CLIN PATH I: EXAM #2 (DERM 2.0)
1/165
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
166 Terms
Functions of skin:
1. maintain body temp
2. protection
3. receive external stimuli
4. control insensible water loss (why burn victims lose a lot of water)
Skin is distinct from mucosa in that it contains:
adnexal structures (ex. eccrine units for sweat and folliculosebaceous units for hair/oil)
Two important skin layers
a stratified squamous epithelium, the epidermis
and a layer of connective tissue, the dermis
Epidermis
superficial layer (thick, protective)
**have keratinocytes, melanocytes, and is where the eccrine sweat glands open
Dermal layer
epidermal junction (undulating basement membrane)
Dermis layer
semi-fluid, which binds the body together
**contains nerve endings, sweat glands, har follicles, blood/lymph vessels
Where do tattoos go?
dermis
What is found in the granular layer?
cells with cytoplasmic granularity (from an accumulation of keratin and structural proteins)
What is found in the spinous layer?
cells with ample cytoplasm and prominent desmosomes
What serves as the foundation in the basal layer?
cuboidal germinative keratinocytes
When your skin grows, ________ layers are on top
older
Dendritic cells that are intercalated among the keratinocytes of the epidermis
Melanocytes and Langerhans cells
Melanocytes are positioned in the ___________ and synthesize ____________
basal layer; melanin (reddish-brown biochrome to protect against UV rays)
Langerhans cells are positioned in the ___________ and are ____________
midspinous layer; antigen-presenting cells
What serves as the scaffolding that supports neurovascular networks?
dermis
If skin loses elasticity, it is the __________ layer
dermis
