FINAL PREP
1/189
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
190 Terms
Which of the following are key functions of hemocytes in the insect body?
a. carry oxygen
b. water reservoir
c. chemical exchange
d. distribution of nutrients
e. ingestion of small foreign particles in the blood
f. encapsulation of parasites
g. coagulation of blood at wound sites
d. distribution of nutrients
e. ingestion of small foreign particles in the blood
f. encapsulation of parasites
g. coagulation of blood at wound sites
In open respiratory systems, oxygen enters the tracheal system in insects through the _____________
spiracles
What carries oxygen to all respiring tissues in an insect body?
trachea
The two functions of hemolymph in the insect body are to facilitate _________ exchange and acts as a ______ _________.
chemical; water reservoir
What are the four most diverse orders of insects from the list below:
hymenoptera, diptera, lepidoptera, coleoptera
The three tagmata of insects are
thorax, abdomen, and head
In houseflies, which mouthpart is heavily modified to form the sponging labellum
labium
the process of shredding the cuticle is called
molting
true or false sclerotization is a permanent change to the cuticle
true
Based on what we discussed in class regarding insect internal systems, explain why we don’t have giant insects today like we had back in the Carboniferous. Be detailed in your explanation.
In the Carboniferous era, there were higher oxygen levels than what is found today. The decrease of oxygen could not support the bigger bodied insects, so the smaller respiratory system was preferred.
Which type of hormone is involved with initiating the molting process?
ecdysteroid
Which Ed Sheeran node on the tree represents the origin of metamorphosis?
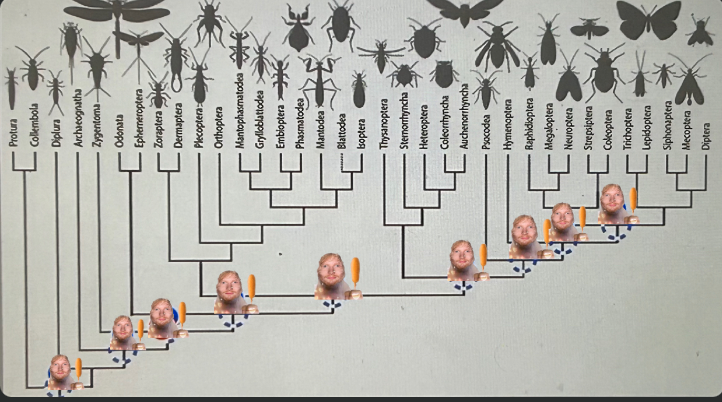
The fourth Ed sheeran node (starting from the right)
The modified hindwings in Diptera known as _______
halteres
Which ed on the tree represents Holometabola?
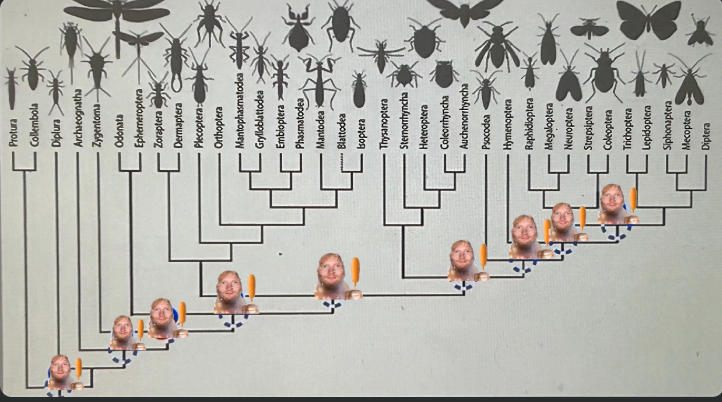
The 8th ed
Emergence from the pupal instar is called what
eclosion
The _________ is the on living layer of the cuticle
epidermis
Why isn’t the lining of the midgut shed when an insect molts?
it is not sclerotized
________ is the process that leads to additional hardening and darkening of the cuticle
sclerotization
Which ed on the tree represents the origin of wings?
