Biochem Exam 3 Study Guide
1/77
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
78 Terms
Hydrogen bond
A weak bond that occurs when a hydrogen atom covalently bonded to an electronegative atom is attracted to another electronegative atom.
Van der Waals forces
Weak attractions between molecules or parts of molecules that result from transient local partial charges.
Amino acids
Organic compounds that serve as the building blocks of proteins, classified based on their side chains.
Primary structure of proteins
The sequence of amino acids that make up a polypeptide chain.
Secondary structure of proteins
The local folded structures that form within a polypeptide due to interactions between non-adjacent amino acids, commonly alpha-helices and beta-pleated sheets.
Tertiary structure of proteins
The overall 3D shape of a polypeptide, determined by interactions among the amino acids.
Quaternary structure of proteins
The structure formed when two or more polypeptide chains assemble into a functional protein.
Enzymes
Biological catalysts that speed up biochemical reactions without being consumed.
Michaelis-Menten Kinetics
A model that describes the rate of enzyme-catalyzed reactions as a function of substrate concentration.
Lineweaver-Burk plot
A double reciprocal plot used to illustrate the Michaelis-Menten equation and determine enzyme kinetics.
Purines
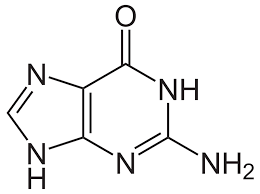
Nitrogenous bases consisting of two fused rings; includes adenine (A) and guanine (G).
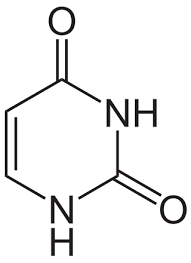
Pyrimidines
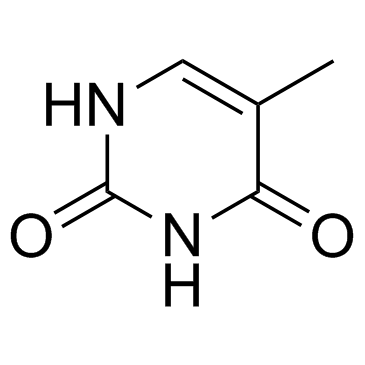
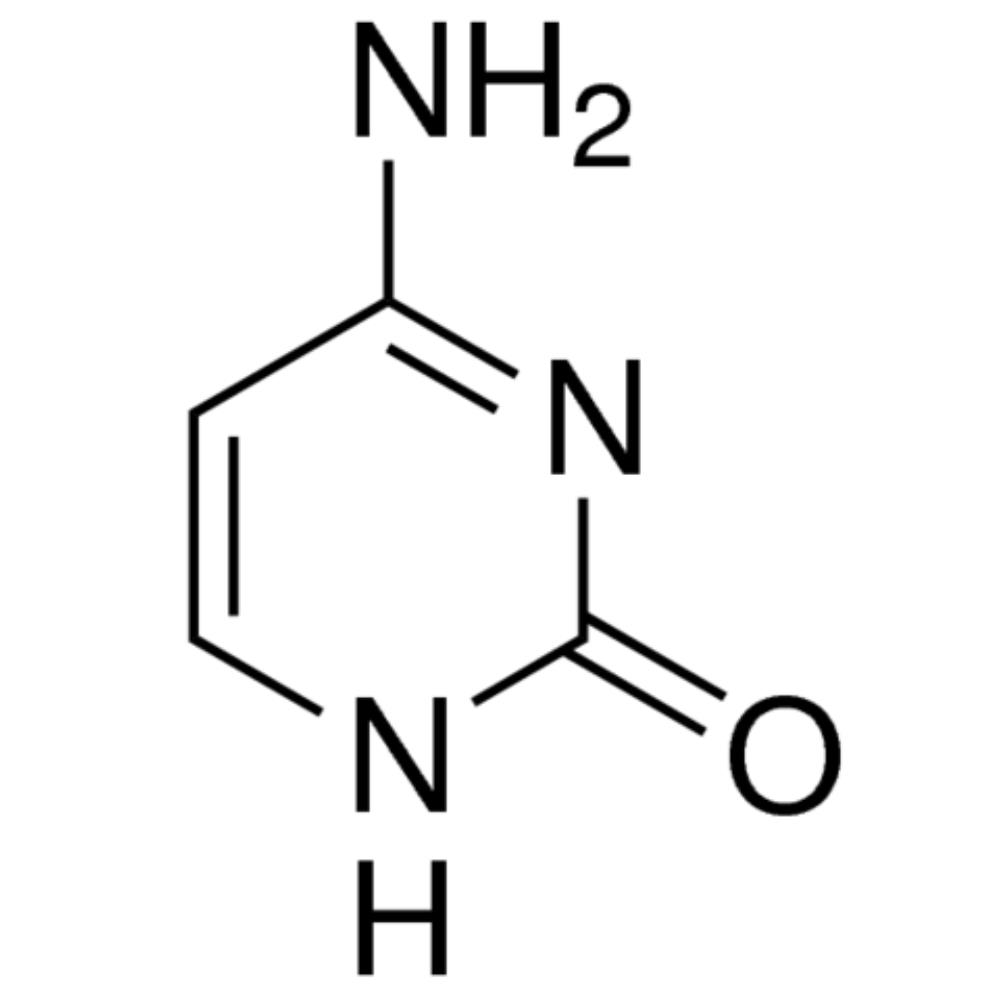
Nitrogenous bases consisting of a single ring; includes cytosine (C), thymine (T), and uracil (U).
Start codon
A specific codon (AUG) that signals the start of translation.
Stop codons
Codons (UAA, UAG, UGA) that signal the termination of translation.
DNA polymerase
An enzyme that synthesizes DNA by adding nucleotides to a growing chain.