**composed of collagen (type I and III and elastic microfibrils)
What are ubiquitous in the dermis layer?
fibrocytes (also mast cells and dendritic immune cells)
Three types of skin diseases:
inflammatory
infectious
neoplastic
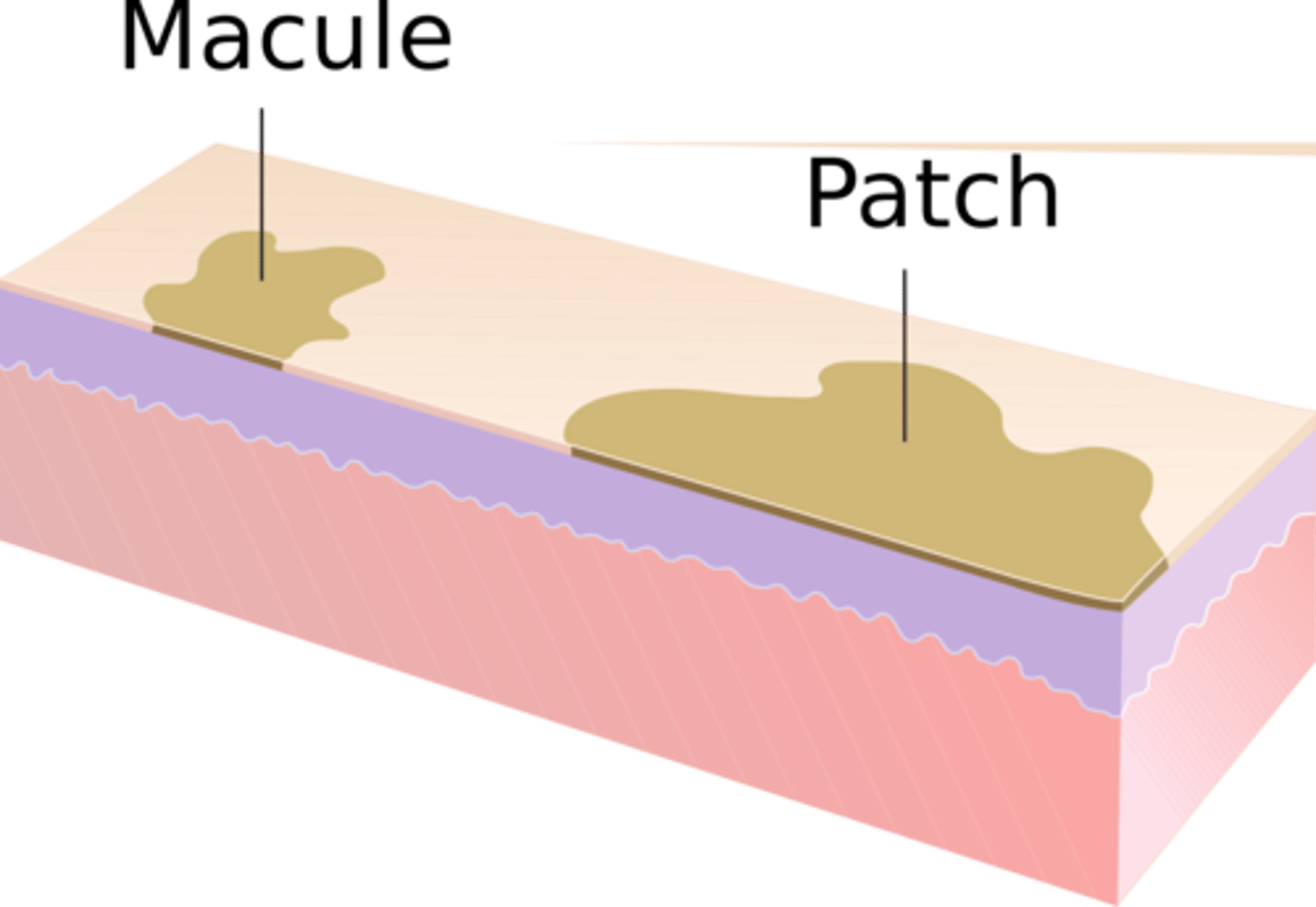
Macule
increased or decrease pigmentation
<1 cm
non-palpable and superficial
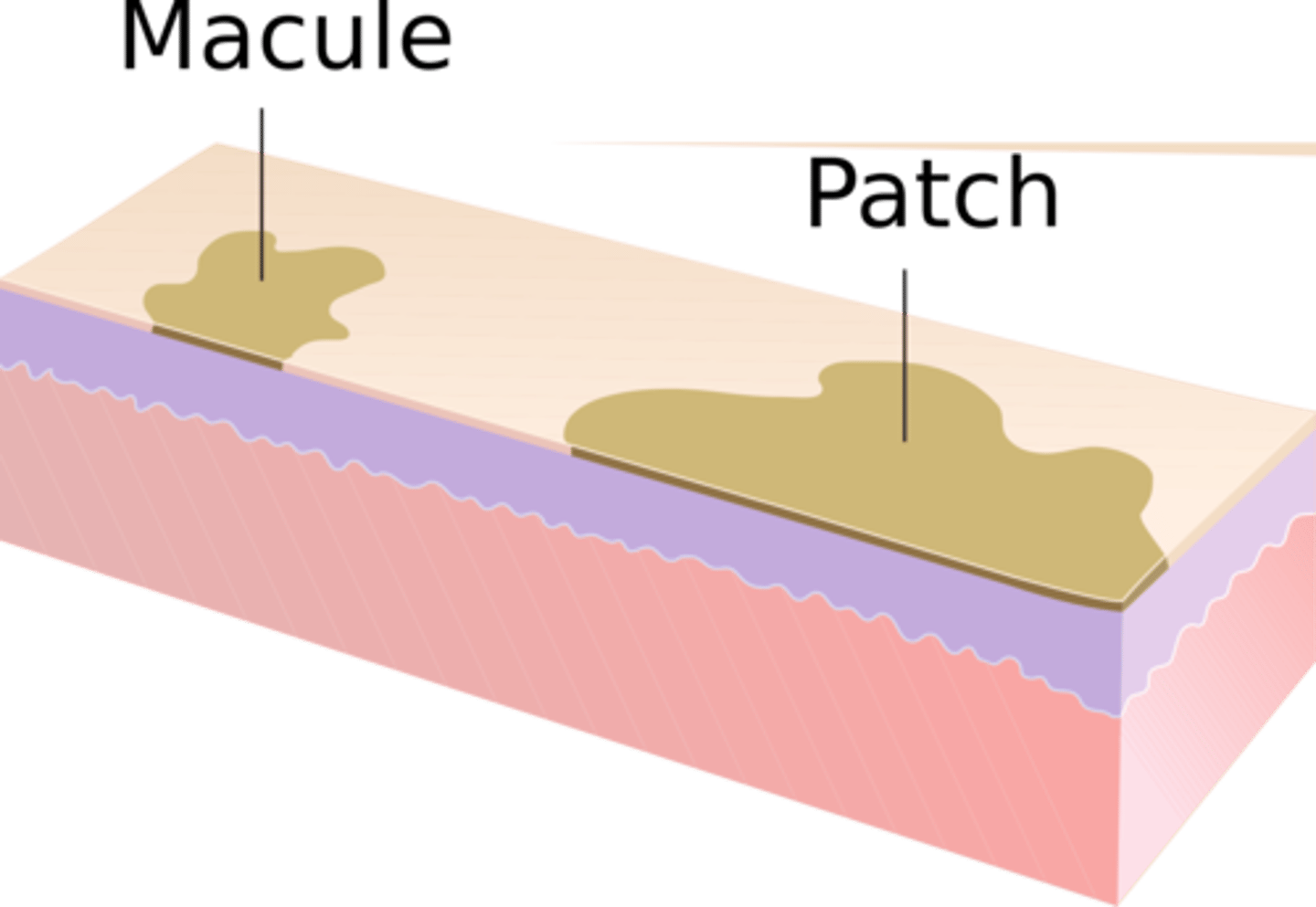
Patch
macular lesions
circumscribed
> 1 cm
Papule
solid and superficial lesion
< 0.5 cm
often in clusters
can accompany rashes
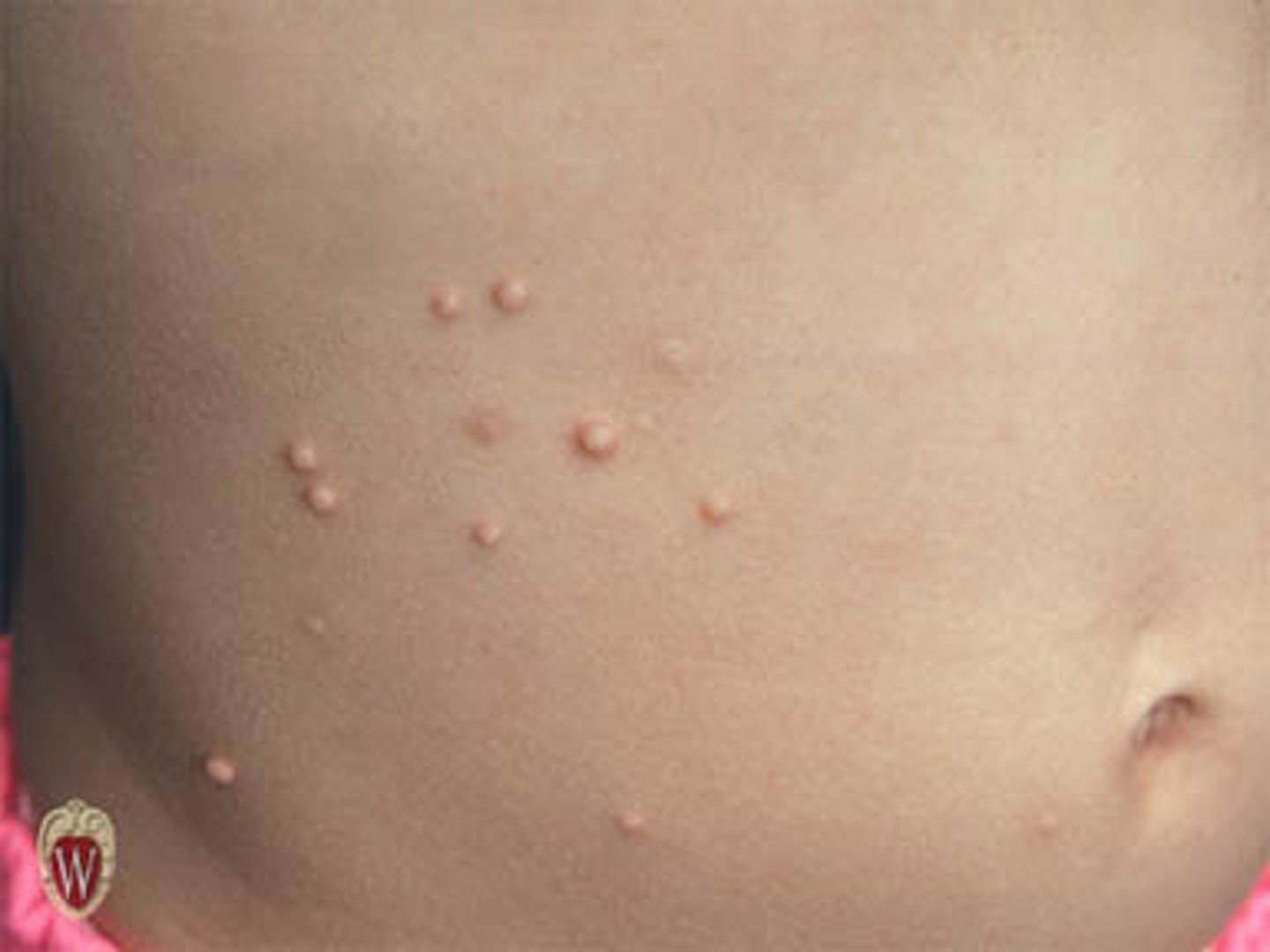
Etiology of papules
inflammation (infected skin)
accumulated secretions
infection (disseminated histoplasmosis)
hypertrophy of skin
acne
Plaque
plateau elevation w/ SA > height
forms by confluence of papules
> 1 cm
Lichenification
surface is rough & thickened and accentuation of normal skin lines
**plaque
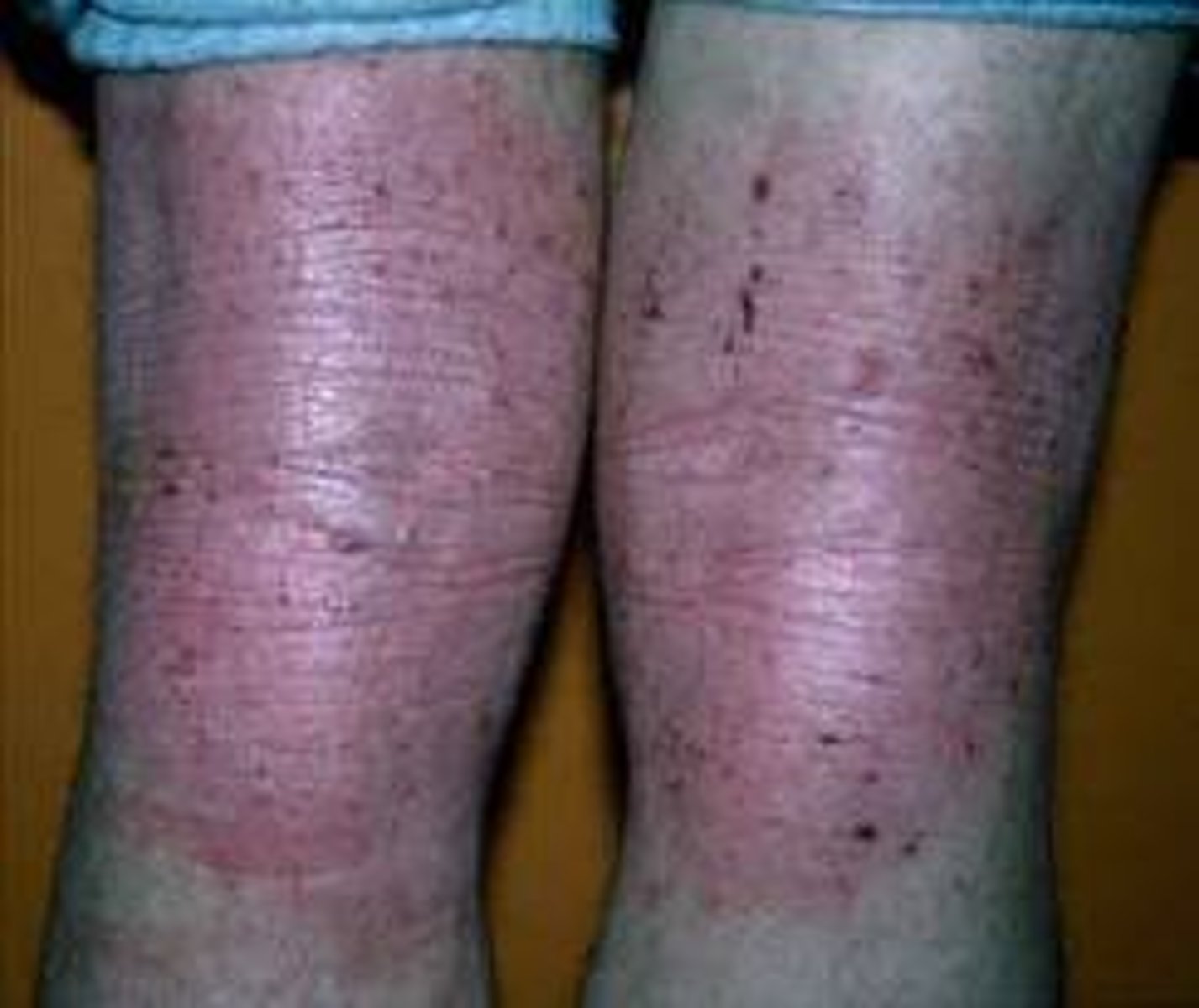
Plaques are often associated with:
pruritic disorders (chronic eczema or atopic dermatitis)
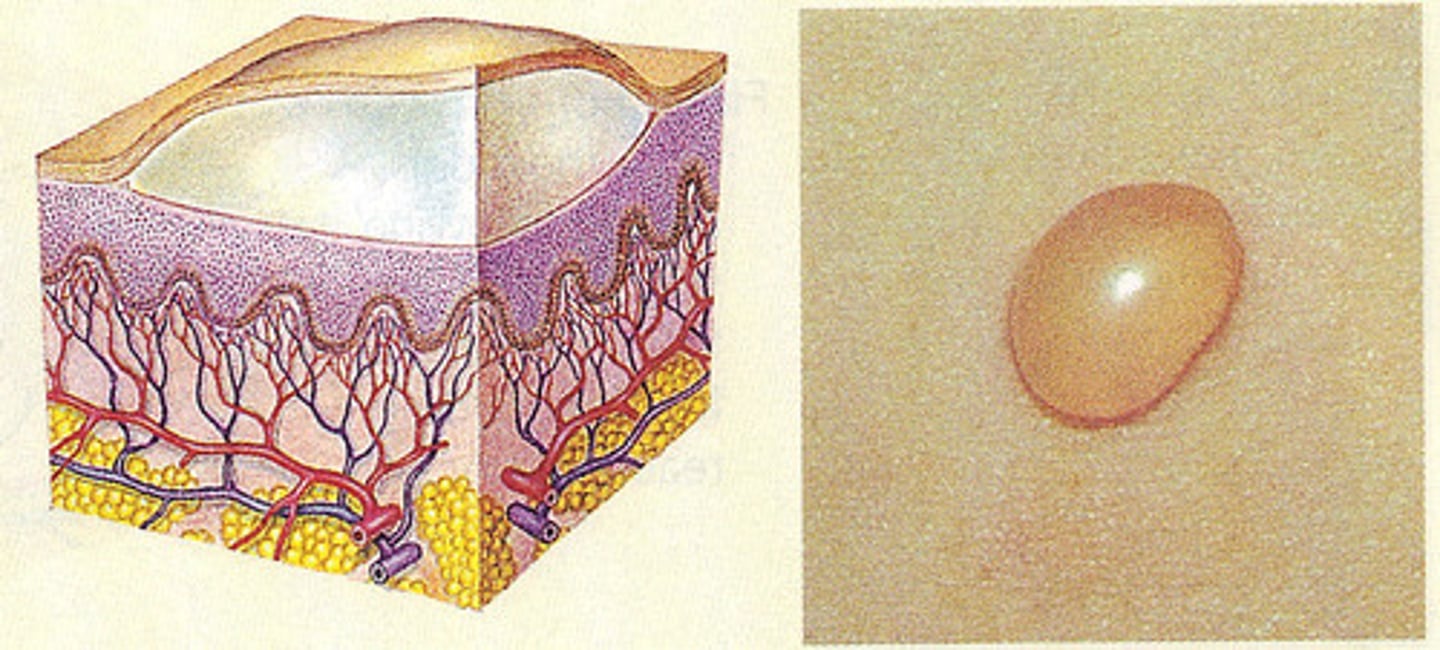
Vesicle
fluid-filled lesions
<1 cm
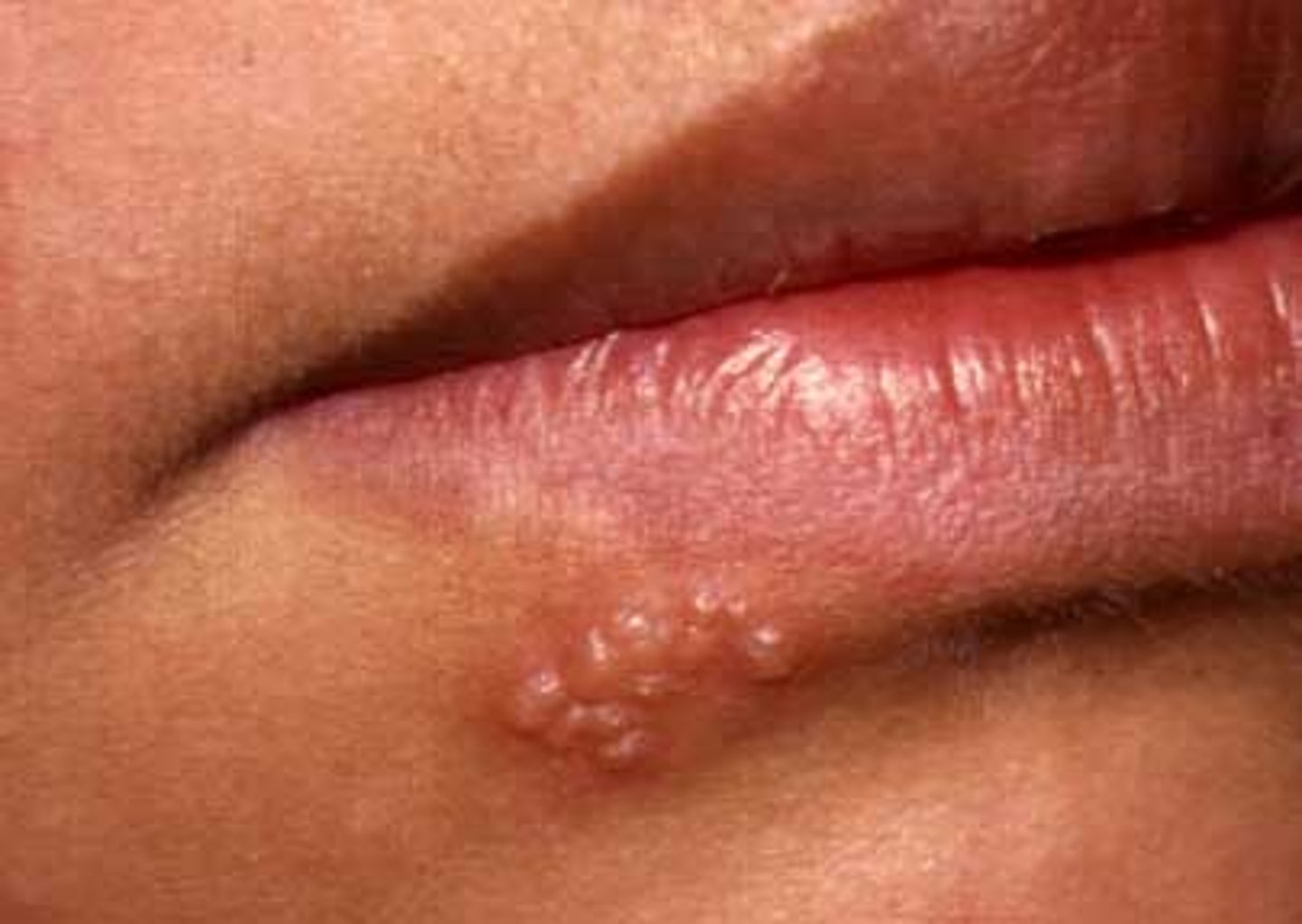
Bulla
collection of free fluid
> 1 cm
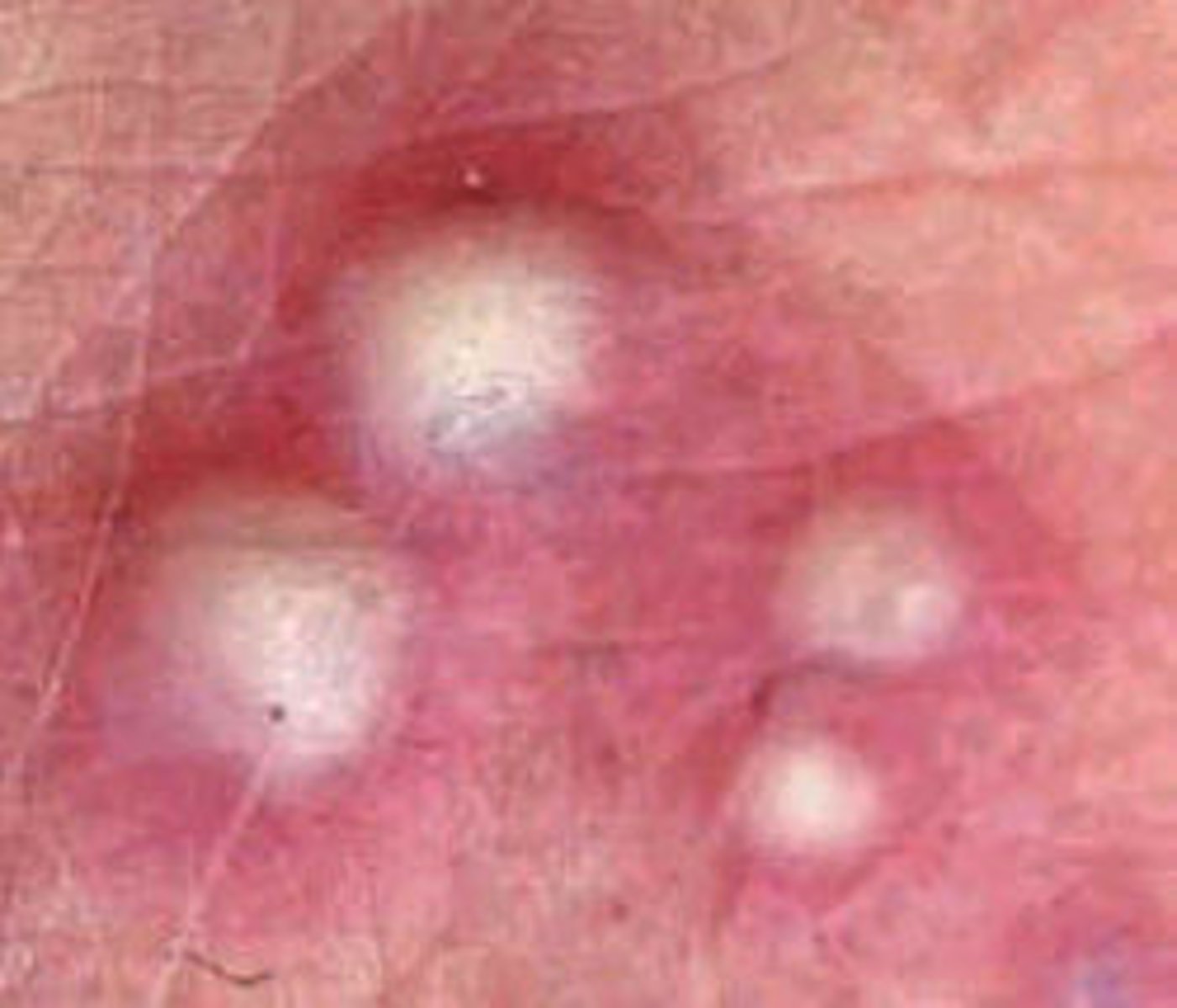
Pustule
vesicle or bulla w/ purulent fluid
superficial
Blisters
bulla or vesicle
defense mechanism (when epidermis separates from dermis, lymph and body fluids collect while the skin regrows)
Etiology of blisteral
chemical or allergic rxn
physical injury (heat, friction, frostbite)
Nodule
solid lesion
> 1cm
epidermis and lower dermis
Wheal
rounded and edematous
well demarcated
no epidermal involvement
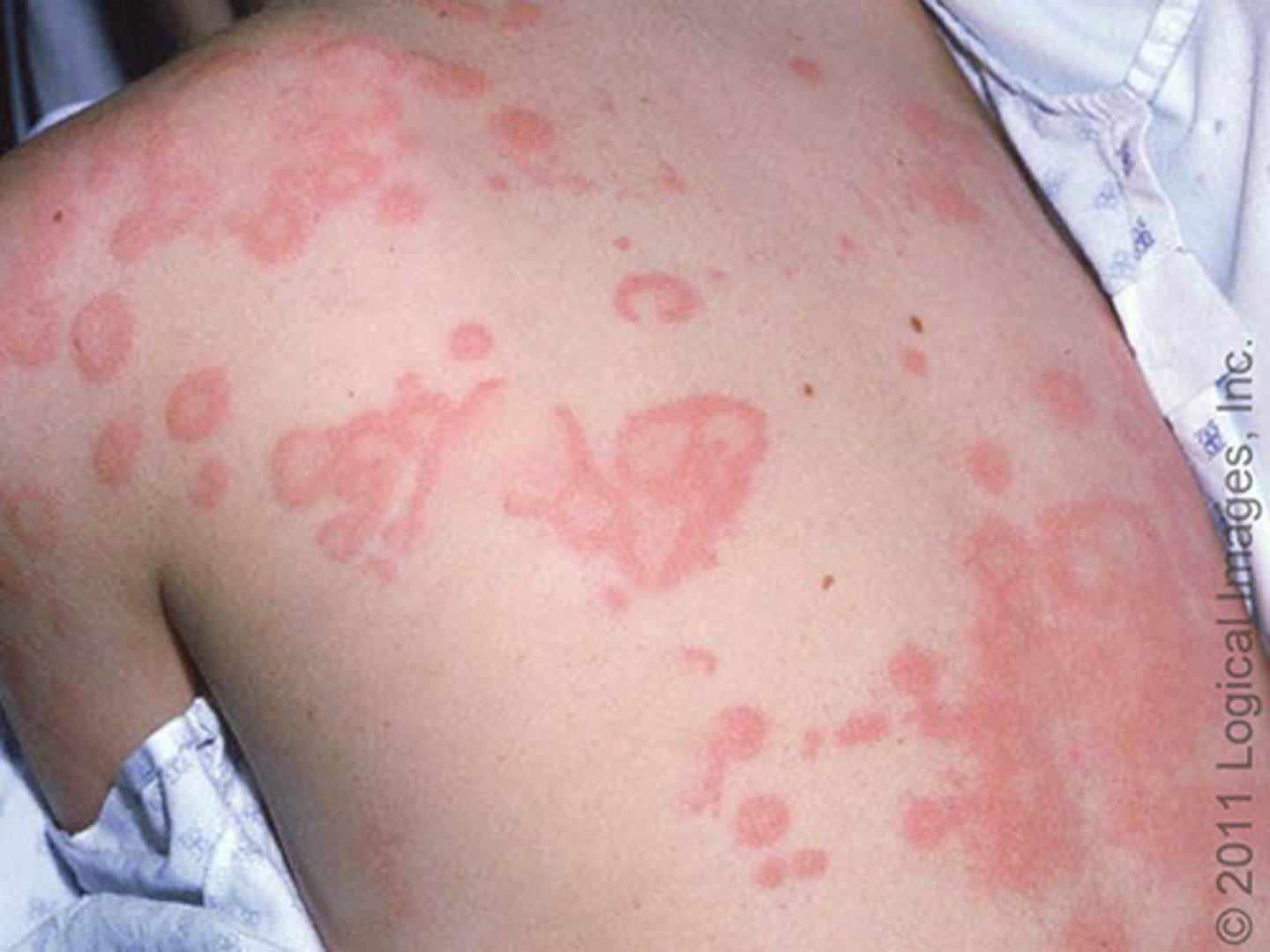
A wheal is an:
allergic response to allergens (such as drugs or insect bites)
How can you reproduce a wheal?