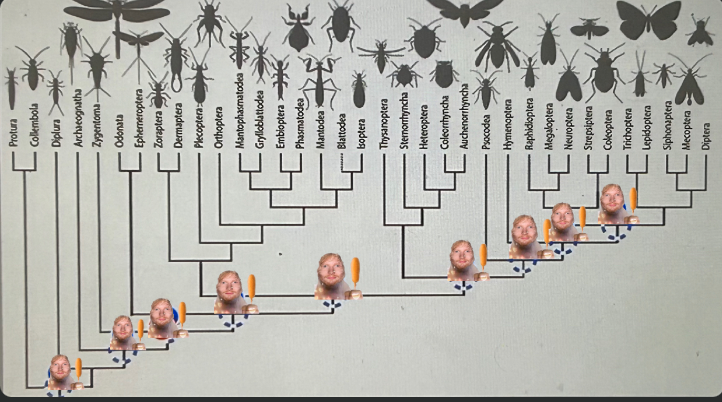
the 4th ed
Which ed on the tree represents insecta?
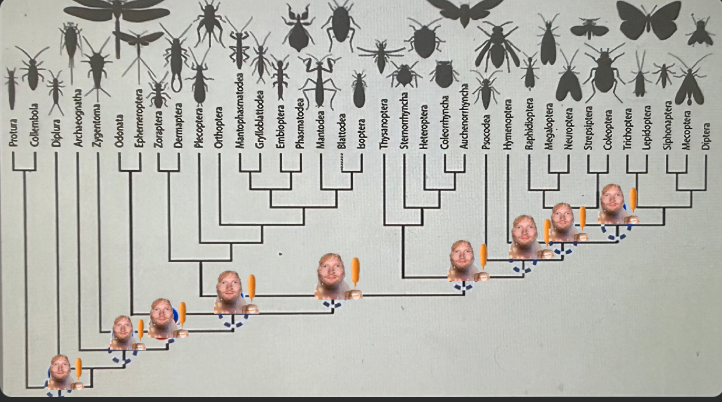
the 2nd ed
___________ is a chemical produced in one part of the body and transported to a different part of the body where it causes some change to occur
hormone
When flight muscles are attached to the inner walls of the thorax and wing movement occurs when the muscles deform the body shape, this is known as ______ muscle arrangement.
indirect
Metamorphosis in beetles occurs between which two instars?
pupa and adult
The _______ is the stage or instar unique to holometabolous insects.
pupa
________ is the developmental fusion of segments into functional body regions (i.e., the process leading to the head, thorax, and abdomen in insects)
tagmosis
Wings can arise out of which of the segments on an insect body
metathorax, mesothorax
What are the four major functions of the wing veins
provide support, house nerves to connect to sensory structures, house trachea, bring water to the wing
The onset of metamorphosis is typically associated with what
reaching a certain size
how do groups like Hymenoptera overcome the in-flight problem of turbulence created by the forewings negatively impacting the hindwings
hook wings together to move as a single unit
the modified forewings in Coleoptera are called ______ and the purpose is to provide _________ __ __________
elytra; protection to hindwing
in the piercing and sucking mouthparts of Hemiptera, the _________ and _________ are modified into long slender stylets
mandibles; maxillae
the three diagnostic characteristics of Hexapoda
one pair of antennae, three pairs of legs, three tagmata
The functions of the arthropod exoskeleton
protection, muscle attachment, water retention, and housing sensory structures
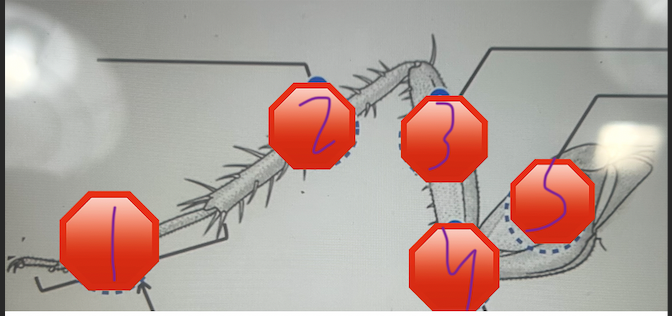
Which stop sign corresponds to the femur?
