Cell Biology 1
1/61
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
62 Terms
Bio
a study of all living things
Scientific Method
Observation, Hypothesis, Supported hypothesis, Theory, and Principle
Bacteriophage
A virus that kills E.coli
Organisms are composed of
Highly Organized Cells
Cell
Smallest unit of life
Organic Molecule
Carbon- Containing building blocks of life
In plant cells, the plasma membrane is replaced by
Cell Wall
HIV only affects which blood cells
White blood cells
Massive switch of the immune system
white blood cells 1
Organelles
Mitochondria, Ribosomes, Lysosomes, Golgi complex, and Endoplasmic Reticulum
Mitochondria
The powerhouse of the cell produces ATP
Ribosomes
Read genetic information encoded in messenger RNA and use it to assemble amino acids into polypeptide chains, which form proteins.
Lysosomes
Membrane-bound structures that fight off viruses and infection
Nuclease
Contains DNA (Genetic material)
Red Blood Cells
Do not have a nuclease and deliver oxygen to your tissues
Cytoplasm
Maintains cell shape (PH=7.2)
Genetic Material
Gene Expression, Duplication, Perpetualism
Perpetualism
The belief that everything is an external process and that intelligent life is apart of the conscious \
ATP
Energy Adenosine Tyi phosphate
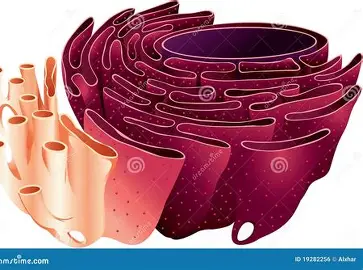
Endoplasmic Reticulum
Eukaryotic cells have a membrane
Smooth ER
Synthesis of Lipid and has no ribosomes
Rough ER
Produces protein and has ribosomes
Microtubules
Helps the cells multiply
Nucleolus
Produces the enzymes for making protein and duplication
Chromatin
DNA molecule is held inside the nuclease, and the cell is tightly held within the chromatin
what holds together chromatin?
Protein
Nuclear Pore
The opening between the nucleus and the cytoplasm of a cell
Subatomic particles
Contain protons, neutrons, and electrons. (All living organisms are made up of this)
Atom