Darier's sign
Dermatographism
Darier's sign
gentle rubbing of lesions (followed by local itching and erythema)
Dermatographism
writing on the skin
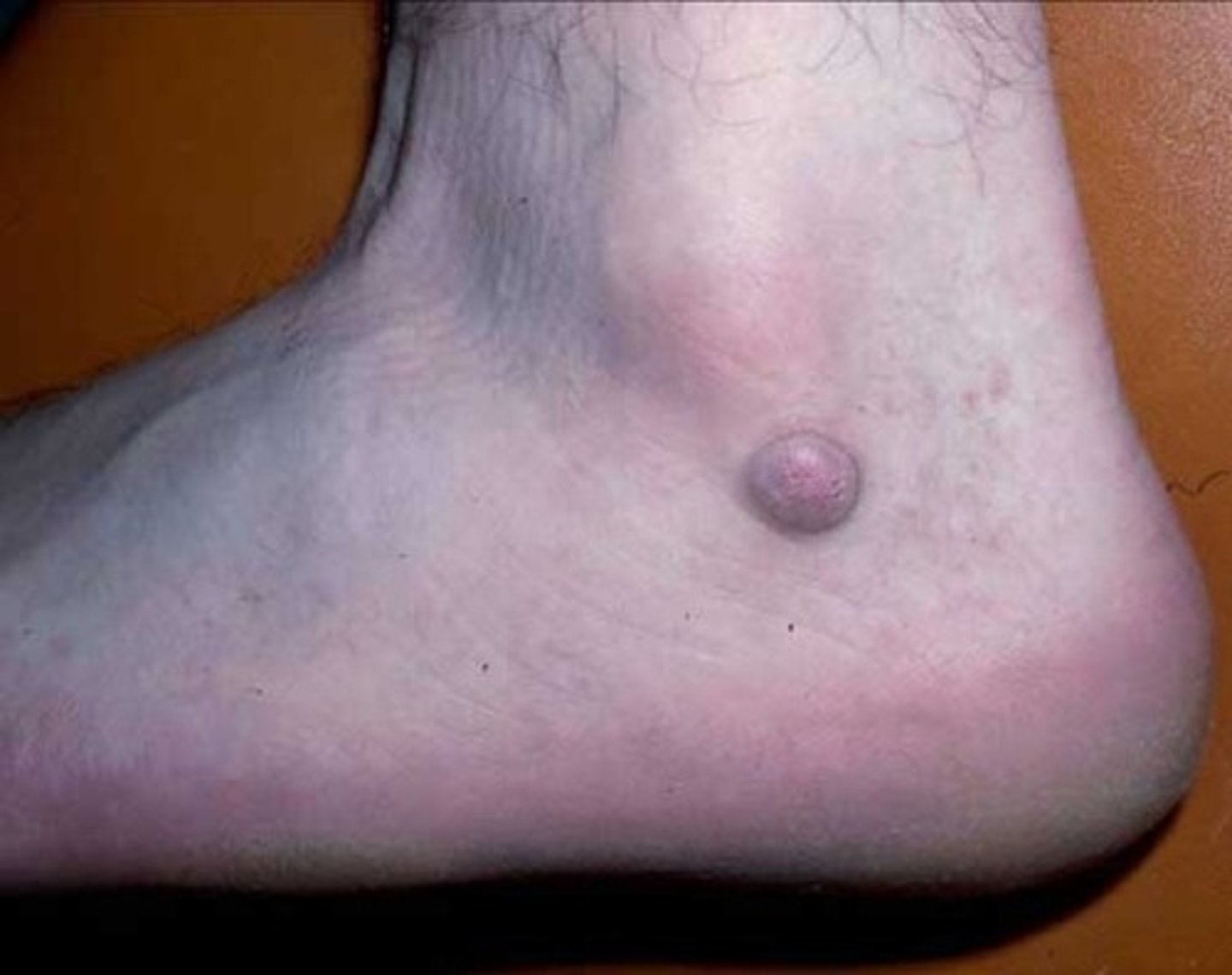
Cyst
lesion w/ fluid or semi-solid material
elevated and palpable
enclosed sac w/
membranous lining
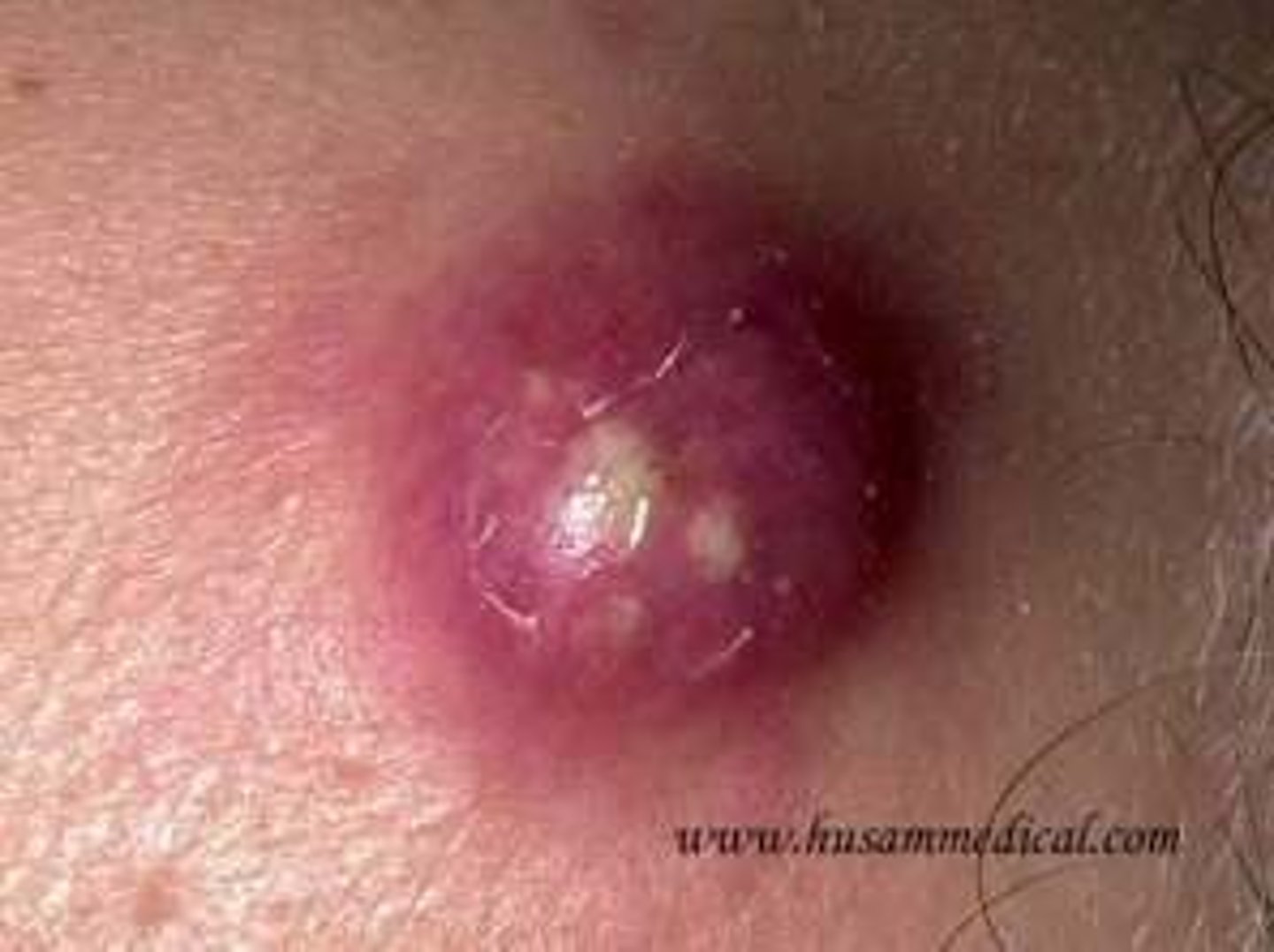
Abscess
collection of pus
Crusts
dried serum or exudates
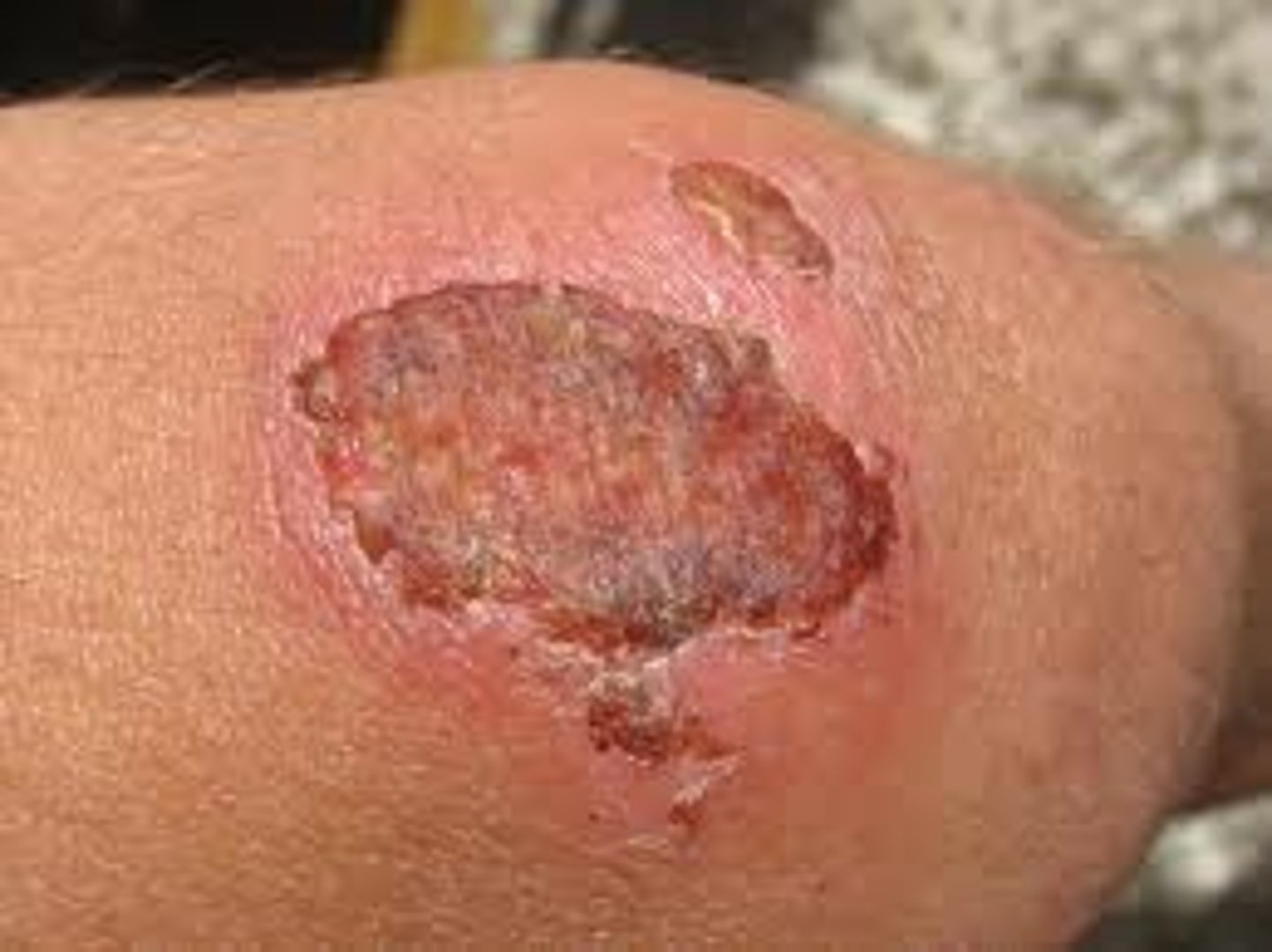
Blood appears _______ as a crust
brown
Serum appears ________ as a crust
honey colored (impetigo)
Pus appears _______ as a crust
yellow/green
When are crusts present?
