Spectrophotometry, Fluoro/Nephelo/Turbimetry
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
21 Terms
transmittance equation
T = Is / I0 (Is < I0)
absorbance equation
A = 2 - log(%T)
Beer’s law is
concentration of a substance is directly proportional (must be linear) to the amount of light absorbed or inversely prop to the log of the transmitted light
Beer’s law equation
A = abc
a = constant
b = light path (cm)
c = conc of absorbing cmpd (g/L)
if b = 1cm, c is in mol/L → a becomes E
calibration constant (K)
cu = Au*K
plug in from standard curve, a conc and absorbance reading to get K
spec light sources
incandescent lamps
tungsten: visible light
hydrogen & deuterium lamps: UV
laser
monochromator function
isolates radiant energy of desired wavelength
types:
filters
prisms
diffraction gratings
prism vs grating vs filter
sep white light into continuous spectrum by refraction
diffraction grating: thin layer of alloy on flat glass plate
holographic grating: v accurate
filter: wide/narrow bandpass, sharp cutoff
fiber optics
aka light pipes
transmit light throughout their lengths by internal reflections
photodetectors
converts light into an electric signal
prop to photons striking detector
photodiode array
2-D arrays of diodes
allows 2nm resolution per diode from 200-340nm
allows a 1nm resolution per diode from 340-800nm
single beam spec
beam of light passes through a monochromator
→ ligth passes through cuvette
→ any light not absorbed is transmitted to a detector
→ detector converts light energy to electrical energy
→ electrical energy registered on a meter
double beam in space spec
all components are x2 except for light source
double beam in-time
uses a light beam chopper inserted after exit slit → mirrors → onto common detector
**compensates for a light source variation & sensitivity changes of detector
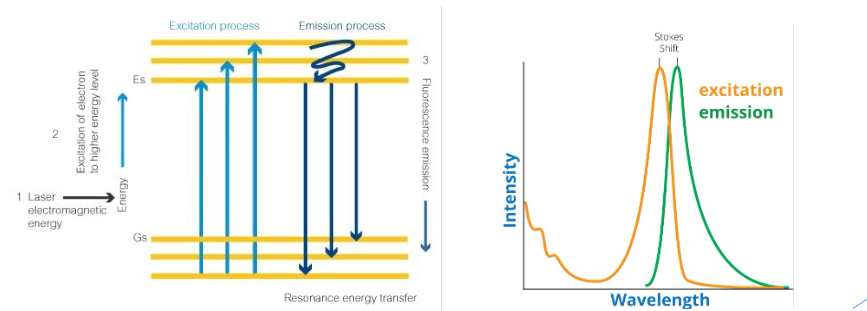
fluorometry
measurement of visible spectrum
light source → light absorbed → electrons excited → energy re-emitted at longer wavelength (lower energy) → electron returns to ground state
Stoke’s shift
a constant that is difference in E or wl b/t max excitation & fluor emission
fluorescence polarization
smaller → faster rotation → light depolarized
bigger when bound → slower → polarized
nephelometry
meas of light scattered produced by soluble immune complexes suspended in solution at right angles to the incident beam
depends on: particle size, wavelength, concentration of particles,
light scatter detected at 90 degree angle
target concentration & light scatter are directly prop
turbidimetry
light transmit detected at 0 or 180 degrees
light transmitted dec => analyte conc inc → inversely prop
nephelo/turbidimetry clinical applications
immunoglobulins
proteins
drugs
nephelo/turb limits
meph more sensitive
antigen xs (post-zone)
lipemia & hemolysis