Med imaging E2: GU
1/80
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
81 Terms
How long are the kidneys?
13 cm
Which kidney sights slightly higher due to the liver pushing it down?
left
which way is the superior pole of the kidney tilted?
medially
What is IVP?
intravenous pyelogram; iodine based contrast material injected IV and rapidly cleared by kidneys (contrast slightly enlarges kidneys)
xray exam that uses injection of contrast material to evaluate kidneys, ureters, and bladder
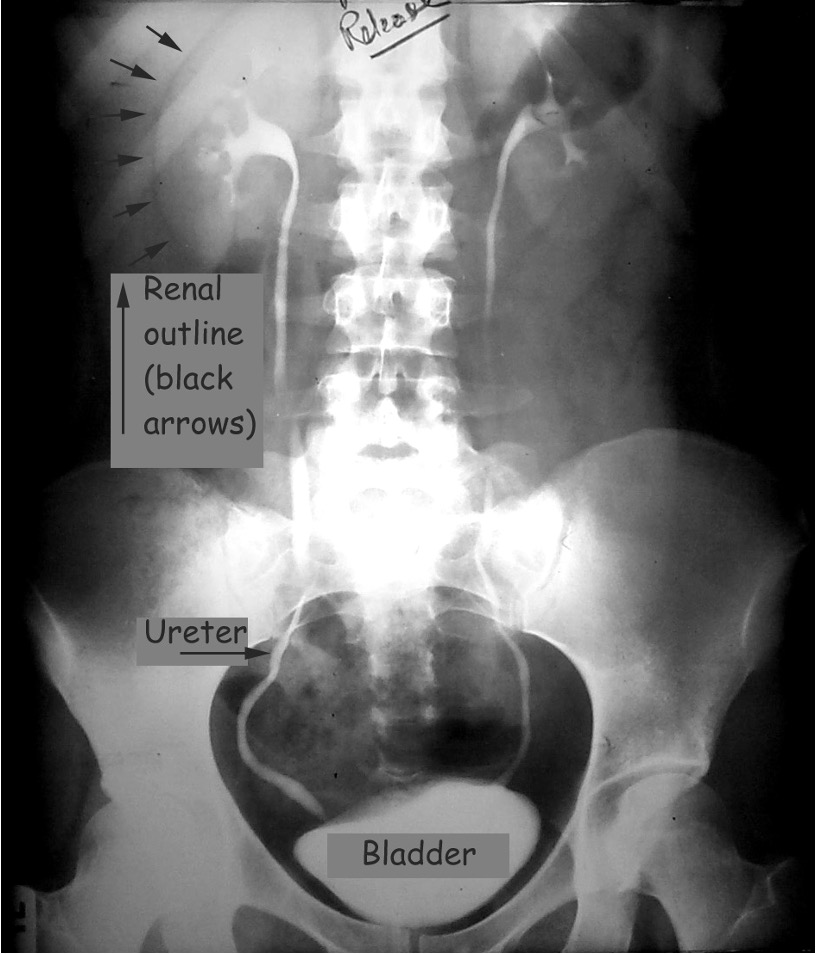
What must be stopped 48 hours after IV contrast administration in IVP?
Metformin (glucophage)- can cause renal failure and lactic acidosis
What is a noninvasive option for patients at risk for a reaction to IVP contrast?
renal ultrasound
What are indications for renal ultrasound?
hydronephrosis or renal cysts
what is the R kidney visualized through on renal ultrasound?
liver
what is L kidney visualized through on renal ultrasound?
back
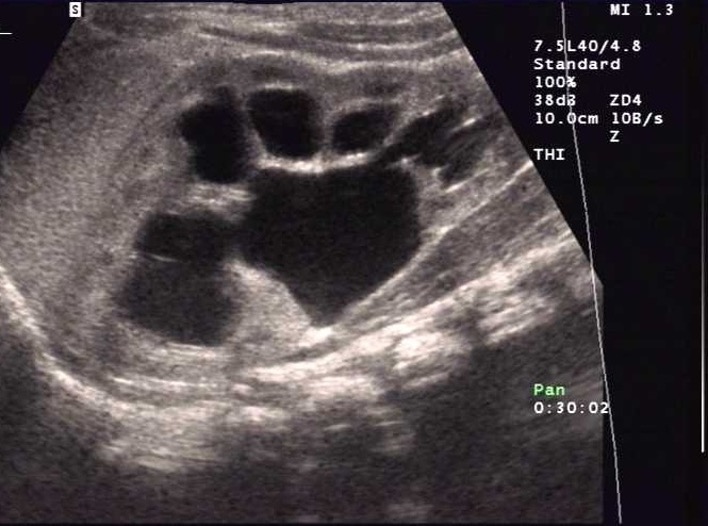
What is this?
hydronephrosis
What is indicated as first line evaluation after major trauma or for obstructive stone disease when IVP contraindicated?
CT scan
What are evaluation method for hematuria?
