Neuroscience Ch. 12
1/44
Earn XP
Description and Tags
The Neurology of Language
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
45 Terms
where is Broca’s Area located?
Inferior Frontal Gyrus
Superior Temporal Gyrus
Primary Auditory Cortex, Wernicke’s Area
there are comprehension areas in which two areas of the brain?
Middle Temporal Gyrus and Inferior Parietal Lobe
Perisylvian Region
the region associated with language processing, encompassing Broca's area Wernicke's area and Primary Auditory Cortex
What does the Perisylvian Region border?
the Sylvian fissure (lateral)
Zone of Language
The Left Perisylvian Language Area, near the sylvian fissure
Precentral gyrus
The primary motor cortex responsible for controlling voluntary movements.
Superior frontal gyrus
Working memory and spatial processing
Middle frontal gyrus
Involved in literacy development
Inferior Frontal Gyrus
Broca’s area - speech production
Postcentral Gyrus
Houses the primary somatosensory cortex, which processes somatosensory information, like touch, pain, and temperature.
Superior Temporal Gyrus
Contains auditory cortex and Wernicke’s area
Supramarginal Gyrus
Integrates sensory info, involved in spatial and phonological processing
Lateral sulcus (Lateral/Sylvian Fissure)
A prominent groove that separates the frontal and temporal lobes of the brain, crucial for language processing and auditory function.
Central sulcus
Separates the frontal lobe from the parietal lobe; plays a key role in motor and sensory processing.
