NEUR 362 Notes: Neurobiology of Memory
1/48
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
49 Terms
Short-term memory
1) Limited capacity (3-4 items)
2) Fades quickly unless rehearsed
3) Can't be regained

Long-term memory
Memories that stay in short-term memory long enough get "consolidated" into long-term memory
Short-term memory duration
seconds to hours
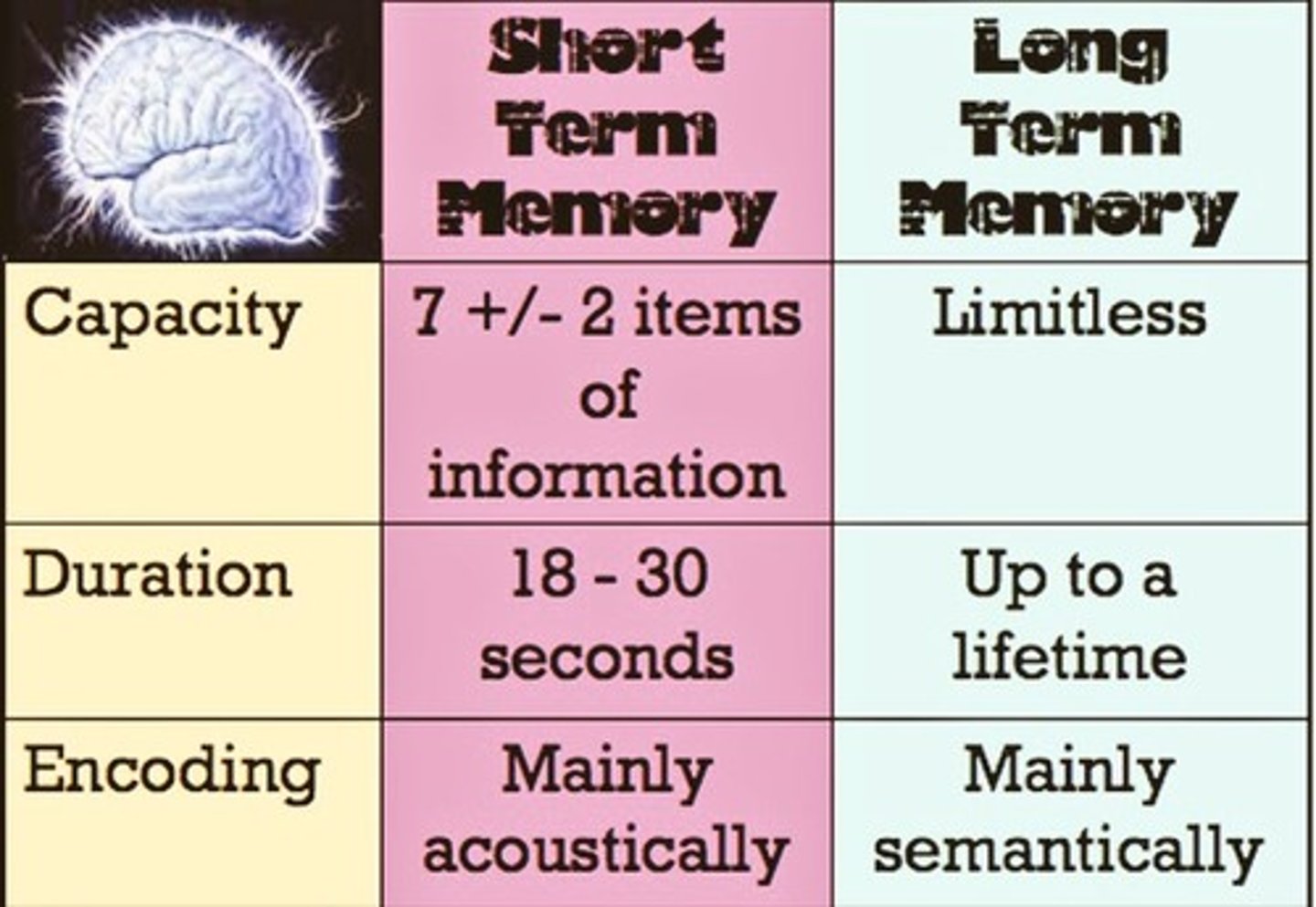
Long-term memory duration
hours to months
Long-lasting memory duration
