Comprehensive Agriculture Types, Revolutions, and Land-Use Models (Unit 5 on ap classroom)
1/71
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
72 Terms
Subsistence Agriculture
Farming mainly to feed the farmer and their family, not to sell.
Commercial Agriculture
Farming to sell products for money, usually large-scale.
Intensive Agriculture
Lots of labor or money on a small area of land (high input, high yield).
Extensive Agriculture
Uses lots of land, but less labor/money per acre (low input per area).
Shifting Cultivation
the cultivation of a plot of land until it resources are exhausted and then moving to another land.
ex: (Slash-and-Burn)- Clear forest by cutting and burning, farm for a few years, then move when soil is used up.
Pastoral Nomadism
People who move with their herds of animals looking for water and pasture
*usually occurs in more arid/ semi-dry climates areas where it is too dry or infertile to grow crops, so people cannot permanently settle and farm and instead must move around.
*pasture- land covered with grass or other plants that animals can eat
Plantation Agriculture
Large farm in tropical areas growing one cash crop (like sugar, coffee, cotton) often for export.
Mixed Crop and Livestock Farming
Farms that grow crops and raise animals together; crops often feed the animals.
truck farming (Speciality agriculture)
Growing fruits/veggies for markets
Dairy Farming
Raising cows for milk and dairy products.
Grain Farming
Growing grain crops like wheat, corn, barley, mainly for food or feed.
Mediterranean Agriculture
Farming in areas with warm, dry summers and mild, wet winters (grapes, olives, citrus).
First Agricultural Revolution (Neolithic Revolution)
When humans first learned to farm and domesticate animals instead of only hunting/gathering.
Second Agricultural Revolution
1700s-1800s: Better tools, crop rotation, and new methods → big increase in food production in Europe.
Third Agricultural Revolution / Green Revolution
Occured in the 1960s/1970s: High-yield seeds, chemical fertilizers, pesticides, irrigation and cross breeding
Domestication
Taming and breeding plants/animals for human use.
