CP363
5.0(2)
5.0(2)
Card Sorting
1/192
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
193 Terms
1
New cards
Database System
computerized record keeping system that consists of related data
2
New cards
Database System Components
Users, Hardware, Software
3
New cards
User Support
Supports single or many users
* Data is Integrated - unify distinct files while eliminating redundancy
* Data is shared - different users will have different access and views to the same data
* Data is Integrated - unify distinct files while eliminating redundancy
* Data is shared - different users will have different access and views to the same data
4
New cards
Database Administrators
create the data base and incorporate technical controls to enforce decisions made by the DBA
5
New cards
Why Database - Data Dictionary
stores definition of data and relationships, changes are automatically recorded
6
New cards
Why Database - multiaccess user support
Shared Data between users, multiple users can access the database at the same time without compromising integrity
7
New cards
Why Database - Reduced redundancy and inconsistency
Inconsistent data happens when one redundant data has been updated and the other has not
8
New cards
Why database - Transaction Support
Several updates in one transaction guarantees all or none are updated
9
New cards
Why Database - Data integrity support
ensures that the data in the database is accurate, reduce redundancy, increase consistency
10
New cards
Why Database - security
only means of access to database is through proper channels, promotes data privacy
11
New cards
Why database - backup/recovery
recovery after possible failures
12
New cards
Data Independence
changing info in one place without changing it in another
* Changes in application programs without changing the structure of the underlying data
* Database can grow without impairing existing applications
* Changes in application programs without changing the structure of the underlying data
* Database can grow without impairing existing applications
13
New cards
Disadvantages of the DBMS
* Increased Costs: hardware and software costs, hiring experts
* Management Complexity: different types of technology is harder to manage
* Vendor Dependence: reluctantly to change the system once it has been established
* Frequent Update/Replacement Styles: costs incurred to update and train people
* Management Complexity: different types of technology is harder to manage
* Vendor Dependence: reluctantly to change the system once it has been established
* Frequent Update/Replacement Styles: costs incurred to update and train people
14
New cards
Conceptual Schema Design - Stage 1
Choice of model: User requirements and real world concepts should go into design
15
New cards
Conceptual Schema Design - Stage 2
Normalization: Reduces complexity and avoids redundancy by adjusting diagrams
16
New cards
Conceptual Schema Design - Stage 3
Optimization: Promotes good performance of the database
17
New cards
Entities
real world entity that has an independent existence, Represented by a table and attributes
18
New cards
Strong Entity
exist on thier own and do not rely on others
19
New cards
Weak Entity
existence depends on the existence of another strong entity
20
New cards
Relationships
associates entities with one another
21
New cards
Mapping Constraints - One-to-One
manager can manage only one department but each department can only have one manager
22
New cards
Mapping Constraints - One-to-Many
Department can have several employees but each employee can only work in one department
23
New cards
Mapping Constraints - Many-to-Many
A supplier can supply parts to several jobs a jobs can receive parts for several suppliers
24
New cards
Total Participation
Relationship is total - (indicated by double lines):
EX: every department must be managed by a manager
\
EX: every department must be managed by a manager
\
25
New cards
Partial Participation
Relationship is partial between two entities (indicated by a single line):
EX: not every employee manages a department
\
EX: not every employee manages a department
\
26
New cards
Simple/Atomic Attributes
Not divisible (ex. Part #, weight)
27
New cards
Composite Attributes
Consists of several simple attributes (ex. Address)
28
New cards
Single valued attributes
unique value, not shared among data entries (ex. SIN#)
29
New cards
Multi valued attributes
attributes that can be shared among data (ex. College majors, skills)
30
New cards
Stored Attribute
are stored in the database (ex. Date of birth)
31
New cards
Derived Attribute
can be derived from stored information (ex. Age)
32
New cards
Key Attribute