months to lifetime
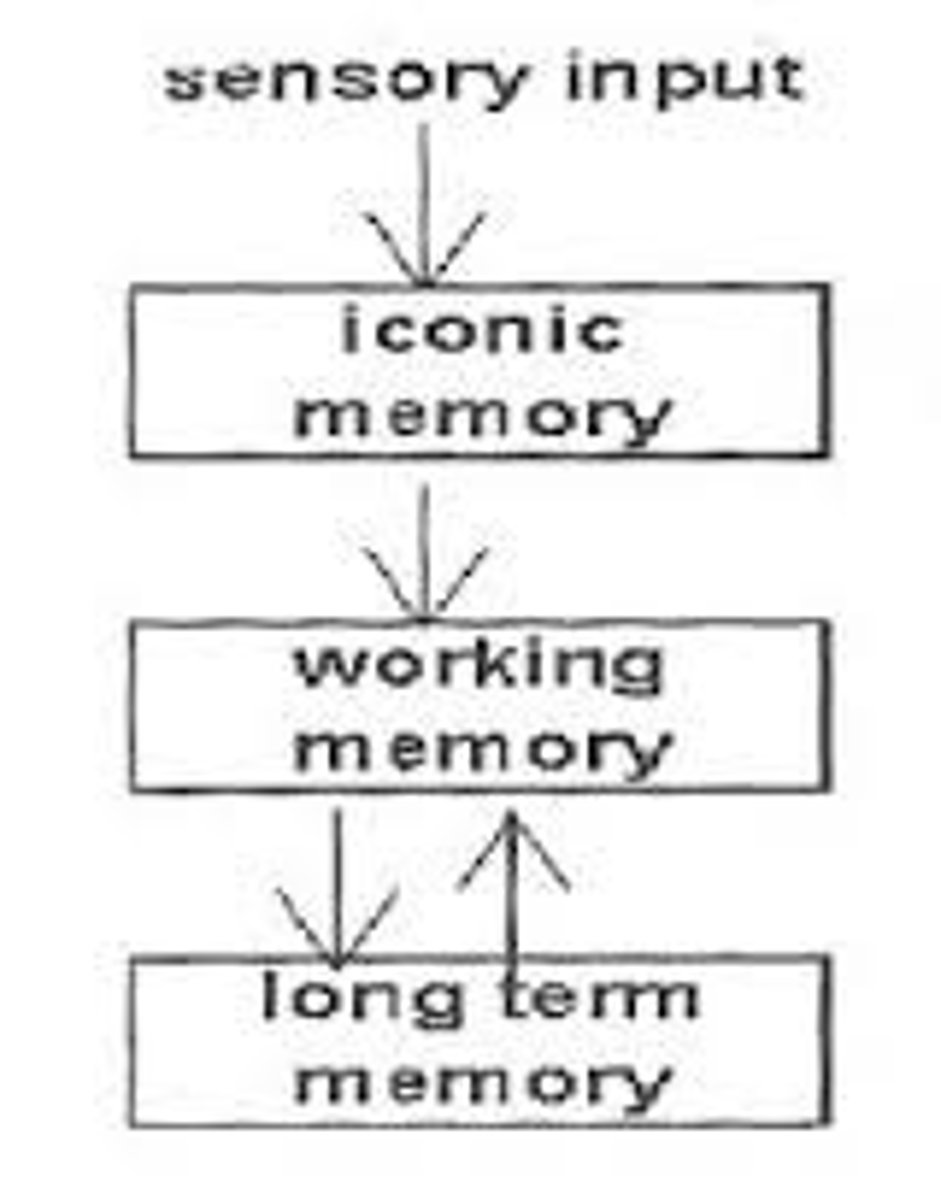
Working memory
Temporary storage for information while we are actively working on it or attending to it
What is a common test for working memory?
Delayed response task

Delayed response task
psychological or cognitive experiment that tests working memory and a subject's ability to remember and use information after a delay period
presenting a stimulus, removing it, waiting for a period, and then requiring the subject to respond based on the remembered information