RNA polymerase
An enzyme that synthesizes RNA from a DNA template.
Exonuclease activity
The activity of an enzyme that removes nucleotides from the ends of a DNA or RNA strand.
Promoter
A DNA sequence that signals the start site for transcription, where RNA polymerase binds.
Restriction enzymes
Proteins that cut DNA at specific sequences, enabling cloning.
Glycoproteins
Proteins that have carbohydrate groups attached, playing roles in cell signaling and recognition.
Saturated fatty acids
Fatty acids with no double bonds between carbon atoms, solid at room temperature.
Unsaturated fatty acids
Fatty acids with one or more double bonds, liquid at room temperature.
Hydropathy plots
Graphs created to predict the transmembrane segments of proteins based on their hydrophobic characteristics.
Integral membrane proteins
Proteins that are permanently attached to the cell membrane and can span the membrane.
Peripheral membrane proteins
Proteins that are temporarily attached to the membrane, often involved in signaling.
Passive transport
The movement of molecules across a cell membrane without the use of energy.
Active transport
The movement of molecules against their concentration gradient, requiring energy (ATP).
primary active transporters: use ATP hydrolysis
secondary active transporters: couple solute transport w/ ion
Na⁺/K⁺ ATPase
An enzyme that pumps sodium out of cells and potassium into cells, essential for maintaining membrane potential.
Transcription
The process of copying a segment of DNA into RNA.
Translation
The process of synthesizing proteins from messenger RNA.
Electrophysiology
The study of the electrical properties of biological cells and tissues.
adenine
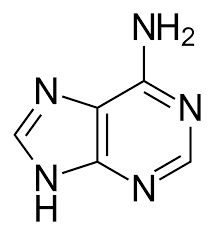
guanine
thymine
cytosine
uracil
hairpin
a secondary structure of RNA where a single strand folds back on itself to form complementary base pairs, creating a loop-like configuration.
