structure and function (human nutrition)
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
36 Terms
balanced diet is made up of (7)
Carbohydrates
Proteins
Lipids
Dietary Fibre
Vitamins
Minerals
Water
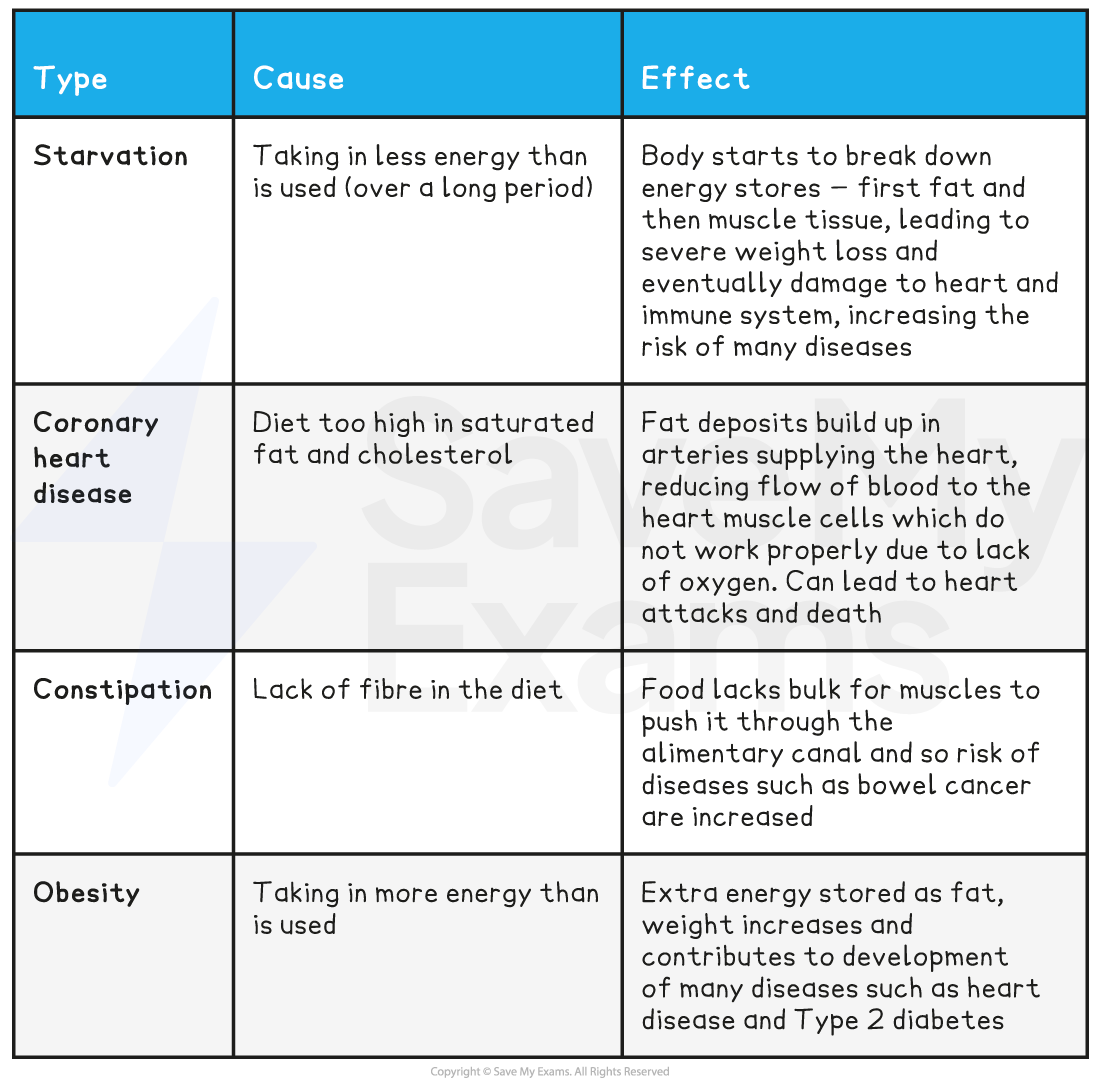
cause | effect | |
|---|---|---|
starvation | ||
CHD | ||
constipation | ||
obesity |
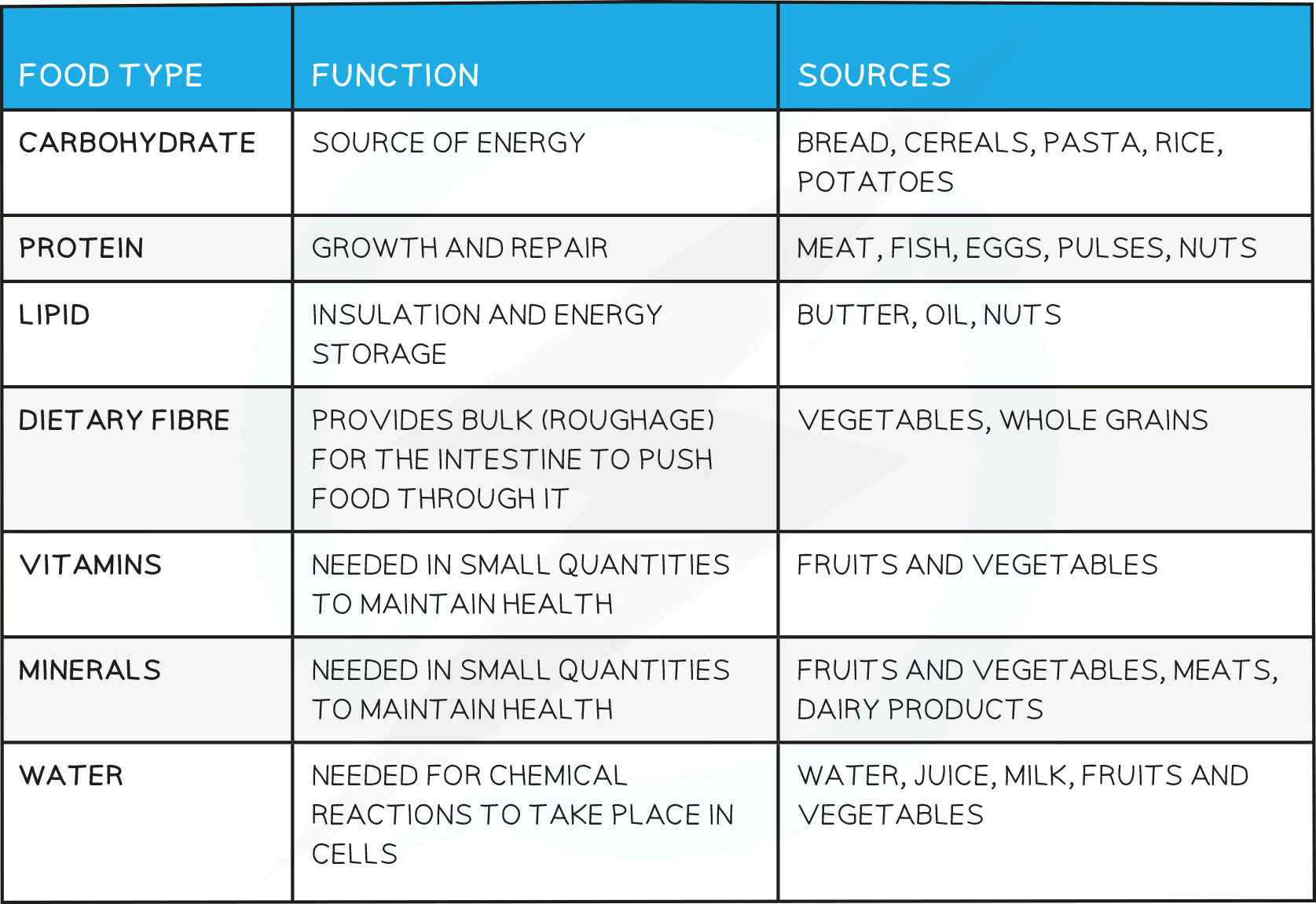
function | source | |
|---|---|---|
carbohydrate | ||
protein | ||
lipid | ||
fibre | ||
minerals | ||
vitamin | ||
water |
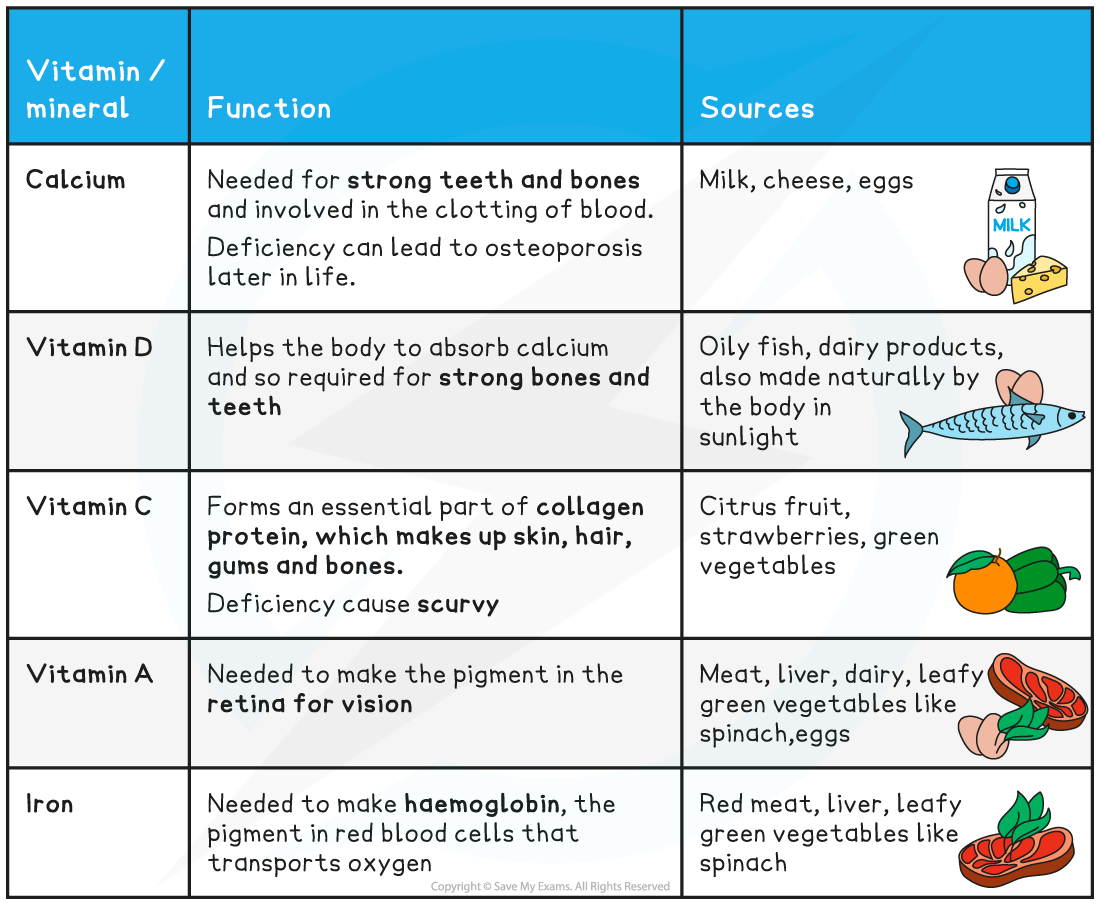
function + deficiency? | source | |
|---|---|---|
Calcium | ||
vitamin D | ||
vitamin C | ||
vitamin A | ||
Iron |
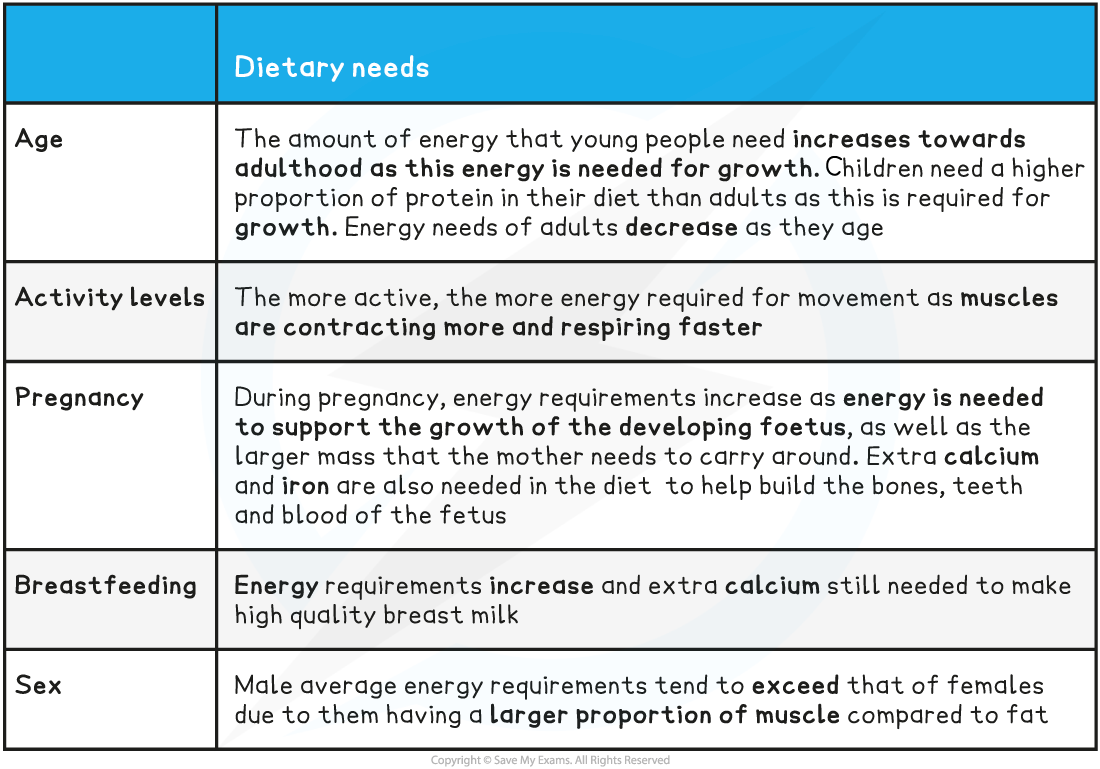
energy requirement | |
|---|---|
age | |
activity levels | |
pregnancy | |
breastfeeding | |
sex |
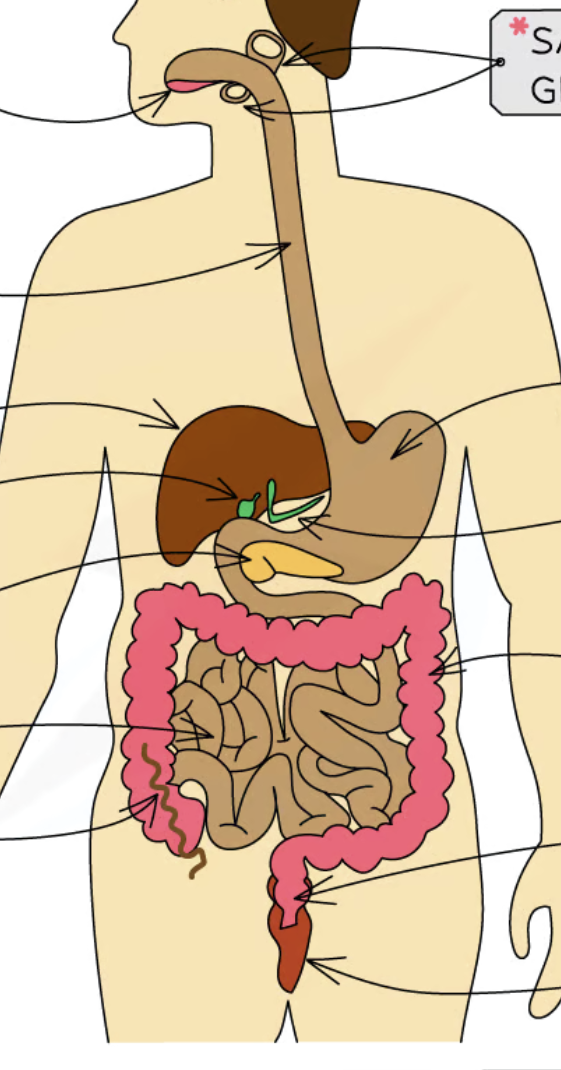
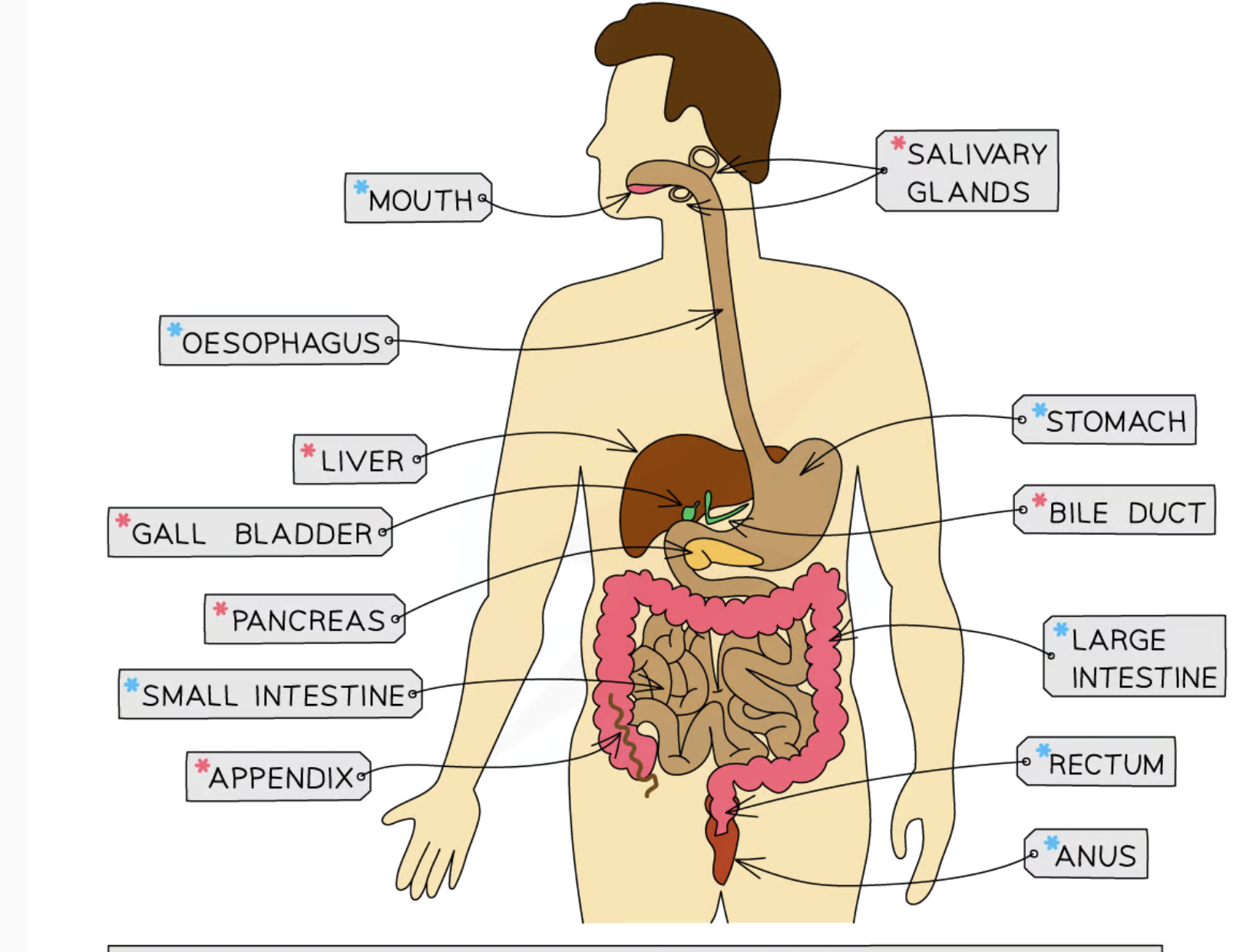
label body diagram
5 stages of digestion (IDAAE)
Ingestion - food enters mouth
digestion - break down large food molecules into smaller molecules
Absorption - small molecules absorbed through small intestine walls into blood
Assimilation - small food molecules are used to build large molecules in body cells