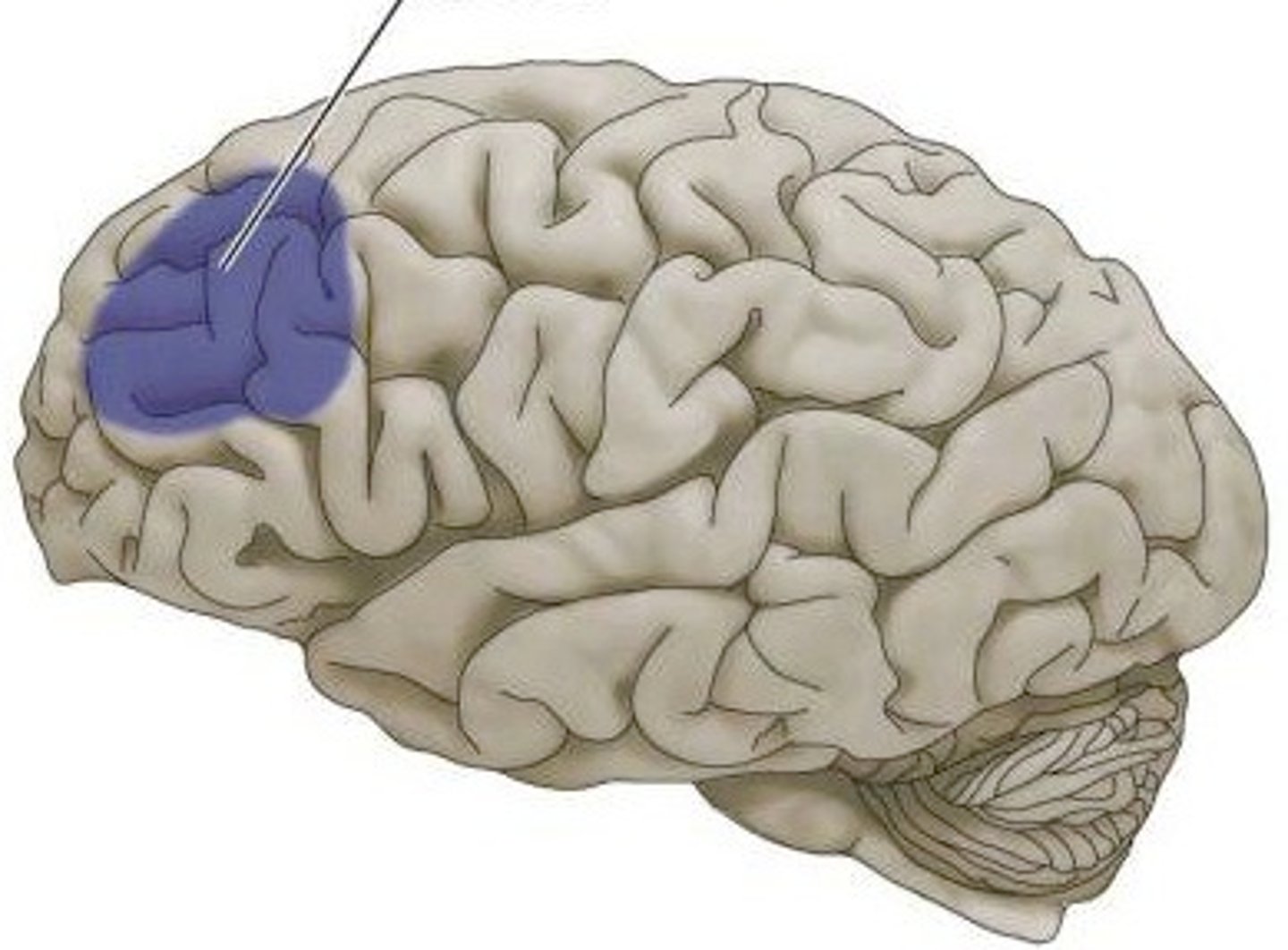
Dorsolateral prefrontal cortex
region of the brain in the frontal lobe that is crucial for executive functions such as working memory, planning, and cognitive flexibility
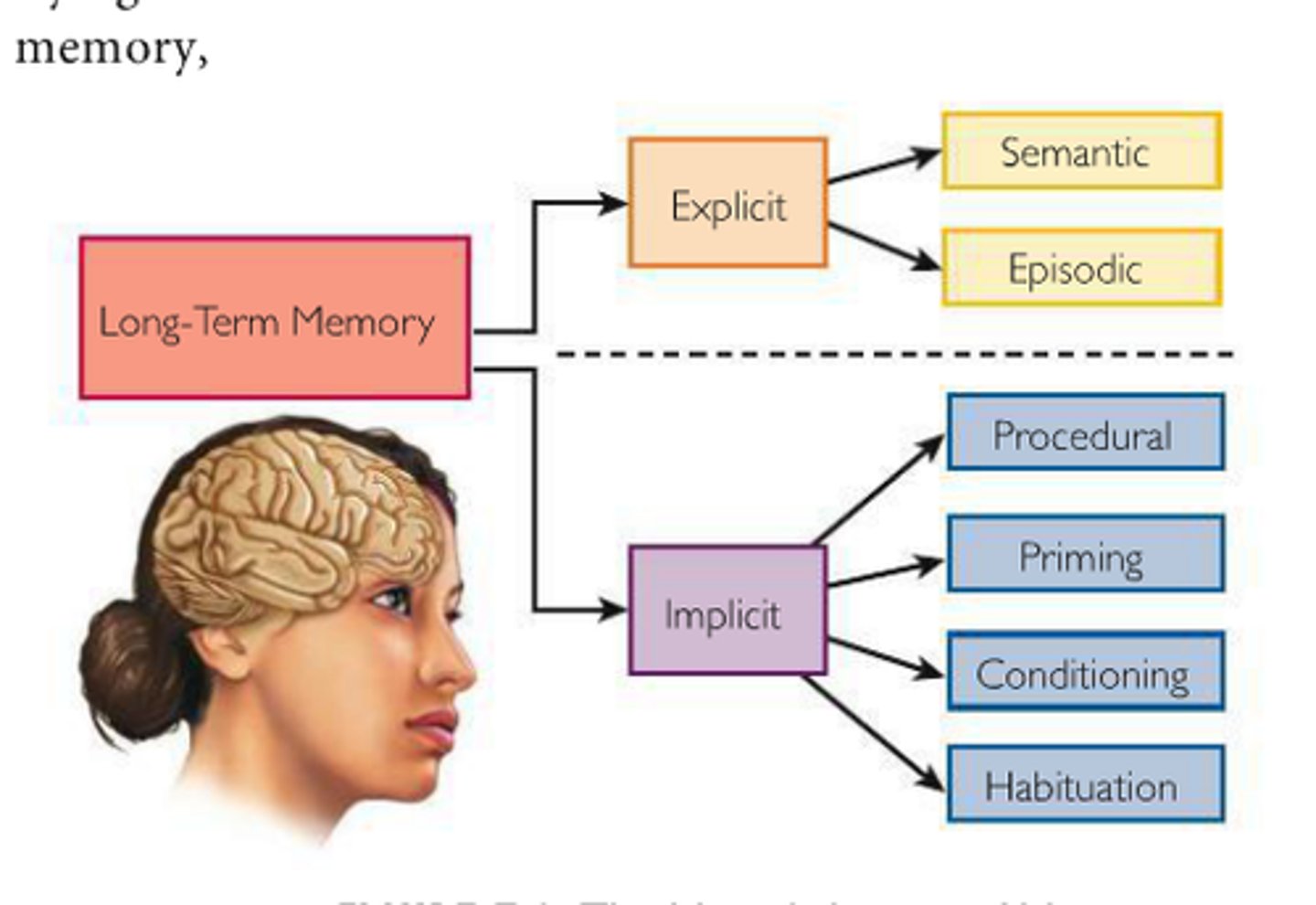
Declarative (explicit) memory
type of long-term memory containing information that is conscious and known
List the two main subdivisions of Declarative (explicit) memory.
