Fundamentals of the Nervous System and Ner
1/49
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
50 Terms
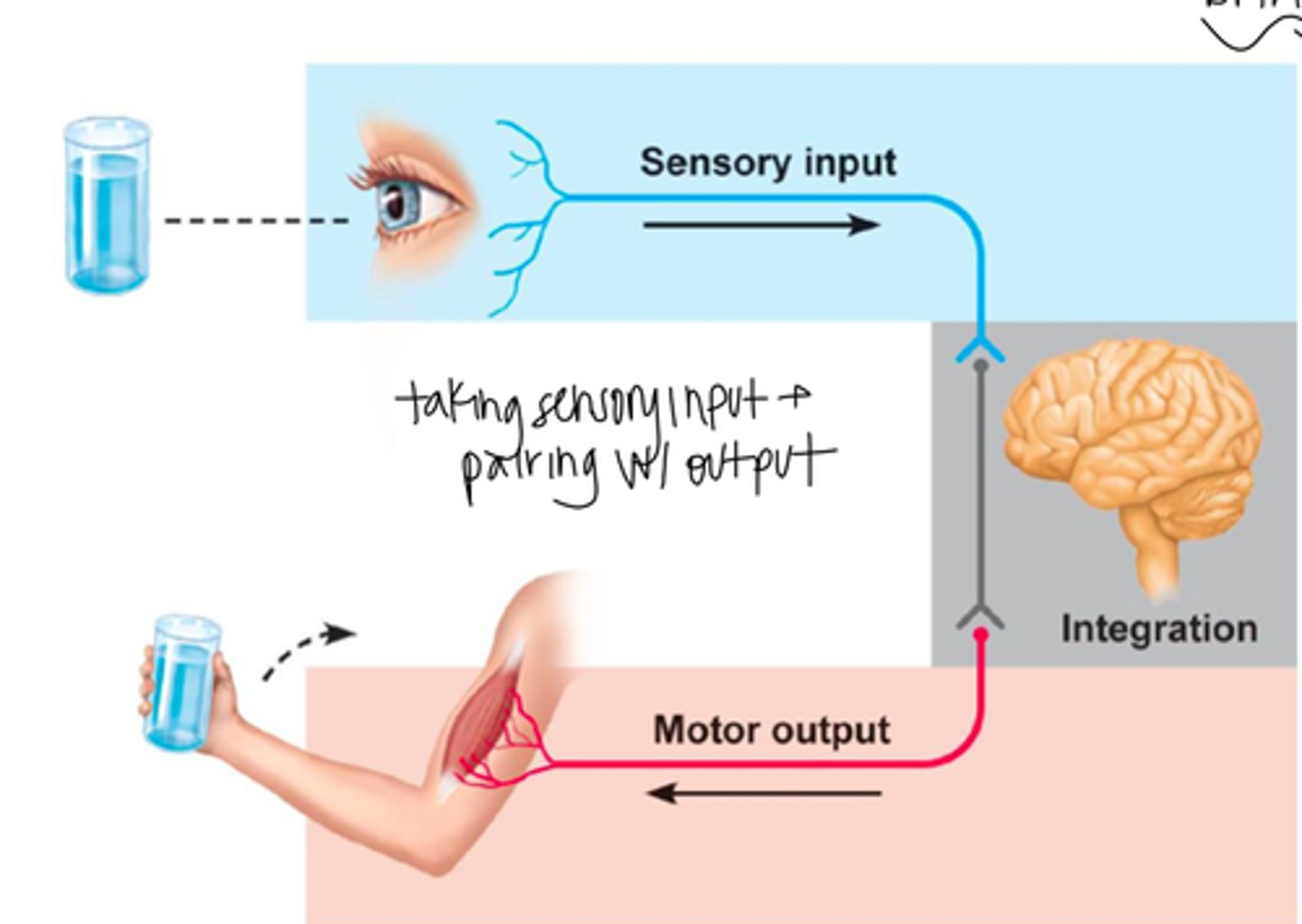
Functions of the Nervous System
Sensory Input, Integration, Motor Output (activates effectors)
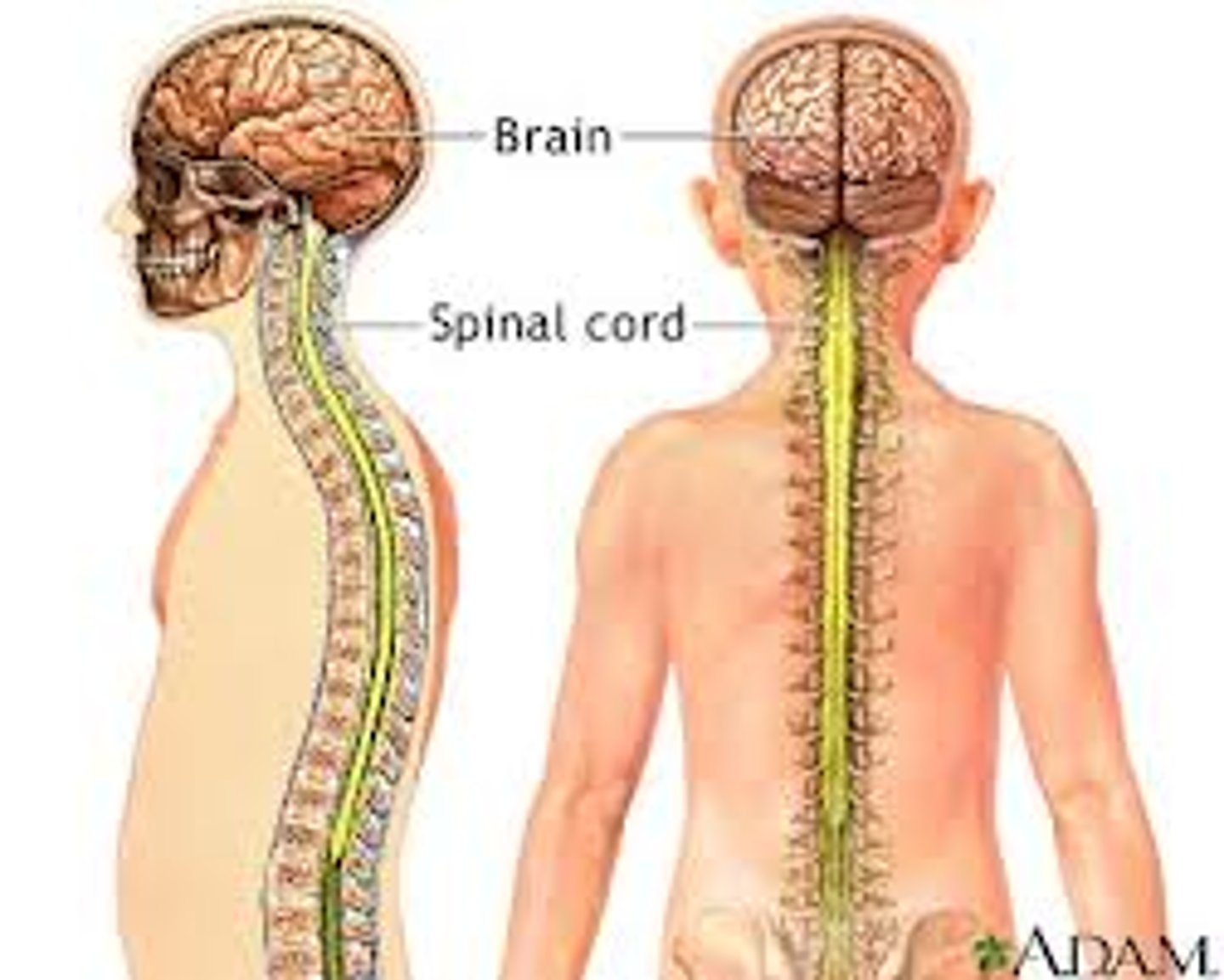
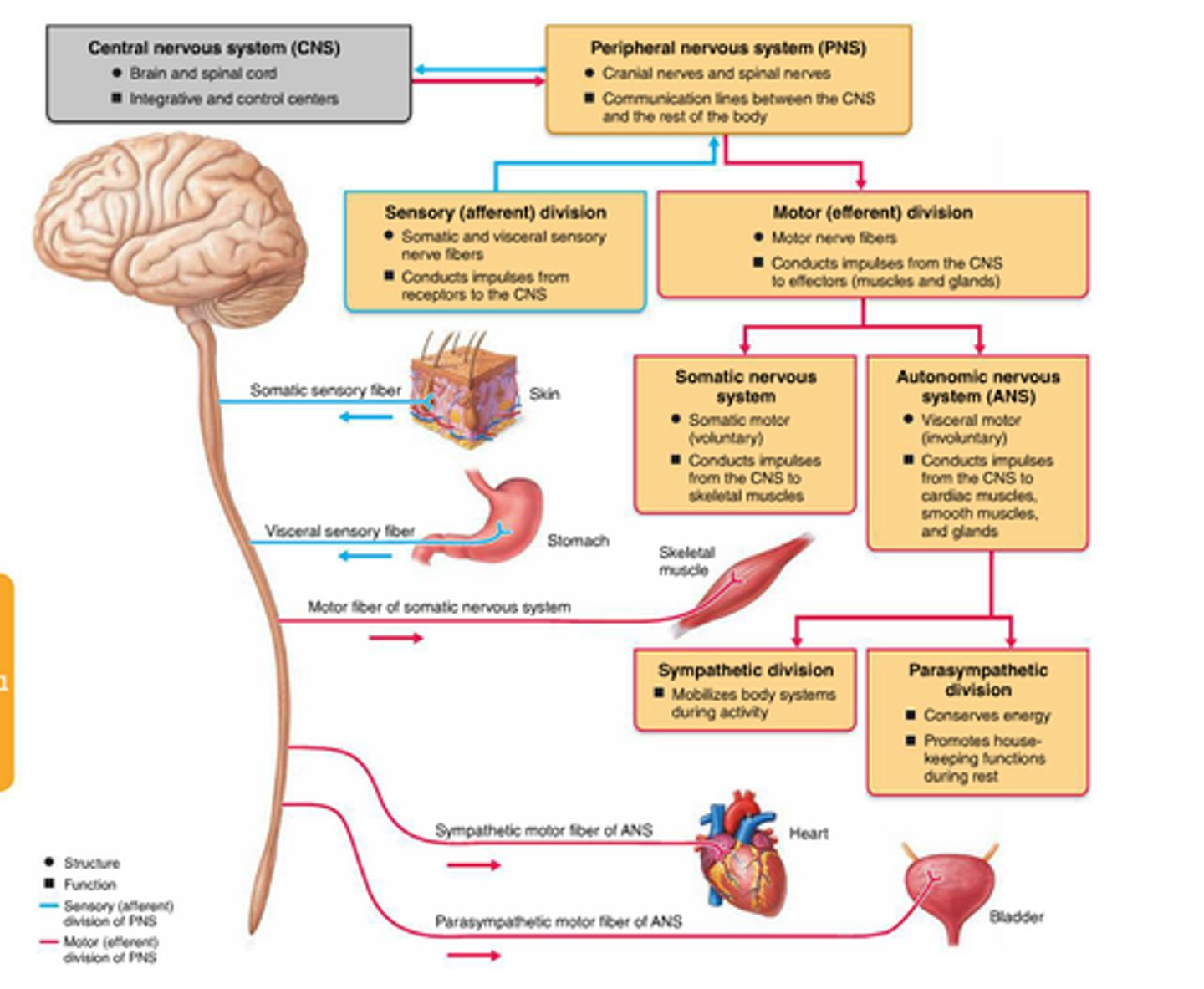
Central Nervous System
Brain and spinal cord
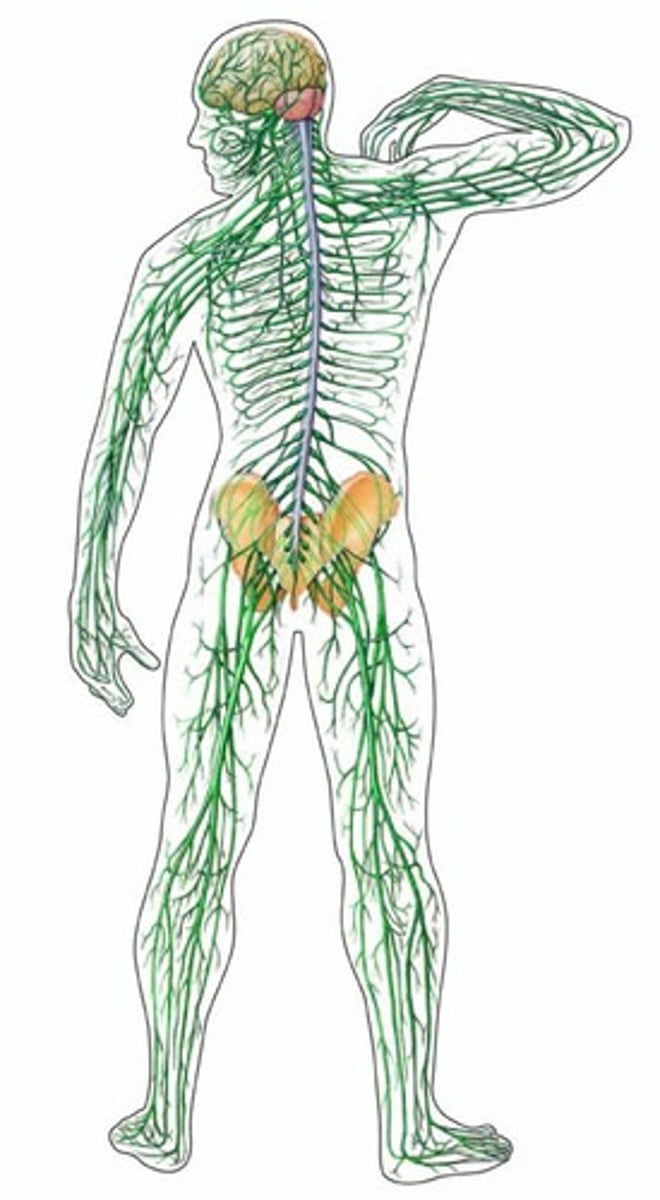
Peripheral Nervous System
Nerves outside the brain and spinal cord
Sensory (afferent) division
Nerve fibers (axons) that carry information to the CNS
Motor (efferent) division
Nerve fibers (axons) that carry impulses away from the CNS, subdivided into the Somatic Nervous System and Autonomic Nervous System (Sympathetic and Parasympathetic)
CNS neuroglia
