Anatomy and Physiology- Ch.3 Cells and Tissues
1/56
Earn XP
Description and Tags
wip
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
57 Terms
4 concepts of the cell theory
a cell is the basic structural and functional unit of living organisms
the activity of the organism depends on the collective activity of its cells
according to the principle of complimentary, the activity of the cells are dictated by their structure (anatomy), which determines function (physiology)
continuity of life has a cellular basis
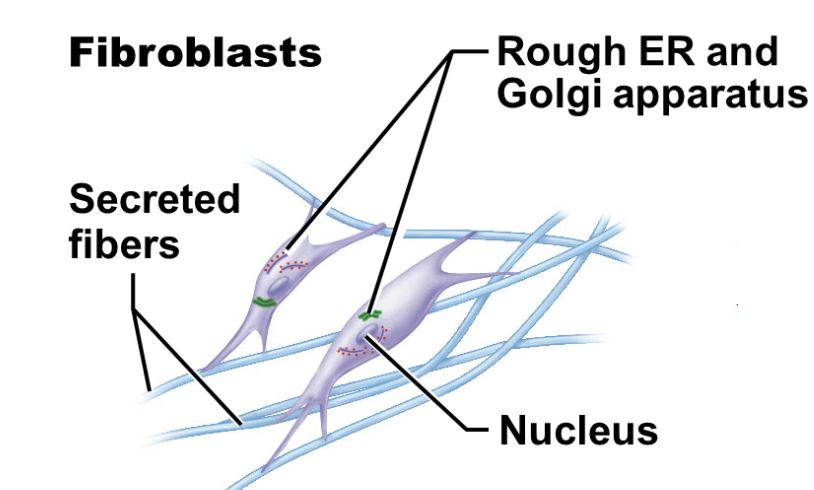
fibroblast function
connect body parts
structure of fibroblast
elongated shape
abundant rough ER and large Golgi bodies to make and secrete proteins
illustration of fibroblast
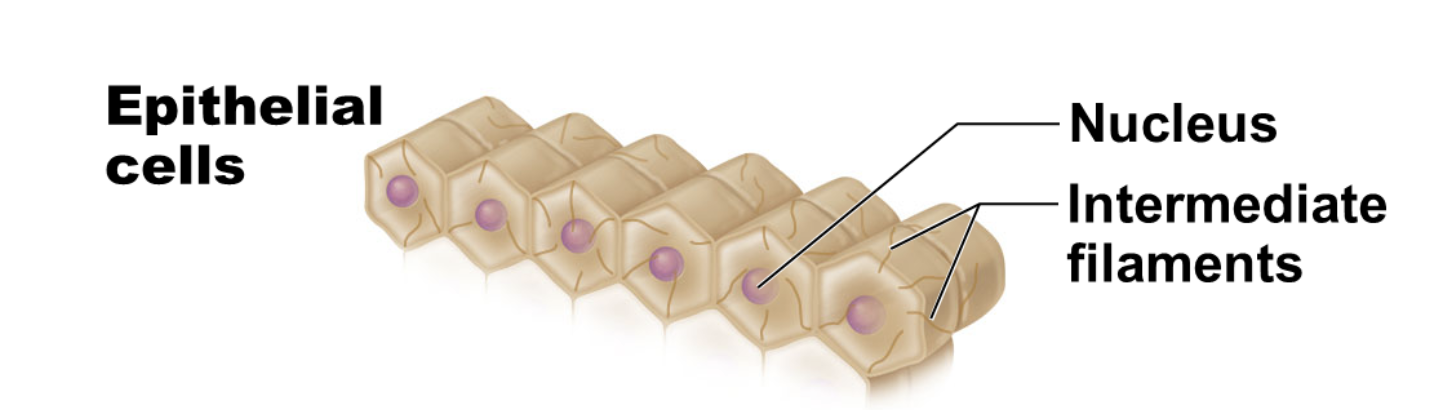
epithelial cell’s function
covers and lines body organs
structure of the epithelial cell
hexagonal/honeycomb shape
allows cells to pack together into sheets
abundant intermediate filaments and desmosomes that resist tearing when epithelium is rubbed or pulled
illustration of epithelial cell
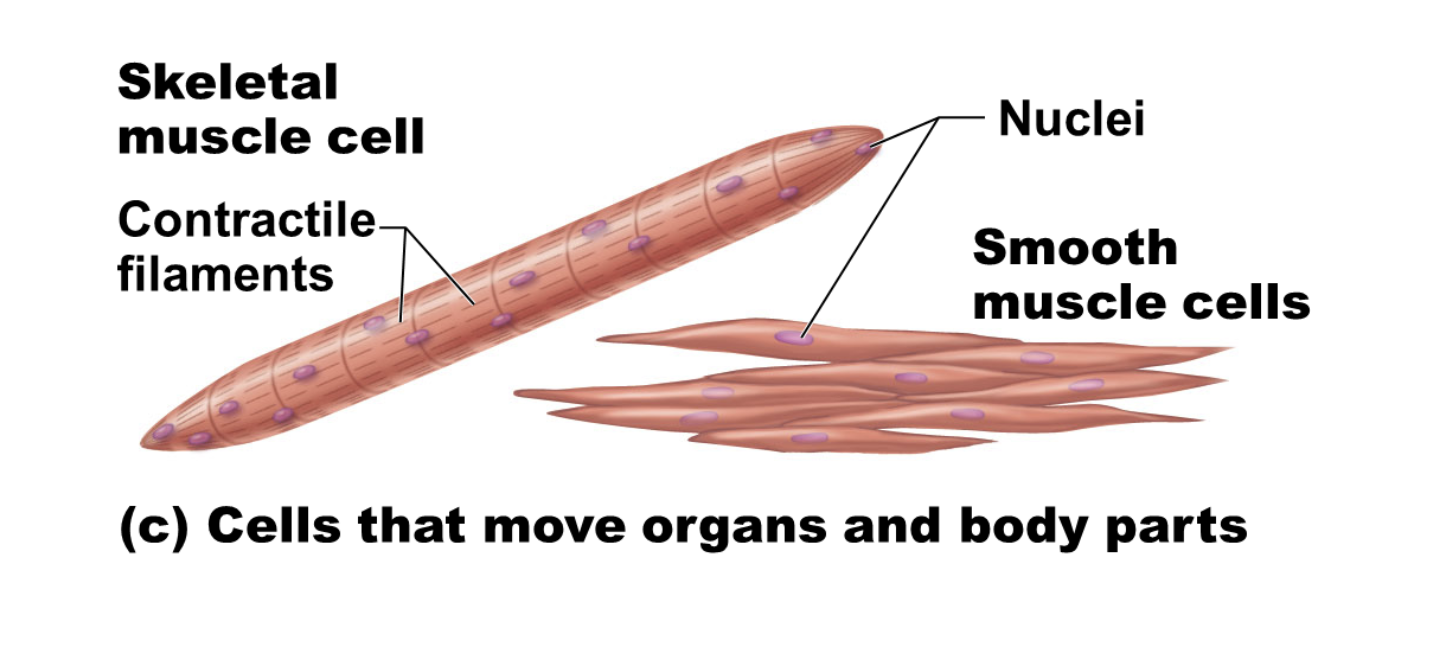
Skeletal muscle cell functions
cells that move body organs and body parts