silent mutation
a type of mutation that does not change the amino acid sequence of the protein
missense mutation
a type of point mutation where one nucleotide base pair in the sequence is changed, resulting in the insertion of a different amino acid into the corresponding protein
nonsense mutation
a type of mutation that occurs when a nucleotide substitution changes an amino acid codon into a stop codon
frameshift mutation
a type of mutation where one or more nucleotides are inserted or deleted, resulting in a shift in the reading frame
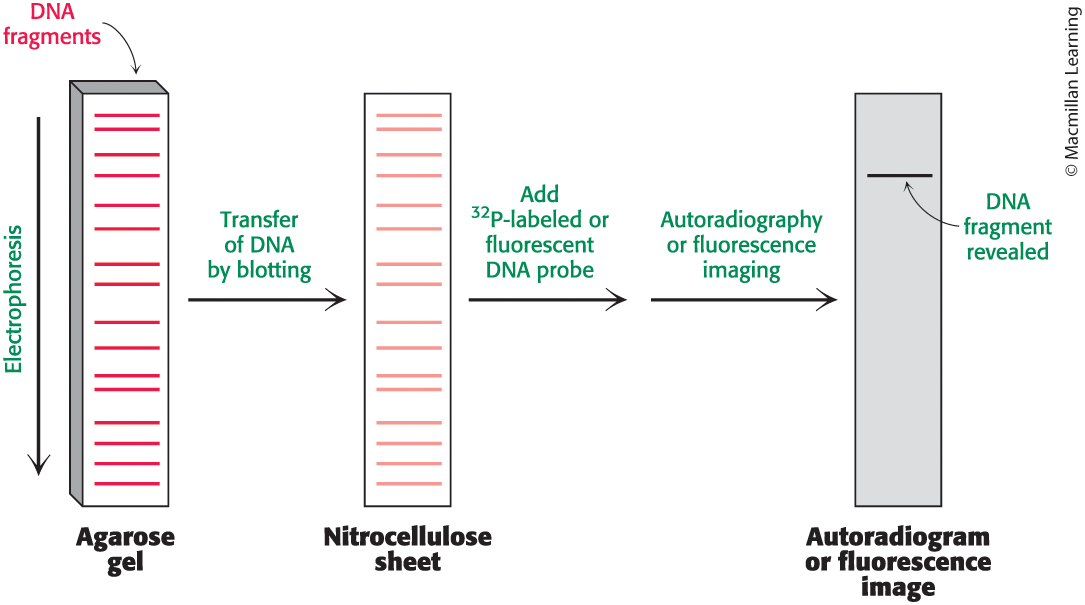
southern blot method
a laboratory technique used to detect specific DNA sequences in DNA samples, involving the transfer of DNA from a gel to a membrane and hybridization with labeled probes.
DNA Synthesis
reaction requires all 4 activated precursors: deoxynucleotide 5’-triphosphates (dNTPs) and Mg+2
DNA polymerase requires a primer to begin
elongation occurs in the 5’ to 3’ direction
nucleic acid hybridization method
synthetic bio method that uses the southern blot method to probe DNA genes
restriction enzymes
synthetic bio method using sequence specific DNAses, proteins that bind and cleave palindromic sequences
restriction enzyme cuts genomic SNA, giving a specific set of DNA fragments of varying lengths
fragments can be separated and visualised by agarose gel electrophoresis
gives a “DNA fingerprint”
DNA Sequencing
synthetic bio method reaction that involves nucleophilic attack of 3’ OH of a DNA primer on a normal substrate (2’d NTP)
polymerase chain reaction (PCR)
synthetic bio method that amplifies a gene from a genome, requires DNAP, dsDNA (template), 2 DNA primers, and 4 dNTPs, involves a thermal cycle of 3 steps, repeated multiple times
Gene Cloning
amplify a gene from a human genome using PCR (include EcoRI sequence in primers)
cut w/ EcoRI: PCR product and plasmid (pSC101)
anneal DNA fragments and join w/ DNA ligase
requirements for expressing a cloned gene in E. Coli
gene must include a complete ORF
