BIOL 101 Lab Final
1/60
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
61 Terms
Steps of Scientific Inquiry
Objective Observation
The process of gathering data through measurable and unbiased observations, eliminating personal feelings or opinions.
Subjective Observation
A type of observation that is influenced by personal feelings, interpretations, or bias, rather than only by factual data. It contrasts with objective observation, which relies solely on measurable, observable evidence.
Prokaryotes v. Eukaryotes
Prokaryotes are unicellular organisms without a nucleus or membrane-bound organelles, while eukaryotes are organisms made up of one or more cells that contain a nucleus and organelles.
Independent Variable
A factor in an experiment that is purposely changed to test its effects on the dependent variable.
Dependent Variable
The variable in an experiment that is measured and affected by changes in the independent variable.
Control Group
A group in an experiment that does not receive the experimental treatment and is used as a benchmark to compare results.
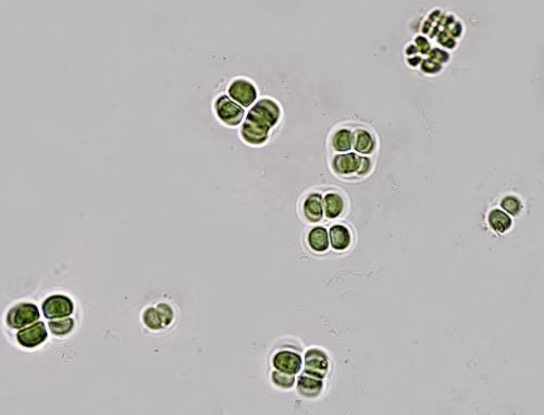
Gleocapsa:
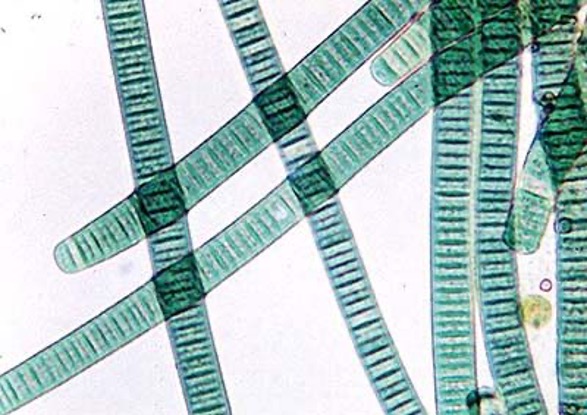
Oscillitoria