skeletal muscle cells structure
elongated cells filled f/ abundant contractile filaments
so they can shorten forcefully and move the bones, pump blood, or change the size of internal organs to move substances around the body
illustration of skeletal muscle cell
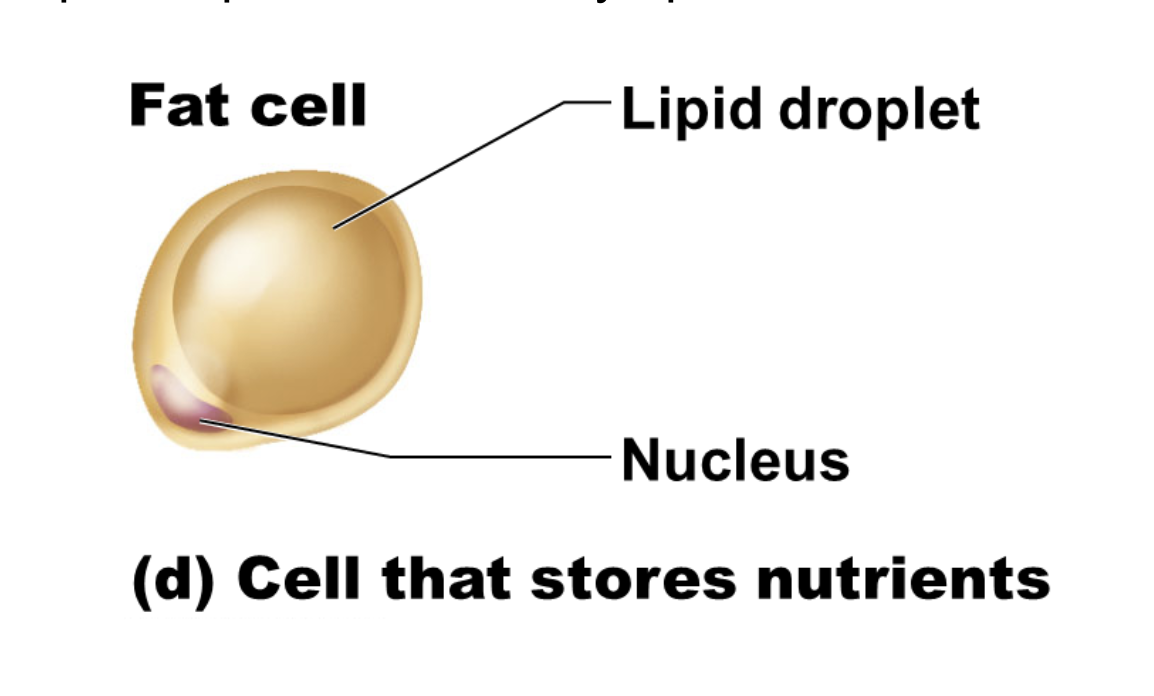
fat cell functions
cells that store nutrients
structure of fat cell
huge spherical shape of a fat cell is produced by a large lipid droplet in its cytoplasm
illustration of fat cell
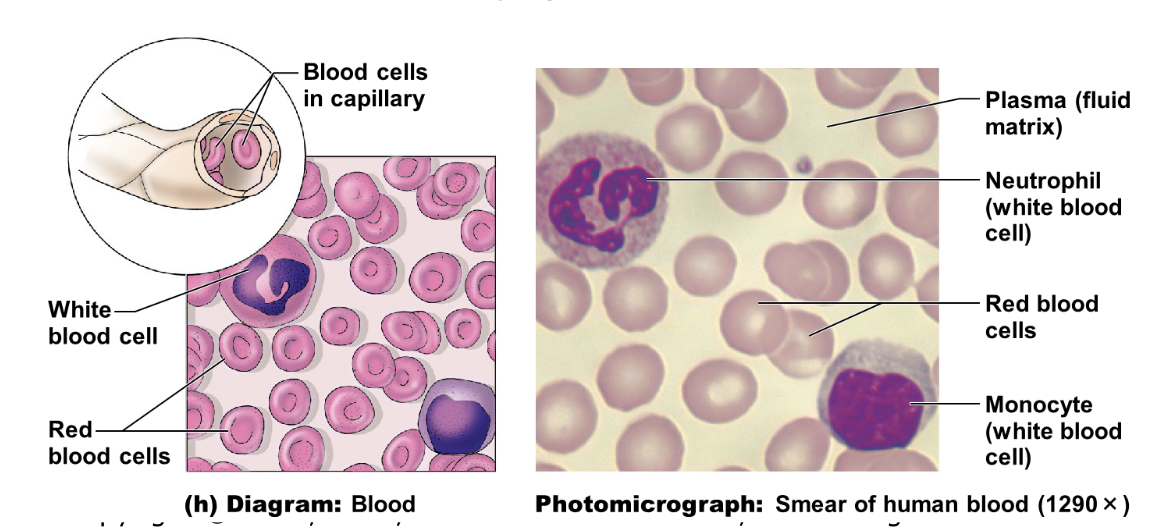
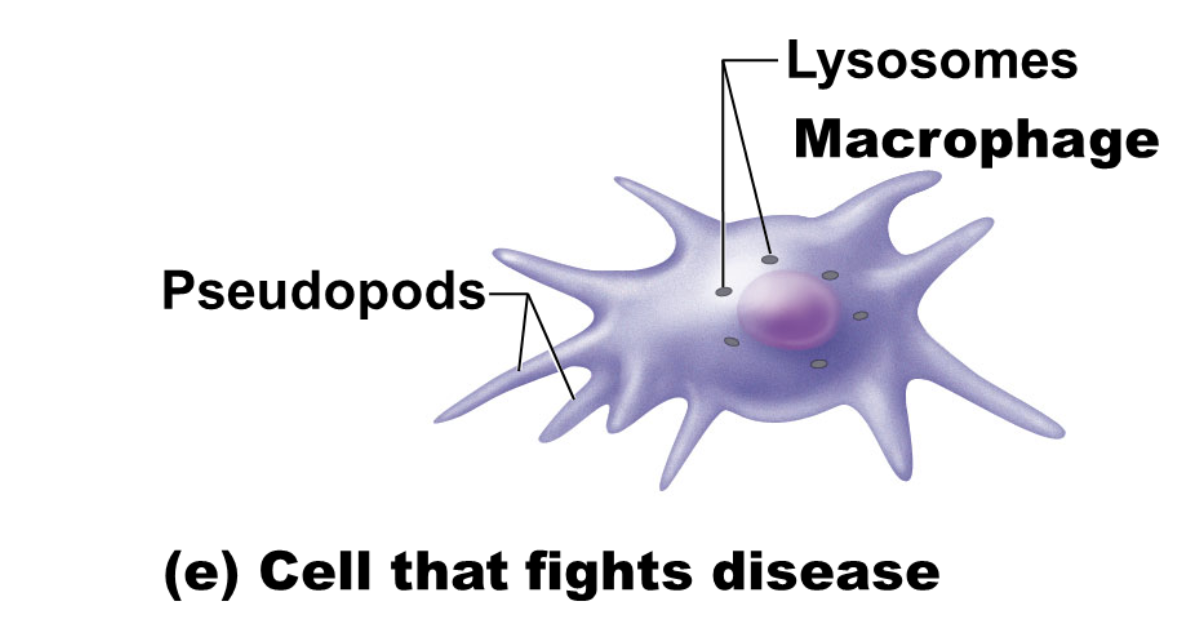
function of white blood cell
cells that fight disease
structure of white blood cells
extends long pseudopods (“false feet”) to crawl through tissue to reach infection sites
the many lysosomes within the cell digest the infectious micro-organism micro-organisms (such as bacteria) that it eats
illustration of white blood cell
list the 4 primary tissue types that for the fabric of the body. include the single term to describe the tissues overall role
epithelial - covering
connective - supportive
nervous - control
muscle - movement
list the 4 characteristics of epithelium
covers and lines body surface