stop three
what are the four characterisitcs below that are diagnostic of Arthropoda?
compound eyes, hardened exoskeleton, jointed appendages, and Malphigian tubules
in insects, primary absorption of nutrients from ingested food occurs in the _____.
midgut
________ is the science of naming and classifying organisms.
taxonomy
One day, a group of slightly demented children caught cockroaches, cut off the cockroach heads, and put them on little pikes around their LEGO castle. Much to their horror, the headless cockroach bodies rose up onto their legs, began walking about, trampled the tiny LEGO soldiers, and pooped all over the castle. They did this for a few hours before wandering off, never to be seen again. Was this some horrible zombie virus? Clearly not, because we all know removing the head of a zombie and destroying the brain is the only way to dispatch beasts. Based on what you know about the inner workings of insects, explain how the beheaded cockroaches were able to seemingly rise from the dead and wreak havoc on the LEGO empire. Be specific by naming the system(s) involved,
The headless cockroach bodies were able to move because of their decentralized nervous system. Instead of one brain, a cockroach has a chain of segmental ganglia—or "mini-brains"—running along its belly. The missing head contained the main brain, but these intact mini-brains control basic functions like walking and reflexes (like running away), allowing the legs to keep moving on autopilot. Furthermore, they didn't bleed out instantly because of their low-pressure open circulatory system and effective clotting. Most importantly, the insect's respiratory system works through tiny holes called spiracles on the sides of the body, which deliver oxygen directly to the tissues, so losing the head doesn't stop them from "breathing." This combination allows the headless body to survive and walk for a period until it eventually dies from dehydration and starvation.
in early insects, protowings likely developed to assist in _____________ and _______
thermoregulation; sensory
the main organs of osmoregulation are
Malphigian Tubulues
The substance throughout the cuticle of an insect that gives it stregth is
chitin
True or false, the cockroaches you find in your friend’s house are native to the US
false
what type of metamorphosis is depicted in the figure
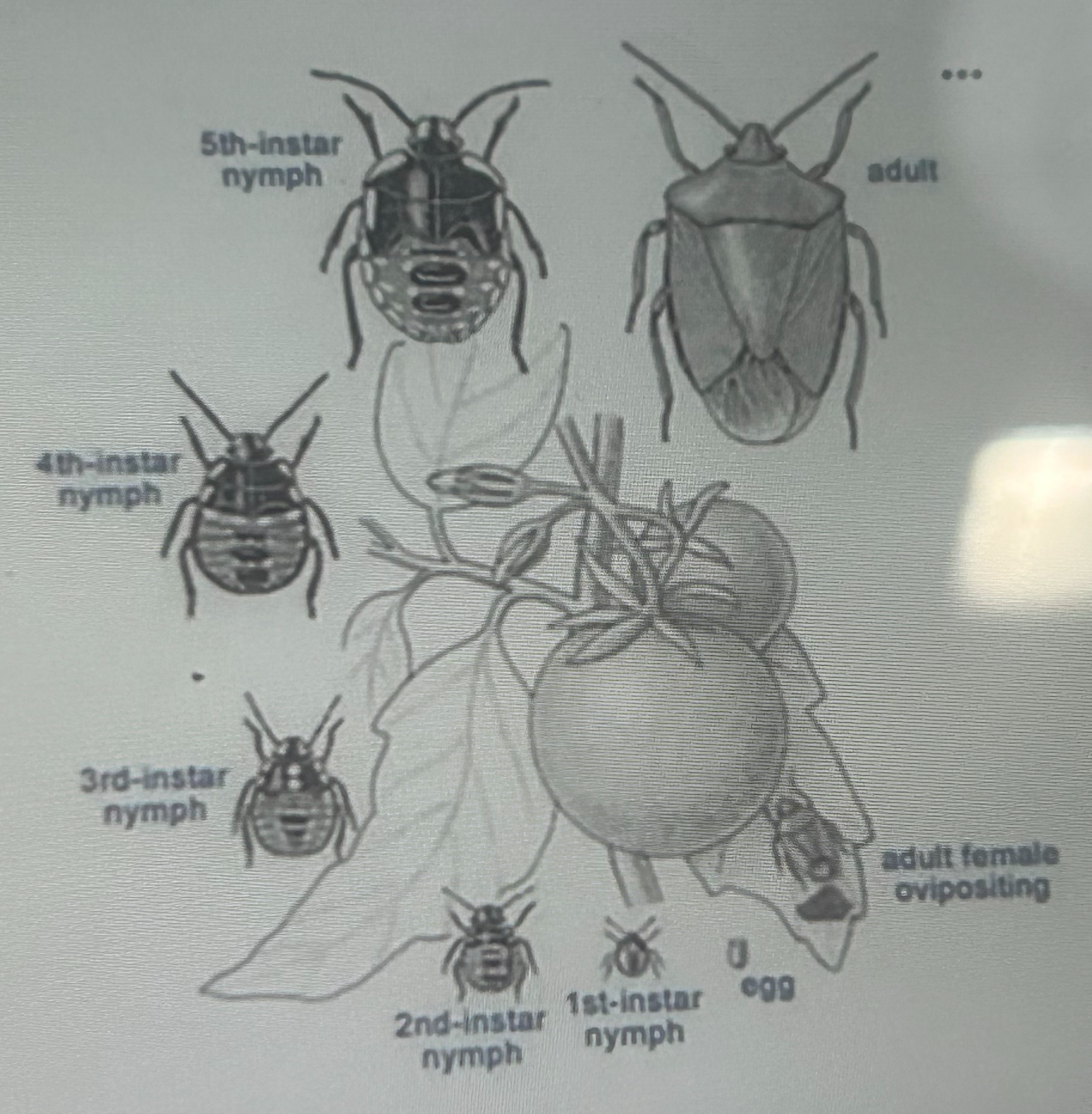
paurometaboly
the type of development discussed in class where each stage looks exactly like the last, just bigger as seen in insects like Archaeognatha is known as _________
