Concept 1.1: The study of life reveals unifying themes
1/29
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
30 Terms

Biology
The scientific study of life, recognizing what living things do

Themes of biology
Organization (different levels of the biosphere)
Information (DNA)
Energy and Matter (food, light, heat)
Interactions (predator, prey)
Evolution (adaptation, natural selection)
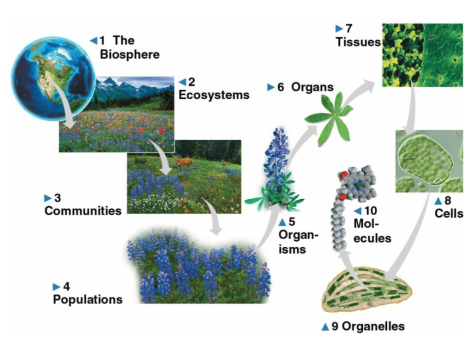
Organization
A theme of biology studying life at different levels, creating subdivisions to reduce complex systems to smaller components
Emergent properties
Properties that become evident as the complexity of a system increases, such as in a bicycle’s or forest’s parts
Systems biology
A study of biology complementing reductionism with analyses of biological parts at all levels

Structure and function
Biological structures give clues about its function while knowing the function of something provides insight into its structure
Finches have varying beak sizes due to dietary variety
Cell
The smallest unit of organization that performs all activities required for life; these are enclosed by membranes regulating particle passage
Cell theory
States that all living organisms are made from cells
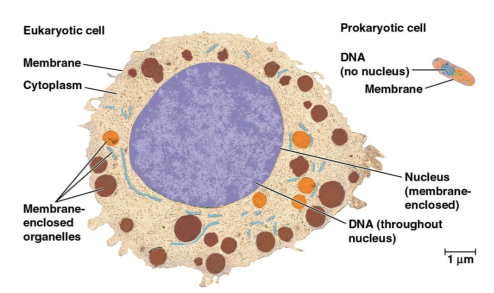
Eukaryotic cells
Cells that form most forms of life with membrane-enclosed organelles and a nucleus
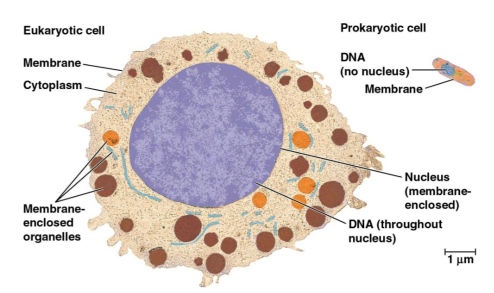
Prokaryotic cells
Cells that form bacteria and archaea that are smaller without a nucleus or membrane-enclosed organelles
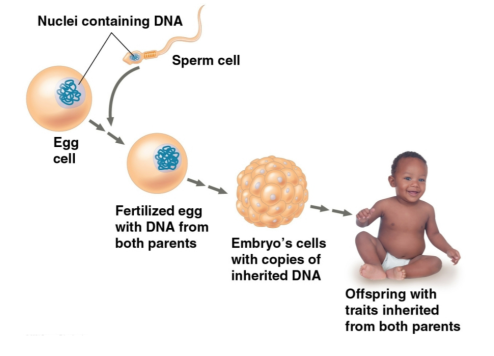
Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA)
Genetic material that forms chromosomes and is passed on in cell reproduction
Chromosome
One long DNA molecule with hundreds or thousands of genes
Genes
Units of inheritance that encode information for molecular construction and the development of an organism
Double helix
The molecular structure of DNA that enables it to store information within long chains of molecules
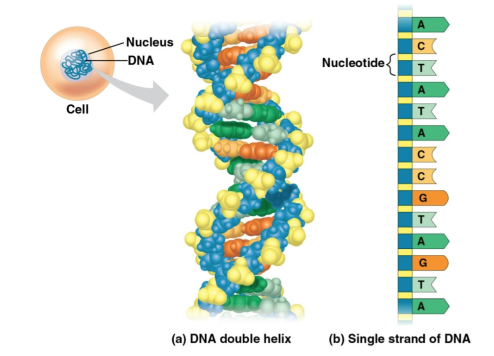
Nucleotides
The chemical building blocks that create double helix structures and store information in DNA, these are shortened to A, G, C, and T
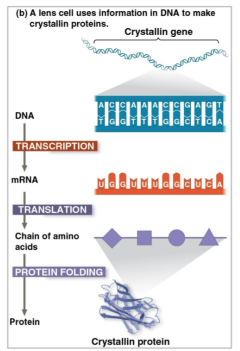
Gene expression
The process of converting information from gene to cellular product as DNA is transcribed into RNA which is then translated into a protein
Genome
An organism’s entire “library” of genetic instructions
Genomics
The study of whole sets of genes in one or more species
Proteomics
The study of whole sets of proteins and their properties
Proteome
The entire set of proteins expressed by a given cell, tissue, or organ
Bioinformatics
The use of computational tools to process a large volume of data very rapidly in genomics
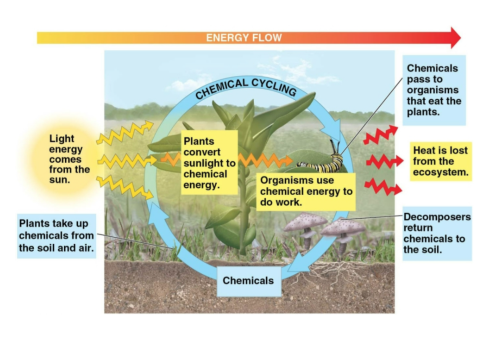
Producers
Photosynthetic organisms and plants that create energy to be passed along to consumers; made possible by the input of energy from the sun
Consumers
Organisms that feed on other organisms or their remains
Heat
The byproduct of work as created by organisms, creating an ecosystem where energy enters as light and exits as heat
Interactions
Integration between the different components of a system; is required for smooth functioning from living organisms to individual cells
Feedback regulation
Process where the product of that process regulates the process
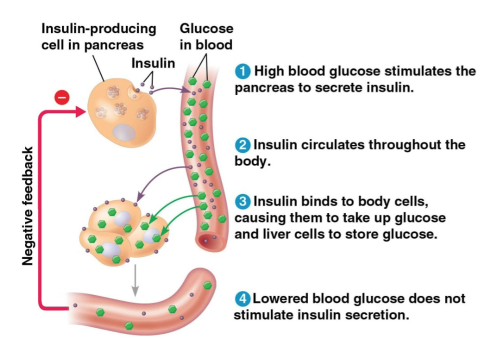
Negative feedback
A form of feedback regulation in living organisms where a response reduces the stimulus
Positive feedback
A form of feedback regulation in living organisms where an end product speeds up its own production
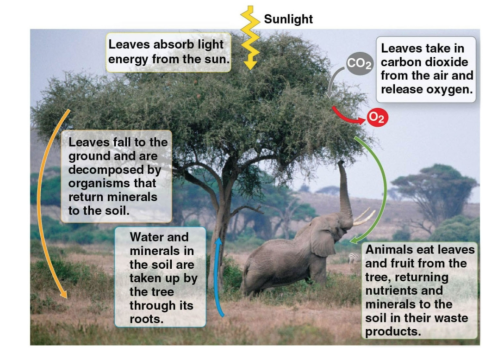
Ecosystem
A system of organisms interacting with each other or environmental physical factors either beneficially or harmfully
Climate change
The result of negative human interaction where carbon dioxide is released into the atmosphere as a result of burning fossil fuels, thus shifting weather patterns to more extreme events and creating decrepit habitats for numerous species