1) Episodic (events)
2) Semantic (facts)
Episodic memory
Memory of specific personal events and experiences
Semantic (facts) memory
Memory of general facts, concepts, and knowledge
Semantic vs Episodic: Which is context-free?
semantic
Semantic vs. Episodic: Which is personal and contextual?
episodic
Non-declarative (implicit) memory
retention without conscious recollection of learning the
skills and procedures to do things
Perceptual priming (Perceptual learning)
prior encounter with a stimulus unconsciously improves the ability to identify or process it later
Example of perceptual priming
Image identification
Image identification (priming)
After repeatedly being shown a degraded or incomplete image, a person will be able to identify it faster and more accurately on subsequent viewings, even if they don't remember seeing the specific image before
Procedural memory/motor skills
Type of long-term, implicit memory that allows people to perform tasks without conscious thought
The "how-to" memory that stores learned skills, which are executed automatically through practice and repetition

Example of procedural memory
Riding a bike
Typing
Associative learning
Process where an individual learns to connect two stimuli or a stimulus and a response, allowing them to predict future events and guide their behavior
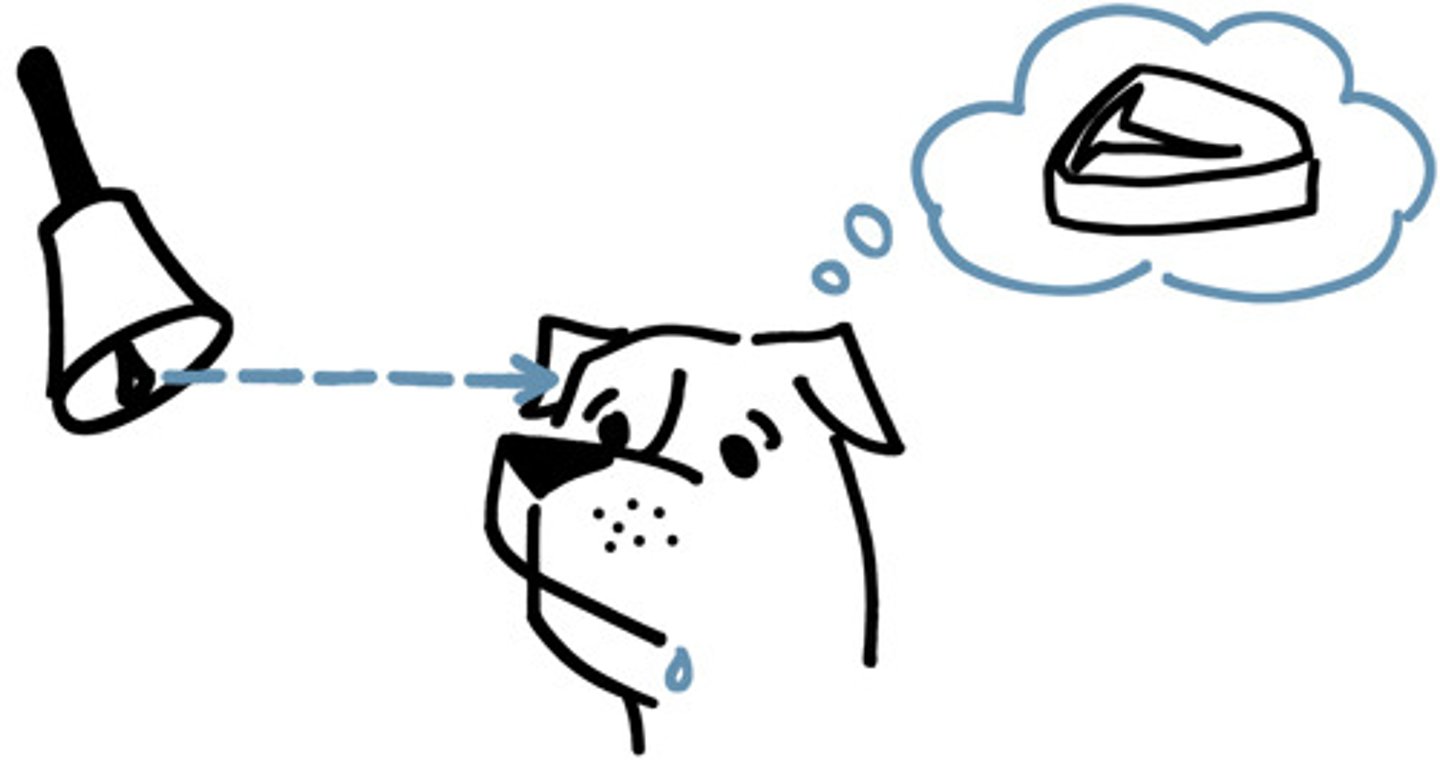
List two examples of associative learning.
