Bio Lab Final - Cell Division | Interphase, Mitosis, Cytokinesis
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
28 Terms
Which stages does the Cell Cycle consist of?
Interphase
Gap 1 Phase (G1)
Synthesis Phase (S)
Gap 2 Phase (G2)
M Phase
Mitosis
Cytokinesis
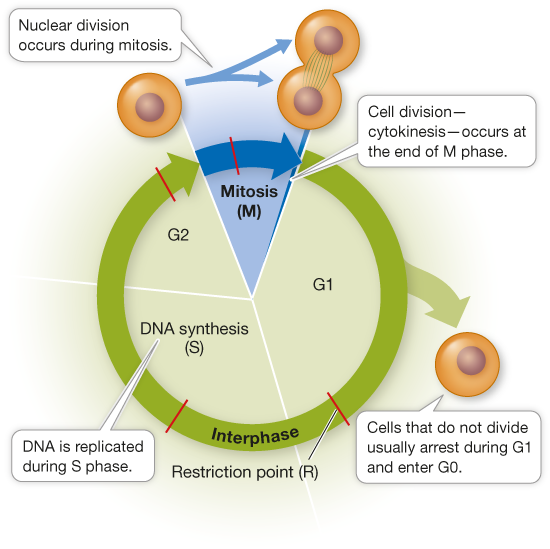
What happens in Interphase?
The cell grows, copies its DNA, and prepares for mitosis by duplicating any necessary organelles.
What are the 3 phases of interphase?
First Gap (G1) Phase
Synthesis (S) Phase
Second Gap (G2) Phase
What happens in the G1 phase?
Cell growths
All organelles including centrioles duplicate
What happens in the S phase?
DNA is synthesized
Centrosomes (contain centrioles) duplicate
When the cell is in interphase, where is the DNA located?
In the nucleus
What happens in the G2 phase?
Additional cell growth
What is the G0 phase?
A resting phase in which a cell is not preparing for the cell division cycle. This can be permanent, but sometimes the cell goes to G1.(The cell doesn’t divide or go through the cycle.)
What does the M Phase consist of?
Mitosis
Cytokinesis
What are the 4 phases of mitosis?
Prophase
Metaphase
Anaphase
Telophase
What happens in Prophase?
Chromatin condenses and shortens (becomes chromosomes or a pair of sister chromatids)
The nuclear envelope breaks down
Centrioles form spindle fibers
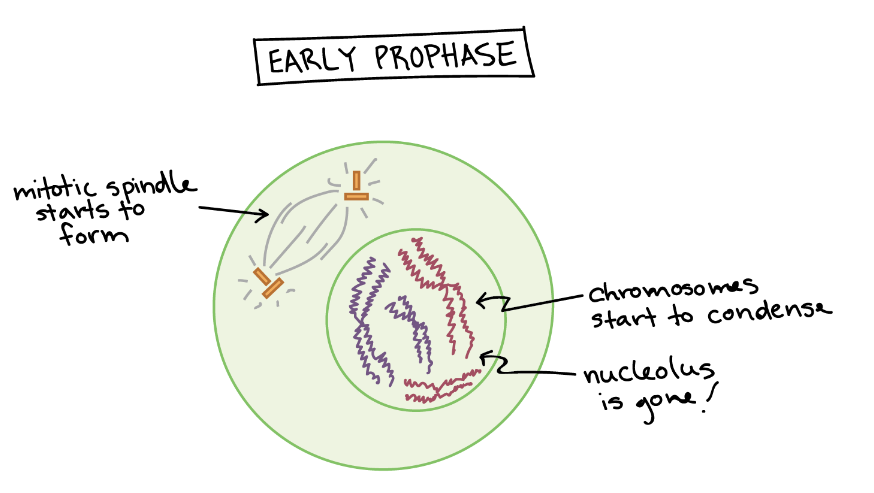
At what region do sister chromatids attach?
