Laurich Biology - Unit 2
1/105
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
106 Terms
Carbon
C, all organic compounds are based on this element
Hydrogen
H, included in all organic compounds
Oxygen
O, an element, one of the 6 molecules of life
Sulfur
S, an element, one of the 6 molecules of life
Phosphorous
P, an element, one of the 6 molecules of life
Nitrogen
N, an element, one of the 6 molecules of life
Element
consists of only one type of atom, ex: carbon, hydrogen, oxygen
Molecule
A group of atoms bonded together
Functional Group
other elements like H,O,S, and P may attach to the carbon backbone to form reactive clusters of atoms called blank blank, these possess certain chemical properties that they impart to the molecules to which they are attached, most of the reactions that occur in living organisms involve this, mostly ionic or strongly polar
Organic
Contains carbon
Carbon-Based
organic
Hydroxyl Group
a functional group with (-OH), it is polar and can form hydrogen bonds with water molecules and help to dissolve organic compounds such as sugars, ex: methanol, ethanol
Carbonyl Group
a functional group with (-CHO) or (-CO), a blank blank group which is at the end of the carbon skeleton is called an aldehyde, a carbonyl group which is within the carbon skeleton is called a ketone, ex(-CHO): methanal and ethanal, ex(-CO): propanone (acetone)
Carboxyl Group
a functional group with (-COOH), acts as acids (can donate H+), ex: ethanoic acid (acetic acid_
Amino Group
a functional group with (-NH2), acts as bases (can take up H+), ex: propanamine, butanamine
Phosphate Group
(PO4), makes up the backbone of a nucleotide with the pentose sugar
Lipid
a macromolecule, contains C,H,O, groups of organic molecules that are insoluble in water, best for storing energy, large/nonpolar, most are composed of a glycerol molecule with attached fatty acids, ex: fats, oils, waxes, phospholipids, steroids, glycolipids, some vitamins, 2:1 H:O
Carbohydrate
Organic compounds, found in ratios of about 1:2:1 C:H:O, source of energy and structural materials, come in the form of monosaccharides (sugars), disaccharides (sugars), and polysaccharides
Nucleic Acid
store and transfer info in the cell, made of C,H,O,N,P, involves DNA, RNA, and nucleotide (monomer)
Protein
polymer constructed from amino acid monomers, has a 3D structure, includes C,H,O,N, acts as biological catalysts (enzymes), a blank's structure depends on four levels of structure
Saturated Fats
these fatty acids have no double bonds between carbon atoms (have maximum number of hydrogen atoms), straight structure, unhealthy-fats usually from animal sources, solid at room temperature (20 Celsius)
Monounsaturated Fats
their fatty acids have some carbon atoms that are double bonded (not fully hydrogenated), kinked (tilted) in shape, healthy, from plant sources, liquid at room temperature, single carbon bond (double bond)
Polyunsaturated Fats
their fatty acids have some carbon atoms that are double bonded (not fully hydrogenated), kinked (tilted) in shape, healthy, from plant sources, liquid at room temperature, have more than one carbon bond (double bonds)
Phospholipids
cell membranes made up of two layers of blank form a barrier, keep things that are supposed to be out, out of the cell, keep things that are supposed to stay in, in
DNA
deoxyribonucleic acid, encodes and stores info used to assemble proteins, double nucleotide chains, nitrogen bases bond in pairs across chains, spiraled in a double helix, stays in a compacted structure called a chromosome, pentose sugar is deoxyribose, uses T nitrogen base (thymine)
RNA
ribonucleic acid, reads DNA info to direct protein synthesis, single nucleotide chain, pentose sugar is ribose, uses information, uses U nitrogen base (uracil)
Nucleotide