gene is often inserted into a polylinker of a plasmid; includes DNA replication origin, antibio resistance gene and sometimes a reporter gene
additional transcriptional and translational sequences are also needed: promotor & terminator, shine-dalgarno sequence
site-directed mutagenesis
synthetic bio method that uses a synthetic primer containing a mismatched nucleotide, this primer was annealed w/ a template strand containing a gene to be mutated
gene knockouts
genes can be replaced in a genome via homologous recombination, this method takes advantage of DNA repair enzymes
genome editing
genes can be mutated via double-stranded DNA breaks, this method is known by the acronym CRISPR
orthologs
homologs present within different species and have very similar/identical functions
paralog
homologs present within one species
homolog
homologous molecules
sequence alignments
used to determine whether two molecules are ortho/paralogs, aligned primary sequences can be used to predict 3D structures of related proteins, comparisons can be used to construct evolutionary trees
ab initio method
relies on computer modeling of protein folding, calculating non-covalent interaction energies (assuming that free energy of the folded protein is minimized
homology modeling methods
newer methods where proteins of unknown structure are first aligned with homologous proteins of known structure, differential interactions are predicted and refined, assuming correlated mutations or covariations
newest approaches in synthetic bio
AI-based modeling software such as AlphaFold and RoseTTAFold
designed proteins
new protein folds have been the cornerstone of de novo design to engineer new enzymes and other functional proteins
ex: enzymes to break down plastics, protein scaffolds to build new drug molecules
glycoproteins
a protein covalently attached to a carbohydrate group, extracellular proteins that regulate cell-cell interactions
N-linked (side chain of Asn) or O-linked (side chain of Ser or Thr)
monosaccharide
the simplest carbohydrate, contains a single aldehyde or ketone that has two or more hydroxyl groups, most have D configurations