much smaller than neurons and outnumber them in the CNS by 10 to 1 (make up half the mass of the brain), astrocytes, microglia, ependymal cells, oligodendrocytes
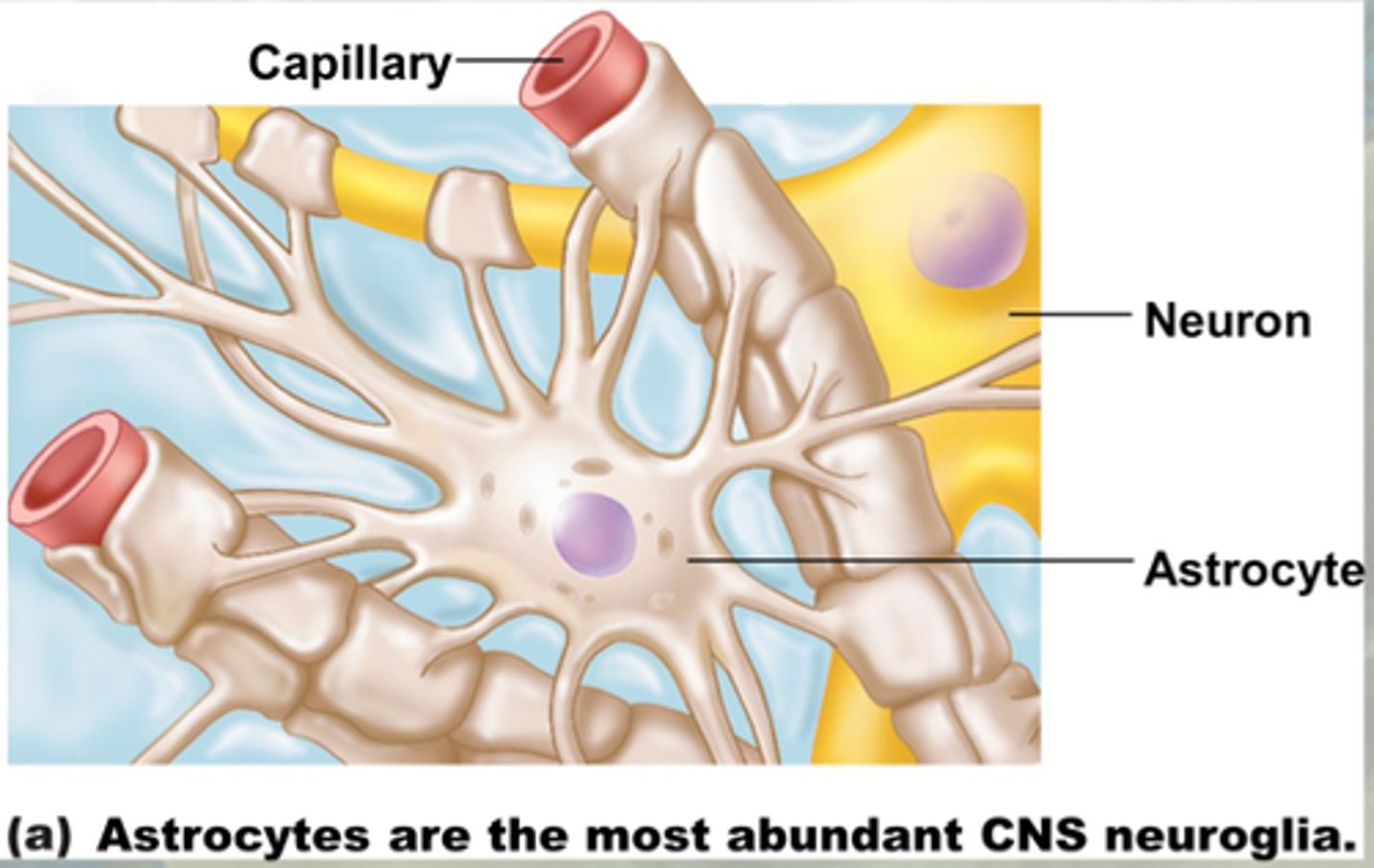
Astrocytes
most abundant and versatile, star shaped, link neurons to their nutrient source (capillaries), form blood-brian barrier between capillaries and neurons, control chemical environment around neurons, mop up K+ ions and recapture released NTs
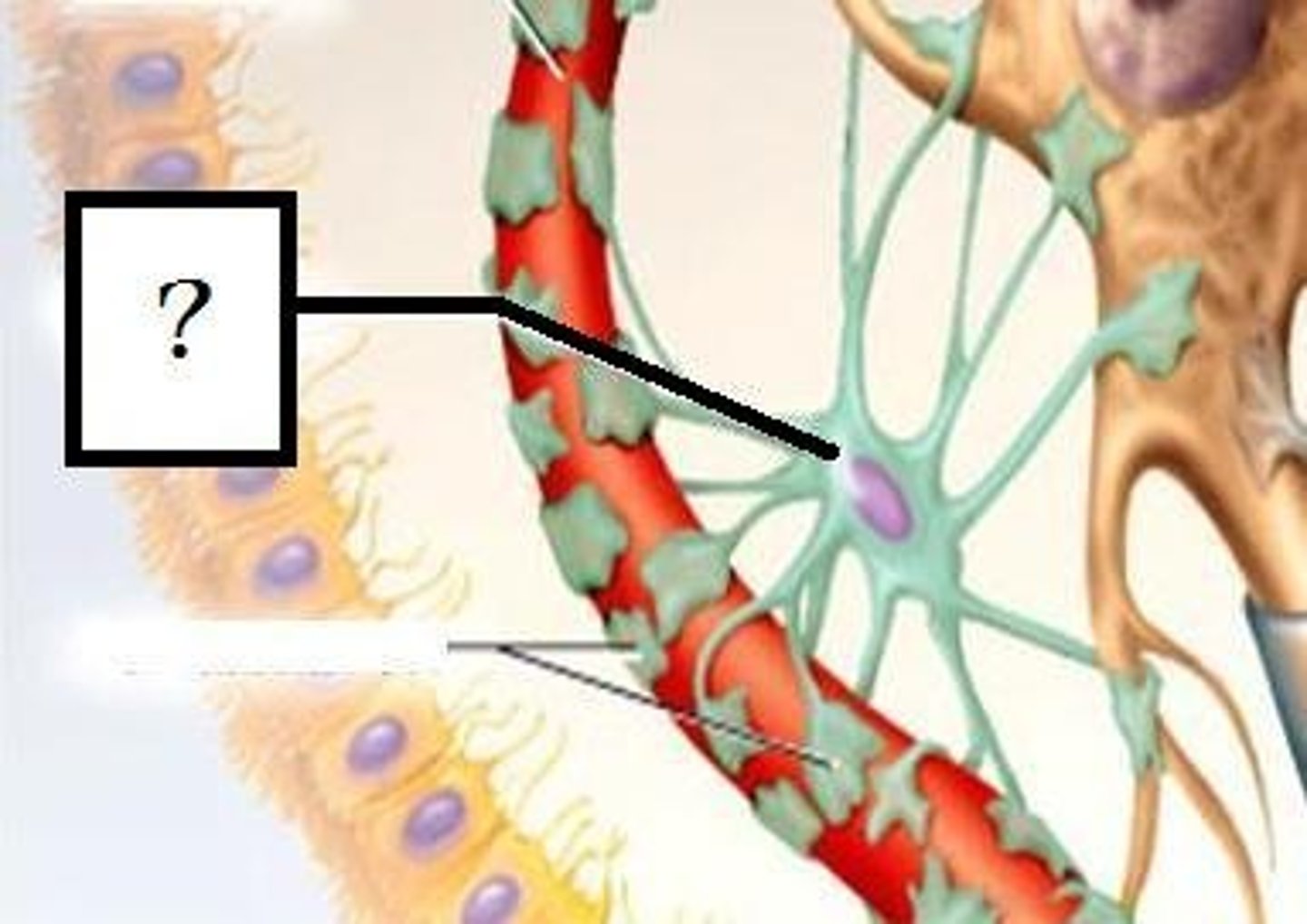
Microglia
spider-like phagocytic macrophages, will migrate toward neurons when they sense they are injured, dispose of neuronal debris and invading microorganisms, (immune system cells cannot access the CNS), increased presence indicate brain damage
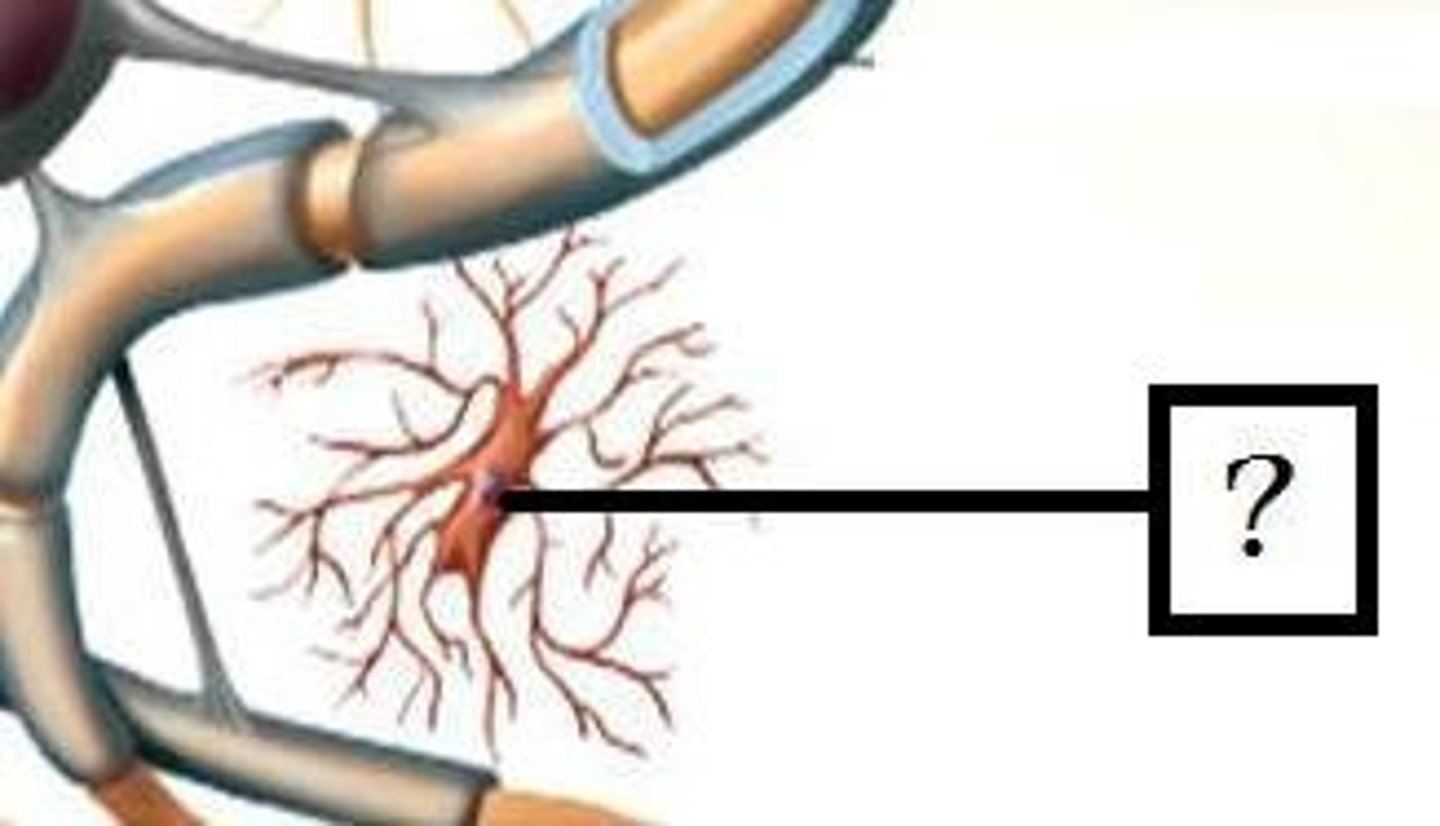
Ependymal Cells
line cavities of the brain and spinal cord, contain cilia that circulate cerebrospinal fluid (CSF)
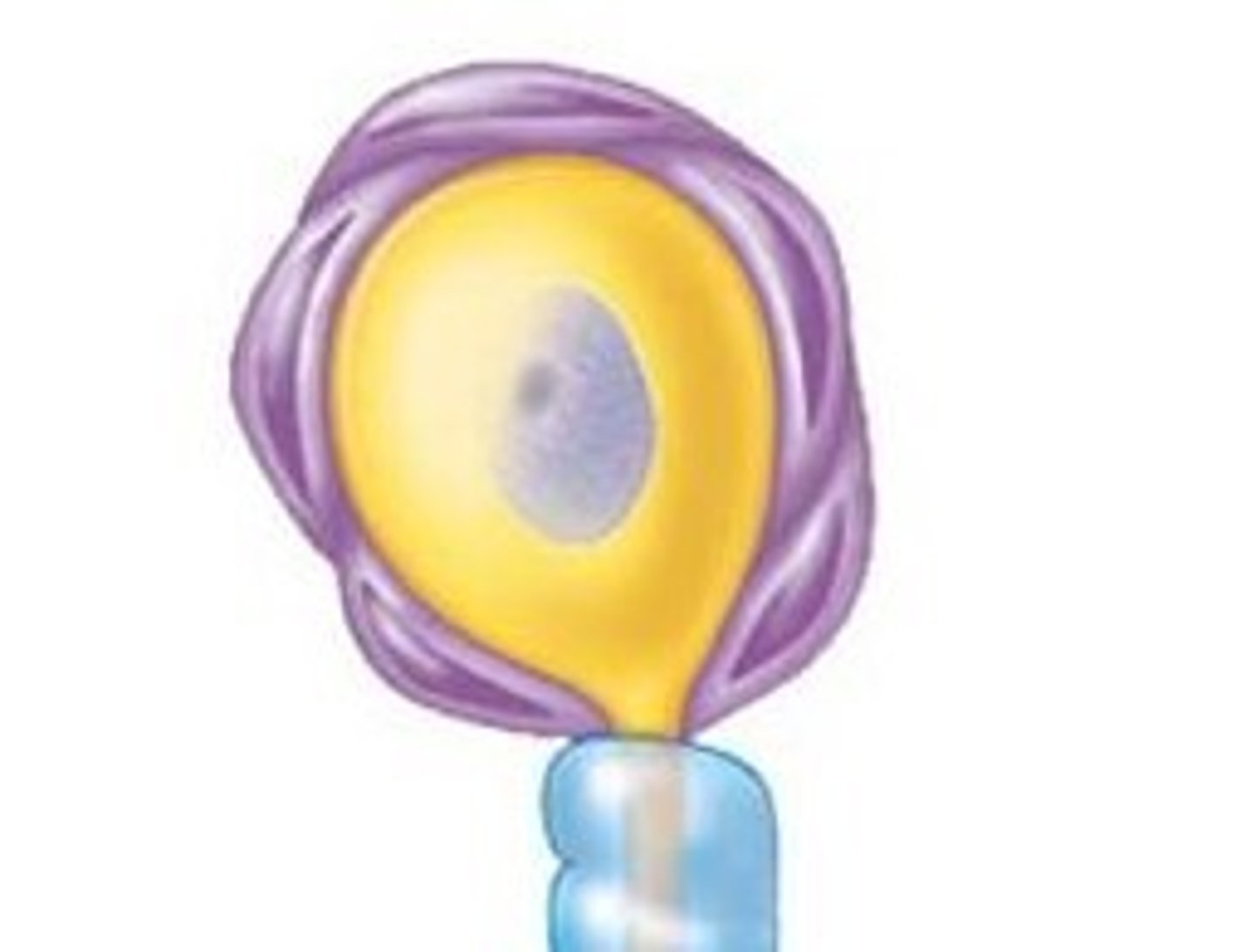