monomer, DNA and RNA are polymers made from it, include a pentose sugar, phosphate group (previous two make up the backbone), and nitrogen base (comes off the backbone), there are two types of blanks, purines and pyrimidines
Nitrogen Base
(C-N ring), includes adenine, thymine, guanine, cytosine, and uracil, part of the nucleotide that contains the actual information, phosphate group and pentose sugar make the backbone
Pentose Sugar
(SC, S sided), ribose acid found in RNA, deoxyribose acid found in DNA, makes up the nucleotide backbone with phosphate group
Double Helix
characteristic of DNA molecule, H bonds between bases join two strands, double nucleotide chian
Adenine
part of the nitrogen base, connects with thymine in DNA and uracil in RNA, (A)
Thymine
part of the nitrogen base in DNA, connects with adenine, (T)
Guanine
part of the nitrogen base, connects with cytosine, (G)
Cytosine
part of the nitrogen base, connects with guanine, (C)
Uracil
part of the nitrogen base in RNA, connects with adenine, (U)
ATP
adenosine triphosphate, modified nucleotide, adenine (AMP) + P + P, provides energy to drive and support many processes in living cells, ready to use energy molecule
Amino Acids
protein monomer, 20 different ones, all have an amino group and a carboxyl group, protein diversity is based on differing arrangements of a common set of just 20 of these, covalently bonded to a central carbon atom, joined together by peptide bonds, a chain of these is a polypeptide
Peptide Bonds
cells join amino acids together in a dehydration reaction that links the carboxyl group of one amino acid to the amino groups of the next amino acid, as a result a water molecule is removed
Polypeptide
additional amino acids can be added together by peptide bonds to form a chain of amino acids, a blank
Central Carbon
the carbon atom of an amino acid that the other amino acid groups (carboxyl group, amino group, etc.) all connect to
R Group
a functional group that defines a particular amino acid and gives it special properties
Primary Structure
(1), order of amino acids in a chain, amino acid sequence determined by gene (DNA), slight change in amino acid sequence can affect protein's structure and its functions, ex: sickle cell anemia
Secondary Strucutre
(2), "local folding," folding along short sections of polypeptide, interactions between adjacent amino acids, H bonds between R groups, ex: a-helix (alpha helix), b-pleated sheet (beta sheet)
Tertiary Structure
(3), "whole molecule folding," determined by interactions between R groups, hydrophobic interactions
Quaternary Structure
(4), more than one polypeptide chain joined together, only then is it a functional protein, hydrophobic interactions, ex: collagen (skin and tendons)
Disulfide Bridge
The covalent bond between two sulfur atoms (-S—S-) linking two molecules or remote parts of the same molecule
Protein Structure
primary, secondary, tertiary, quaternary
Monomer
A simple compound whose molecules can join together to form polymers
Polymer
molecules composed of many monomers; makes up macromolecules
Macromolecules
large molecules found in living things, ex: carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, nucleic acids
Condensation Polymerization
also known as dehydration synthesis, removes an OH and H during the synthesis of a new molecule, builds up polymers, ATP is required
Dehydration Synthesis
also known as condensation polymerization, removes an OH and H during the synthesis of a new molecule, builds up polymers, ATP is required
Hydrolysis
breaks a covalent bond by adding OH and H from a water molecule, purpose if for breaking down polymers, water is required
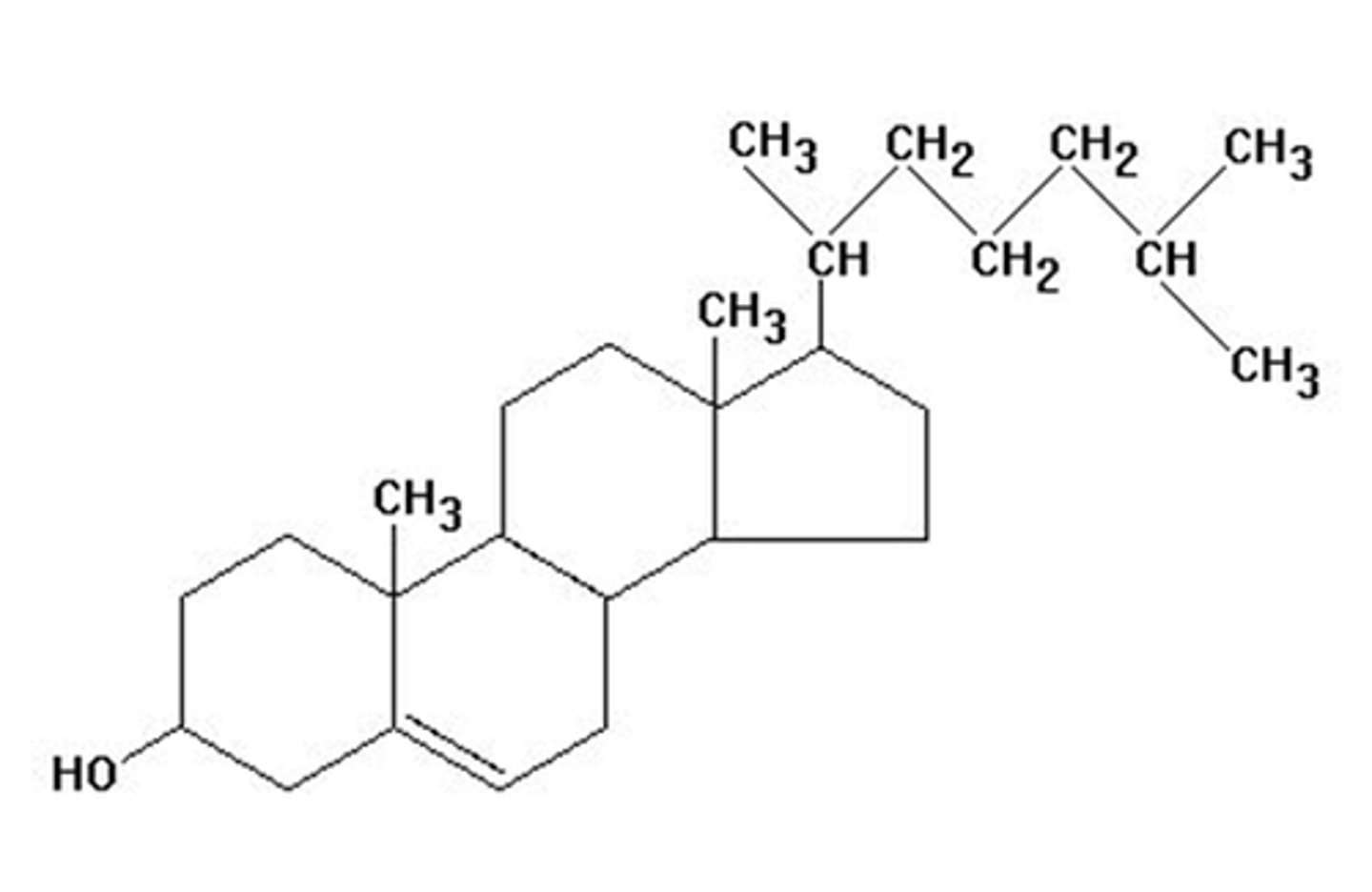
Steroids
fatty 4 rings, cholesterol and sex hormones, made of 4 fused rings, ex: cortisol (stress adaptation)
Triglycerides
three fatty acids attached to a molecule of glycerol, there are saturated blank and unsaturated blank
Glycerol
Combines with fatty acids to make lipids.
