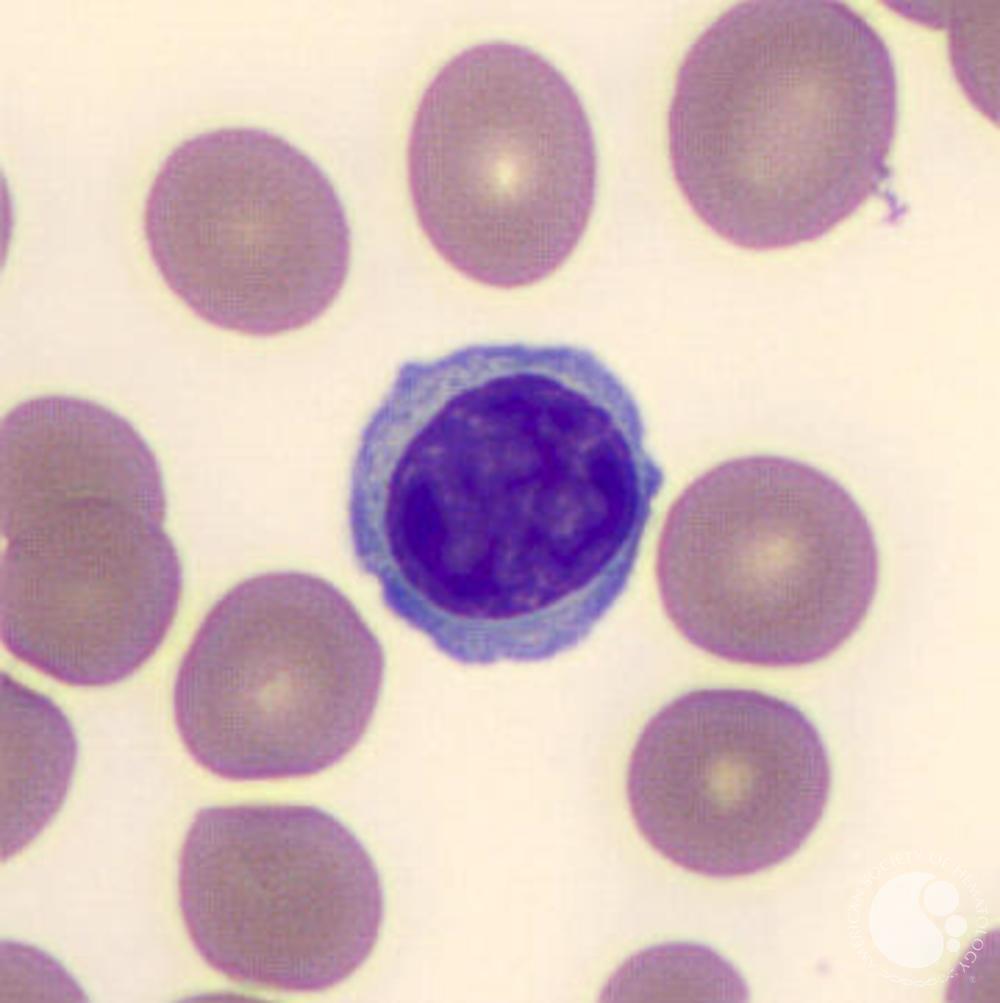
20-40%
agran
increased numbers with viral infections
lymphocytes
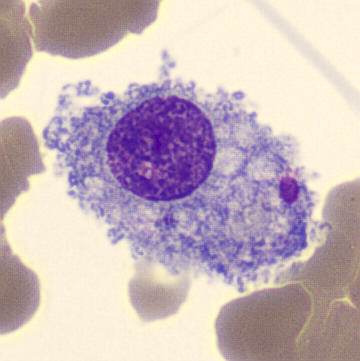
2-8%
agran
increased numbers with tuberlosis
Monocytes
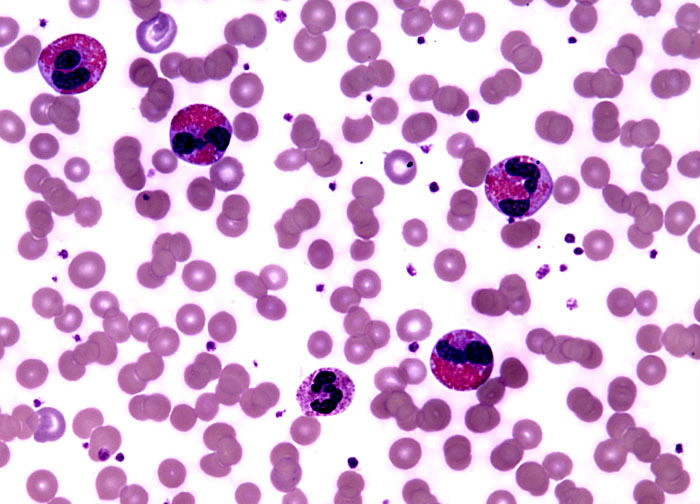
1-4%
gran
increased numbers with allergic reactions
Eosinophil
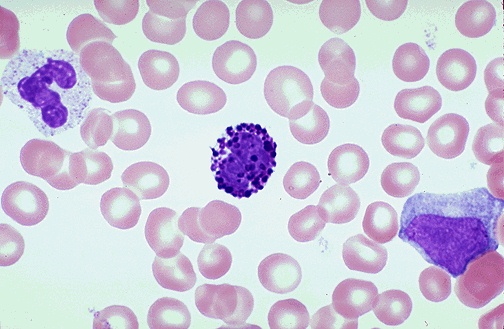
0.5-1%
gran
increased numbers with myeloproliferative disorders
basophil
what are the four ABO blood types
A, B, AB, O
Surface antigen: A, Rh
Antibodies: anti-B
Can receive blood from: A+, A-, O+, O-
A+
Surface antigen: A
Antibodies: anti-B, anti-Rh
Can receive blood from: A-, O-
A-
Surface antigen: B, Rh
Antibodies: anti-A
Can receive blood from: B+, B-, O+, O-
B+
Surface antigen: B
Antibodies: anti-A, anti-Rh
Can receive blood from: B-, O-
B-
Surface antigen: A, B, Rh
Antibodies: none
Can receive blood from: A+, A-, B+, B-, AB-, O+, O-
AB+
Surface antigen: A, B