oligodendrocytes
forms myelin sheath in the CNS
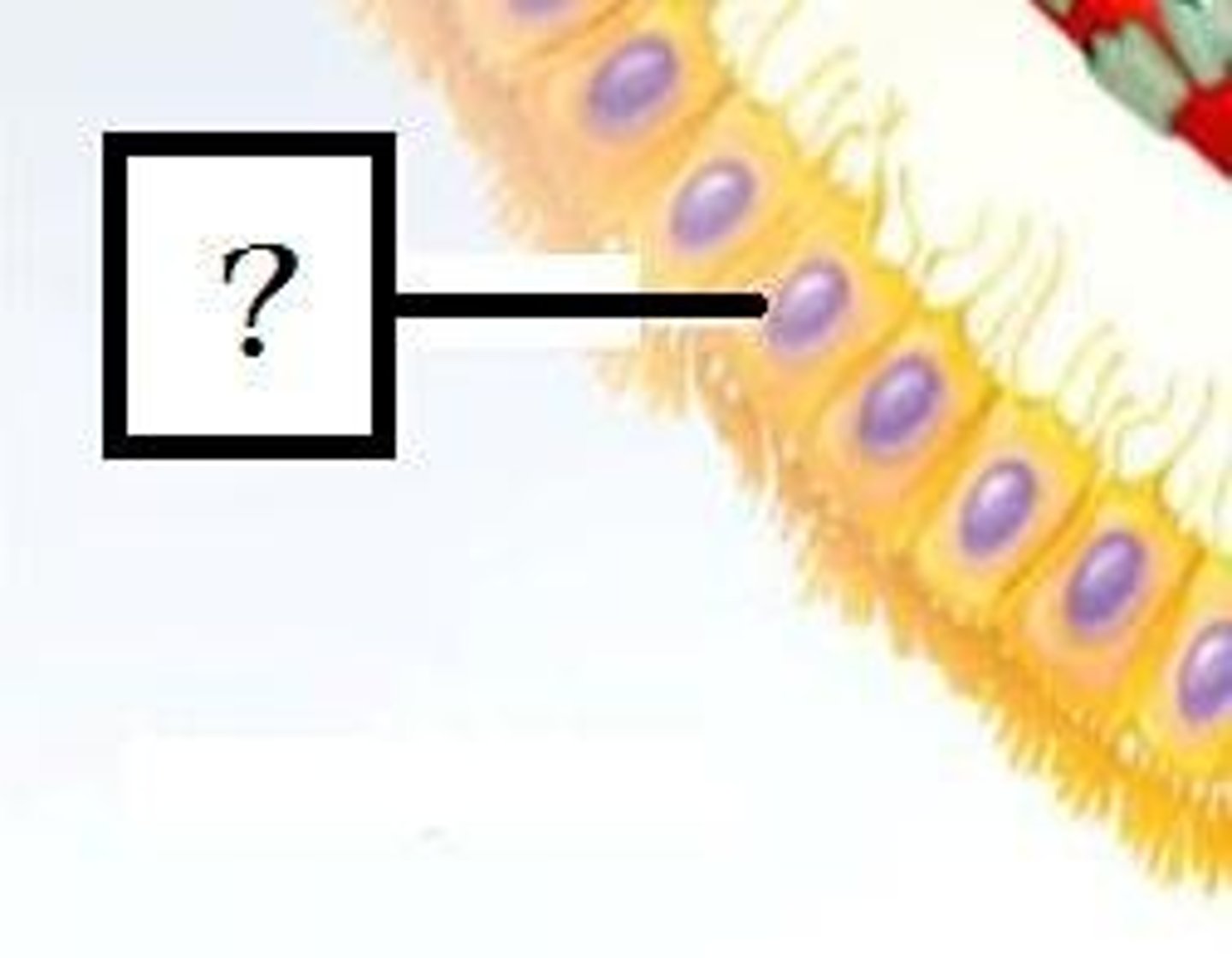
Satellite cells
surround and protect neuronal cell bodies in PNS
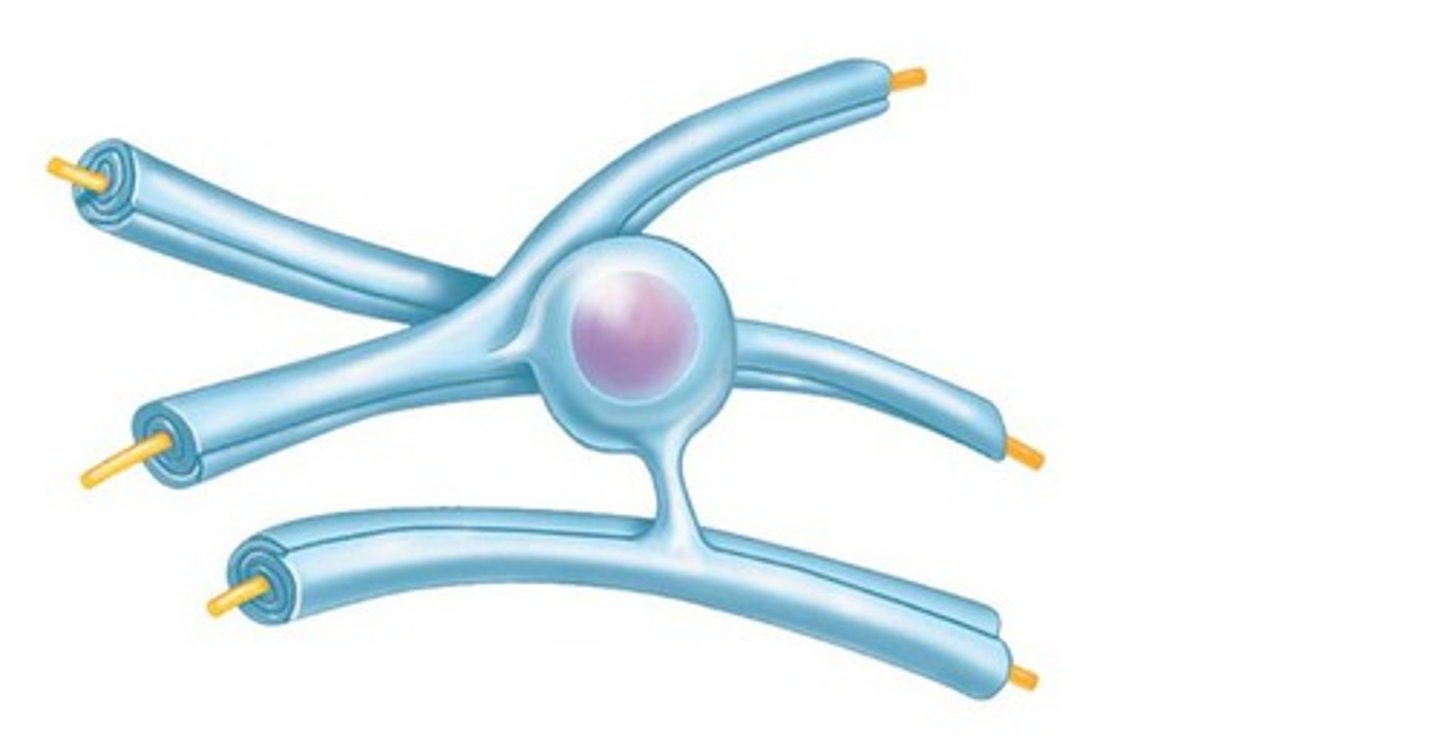
Schwann cells
forms myelin sheath around axons in PNS, also vital to regeneration of damaged peripheral nerve fibers
Nuerons (nerve cells)
irritability, conductivity, extreme longevity, amitotic, high metabolic rate
Ganglion
collection of cell bodies outside the CNS
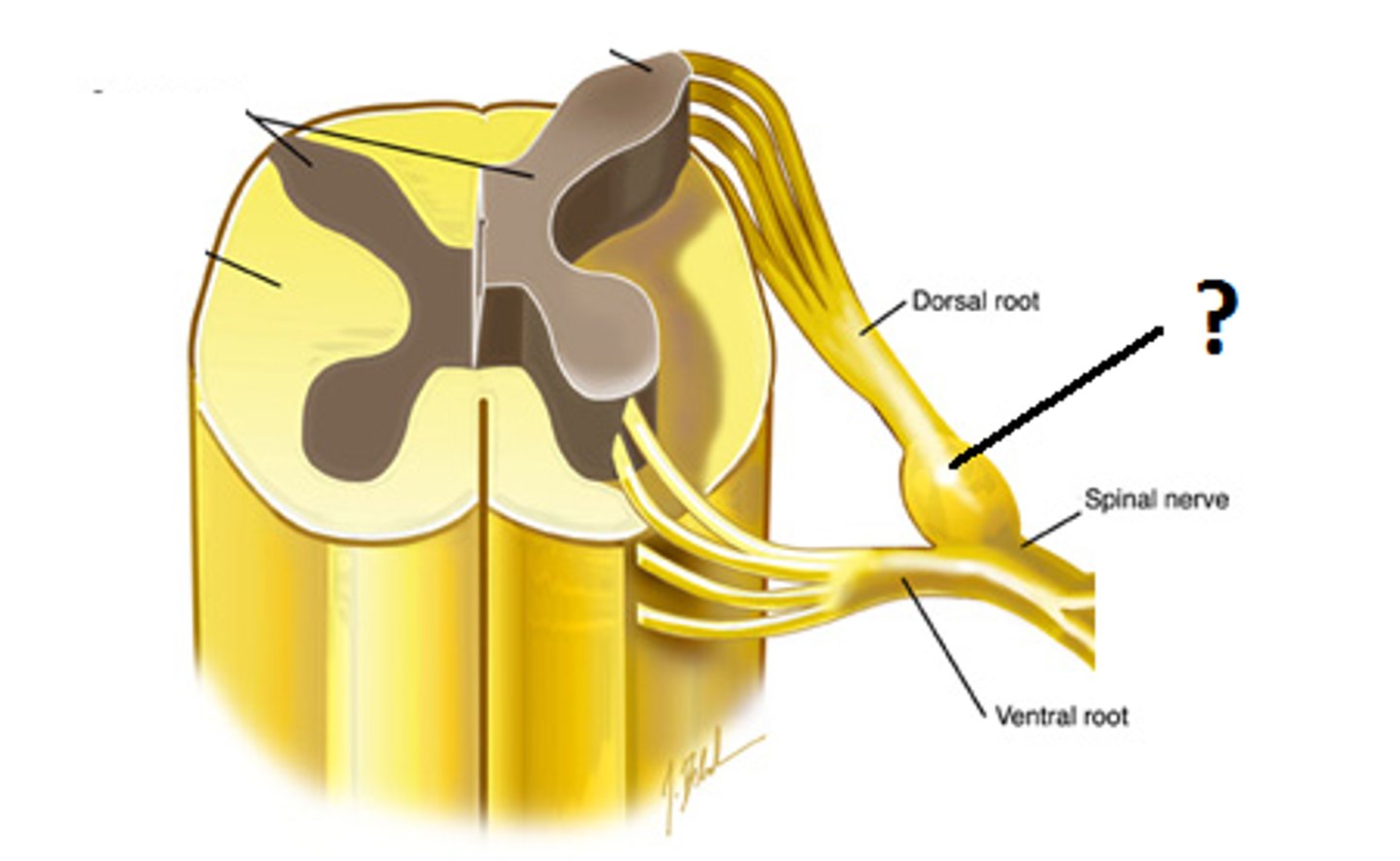
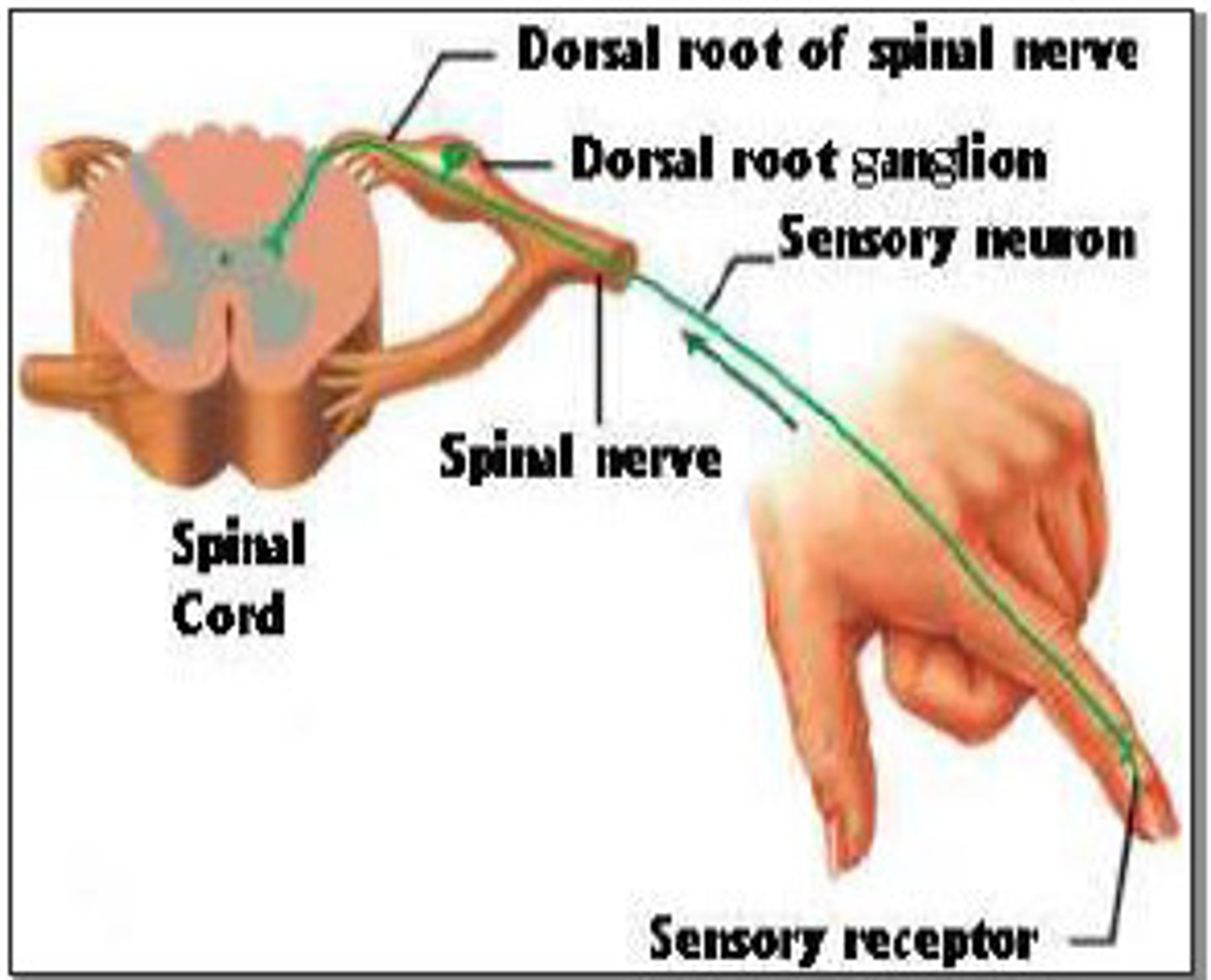
dorsal root ganglion
contains cell bodies of sensory neurons
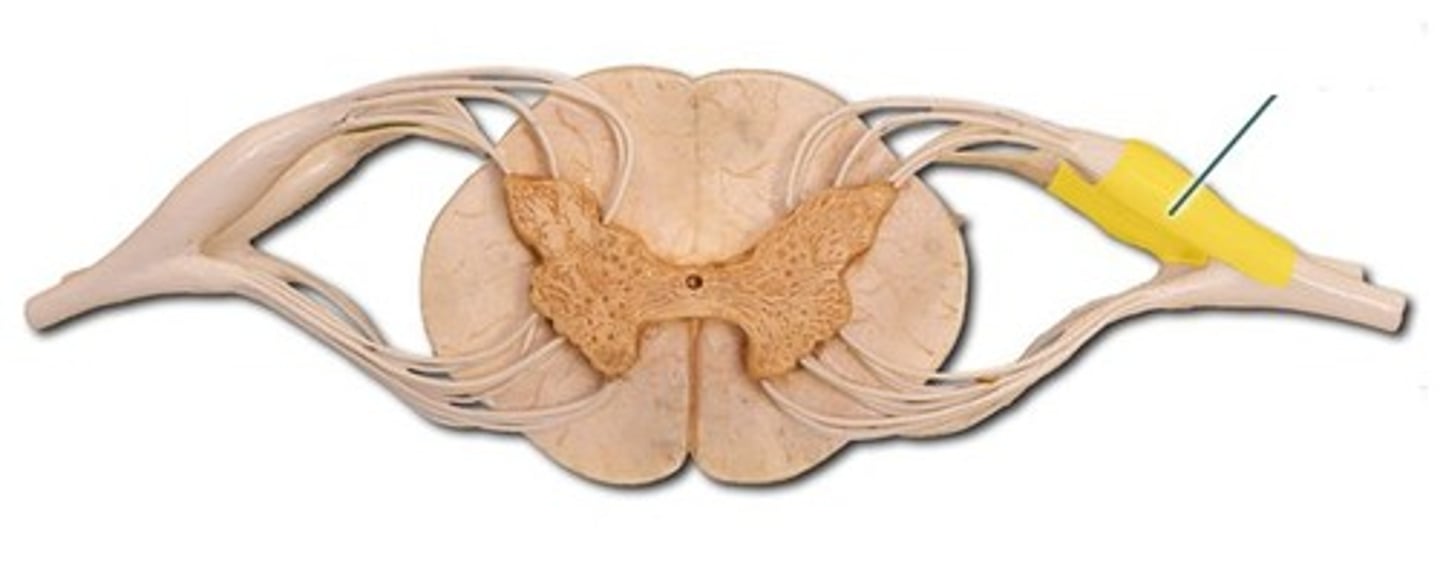
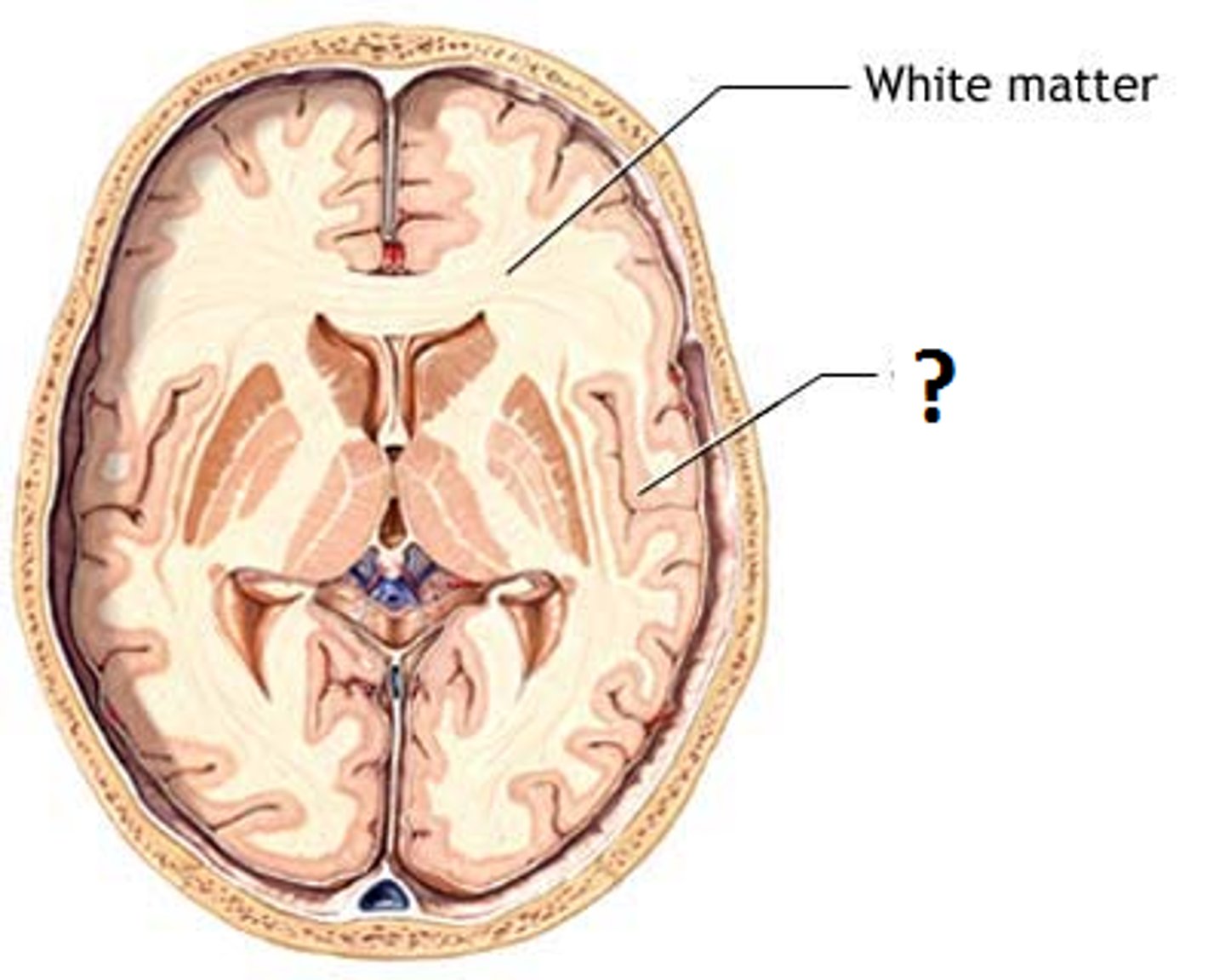
White matter
dense collections of myelinated fibers (on the outside in spinal cord)
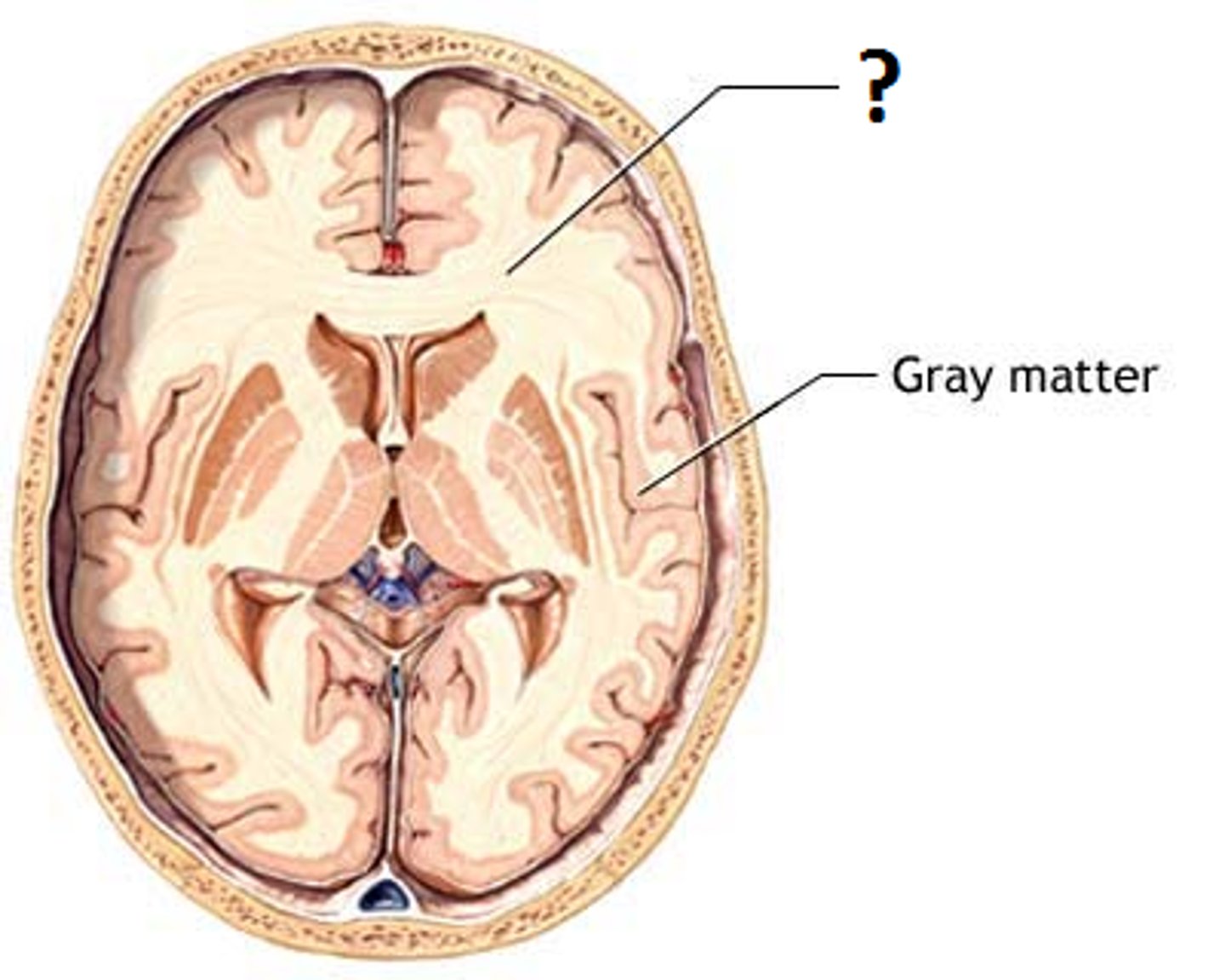
Grey matter
