BU111 Final
1/94
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
95 Terms
Identify variables that might be estimated when determining the impact of a solution or proposal
1. Population
2. Individual
3. Household
4. Proxy (easiest to observe)
When do you use population? and give an example
- Driven by population in an area
- Market size/share, revenue, profitability, supply needed, saturation, competition
- USE IT ANYTIME BASICALLY
When do you use household? and give an example
- When calculating a group consumable/demand, ie. lightbulbs
- Market size/share, revenue, profitability
When do you use individual? and give an example
- When calculating a single person's consumable/demand
- Market size/share, revenue, profitability
When do you use proxy? and give an example
- When finding # of stores in an area; population per store
- Company revenue/profitability, market size, profitability, supply, saturation of the market
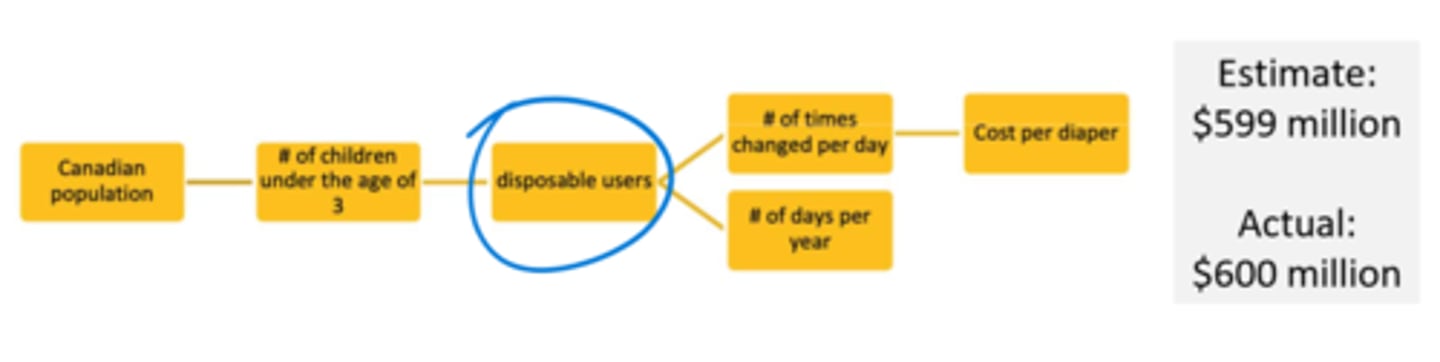
Canadian Population -> # of children under the age of 3 -> #of times changed per day -> # of days per year -> cost per diaper
Given this, what refinements would you make to make to improve accuracy
Add the usage of disposable diapers
TAM
SAM
SOM
Total Addressable Market
Serviceable Available Market