UA, IVP, U/S, cystoscopy, and CT scan w/ IVP
what is indicated for visible hematuria w/ known trauma?
CT scan
What are the most common kidney congenital abnormalities?
ureteral duplication, pelvic kidneys, horshoe kidney
T/F: it is more common to have 2 kidneys w/ 1 displaced than to have only 1 kidney
T
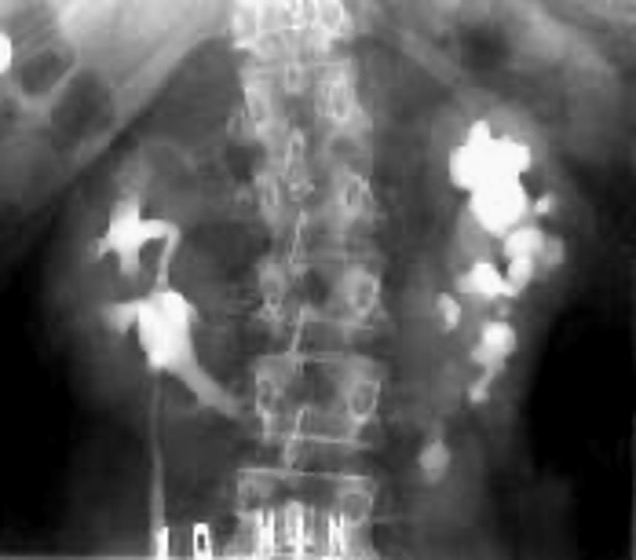
what is this?
horseshoe kidney
what is this?
pelvic kidney
What is good for following benign appearing renal cysts?
U/S
What is indicated if renal cyst has septa (dividing walls) or internal echoes (to r/o CA)?
CT
What can polycystic renal dz be followed by?
u/s or CT
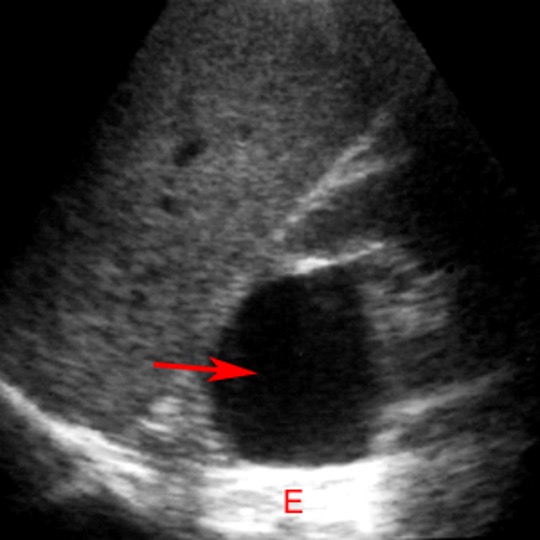
what is this?
renal cyst
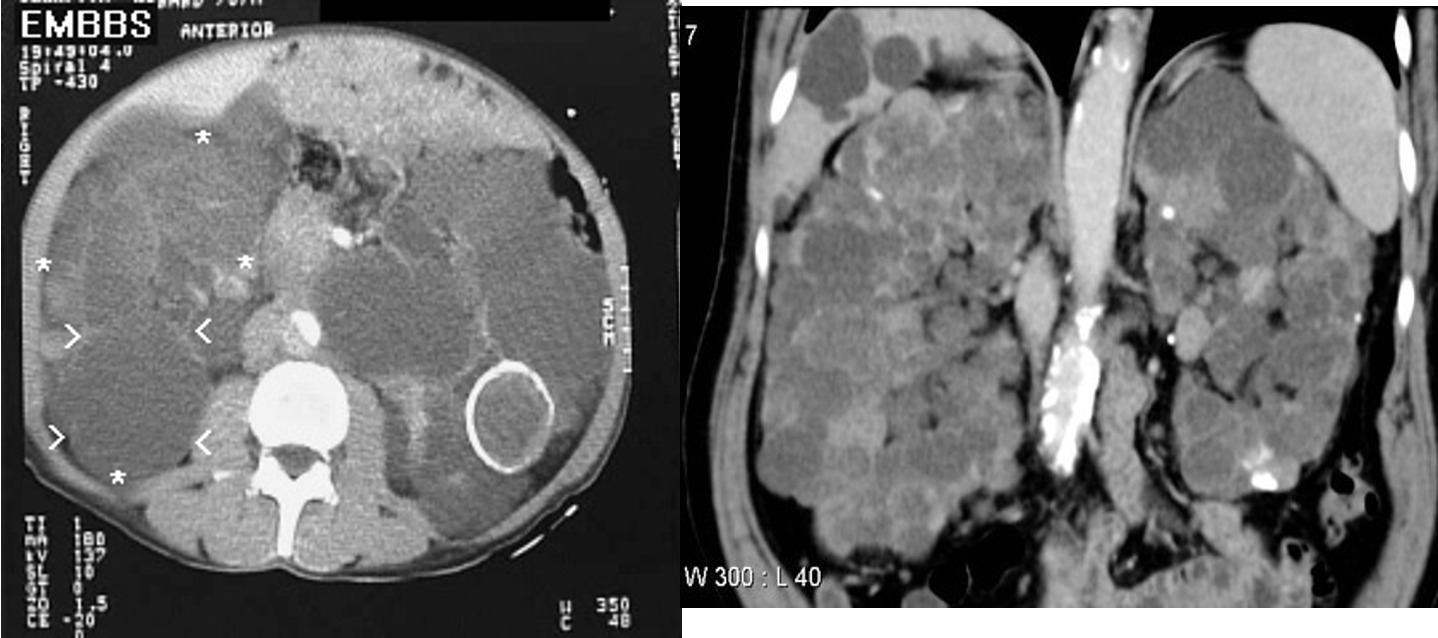
what is this?