unique attribute that is distinct for each individual entity instance and can be used to identify an entity
33
New cards
Candidate Key
minimal subset attributes that uniquely identifies an entity (ex. Employee #)
* Can be specified using the unique clause
* Can be specified using the unique clause
34
New cards
Primary key
candidate key chosen by designer to access each entity
* Only one primary key per table
* Can be specified after the variable type or before with the values that make up the key
* Only one primary key per table
* Can be specified after the variable type or before with the values that make up the key
35
New cards
Null Values
Represents not applicable, unknown missing information or not known information
36
New cards
Database Schema
created in the database design phase to describe the database and not expected to change
37
New cards
Database Instance
data in the database at a particular moment in time
38
New cards
Levels of Database Architecture (ANSI/SPRAC) - Internal Level
shows how data is stored inside the system such as file organization and access paths
39
New cards
Levels of Database Architecture (ANSI/SPRAC) - Conceptual Level
deals with the modeling of the whole database, conceptual schema is defined
40
New cards
Levels of Database Architecture (ANSI/SPRAC) - External Level
models user oriented description of parts of the database, views for users
41
New cards
Logical Data Independence
(external/conceptual): ability to modify conceptual schema without changing external views and application programs
42
New cards
Physical Data Independence
(internal/conceptual): modify internal or physical schema without changing conceptual or view level schema or application programs
43
New cards
Data Definition Language (DDL)
* For defining schemas at various levels
* Used by database designers and administrators
* Used by database designers and administrators
44
New cards
Data Manipulation Language (DML)
* Used to construct and use the database
* Used by end users for insertion, deletion, updates, retrievals
* Used by end users for insertion, deletion, updates, retrievals
45
New cards
Subclass
allows sub groupings of entities
* Members of a subclass inherit all the attributes of the superclass
* Each sub class has its own attributes along with inherited attributes
* Members of a subclass inherit all the attributes of the superclass
* Each sub class has its own attributes along with inherited attributes
46
New cards
Superclass
main type of the sub grouping
47
New cards
Specialization
* Process of defining a et of subclasses of an entity type
* Based on some distinguishing characteristic of the entity type
* Multiple specializations can be defined on a single entity type
* Based on some distinguishing characteristic of the entity type
* Multiple specializations can be defined on a single entity type
48
New cards
Specialization - Disjointness Constraint
* Disjoint: an entity can be a member of at most one of the subclasses of the specialization
* Overlapping: the same entity can be a member of more than one subclass of the specialization
* Overlapping: the same entity can be a member of more than one subclass of the specialization
49
New cards
Specialization - Completeness Constraint
* Total: every entity in superclass must be a member of some subclass
* Partial: an entity might not belong to any of the subclasses in the specialization
* Partial: an entity might not belong to any of the subclasses in the specialization
50
New cards
Generalization
Result of taking the union of two of more lower level entity types to produce a higher level entity type
51
New cards
Aggregation
Abstraction through which relationships are treated as higher level entities
* Create new higher level entity called assignment to treat as the new entity
* Create new higher level entity called assignment to treat as the new entity
52
New cards
Relational Model
* Uses tables called relations to represent a collection of related data values
* Rows are called tuples
* Columns are called attributes
* Number of attributes (# of columns) is called the degree/arity
* Rows are called tuples
* Columns are called attributes
* Number of attributes (# of columns) is called the degree/arity
53
New cards
Relational Model - Domain
data type describing the values that can appear in each column
* Domain is a set of atomic values that are indivisible
* Domain is a set of atomic values that are indivisible
54
New cards
Super Key
key attributes and other attributes of a relation
* Allows you to be more specific to find a record
* Allows you to be more specific to find a record
55
New cards
Relations
values that can be read but not updated by definition
56
New cards
Relvars