Serviceable Obtainable Market
Market Sizing Approach
Population (household or individual) -> Defining characteristics of the population (% of population) -> x purchase frequency (replacement frequency) -> x purchase quantity -> x unit cost
Revenue Approach
Revenues per store/day/customer -> # of stores/days/customers -> total revenues
Use average selling price
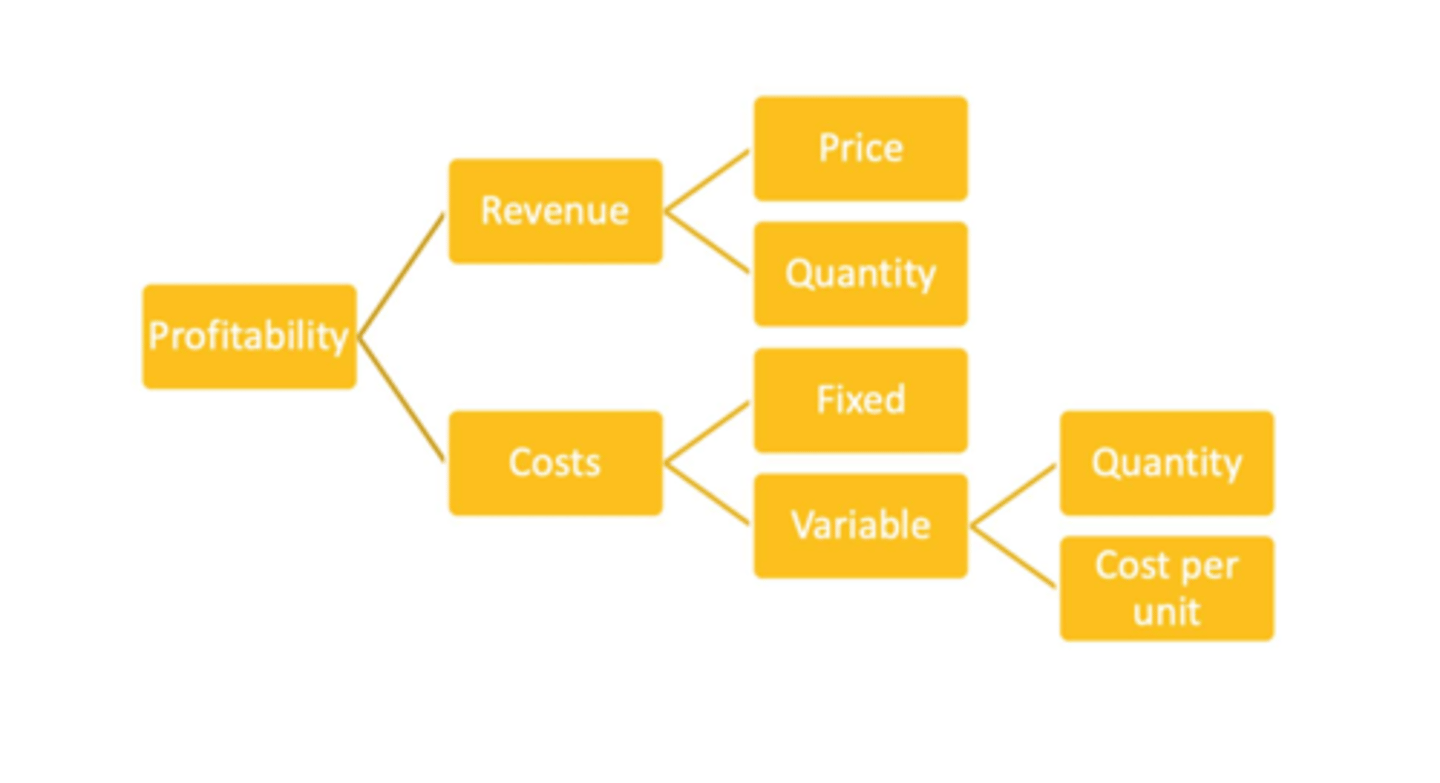
Profitability Framework
Defending Your Numbers
Just know to be able to defend your numbers with explanation
Example #1: Lightbulbs sold in Canada annually
$1.5 Billion
Example #2: Revenue of Starbucks nationwide
$3.5 Billion
Five industries radically changed by technology
Music
Travel
Transportation
Publishing
Retail
Opportunities of Technology
1. Products - innovation, uniqueness, value
2. Improved information use, access and sharing
3. Competitive advantage; barriers to entry
4. Customization
Threats of Technology
1. Imitation - information costly to develop but cheap to share
2. New technologies and new entrants in unfamiliar areas - need new capabilities, resources and learning
3. Information overload and security
4. Disconnected employees and customers (e-commerce and working at home)
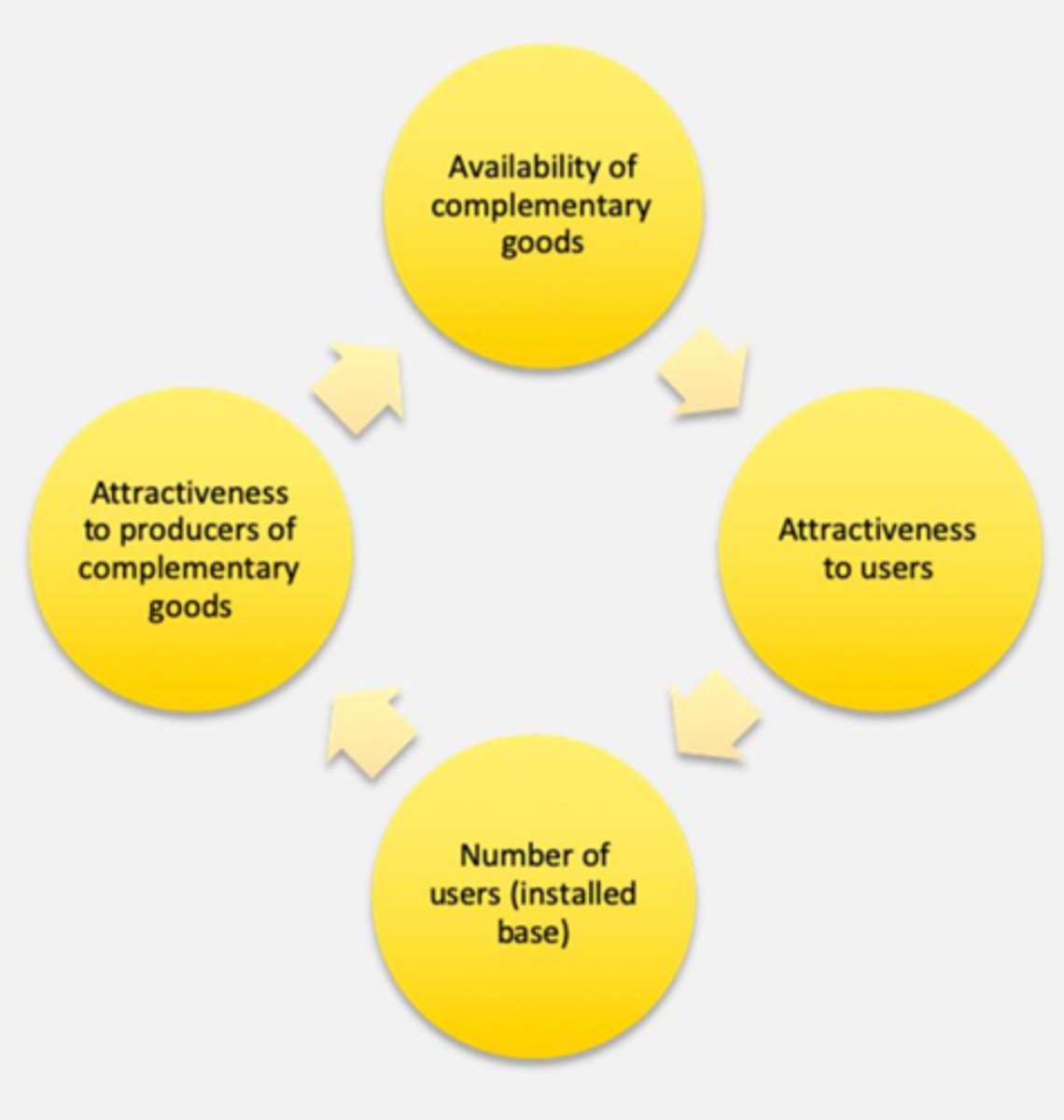
What is installed base?