renal cysts / polycystic kidney disease
What are stag-horn calculi?
large stones that fill most of the collecting system
what is the clinical presentation of renal stone disease?
intense unilateral flank pain w/ hematuria and nausea w/ vomiting
What is indicated for evaluation of renal stone disease?
IVP or CT scan
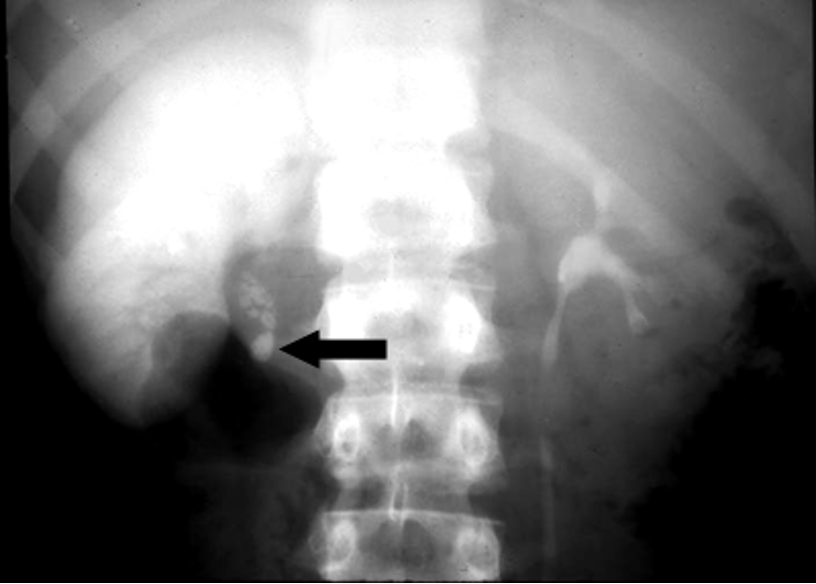
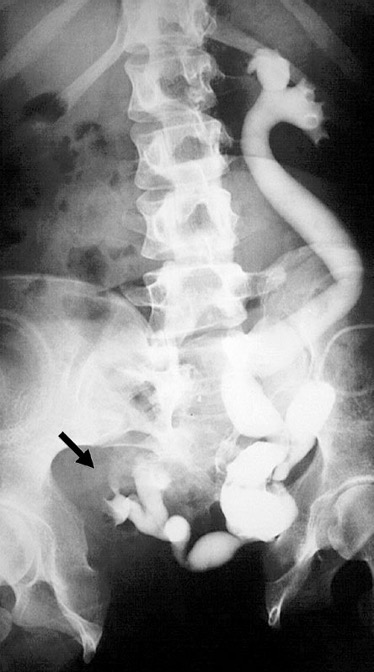
What is this?
kidney stone (radiopaque stone visible at origin of right ureter; producing acute obstruction)
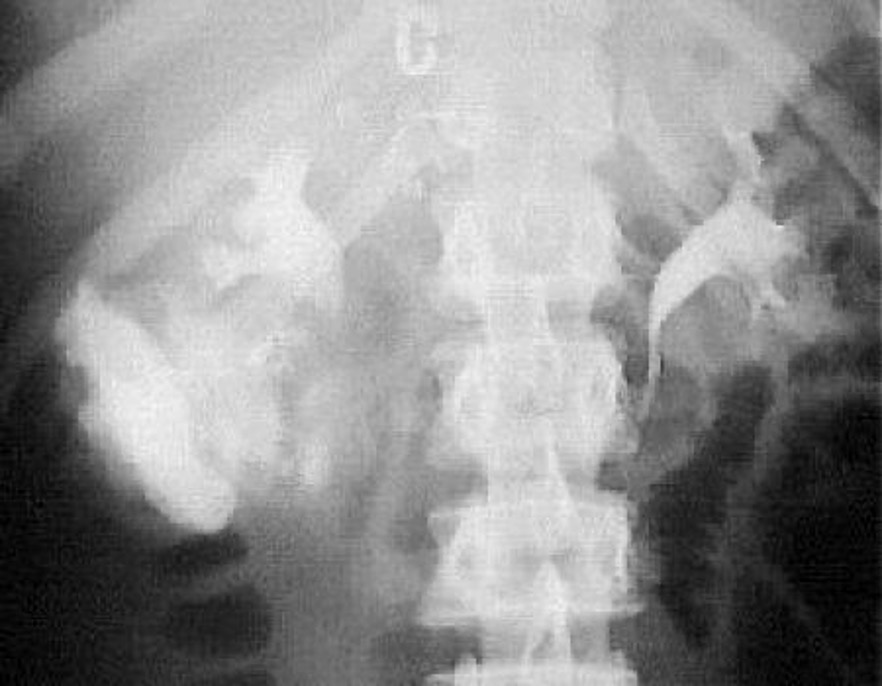
what is this?
