Bio Enzyme Quiz
1/49
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
50 Terms
proteins
molecule made up of amino acids
amino acids
molecules that combine to form proteins
nucleotides
the basic building block of nucleic acids (RNA and DNA)
peptide bonds
a covalent bond that links amino acids together to form a protein
polypeptides
A substance that contains many amino acids (the molecules that join together to form proteins).
denaturation of protein
process modifying the molecular structure of a protein.
enzymes
organic catalyst (proteins encoded by genes)
functional groups in proteins
amino, hydrogen, carboxyl, and R group
list 3 different proteins, and their functions.
Contractile proteins - Proteins that allow for contraction, like actin and myosin.
Enzymes - Proteins that speed up chemical reactions, like lactase.
Hormonal proteins - Proteins that carry chemical messages through the body, like insulin.
What are enzymes, and why are they so important to Biology?
Enzymes are proteins, they act as catalysts, which means that they make biochemical reactions happen faster than they would otherwise.
Why are enzymes classified as catalysts?
they increase the rate of chemical reactions without themselves being consumed or permanently altered by the reaction.
what do the various enzyme graphs look like? (reaction rate vs. pH, Temp., substrate concentration, or enzyme concentration)
substrates need to be in excess for line and curve is for limited substrates
substrate
reactants of an organism+breaks things down
induced fit
hugs substrate to fit (changes shape in enzyme)
active site
where substrates undergo a chemical reaction
activation energy
The initial energy needed to start a chemical reaction is called the free energy of activation
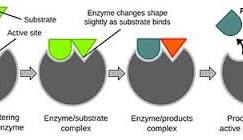
enzyme-substrate complex
a temporary molecule formed when the substrate binds to the enzyme
cofactors
non protein enzyme helpers
coenzyme
An organic cofactor (includes vitamins)
competitive inhibitors
bind to the active site of an enzyme, competing with the substrate
non competitive inhibitors
bind to another part of an enzyme, causing the enzyme to change shape and making the active site less effective
allosteric regulation
any form of regulation where the regulatory molecule (an activator or inhibitor) binds to an enzyme someplace other than the active site.
activator
a molecule that increases the activity of an enzyme or a protein that increases the production of a gene product in DNA transcription.
inhibitor
chemical or biological molecules that regulate chemical reactions by slowing down or blocking them from occurring.
Free Energy (ΔG)
a measure of energy that is available to do work.
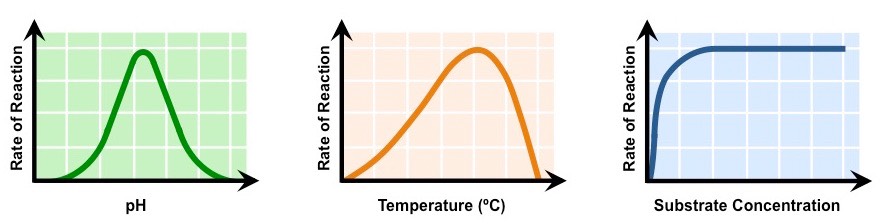
Compare and pH, Temperature, Substrate, and Enzyme reaction graphs.
