Medical Imaging Exam 1
1/58
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
59 Terms
Specific Ionization
the average number of primary and secondary ion pairs produced per length of a charged particles path
alpha particles
helium nucleus; high energy; doesn’t travel far; large for particle
water ionization / ionization begins where
10 eV
Nucleons
neutrons and protons
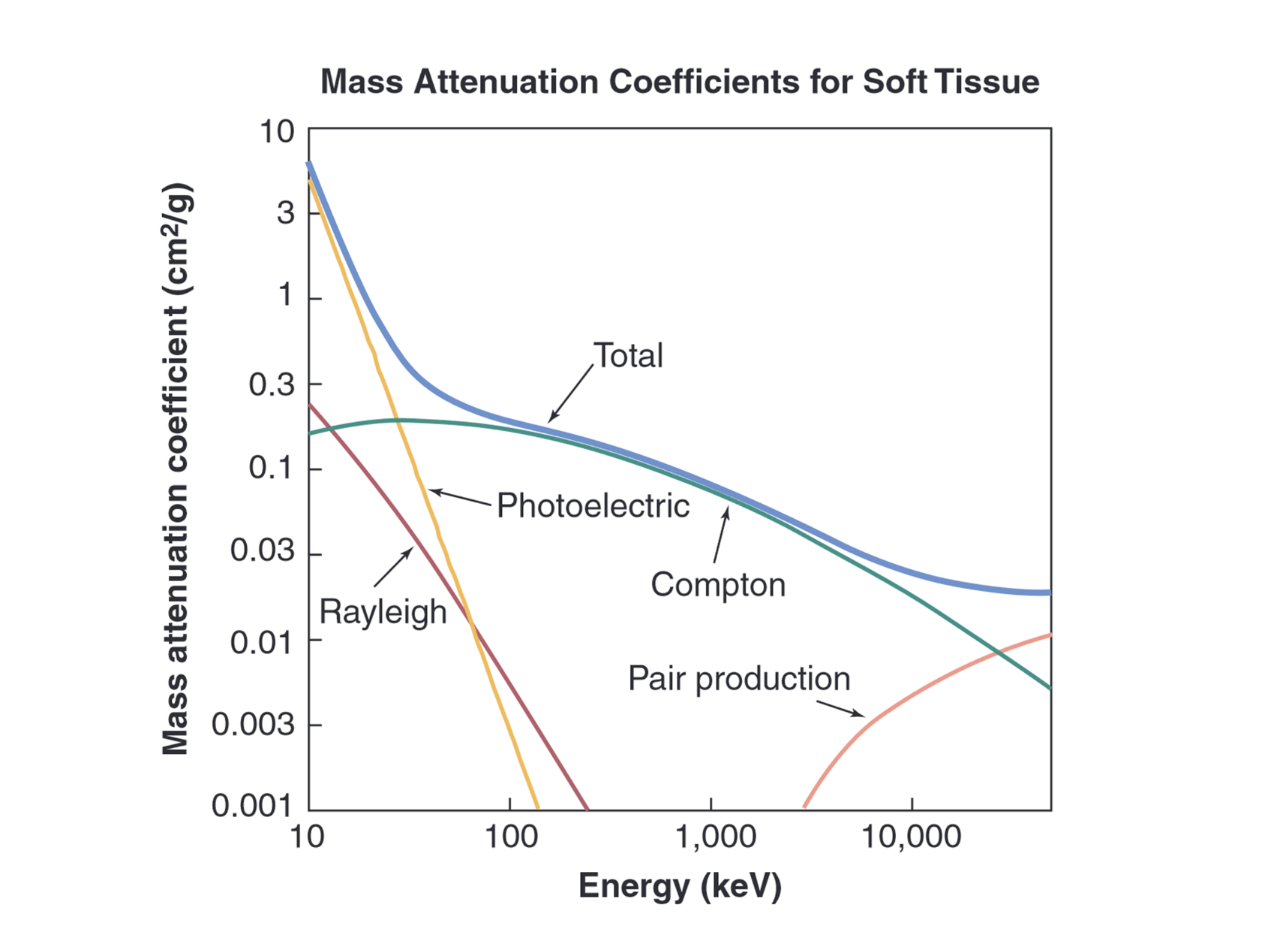
photoelectric effect dominates
in lower photonic energies (in x ray range)
pair production
1.02 MeV, uncommon in medical imaging, creates a positron and electron pair, they annihilate. Energy above 1.02 MeV goes to KE
created from x ray interacting with electric field of nucleus
Compton Scattering dominates
higher photonic energies
Raleigh scattering in medical imaging
10% of interactions in mammography
5% of interactions in chest radiography
Impact of Particle interactions in medical imaging
at lower energies, photoelectric dominates
at higher energies, compton.
Reighleigh is less than both, but still present.
pair production doesn’t lie in the medical imaging range
Beam hardening
As radiation passes through a medium, the lower energies will be attenuated, so the beam that arrives at the other side of the medium will predominately be higher energy.
Convolution
blurring processes in imaging. There is an equation.
Smoothing, average, add in more data, but don’t destroy relevant structures.
Use kernals for smoothing/changing functions
Spatial resolution
how close can two objects be together before you can’t tell the difference between them
range for x ray medical imaging (eV)
30 - 511 keV
Beta particle
high speed electron or positron
Auger Electron
an electron is emitted after another electron transitions to another electron shell, and it leaves with KE and no emitted X ray.