renal stone (extravasation of contrast from right kidney)
what is indicated for initial evaluation of renal failure due to obstruction or renal disease?
ultrasound
what can cause worsening renal failure?
IVP
what is clinical presentation of pyelonephritis?
fevers, flank pain, lower back pain (CVA tenderness), nausea, dysuria, and pyuria
When is imaging indicated in pyelonephritis?
abscess suspected or pt is diabetic
what is the study of choice to evaluate renal trauma?
CT scan
When should kidney trauma be suspected?
fracture of 12th rib or of transverse process of lumbar vertebrae
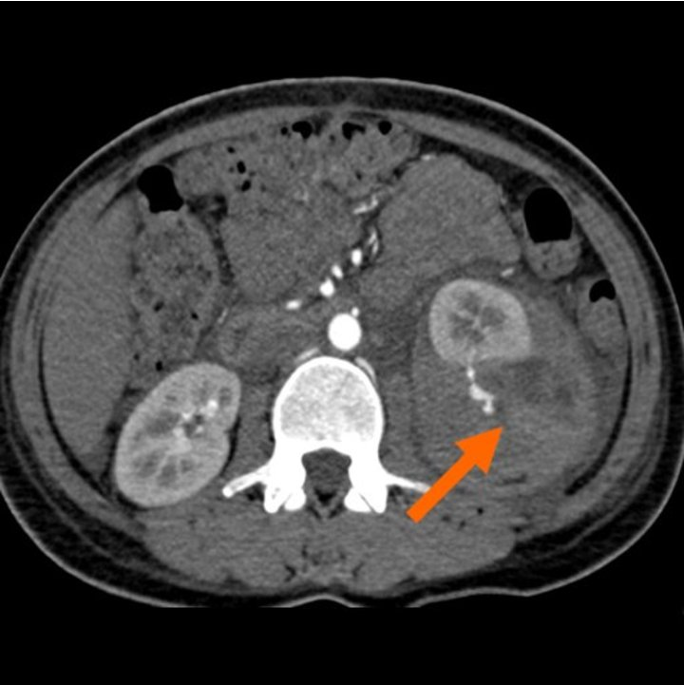
what is this?
left renal hematoma
what is clinical presentation of kidney tumors?
hematuria, flank pain, flank or abdominal mass
what is the study of choice for suspected renal tumors?
CT scan
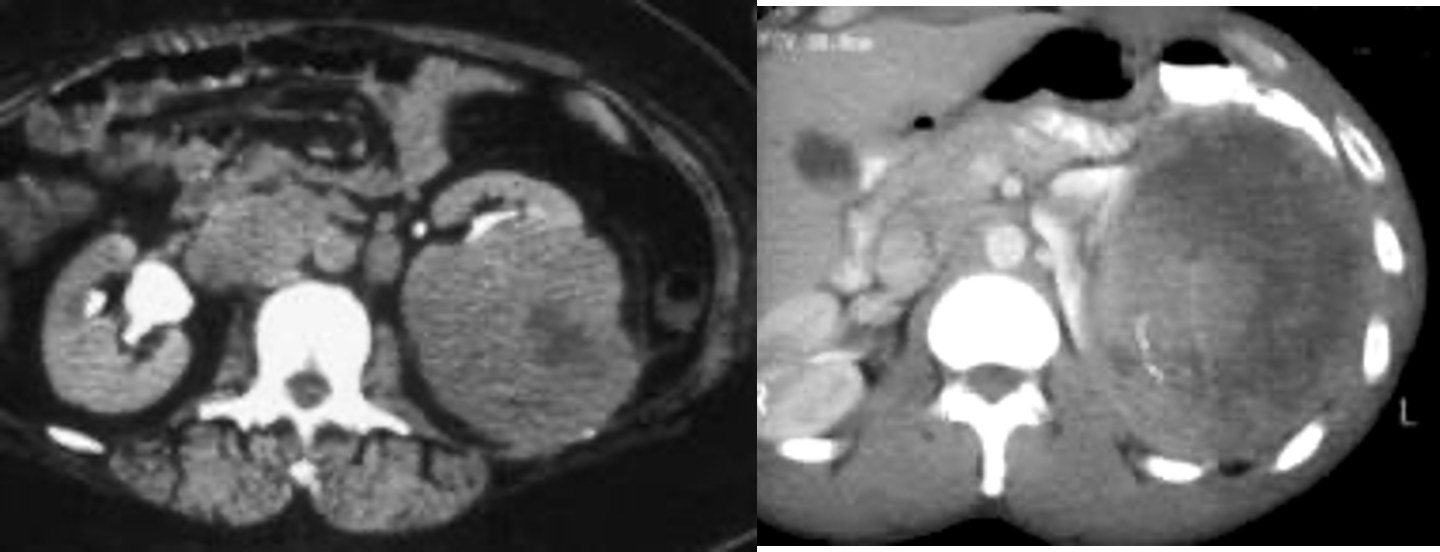
What is this?