regens easily if well nourished
often form sheets w/ one free surface, the apical surface, and an anchored surface, the basement membrane
avascular (no blood supply)
what are the 6 types of epithelial tissue
simple squamous
simple cuboidal
simple columnar
pseudostratified ciliated columnar
transitional
stratified squamous
illustration of simple squamous
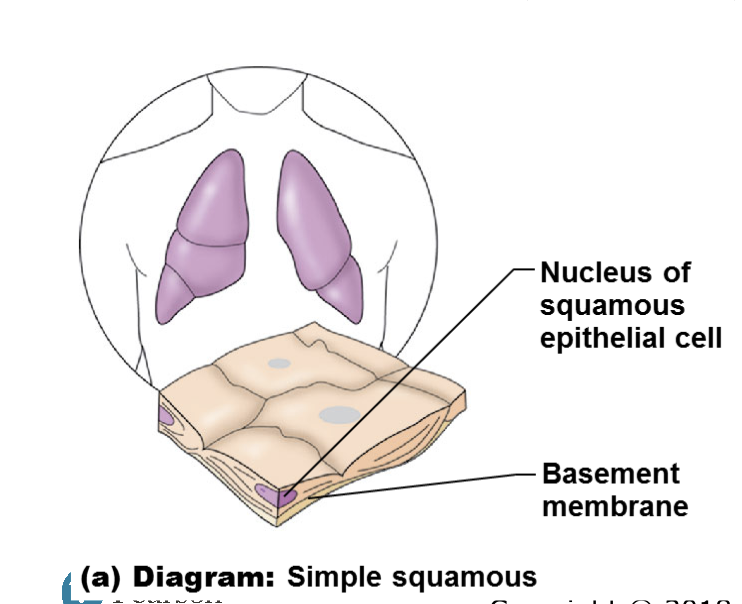
illustration of simple cuboidal
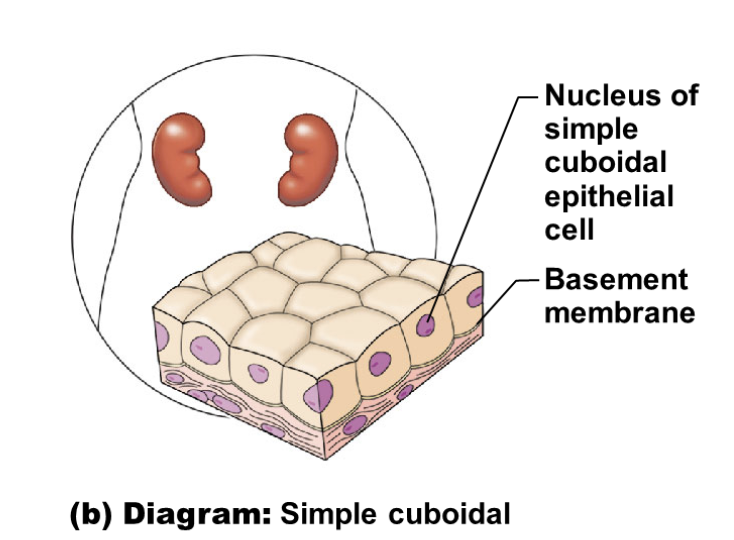
illustration of simple columnar
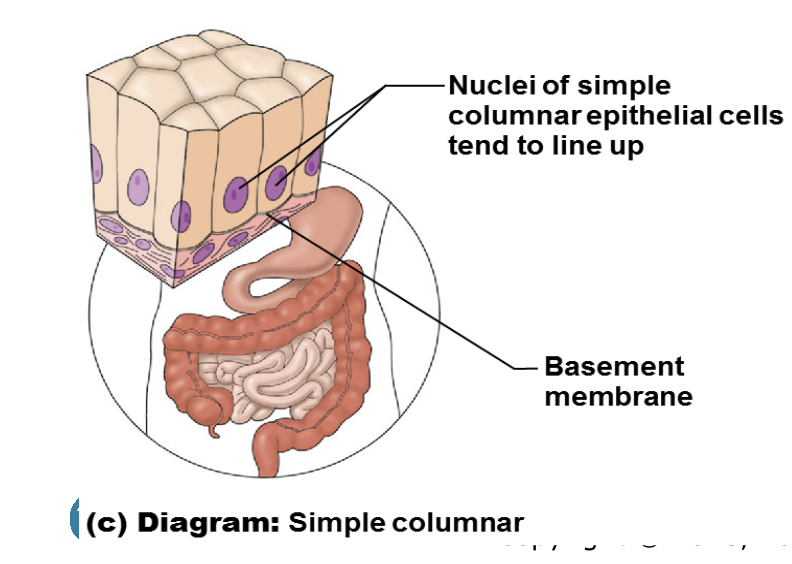
illustration of pseudostratified ciliated columnar
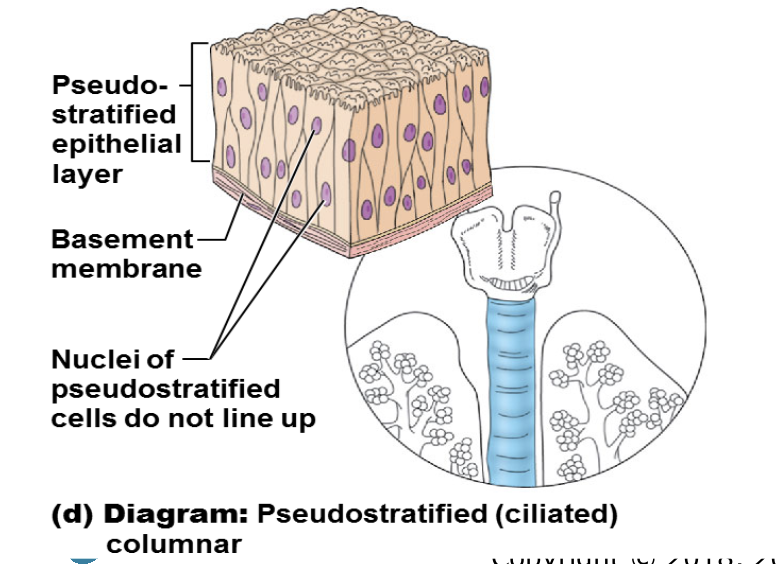
illustration of transitional
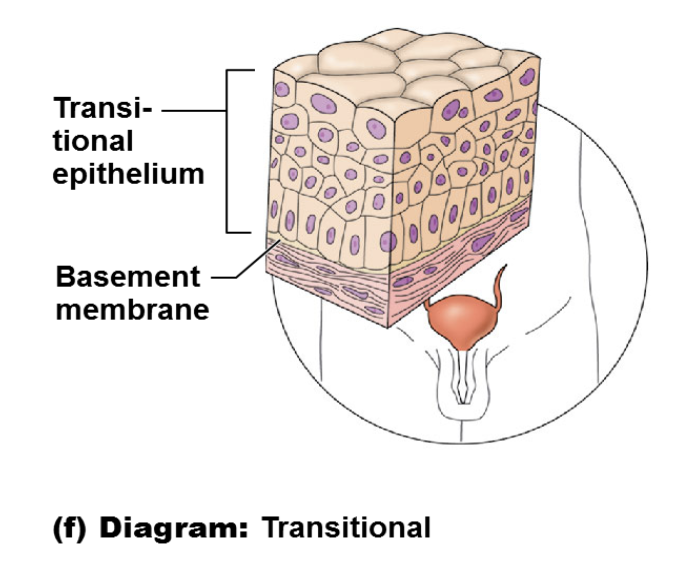
stratified squamous
describe structure: arrangement of cells
Simple Squamous
single layer of flat cells
function of simple squamous
diffusion, filtration, or secretion in. membrane
location of simple squamous
usually forms membranes
lines air sacs of lungs
forms walls of capillaries
forms serous membrane (serosae) that line and cover organs in ventral cavity
describe structure: arrangement of cells
Simple Cuboidal
single layer of cube-like cells
function of simple cuboidal