variables that can be read and updated by definition
57
New cards
Optimization
system component that determines how to implement user requests
58
New cards
Catalog
set of system relvars that contain descriptors regarding various objects that are of interest to the system itself
59
New cards
Transaction
logical unit of work involving several operations that begins by begin transaction and terminates normally or abnormally
60
New cards
Atomicity
Transactions are guaranteed either to execute or not execute at all
61
New cards
Durability
once a transaction successfully commits its updates are guaranteed to be applied to the database even if the system fails
62
New cards
Isolation
database updates by given transactions are kept hidden from all distinct transactions unless the first transactions are successfully committed
63
New cards
Serializability
interleaved execution of concurrent transaction is guaranteed to produce the same result as executing the same transactions in an unspecified order
64
New cards
Commit (normal Termination)
operation that signals the end of a successful transaction
65
New cards
Rollback (abnormal termination)
operation that signals the unsuccessful end of transaction
66
New cards
SQL
Structural Query Language
* Non procedural Language - no loops, conditionals or functions
* Combine with other programming languages for more functionality
* Non procedural Language - no loops, conditionals or functions
* Combine with other programming languages for more functionality
67
New cards
SQL Data Types
* Numeric
* Integer and floating point numbers
* Integer - size to 40 digits, 4 bytes in DB2
* Small int - smaller storage space, 2 bytes in DB2
* Fractional Numbers - specify scale(default) and size or none
* Character String
* Fixed: CHAR(size) specified, reserved fixed amount in memory
* VARCHAR(size), does not reserve max space
* Date / Time
* YYYY-MM-DD for dates
* HH.MM.SS for times
* Integer and floating point numbers
* Integer - size to 40 digits, 4 bytes in DB2
* Small int - smaller storage space, 2 bytes in DB2
* Fractional Numbers - specify scale(default) and size or none
* Character String
* Fixed: CHAR(size) specified, reserved fixed amount in memory
* VARCHAR(size), does not reserve max space
* Date / Time
* YYYY-MM-DD for dates
* HH.MM.SS for times
68
New cards
Foreign Key
* Combination of columns in one relationship that references primary key attributes of a second relationship
* Uses the keyword references
* Uses the keyword references
69
New cards
Default Value
specifies a value to when no value is given
70
New cards
Check Conditions
* Ensures that every row in the table satisfies a set condition
* Condition can be any valid expression that evaluates to true or false
* Condition can be any valid expression that evaluates to true or false
71
New cards
Referential Integrity Actions
* Set Default - the attribute value is set to default value
* Set Null - attribute value is set to null
* Cascade - updates are propagated, each attribute value is updated
* No Action
* Set Null - attribute value is set to null
* Cascade - updates are propagated, each attribute value is updated
* No Action
72
New cards
Alter Table
to update and modify an existing table by adding/update/delete an existing column
* Add/Delete column by using ADD command
* Add column at any time if not null is not specified
* Modify column definition using MODIFY command
* Can increase character column width, number of decimal place and number of digits at any time
* Add/Delete column by using ADD command
* Add column at any time if not null is not specified
* Modify column definition using MODIFY command
* Can increase character column width, number of decimal place and number of digits at any time
73
New cards
Drop Table
* Use DROP TABLE command at the bottom of the dependency chain to properly delete
* Use CASCADE CONSTRAINTS to drop all constraints that refer to professor table
* Use CASCADE CONSTRAINTS to drop all constraints that refer to professor table
74
New cards
INSERT
* Insert - adds a new row to the selected table
* Insert by explicitly or implicitly specify a query
* Insert results of a query into a table
* Insert by explicitly or implicitly specify a query
* Insert results of a query into a table
75
New cards
DELETE
removes a row or a set of rows from the selected table
\
__Basic Syntax:__
DELETE FROM table
WHERE
\
__Basic Syntax:__
DELETE FROM table
WHERE
76
New cards
UPDATE
changes values of existing row in table
\
__Basic Syntax:__
UPDATE table
SET attribute1 = expression……
WHERE
\
__Basic Syntax:__
UPDATE table
SET attribute1 = expression……
WHERE
77
New cards
Views
Virtual Table opposed to a base table - specific view of a database group for users