kidney tumor
what is the best study to evaluate for dilation of collection system (hydronephrosis)?
ultrasound
what is ureterocele?
dilatation of distal ureter (greater than 8mm)- appears as cobra head deformity on IVP
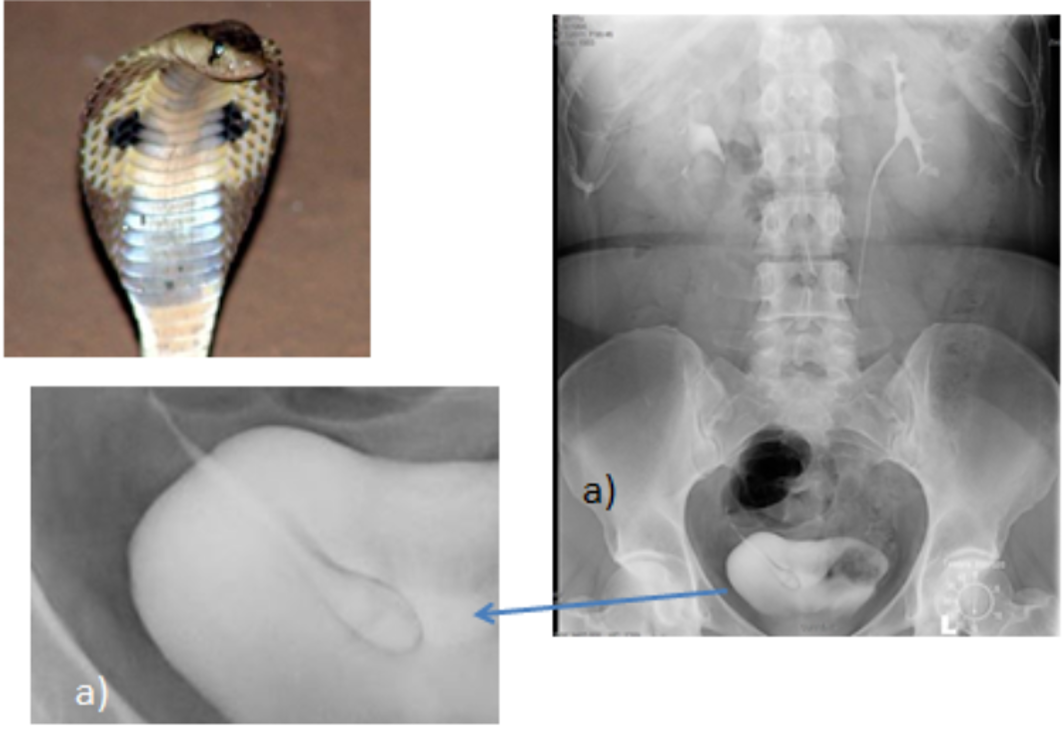
what is this?
ureterocele
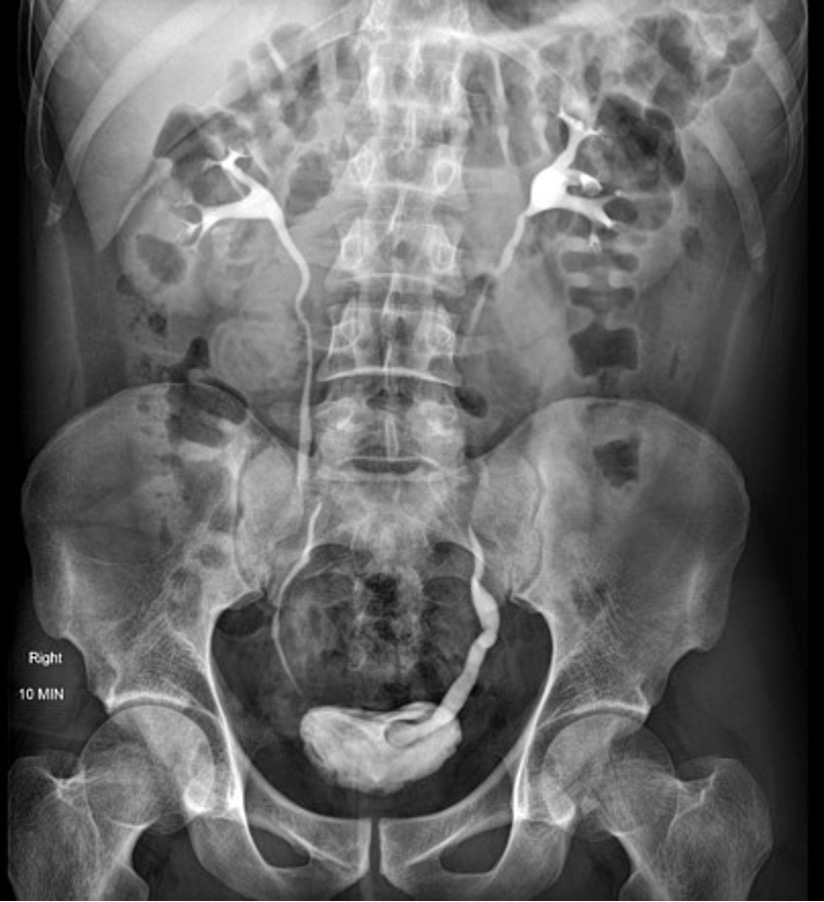
what is this?