- Number of users that use goods compatible with the goods
Lock-in
- extent to which a customer is "committed" to a product or service
- larger = greater resistance to switch
Switching Costs
- the price it takes the consumer to switch to another product or company
Complementary Goods
- goods that enhance the goods that they are part of
- rely on other good being present in order for original goods to have value
Technology Standards
- enables compatibility of complementary goods
- in order for complementary goods to create value for each other, they must have a particular technology standard
Network Effects and it's solutions
- value increases as user base grows
Solutions: compatibility, partnerships, incentives for complementary goods suppliers; build base
Name the 4 Steps to Vicious/Virtuous Cycle
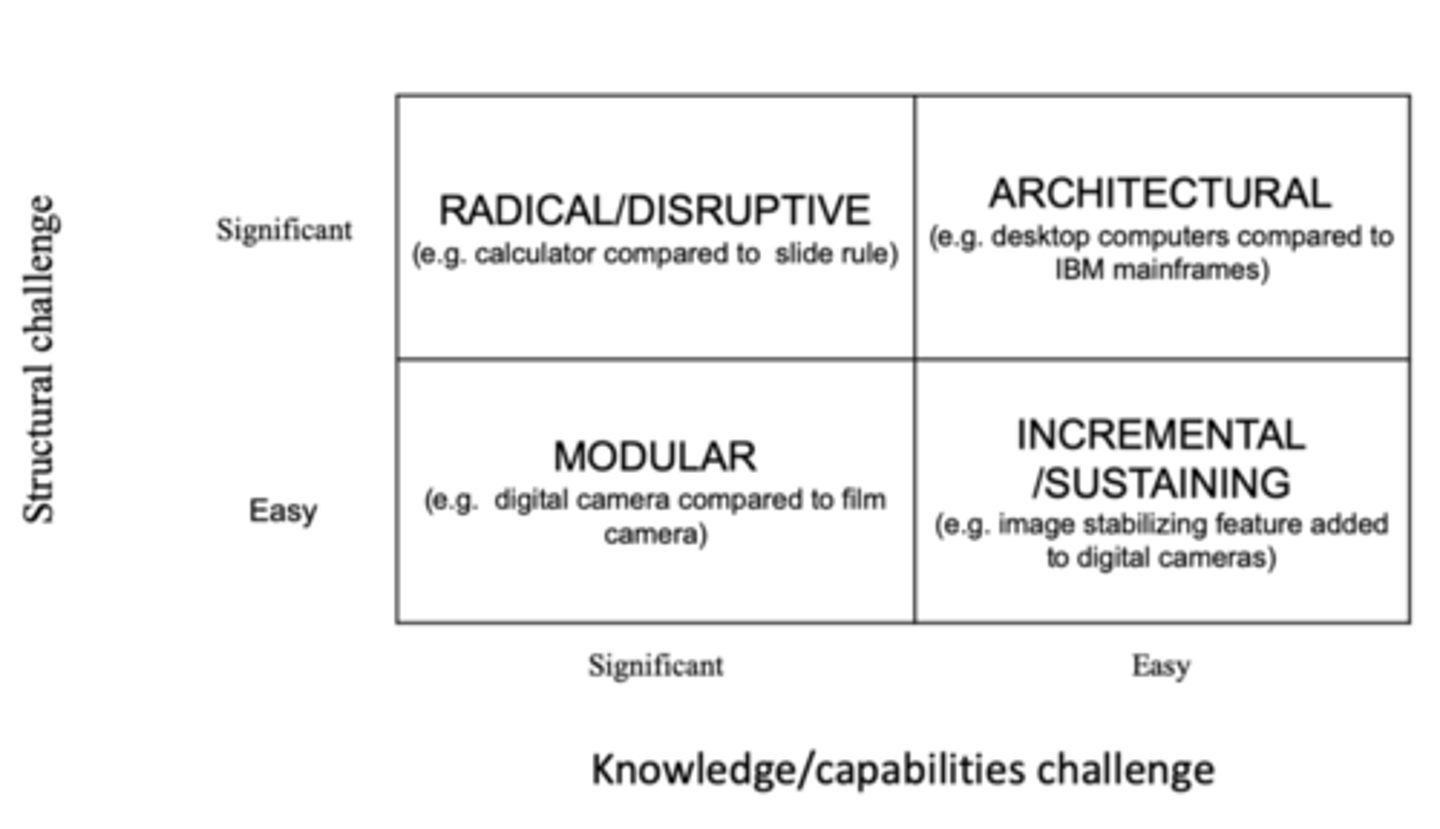
4 Types of Innovation and Challenges they create
1. Radical/Disruptive: significant structural, significant knowledge
2. Architectural: significant structural, easy knowledge
3. Incremental/Sustaining: easy structural, easy knowledge
4. Modular: easy structural, significant knowledge
Sustaining innovation (what and who)
- improves existing products in expected ways
- Target: mainstream, high-margin customers, with enhancements in product functionality
- incumbents usually win
Disruptive Innovation (what and who)
- different performance attributes not valued by mainstream
- starts in lower performance segment, improves rapidly; enters mainstream market
- New, disrupting firms often win
Why disruptive innovations can cause large firms to fail
- Organization structure and capabilities slow response time/ability and influence choices
- Organizational processes weed out ideas that don't address current customer needs
- Focus on satisfying mainstream customers (ignore new tech.)