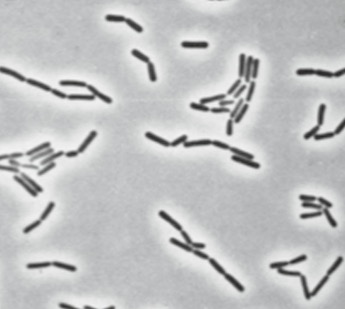
Lactobacillus
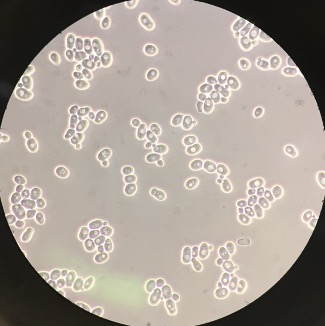
Yeast
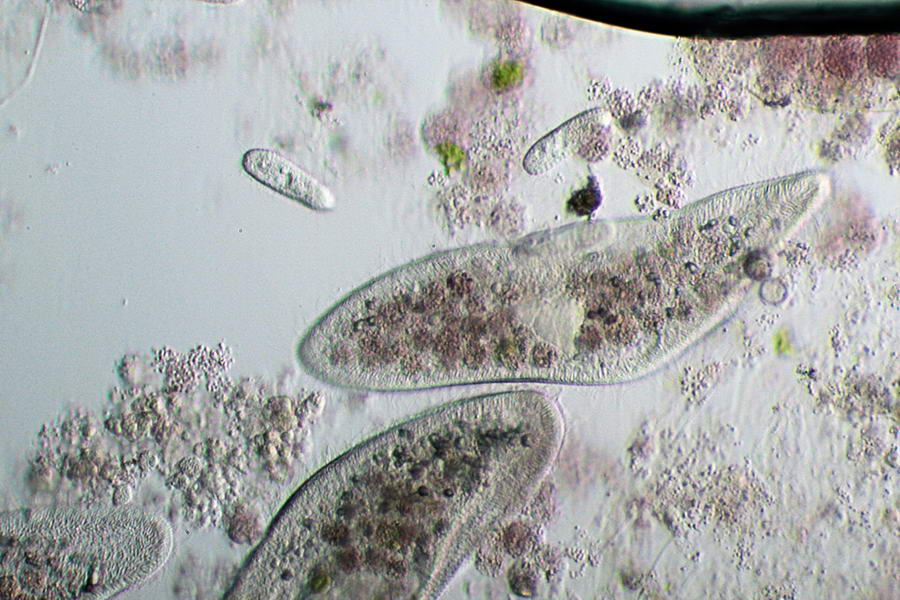
Paramecium
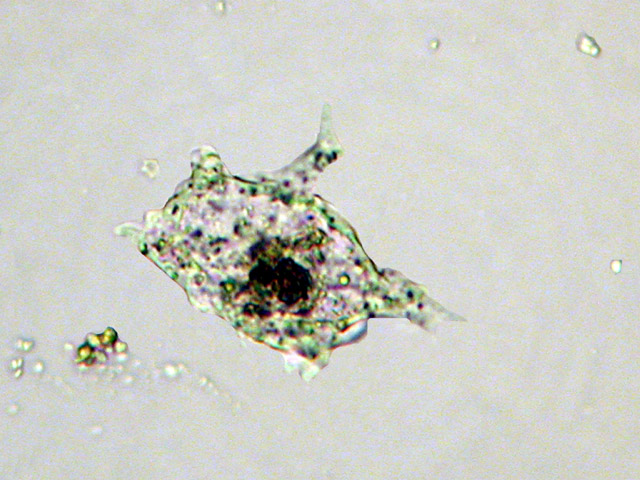
Amoeba
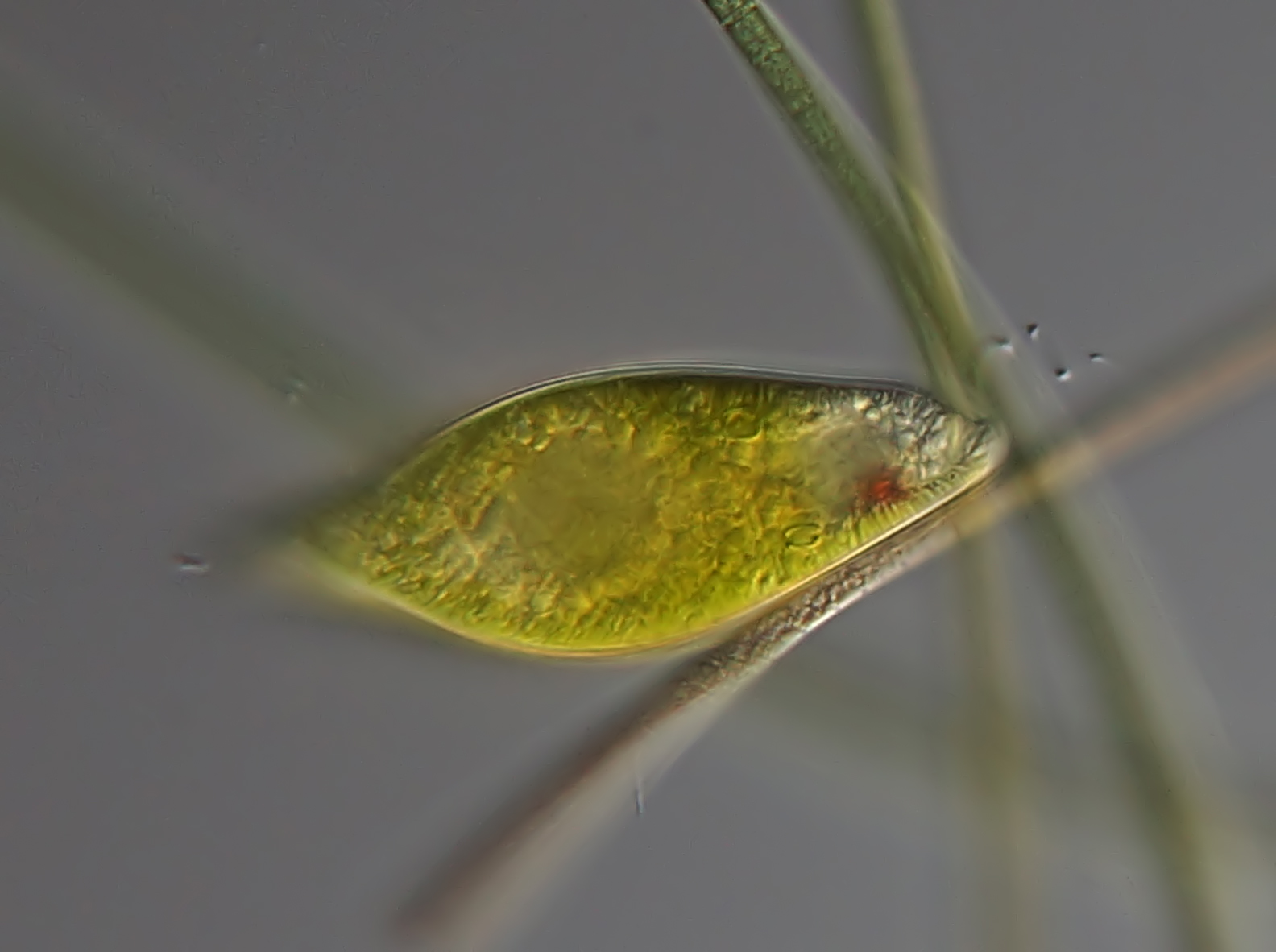

Euglena
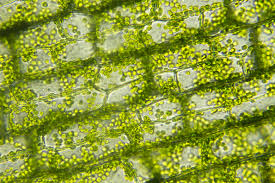
Elodea
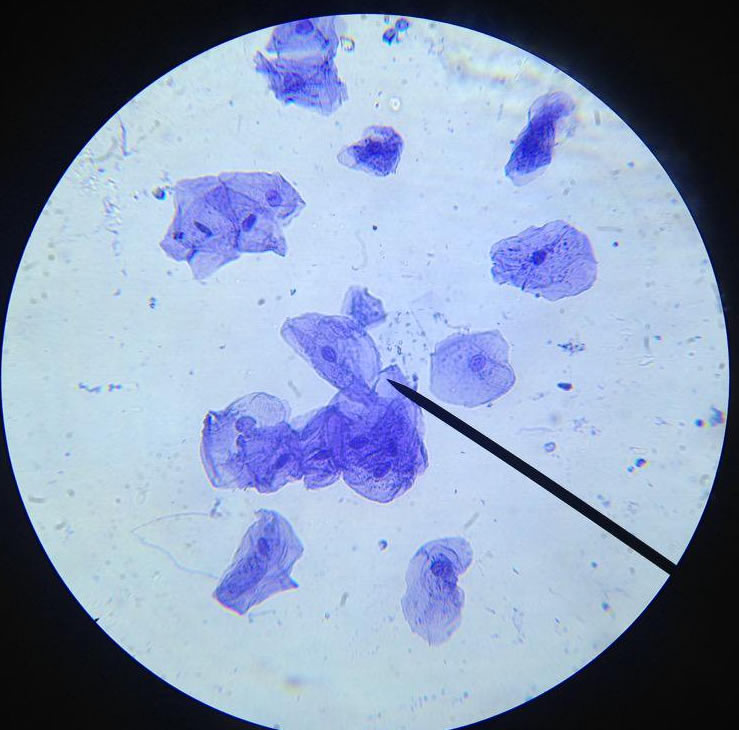
Epithelial Cells
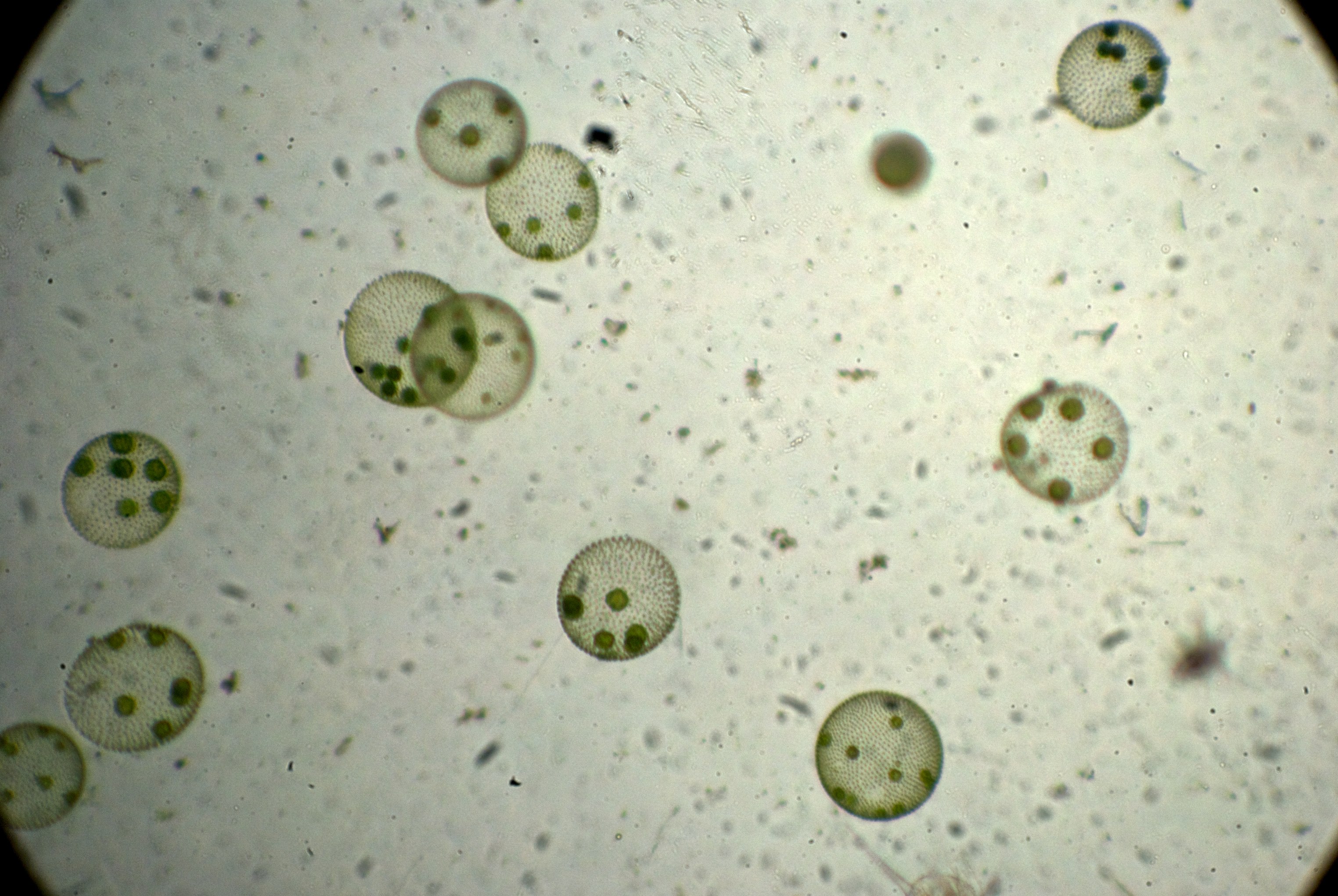
Volvox
Compare and Contrast Plant and Animal Cells
Passive Diffusion
The movement of molecules from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration without the use of energy or transport proteins.
Active Diffusion
A cellular process that requires energy to move molecules against their concentration gradient through membrane proteins.
Osmosis
The movement of water molecules across a semipermeable membrane from an area of low solute concentration to an area of high solute concentration.
Hypotonic
A solution with a lower solute concentration compared to another solution, causing cells to swell as water enters.
Hypertonic
A solution with a higher solute concentration compared to another solution, leading to water exiting cells and causing them to shrink.
Gram Positive
