Abdomen Quiz Study Guide Filled Out
1/80
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Abdomen Anatomy
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
81 Terms
The membrane that lines the Abdominopelvic Cavity:
A double walled membrane including; Parietal Peritoneum (lines walls) + Visceral Peritoneum (covers organs)
Omentum:
double-fold of peritoneum( abdominopelvic membrane (parietal + visceral)) that attaches the stomach to other abdominal organs
creates the Greater and Lesser Sacs
(yellow bits in the image)
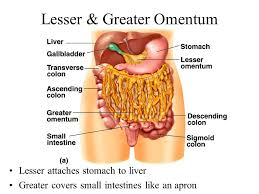
Intraperitoneal structures
where is it?:
Mnemonic is?:
list all the structures:?
in peritoneal sac (membrane lining the abdominopelvic cavity ie parietal & visceral)
Mnemonic: slips tjc ct
Liver, Gallbladder, Spleen, Stomach, Jejunum, Ileum, Cecum, Transverse and Sigmoid Colon
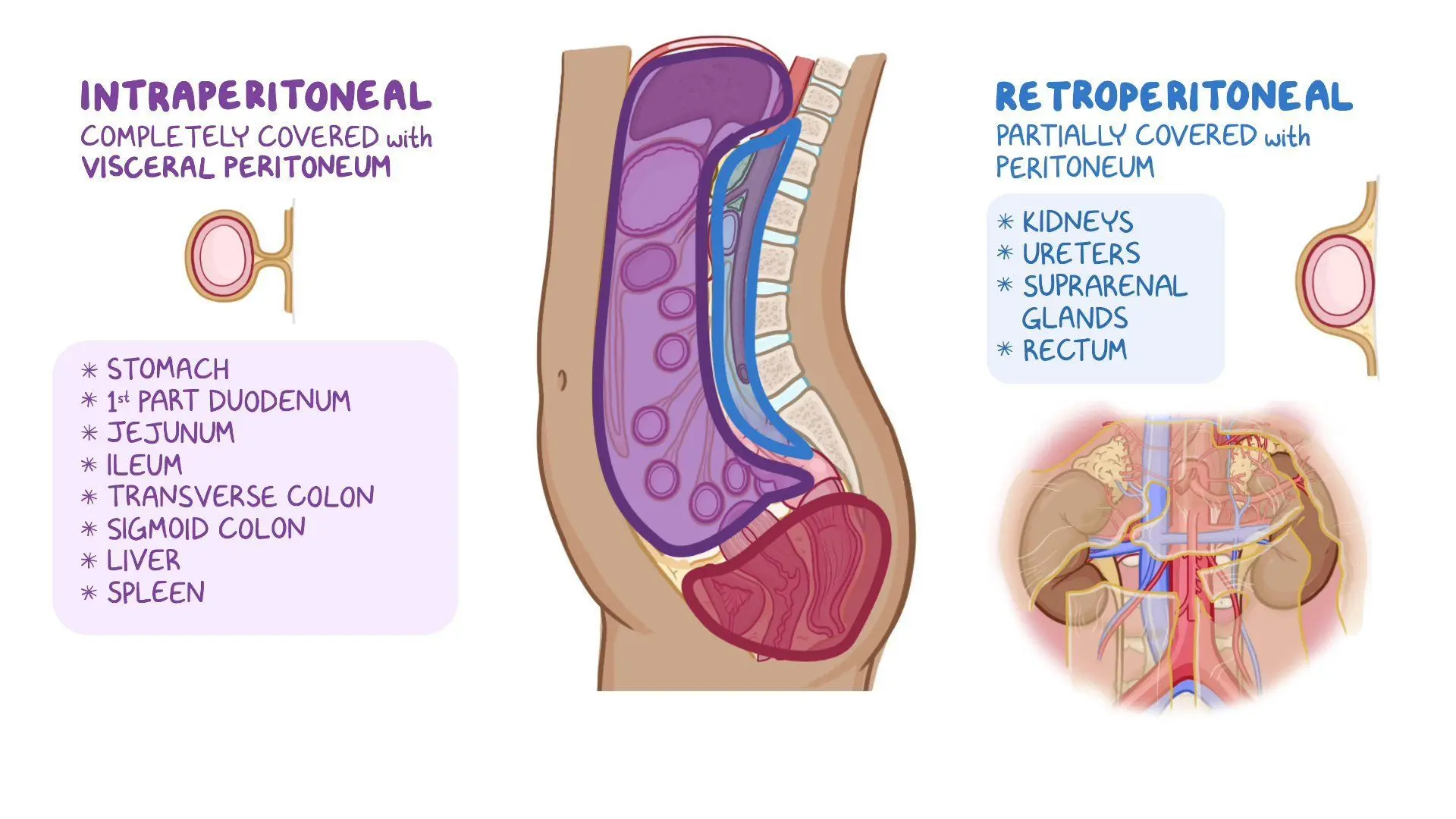
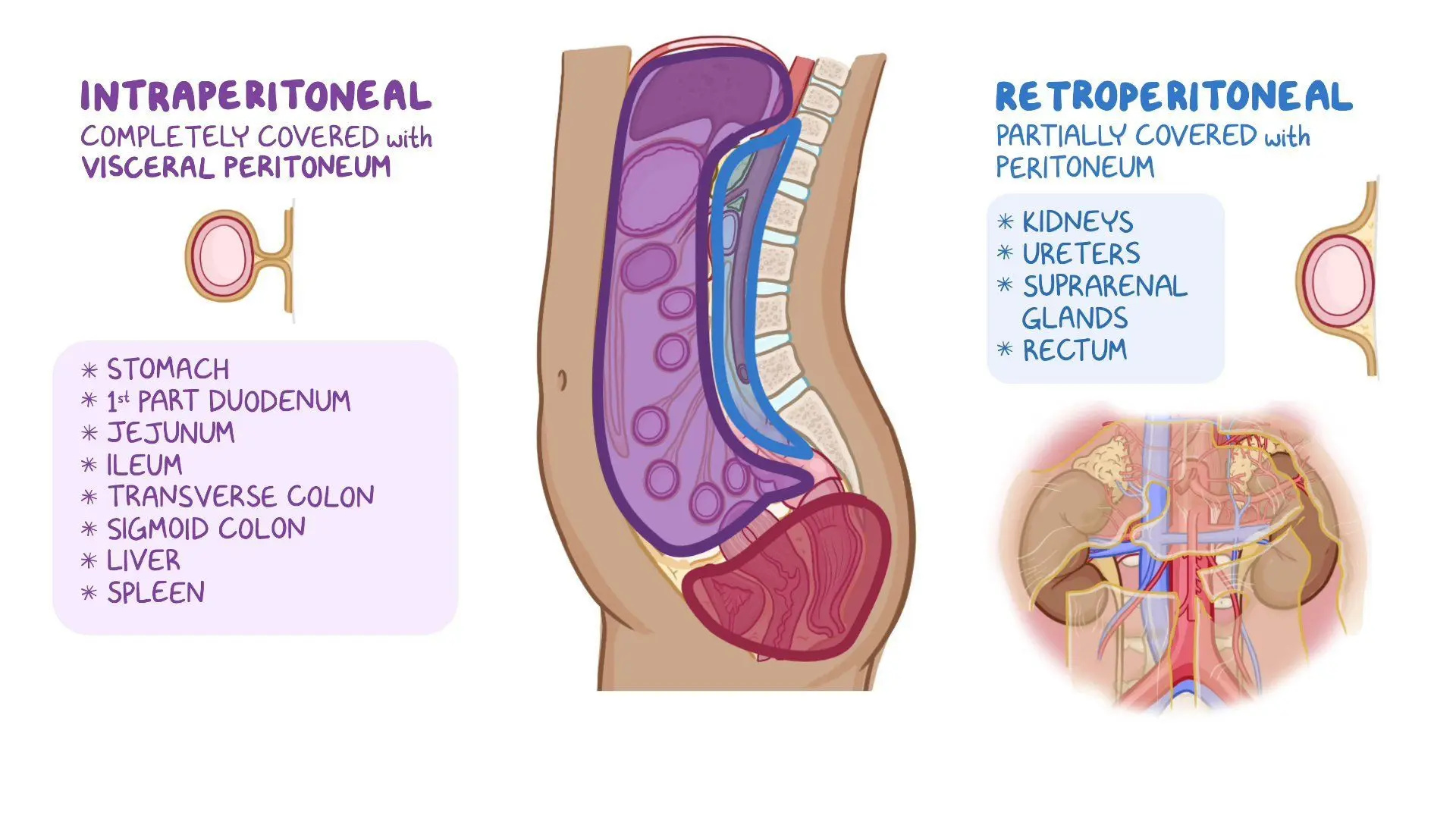
Retroperitoneal structures
where is it?:
Mnemonic is?:
list all the structures:?
in peritoneal sac (membrane lining the abdominopelvic cavity ie parietal & visceral)
Mnemonic: SAD PUCKER
Kidneys, Ureters, Adrenal Glands, Pancreas, Duodenum, Ascending and Descending Colon, Proximal Rectum, Abdominal Aorta, Inferior Vena Cava
Positive Contrast Media
what does it mean?
what contrast
How does it work and what does it look like on an image?
radiopaque
Barium Sulfate or iodinated
absorbs radiation thus appearing white
Negative Contrast Media
what does it mean?
what contrast
how does it work and what does it look like on an image?
radiolucent
Air / CO₂
allowing X-rays to pass through structures more quickly; black
Contra-indications for Barium Sulfate
1)contraindicated (dont use) for the following circumstances:
2)this is because:
3)so what bad things can happen if it leaks into the body because its used during those circumstances? (2)
1)Suspected GI or bowel perforation (penetration); Pre-surgery; Post-surgery
2)not soluble (dissolvable) and cannot be absorbed by the body
3)peritonitis or avascular adhesions
IVU
means?:
what contrast is it?:
purpose?;
Intravenous Urogram
water-soluble iodinated contrast
Used to visualize the area of the urinary bladder by highlighting KUB (kidney, ureter, bladder)
KUB
means?:
what is it?
kidney, ureter, bladder
organs of the urinary bladder
Motility examination
examines what?
otherwise known as what?
a study designed to observe how quickly and efficiently the small intestine moves material along
SBFT
SBFT
means?:
what is it:?