- Avoid small, uncertain, familiar markets (growth potential uncertain)
tactics for small companies to succeed
- enter with a product or market large firms don't care about
- not in mainstream, not interested
- not what they are good at
- margins/market is too small
- once you are strong, move up-market
How can large companies avoid failure
1. Monitor outside of industry
2. Partner with young firms
3. Establish venture units
4. Design by JOB not customer
Connect technology's impact to porter's five forces
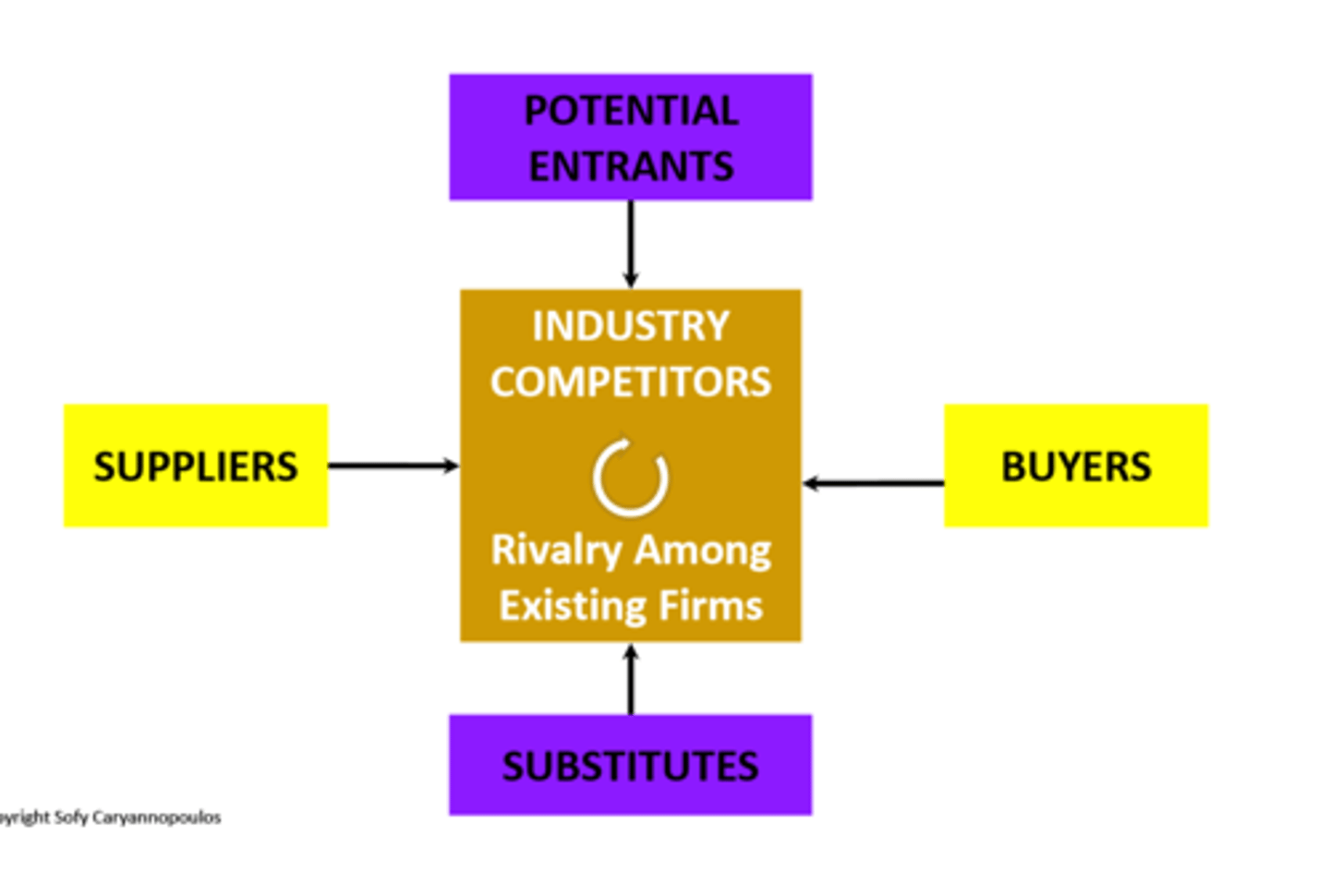
4 Pillars of the Canadian Financial System
1. Chartered Banks
2. Alternate Banks
3. Specialized Savings and Lending Intermediaries
4. Investment Dealers
Chartered Banks
- make deposits, and borrow money
- small and medium enterprises' primary lending source
Alternate Banks
- Private equity financing/borrowing
- Small and medium enterprises' primary lending source
Specialized Savings and Lending Intermediaries
- Private equity financing and borrowing
- Midsize to large size enterprises
Investment Dealers
- Going public; selling stocks and bonds
- Helps corporations access more investors
- Large and established enterprises
Debt vs. Equity Financing
Debt - borrow money; retain control
- must be repaid
- must pay interest
- legally binding
Equity - give up ownership
- no interest or repayment
- share control and profits
What is a bond? Is it debt or equity financing?
- legal binding agreement
- company/government borrows money from you, they pay interest each year and pay off the debt on an agreed date
- Debt financing
Fixed annual return
- Coupon payments (interest payments)
- often paid semi-annually (twice a year)
Fixed Term
- face value is paid at maturity date
- on a certain date you will be paid back the amount you gave, or a certain amount
Does a bond owner have priority over stockholders? Why or why not?
Yes, because a bond is a debt to a company, where stockholders own part of the company
SunLife 5.3 of 2021 at 91.75, name the characteristics
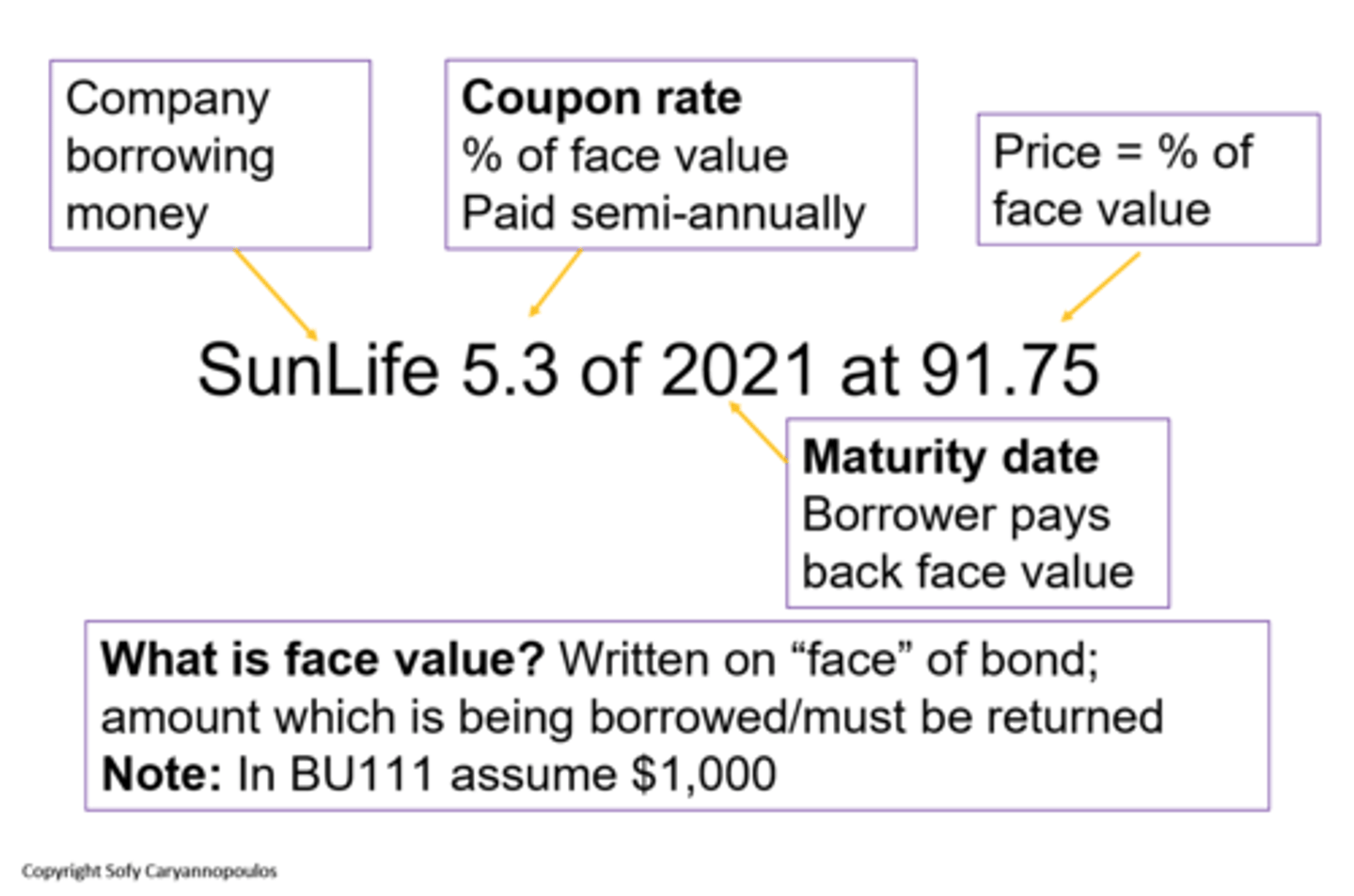
When do bond prices change?
Only when the yield has changed
How do you calculate the approximate yield to maturity?
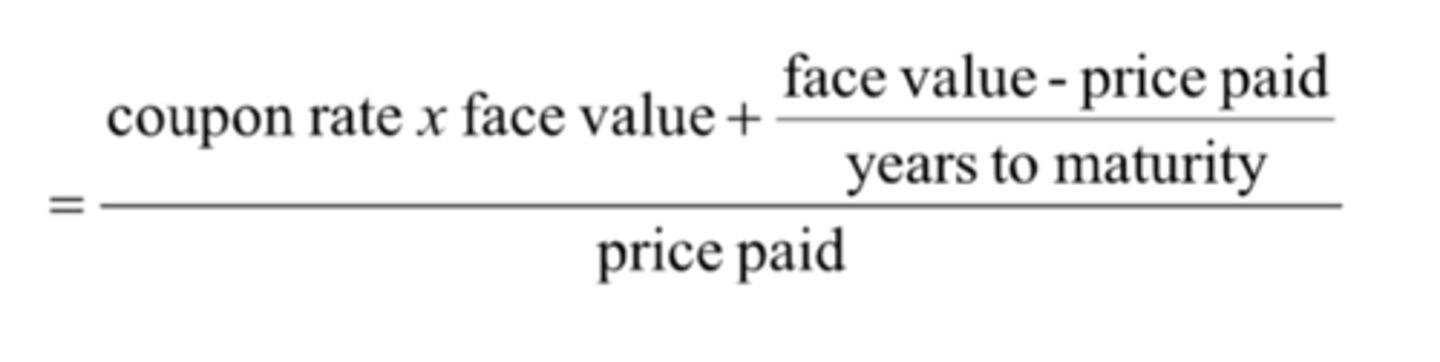
What happens to bonds when interest rates go up?