1) Classical conditioning
2) Operant conditioning
Classical conditioning
An automatic, unconscious response becomes associated with a specific stimulus
(Neural stimulus paired with Unconditioned stimulus to become Conditioned stimulus to elicit a Conditioned response)
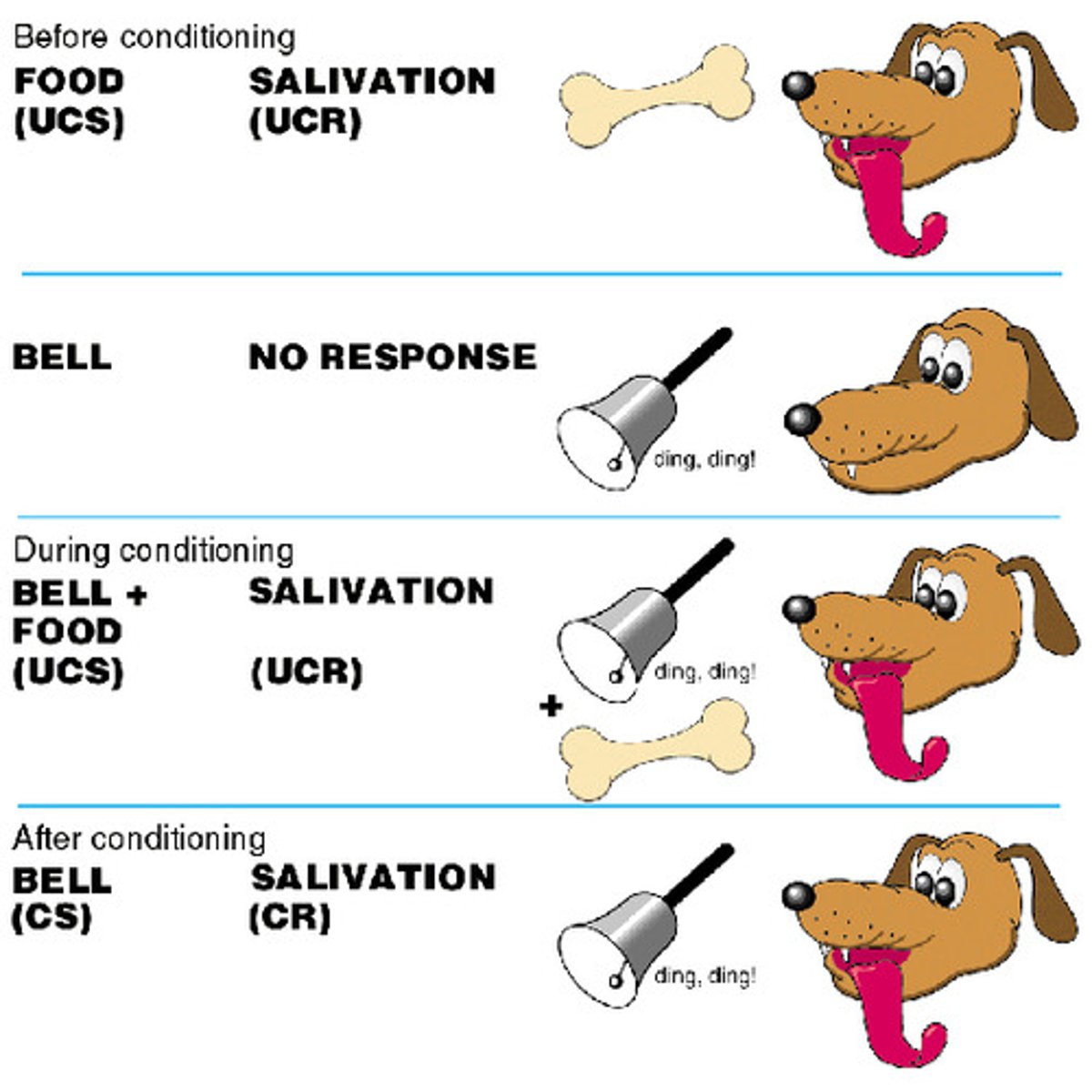
Operant conditioning
Learning occurs through the consequences of a behavior.
Actions followed by reinforcement become more likely to be repeated, while those followed by punishment become less likely.

Non-associative learning
Fundamental form of learning involving a change in a response to a single stimulus upon repeated exposure
Associative learning -> one stimulus or multiple stimuli?
multiple stimuli
Non-associative learning -> one stimulus or multiple stimuli?
one stimulus
List the two main types of non-associative learning.