Secretion and absorption; ciliated types
propel mucus or reproductive cells
location of simple cuboidal
common in glands and their ducts
forms walls of kidney tubules
covers surface of ovaries to the exterior
describe structure: arrangement of cells
simple columnar
single layer of tall cells
function of simple squamous
Secretion and absorption; ciliated types
propel mucus or reproductive cells
location of simple columnar
lining of digestive track from stomach to anus
mucous membrane (mucosae) line body cavities opening to the exterior
describe structure: arrangement of cells
pseudostratified columnar
singe layer, but some cells are shorter than others, giving a false (pseudo) impression of stratification. all rest on a basement membrane
function of pseudostratified columnar
absorption or secretion
location of pseudostratified columnar
respiratory tract, where it is ciliated and known as pseudostratified ciliated columnar epithelium
describe the structure: arrangement of cells
stratified squamous
most common stratified epithelium
named for cells present at the free (apical) surface, which are squamous
function of stratified squamous
protective covering where friction is common
location of stratified squamous
lining of the:
skin (outer portion)
mouth
esophagus
describe the structure: arrangement of cells
transitional
composed of modified stratified epithelium
shape of cells depend on the amount of stretching
function of transitional
stretching and the ability to return back to normal
location of transitional
lining of urinary organs
define gland
one or more cells responsible for secreting a particular product
define secretion
contains protein molecules in an aqueous (water-based) fluid
what is the difference between an exocrine gland an an endocrine gland? provide an example of each type of gland
endocrine gland
ductless; secretions (hormones) diffuse into blood vessels
exocrine gland
secretes through ducts to the epithelial surface
includes sweat and oil glands, liver, and pancreas (both internal and external)
list the 3 functions of connective tissue
protection
support
bind
list the 2 unique characteristics of connective
varied cell types
variation in blood supply (some tissue types are well vascularized, poor blood supplied, or avascular)
explain extracellular matrix. what are the 2 main elements?