- Bond prices go down
- Interest rates and bond prices are closely related
What are Common Stocks and what do they do?
- ownership shares in corporations
- Reduces profits, dilutes ownership, dilutes control
What returns do stockholders get?
Dividends
What is a dividend? and is it guaranteed?
- portion of money thar the company has "left over" to share with the stockholders
- It is not guaranteed to get a dividend from a company
Is there a fixed term on a stock?
No, stocks will exist as long as the company is alive
Does a stockholder or bond owner get priority in a bankruptcy situation?
Bond Owner
What voting rights do shareholders have?
- Common shareholders have voting rights
- Preferred Shareholders do not
Who gets paid first, preferred or common shareholders?
preferred
What affects the price of a stock?
- company profit
- company performance (innovation)
How do you calculate yield?
Capital gain divided by investment
What type of financing is stocks?
Equity financing
What is the appropriate investing strategy?
When you can make an investment worth more than your dollars you have in hand today
- Creates potential to make a larger return
What is buying on margin?
paying a percentage of a stock's price as a down payment and borrowing the rest from a broker
4 Rules of buying on margin
- must qualify for margin account
- must sign 'hypothecation' agreement (Margin Account Agreement Form) -- pledging of securities as collateral for a loan
- must pay interest on loan
- the investors % equity (margin) in the margined stock must always be greater than or equal to the minimum margin requirement

What is the maximum loss and profit of buying on margin?
Profit: infinite in theory (less interest and commissions)
Loss: price paid for the stock (plus interest and commissions)
margin call
- demand by a broker that investors pay back loans made for stocks purchased on margin
- broker uses margin call money to reduce your loan
Does a mortgage represent equity or debt financing?
Debt
Why would you obtain a mortgage?
You have insufficient funds to buy real estate
What is the process of determining mortgage payments?
1. Determine amount to be borrowed
2. Decide on amortization period
3. Calculate payments to be made
What does it mean to "renew your mortgage"?