ureterocele (cobra head sign)
what should be performed as an initial study for suspected bladder cancer?
cystoscopy (bladder endoscope)
what is cystogram?
Catheter placed directly into bladder, urine is drained and water soluble contrast is injected
urethral evaluation is done during voiding the contrast material
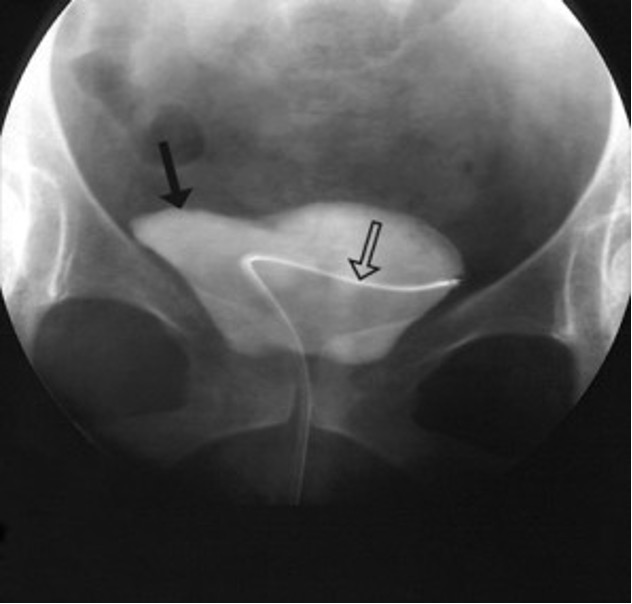
what are indications for cystogram?
after trauma (r/o leaks in bladder), fistulas, incontinence
what should also be suspected if a patient has a pelvic fracture?
bladder rupture
How do bilateral hematomas affect the bladder if not ruptured?
displace- usually elevated centrally; may have upside down tear drop appearance
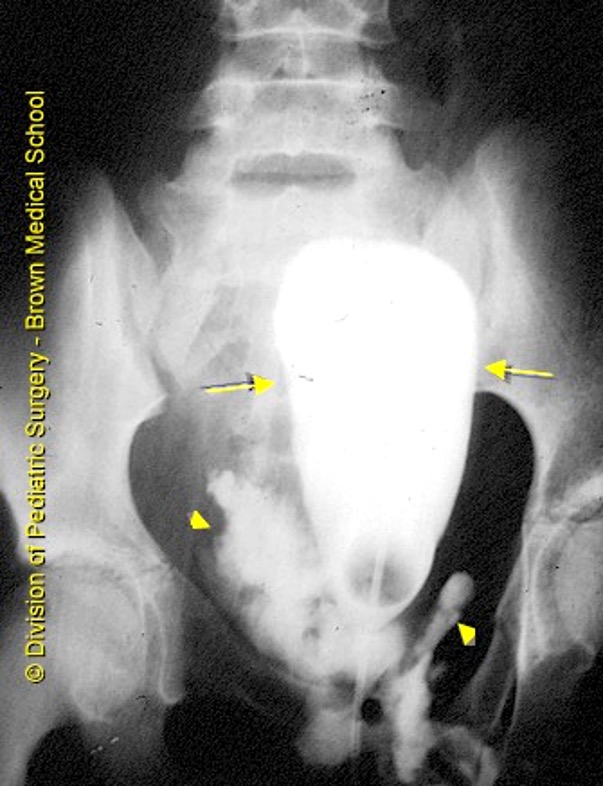
what is this?
bladder neck rupture due to pelvic hematoma from pelvic fracture
what is the study of choice for bladder rupture caused by trauma?
CT scan w/ cystogram
what is intraperitoneal bladder rupture?
extravasation of contrast into the peritoneal cavity (above the bladder). that outline loops of bowel
what is extraperitoneal bladder rupture?
leak stays OUT of peritoneal cavity (stays in pelvis)
What is indicated for recurrent cystitis in females or initial episode of cystitis in males?