Purpose + contrast used?:
Small Bowel Follow-Through
a motility examination
fluoroscopic procedure using barium sulfate contrast to watch the process of small intestine→large
Fluoroscopy
used for what?
what contrast is used for & +or-?
-Digestive system
-Urinary & Biliary systems
-Double contrast studies
visualize all structures of Digestive system
-Barium Sulfate (positive)
-Water-Soluble Iodinated Contrast (positive)
-Air (negative)
SPOT image
when used?
equipment position?
During fluoroscopy
Tube is under the table
Overhead image
when used?
equipment position?
After fluoroscopy
Tube is overhead of patient
Bolus
food+saliva ball in mouth
chyme
partially dissolved food in stomach
Indentations (smth presses into it) of esophagus (2)
1)At Aortic Arch
2)At Left Main Bronchus
Constrictions (passage narrows) of Esophagus (2)
At thoracic inlet (where it enters thorax cavity)
At the Esophageal Hiatus (at diaphragm)
the opening in the diaphragm where the Esophagus enters the abdominal cavity?
what does it connect?
Esophageal hiatus
esophagus to the stomach
Duodenal Bulb
what hormone does it produce?
what does that hormone do?
Cholecystokinin (CCK)
causes the Gallbladder to contract
Descending Duodenum
recieves what ducts?
where located?
does what?
receives Common Bile Duct and Pancreatic Duct
at Ampulla of Vater
fat digestion
sphincter of oddi
involves what ?
where located?
does what?
Descending Duodenum
Ampulla of Vater
Controls flow of bile and pancreatic enzymes
Proximal to distal structures of the Duodenum (Also called C-Loop of Abdomen)
Portion of the digestive tract that has finger-like projections called microvilli, which absorb digested
nutrients
ACBE
BE
Polyps best demonstrated on ACBE
Contrast procedure that requires fluoroscopic imaging of the Ileocecal Valve at the conclusion of the
examination (SBFT)
what performs the MECHANICAL digestion of fats
Liver produces bile for
what performs the CHEMICAL digestion of fats
Pancreas produces enzymes for
Biliary Tree – All Ducts
Portal Vein
tunnel used to transport absorbed nutrients from Jejunal microvilli to Liver
Pancreatic Duct – other name
(Duct of Wirsung)
Contrast procedure that will demonstrate an obstruction caused by the presence of choleliths (ERCP)
Parts of the Kidney (Cortex / Medulla / Minor and Major Calyces / Renal Pelvis / Upper Pole / Lower
Pole
UVJ / UPJ – what structures meet to form these junctions?
Anatomy of Urinary System on IVU image and distinguishing what procedure it is
Purpose of PA Projection (prone position) for IVU
fills distal ureters with contrast media
Contrast procedure performed to rule out reflux of urine from the Urinary Bladder into the Ureters
Volvulus
type of what
Mechanical Bowel Obstruction
Adhesions
type of what
Mechanical Bowel Obstruction
Intussusception
type of what
Mechanical Bowel Obstruction
Ileus
type of what
causes of
adynamic Bowel Obstruction
Ascites
type of what?
what is it?
Abdomen pathology (disease?)
Fluid in the Peritoneal Cavity
What body plane is perpendicular for AP projection of the Abdomen?
Midsagittal
Where is the CR directed for the AP Projection of the Abdomen?
Perpendicular to Iliac Crest
Projections performed for AP Upright for Diaphragm
Projections performed for Upright for Symphysis Pubis
Projections performed for Supine AP Projection
Labeled anatomical structures for the AP Projection of the Abdomen (Upright also)
Positions / projections of the Abdomen that would be performed to demonstrate free air from a
perforation in the GI tract
Upright / Left Lateral Decubitus
Determining rotation on the AP projection of the Abdomen (symmetrical appearance of Iliac wings,
Obturator Foramen, SI Joints)
Structure that MUST be included on AP Upright Abdomen and Left Lateral Decubitus
Right Hemidiaphragm
Structure that MUST be included on AP Supine Recumbent position of the Abdomen
Symphysis Pubis
SCOUT
post-evac
post-void
How to determine proper exposure factors on AP projection of the abdomen
Outline of Psoas Muscles
When is a Left Lateral Decubitus position performed?