ametaboly
when an arthropod can continue to shed its cuticle and grow, even after reaching the adult stage, this is known as ___________ growth
indeterminant
a specialized form of cuticle that has high elasticity and strength (think honeypot ants) is called
arthrodial membrane
When a female modifies the environment to form an area for oviposition, this is known as _______
nesting
in addition to compound eyes, what are the other two types of “eyes” insects can possess?
stemmata and ocelli
What are the methods used by males to ensure (or increase the likelihood of) paternity?
sperm plugs, removal of competitor sperm, and mating marathons
physiological dormancy with very specific set of conditions required to initiate and end the dormancy is known as
diapause
the specialized organs responsible for detecting sounds that pass through the tympanum are _________ ____
chordotonal organs
What type of receptor is used to relay information to the insect about pressure being exerted on joins of legs?
hair plate
We discussed an example where a parasitic wasp laid a single egg in a caterpillar egg and utlimately thousands of adult wasps emerged. One egg leading to thousands of individuals is known as ____________
polyembryony
the ability of an insect to completely dehydrate itself, halting its metabolism, but staying alive until the next rain comes is called
cryptobiosis
in terms of reproduction, all known species of Hymenoptera are
arrhenotokous
a ___________ is a substance secreted by one individual and received by a second individual of the same species, which then causes a specific action to occur in the receiver
pheromone
the amount of sunlight during a 24 hour period is termed
photoperiod
seta are ______ mechanoreceptors
tactile
moving from a home range in order to track resources in space rather than time is called ________
migration
____________ a method for producing sound where two body parts are rubbed together
stridulation
in insects, when unfertilized eggs result in males and fertilized eggs. in females, this is called __________
Arrhenotoky
Three pheromone types other than sex pheromones
aggregation, alarm, and trail-marking
oviporous insects are those that
lay eggs
As described in class, what were the three different behaviors that male giant water bugs would perform to increase the hatch rates of eggs
underwater pushups, surface brooding, and brood stroking
true or false, bugs with compound eyes see multiple small images in little cyclohexanes.