IVP
What is emphysematous cystitis?
gas present in wall or lumen of bladder (can occur in diabetic patients who also have pyelonephritis)
What are 95% of bladder tumors?
transitional cell carcinomas
What is clinical presentation of bladder tumors?
hematuria, ± dysuria and frequency
what is the study of choice for bladder tumors?
cystoscopy- for direct visualization and bx
How can BPH affect the bladder?
cause elevation (may be seen on IVP)
what imaging is indicated for evaluation of BPH or prostatitis?
no imagining needed
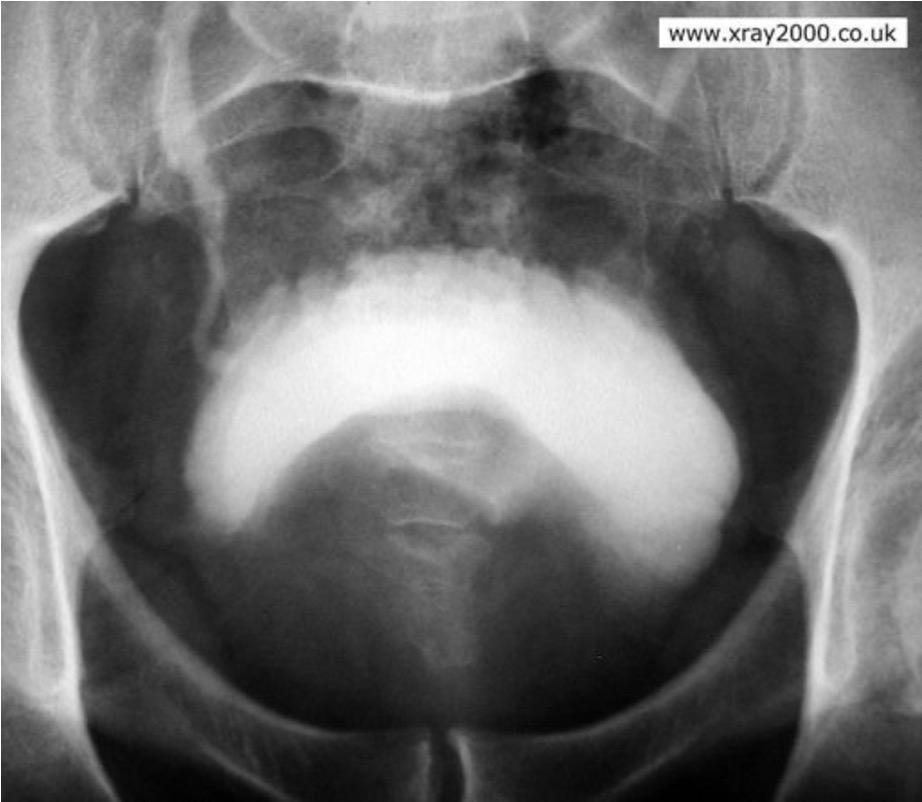
what is this?
BPH (smooth defect on inferior portion of the bladder)
what is the study of choice for evaluation of possible bone metastases?
bone scan
what is often the first line study for any testicular problem?
u/s
what scans are indicated for staging of testicular cancer?
CT scan and CXR
what is the next step if history and PE suggest testicular torsion?
go directly into surgery w/o any delay to perform imaging studies
what is the most common and useful study of the female pelvis?
ultrasound - transabdominally or transvaginally
(easy to evaluate uterus and adnexal regions)
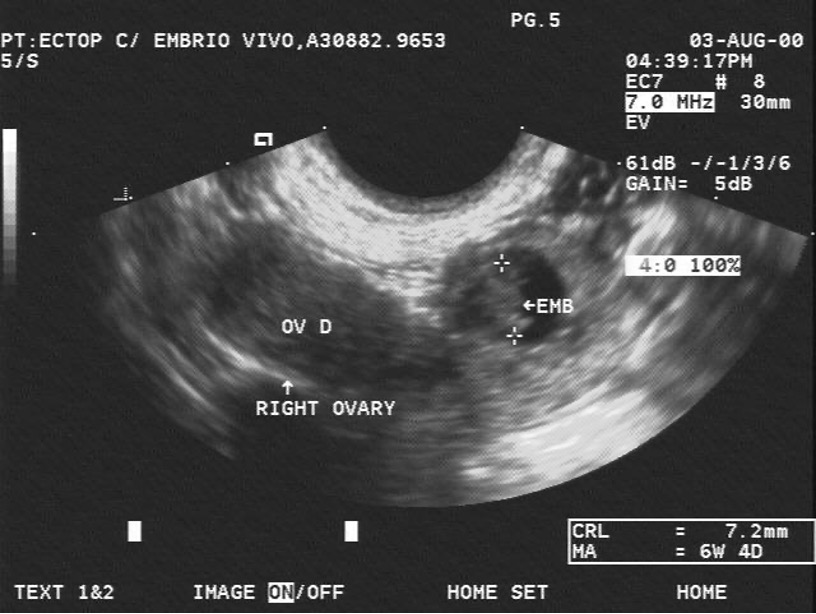
what is this?