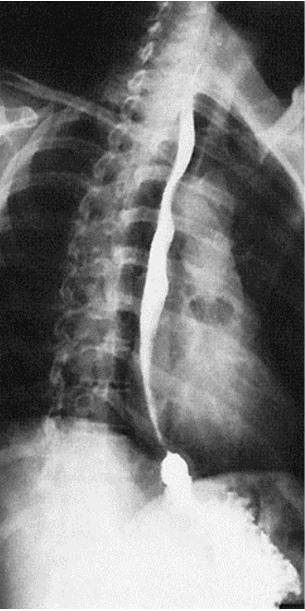
What contrast procedure was performed to produce this image?
Esophagram
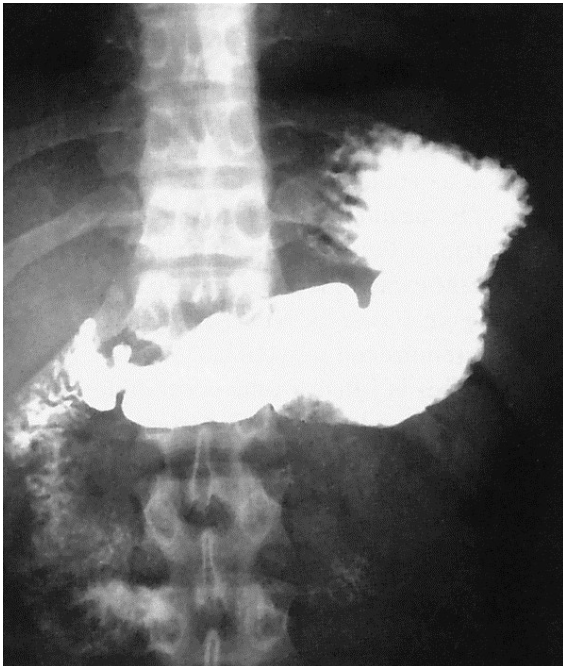
What contrast procedure was performed to produce this image?
Upper Gastrointestinal (UGI) Series
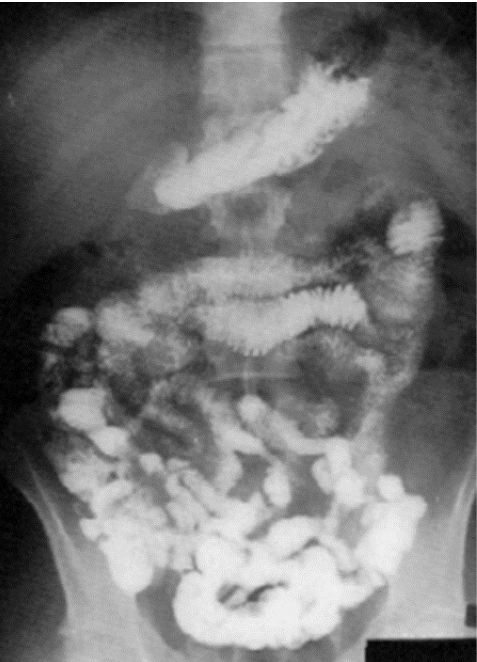
What contrast procedure was performed to produce this image?
Small Bowel Follow-Through (SBFT)
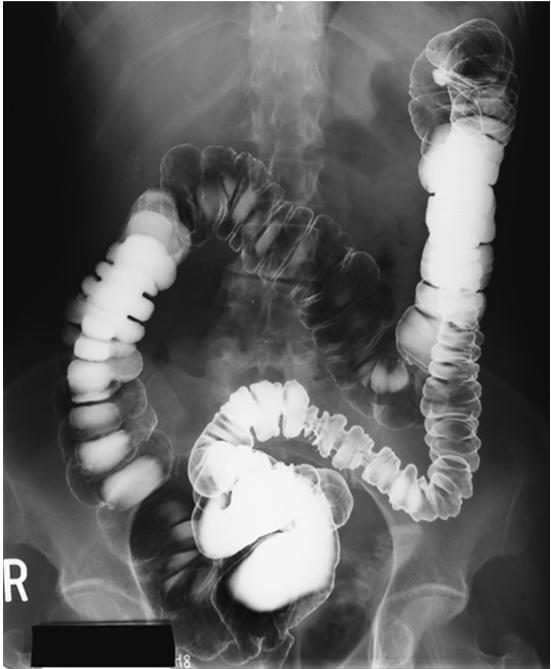
What contrast procedure was performed to produce this image?
Air-Contrast Barium Enema (ACBE)
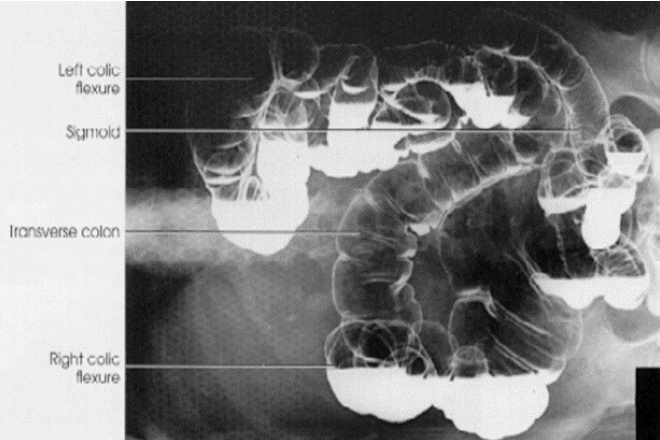
What contrast procedure was performed to produce this image?