At the centromere
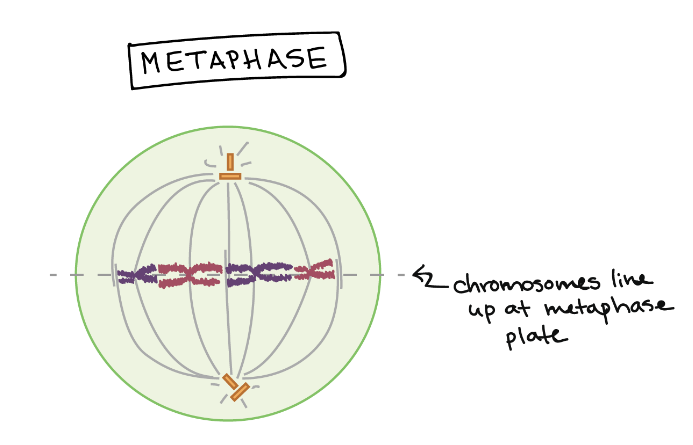
What happens in Metaphase?
Chromosomes line up at the metaphase plate
Each sister chromatid is attached to a spindle fiber from opposite poles
What happens in Anaphase?
Spindle fibers attach to kinetochores of each chromosome
Chromatids are separated and pulled apart toward opposite ends of the cell
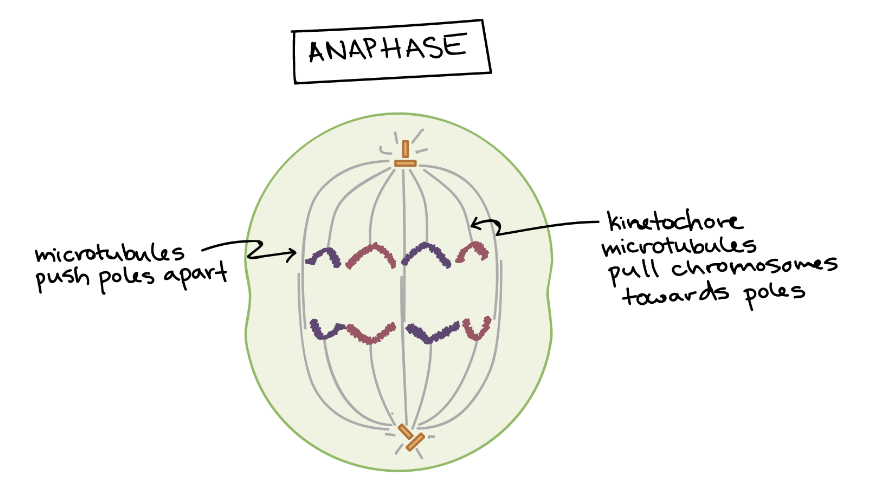
What is a kinetochore?
A specialized protein structure on a centromere to which spindle fibers attach.
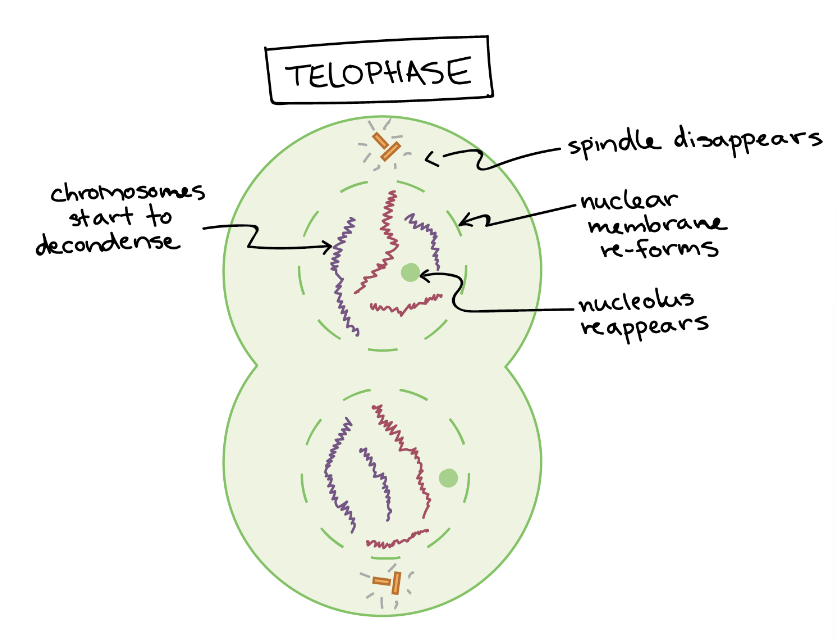
What happens in Telophase?
