Unit 8: Globalization
1/26
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
Globalization
The expansion of economic, political, and cultural processes to the point that they become global in scale and impact.
Commercial Industry
Companies are usually factory based and employ many workers. The goal is to produce as many products as possible.
Seen primarily in countries of medium and high levels of development
Cottage Industry
A small scale manufacturing business owned and operated by an individual often from home.
Seen primarily in countries of low levels of development, BUT occurs in all levels of development (ex: Etsy in the US)
Subsistence Agriculture
Agriculture designed primarily to provide food for direct consumption by the farmer and the farmer's family.
Seen primarily in countries of low levels of development and a large portion of the country's workforce is employed as farmers
Commercial Agriculture
Agriculture undertaken primarily to generate products for sale off the farm.
Seen primarily in countries of medium and high levels of development and a small portion of the country's workforce is employed as farmers
Trade Agreement
An enforceable agreement between two or more countries that involves establishing the terms of trade, the movement of goods and services, the elimination of trade barriers and encourages foreign investments.
NAFTA
North American Free Trade Agreement; allows open trade between US, Mexico, and Canada with the elimination of trade barriers. It sets the rules for the movement of goods, services and investments.
TPP11
Trans-Pacific Partnership; a trading bloc of 11 countries surrounding the Pacific Ocean that aims at strengthening and diversifying trade and investments in the region.
EU