What position was performed to produce this image?
Barium Enema (BE)
supine projection shown by transverse colon and sigmoid being filled with air
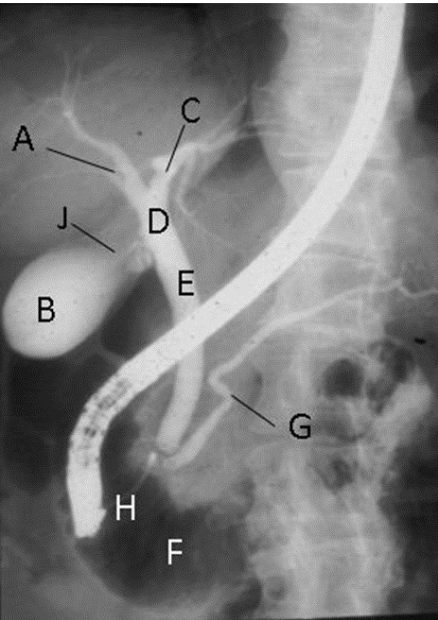
What contrast procedure was performed to produce this image?
Identify A – H:
ERCP – Endoscopic Retrograde Cholangiopancreatography
A-Right Hepatic Duct
B-Gallbladder
C-Left Hepatic Duct
D-Common Hepatic Duct
E-Common Bile Duct (CBD)
F-Duodenum
G-Pancreatic Duct (Duct of Wirsung)
H-Ampulla of Vater (Hepatopancreatic Ampulla)
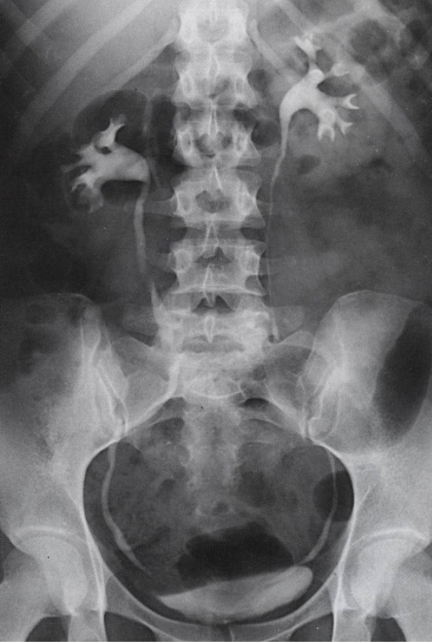
What contrast procedure was performed to produce this image?
IVU – Intravenous Urogram
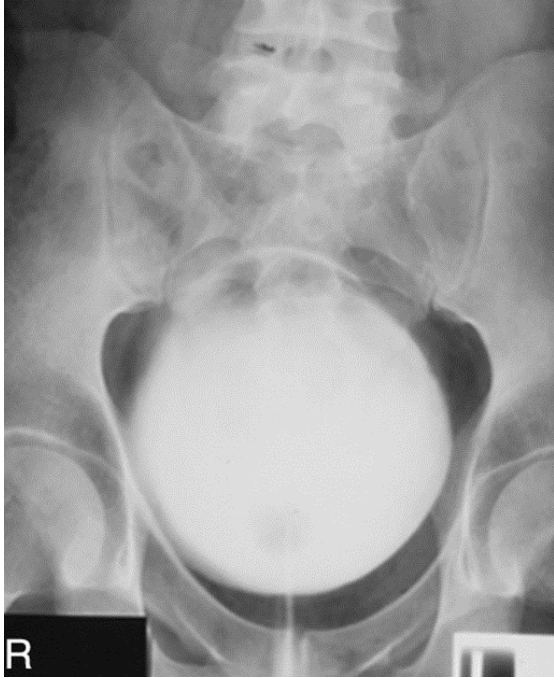
What contrast procedure was performed to produce this image?
VCUG – Voiding Cystourethrogram
NOT A cystography bc they are voiding in the image as shown by the line below of the urethra
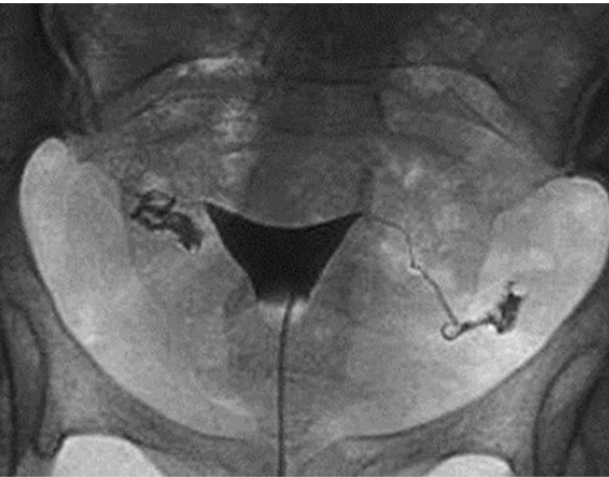
What contrast procedure was performed to produce this image?