after blisters rupture
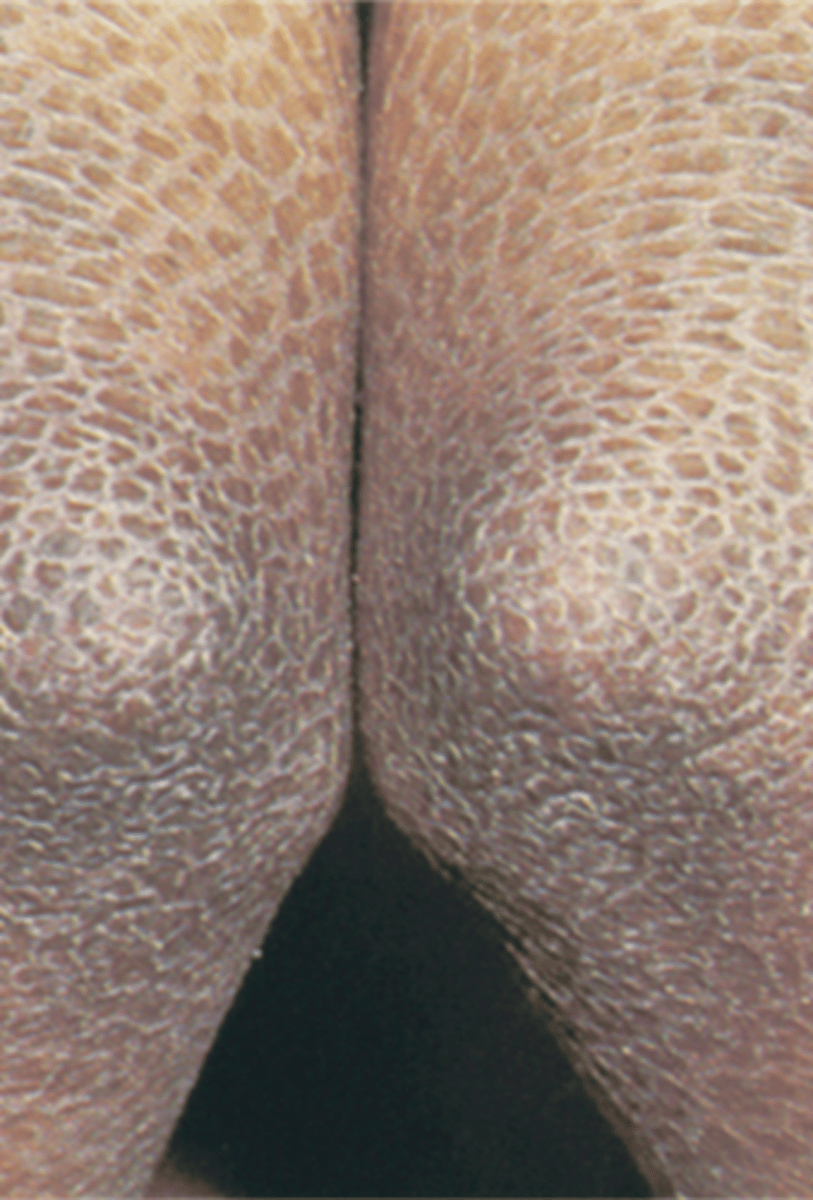
Scales (desquamation)
abnormal areas of stratum corneum (increased rate of epidermal cell proliferation)
**sheet-like, adherent or loose
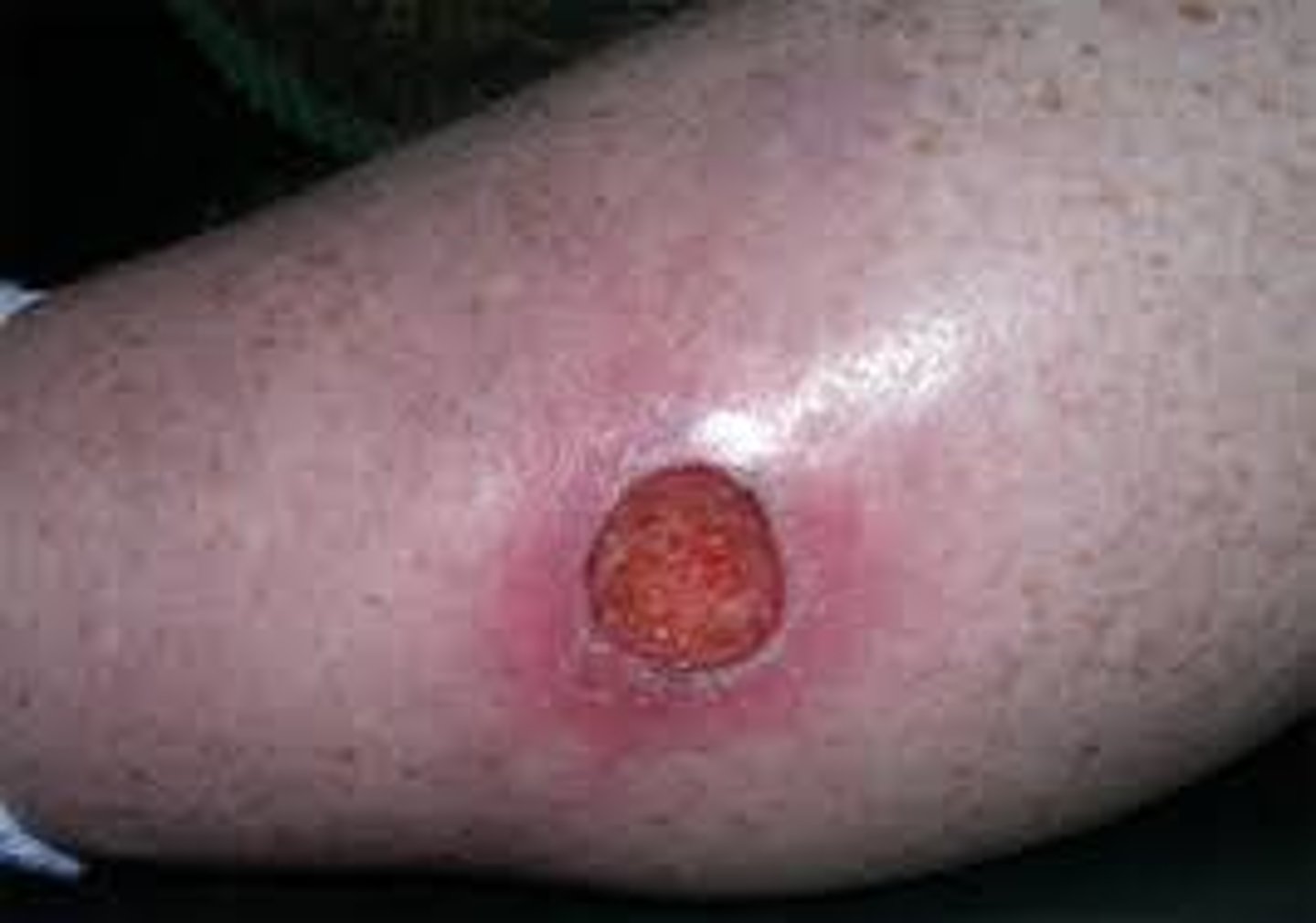
Erosion
loss of epidermis - heals without a scar
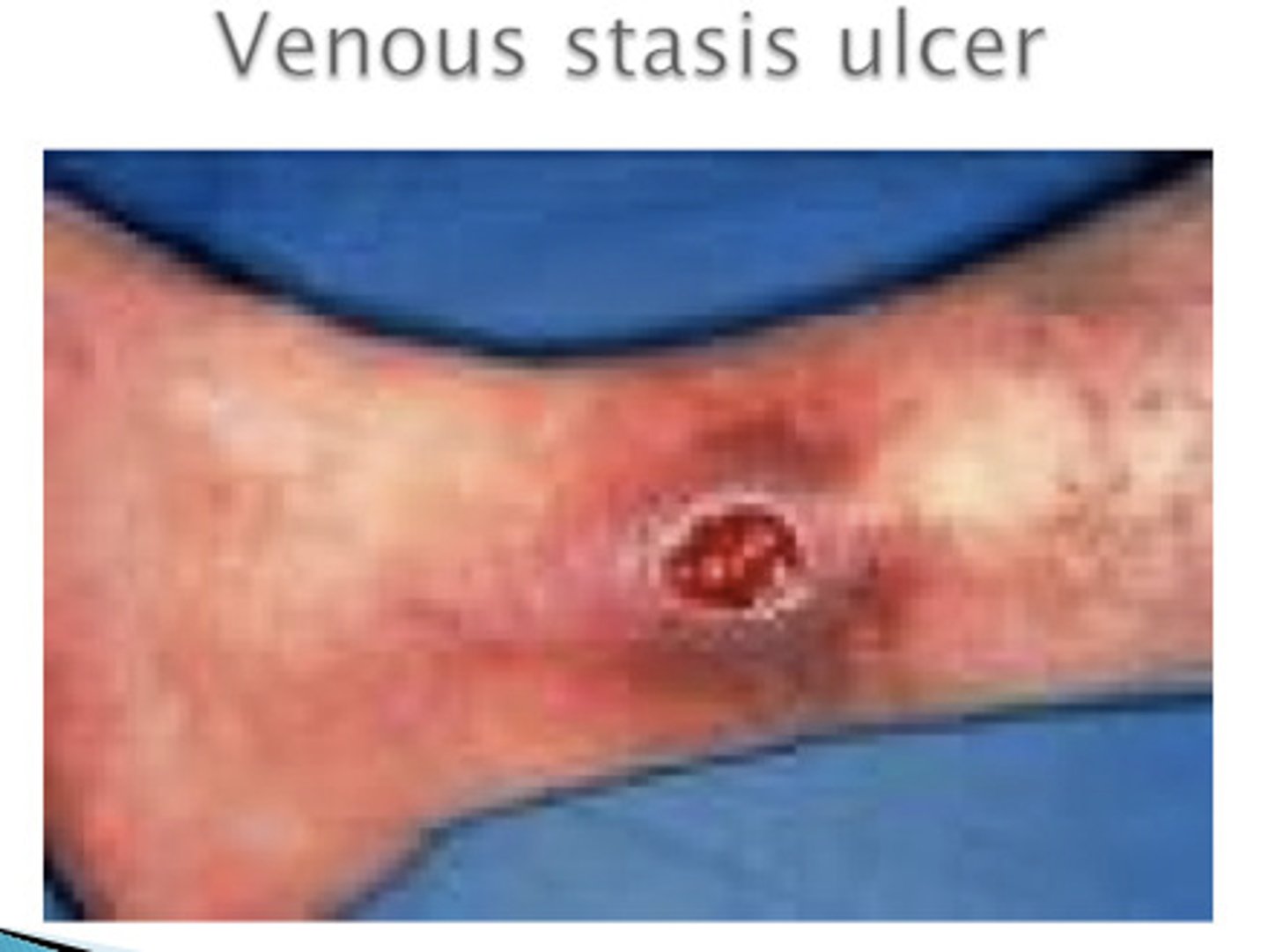
Ulcer
loss of epidermis and dermis
heals with a scar
Telangiectasias
small enlarged blood vessels near skin surface
**often a sign of alcholism
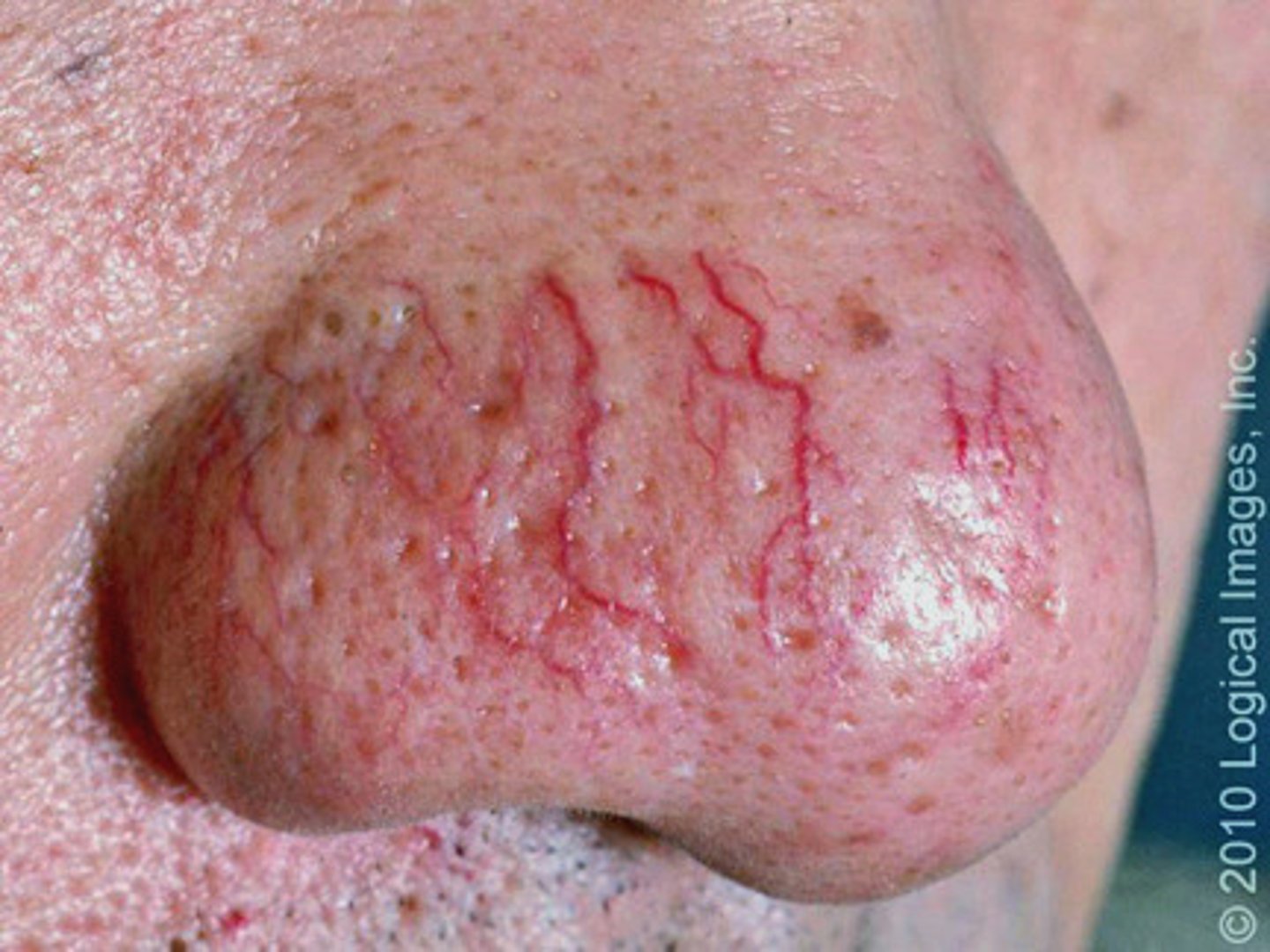
