Odontogenic Cysts/Tumors
1/84
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
85 Terms
most common odontogenic tumor
odontoma
what is the difference between a malignant ameloblastoma and ameloblastic carcinoma
metastases
fibro-osseous lesion of jaw most often encountered by dental practitioners
cemento-osseous dysplasia
most frequently occurs in african-american women
periapical cemento-osseous dysplasia
osteogenesis imperfecta and dentinogenesis imperfecta are associated with the same gene
false
squamous odontogenic tumors arise from
rest of malassez and rest of dental lamina
clear cell odontogenic carcinoma associated with what gene
ESWR1
cotton wool appearance
paget’s disease
most odontogenic tumors are
benign
most odontogenic tumors grow at a _____ rate
slow
ameloblastoma - asymptomatic/symtomatic
asymptomatic
most common site for oral lymphoma
palate
second most common odontogenic tumor
ameloblastoma
what is most commonly associated with graft-versus host disease
allogenic bone graft
“ghost lesion” (missing nucleus) associated with
calcifying odontogenic cyst
which benign entity can be aggressive
ameloblastoma
which benign entity can be aggressive
glandular odontogenic cyst
PTCH1 mutation associated with
nevoid basal cell carcinoma
cysts characteristically have
epithelium lining
periapical granuloma
mass of chronically inflamed granulation tissue
a chronic periapical granuloma may be
asymptomatic
on a radiograph a periapical granuloma appears as a
radiolucency
periapical granuloma’s occur in
non-vital teeth
what is benign but aggressive
odontogenic myxoma
periapical (redicular) cyst occurs in
non-vital teeth
most common jaw cyst
periapical (redicular) cyst
when is a periapical (redicular) cyst symptomatic
when acute
when is a periapical (redicular) cyst asymptomatic
when chronic
Lateral radicular cysts arise from
rest of malassez
pushing of structures usually indicates
benign lesions
which cyst has the highest likelihood of malignant transformation
residual cyst
residual cysts are notably located at
previous extraction sites
what kind of lesions produce rushton bodies
chronic
most common location of buccal bifurcation cyst
mandibular 1st molar
most common developmental cyst
dentigerous cyst
most common location for dentigerous cyst (but can be anywhere)
mandibular 3rd molars
associated with crown of unerupted tooth - attached at CEJ
dentigerous cyst
marsupialization allows for
shrinkage of lesion and for bone to fill in
eruption cyst
soft tissue counterpart of dentigerous cyst
eruption cyst characteristics
no radiographic presentation
bluish
common in kids
where does the odontogenic keratocyst arise from
rests of dental lamina
what direction do odontogenic keratocysts grow in
anterior-posterior
patients younger than 18 with multiple OKC’s should make you think what
syndrome
unilocular and multilocular pertain to
radiolucencies
if a PA cyst or lateral radicular cyst is restorable what is the tx
RCT or retreat/apico
what age group are buccal bifurcation cysts most common
5-13 years
what type of radiographic experience does a eruption cyst have
none
what grows in an anterior-posterior direction
odontogenic keratocyst OKC
what gender predilection do OKC’s have
male
what age range is associated with OKC’s
10-40 years
inheritance pattern for nevoid basal cell carcinoma syndrome
autosomal dominant
PTCH1 mutation is associated with
nevoid basal cell carcinoma syndrome
OKC’s have what kind of tissue
parakeratinized
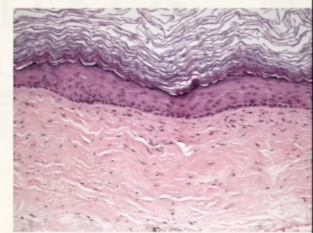
orthokeratinized epithelium
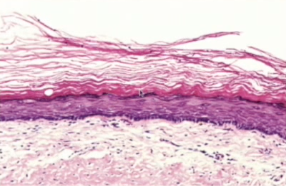
orthokeratinized epithelium
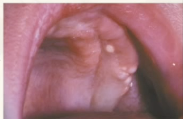
gingival cyst of newborn
most common area is between lateral/canine/premolars in mandible 75-80%
lateral periodontal cyst
although they look the same what’re the differences between the lateral radicular cyst and the lateral periodontal cyst
symptomatic vs asymptomatic respectively
occurance in non-vital/vital teeth respectively
most common area is canine/premolars area in mandible 60-75%
gingival cyst of adult
gingival cyst radiographic appearance
none
calcifying odontogenic cyst radiographic appearance
mixed
glandular odontogenic cyst radiographic appearance
multilocular radiolucency
lateral periodontal cyst occurs between
vital teeth
between odontogenic cysts and tumors which are more common
cysts
intraosseous ameloblastomas radio______
radiolucent
major difference between malignant ameloblastoma and ameloblastic carcinoma
metastasis vs no metastasis
2/3 tumor occurence in gender
females
2/3 tumor location of occurrence
anterior maxilla
2/3 tumor occurrence radiographically
radiopaque
2/3 tumor occurrence in tooth
unerupted permanent canine
adenomatoid odontogenic tumor
2/3 tumor
most common location for ameloblastoma
posterior mandible
what is associated with EWSR1-ATF1
clear cell odontogenic carcinoma
radiographic appearance is honey-comb/soap bubble like
ameloblastoma and odontogenic myxoma
most common location is root of the mandibular first molar
cementoblastoma
cementoblastoma radiographic appearance
mixed or mainly radiopaque
ameloblastic fibroma age predilection
first two decades
ameloblastoma age predilection
40-50’s
adenomatoid odontogenic tumor most commonly found in
maxilla
compound odontoma radiographically
radiopaque w/ RL rim - resembles multiple mini teeth
complex odontoma radiographically
radiopaque - irregilar calcifications
where does the periapical radicular cyst arise from
rest of malassez
where does the gingival cyst of an adult arise from
rest of serres
BRAF mutation associated with
ameloblastoma