The smallest particle contains hydrogen, carbon, nitrogen, and oxygen.
makes up an atom
Subatomic Particle
All proteins in the cell contain?
Nitrogen’s
what does nitrogen contain?
Amino Acids
What is present in living cell?
Hydrogen and Carbon
What is ATP synthesized by
Oxygen
2 or more atoms inside the cell
Molecule
Ribosomes
Composed of RNA and proteins, it reads genetic information encoded in messenger RNA and uses it to assemble amino acids into polypeptide chains, which form proteins.
Polypeptide Chain
A linear sequence of amino acids
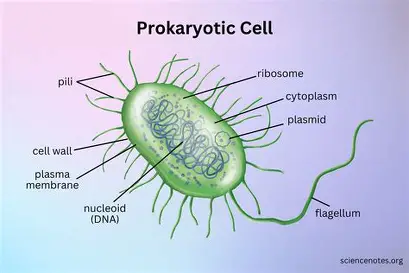
Prokaryotic Cell
Unicellular bacteria that have no membrane
Bacteria Cells
No nuclease, ER, Golgi complex, or mitochondria. Have ribosomes, but the ribosomes do not have a membrane
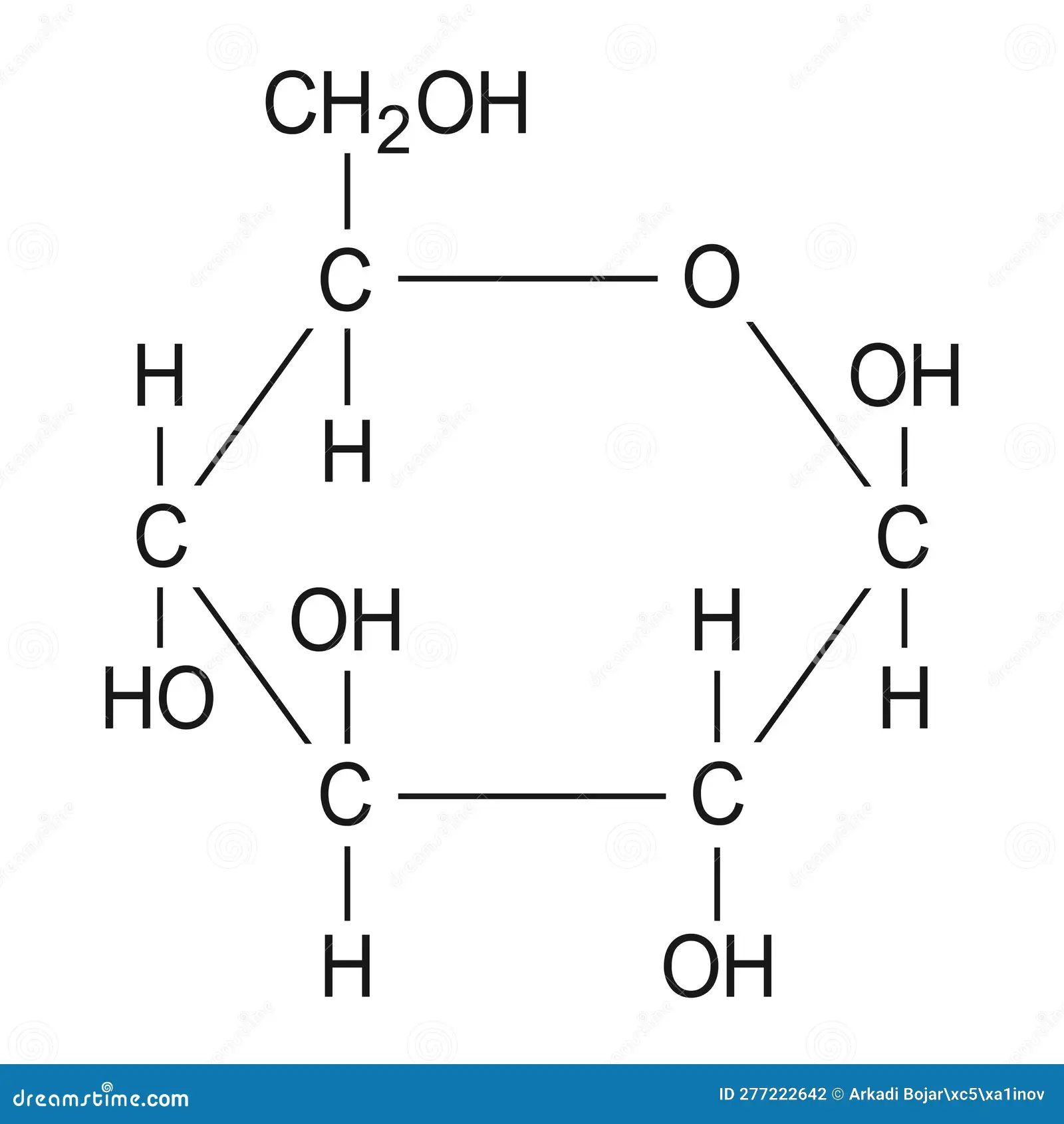
Glucose
A type of carbohydrate that provides energy to the cell
Starch
Made up of several glucose molecules.
The sugar found in animals
Glycogen
What is Genetic Material?
Nucleic Acid
Nucleic Acid
Carbon, Hydrogen, oxygen, and nitrogen
Sugar
Carbon + Hydrogen + Oxygen
Base
Adenine, Thymine, Guanine, Cytosine
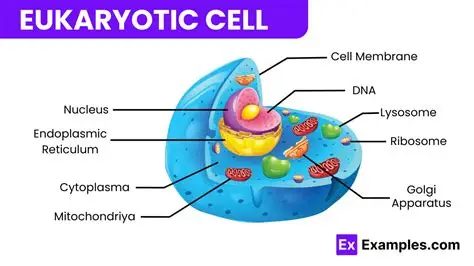
Eukaryotic cells
Organelles are specialized structures within a cell that include the mitochondria, Chloroplasts, and Nucleus.
Chloroplast
Conducts photosynthesis
Photosynthesis
The process by which the plant absorbs the sunlight to produce sugar
Frutos and Sucrose
Sugar found in fruit and Table sugar
Radioactive Material
Amplifies Carbon = Radioactive Phosphate
Kinetic Energy
Energy from the sun
DNA
Deoxy Ribose Nucleic Acid
4 bases
Adenine, Thymine, Guanine, and Cytosine
phosphate
Po4
Tissue
Groups of cells that perform a specialized function
Living things respond to ?
Stimuli
Living things maintain?
Homeostasis
Homeostasis
State of internal constancy
The storage form of sugar
Glycogen
Glucagon
Present inside the pancreas, which are insulin-producing cells