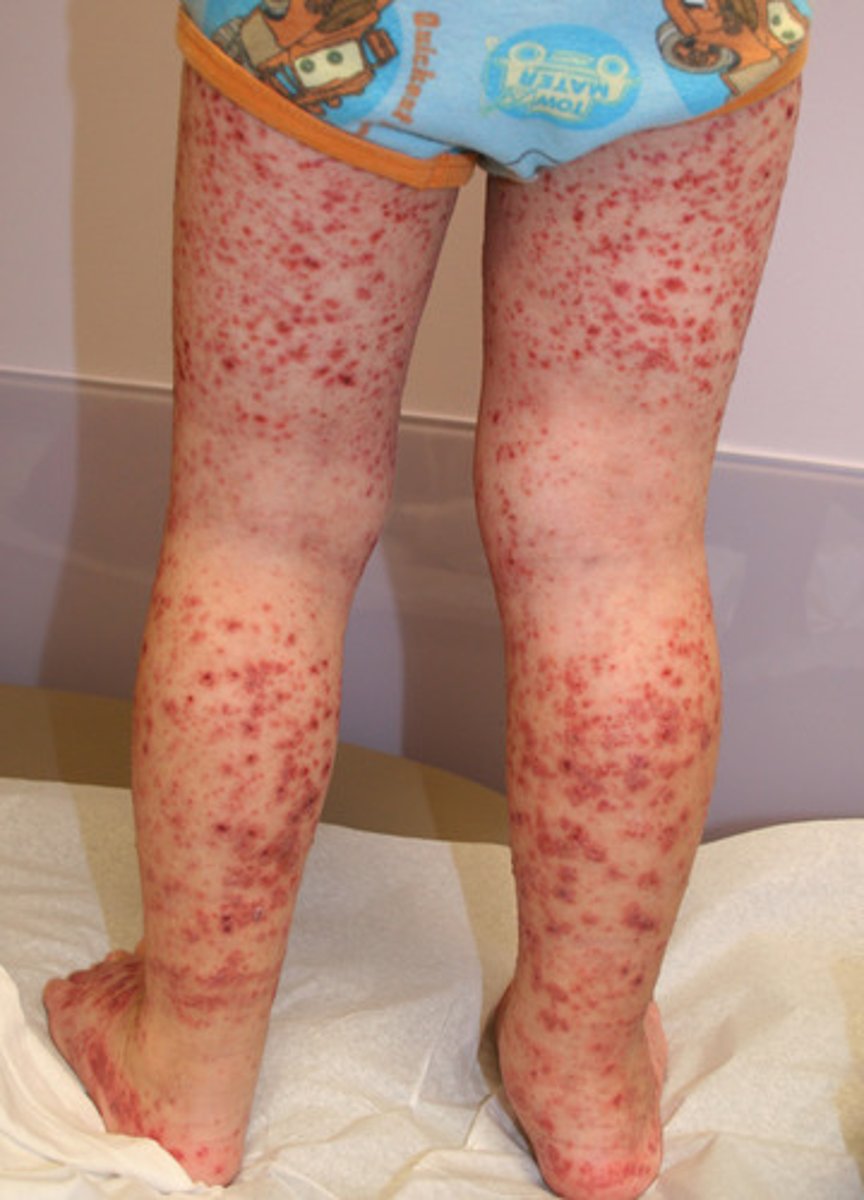
Petechiae
small red/purple spot
<3 mm
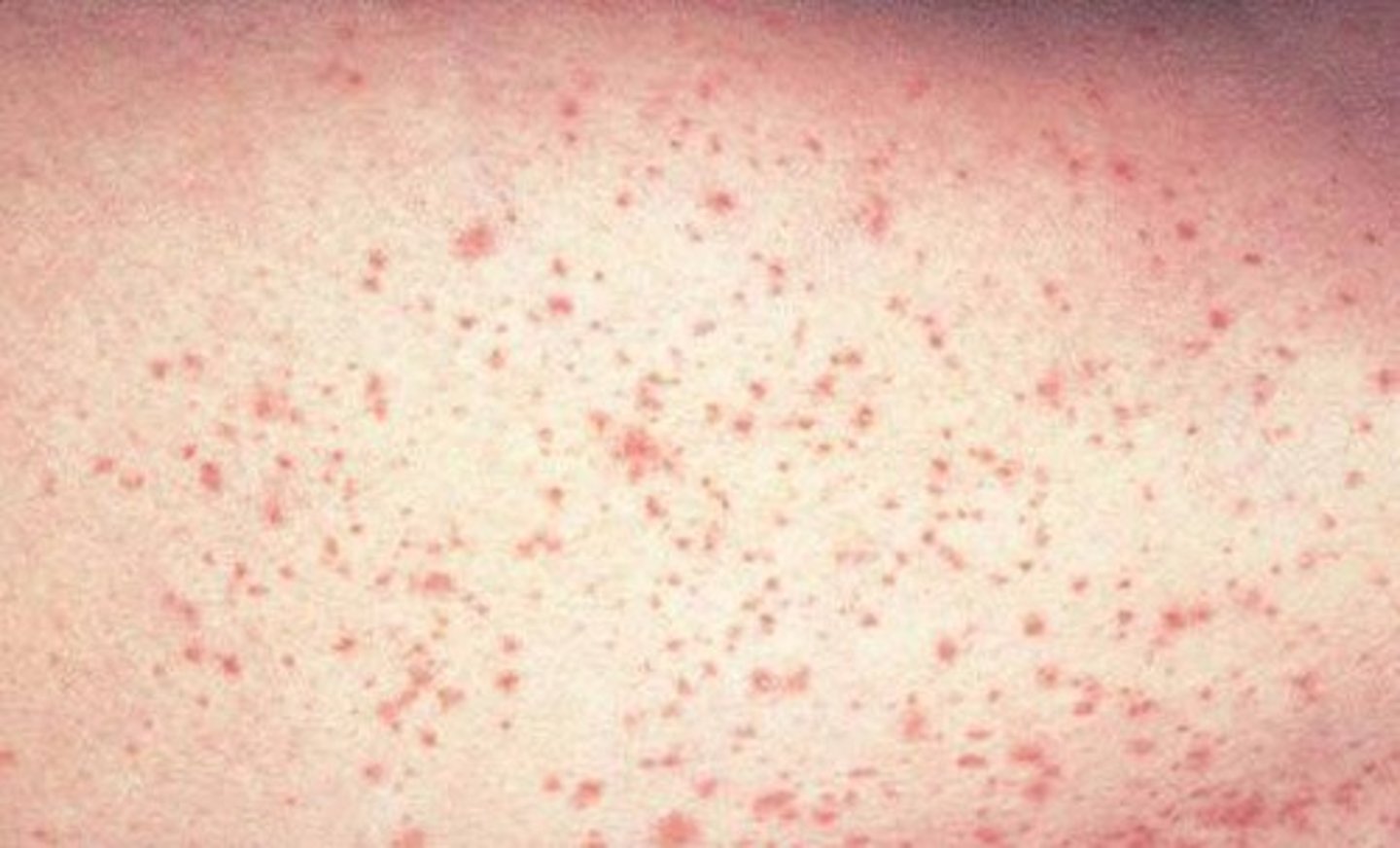
Etiology of petechiae
minor hemorrhage (capillary)
thrombocytopenia
decreases platelet function
Purpura
larger red/purple discoloration
3mm-10mm
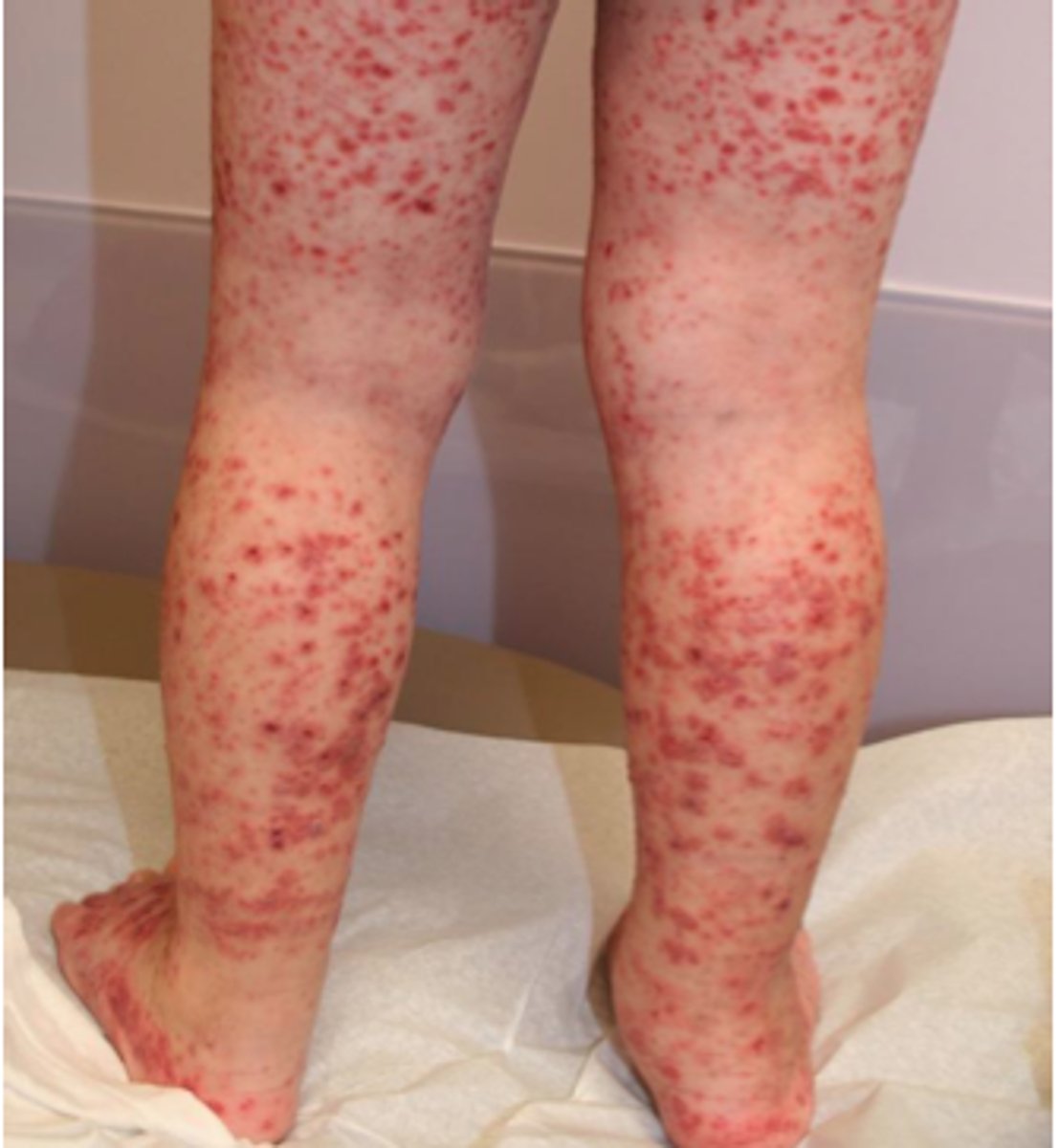
Etiology of purpura
bleeding under skin
Ecchymosis
capillary damage allows blood to extravasate into surrounding tissues
>1 cm
Etiology of Ecchymosis
usually blunt trauma
Will petechiae, purpura, and ecchymosis blanch with pressure?