pH is curve up slope down, temprature is straight line up curve down, substrate is slope up and straight ascent,
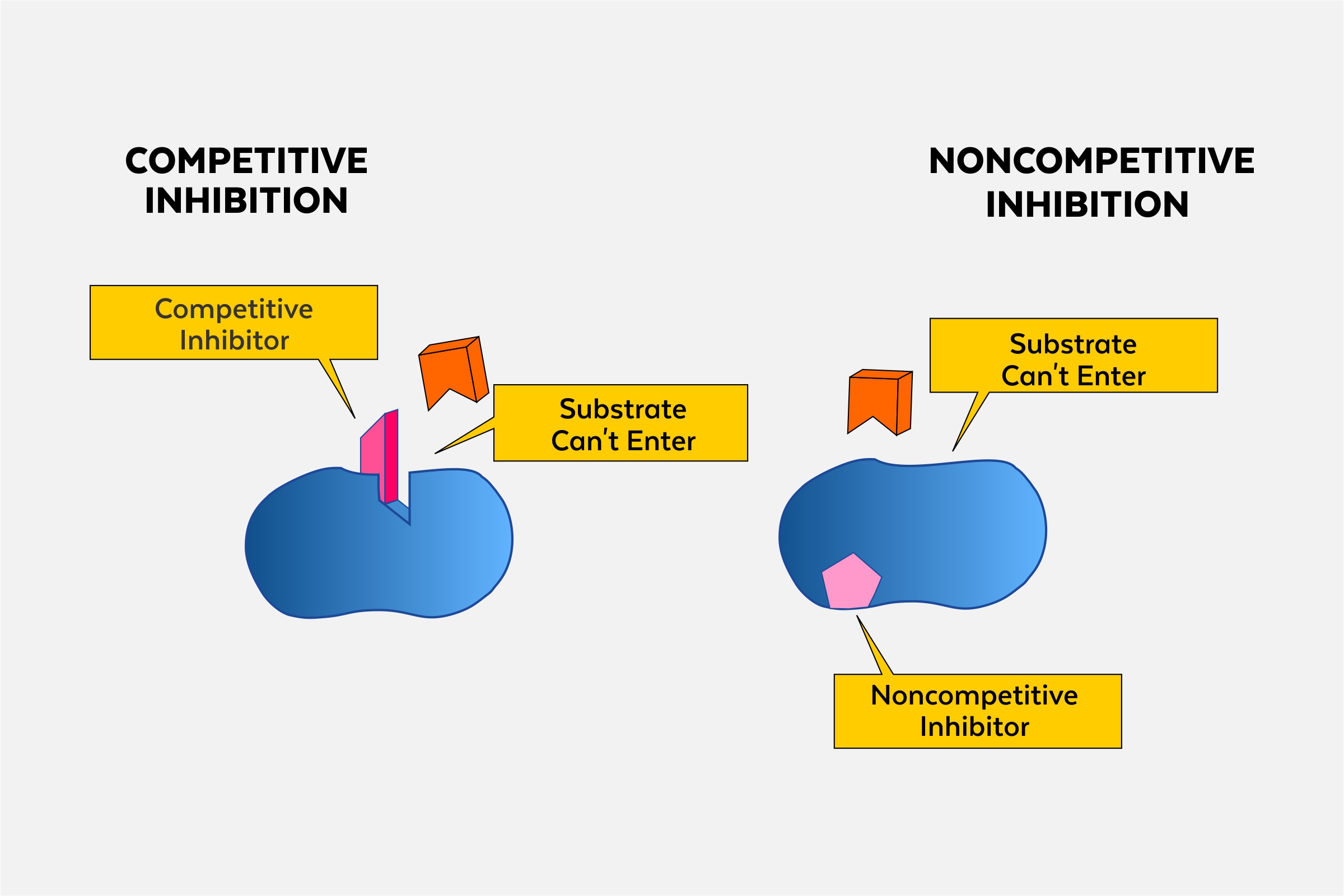
Compare and contrast competitive vs. non-competitive (allosteric) enzyme inhibition.
Allosteric involves binding to a site other than the active site, competitive is direct competition at active site.
Is delta G affected by enzyme and does it change?
Delta G never changes and is never affected by enzyme.
non competitive enzyme
allosteric
ANY molecule that helps speed up a chemical reaction is called?
catalyst
What do enzymes do to the activation energy of a reaction?
Decrease the amount
How do enzymes affect the rate of a chemical reaction?
Increase the rate
What is the biological molecule called that the enzyme acts on?
substrate
When an enzyme is catalyzed and the substrate is broken down, what is formed?
products
In a rate of reaction graph, why might the graph level off as you add substrates?
limited amount of enzymes
What type of inhibition stops enzyme activity by having the same shape and directly attaching to the active site?
competitive
How does an enzyme increase the rate of reaction?
by lowering activation energy
The substance that goes into the active site is called
substrate
The intermediate step in the enzymatic process is called
enzymes substrate complex
Can an enzyme work with any substrate?
no
The process where by a substance is broken down is called
catabolic
The process where by a substance is built up is called
anabolic
Do all enzymes work at the same pH?
no (ph)
catalyst
chemical agent that speeds up a reaction without being consumed by the reaction
Activation energy is often supplied in the form of ___ energy that the reactant molecules ___ from their surroundings
thermal, absorb
enzymes ___ energy that would have happened already
quicken
The active site can lower an EA barrier by
orienting substrates correctly
straining substrate bonds
provided a favorable microenvironment
are cofactors organic?
yes and no (could be both)
what do mutations lead to?
changes in amino acid composition of an enzyme
how do altered amino acids alter a substrate
specifically