nonliving material that surrounds living cells
ground substance - mostly water, along with adhesion proteins and polysaccharides molecules
fibers
Collagen (white) fibers
Elastic (yellow) fibers
Reticular fibers (a type of collagen)
describe the connective tissues
collagen fibers
elastic fibers
reticular fibers
collagen fibers (white) - glue
elastic fibers (yellow) - elastic
reticular fibers - a type of collagen, support
illustration of bone
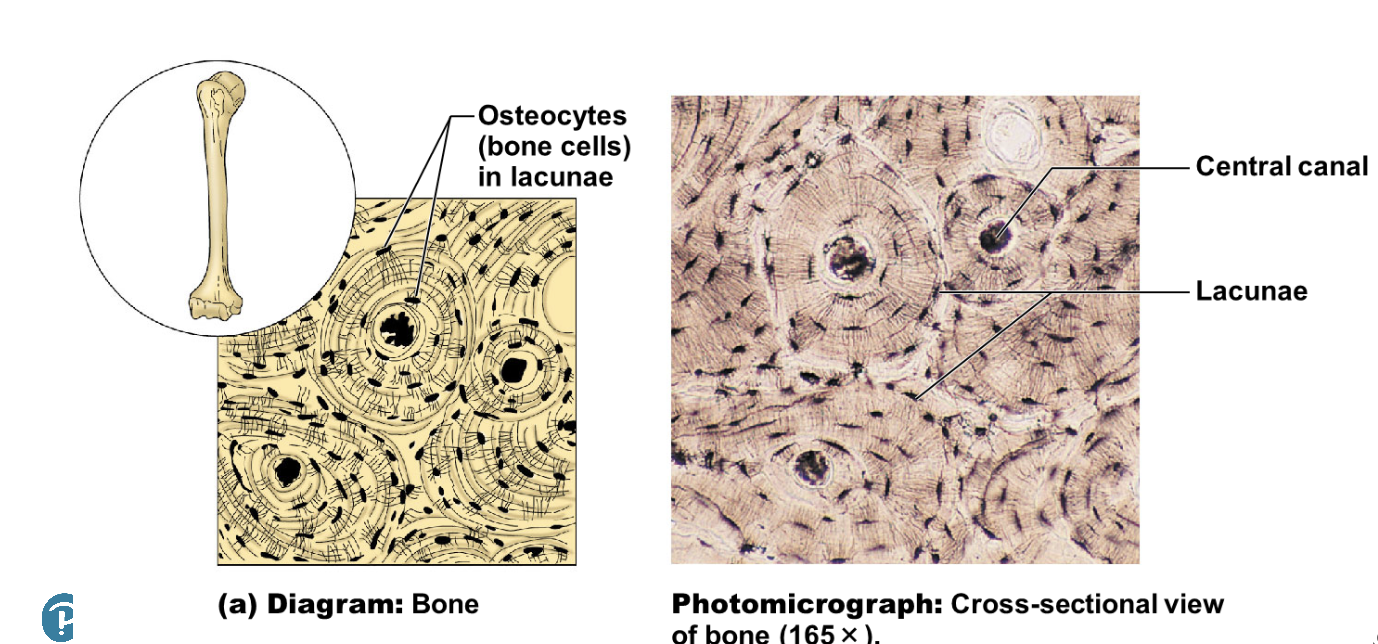
illustration of hyaline cartilage
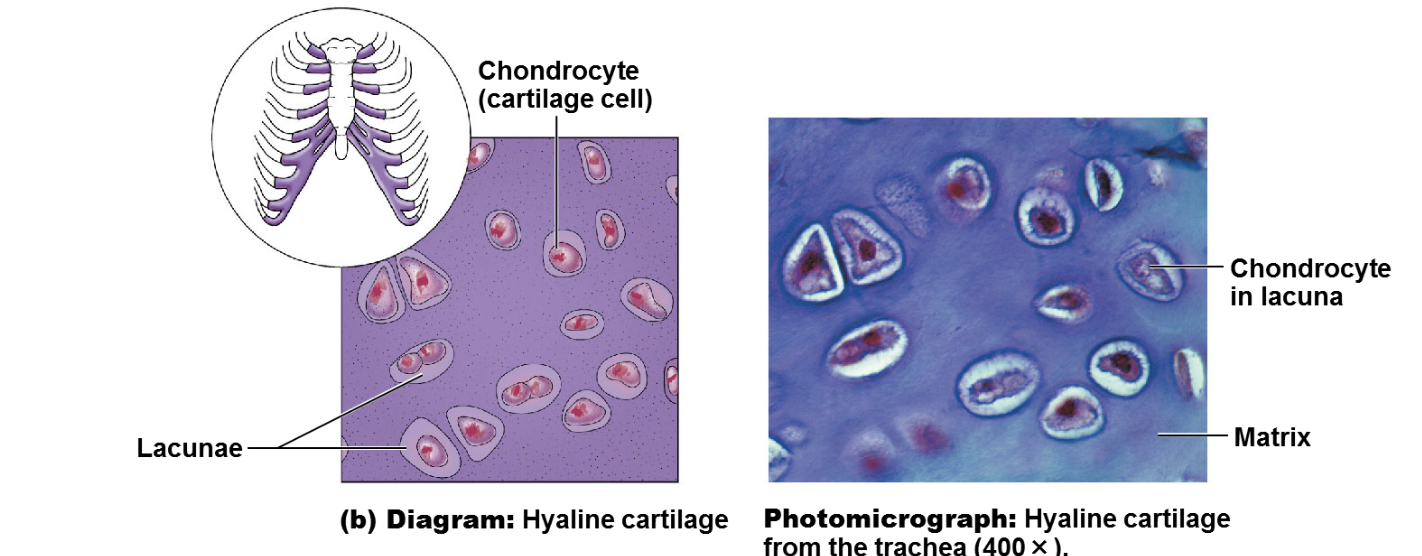
illustration of fibrocartilage