Hysterosalpingogram (HSG)
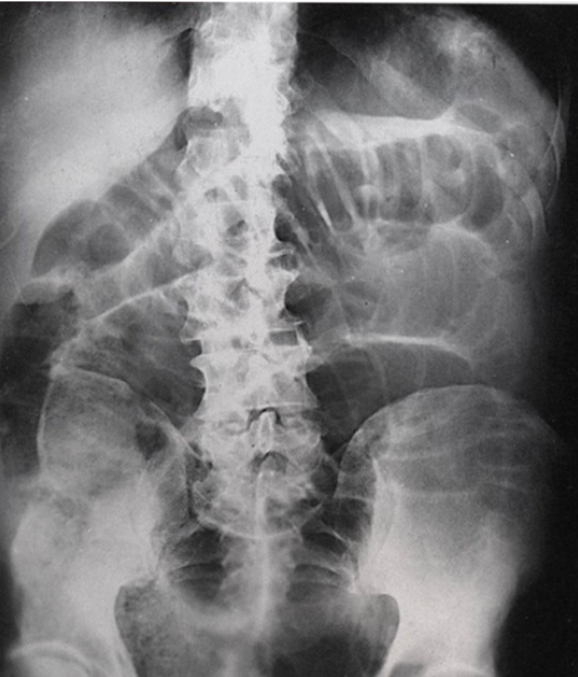
What pathology is represented on the image above?
Adynamic Ileus
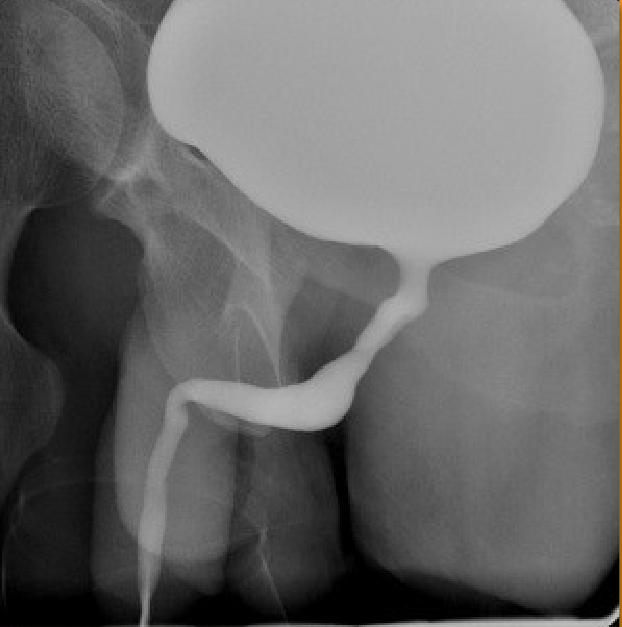
1)contrast procedure performed?
2)contrast media used?
3)What abnormality will they look for when performing images during the fluoroscopic portion of the examination?
1)Voiding Cystourethrogram (VCUG)
2)Water-Soluble Iodinated Contrast
3)Vesicoureteral Reflux (VUR) (backward flow of urine)
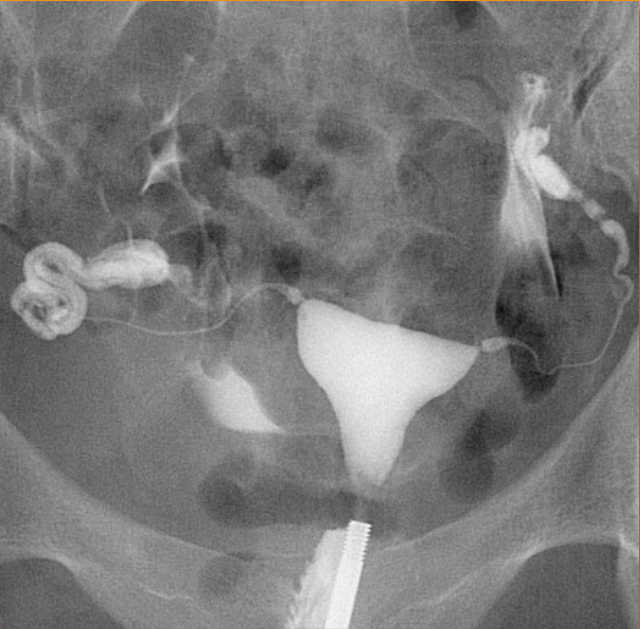
1) contrast procedure performed?
2) contrast media used?
3)What will the doctors be trying to rule out from this examination?
