Biological molecules
1/438
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
439 Terms
Name the 9 properties of water
-High latent heat of vapourisation
-High specific heat capacity
-surface tension
-ice is less dense than water
-metabolic
-solvent
-cohesion
-liquid at room temperature
Is amylopectin a
Polymer
Monomer
EQ
Polymer
Is glucose a
Monomer
Polymer
EQ
Monomer
Is sucrose a
Polymer
Monomer
EQ
Neither it is a polysaccharide
Describe the bond between 2 glucose monomers in maltose
EQ
Alpha 1-4 glycosidic bond
What is the molecule formula of lactose
EQ
C 12 H22 O11
Right one
Outline how the properties of glucose relate to its function
EQ
Soluble
Source of energy
Outline how the properties of starch and glycogen relate to their functions
EQ
Energy storage
Insoluble
compact
Explain how the structure of glucose allows it to move from the plant to the bacterium
EQ
Small so can cross membranes
OH groups allow bonding with water molecules.
A common symptom of lactose intolerance is the creation of extra fluids in the large intestine
Suggest why this occurs
EQ
Undigested lactose lowers H2O potential
Water enters by osmosis
True or false:
Lipids that contain fatty acids with carbon carbon double bonds are liquid at room temperature
EQ
True
Name 2 groups involved in an amino acid
EQ
Carboxyl
Amino
What bonds are present in the tertiary structure
EQ
Disulfide Bonds
Name the enzyme in an erythrocyte that allows haemoglobinic acid to be formed
EQ
Carbonic hydrase
Name and describe the reaction that produces amino acids from polypeptides
EQ
Hydrolysis
Peptide bonds broken
State 2 properties of collagen
EQ
Fibrous
Insoluble
Are disulfide bonds involved in the secondary structure
EQ
No
True or false
Each single polypeptide chain in secondary structure is either alpha helix or beta pleated sheet
EQ
False
can be alpha helix and beta pleated in the same chain
Name the bond present in the primary structure of a protein
EQ
Peptide bond
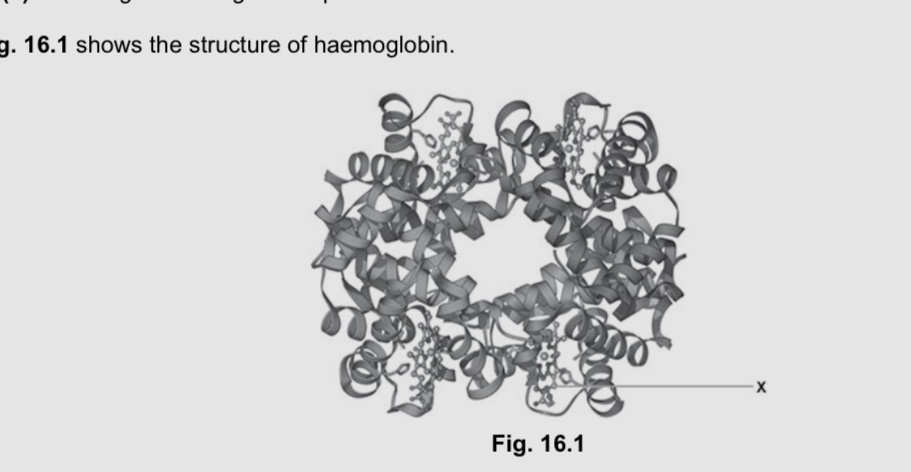
Name the structure labelled x
Haem
Effect of cohesion on water molecules
EQ
Holds water molecules together
Which bond is not formed when a conjugated protein folds into its quaternary structure
Disulfide
Hydrogen
Ionic
Peptide
EQ
Peptide
What does starch hydrolyse to?
EQ
Glucose
Explain what is meant by a conjugated protein
EQ
Prosthetic group
Attached by covalent bonds
Contains non protein groups
Describe how the structure of llama haemoglobin is likely to be different from that of a camel haemoglobin
EQ
Different primary structure
Different base sequence
No change to quaternary structure
Different secondary structure
State 3 properties of fibrous protein that are different from those of a globular protein
EQ
Insoluble
Strong
Unreactive
Properties and functions of fibrous proteins
EQ
Insoluble strong flexible
Collagen in bones
Keratin in hair -protection
Elastin-elasticity in artery walls
functions of fibrous proteins
EQ
Enzymes -catalyse reactions
Hormones-cell signalling
Transport -haemoglobin to carry oxygen
Describe and explain why collagen is a fibrous protein
EQ
Long chain
No tertiary structure
Insoluble
Suggest why collagen is such a strong molecule
EQ
Many hydrogen bonds
Explain how hydrophilic and hydrophobic interactions contribute to the spherical shape of ferritin
EQ
Hydrophobic inside molecule
Hydrophilic outside molecule
Name the covalent bonds Contains non that links 2 cysteine amino acids
EQ
Disulfide links
Name the type of monomer from which collagen is made and explain how two such monomers are joined together
EQ
Amino acid
Peptide bonds
In a condensation reaction
Order these from most soluble to least soluble
Ribose
Amylose
Glucose
Amylopectin
EQ
Glucose
Ribose
Amylose
Amylopectin
What type of glucose molecules is amylopectin made of?