Negotiating a new mortgage agreement when the old one has expired and you still haven't fully paid off your mortgage
What are demographics?
- study of human populations
- Cohorts = homogenous groups within the larger population that share common characteristics
Why is it important that businesses understand Demographics?
- Demographics are a powerful predictor of behavior/trends
- Certainty and simplicity of age data
- Predicts supply and demand and informs environmental analysis and human resource decisions
What are two notable trends about Canada's demographic?
- Large number of people in the "baby boom" generation
- Smaller youth group (sandwich generation)
What problems do the baby boomers create?
- Increased elder care needs
- Increased number of vulnerable seniors
What are the 5 cohorts in Canada's demographic? Describe each
1. Maturists - pre-1945
2. Baby Boomers - 1945-1960
3. Gen X - 1961-1980
4. Gen Y - 1981-1995
5. Gen Z - born after 1995
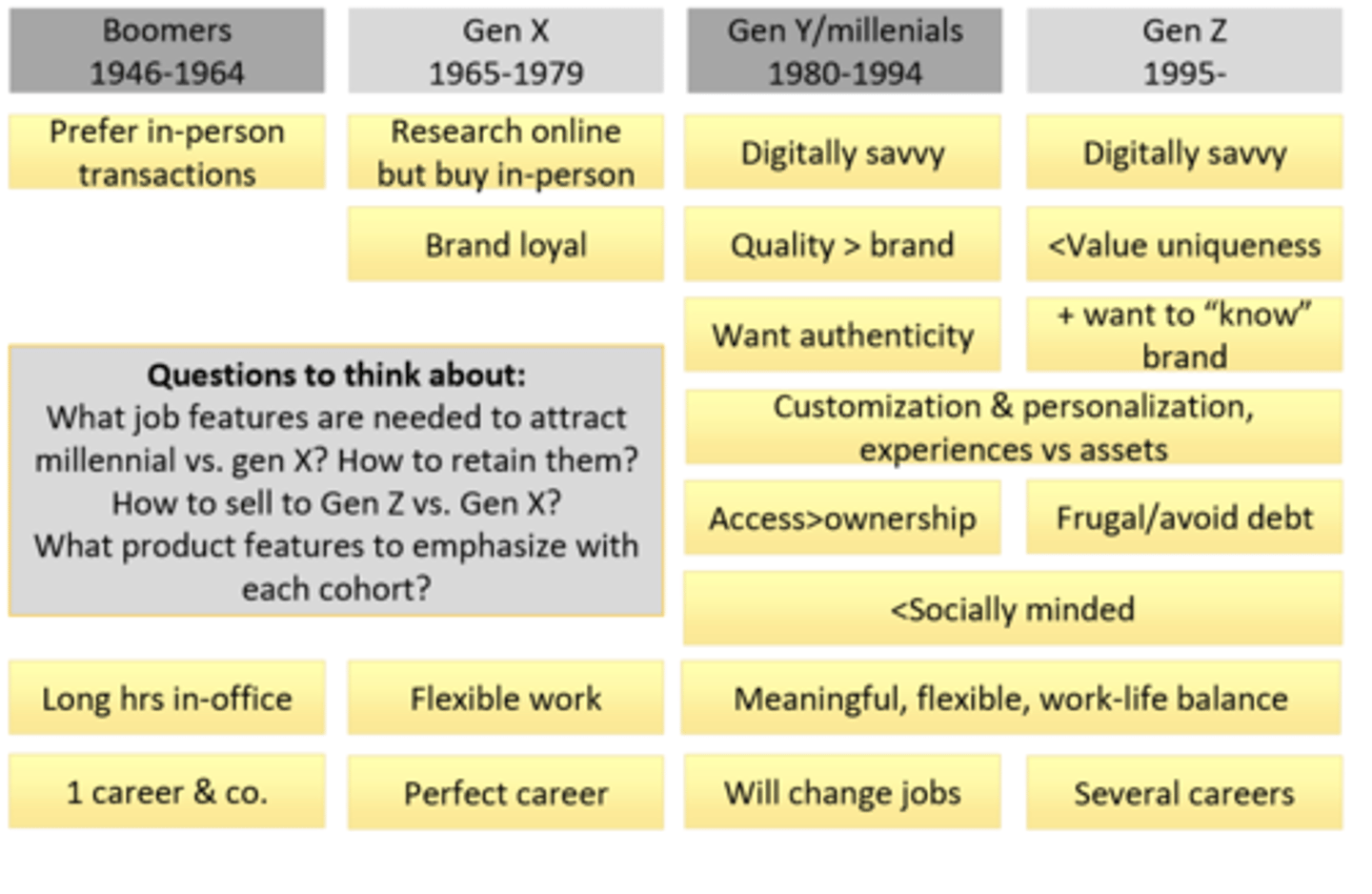
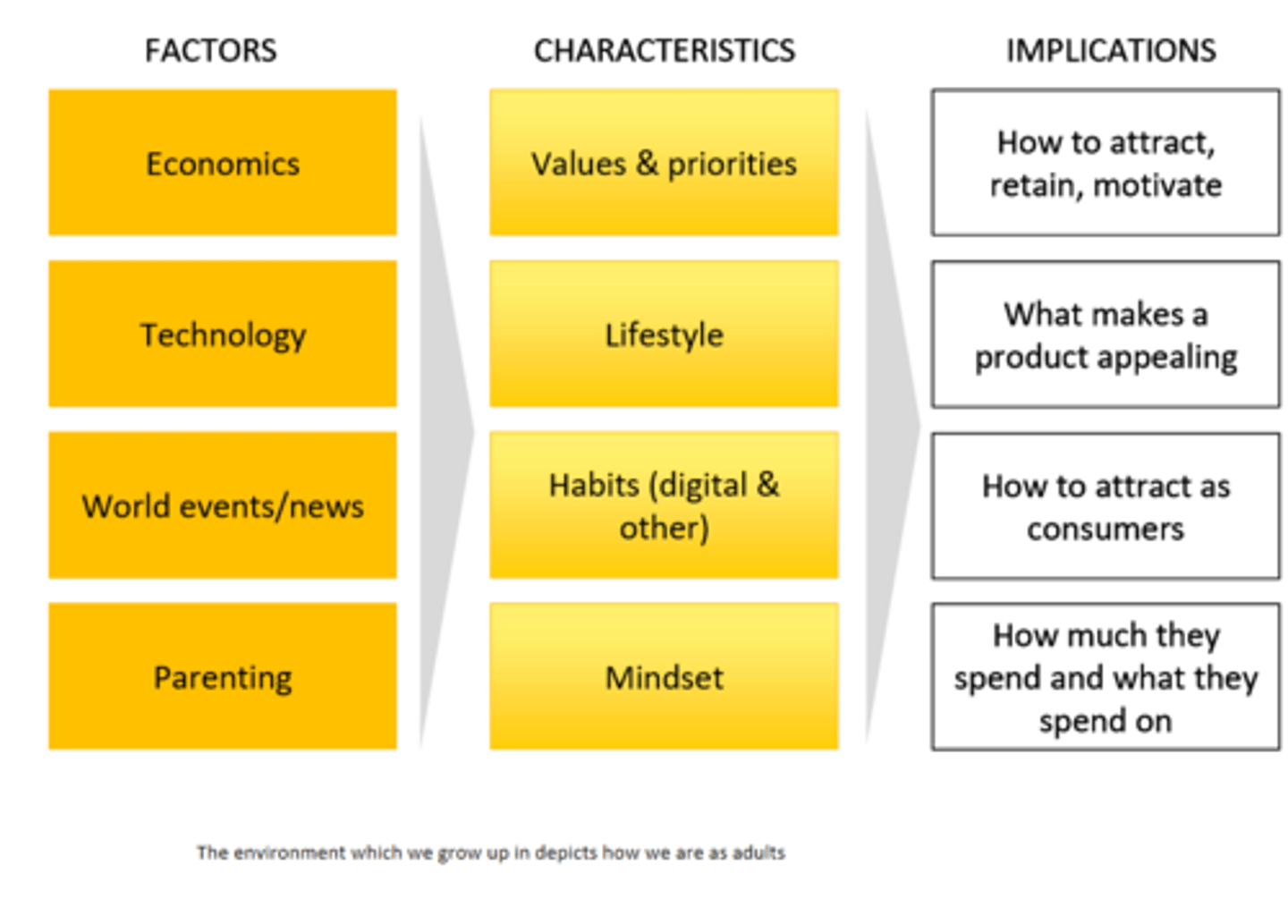
Factors and how they influence demographic characteristics
Acronym "WET-P makes Van Halen Like Men"
How does government influence over businesses? (4 roles)
1. Service Provider: mail services and schooling - competition and social goals
2. Business Support: Subsidies and trade agreements - creates opportunity and protection
3. Laws, Regulations: competition, consumer, pollution laws and IP rights - mitigates competition, creates consumer protection, promotes innovation, creates social goals and barriers (ie. competition act)
4. Taxation: Income tax, sales tax, property restrictive - controls consumer spending, creates incentives and barriers
How does business influence government? (3 Items)
1. Lobbying: businesses or individuals go and influence government to affect the environment
2. Collaboration/Input: CRTC consults with industry members
3. Advertising: corporations influence voters to vote for laws they want