Nuclear membranes reform around each group of chromatids
2 nuclei form
Organelles start to reappear
What happens in Cytokinesis?
Division of parent cell cytoplasm into 2 daughter cells
Cell membranes form
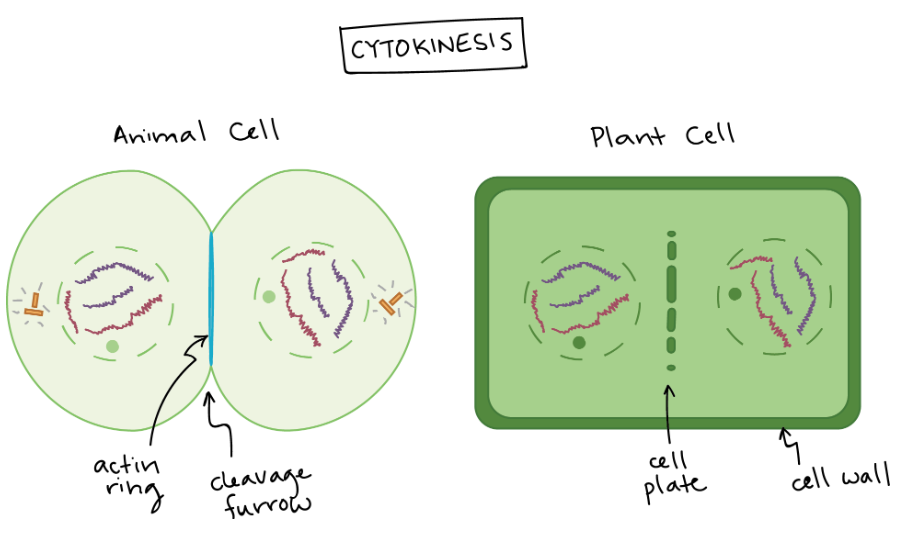
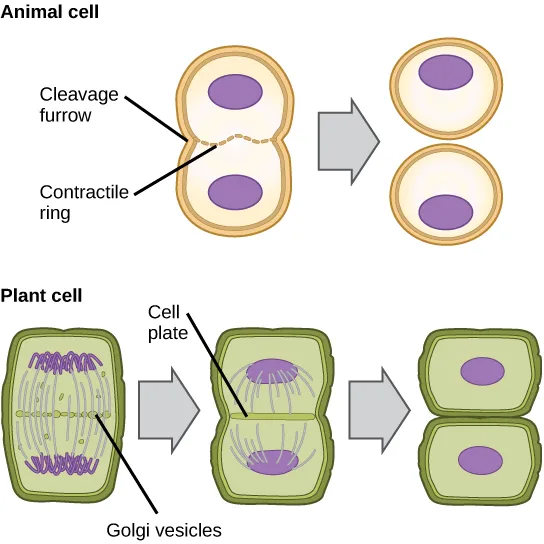
What is the difference between a plant and animal cell during cytokinesis?
In animal cells, a cleavage furrow is present in between the two daughter cells when splitting.
In plant cells, a cell plate is present in between the two daughter cells when splitting.
Are the resulting daughter cells in mitosis diploid or haploid?
Diploid
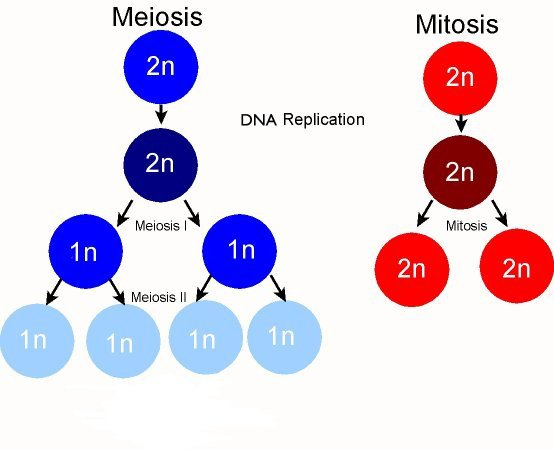
What does meiosis consist of?