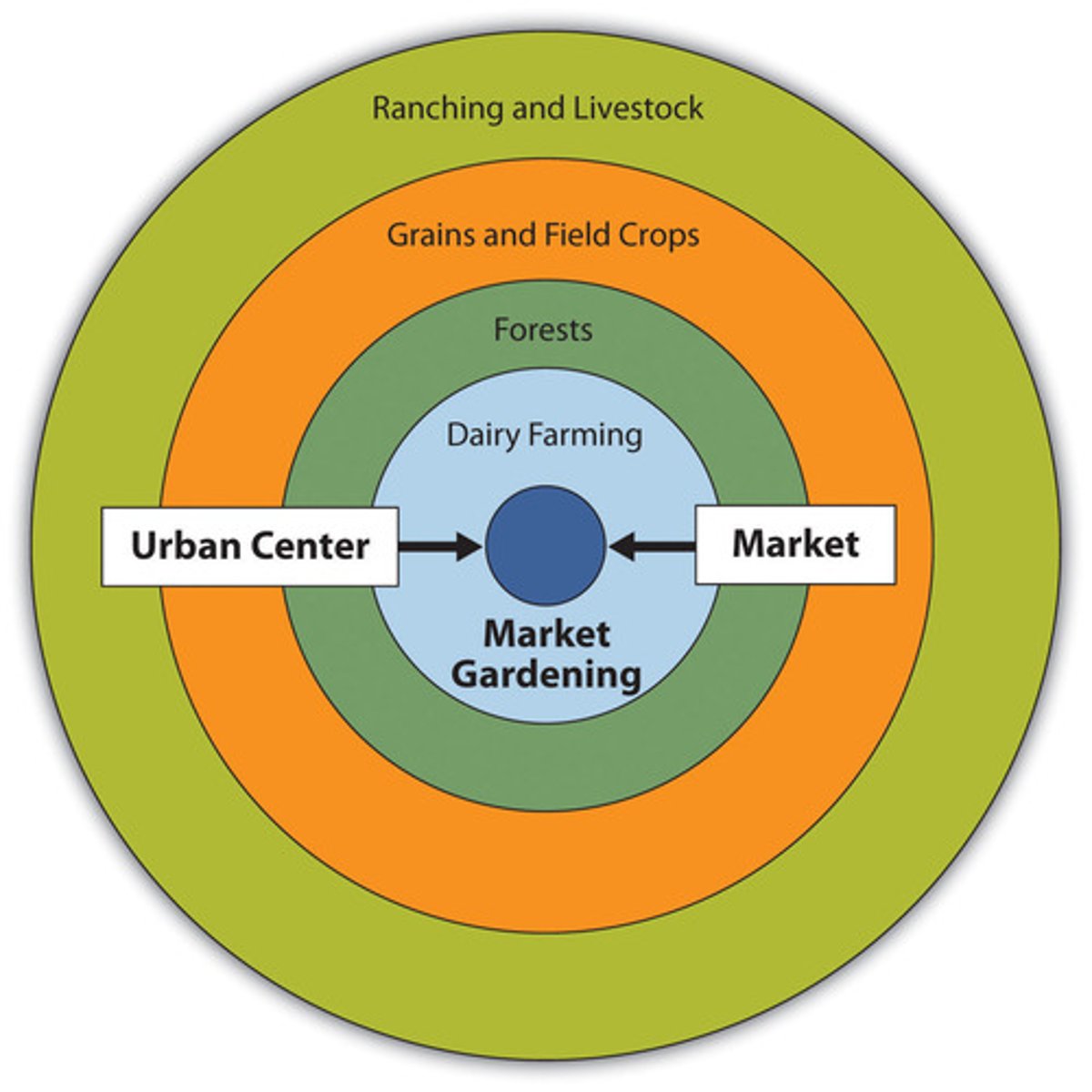
Von Thünen Model
Model showing how different types of farming are located around a central city based on transport cost & land cost.
1. in the center there the town/village
2. First ring: intensive farming and dairy
3. second ring: forest
4. Third ring: grains/ cereal crops
5. fourth ring: ranching and livestock
High-Yield Variety (HYV) Seeds
Special seed types bred to give more grain per plant.
GMOs (Genetically Modified Organisms)
Plants/animals whose DNA has been changed in a lab to improve traits (bigger, pest-resistant, etc.).
*please remember that this is NOT a products of the 3rd agricultural revolution. GMO'S occured much later. Specifically they occured in the 90s/2000s
Agribusiness
Large-scale, commercial farming controlled by corporations (from seeds → farming → processing → sale).
Monocropping
Growing only one crop over a large area.
Commodity Chain
The steps a product goes through from farm to final consumer (grow → process → transport → sell).
*this can happen on a global scale as well
Food Security
When people have reliable access to safe, nutritious food.
Food Insecurity
Not knowing if you'll have enough safe, nutritious food.
Cash Crop
Crop grown to sell for money, not to eat locally (cotton, coffee, sugar).
Staple Crop
Main food people eat every day (rice, wheat, corn).
Desertification
Fertile land turning into desert (often due to overgrazing, deforestation, climate change).
Soil Degradation
Soil becomes less productive (from overuse, chemicals, erosion).
including: Soil salinization (when land in arid region is converted into farmland: salt get in soil --> strips soil of nutrients --> soil no longer good for farming
Deforestation
Large-scale cutting down of forests.
Sustainable Agriculture
Farming that protects the environment and can continue long-term (crop rotation, less chemicals).
Irrigation
Artificially bringing water to crops (dams, sprinklers, drip systems).
Clustered Settlement
Houses and buildings grouped close together, near fields.
Dispersed Settlement
Farms and houses spread far apart.
Linear Settlement
Buildings lined up along a road, river, or coastline.