no
Tumor
solid lesion with elevation and depth (epidermis and dermis - possible SC tissue)
> 2 cm
pigmentation
Common serpiginous lesion
hookworm
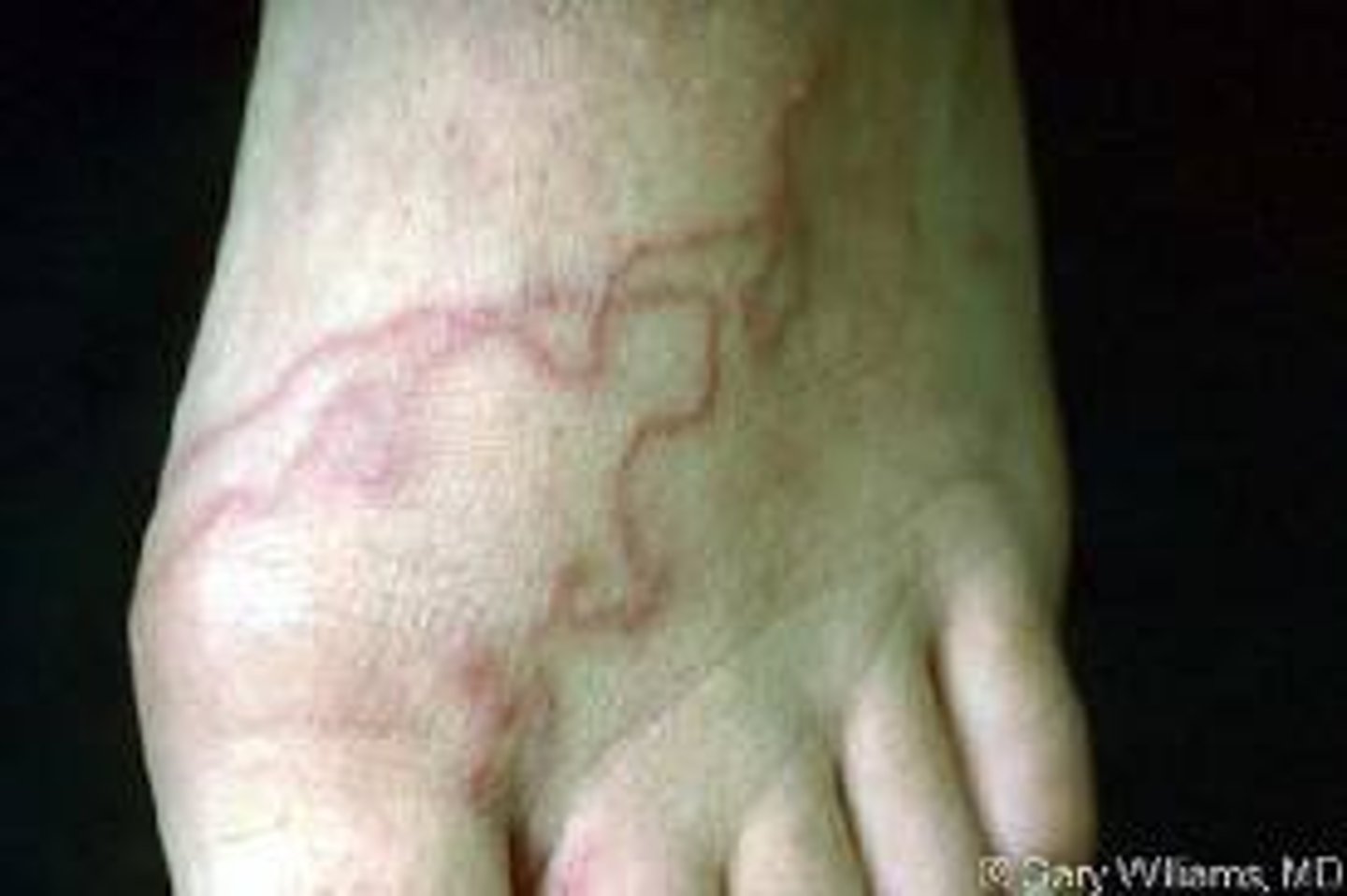
What will move deeper into the skin (past superficial layer)
nodula
bulla
pustule
fissure
Perivascular dermatitis
inflammatory infiltrate with no significant epidermal involvement
ex. hives
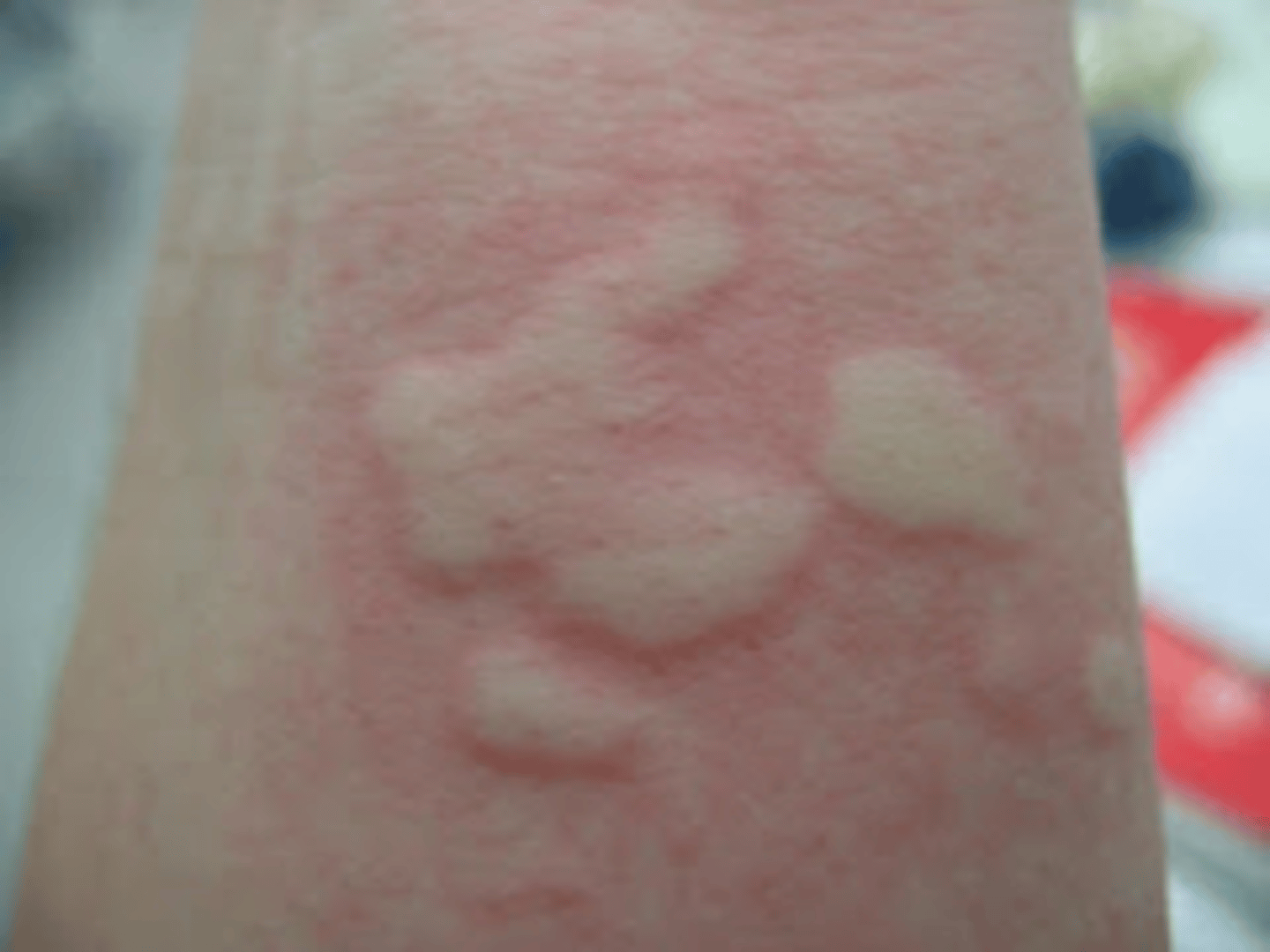
Spongiotic dermatitis
intercellular epidermal edema (spongiosis)
ex. allergic contact dermatitis
Psoriasiform dermatitis
epidermal thickening from elongated rete ridges
ex. psoriasis
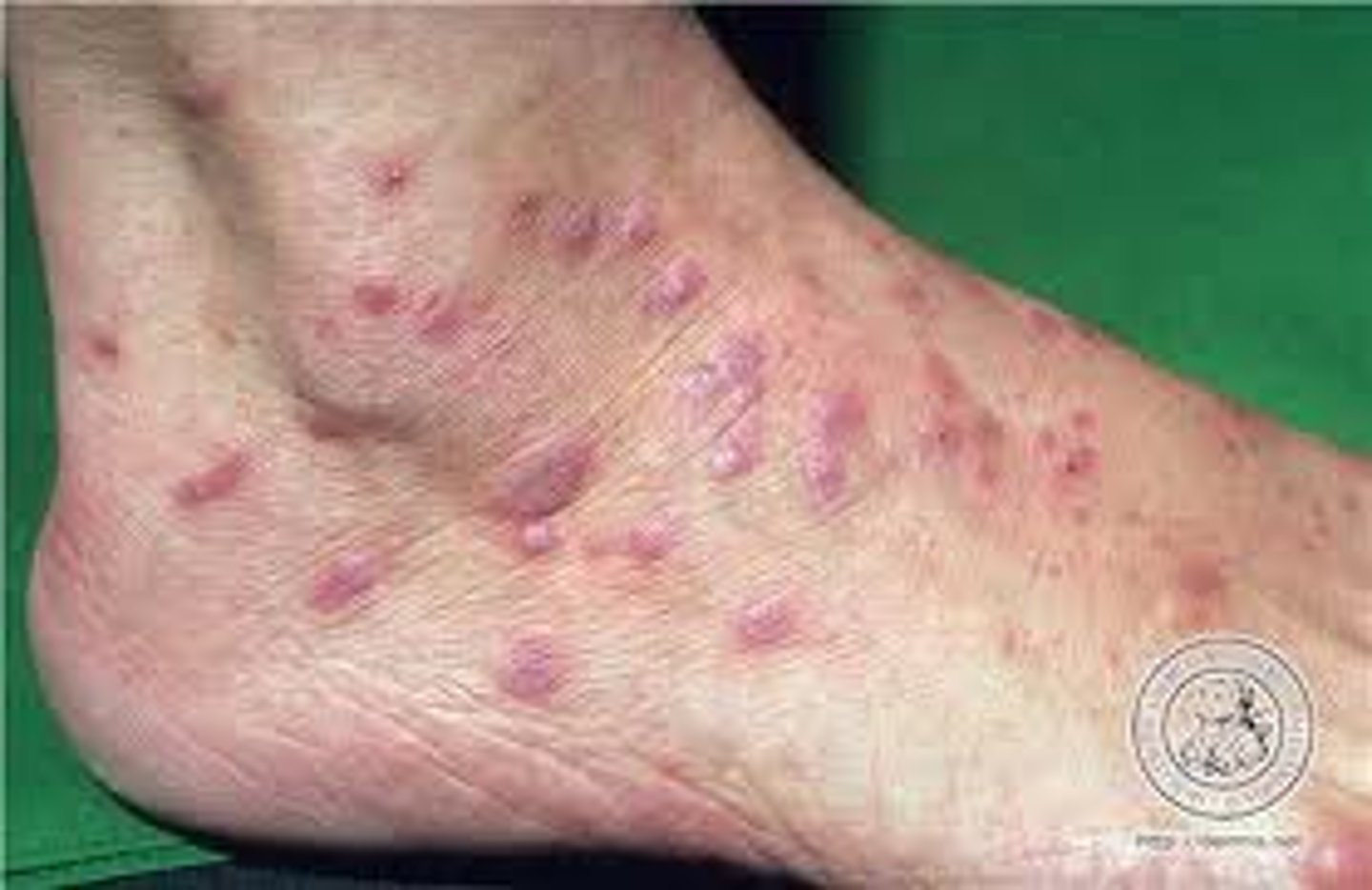
Interface dermatitis
cytotoxic rxn (dermis and epidermis)
characterized by vacuoles and lymphocyte infiltrates
ex. lichen planus
Vesiculobollous dermatitis
intradermal and subepidermal cleavage
ex. bullous pemphigoid
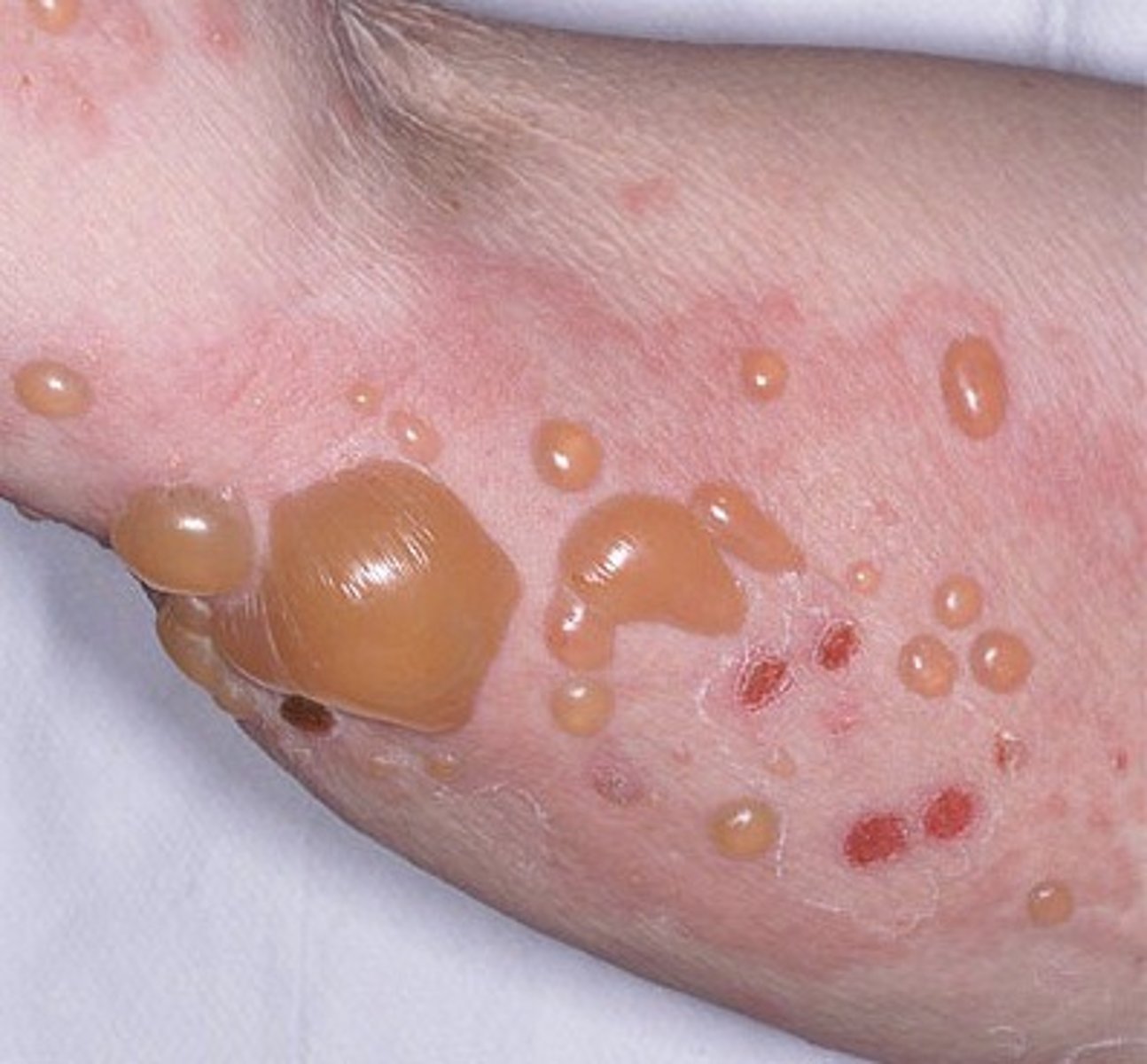
Vasculitis
damage to cutaneous vessel walls
ex. leukocytoclastic vasculitis