Fatty Acids
made with C,H,O, insoluble in water, store E, insulation, protective coverings, major part of cell membranes, blank acids
Hydrophilic
Attracted to water
Hydrophobic
Not attracted to water
Steroid Hormones
4 fatty rings
Lipids are Good
used to store energy (~36kj/grams), concentrated sources of energy that can be broken down, acts as a shock absorber and a good insulator, reduce heat losses to environment, waterproofing of some surfaces, transmits chemical messages via hormones, this proves that...
Monosaccharide
carbohydrates, simple sugar molecule, simple ring structures, ex: glucose, fructose, galactose
Disaccharide
carbohydrates, a double sugar molecule made of two monosaccharides bonded together through dehydration synthesis, ex: lactose, maltose, sucrose
Polysaccharide
carbohydrates, 3 or more monosaccharides, ex: glycogen, starch, cellulose
Glucose
the form of sugar that circulates in the blood and provides the major source of energy for body tissues. When its level is low, we feel hunger
Fructose
monosaccharide, fruit sugar
Galactose
monosaccharide, milk sugar
Glycogen
polysaccharides, how animals store glucose
Starch
polysaccharides, how plants store glucose
Cellulose
polysaccharides, structure in plants, makes up the cell walls, ex: corn starch
Chitin
a structural carbohydrate, arthropod exoskeleton and fungal cell wall, modified form of cellulose
Isomer
molecules with the same chemical formula but different structures
Compounds
2 or more elements chemically combined
Ionic Bonds
the outermost electrons of one atom are transferred permanently to another atom. The atom that loses the electrons becomes positively charged; the atom that gains the electrons becomes negatively charged
Covalent Bonds
Bonds created by sharing electrons with other atoms
Hydrogen Bonds
holds together different compounds, one side is negatively charged, one side is positively charged, weak bond
Polarity
Molecules having uneven distribution of charges
Cohesion
when two of the same polar molecules form H bonds with each other
Adhesion
when two different molecules form H bonds with each other
Specific Heat Capacity
the energy required to raise the temperature of one gram of a substance by one degree Celsius, cohesion between water molecules raises this
Solvent
A liquid substance capable of dissolving other substances
Solution
a mixture that forms when one substance dissolves another, homogeneous mixture
Solutes
substance dissolved in a solution
Organic Compounds
Compounds that contain carbon
1:2:1
ratio of C:H:O in carbs
Elements in each macromolecule
Carbohydrates (CHO)
Lipids (CHO)
Proteins (CHON)
Nucleic Acids (CHONP)
Enzymes
an organic catalyst made of protein, lowers the activation energy of a chemical reaction, speed up chemical reactions that take place in cells, typically they are bigger than their substrates
Catalyst
a substance that speeds up the rate of a chemical reaction without entering the reaction itself, they can be inorganic (heat) or organic (enzymes), most are organic
Active Site
a region on an enzyme that binds to a protein or other substance during a reaction.
Substrate
The reactant on which an enzyme works.
Product
A substance produced in a chemical reaction
Lock and Key Model
The model of the enzyme that shows the substrate fitting perfectly into the active site
Induced Fit
a type of model, enzyme is not rigid and changes shape slightly when the substrate enters, still specific to one substrate
Enzyme-Substrate Complex
A temporary complex formed when an enzyme binds to its substrate molecule(s).
Coenzymes
enzyme helpers, bind to enzyme and help it to better fit with its substrate, organic (vitamins)
Cofactors
enzyme helpers, bind to enzyme and help it to better fit with its substrate, inorganic (metal ions like iron)
Factors that effect enzyme activity
pH, concentration, temperature
pH and Enzyme Action
each enzyme has a specific pH in which it will work, different enzymes work at different pH levels, ex: enzyme in stomach is more acidic so lower pH better, enzyme in mouth touches many different substances so in between pH better, changes in pH can denature enzymes
Temperature and Enzyme Activity
all enzymes have an optimal temperature at which they work the most effectively, if temperatures get too high enzymes change shape (become denatured), cannot bind with its substrate and can no longer do its job
Denature
polypeptide chains unravel, losing their specific shape and as a result their function, ex: changes in salt concentration, changes in pH, excessive heat