Egestion - removal of undigested food/waste/faeces through anus
what is mechanical digestion vs chemical digestion:
and what it does that for
mechanical - physical break down of food particles into smaller pieces (so enzymes have a bigger surface area to work on)
chemical - chemical break down of food molecules into smaller particles by enzymes, for absorption into bloodstream through small intestine walls
define digestion
… SO THAT
the breaking down of large, insoluble molecules in food into smaller, soluble molecules that can be absorbed into the bloodstream/delivered to cells in the body
mouth:
what kind of digestion/how it happens and why
any enzymes? - where produced/what do they do
in what form does the food leave
mechanical digestion - teeth chew food to break it into smaller pieces to increase its surface area for enzymes to work on it
amylase - from salivary glands starts digesting starch into maltose
food shaped into bolus (ball) by the tongue and lubricated in saliva to be swallowed easily
oesphagus:
what is it
how does food move down it
without relying on _______
tube that connects mouth to the stomach
wave-like contractions (peristalsis) take place to push food bolus down without relying on gravity
stomach:
mechanical vs chemical
enzymes/other substances? why produced
in what form does the food leave
mechanical digestion - churns/pummels food with its muscular walls
chemical digestion
- produces protease PEPSIN to break down proteins
- produces hydrochloric acid to kill bacteria and give optimum pH for protease enzymes to work (pH2 - acidic)
food leaves stomach as chyme
what is the alimentary canal
long channel through which food is digested - starts from mouth, ends at anus
small intestine:
what kind of digestion/how
what enzymes produces
first part vs second part
chemical digestion - produces protease, amylase and lipase
also where nutrients are absorbed out of alimentary canal into body
first part - duodenum, second part - ileum
large intestine:
type of digestion, what happens
first part vs second part
no chemical digestion - no digestive enzymes
excess water is absorbed from remaining food stuff, produces faeces
stored in rectum, removed through anus
pancreas:
what enzymes does it produce
secretes enzymes in an a____ fluid into _____ ______ to…
produces amylase, protease, lipase