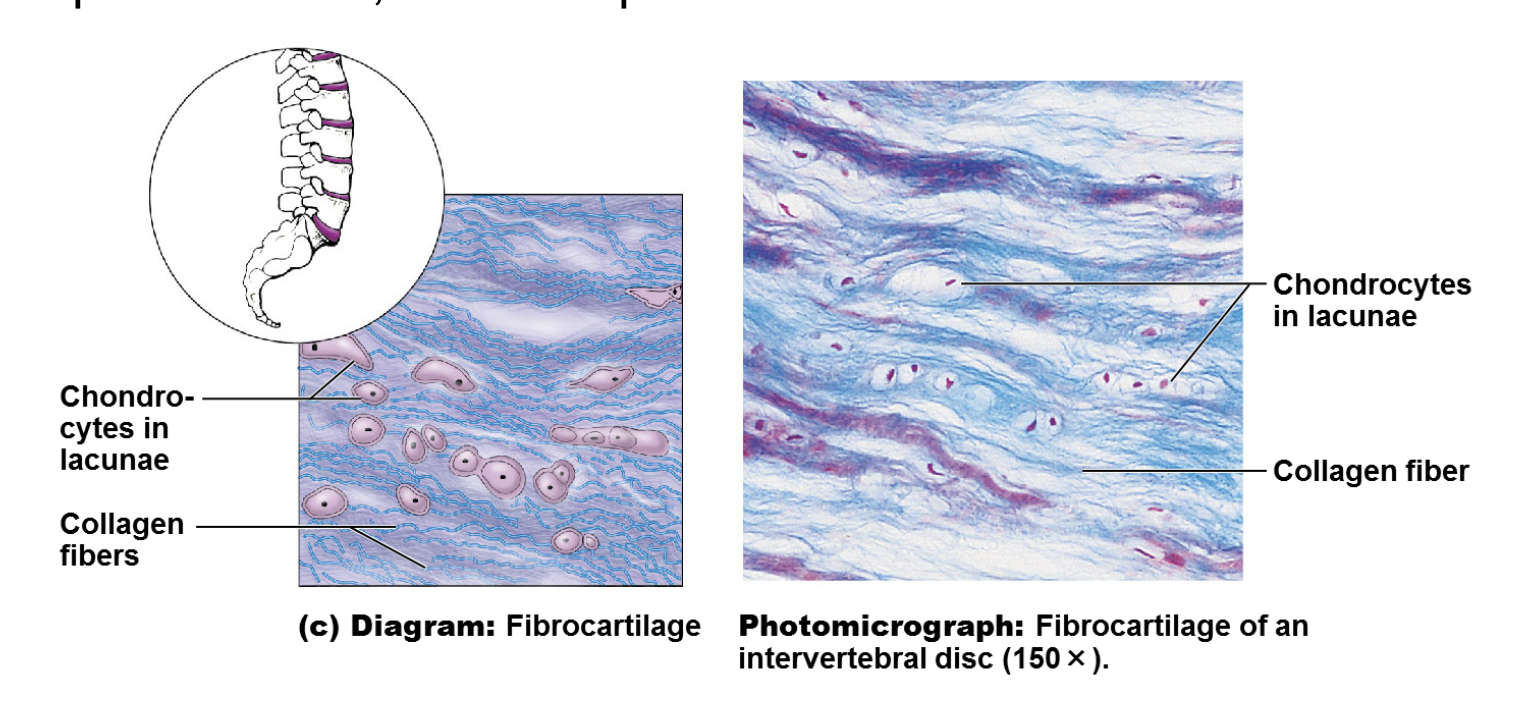
illustration of tendon (dense connective)
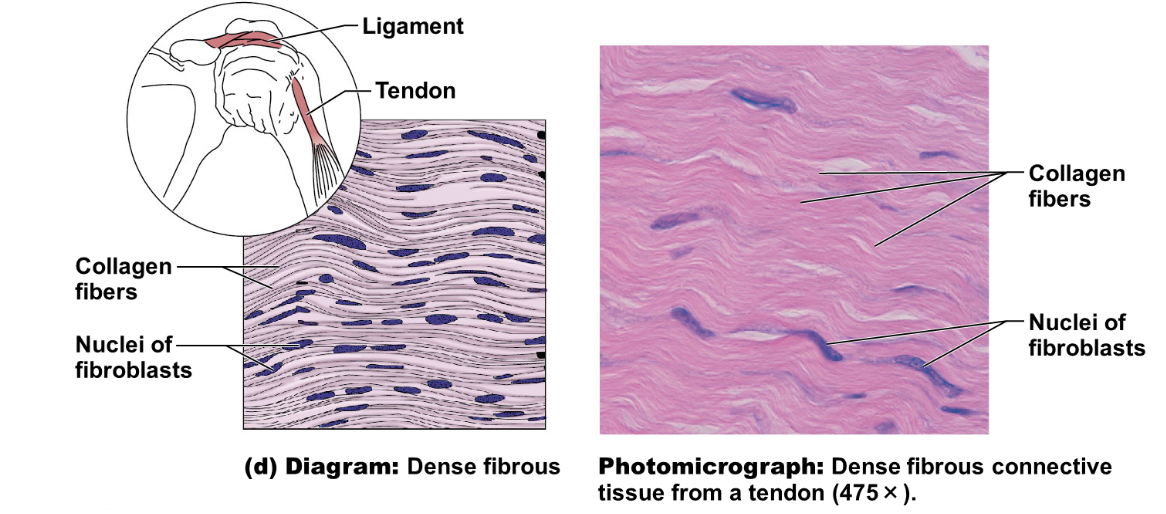
illustration of areolar tissue
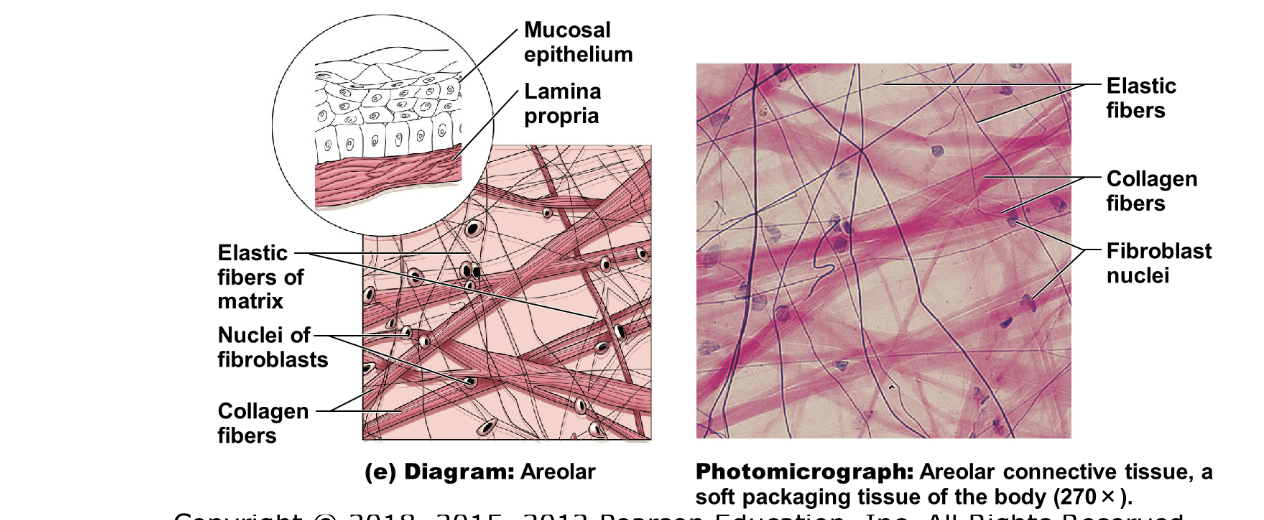
illustration of reticular connective tissue
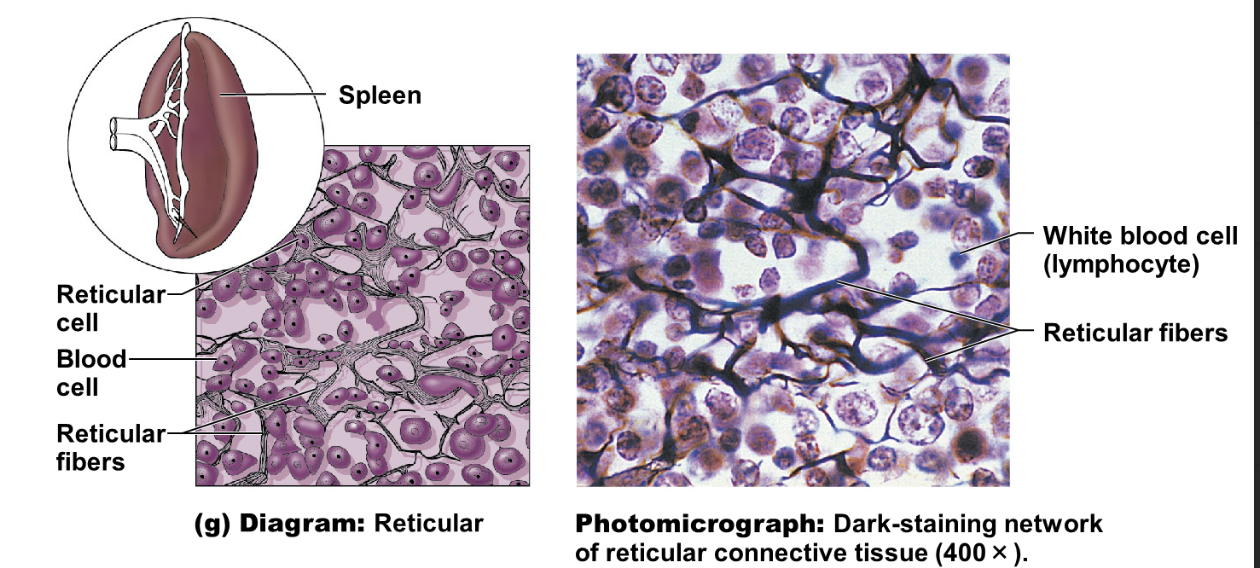
illustration of blood