EQ
Alpha glucose
What is amylose made of?
EQ
Alpha glucose molecules
Describe the formation of chitin molecule from its monomers
EQ
Bonds formed by condensation reactions
Water released
Alternate monomers flipped by 180 (because made of N-acetylgluocsamine made fo beta glucose molecules)
Because of the OH groups
Describe and explain the structure and properties of lipids
EQ
Energy rich
More carbon carbon bonds
Insoluble compact
Long chains can be broken down to release 2 carbons
Describe and explain the structures and properties of different carbohydrates
EQ
Polymers of glucose
-glucose used in respiration
Large molecules
Insoluble-doesn’t affect water potential
State 2 ways in which the molecular structure of cholesterol is similar to the molecular structure of glucose
EQ
Contains carbon and hydrogen
Contains oxygen
State the physical property of glucose that allows it to be easily transported into the bloodstream
EQ
Glucose is soluble
Is glucose compact?
EQ
No
State 2 structural similarities between lactose and maltose
EQ
Two hexoses
1-4 glycosidic bond in both
Identify the differences between the structures of lactose and maltose
EQ
Lactose:
Beta glucose
Beta glycosidic bonds
Sugars in opposite direction
Maltose:
Alpha glucose
Alpha glycosidic bonds
Same direction monomers
Suggest why lactose is unable to cross membranes
EQ
Unable to pass between phospholipids
As too large
Give 3 properties of cellulose that make it suitable as the basis of plant cell walls
EQ
High tensile strength
Insoluble
Flexible
2 Similarities between chitin and glycogen.
EQ
Polymers
1-4 glycosidic bonds
2 differences between the structures of chitin and glycogen
EQ
Chitin has nitrogen
No 1-6 glycosidic bonds in chitin
How does branching affect the process of respiration
EQ
Speeds up hydrolysis
As more free ends
Is amylose soluble
EQ
No
Which phase of interphase has the least DNA?
EQ
G1
Which phase of interphase has the highest number of cells
EQ
G1
Why would one cell spend more time in the S phase?
EQ
It has more DNA than the other cell
State one observation of a white blood cell that has stopped dividing in at the G2
EQ
Large number of organelles
During which stage of the cell cycle does semi-conservative DNA replication take place?
EQ
Synthesis phase
State 2 roles of mitosis in multicellular organisms
EQ
Production of new stem cells
Asexual reproduction
Why do plant reproduce asexually when conditions are favourable
EQ
Genetically identical offspring produced rapidly
Describe the spindle fibres
EQ
Spindle fibres attach to chromosome
Explain why type of nuclear division in a zygote is mitosis and not meiosis
EQ
Genetically identical clones To grow into an embryo

Prophase
Explain how the organisation of homologous chromosomes during metaphase1 Increases genetic variation
EQ
Each chromosome of homologous chromosomes pair is genetically different
Chromosomes line up across center of cell
Other than having specific receptors describe one way in which the structure of the neutrophil is specialised
EQ
Well developed cytoskeleton
Describe the changes that must occur inside these stem cells as they differentiate to form erythrocytes
EQ
Digest organelles associated with protein synthesis
Suggest 3 ways in which the use of embryonic stem cells in reasearch has practical benefits to biological knowledge
EQ
Test effectiveness of new medical drugs
Test side effects of new drugs