1)Hysterosalpingogram (HSG)
2)Water-Soluble Iodinated Contrast
3)Uterine and Fallopian Tube Abnormalities
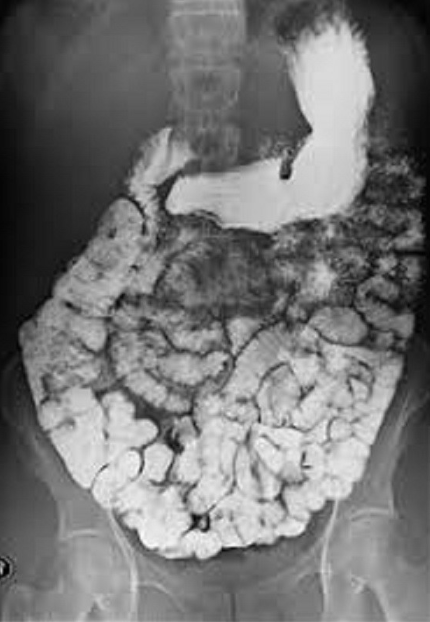
1)contrast procedure performed?
2)contrast media used?
3)motility study means__?
4)Why is this examination done at different time intervals?
1)Small Bowel Follow-Through (SBFT)
2)Barium Sulfate
3)how quickly and efficiently the small intestine moves
4)observe motality
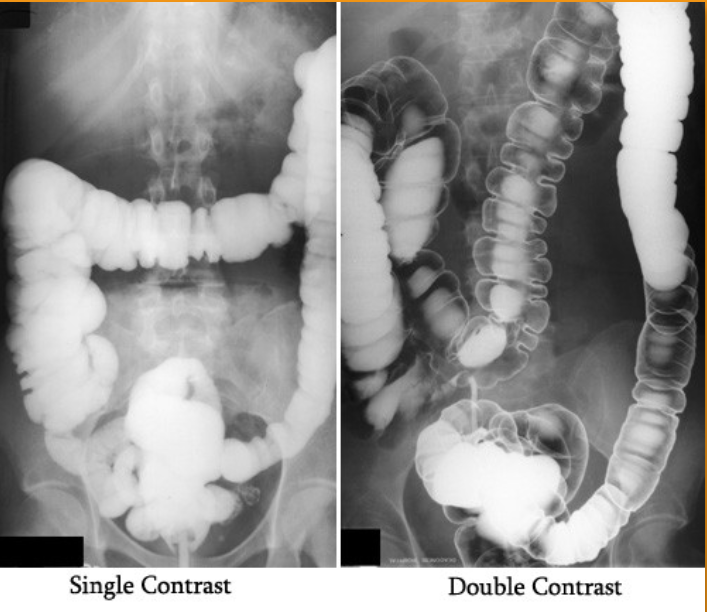
1)What does single contrast mean in the first image?
2)What does double contrast mean in the 2nd image?
3)contrast media used for this examination?
4)the 3 contraindications of the contrast used?
1)entire colon is filled only with barium sulfate (this is a BE)
2)both barium sulfate and air. (this is a ACBE)
3)Barium Sulfate
4)DON’T us if suspected bowel perforation; Bowel obstruction (high risk of retention or perforation);
Pre- or post-surgy
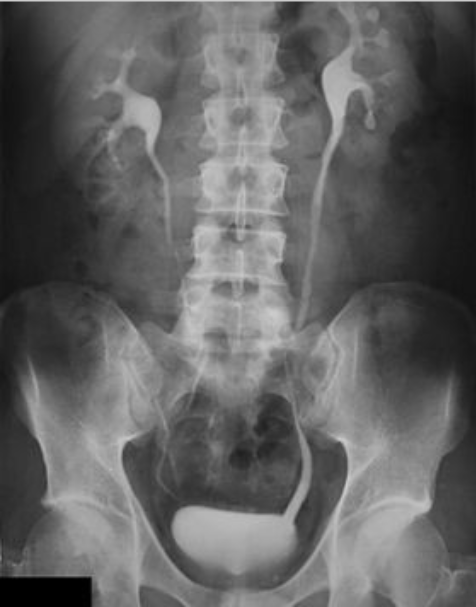
1)procedure performed?
2)contrast media used?
3)How contrast media administered?
4)List contraindication for this type of contrast media:
1)IVU – Intravenous Urogram
2)Water-Soluble Iodinated
3)Injected intravenously (bc travels through the bloodstream → filtered by kidneys → passes through renal pelvis → ureters → bladder)
4)dont use if: Allergic; Poor kidney function / renal failure; Dehydration; Severe asthma or thyroid disorders
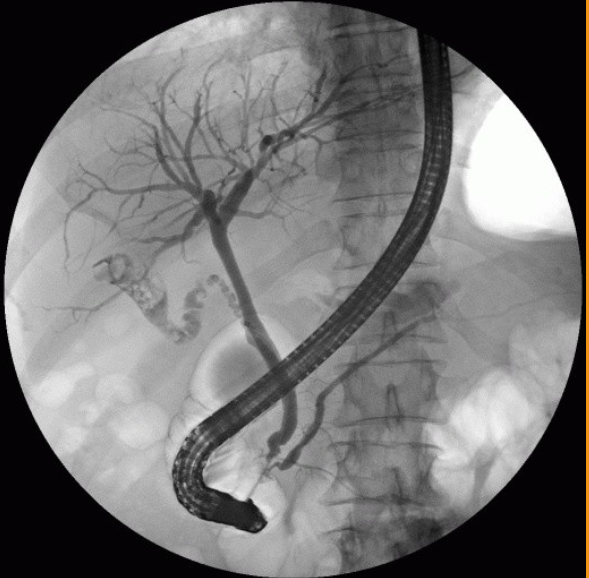
1)procedure performed?