secretes enzymes in an alkali fluid into small intestine to lower pH coming out of stomach
liver:
what does it produce
produces bile (more on later)
gallbladder function
stores bile
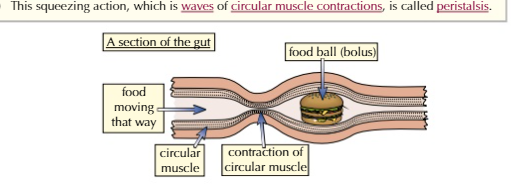
what is peristalsis + draw diagram
a mechanism that helps moves food along the alimentary canal
waves of contractions
w
what are carbohydrases
break down ____ into ____ _____ (general name)
break down carbohydrates into simple sugars
amylase:
where produced (3)
and what does it do
produced in salivary glands, pancreas and small intestine
breaks down starch into maltose
what then breaks maltose into glucose
maltase breaks maltose into glucose
diagram of starch to glucose via enzyme break down draw

what are proteases, where made (3), what does it do
a group of enzymes that break down proteins into amino acids
made in pancreas, stomach, small intestine
what are lipases, where produced
enzymes that break down lipids (fats) to glycerol and fatty acids
produced in pancreas and small intestine
where is bile produced vs stored vs released
is an a____ substance
produced in the liver
stored in the gallbladder
released into small intestine
is an alkaline substance, high pH