Collections of unmyelinated fibers and cell bodies
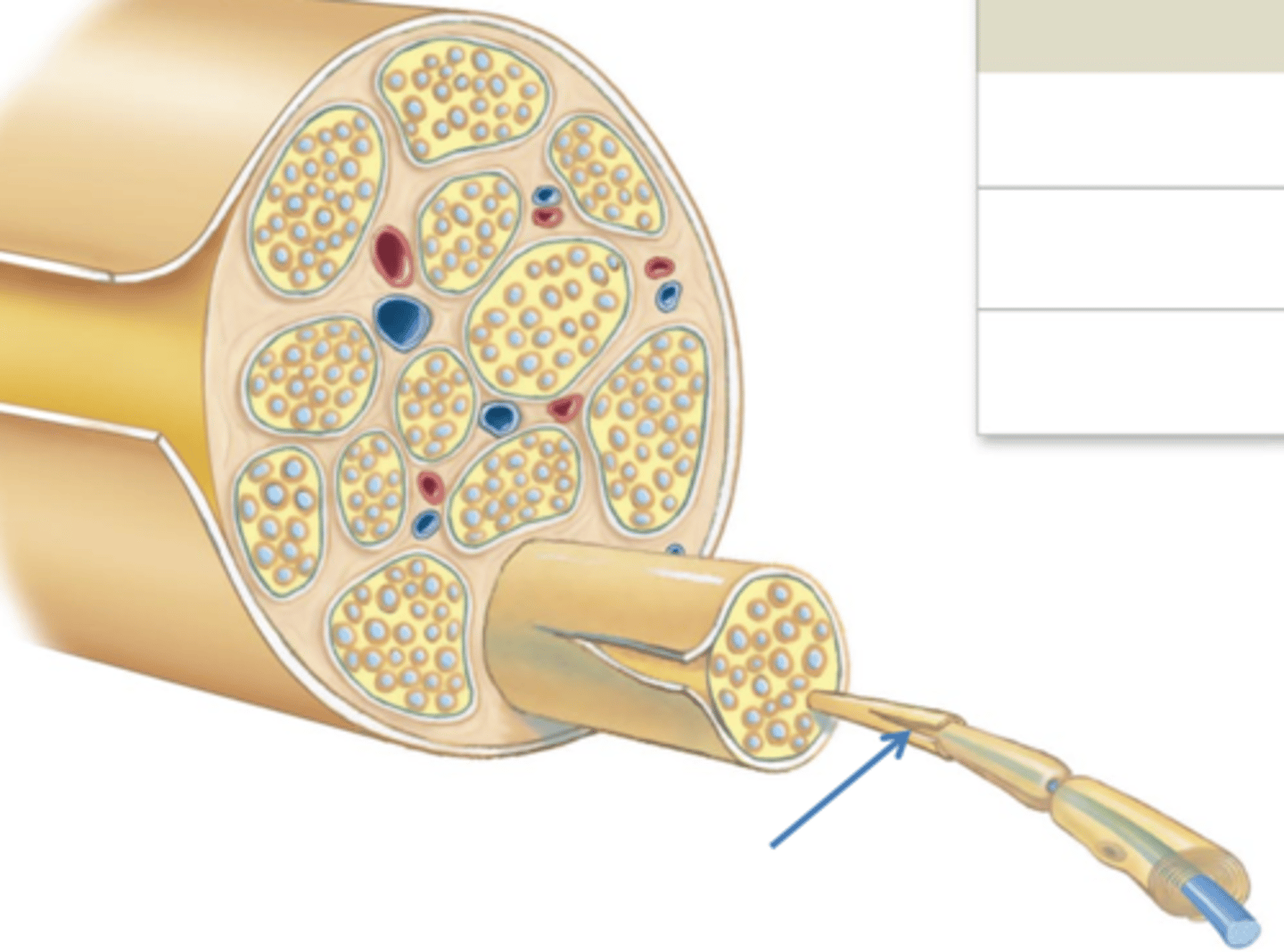
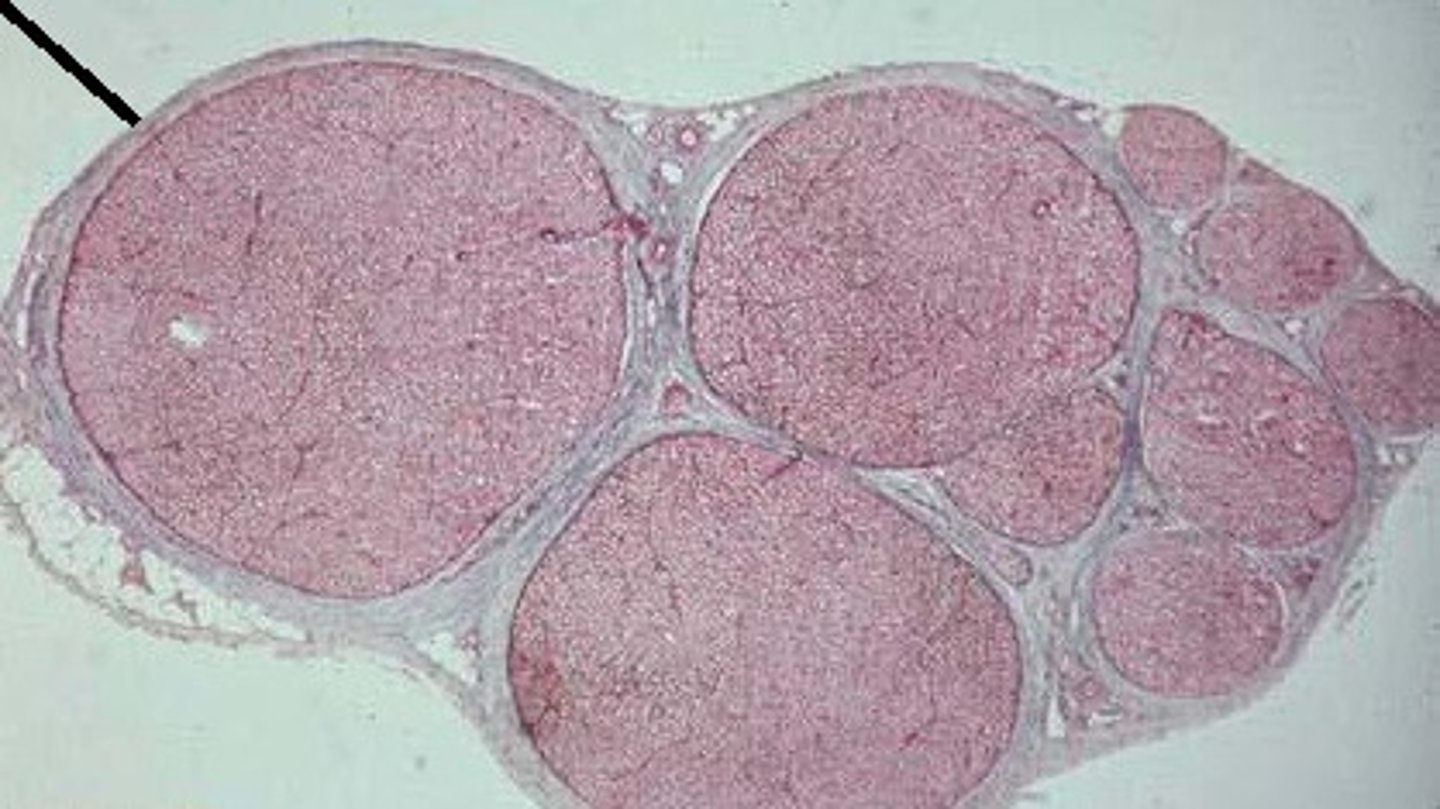
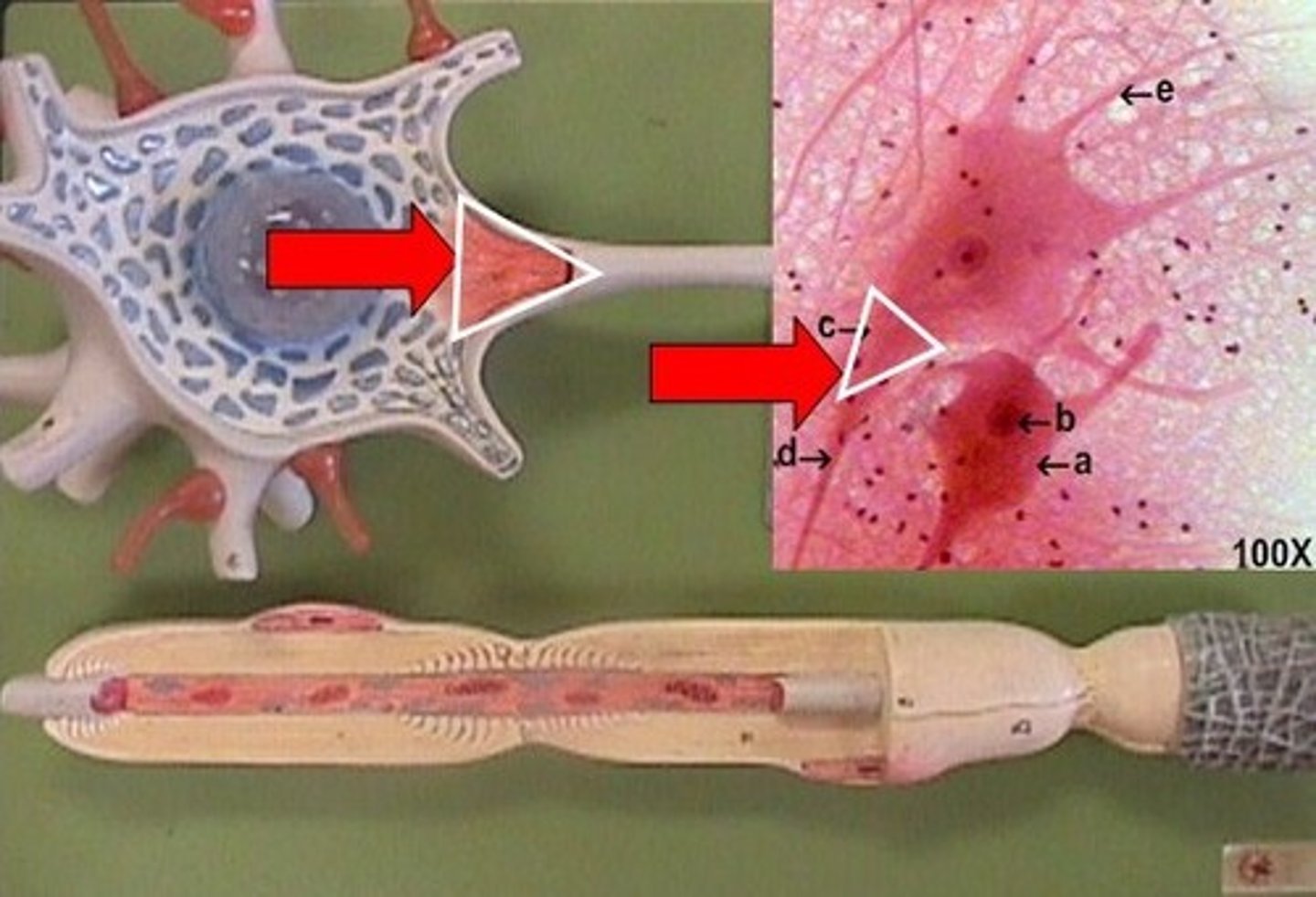
Endoneurium
delicate connective tissue around individual nerve fibers in nerve
Perineurium
coarse connective tissue that bundles fibers into fascicles
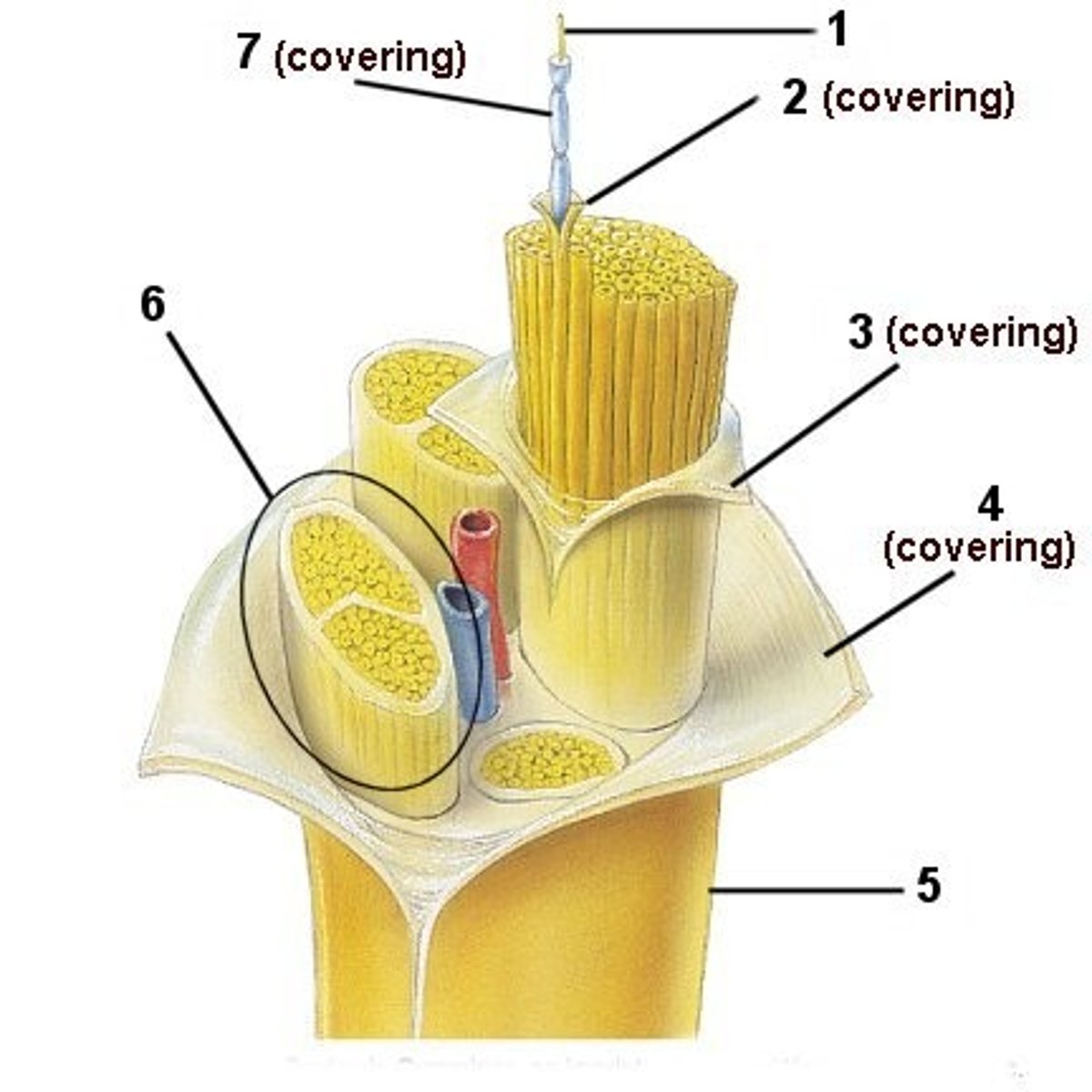
Epineurium
surrounds the entire nerve
Cell body (soma)
signal integration, metabolic center of cell and contains organelles
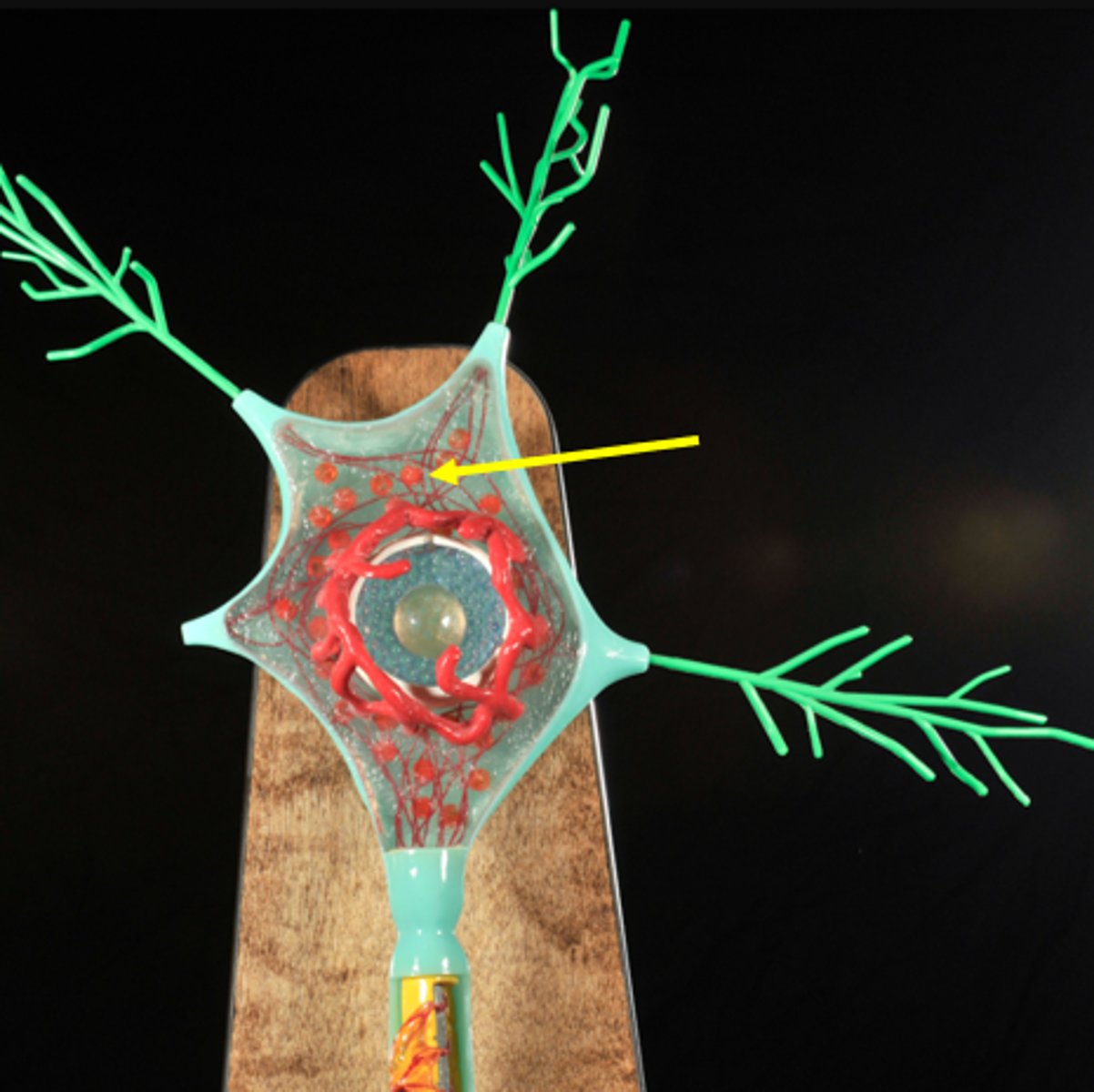
Chromatophilic Substance (Nissl bodies)
clusters of RER and ribosomes which produce membrane and proteins
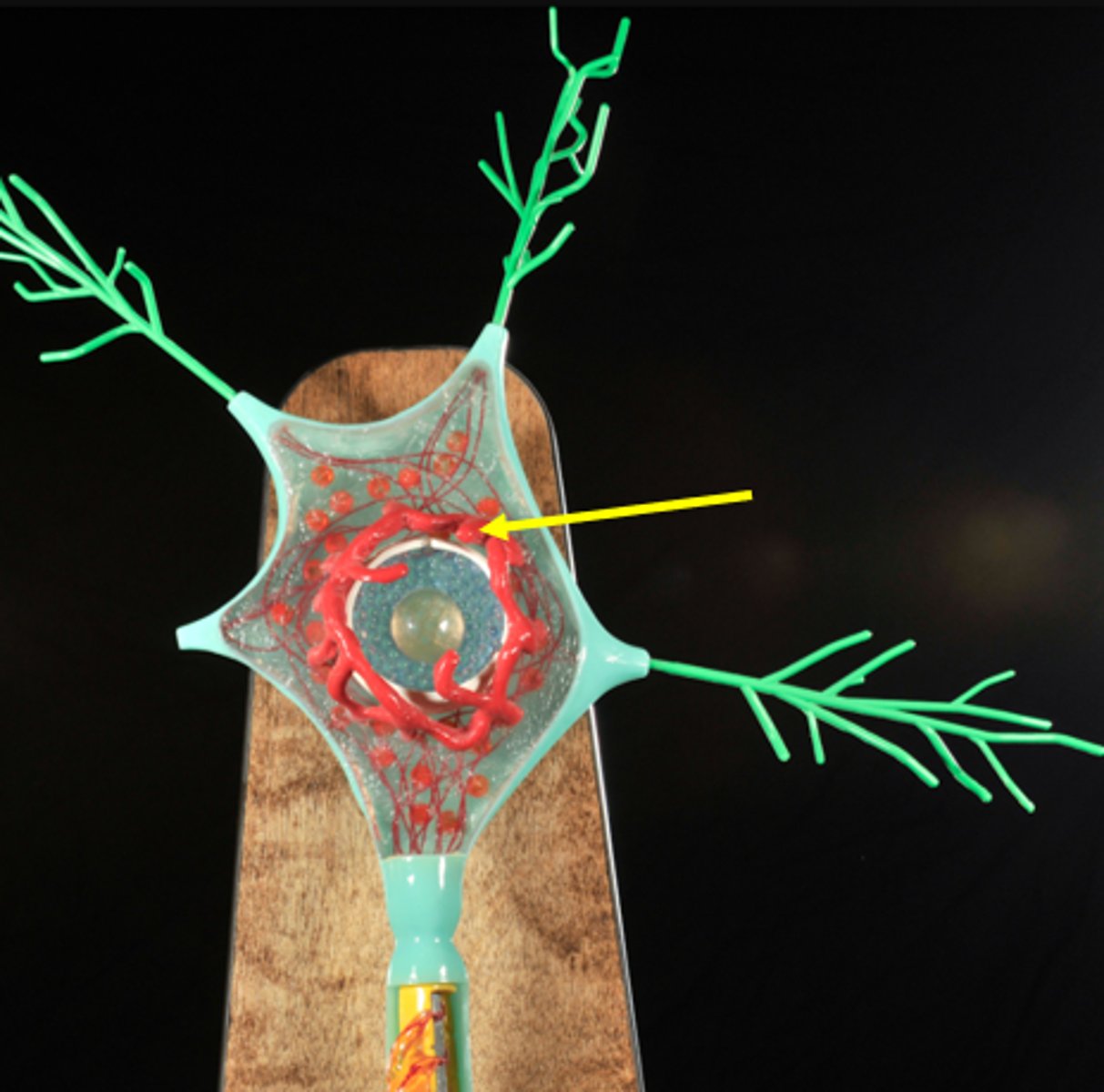
Golgi Apparatus
forms complete circle around nucleus
Neurofibrils
maintain cell shape and integrity
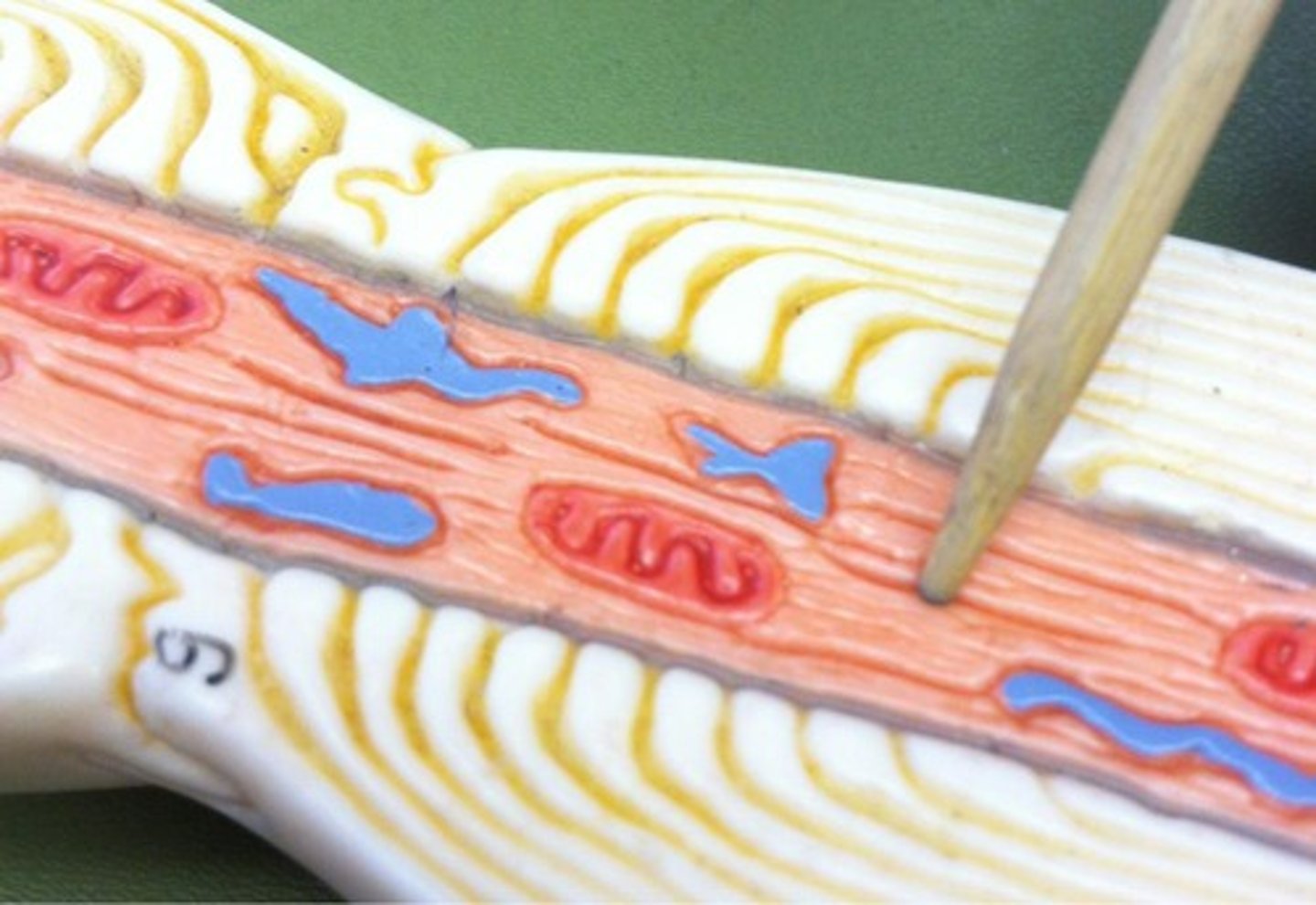
Nucleolus
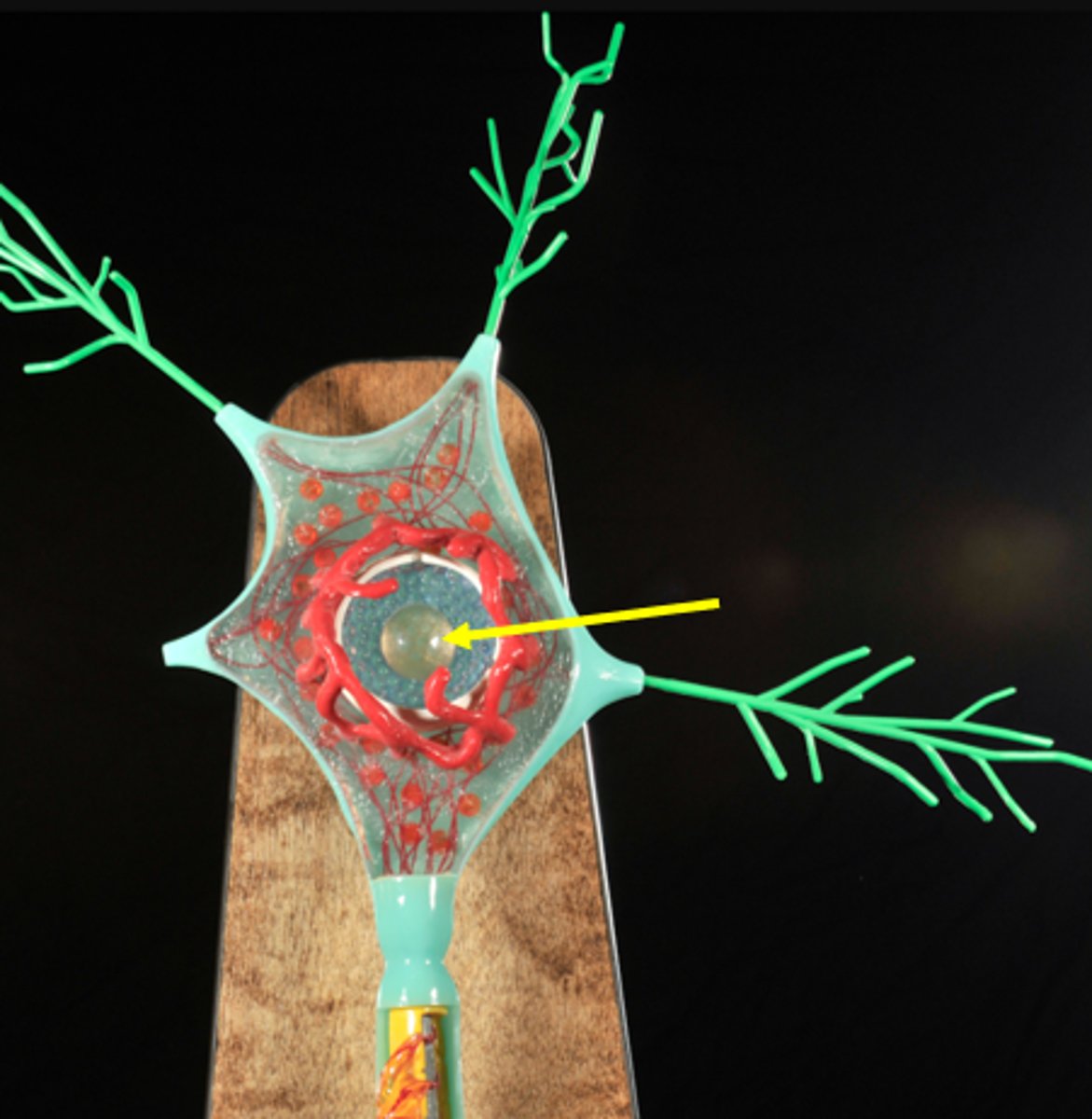