What areas are involved in auditory comprehension?
Heschl’s gyrus (PAC), Wernicke’s Area, Broca’s Area
Where does processing for auditory comprehension begin?
Primary Auditory Cortex - Heschl’s Gyrus
Step 1 of processing for auditory comprehension
PAC analyzes the signal. Left PAC - sensitive to speech characteristics. Right PAC - sensitive to pitch.
Step 2 of processing for auditory comprehension
Information is sent to Wernicke’s Area to attach meaning - semantic processing - and phonological processing
Step 3 of processing for auditory comprehension
When syntax is complex, Broca’s area is recruited
What structure is involved in syntactic structure
Superior Temporal Gyrus
What structure is involved in verb processing
Posterior Temporal Lobe
When syntax is complex, what area is involved?
Broca’s area - inferior frontal gyrus
Aphasia
An acquired language disorder that can involve all modes of communication to varying degrees; core symptom is some degree of anomia
2 main classifications of aphasia
fluent or nonfluent
KNOW THIS CHART
Aphasia classifications
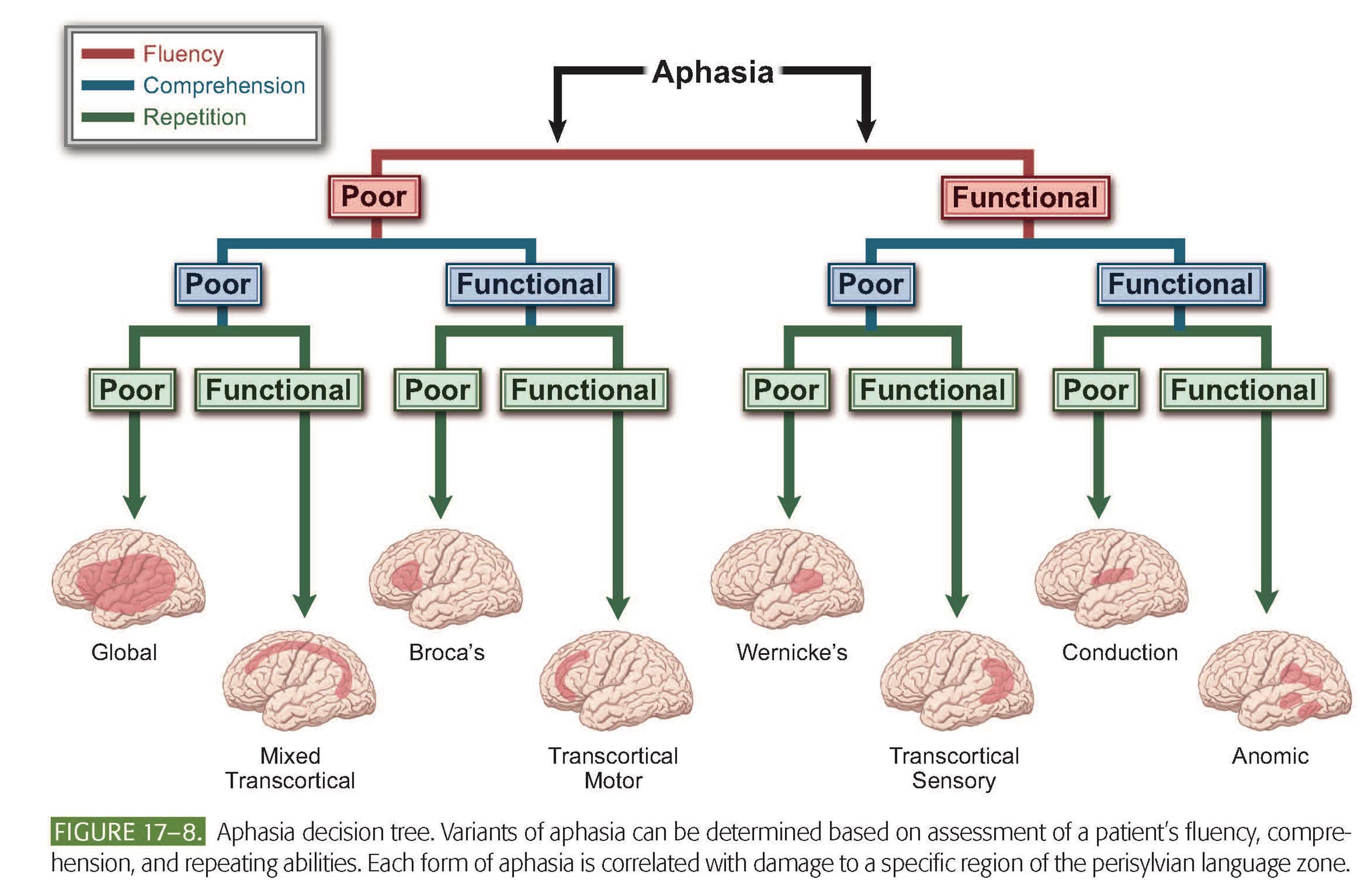
Nonfluent Aphasias
Broca’s Aphasia, Transcortical Motor Aphasia, Global Aphasia, Mixed Transcortical Aphasia
Fluent Aphasias
Wernicke’s Aphasia, Transcortical Sensory Aphasia, Conduction Aphasia, Anomic Aphasia
What is the common uniting characteristic of all persons with aphasia?
Anomia - word retrieval and word finding difficulty
What are 3 characteristics of aphasia?
