CHEM 1311 FINAL
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
Amorphous Solids
have disordered structures (short range order)
ex: glass
Crystalline Solids
have a highky regular arrangement of components (long range order).
Positions of components are represented by lattice(s)
Lattice(s)
a thrree dimensional system of points that designates the position of components of a substance. Also defined as an infinite array of points in space, in which each point has identical surroundings to all others.
A lattice point is a coordinate or position in a crystal lattice that represents a constituent particle, such as an atom, molecule, or ion.It serves as a framework for the arrangement of atoms in crystalline solids.
it is NOT the arrangement of atoms, IT IS the lattice points onto which atoms are placed
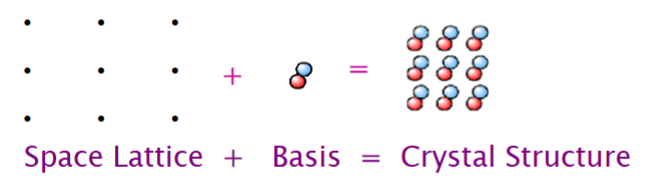
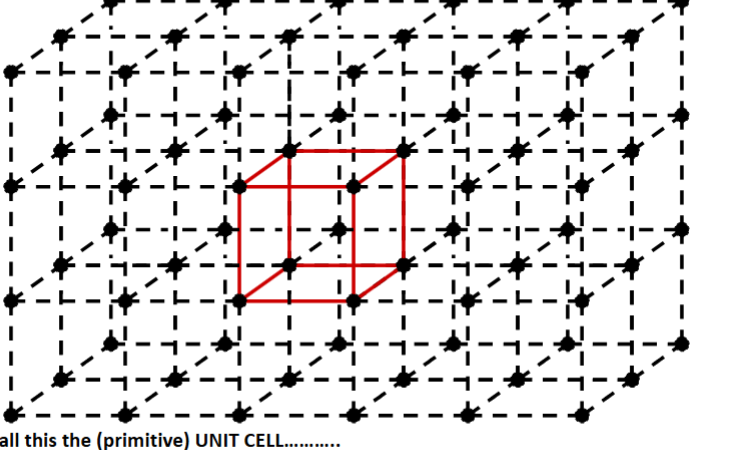
Unit cell
the smallest repeating unit. on a lattice.
Smallest component of the crystal, which when stacked to =gether with pure translational repetition reproduces the wholle crystal
in 3d it shows the full symmetry of the sructure.
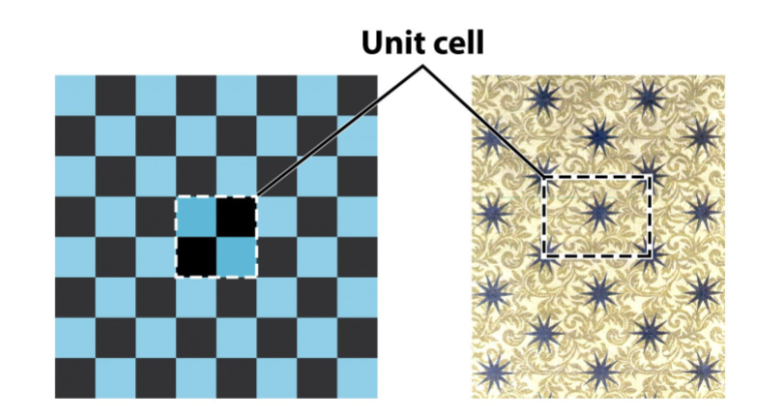
Crystal Lattices (patterns)
a mathematical construct of repeating patters in space.
is an imaginary grid system in three dimensions in which every point (lattice point or node) has an enviorment that is identical to that of any other point or node
the individual shapes of the lattice, then form ‘tiles’ (azulejos) also called unit cells, that need to fill up the solid.
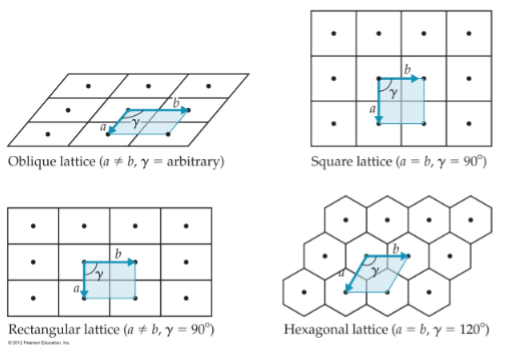
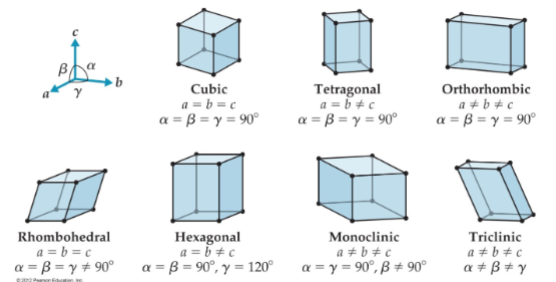
Structures of Crystal Lattices
there are 7 basic three dimensiona; lattices
cubic
tetragonal (4)
Orthorrhombic
Rhombohedral
hexagonal
monoclinic
triclinic
Basis (for lattice)
Elemental solids: Basis= single atom
Polyatomic Elements: Basis = teo or four atoms
Complex organic compounds: Basis = thousands of atoms
Counting Atoms in Unit cells
each atom/lattice point are shared between 8 unit cells