Bacteria that retain the crystal violet stain used in the Gram staining protocol, appearing purple under a microscope. These cells contain an thick peptidoglycan layer in their cell wall.
Gram Negative
Bacteria that do not retain the crystal violet stain and instead take up the counterstain, appearing pink under a microscope. They have a thinner peptidoglycan layer and an outer membrane.
Chlorophyll A
Blue-Green Color
Chlorophyll B
Olive-Green Color
Chlorophyll C
Found in certain algaes
Beta-Carotene
Yellow-Orange
Xanthophylls
Yellow
Solvent Front
Calculation for Rf
Polarity of Chromatography Paper
Polar
Polarity of Solvent
Photosynthesis Reaction
Rate of Photosynthesis Equation
DPIP and Significance in Experiment
Calvin Cycle
Part of the Calvin Cycle that takes place in the stroma of chloroplasts, where carbon dioxide is fixed into organic molecules using ATP and NADPH produced during the light-dependent reactions.
Light-Dependent Reaction
The phase of photosynthesis that converts solar energy into chemical energy in the form of ATP and NADPH, occurring in the thylakoid membranes of chloroplasts.
Steps of Gel Electrophoresis
Charge of DNA
Negative
Genetic Dominance
The genetic principle where one allele masks or suppresses the expression of another allele at the same locus, determining the phenotype.
Sex-Linked Inheritance
A pattern of inheritance where genes located on sex chromosomes, particularly the X chromosome, influence traits, often resulting in differing expression of traits between males and females.
Chi-Square Calculation
Chromosome
A thread-like structure made of DNA and protein that carries genetic information in the form of genes.
Gene
Homologues
Alleles
Mendel’s Law of Segregation
The principle stating that during the formation of gametes, the two alleles for a trait separate from each other, resulting in each gamete carrying only one allele.
Mendel’s Law of Independent Assortment
Mendel's principle stating that alleles for different traits are passed independently of one another from parents to offspring.
Natural Selection
The process by which organisms better adapted to their environment tend to survive and produce more offspring. This mechanism drives evolution.
Natural Selection to Evolution
4 Key Characteristics of Mollusks
Foot, radula, mantle, shell
Foot
Radula
Shell
Mantle
Characteristics of Chiton
Characteristics of Snails
Characteristics of Clams
Characteristics of Squids