Anomia, Paraphasia and Perseveration
What is a paraphasia
Substitution in speech
Semantic Paraphasia
substitution of a word related in meaning or from the same semantic class
ex: fork for spoon; hammer for nail
Formal Paraphasia
substitution that is phonologically similar to the target word by sound but not associated by meaning
ex: rabbit for rapid
Phonemic paraphasia
substitution that has some phonemic errors of the intended word
ex: lelophone for telephone
Neologistic Paraphasia
substitution of a jargon word that may or may not have similarities to the intended word
ex: repuco for cat; glat for cat
Perseveration
Repetitive verbal behaviors; person “gets stuck” on a verbal production
KNOW THIS CHART
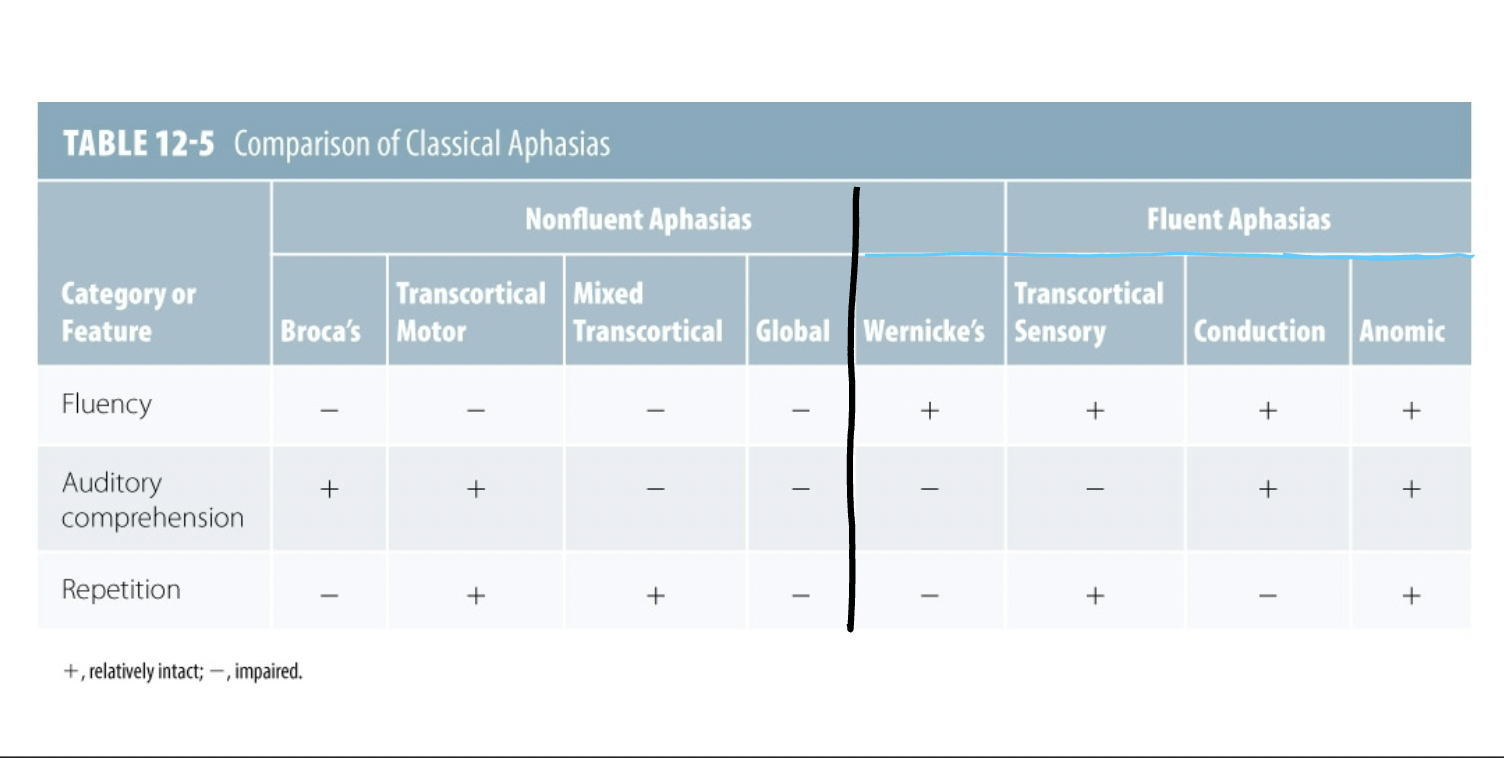
Broca’s Aphasia characteristics
Effortful speech, agrammatism, aware
Transcortical Motor Aphasia characteristics
Like Broca’s, but can repeat
Global Aphasia characteristics
severe, minimal speech output
Mixed Transcortical Aphasia
like global but can repeat
Wernicke’s Aphasia
Fluent nonsense, paraphasias, unaware, press of speech
Transcortical Sensory Aphasia
like wernicke’s, but can repeat
Conduction Aphasia characteristics
Can’t repeat, self-correcting behaviors
Anomic Aphasia characteristics
just word-finding issues