Antibodies: anti-Rh
Can receive blood from: A-, B-, O-
AB-
Surface antigen: Rh
Antibodies: anti-A, anti-B
Can receive blood from: O+, O-
O+
Surface antigen: None
Antibodies: Anti-A, anti-B, anti-Rh
Can receive blood from: O-
O-
Which blood type is the universal recepient
AB+
Which blood type is the universal donor
O-
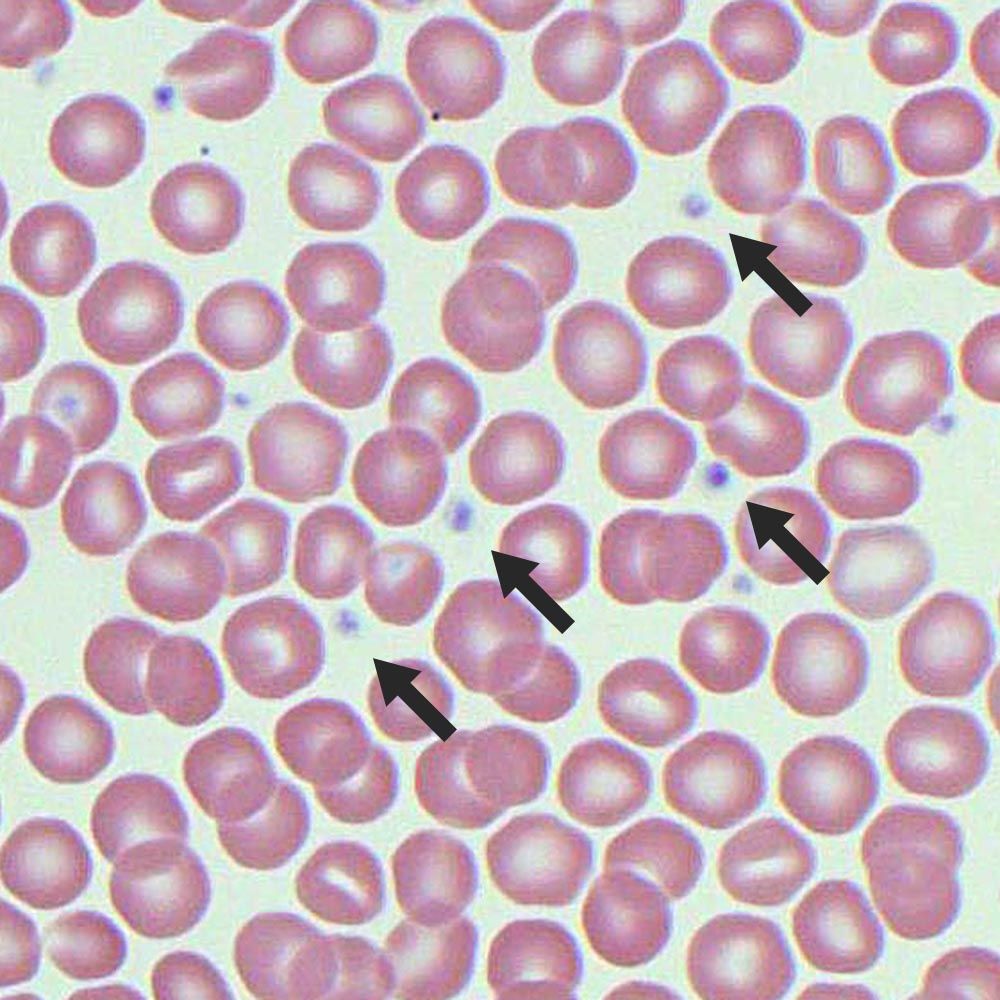
clot blood and prevent blood loss from damaged vessels
small cell fragments, irregularly shaped, participate in all 3 phases of hemostatis (stoppage of bleeding)
Thrombocytes (platelet)
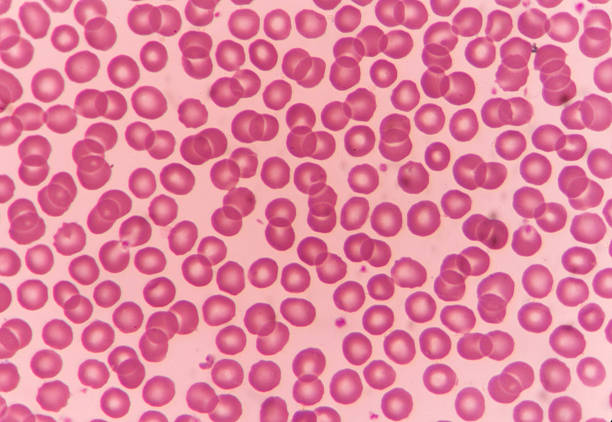
transport respiratory gases in blood oxygen and CO2
small and flexible, biconcave disc shape, lack organelles, contain hemoglobin to bind O2
Erthrocyte (RBCs)
defend body against pathogens
contain nucleus, mortile, attracted to infection via chemotaxis, 5 types divided into 2 classes (granulocytes, Agranulocytes)
Leukocytes (WBCs)