European Union; includes 27 countries in Europe with the goal of promoting greater unity by creating interdependent economies
Fair Trade
Trade between companies in developed countries and producers in developing countries in which fair prices are paid to the producers.
Difference between fair trade and free trade
- Fair trade benefits small farmers and producers
- Fair Trade includes reinvesting in producer communities
- Fair Trade helps ensure safe working conditions, environmental practices and promotes equity.
Suez Canal
located in Egypt and provided shorter route to India and East Asia
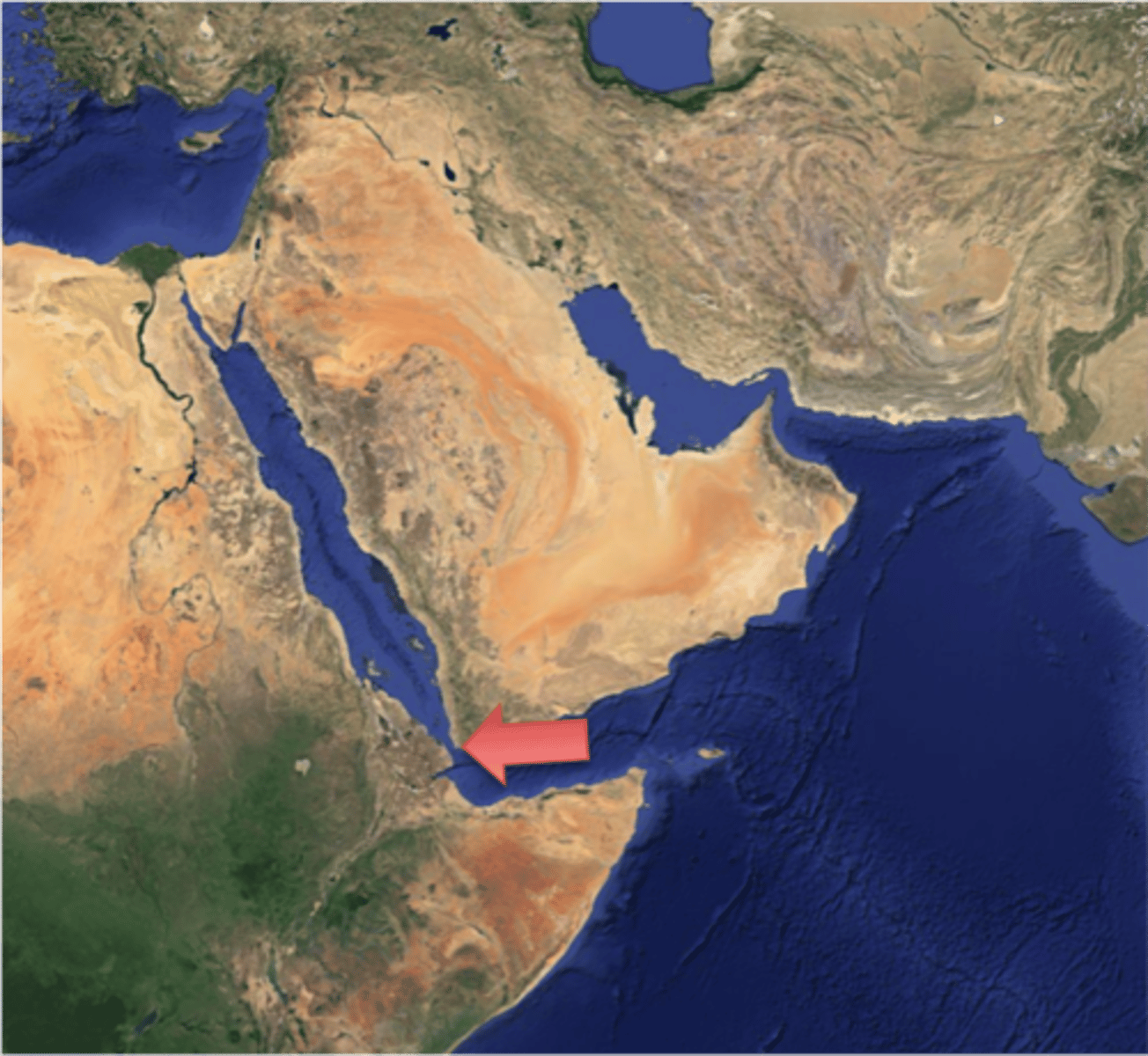
Mandeb Strait
It connects the Red Sea to the Gulf of Aden.
English Channel
body of water that separates France and England
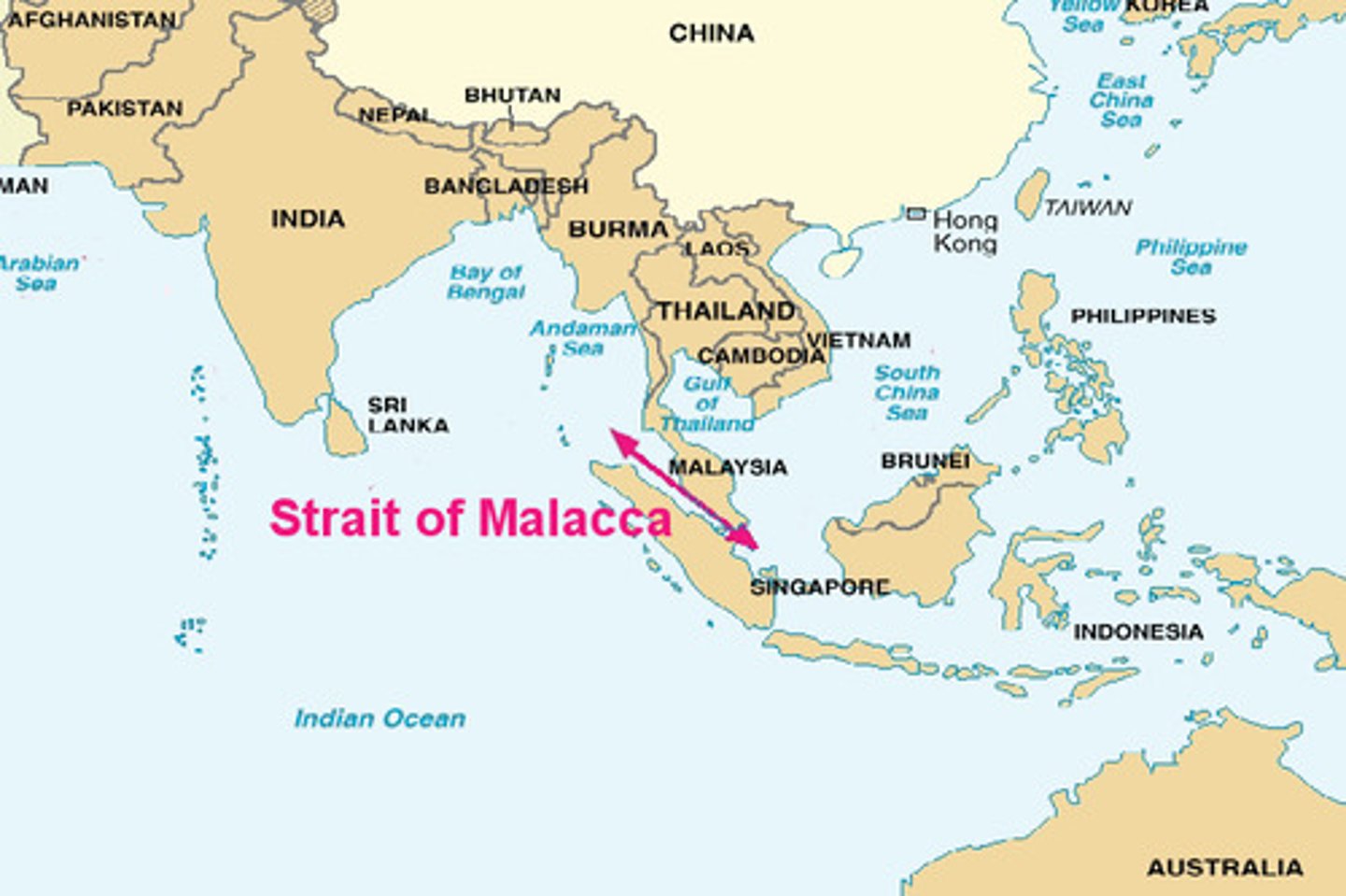
Strait of Malacca
Narrow waterway located between the islands of Sumatra and Java, Body of water connecting the Indian and Pacific Ocean near Singapore.
Panama Canal
Ship canal cut across the isthmus of Panama, connects the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean
Evolution of trade
1. Barter System: exchange of goods before money
2. Silk Road: movement of goods, ideas, religions and diseases from Asia to Europe
3. Gold & Salt Trade: In Africa, camels moved salt across the desert in exchange for gold
4. Columbian Exchange: used ships to transport goods and people between Europe, Africa and the Americas.
5. Railroads: trains moved goods quickly across long distances.
6. Trucking: most efficient way to transport goods to individual stores and consumers
Trade Liberalization
The reducing of restrictions on trade
Benefits of shipping/containerization
- shipping containers come in standard sizes, making them easier to stack and transport