Fertile crescent (Southwest Asia)
Mediterranean / semi-arid climate
grows: Wheat ,barley, peas, olives, oats
domesticated: sheeps, goats, pigs, cattles
Yangtze River Valley (East Asia)
Subtropical & temperate climate
grows: Rice, Millet(grain), soybeans, walnuts
Sub-Saharan Africa
Tropical climate & savana
grows: Yams, coffee, sorghum (grain)
Mesoamerica
Subtropical/ tropical climate
grows: Maize, squash, beans, peppers
Domesticated: Turkey
South Asia
Indus River valley (tropical climate)
Grows: Wheat, barley, peas
domesticated: cattles, camels, buffalo
Metes and Bounds
A method of land description which uses natural land features to define property line
ex: My house is from the big oak tree to the river, then 100 feet north of blah blah blah
Township and Range (Rectangular surveys)
A rectangular/square land division (grid system)
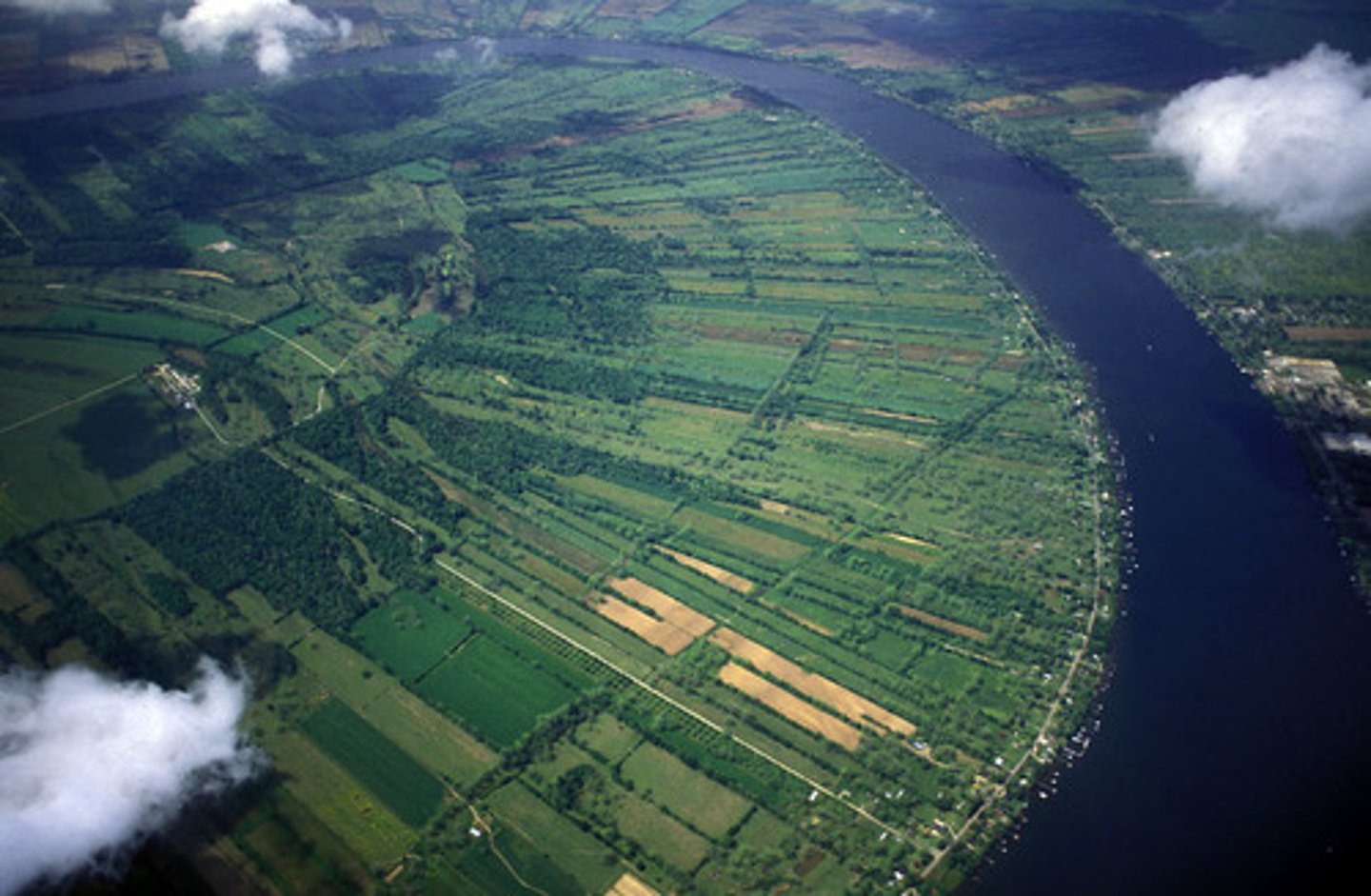
long-lot survey system
long plot of land that all touch a river, road, or canal

Ranching
A practice that involves raising lives stocks on a large, open, and fixed land
Columbian Exchange
The interchange of plants, animals, diseases, and human populations between the Old World and the New World.