Two nuclear divisions that reduce the number of chromosomes to the haploid number, in preparation for sexual reproduction.
Meiosis I
Meiosis II
What do Meiosis I and Meiosis II consist of?
Prophase I & II
Metaphase I & II
Anaphase I & II
Telophase I & II
What happens in Prophase I?
Chromatin condenses to form chromosomes (in mitosis)
Homologous chromosomes form pairs known as tetrads/bivalent
Crossing over occurs (genetic material is exchanged)
Chromosomes form a new combination of genes
(The last 4 points also occur in mitosis)
Chromatin condenses to form chromosomes
Nuclear membrane disappears
Nucleolus disappears
Centrioles move to opposite ends
Spindle fibers start to form
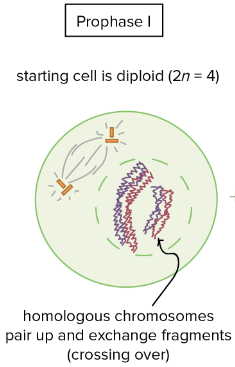
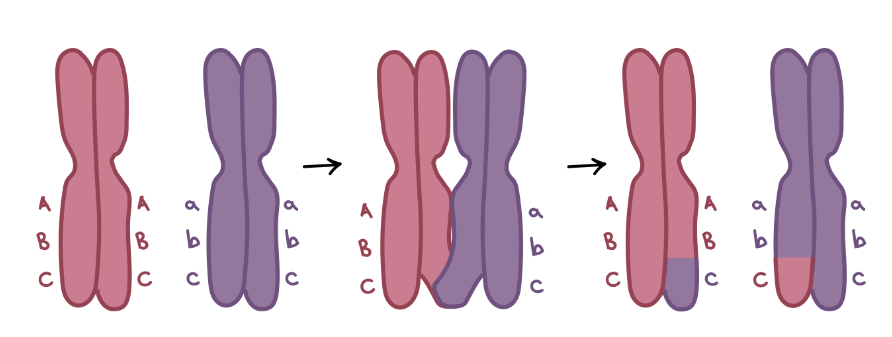
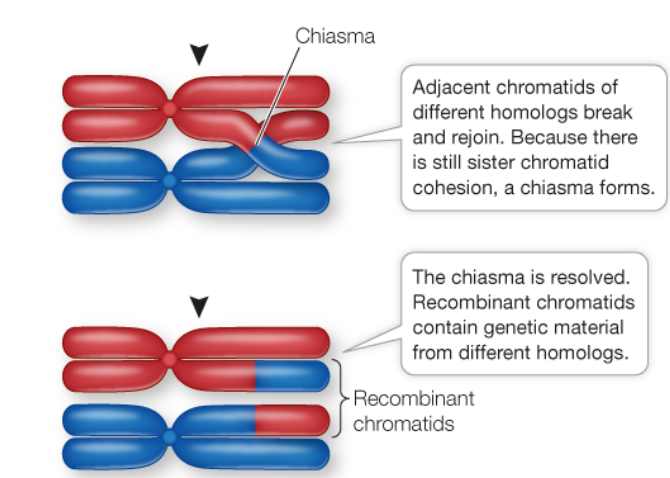
Define Crossing Over
The mechanism by which linked genes undergo recombination. The exchange of corresponding segments between two homologous chromatids.