bile function (2) and why it is important
Neutralising the hydrochloric acid from the stomach
The alkaline properties of bile allow for this to occur
This neutralisation is essential as enzymes in the small intestine have a higher (more alkaline) optimum pH than those in the stomach
Breaking apart large drops of fat into smaller ones (and so increasing their surface area)
This is known as emulsification
The more alkaline conditions and larger surface area allows lipase to chemically break down the fat (lipids) molecules into glycerol and fatty acids at a faster rateglycerol and fatty acids at a faster rate
what kind of digestion does bile do
mechanical - big chunks into small chunks, has no enzymes
what is emulsification
Breaking apart large drops of fat into smaller ones, increasing their surface area
general adaptations of small intestine
very long
highly folded surface
with millions of villi
increase surface area so absorption takes place faster and more efficiently
how specifically do villi help small intestine
large surface area
microvilli on surface of villus further increase SA available for absorption
wall of villus only one cell thick
short diffusion distance = faster diffusion
network of capillaries
network of blood capillaries transport glucose/amino acids away from small intestine in the blood
has a lacteal (lymph) which runs through centre of villus, transports fatty acids and glycerol away
keeps a steep concentration gradient - faster diffusion
how to find Energy Content of a Food Sample, unofficial
use a MOUNTED NEEDLE to burn a piece of food under a boiling tube of water, record temperature of water after
the larger the increase in water temperature, the ______ energy
the larger the increase in water temperature, the more energy
energy transferred formula + units
what does the constant mean
4.2 - it takes 4.2J of energy to raise 1g of water by 1oc
(specific heat capacity of water)
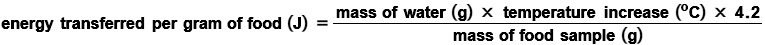
limitations (2)
incomplete burning
heat energy lost to surroundings
energy in food sample CORMMS
C - change type of food in sample
O - n/a
R - repeat x3 for each food sample, take avgs.
M - measure change in temperature of water
M - in oC, once all food has been burnt
S - control volume of water, distance between food and boiling tube, food will be relit every time it goes out