78
New cards
Characteristics of Views
* View is not created at definition, instead materializes on the first use
* Do not need to create a physical table --> derive table from implementation
* View tables are updated automatically if the base table info is updated
* Do not need to create a physical table --> derive table from implementation
* View tables are updated automatically if the base table info is updated
79
New cards
Purpose of Views
* Performance optimization
* Used when subqueries are repeated through existing queries
* Security
* Users only can be provided with data that is needed and not all of it
* Provide read only access
* Used when subqueries are repeated through existing queries
* Security
* Users only can be provided with data that is needed and not all of it
* Provide read only access
80
New cards
Creating Views
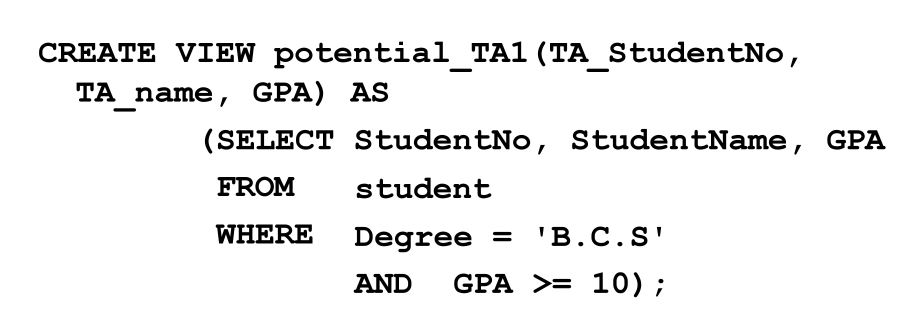
81
New cards
SELECT
* Use \* to list all the attributes
* If Using \* the WHERE clause is optional
* Can pass strings and conditional statements through
* If Using \* the WHERE clause is optional
* Can pass strings and conditional statements through
82
New cards
ORDER BY
* Order by Descending (DESC) or Ascending (ASC)
* Ascending order is the default
* Specify ordering with multiple different attributes
* Ascending order is the default
* Specify ordering with multiple different attributes
83
New cards
AS
* Serves as an Alias to rename an attribute to be more specific
84
New cards
DISTINCT
* Eliminates duplicate values
85
New cards
LOGICAL OPERATORS
* AND, OR, NOT can be used to combine simple conditionals
* Precedence: NOT --> AND --> OR
* Precedence: NOT --> AND --> OR
86
New cards
JOINING TABLES
* Same attribute names in different tables
* Use . To specify the attributes from the tables
* Use . To specify the attributes from the tables
87
New cards
EXISTS
* Used to test he existence of any record subquery
* Returns true of conditions are met
* Returns true of conditions are met
88
New cards
UNION
* Combines the result set of two or more select statements
* Both tables must have the same number of columns and be similar types
* Both tables must have the same number of columns and be similar types
89
New cards
MINUS/NOT IN
* Not conditions for entries
* Minus does not work for MySQL, you must use NOT IN
* Minus does not work for MySQL, you must use NOT IN
90
New cards
LIKE
* Allows you to pull entries that are similar to a given condition
* Can be used in place of an equals sign to a string
* Case sensitive matching
* % will match 0 or more characters
* _ will match a single character
* Can be used in place of an equals sign to a string
* Case sensitive matching
* % will match 0 or more characters
* _ will match a single character
91
New cards
BETWEEN
* Simple shorthand for a range restriction instead of using relational operators
92
New cards
Aggregate Functions
* Take a multiset of values and return a single value
* Average, Minimum, Maximum, Total/Sum and Count
* Average, Minimum, Maximum, Total/Sum and Count
93
New cards
GROUP BY
* Group by a certain table column that have the same value
94
New cards
HAVING
* List records that have a certain condition
* Can be combined with conditionals to create constraints
* Can be used with nested queries
* Can be combined with conditionals to create constraints
* Can be used with nested queries
95
New cards
Problems with Poor database design
* Redundancy - duplicate data
* Update anomalies - Direct consequence of redundancy
* Insertion Anomalies - Cannot insert new data unless there is a record that applies to it
* Deletion Anomalies - Lose important information from deletion
* Update anomalies - Direct consequence of redundancy
* Insertion Anomalies - Cannot insert new data unless there is a record that applies to it
* Deletion Anomalies - Lose important information from deletion
96
New cards
Decomposition
* Split the relation into two or more relations
* Use join to get back to the original information
97
New cards
1NF Normalization
* A relation is said to be in 1NF if it contains only atomic, simple and scalar data
* This data is usually comma delimited and contains multiple values associated with one record
98
New cards
Full Functional Dependency
* FD between X -> Y is full if the removal of any attribute from X means that the dependency does not hold
99
New cards
Partial Dependency
FD between X -> Y is partial if there is some attribute AeX that can be removed from X and the dependency will still hold
100
New cards
2NF Normalization
A relational schema is in 2NF if it is at first in 1NF and every non key attribute is fully functionally dependent on the primary key / candidate key of the relation