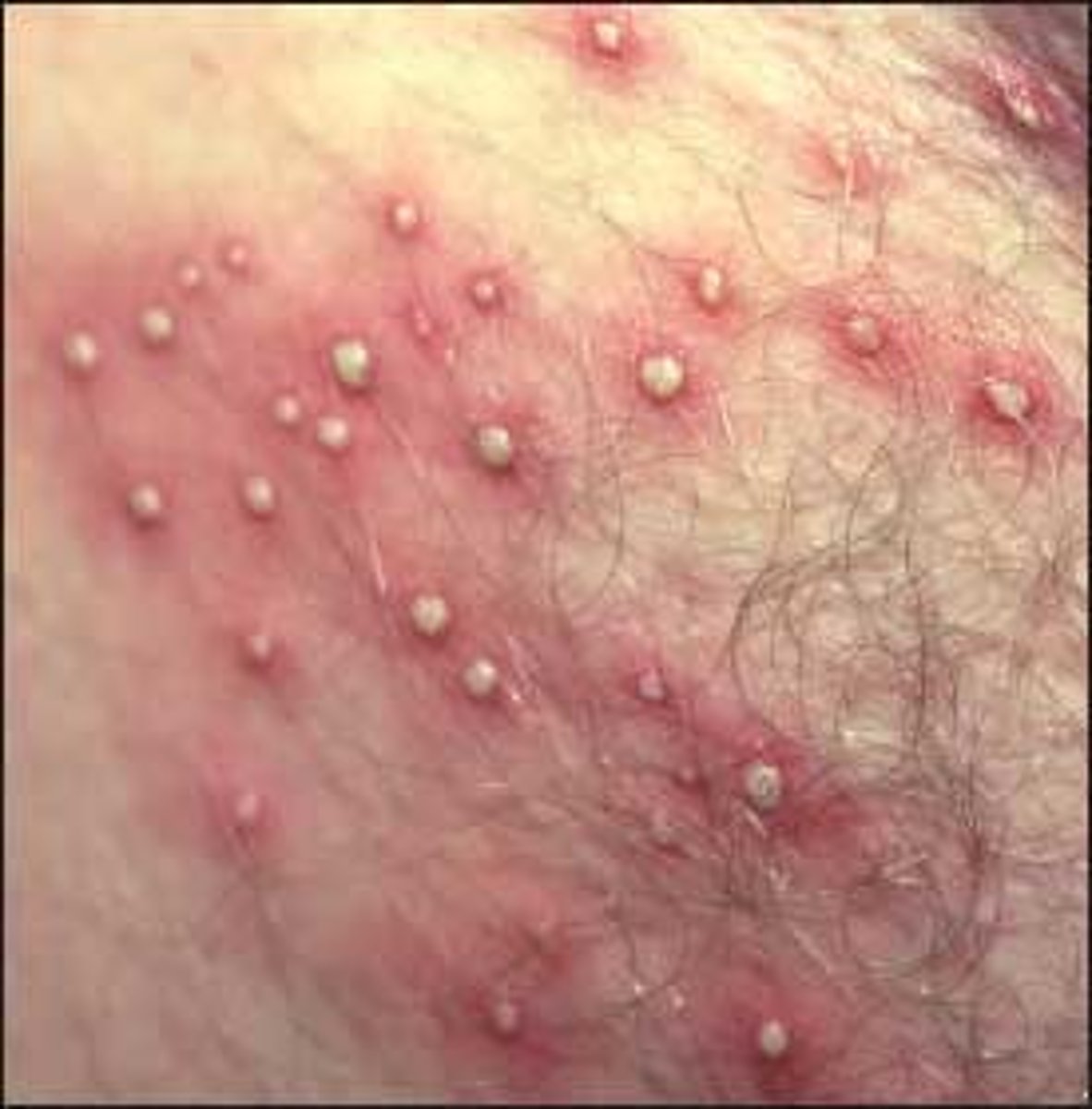
Folliculitis
rxn directed against colliculo-sebaceous units
ex. acne folliculitis
Nodular dermatitis
nodular or diffuse dermal infiltrate without significant epidermal changes
ex. cutaneous sarcoidosis
Panniculitis
involves subcutaneous fat
ex. erythema nodosum
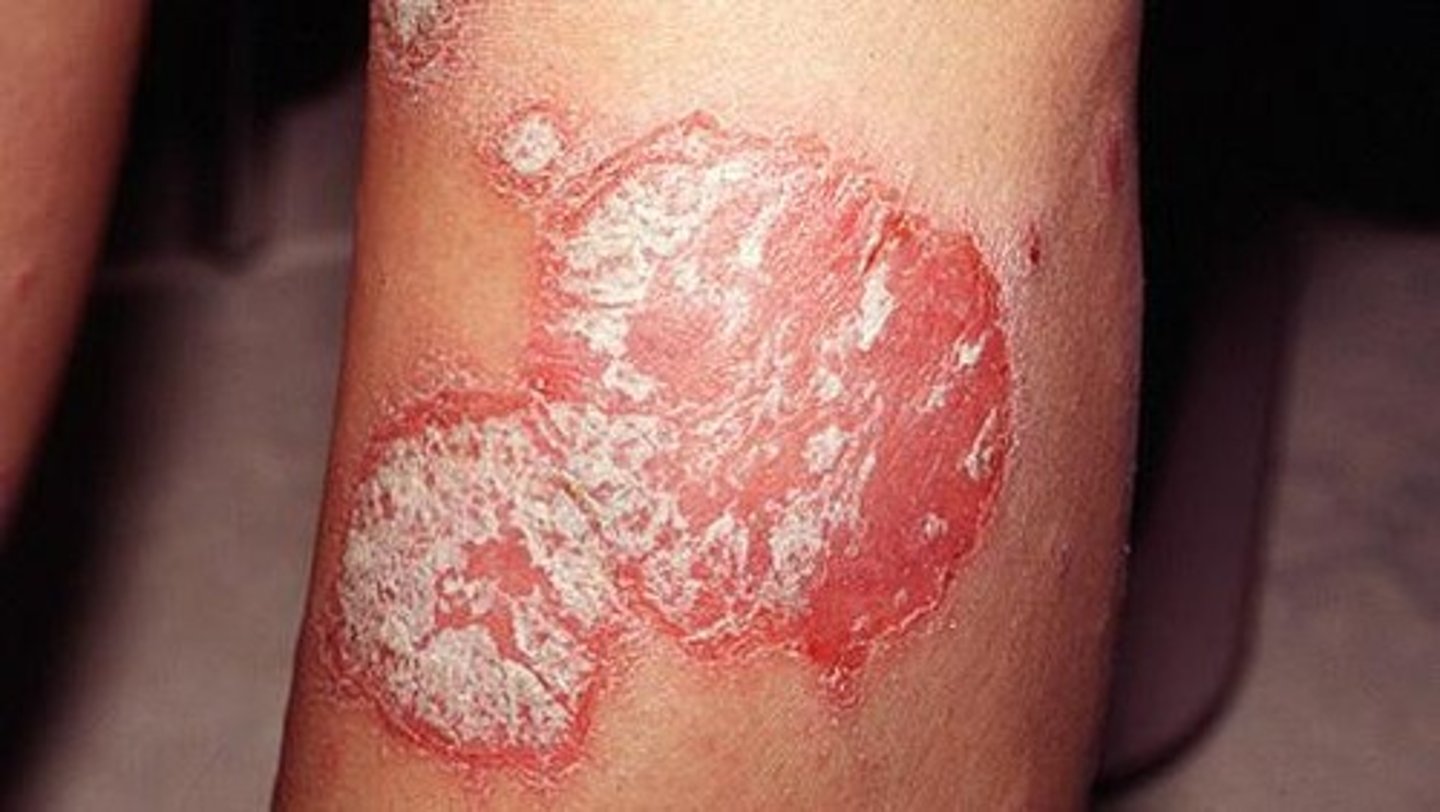
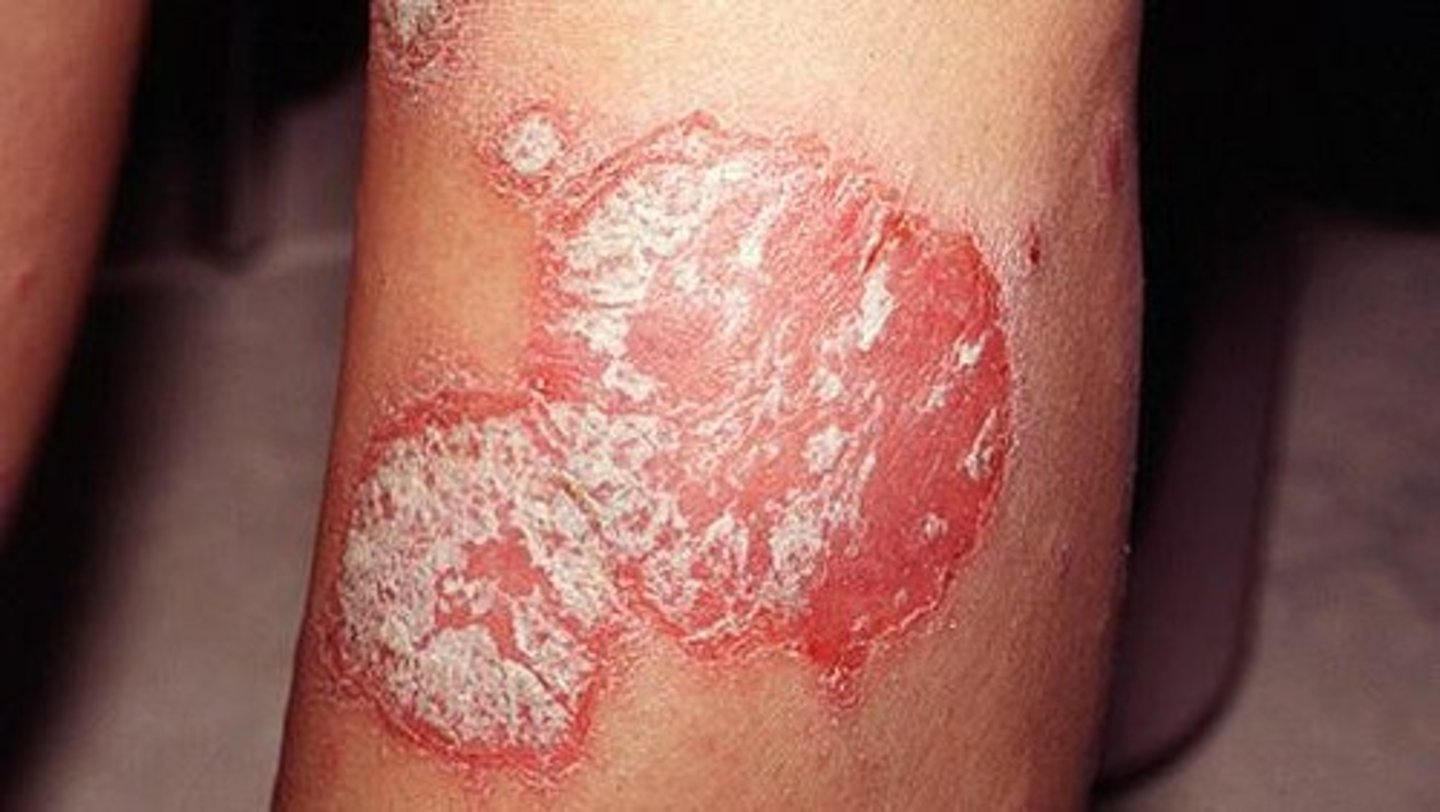
Psoriasis clinical presentation
common chronic, persistent or relapsing, scaling skin
sharply marginated and erythematous w/ silvery scales
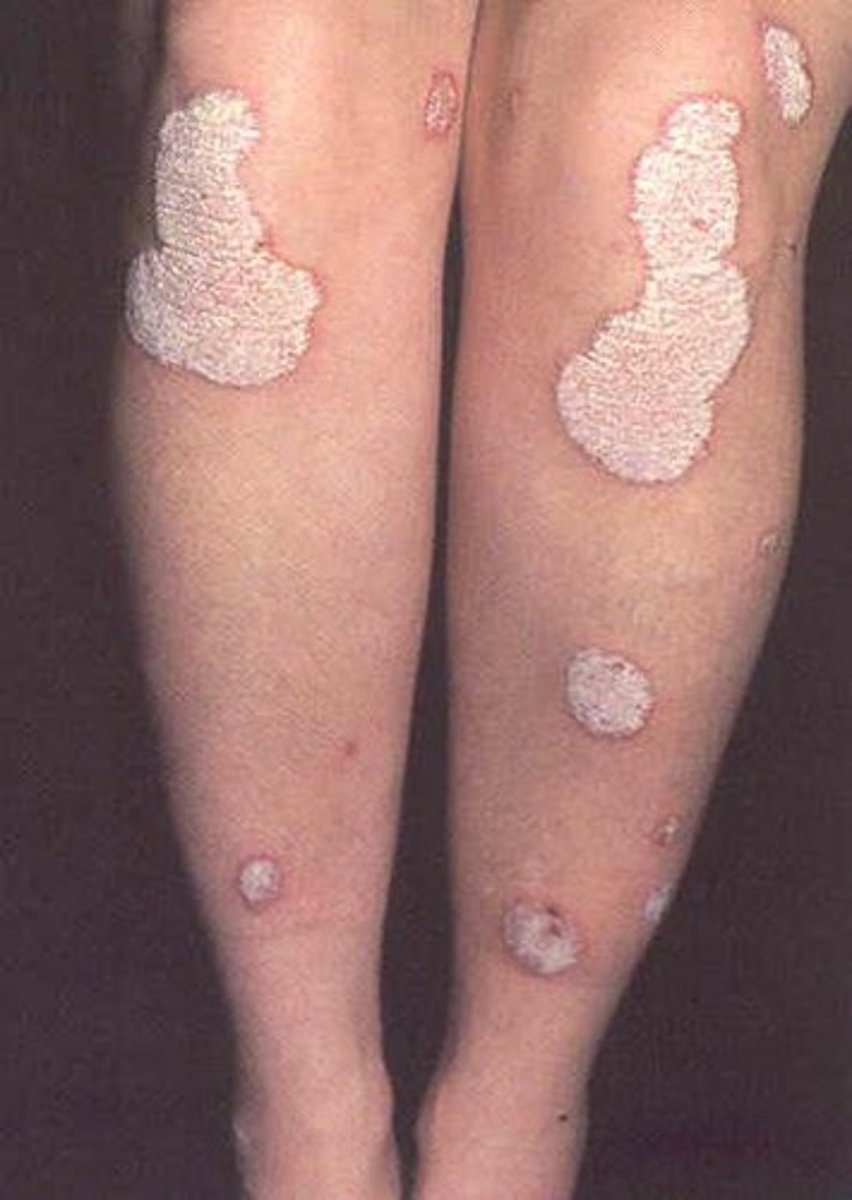
Psoriasis pattern
psoriasform dermatitis
Epidemiology of psoriasis
3rd decade - most common
genetic factors
Psoriasis is characterized by:
epidermal hyperplasia
elongation of rete ridges (as well as clubbing, fusing, and thickening)
thinning of suprapapillary plate
Parakeratotic hyperkeratosis
Migration of neutrophils from the dermal papillae into the overlying epidermis
Squirting dermal papillae (occurs in psoriasis)
Where does psoriasis occur?