Processes
fibers that extend from the cell body
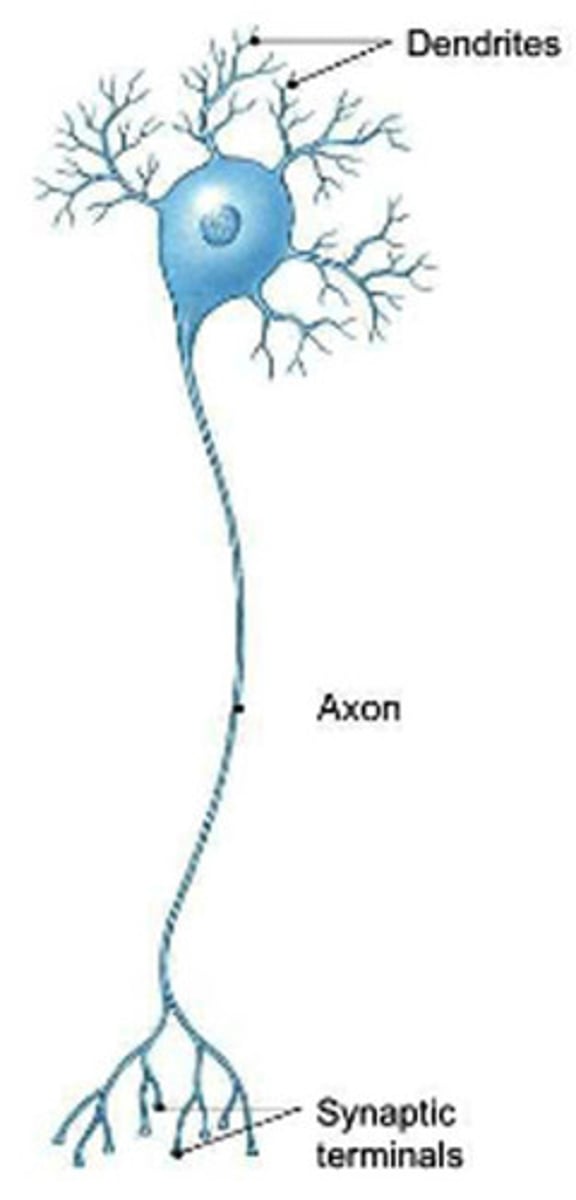
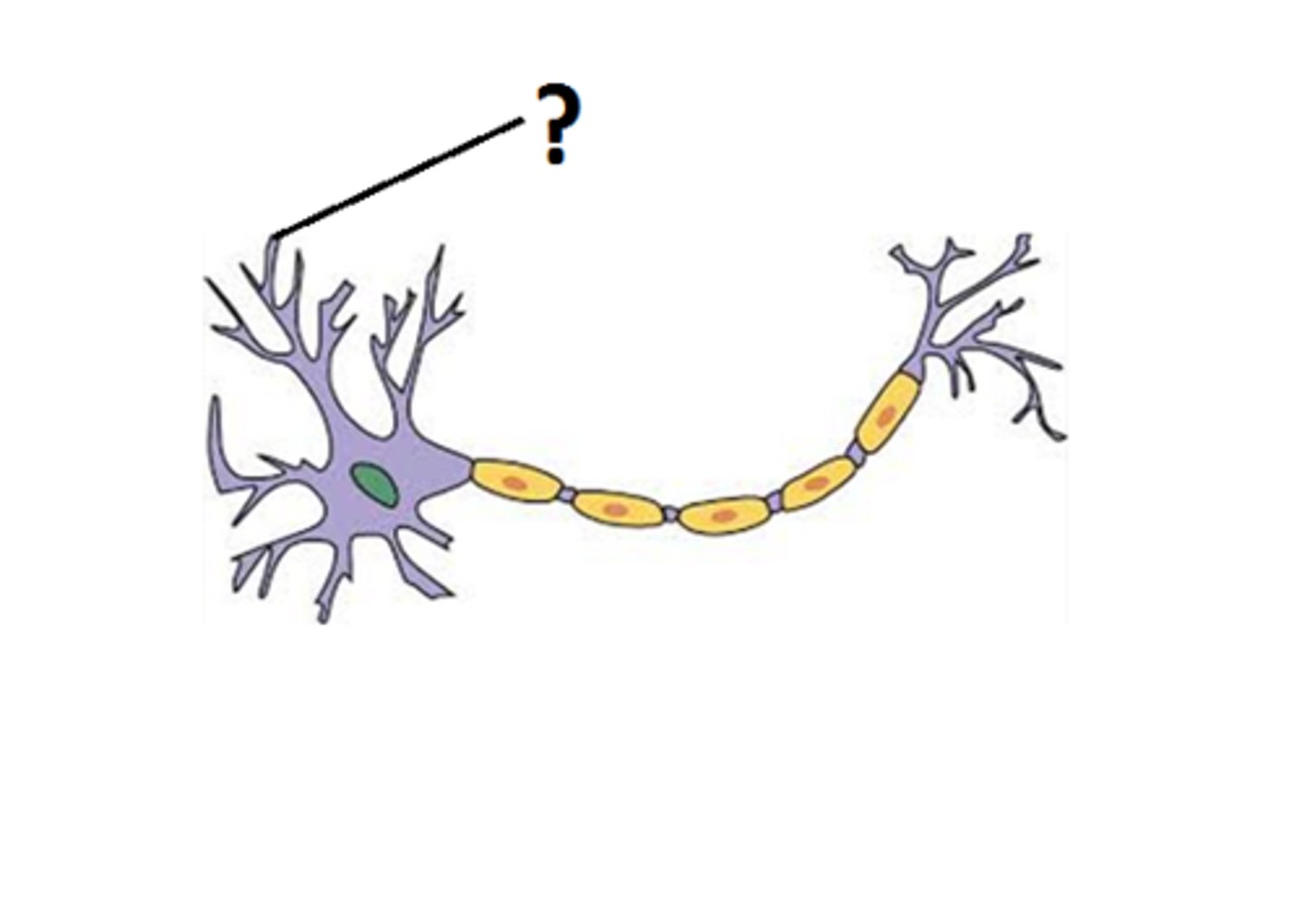
Dendrites
signal input, hundreds of highly branched extensions that increase surface area to accommodate maximum number of synaptic contacts, receive signals and conducts impulses (local depolarization) toward cell body
Axon
signal transmission, conducts impulses away from the cell body, "nerve fiber"
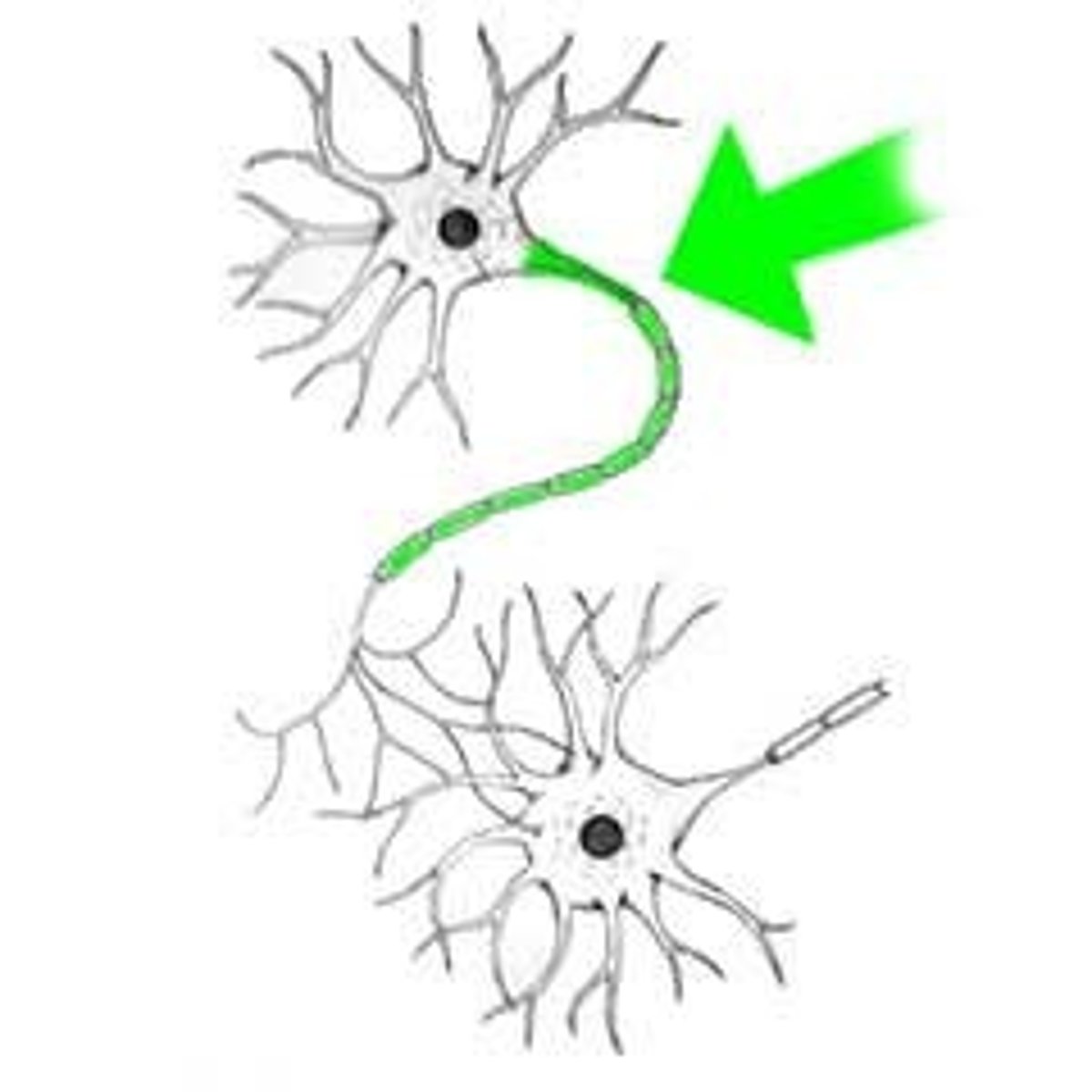
Axon hillock
trigger zone for AP, cone-shaped area of cell body that serves as action potential trigger zone (determines if threshold has been achieved)
axons end at axon terminals
contain synaptic vesicles with NTs, synaptic cleft, synapse
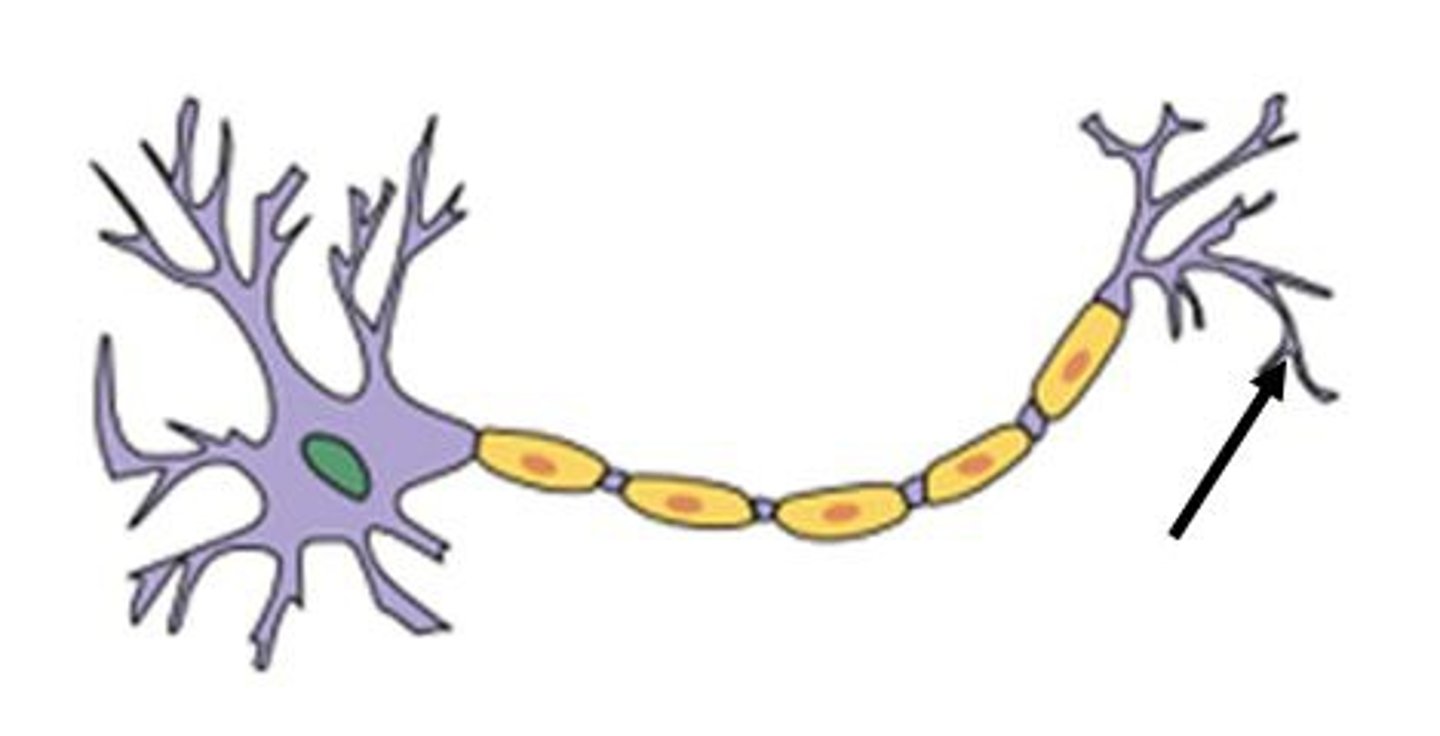
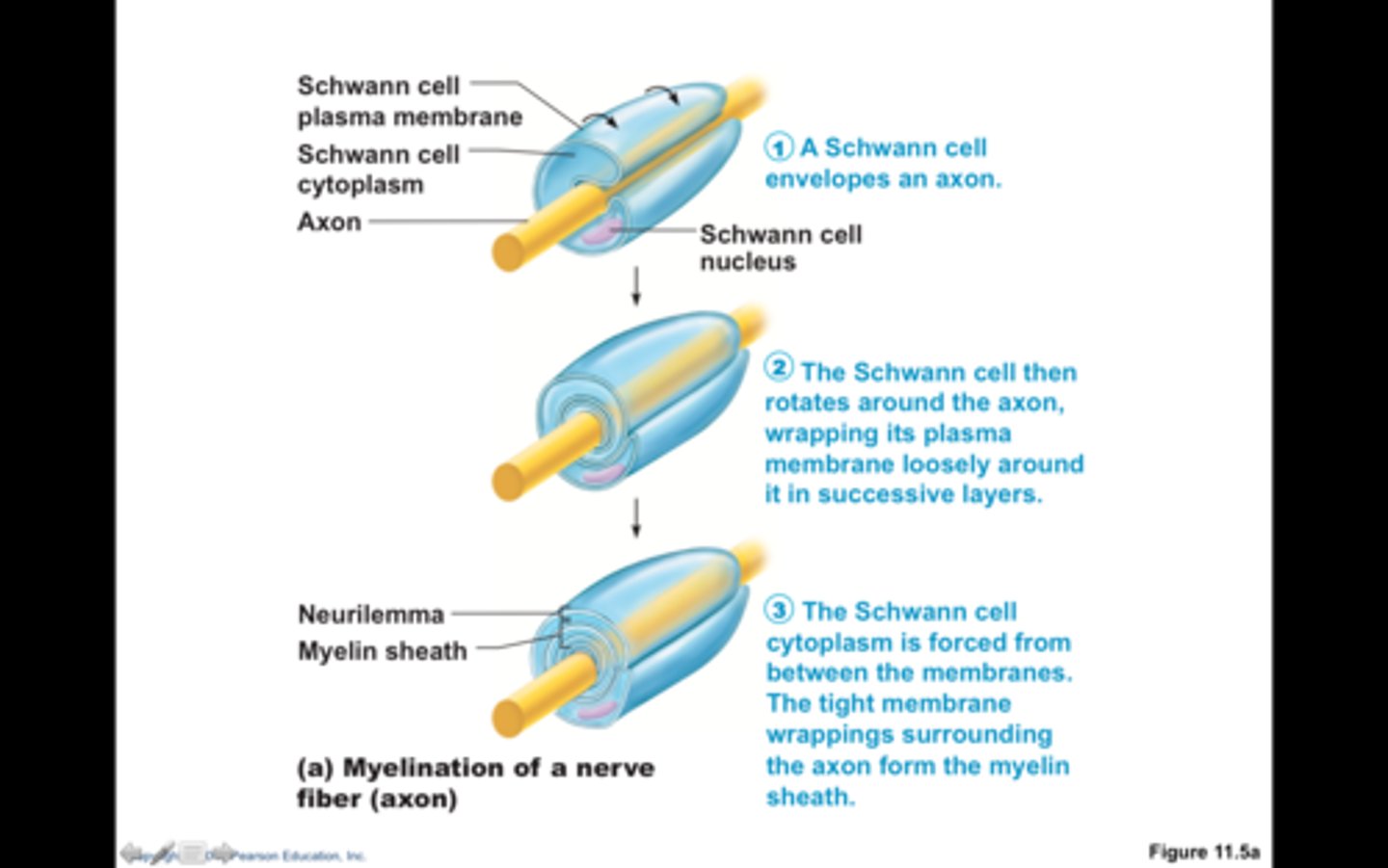
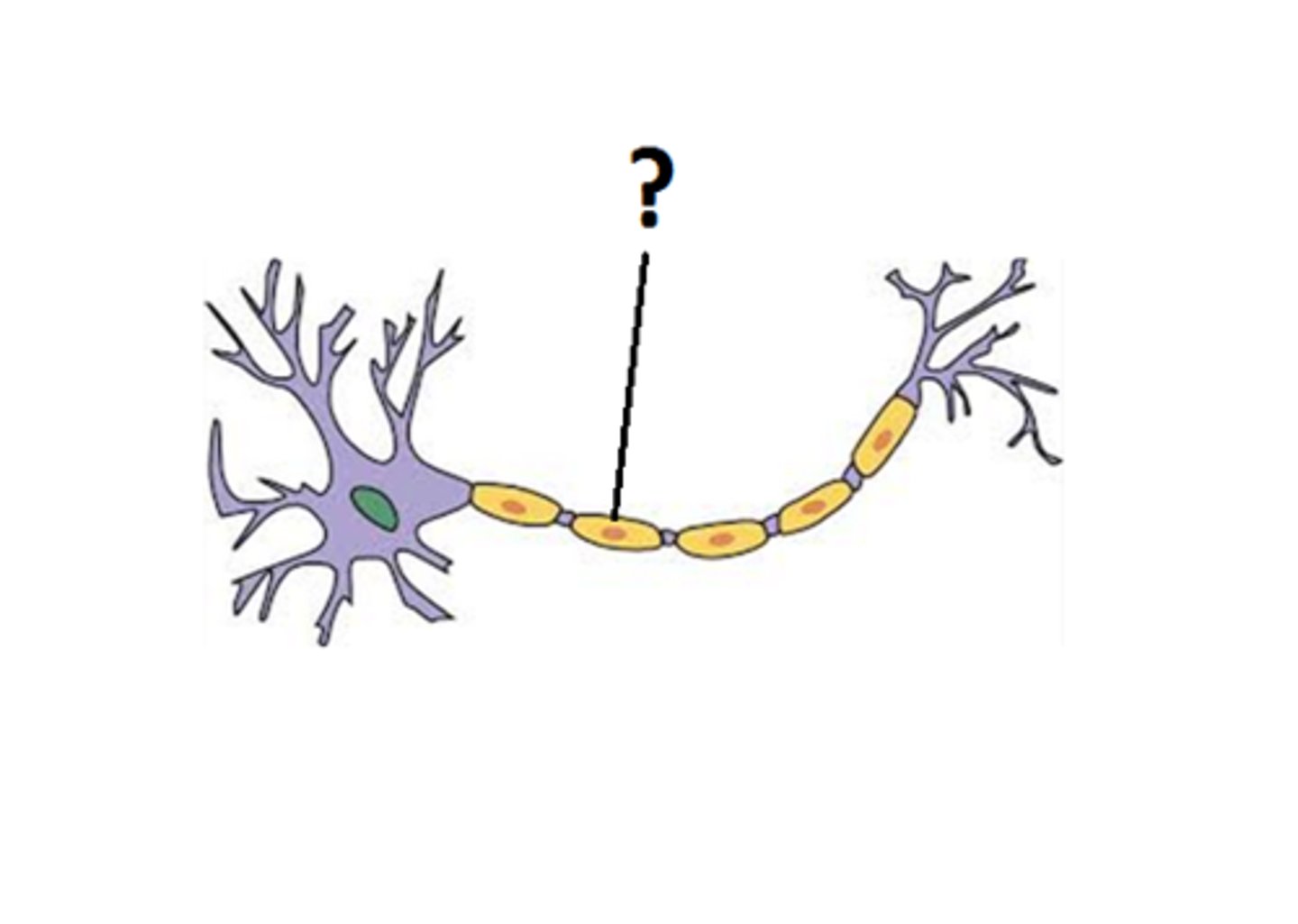