ectopic pregnancy
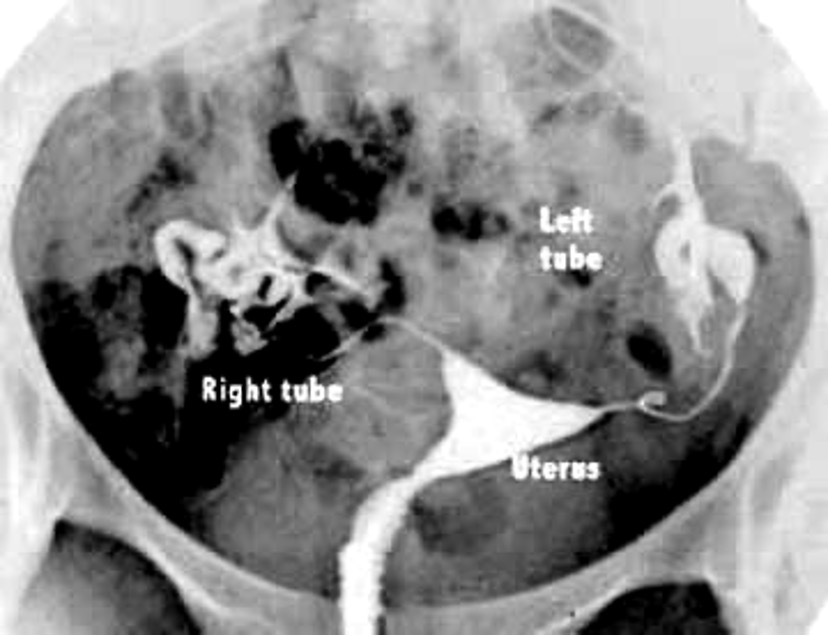
What is hysterosalpingogram (HSG)?
evaluate patency of fallopian tubes
what is the study of choice for imaging during pregnancy?
ultrasound
what are signs of pregnancy at 28-30 days on u/s?
gestational sac
what are signs of pregnancy at 5-6 weeks on u/s?
yolk sac and heartbeat
what is u/s used to evaluate during the second and third trimester?
fetal growth, gestational age, surgery of fetal organs to look for congenital abnormalities, placental location, amount of amniotic fluid
what are clinical presentations of ectopic pregnancy?
lower abdominal pain, bleeding, + HCG test
If a gestational sac and heartbeat are not seen on an ultrasound after 5 wks, what is possible?
ectopic pregnancy
what does not R/O an ectopic pregnancy?
normal u/s of uterus and adnexa- should be repeated in 7-10 days
What is there high suspicion of w/ normal appearing uterus + complex adnexal mass?
ectopic pregnancy
what is the most common benign tumor of the uterus?
fibroid- often calcified and seen on plain films
What is necessary to dx endometrial cancer?
biopsy (bc difficult to assess by radiological studies)
How is cervical cancer usually detected?
PAP smear w/ f/u colposcopy (CT and MRI for further eval)
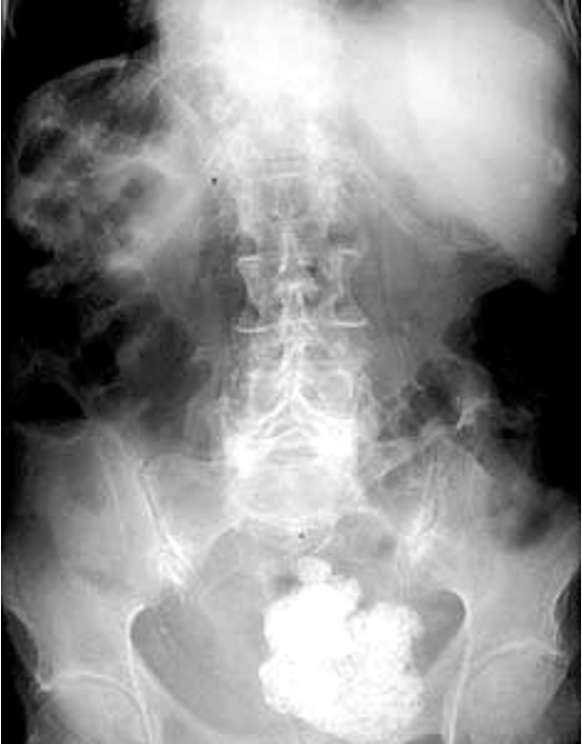
what is this?
fibroid
what are possible clinical presentations of ovarian/pelvic tumors?
bloating or weight gain due to ascites
What scans are done for ovarian/pelvic tumors?
u/s to recognize mass, CT to evaluate tumor and assess for metastatic dz
what is the study of choice for adrenal glands?
CT scan
what is the study of choice for suspected retroperitoneal adenopathy?
CT scan- performed while also looking for metastases in other abdominal organs