ex: glucose, ribose, deoxyribose, mannose, galactose, fructose
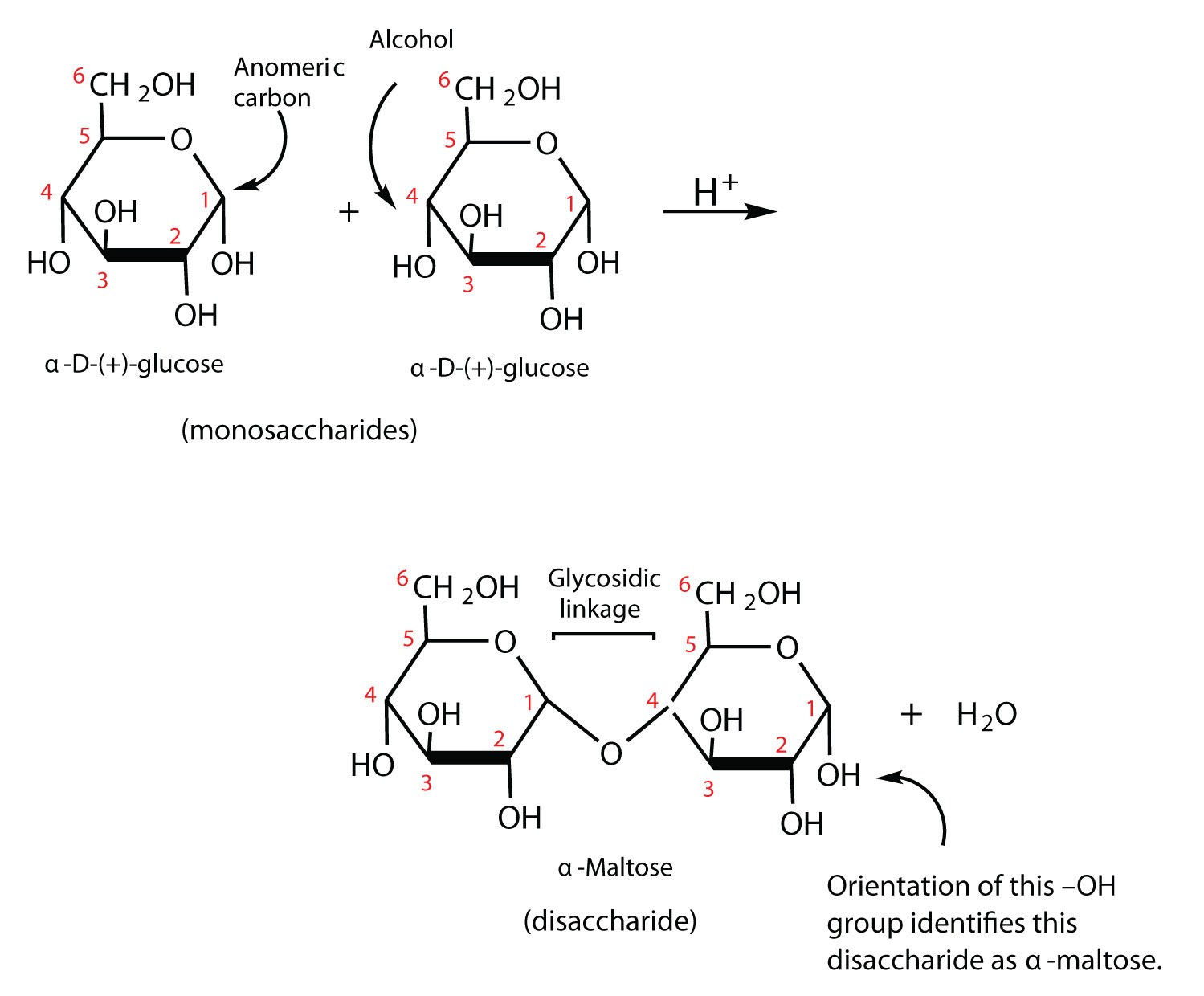
disaccharide
composed of two monosaccharides, ex: sucrose, lactose, maltose
polysaccharide
composed of many monosaccharides, ex: cellulose, glycogen, amylose (starch), chitin
formation of a disaccharide
condensation forms a disaccharide, hydrolysis breaks one down
lectins and selectins
glycoproteins important for development in multicellular animals
proteoglycans
A protein containing one or more covalently linked glycosaminoglycan chains.
collagen
Cartilage proteoglycan, contains keratan sulfate and chondroitin chains linked to a polypeptide backbone. breakdown/lack of this causes arthritis
mucins (mucoproteins)
One of a class of glycoproteins, consisting mainly of carbohydrate, in which the protein component is extensively glycosylated to serine or threonine by N-acetylgalactosamine.
common features of biological membranes
Sheetlike structures (two molecules thick, 60Å to 100Å).
Lipid bilayers with both hydrophobic and hydrophilic components.
Proteins serve as pumps, channels, receptors, energy transducers, and enzymes.
Asymmetric with distinct inner and outer surfaces.
Fluid structures; 'lipids and proteins diffuse rapidly in the plane of the membrane. They do not readily rotate across the membrane.
Most cell membranes are electrically polarized (inside negative, -60 mV). Membrane potential is key for transport, energy conversion, and excitability.
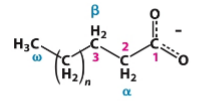
general structure of fatty acids
three major kinds of lipids
phospholipids, glycolipids, and cholesterol
protein mediation in membranes
transport of molecules and ions (channels and pumps)
response to extracellular signals (receptors for hormones and light)
conduction of electrical currents (along the axons of nerve cells)
integral membrane proteins
(A, B, & D)
interact extensively with the hydrocarbon chains of membrane lipids, and they can be released only by agents that compete for these nonpolar interactions.