Fluorescence / Characteristic X ray
emission of an x-ray after a particle interaction instead of KE
secondary electrons/delta rays
electrons get knocked off, which can affect a neighbor, and another neighbor until it loses energyand creates secondary ionizations.
soft tissue ionization
70% of energy deposition of energetic electrons is from ionization
less energetic electrons: ionization % goes up
at 40 eV, excitation and ionization equal out
ionization decreases until 10eV
elastic collision
kinetic energy is conserved
electron knocks out a valence electron (loses little energy)
inelastic collision
KE is not conserved
electron knocks out an inner shell electron (like K)
Bremsstrahlung
inelastic
electron passing an atom nucleus is deflected
follows a curved path and accelerates (faster or slower) and emits x ray as a result
electrons
most intense when electron have high energies and when the material has a high atomic number
high N, high E
fraction of energy of electron has an equation, f = 0.0007ZE
Resting energy of an electron
0.511 MeV
Rayleigh Scattering
coherent/classical scattering
entire atom is excited (oscillation)
atom re-radiates at the same energy, excites another atom in a random direction
E in = E out
Compton Scattering
Nonclassical/Inelastic scattering
most common in diagnostic x-ray
interaction between photon and outer electron
photon will come in, knock out the electron, some of the energy goes to KE, the rest goes to a scattered photon.
There are two equations. Please take a moment to look at them and remind yourself of them!
as photon energy increases, photons and electrons (scattered) move toward forward direction.
more likely to be detected
at higher incident energies, more energy will go to the electron
Photoelectric Effect
all incident photon energy is transferred to an electron, which is ejected from the atom
this creates a vacancy that another electron will fill
this results in an Auger electron or a characteristic x ray
there is an equation for this related to atomic number and energy
there are no photons to degrade the image
for each electron shell, there is a jump in energy
mass and linear attenuation coefficient
how likely x rays/ other EM are to make it through a medium. Coefficients depend on energy of incident photons and the medium. One takes into account the density.
Half Value Layer (HLV)
how much does it take for ½ of the beam to be gone
narrow beam geometry, we use broad - beam most of the time in imaging
__ = ln(2)/ mu
Tenth value layer (TVL)
ln(10)/mu = ___
how much does it take for 1/10 of the beam to be gone?
Effective energy
more energy penetrates deeper
broad band, polyenergetic (range of x rays)
HLV through aluminum is___
Fluence
Photons/area
Flux
Photons / Area X Time
Energy Fluence
Fluence X Energy
Strong Force
Force keeping protons and neutrons together in nucleus, ineffective over large distances
line of stability : too many or too few neutrons can screw it up
unstable nucleus becomes stable: radioactive decay
Fission and Fusion
2 hydrogens fuse together, requires E
2 hydrogens are forced apart, releases E
Kerma
Kinetic Energy released in matter
there is an equation related to this and mass energy transfer coefficient
Mass energy transfer coefficient
mass attenuation x fraction of E photons transfer to charged particles as KE
higher energies have a lower coefficient of this
Absorbed Dose
D = E/m
measured in rads or Gray or J/kg
mass energy adsorption coefficient dependent
mass energy adsorption could be smaller if electrons make bremsstrahlung
Exposure
X = Q/M
___ in air is proportional to the dose in soft tissue (atomic numbers are similar)
W is here. It is related to dose and air and the equivalent dose.
Point Spread Function
most basic measure of resolution and properties of an imaging system
based on a point
there will be some blurring
shift invariant
Line spread function
resolution analyze
a larger area than PSF
A line object is used
Edge Spread function
used with edges, there will be a certain spread. Turning the incident can help it be more accurate.
Modular Transfer Function
a way to measure resolution as well
large and high frequencies —> amplitude will get smaller, will continue getting smaller with higher and higher f
at 10% of this, the spatial frequency can be determined.
Image will blur at a certain frequency of beam
Phantom
Physical way of measuring resolution, has spacing on an object where the distance can help determine the resolution
Contrast resolution
There is an equation for this
Intrinsic: anatomic factors —> contribute most
Extrinsic: x ray energy, machine related things
Detector Contrast
X rays hit detector they are transformed into a signal
detector’s response affects contrast
Display Contrast
Data collected has more bits than can be displayed. The higher resolution raw data must be turned into gray values for a monitor.
uses a Look Up Table (LUT)
contrast can be changed to highlight certain gray values
Noise
precision of the image
can be reduced by number of photons increased or increase time of acquisition
Quantum Noise
Noise from randomness of photons
Anatomic Noise
Noise created by unwanted anatomical structures
Electronic Noise
Noise that involves electronics
Measurements involve flow of electrons.
actual signal
thermal sources and other electrical signals
amplify signal may amplify noise
Structural Noise
Noise from pixelated detectors with parallel channels, each of which has its own amplifier circuit — not perfectly tuned
Contrast Detail Diagrams
compare different systems to see how they compare in terms of their contrast and detail.
Reciever Operating Characteristic Curves (ROC)
Involves a truth table with normal, abnormal; true negative, false negative, true positive, false positive.
pick a true value and pick what is normal and abnormal around it
based on sensitivity and specificity of diagnosis
sensitivity
True positive / true positive + false negative
how sensitive you are to to tell if there is a disease
specificity
True Negative / True negative + False positive
more people may be called back that may not need it if this is reduced (False positives)
PACS
Picture Archiving and Communication System
everything goes through this, where stuff is stored
Includes DICOM, HL7, EMR, and RIS
big firewall
Image compression
Lossy compression is bad —> can’t be reverted
reversible compression —> good
Grayscale Standard Display Function (GSDF)
calibrate luminance of displays according to predetermined values and such. Calibration is through a 3rd party software. Adjust luminance based on input pixel value
Display Interface and Value of Interest (VOI) Look up Table (LUT) conversion
image is put through the look up table, a digital to analog converter will put it over to the display