Sole Proprietorship - Advantages and disadvantages
- business owned by one person
- Simple and inexpensive
- Few regulations
- Complete control
- Owner brings resources and capabilities
- Taxed on personal income (advantage if business has losses)
- Unlimitied liability
Partnership - advantages and disadvantages
- business owned by 2+
- simple and inexpensive
- few regulations
- shared control over profits and decisions
- more partners = more resources
- Shared amount of taxation
- Unlimited liability except if limited partner
general vs. limited partnership
GENERAL: all partners have joint and several liability
LIMITED: limited partners liability, cannot be active management, at least one general partner
Private Corporation - Advantages and Disadvantages
- Straightforward, relatively inexpensive
- Relatively few regulations
- Control and profits are shared with other shareholders
- Resources and capabilities are from owner
- Private corporate tax rates
- Limited liability to investment, except personal assets brought
Public Corporation - Advantages and Disadvantages
- Expensive and complicated
- Many regulations
- Board of directors = less control
- Can afford to buy resources and capabilities
- Taxed separately from shareholders, slightly higher taxes then private
- Liability limited to investment
What do social enterprises do?
- Social enterprises generate social value while operating with the financial discipline, determination and innovation of private sector businesses
Difference between social enterprise and a traditional for-profit enterprise
A social enterprise's main goal and first priority is the social value
what is globlization?
- the result of Internationalization
- world becoming single interdependent system
What are the 3 driving forces of globalization?
1. Cost and market benefits
2. Technology makes it easier, faster, cheaper
3. Competitive pressure
4 decision components to go international
1. can we?
2. should we?
3. where?
4. how?