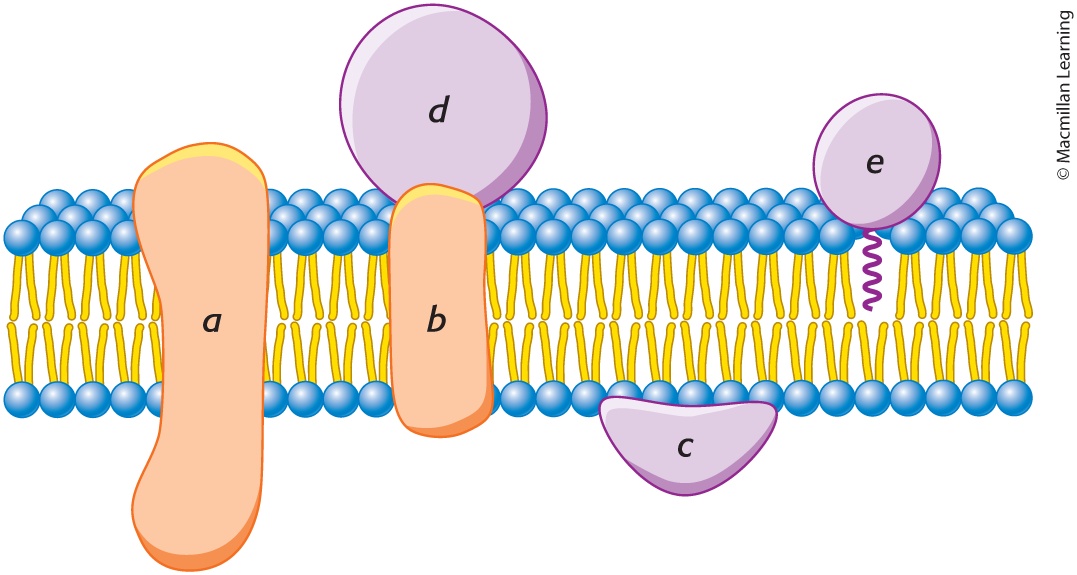
peripheral membrane proteins
(C)
bound to membranes primarily by electrostatic and hydrogen-bond interactions with the head groups of lipids. Many are bound to the surfaces of integral proteins, on either the cytoplasmic or the extracellular side of the membrane. Others are anchored to the lipid bilayer by a covalently attached hydrophobic chain, such as a fatty acid.
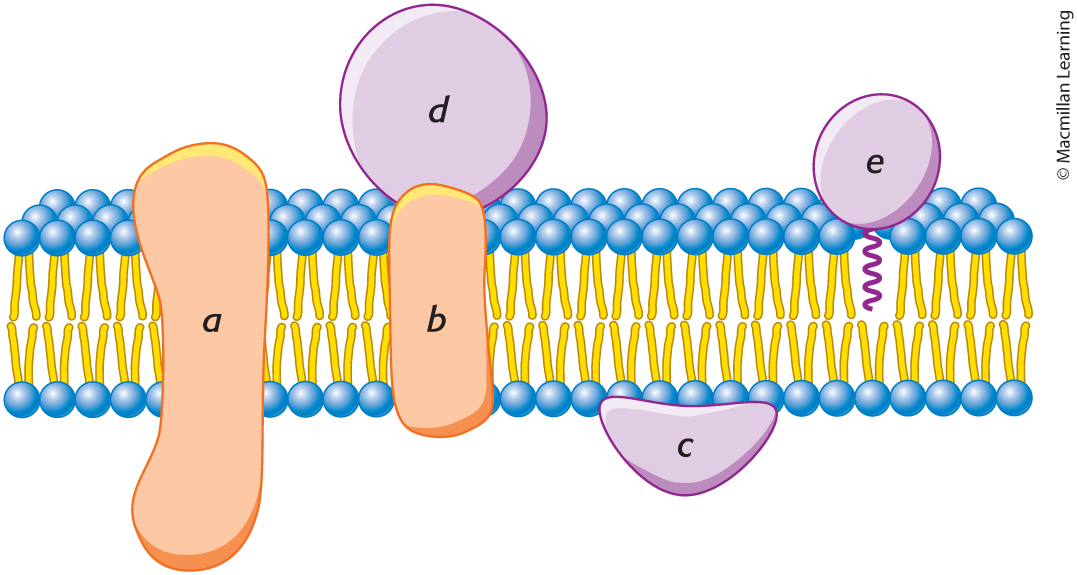
membrane-spanning alpha helices
the most common structural motif in membrane proteins, span the hydrophobic part
allows proteins to interact with the membrane
three transporters in conduction of nerve impulses
Na+/K+ ATPase
Na+ channel
K+ channel
selectivity filter
the narrowest diameter of the channel matches the size of a single K+ ion