1) Habituation
2) Sensitization
Habituation
response to a repeated stimulus decreases
Sensitization
response to a repeated stimulus increases
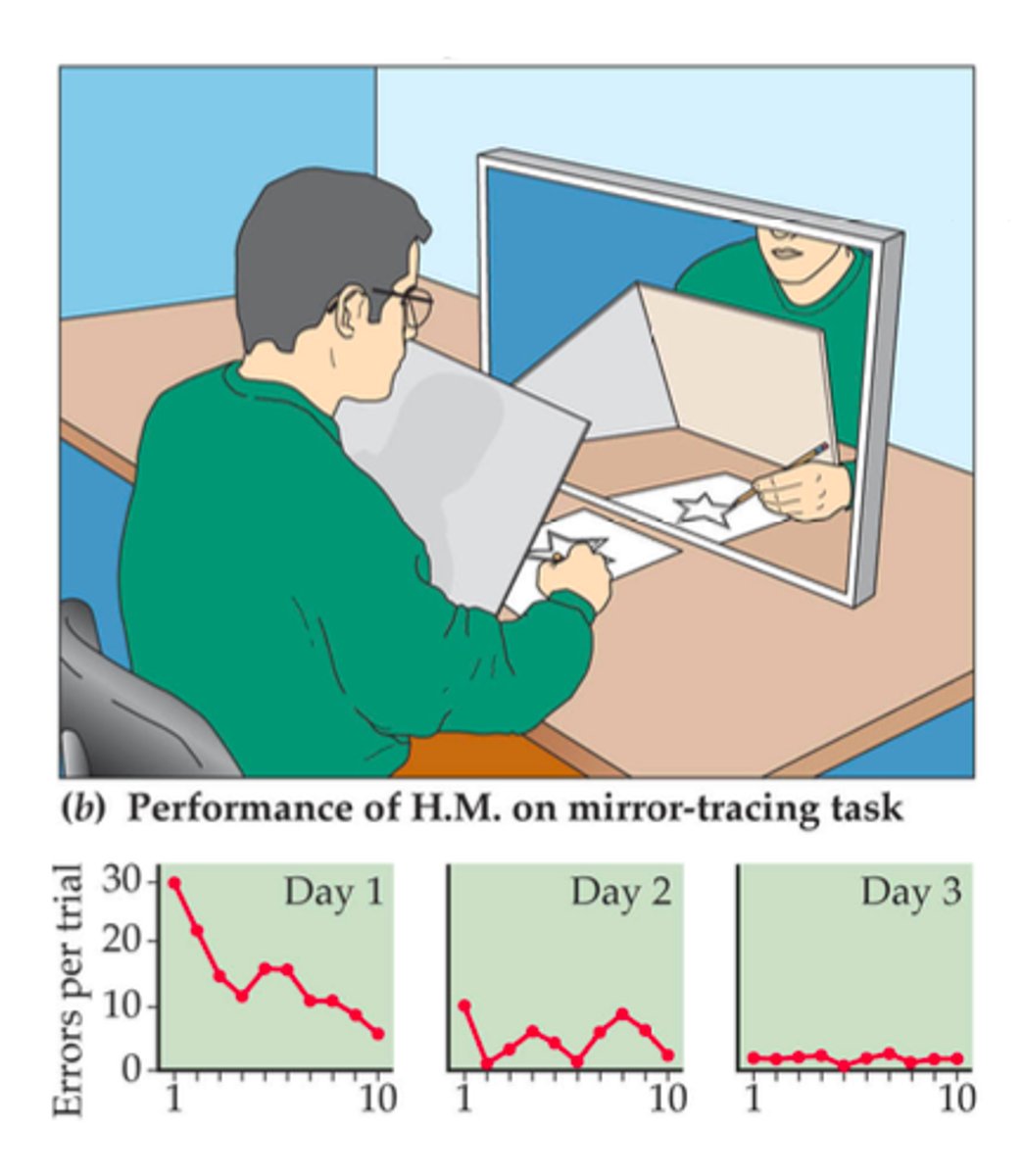
H.M. 1953
bilateral medial temporal lobe removal
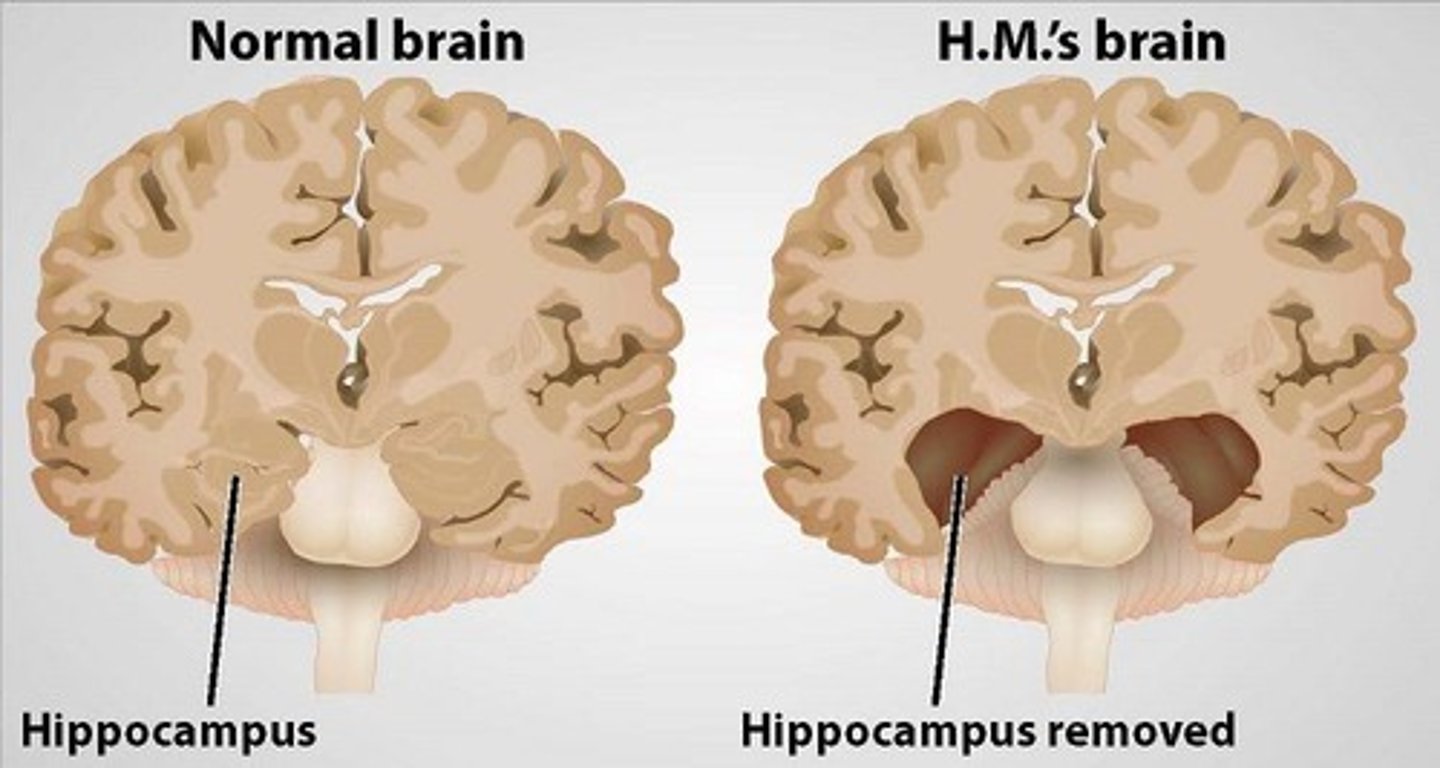
What could H.M. still learn (and retain)?
1) New motor skills
2) Perceptual learning
3) Working memory
4) Classical conditioning
Which brain area corresponds to Declarative Memory (Facts, Events)
Medial Temporal Lobe
Medial Temporal Lobe