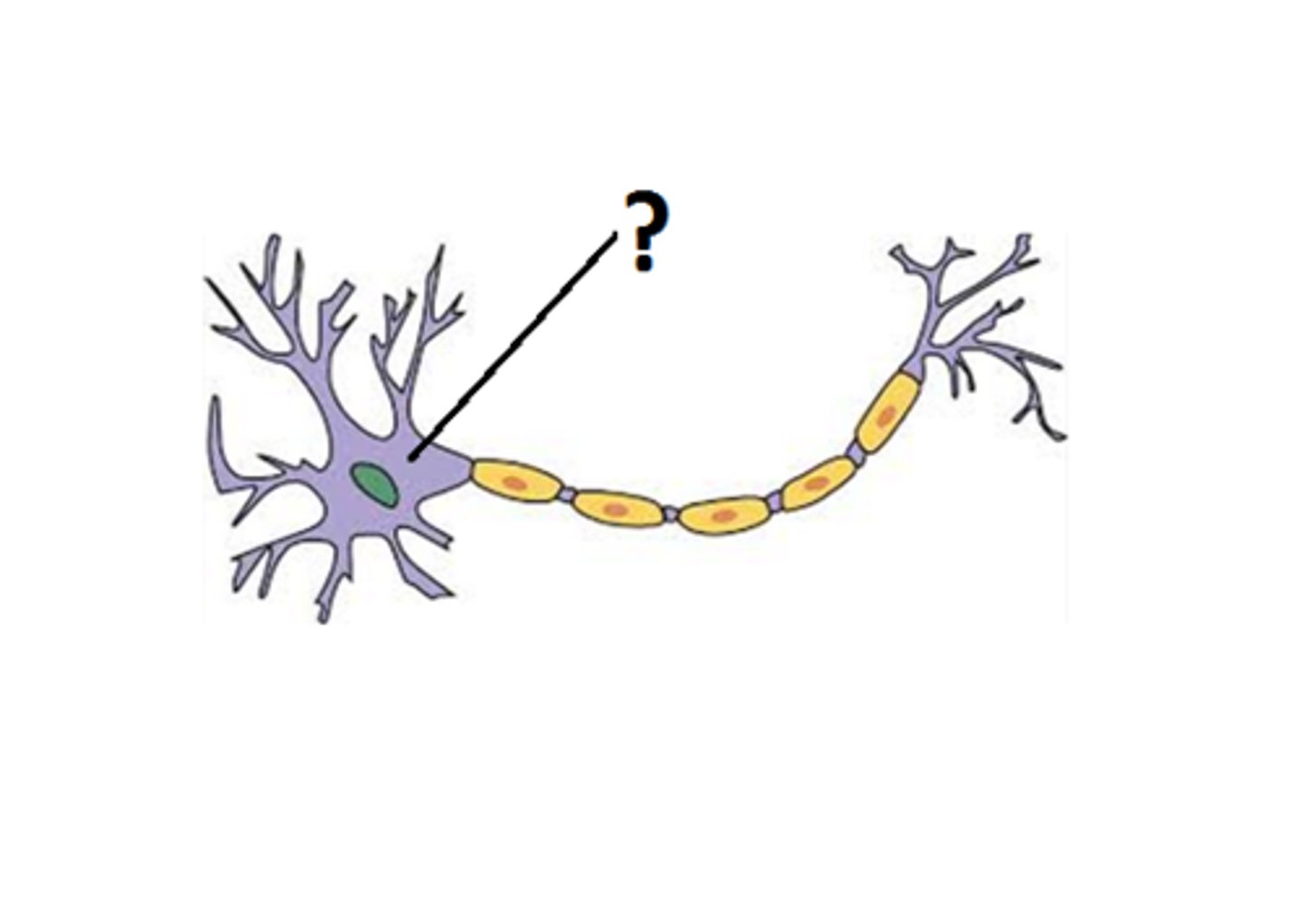
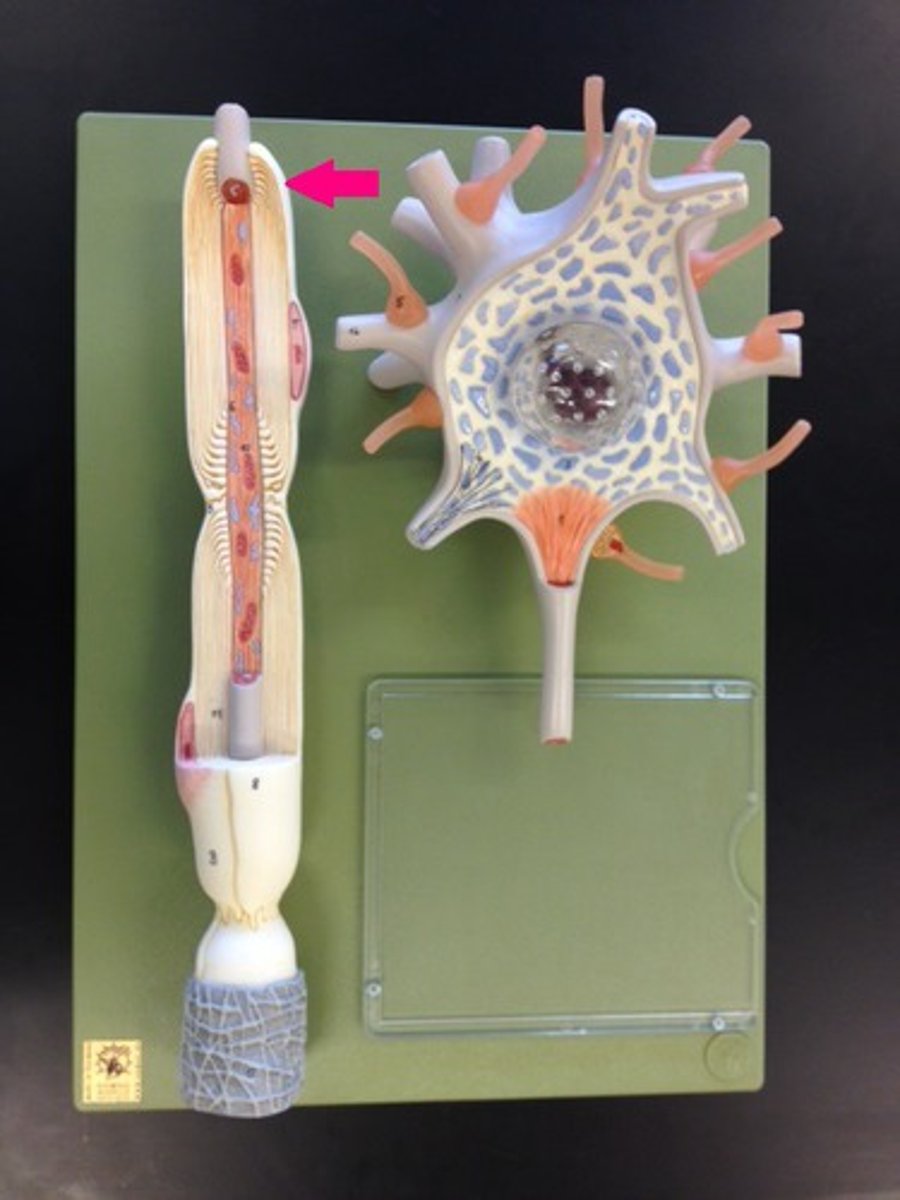
Myelin sheath
high lipid concentration, formed by oligodendrocytes in CNS and Schwann cells in PNS, protects and electrically insulates, increases speed of impulse travel
Neurilemma
only part of PNS myelin sheaths, formed by nucleus and cytoplasm of Schwann cell that gets pushed to outside
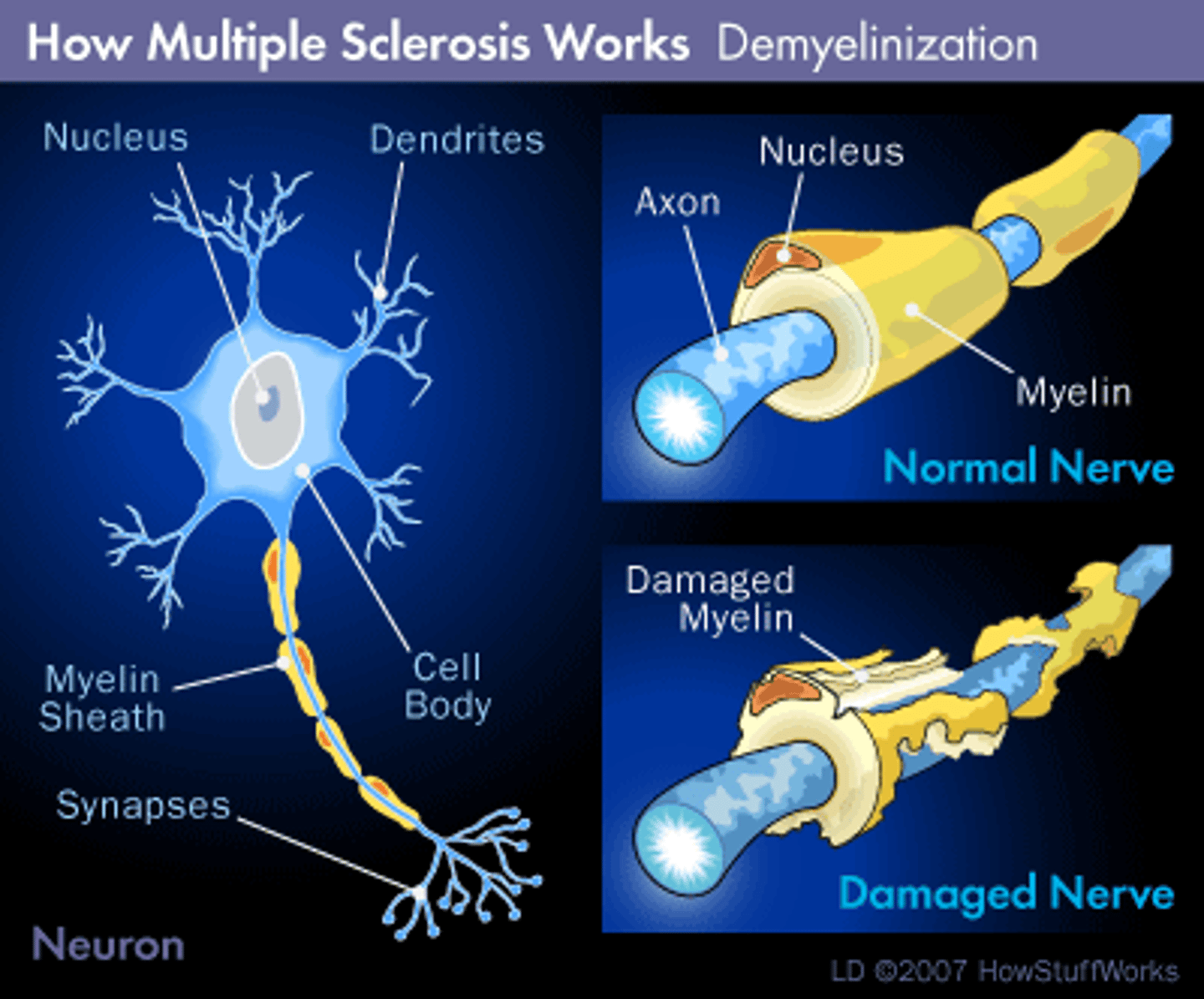
Multiple Sclerosis
CNS myelin sheats are gradually destroyed and reduced to non-functional hardened lesions called scleroses, loss of myelin causes such a slow down that impulse conduction eventually ceases, symptoms: visual disturbances, problems controlling muscles etc., cycles of relapse and remission
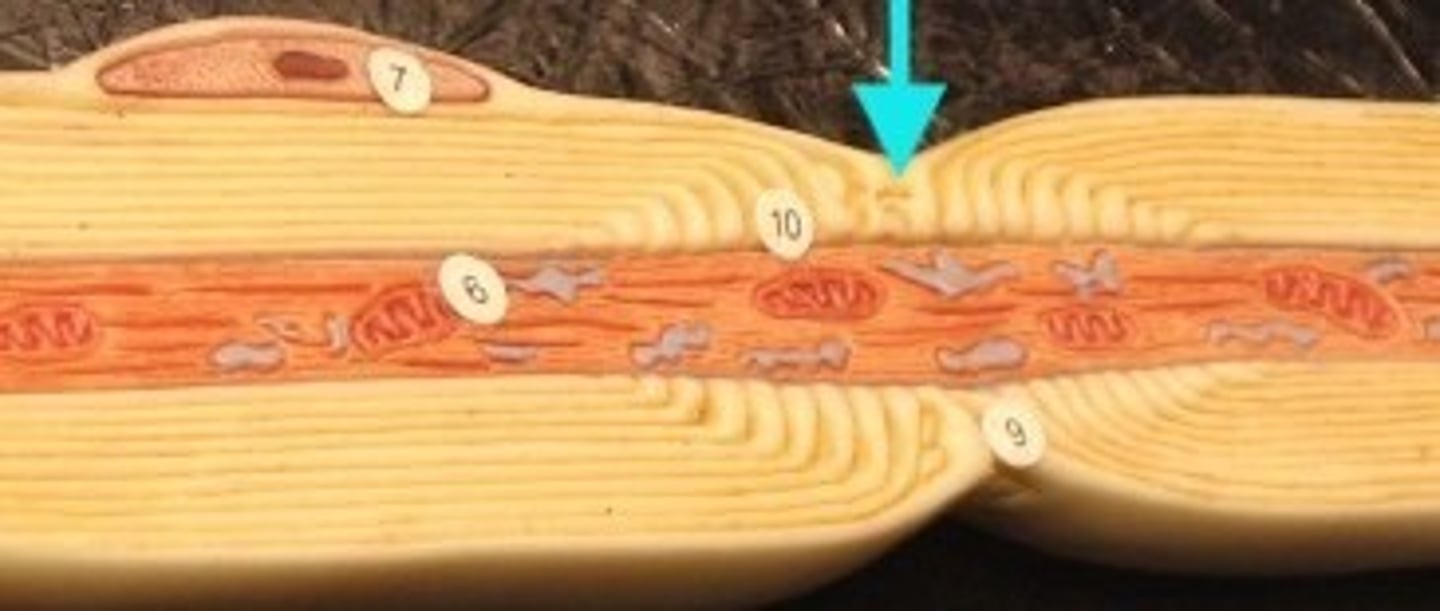
Nodes of Ranvier
Gaps in the myelin sheath to which voltage-gated sodium channels are confined.