false
The photoreceptive structure in the individual ommatidia containing nerve cells and visual pigments is the __________
rhabdom
an enduring or permanent change in behavior that occurs as a result of experience or practice is _______
learning
the individual light sensing structures that make up the compound eye are called
ommatidia
What are used to track resources in time
diapause and quiescence
the highest mortality rates in insects occur in what two stages
egg and first larval
what is the most basic characteristic and fundamental behavior in insects used to find mates?
swarming
Ability to form an association with previously meaningless stimuli and reinforcement such as reward or punishment
associative learning
What type of receptor tells a mosquito when to stop feeding on blood?
stretch receptor
What are ways insects might attract mates?
sound production, sex attraction pheromones, and light production
when males aggregate in a specific area and engage in competitive displays to entice females to mate, this aggregation is known as a
lek
the female structure used to deposit eggs in a specific place is called
ovipositor
Large gametes, optimal strategy is to fertilize eggs with best sperm, and reproductive success is limited by physiology is true of what?
female insects
in some species, males of preying mantises have a tympanum on their chest. This is used for what?
to hear bat echolocation
the measure of the amount of heat required over time for an insect to complete development (often measured in degree-days) is known as
physiological time
during larval development, adult appendages are already developing in the form of
imaginal discs
When a male insect deposits spermatophores on the ground for a female to pick up, this is known as what type of sperm transfer?
indirect sperm transfer
Which of the following would be considered forms of parental care?
oviposition on the larval food source
provisioning a nest with food for developing larva
creating a nest in which to lay eggs
behaviors by adults to increase hatch rates of eggs
oviposition on the larval food source
provisioning a nest with food for developing larva
creating a nest in which to lay eggs
behaviors by adults to increase hatch rates of eggs
how many generations in a year does a bivoltine insect have?
2
true or false, like humans insects are able to maintain a steady temperature 24 hours per day
false
what color do insects not see
red
insects use hearing to
find mates, prey, hosts, and avoid predators/parasitoids
true or false some insect species that specialize on ephemaral food sources are able to speed up their development before resources vanish
true
Which of the following are functions of male insect accessory glands?
provide lubrication for sperm transfer
provide nourishment for the female
induce female to oviposit
provide nourishment for sperm maturation
provide lubrication for sperm transfer
provide nourishment for the female
induce female to oviposit
provide nourishment for sperm maturation
In the presence of unlimited food, what is the limiting factor on growth rate of an insect?
temperature
tympanal receptors are used by insects to detect
airborne vibrations
structures on the insect body to detect chemical odors are
chemoreceptors
male cicadas use a ______ to produce sound
tymbal
The structure in the female reproductive system used to store sperm is the
spermatheca
Why type of mimicry system has a harmful model and harmless mimic?
Batesian
What order of insects are the primary decomposers of dead vertebrates?
Diptera
Bed bugs are a good example of a nidicolous insects because they feed on what?
Blood
During the putrefaction stage of a decomposing vertebrate, many beetles will come to the body, What are the feeding on?
fly larvae
Which of the following is a “first responder” to a dead vertebrate?
Blow Flies
The first pollinators of plants were likely what order of insects
coleoptera
non-random active foragers might cue in on which of the following to locate their pray
carbon dioxide
prey pheromones
plant volatiles
mating calls
carbon dioxide
prey pheromones
plant volatiles
mating calls