Crucial brain region located on the inner surface of the temporal lobes that is essential for memory, especially for forming new long-term, declarative memories for facts and events
Includes the hippocampus, the amygdala, and the parahippocampal gyrus, and plays a vital role in memory functions like encoding, consolidation, and retrieval
Hippocampus and Spatial Memory
Helps form a mental/cognitive map of an environment, which is crucial for navigation
Place cells
fire when an organism is in a specific location
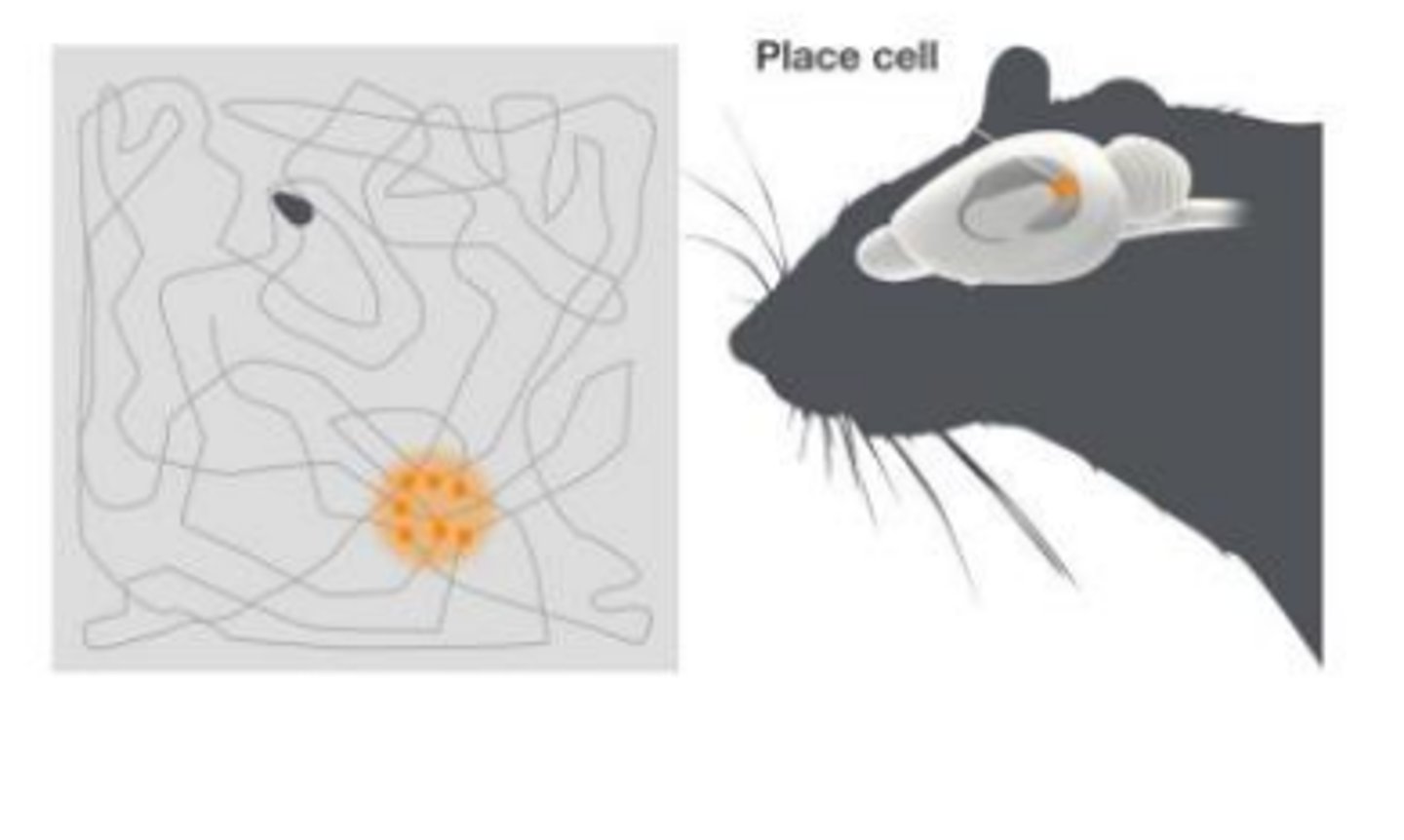
Where are place cells located in the brain?