Biodiversity
the variety among species and ecosystems
hearth
The region from where stuff originated from
transhumance
The seasonal migration of livestock between summer and winter pasture (this is a form of pastoral nomadism)
free range
allowing animal to move around in a more natural environment
Process food
Food that has been tampered with in any way (washing, cutting, heating and so on)
organic farming
grown without artificial chemicals (more intensive)
bid rent
the price at which farmers are willing to rent/'bid" land based on their needs
*land that is closer to the town tends to be more expensive and intensive than land further from the town
Von Thunen equation
rent = Y (P-C) - YFM
Y- Crop yield per unit of land
P- Market price per unit yield
C- cost of production per unit/ acre
F- transport cost per unit/ mile (weight and perishability)
M- distance from the market
Crop yield
How much you can harvest per unit of land
Malthusianism theory
theory that states - Population growth will outpace food supply which will eventually lead to people killing one another or famine and diseases the typical yk
subsidies
when the government pays farmer to grow certain crops
One acre model
One acre of land for subsidence farming and the rest of the land is used for commercial farming
Functional zoning
Dividing space based on specific functions such as residential, commercial and industrial to avoid conflicting land uses
Ownership rule
legal entitlement to use and transfer property
ex: Primogeniture: land goes to chosen relative usually a man
Urban farming
the practice of growing fruits and veggies on a small private plots or shared community farms within the confines of a city
Community Supported Agriculture (CSA)
A direct-to-consumer marketing arrangement in which farmers are guaranteed buyers for their produce at guaranteed prices and consumers receive fresh food directly from the producers
farmer's market
markets at which local farmers and food producers sell fresh locally grown items
Value-added agriculture
processing raw agricultural product to increase their market value
ex: A farmer (themself) processes raw milk into cheese and then selling it at a farmers market
fair trade movement
Produce are a little more pricey because the farmers producing them are getting payed a fair wage
food safety
keeping food safe to eat by following proper food handling and cooking practices
Food Insecurity experience scale
a survey developed by the food and agriculture organization ( FAO) it measure food insecurity
Köppen climate classification
System categorizing climates based on temperature and precipitation.
nucleated settlement
a type of community where buildings and homes are clustered closely together around a central point, such as a market, church, or public square
Terrace farming
cutting of "steps" into mountains or hills to create level plot farming
Draining wetlands
wetlands (swamps, marshes) were consider useless so draining the water out of them to make them farmable was a common practice.
Food Deserts
Areas where it is difficult to find affordable, healthy food options. More common in area where there is a lack of transportation to groceries store
Monoculture
Still planting one type of crop the difference is that they change the type of crop each year.
*Monocropping does not. they stick with the same crop every year
Southeast Asia
grows: sugar cane, root vegetables, bananas
domesticated: chickens and pigs