2)contrast media used?
3)How contrast media administered?
1)ERCP – Endoscopic Retrograde Cholangiopancreatography
2)Water-Soluble Iodinated
3)retrograde (tube through mouth→ampulla of vater then backwardly injected in bile duct)
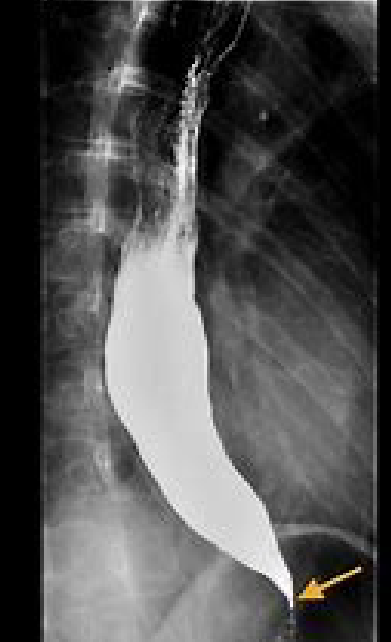
1)procedure performed?
2)contrast media used?
3)How contrast media administered?
1)Esophagram
2)Barium Sulfate
3)orally
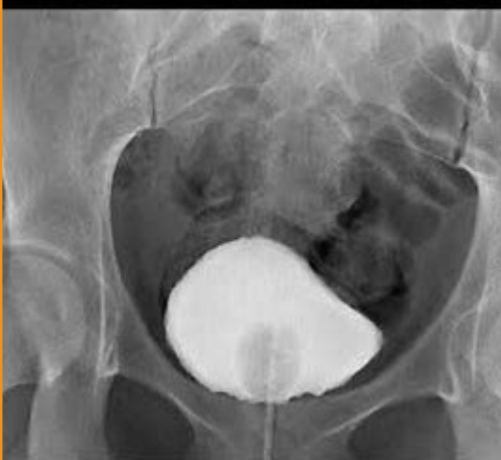
1)procedure performed?
2)contrast media used?
3)How contrast media administered?
1)Cystogram (Retrograde Cystography)
2)Water-Soluble Iodinated Contrast
3)retrograde (tube through urethra)
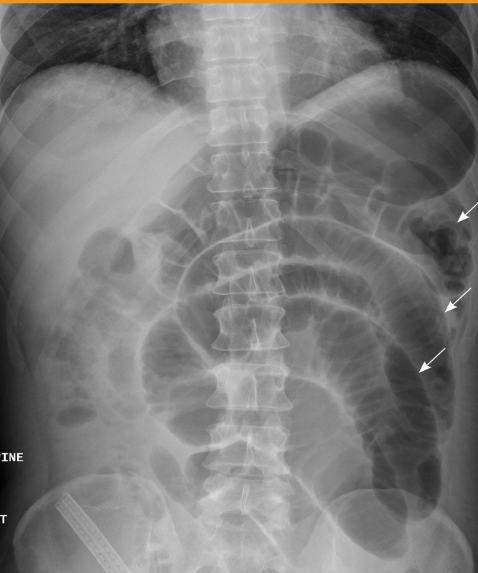
What abnormality is visualized?
Small Bowel Obstruction (SBO) bc larger than normal
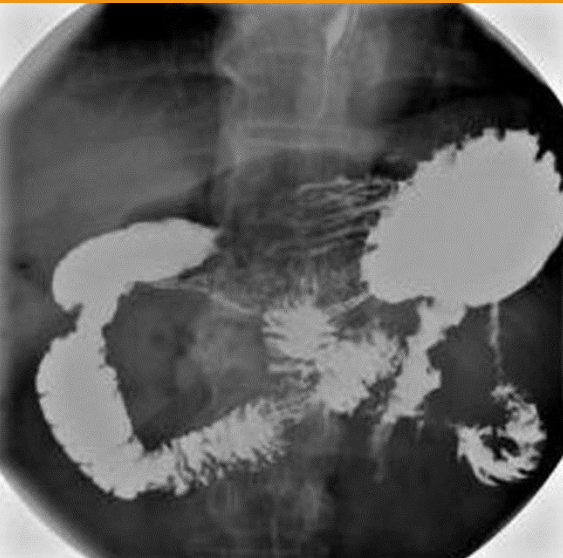
What body habitus is visualized?
hypersthenic (because stomach is balled up)