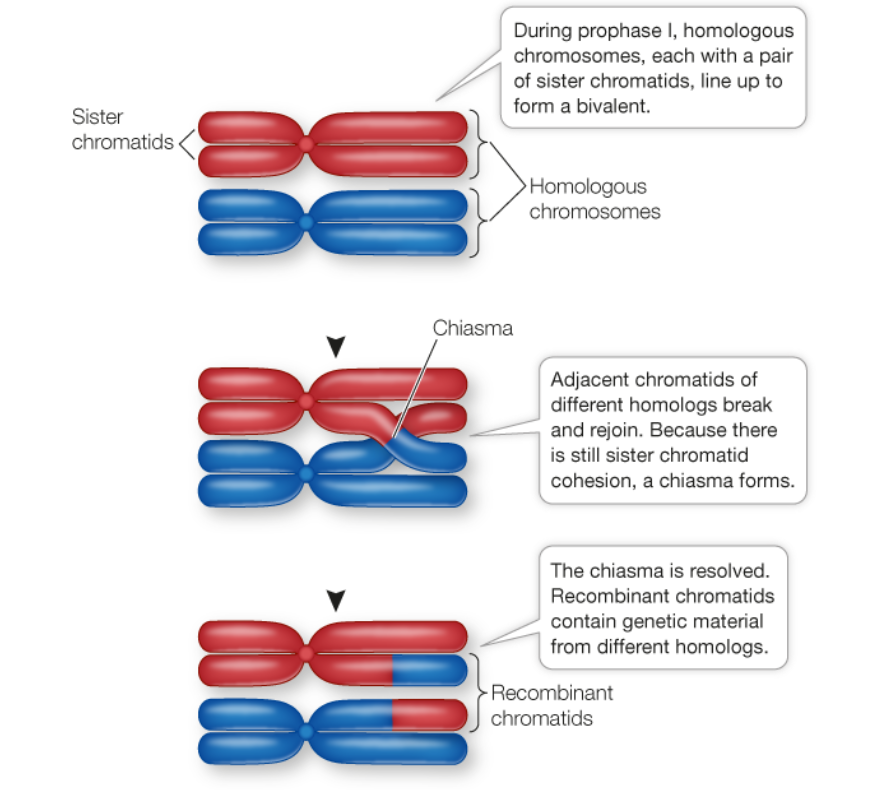
Define Chiasmata
An X-shaped connection between paired homologous chromosomes in prophase I of meiosis.
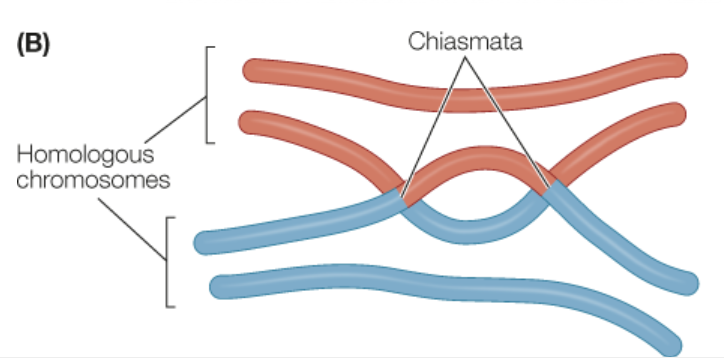
Define Chiasma
The visible manifestation of crossing over between homologous chromosomes.
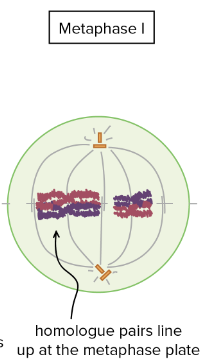
What happens in Metaphase I?
Instead of individual chromosomes aligning at the equatorial plane, homologous pairs align at the plane
Each chromosome from the pair is tied to a spindle fiber from opposing sides
Centromere doesn’t separate
Sister chromatids are still together
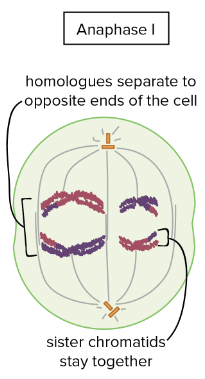
What happens in Anaphase I?
Homologous chromosomes separate and are pulled to opposite sides
Spindle fiber shortens
What happens in Telophase I?
Homologous chromosomes arrive at opposite ends
Each pole contains half the number of chromosomes (haploid)
Nuclear membrane is formed
Nucleoli reappear
Spindle fiber disappear
Cytokinesis follows