- contents are unknown, which makes it less prone to spoilage
- containers make loading and unloading more efficient
Benefits of railroads
- cost effective to move large quantities of goods long distances
- helps reduce congestion of roads and highways
- developing and maintaining railroads can create jobs and stimulate the economy
Benefits of trucking/roads
- roads can be built in remote places making isolated areas more accessible
- roads can be in countries of all levels of development
- roads can provide direct routes and thus reduce travel time and fuel consumption
Outsourcing
Setting up business abroad to produce parts or products for domestic use or sale
Companies outsource for the following reasons:
- to be closer to natural resources needed for the production of goods
- cheaper labor costs
- the locations chosen for outsourcing already had the infrastructure required (i.e. ports and factories)
Pandemic
Spread of a disease across a large area, country, continent, or the entire world
Actions that can be taken to combat a pandemic:
- stay at home/ quarantine procedures
- countries close borders and trade slows down
- develop vaccines against the virus that is spreading
Cultural Convergence
When two or more cultures influence each other and become similar with increased contact
This occurs in our globalized world today through the use of social media
Benefits of a fully connected world
- increased connectivity
- improved access to information
- greater convenience
- global connections
Downsides of a fully connected world
- privacy concerns
- cybercrime
- dependency on technology
- disinformation
Impact of migrant labor
Agricultural migrant labor contributed $9 billion per year to the fruit and veggie industry in the United States