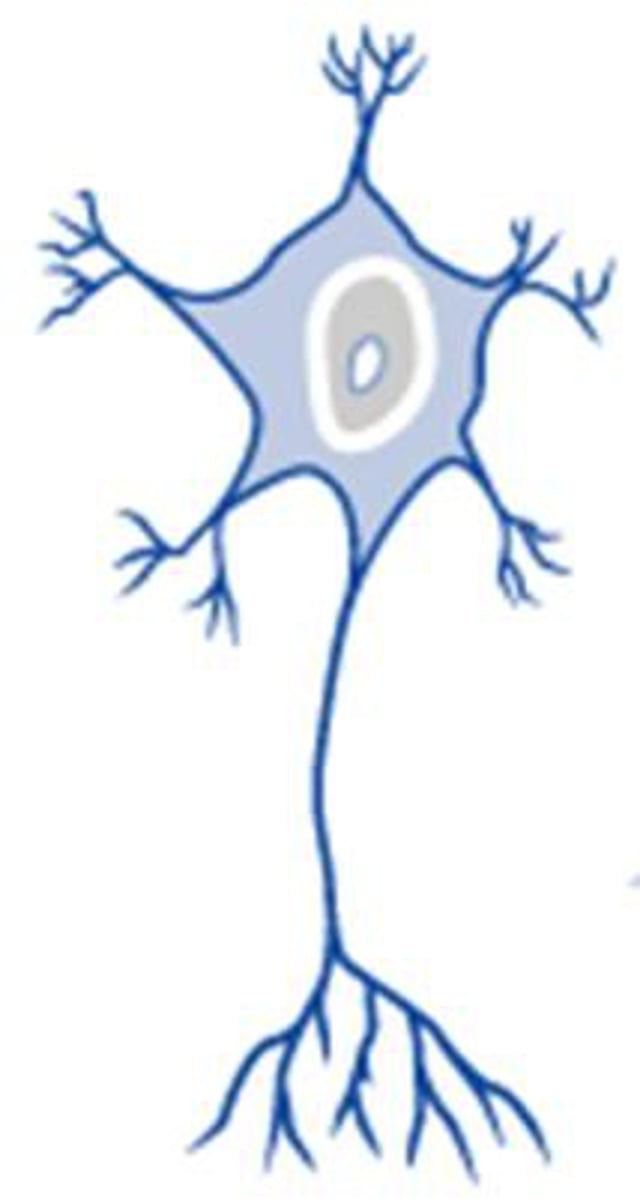
Multipolar neurons
Unipolar neurons (pseudounipolar)
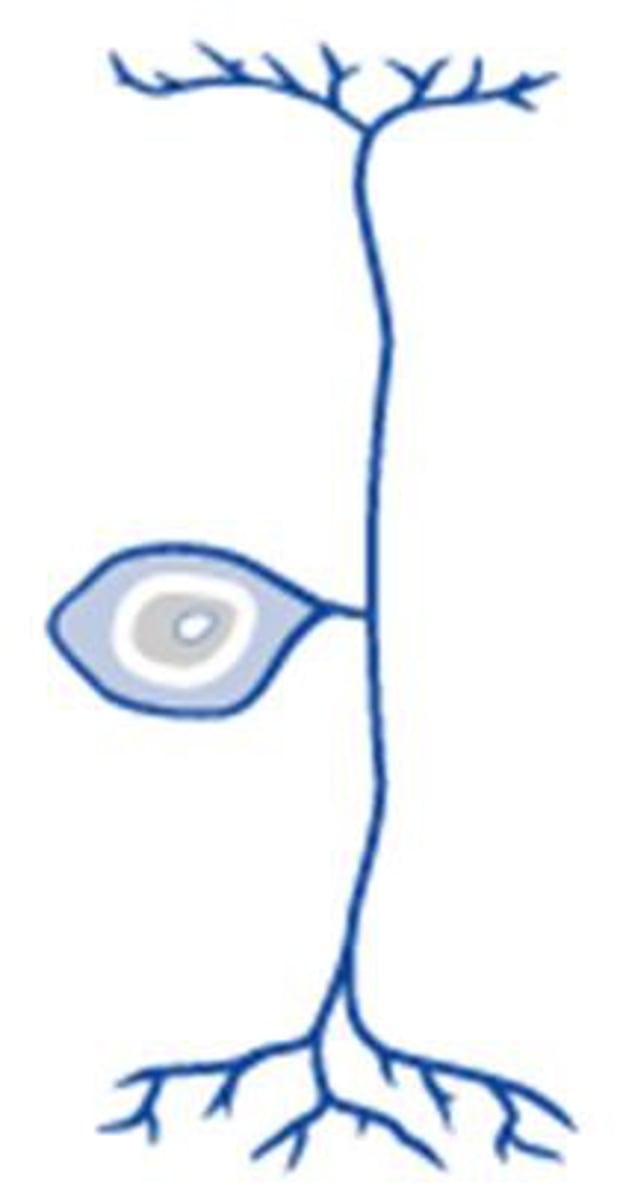
bipolar neuron
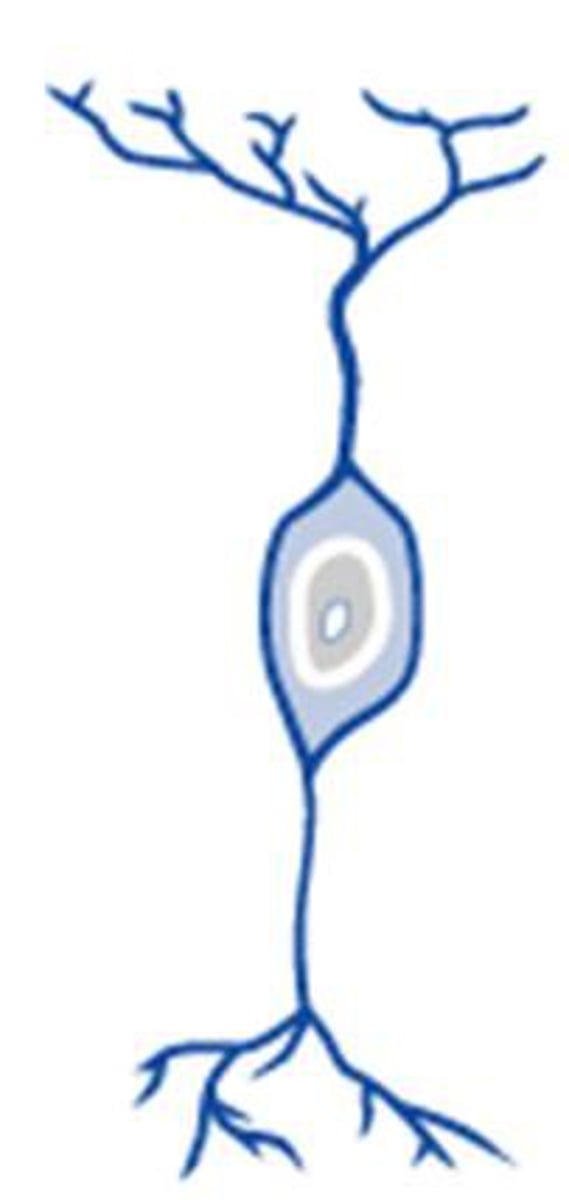
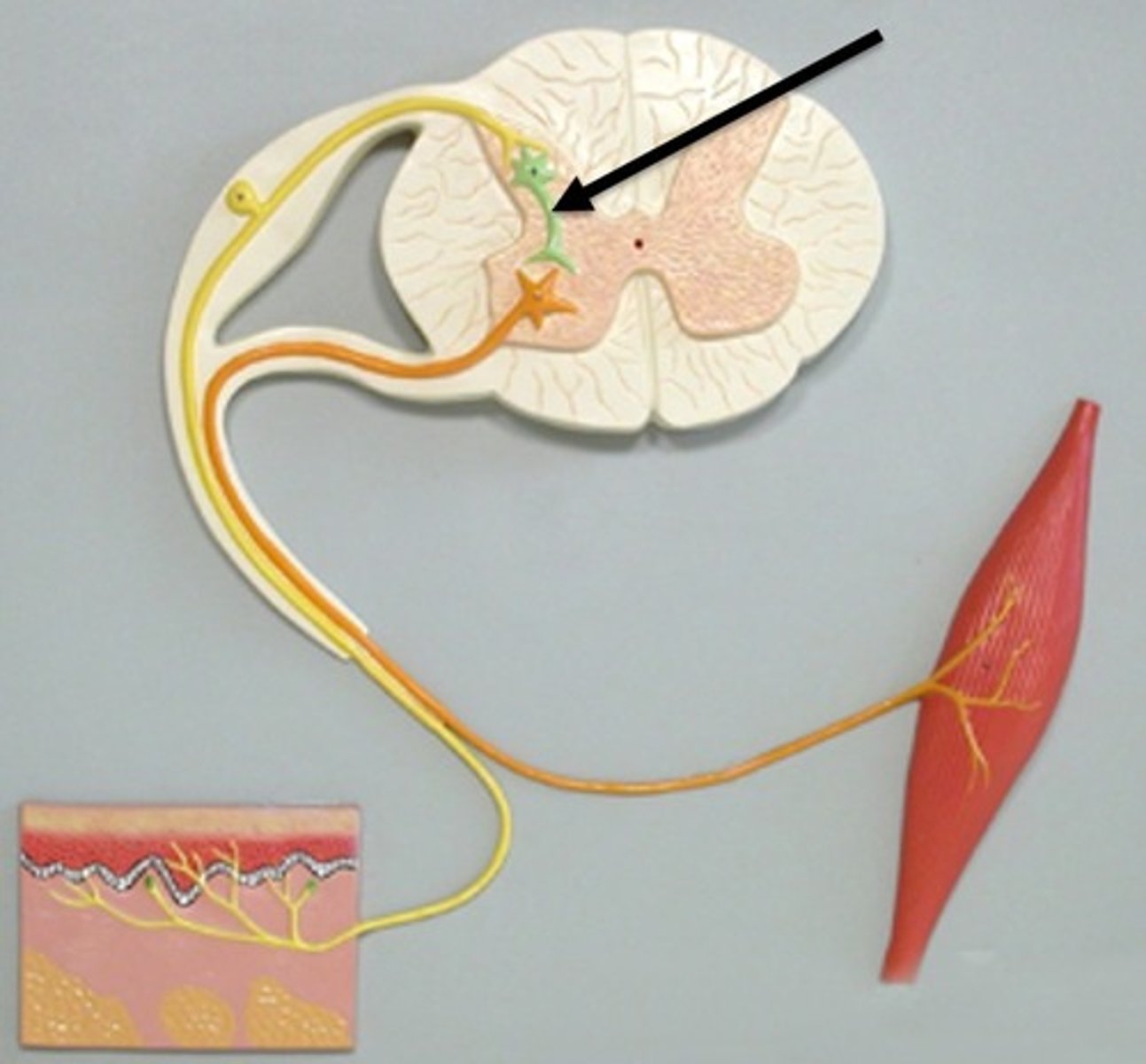
sensory (afferent) neurons
bring impulses toward the CNS from receptors, unipolar with cell body in ganglia outside the CNS
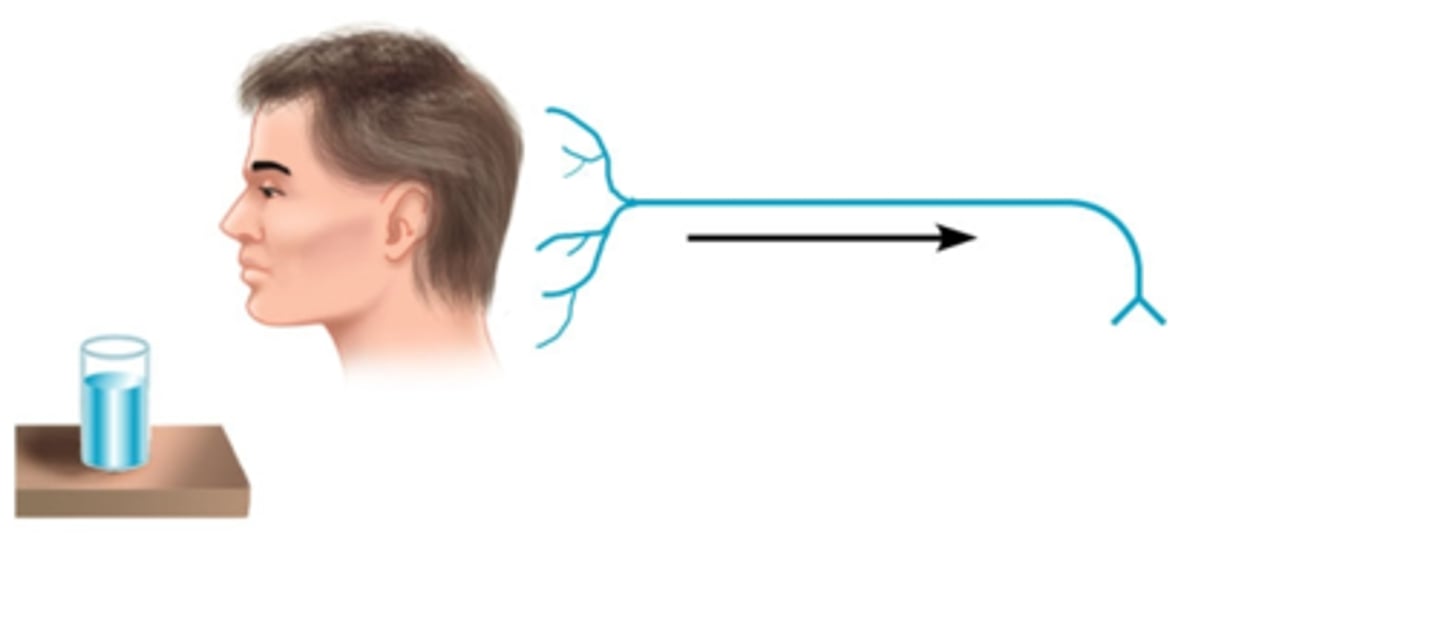
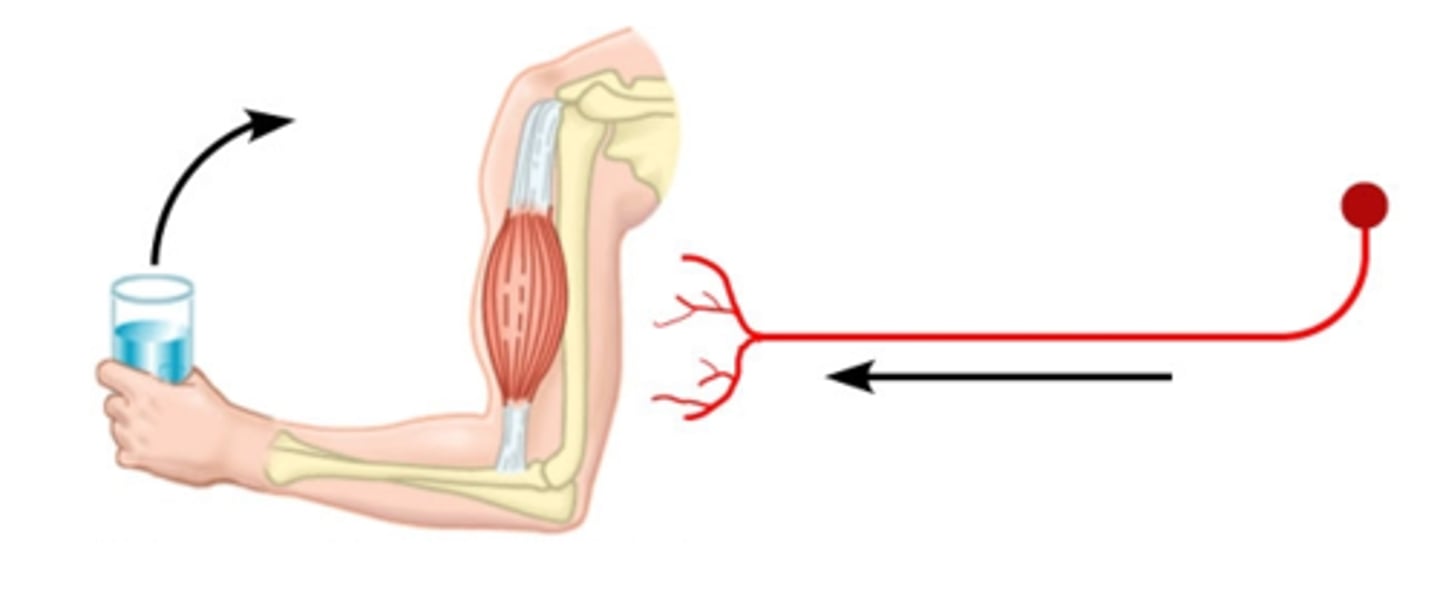
motor (efferent) neurons
carry impulses away from the CNS to effector muscles and glands, cell body in the CNS
Interneurons
cells confined to the CNS and make up over 99% of all neurons in body, multipolar and usually have short extensions, lie between motor and sensory neurons in neural pathways and shuttle signals through CNS
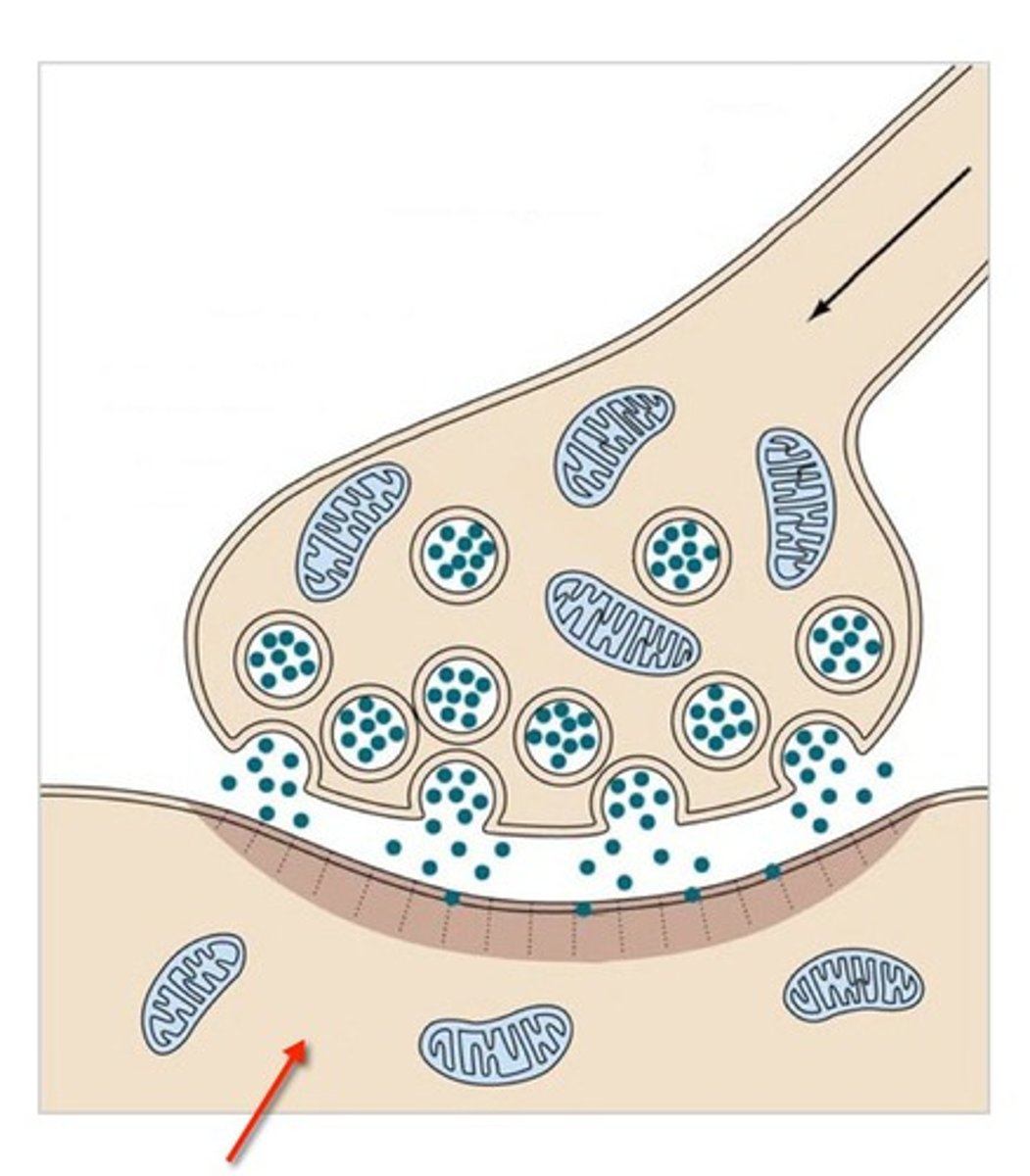
Synapse
mediates information transfer from one neuron to the next or to an effector cell
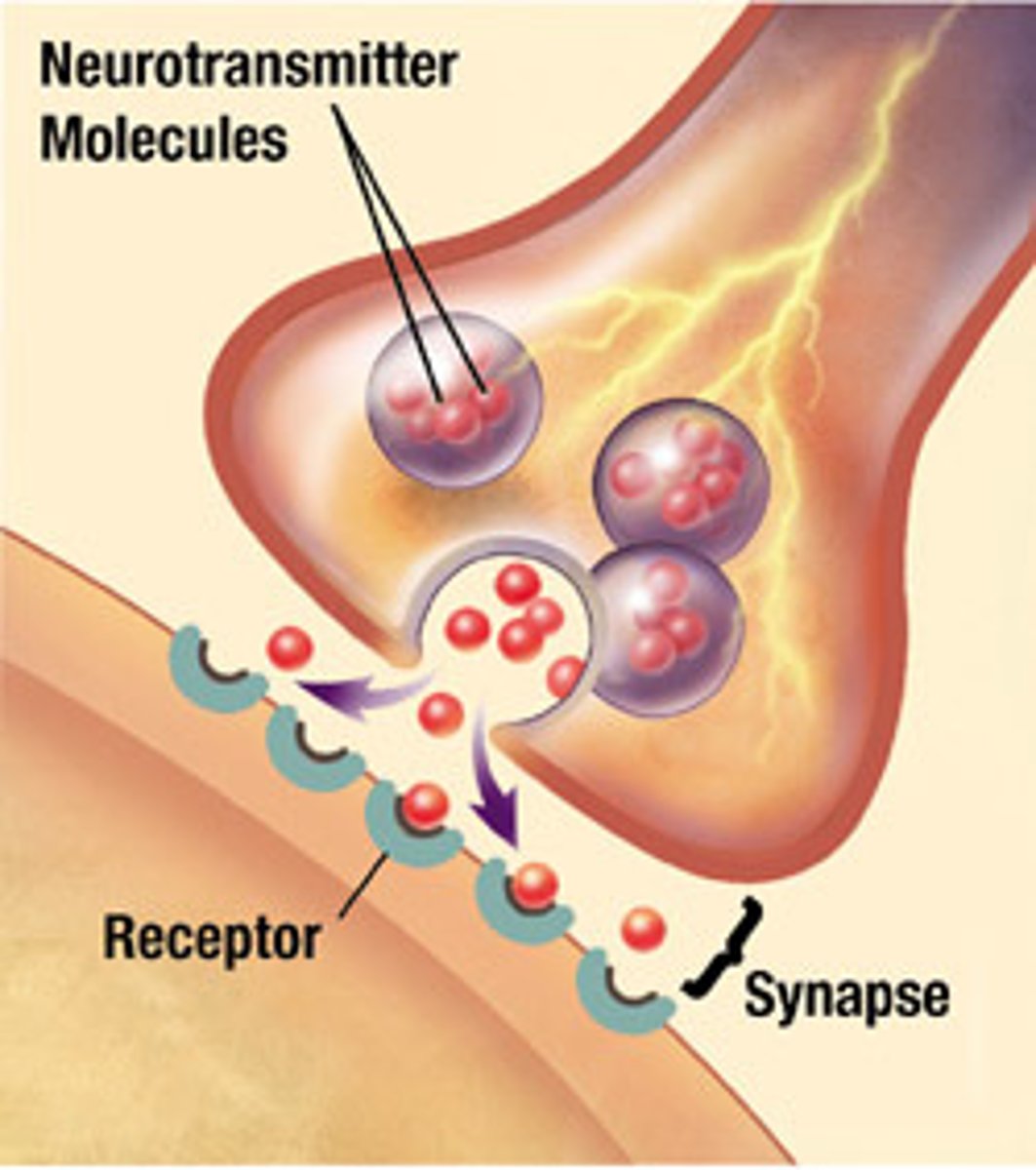