Hippocampus
Grid cells
provide a coordinate system with a hexagonal grid-like firing pattern that helps with navigation and distance estimation
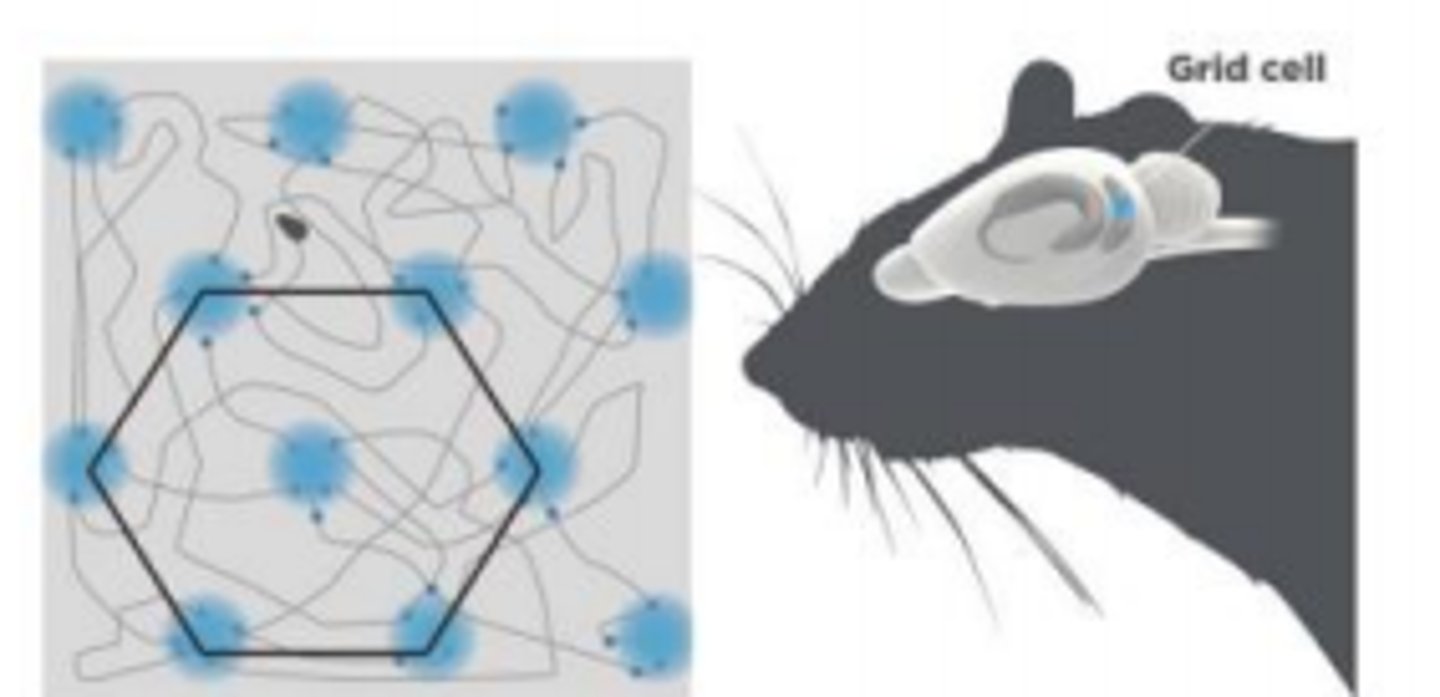
Where are grid cells located?
Entorhinal cortex (near the hippocampus)
Posterior Hippocampus and Spatial Memory
The posterior hippocampus is the region of the brain that stores a spatial representation of the environment
Studies on London taxi drivers show that the ____________________ __________________________ is enlarged in experienced drivers compared to non-drivers
posterior hippocampus
The longer a taxi driver has been licensed . . .
the larger their posterior hippocampus tends to be
Which brain area corresponds to Procedural Memory (Non-declarative)?
Basal ganglia
Which brain area corresponds to Classical Conditioning (Non-declarative)?
Cerebellum
Which brain area corresponds to Perceptual Memory? (Non-declarative)
(Visual and Temporal) Cortex
Cortex and Perceptual Memories
Perception vs Memory
Perception
immediate processing of sensory information
Recall
retrieval of stored information