Studied to se how develop into different cell types
Explain the difference between a muscle tissue and a muscle
EQ
Muscle tissue is a collection of dif cells that contract together
Muscle is an organ and a collection of tissues
Explain the benefits to plants on internal transport systems
EQ
High metabolic rate
Ensures nutrients reach all tissues
Where are companion cells located
EQ
Phloem
Example of substance transported by a companion cell
EQ
Sucrose
Example of substance transported by a root hair cell
EQ
Nitrate ions
Does a guard cell have chloroplasts
EQ
Yes
Explain why a leaf is described as an organ
EQ
Leaves have phloem and xylem to carry out photosynthesis
And organ definition
Explain why podocytes are unable to undergo mitosis
EQ
Have already differentiated
In G0 phase
Shape too irregular
What features of adult stem cells make them suitable for regeneration of tissues in the kidney
EQ
Adult stem cells are multipotent and can differentiate into any cell type
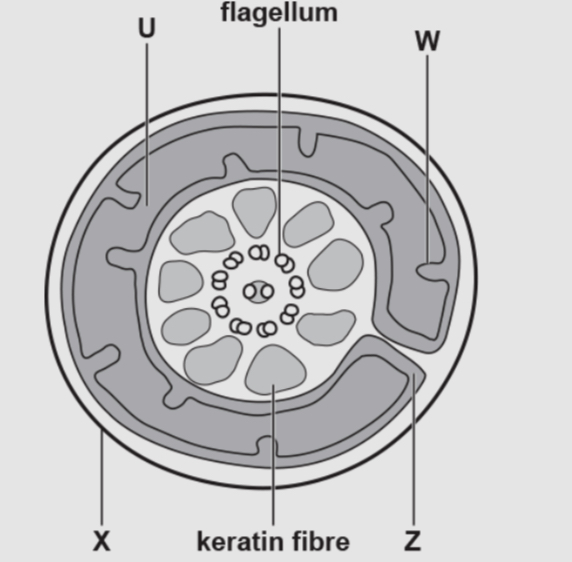
Identify the structures
U
W
Z
U-matrix
W-cristae
Z-inter membrane space
Explain the role of embryonic stem cells in the development of the embryo
EQ
Renewing source of cells
Can differentiate into any cell type
Totipotent
EQ
Can form whole organisms
Can’t give rise to extra embryonic tissues
Do mature sieve tube elements contain nuclei
EQ
Yes
Do xylem vessels have non lignified pits to allow movement in and out
EQ
Yes
Are companion cells linked to xylem vessels by plasmodesmata
EQ
No
Is the cell wall thicker or thinner on the side furthest away from the stoma
EQ
Thinner
Squamous epithelial
EQ
Flattened shape
Pack close together
Short diffusion distance
Describe an ethical issue associated with the use of embryonic stem cells
EQ
Embryo destroyed
used in IVF
What type of cell is present in meristematic tissue
EQ
Stem cells
How are xylem vessels formed from stem cells
EQ
Differentiation
Lignification
Cell elongation
How does the iodine test work
Iodine forms triiodide ion that enters the middle of the amylose helix causing the colour change
Colour change in iodine test
Brown to blue black
Method for testing for lipids
Take sample and mix with ethanol
Lipid dissolves in ethanol
Filter
Pour solution into water
Cloudy white precipitate forms if positive result
Why do you filter the ethanol test
To remove the undissolved ethanol
How does the burnet test work
Colour formed by complex between nitrogen atoms in peptide chain and cu2+ ions
Method for testing for proteins
Add 5ml of biuret solution to sample
If protein is present colour changes from blue to lilac
Colour change in biuret test
Blue to purple
Colour change in reducing sugar
Blue-no colour change
Green-little glucose
Amber-some glucose
Red-lots of glucose
Iodine dissolved in potassium iodide solution when heated disappears but when cooled returns why
Bonds break when heated
Biosensors
Machines that tell you if a biological molecule is present
How do you estimate the amount of a sample without using a biosensor
Compare with standard solution
Two functional groups in an amino acid molecule
Amine
Carboxyl
R group
True or false
Sucrose is a polymer
FALSE SUCROSE IS NOT A POLYMER
Quaternary structure in insulin
Polypeptide chains that are linked by disulfide bonds
Quaternary structure in haemaglobin
Two alpha globin chains and two beta globin chains
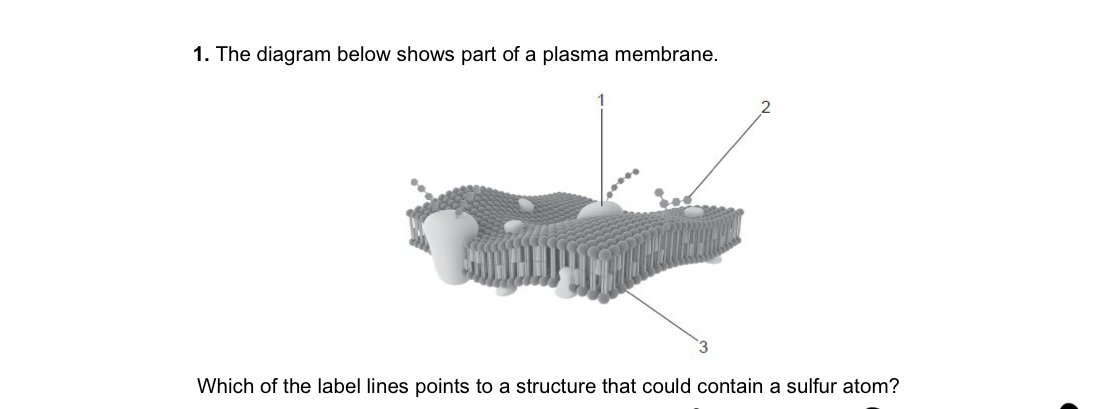
1 only