axon/presynaptic terminal
contains synaptic vesicles with neurotransmitters
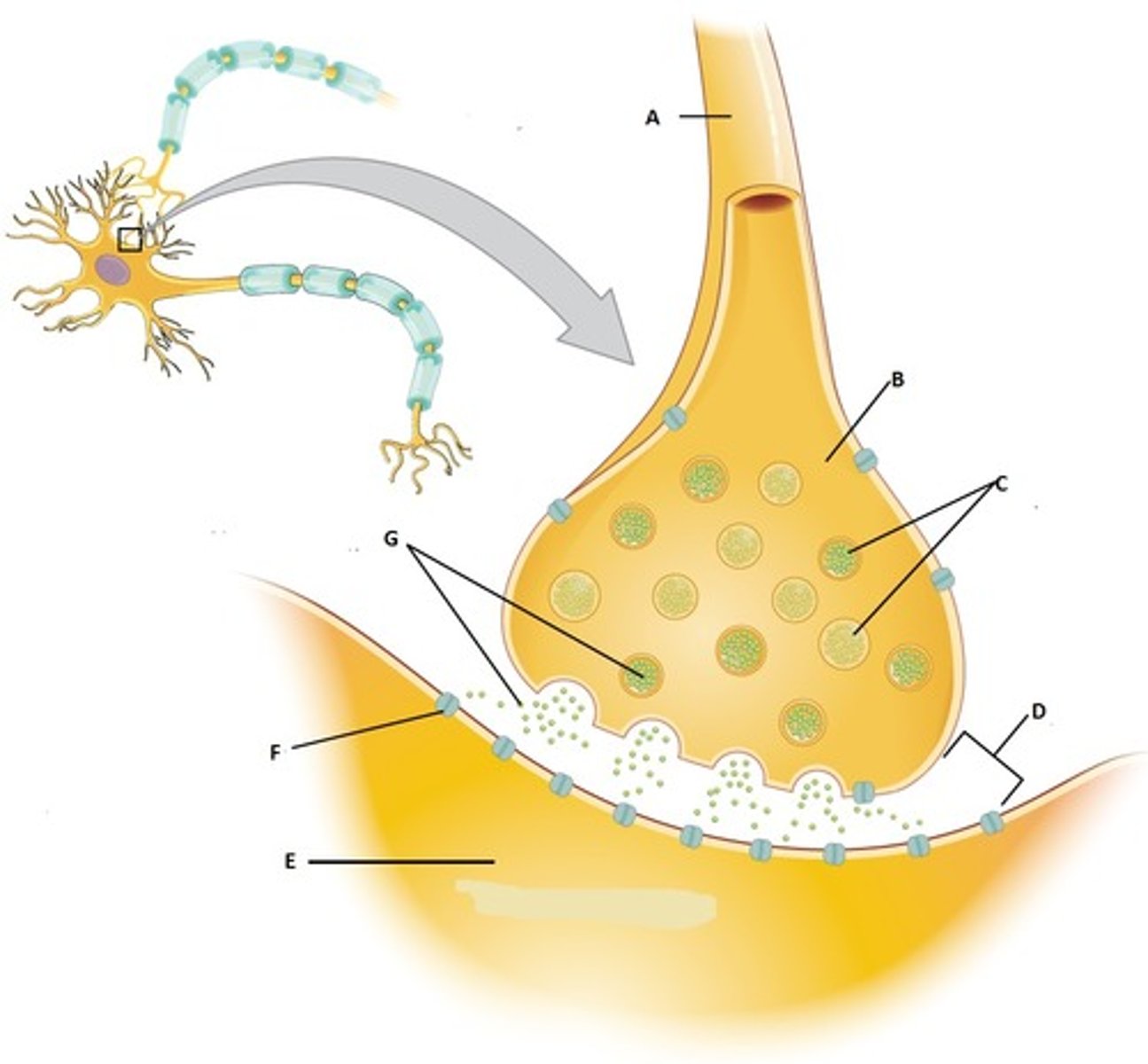
synaptic cleft
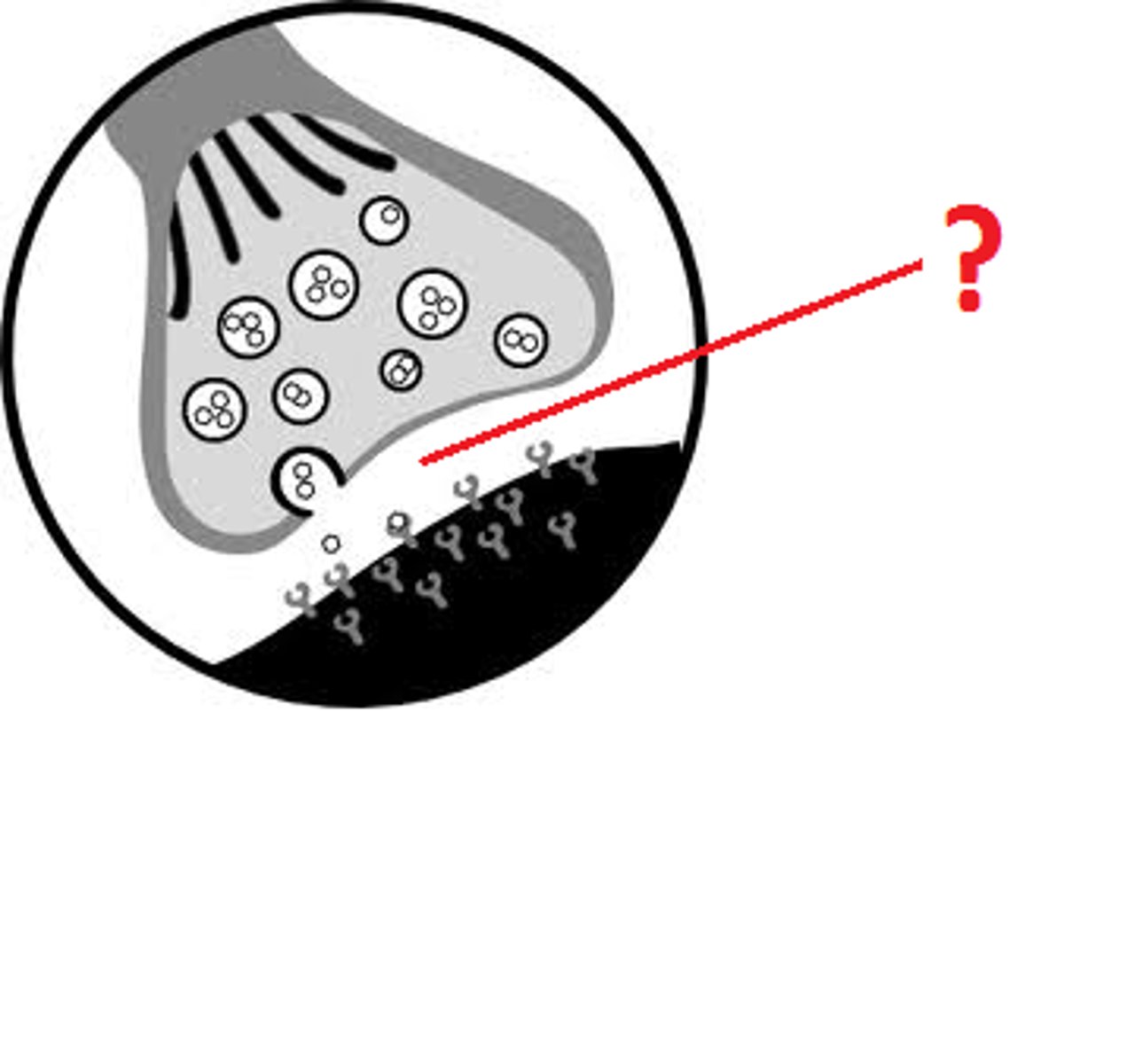
postsynaptic membrane
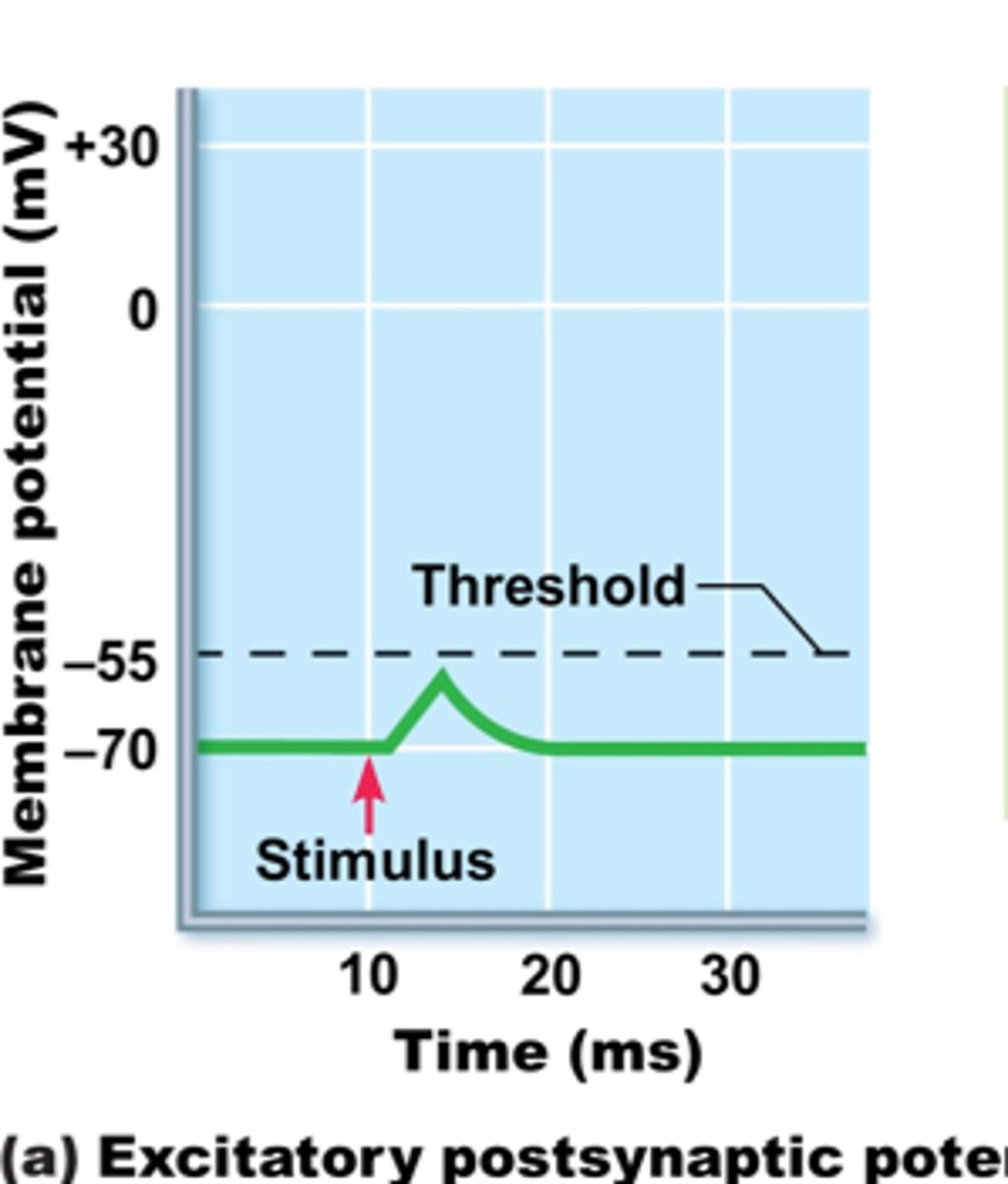
Excitatory Postsynaptic Potentials (EPSP)
increases membrane permeability to NA+ and depolarizes postsynaptic membrane, is excitatory (increases likelihood of firing an action potential)
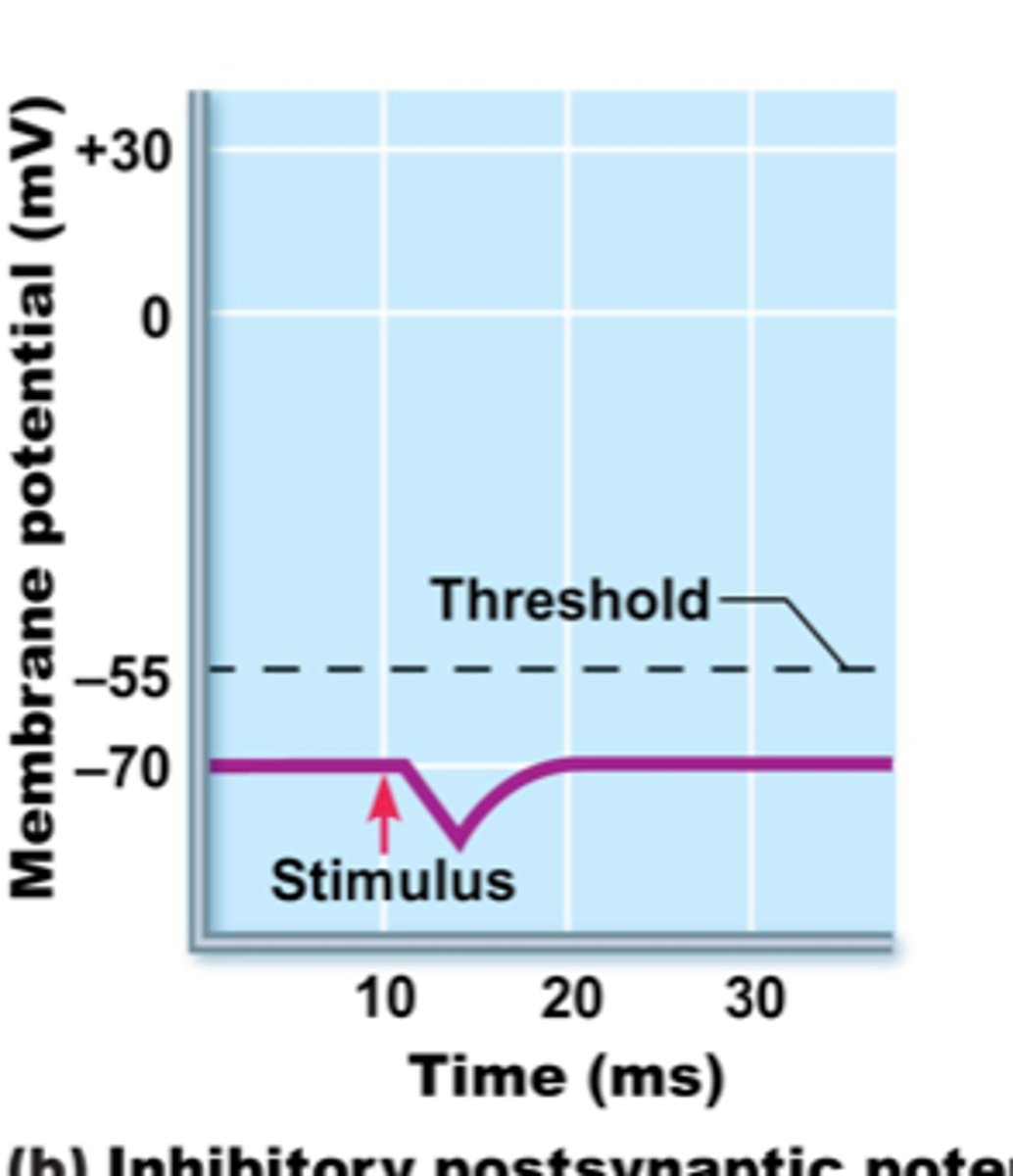
Inhibitory Postsynaptic Potentials (IPSP)
increases permeability to K+ and hyper polarizes postsynaptic membrane, is inhibitory, (anesthetics)
Norepinephrine
helps control alertness and arousal, regulated by MAO monoaminoxidase
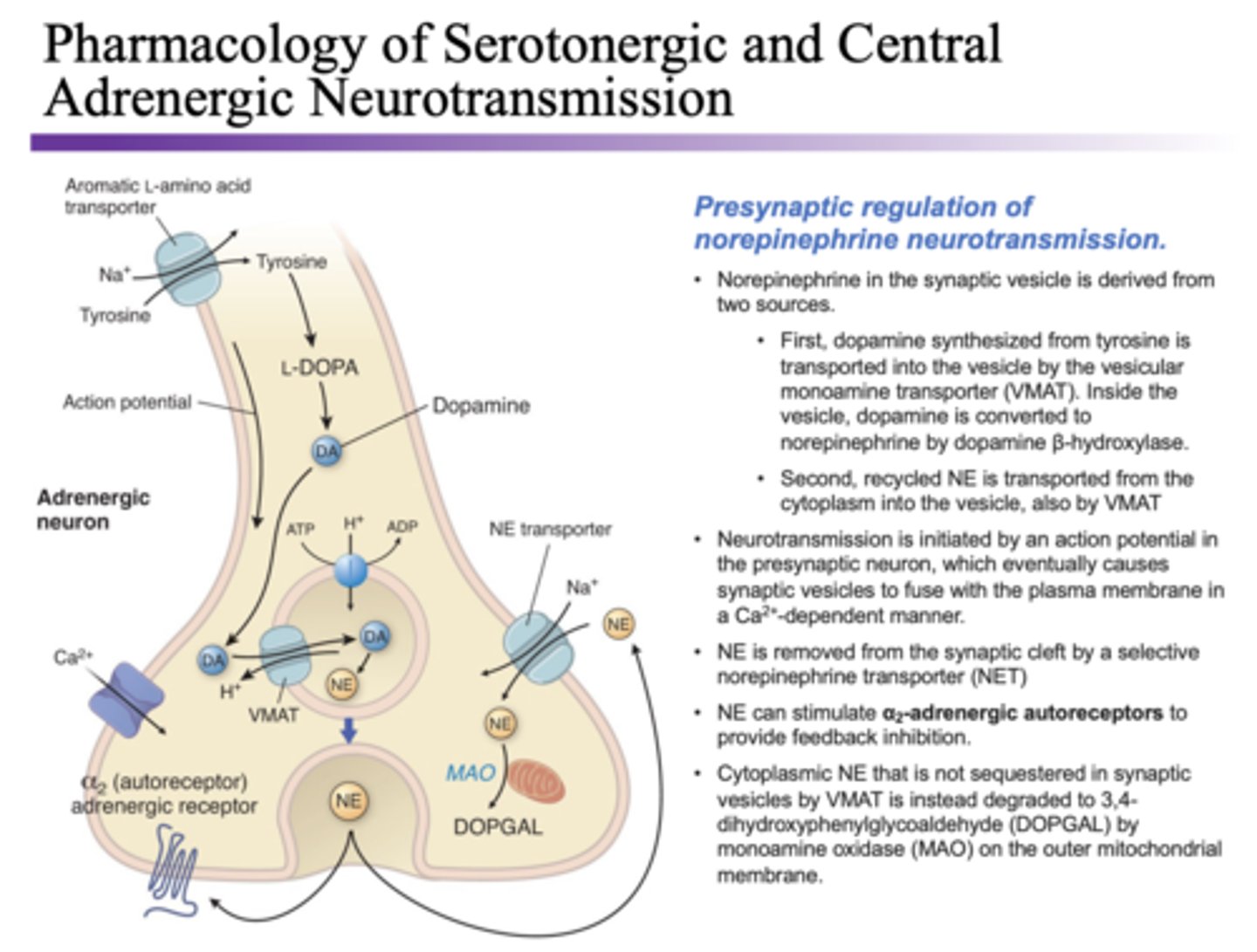
Too much norepinephrine
over excitation and euphoria, cocaine and amphetamines
Too little norepinephrine
depression, treated with MAOIs (monoaminoxidase inhibitors)
Myelination of a nerve fiber