Factors to consider where to expand internationally
Consider countries:
- population
- average spending
- customer reachability
- competition
- liability of foreignness
- distance
- administrative barriers
6 Foreign entry strategies
1. Indirect Export
2. Sales Agent or Distributor
3. Licensing/Franchising
4. Alliance/Joint Venture
5. Local Sales Office
6. Foreign Subsidiary
Indirect Export - What, Why, Risks/Costs
What: sell to a third-party export merchant in own country, and export company decides where to sell
Why: No additional cost, export has market knowledge, no risk from foreign market political volatility
Risks: share attention with other organizations; limited market control; subject to trade barriers
Sales agent or distributor - what, why, risks
What: hire an agent or distributor to sell your product using their local network, you manufacture domestically and ship abroad
Why: You aren't familiar or have the network resources to easily tap into foreign market, limited understanding of foreign market
Risks: share attention with other organizations; limited marketing control; subject to trade barriers
Licensing and Franchising - what, why, risks
What: giving local organization the right to use your intellectual property in exchange for royalties; another company produces goods or services using your intellectual property in exchange for royalties
Why: Faster and larger expansion with fewer financial resources, no need to overcome trade barriers or acquire additional resources
Risks: damage to intellectual property
Joint Venture - what, why, risks
What: Partnering with a local firm for mutual benefit; partnership can take many forms - mutual distribution, sharing of knowledge, investment
Why: Political or trade barriers; overcome market barriers with lower investment or risk; overcome production constraints
Risks: Time, personnel, money, partnership doesn't work - partner doesn't deliver, doesn't deliver as expected or promised or is difficult to work with
Sales Office - what, why, risks
What: establishing your own sales office but manufacture in your domestic market and ship abroad
Why: retain marketing control, insufficient volume to justify facility, have excess capacity in domestic facility, don't have resources to build foreign facility, don't want to take risk
Risks: trade barriers, market knowledge. investment to establish foreign sales capabilities
Foreign subsidiary - what, why, risks
What: manufacture and sell in foreign market
Why: overcome trade barriers, control of intellectual property and marketing
Risks: cost of facility and establishment of operations; sometimes need permission of foreign government
4 Models of Ansoff Matrix
1. Market Penetration
2. Market Development
3. Product Development
4. Diversification
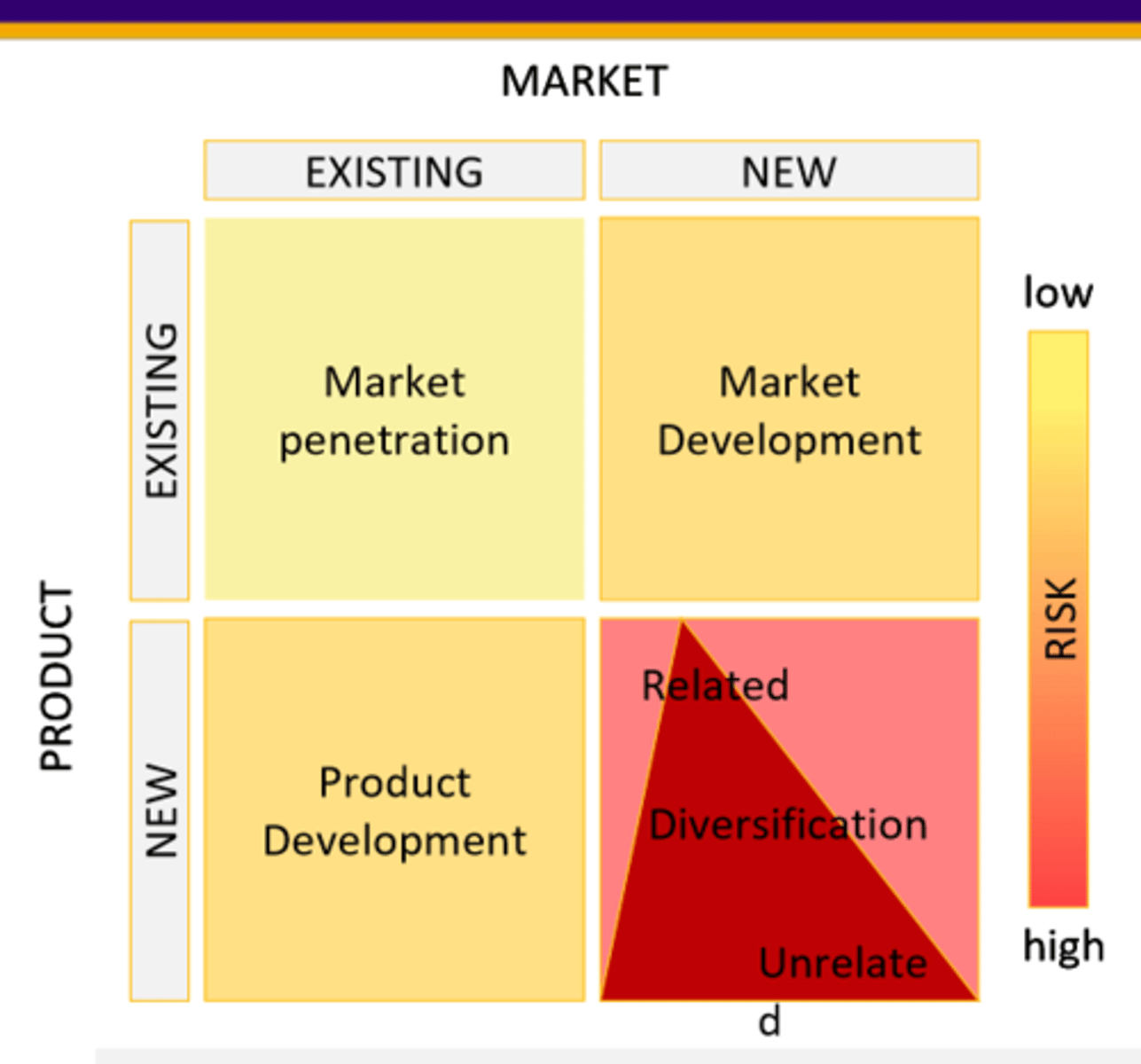
market penetration
- sell more of the existing product to existing target market
- build on what you have and know
- cut prices, increase advertising, increase distribution channels, buy a competitor
market development
- same product, new customer
- selling what you already produce to new target markets or new geographic markets
- capitalize on production capabilities
- customer access and awareness are challenges
- create awareness in new market
product development
- new products, same customers
- develop related or unrelated products your customers value, product line extension
- build customer knowledge and brand equity
- extend product, repackage existing products
Diversification
- new product, new market
- chasing new customer with new products, creating new businesses
- diversify business portfolio by building new business, capitalize on existing capabilities in higher growth areas
- acquire other business
Risks of each model
Market Penetration: competitor reaction, winning customers
Market Development: customer access and awareness
Product Development: cannibalization; give up production efficiencies; must know what and how to develop new product
Diversification: many activities and capabilities must be created or changed = high risk or failure