scalp, extensor surfaces, flexural surfaces, nail bed
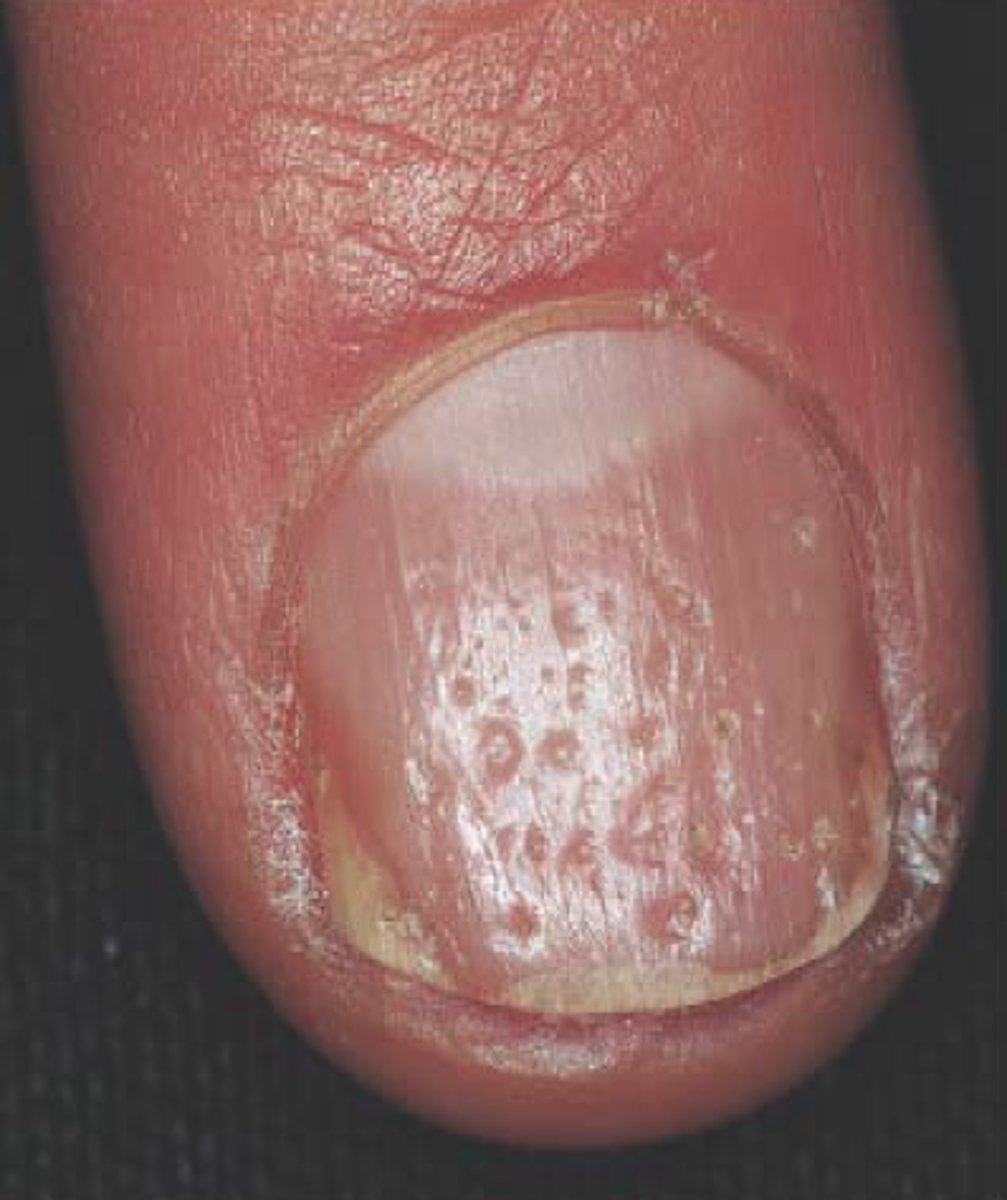
What is spared in psoriasis
mucosal surfaces
Psoriatic arthritis
extracutaneous manifestation of psoriasis - derforming, asymmetric oligoarticular arthritis
Psoriatic arthritis is classified as:
seronegative spondyloarthropathy
What is an inflammatory skin disease in which the junction between the papillary dermis and epidermis is obscured?
interface dermatitis
During interface dermatitis, lymphocytes attack the basal layer of the epidermis causing:
vascular change in basal cells or necrosis of basal keratinocytes
Acute interface dermatitis
erythema multiforme
Pathophysiology of interface dermatitis
T-cell mediated damage to keratinocytes and remodeling of the basement membrane zone
**injury produces vacuoles alone dermoepidermal junction
Lichen planus epidermiology
adulthood
more common in women
**can be caused by drugs, but etiology is mostly unknown
Pathogenesis of lichen planus
dense infiltrate of T lymphocytes in the papillary dermis and superficial dermis; then vacuoles appear in the lower epidermis
**damages keratinocytes and melanocytes
Mature lichen planus lesions are composed of:
CD8 and cytotoxic T cells
Physical exam - Lichen planus
pruritic eruption of small papules (bilateral and symmetrical) w/ angular borders
violaceous in color
solitary lesions coalesce to form larger plaques
Wickham's striae
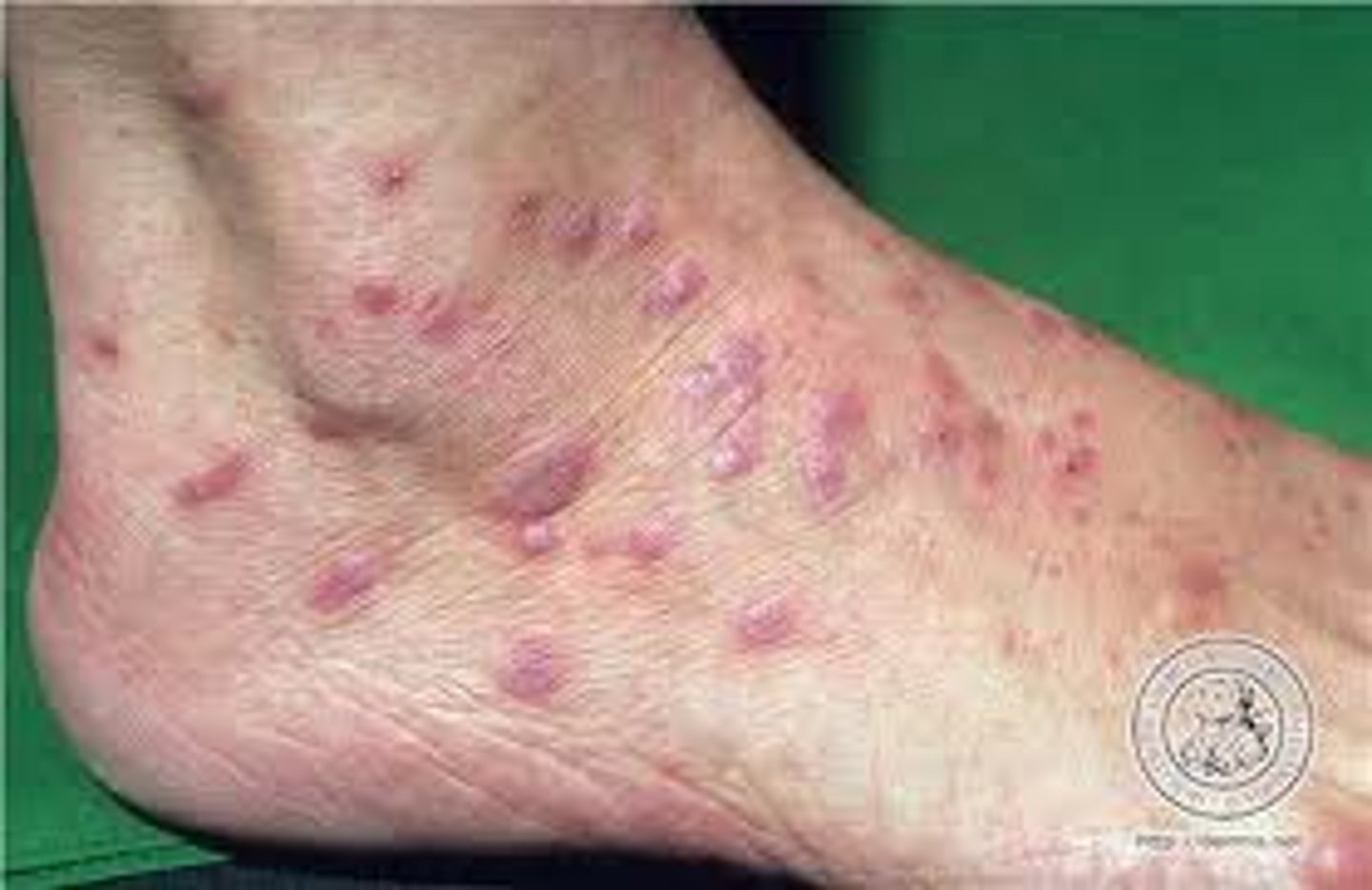
Wickham's striae
minute white streaks on lesion surfaces
Common sites of lichen planus
flexor surfaces
genital skin
mucous membranes
Erythema multiforme
uncommon
peaks in 2nd to 4th decade
What is Erythema multiforme
cell mediated immune reaction that results in necrosis of epidermal keratinocytes
Etiology of Erythema multiforme
HSV infection
Rxn to meds
Idiopathic
Physical exam of Erythema multiforme
brief and self-limited
in crops of acral surfaces (distal portions of limbs)
prototypical lesion (monomorphous) - target-like
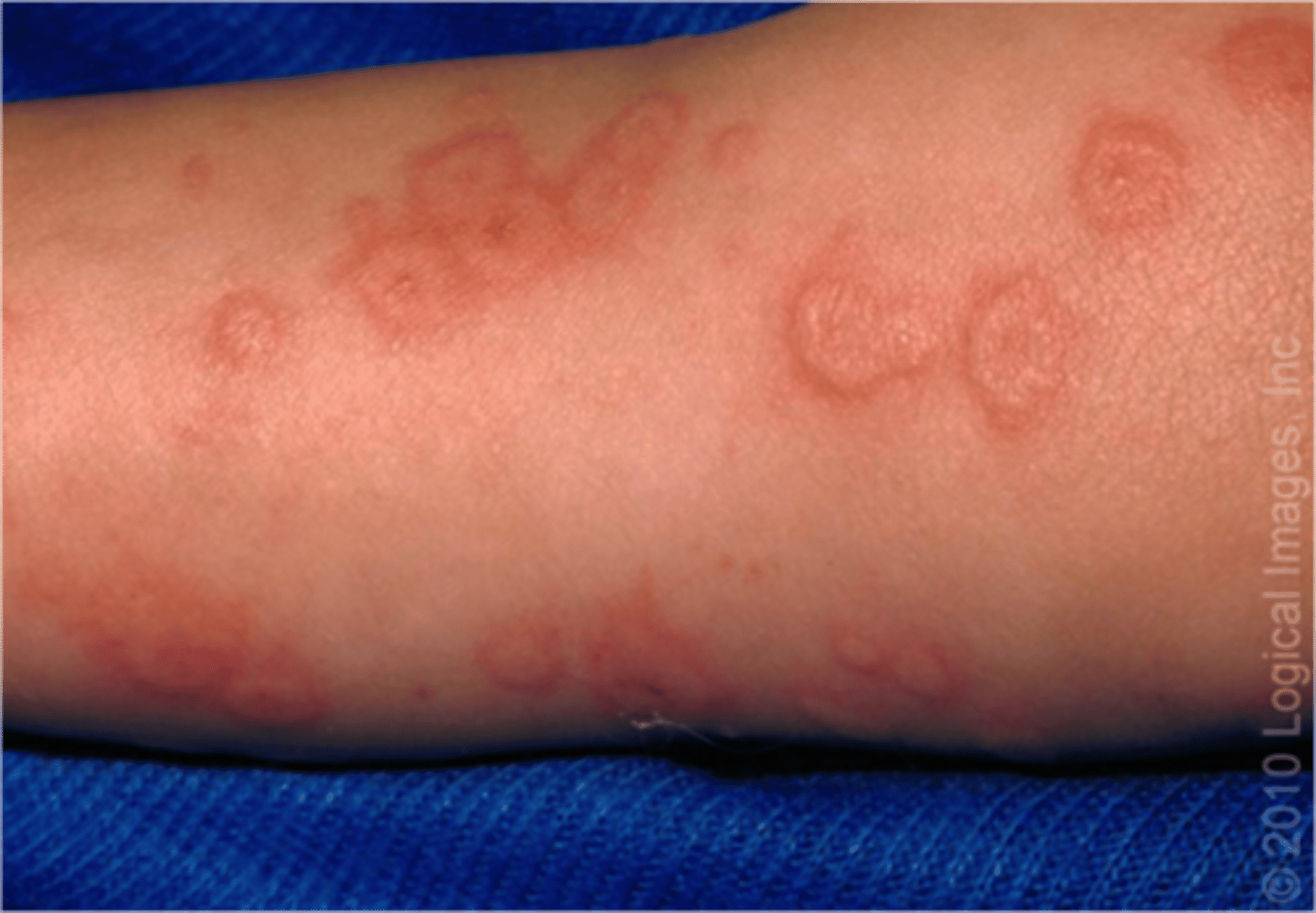
Pathogenesis of Erythema multiforme
keratinocyte necrosis and CD4/CD8 infiltrate
Mild cases of keratinocyte necrosis have been triggered by:
HSV
EM minor
scattered lesions w/ limited mucosal involvement
EM major
prominent involvement of 2-3 mucosal sites (oral, anogenital, conjunctival)
Examples of EM major
Steven-Johnson Syndrome
Toxic epidermal necrolysis (caused by a drug rxn)
Bullous Pemphigoid (vesiculobolous dermatitis pattern)
blistering disease in which tense fluid-filled spaces develop within erythematous, inflamed skin
**detachment of the epidermis from the dermis
Pemphigus vs. Pemphigoid
intraepidermal rather than subepidermal vesiculation
**pemphigus is deeper
Bullous Pemphigoid - Epidemiology
elderly
Bullous Pemphigoid - etiology
Immunoglobulins and complement are deposited along the epidermal-dermal junction in bullous pemphigoid --> form of autoimmune disease
Subepidermal cleft contains:
eosinophils and lymphocytes
Clinical manifestations of Bullous Pemphigoid
present w/ large tense blisters (extremities and lower trunk)
**often associated w/ pruritis