Fundamentals 2
1/52
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
53 Terms
Diabetes and skin health
High glucose causes stiff arteries leading to poor perfusion. Decreased leukocyte function impacts healing. Diabetic neuropathy-delayed care. FEET HEALTH
Nutrition and Skin health
Protein: essential requirement for skin healing, in pressure injuries 30-35 kcals are necessary
Vitamin C: collagen synthesis
ZInc: cellular proliferation
Obesity: Moisture injuries, friction and shear forces, and fungal infections are more common. Fat tissue has low blood supply=risk of infection, hematomas, venous ulcers
Evisceration
Definition: medical emergency where internal organs protrude through a wound. Often after abdominal surgery
RISK: poor wound healing (obesity, malnutrion), steroid use, increased ab pressure, coughing, etc
NURSE: NOTIFY PROVIDER IMMEDIATLY, cover area in wet saline gauze
Moisture related skin damage
Often Incontinence associated dermatitis (stool or urine) or Intertriginous Dermatitis (skin folds, may develop into fungal)
DX: BLANCHES.
TX: use dimethicone barrier wipes and keep area dry, separate folds w pillow case
Smoking and wound healing
Smoking causes vasoconstriction=poor perfusion
Causes: Tissue hypoxia
Primary Intention, secondary, and tertiary
Primary: Wound edges are approximated, so can be closed with sutures or staples EX: surgical incisions
Secondary: would edges are not approximated, heals w granulation from the bottom up-skintears/scrapes
Tertiary intention: wound kept open or reopened due to infection/swelling. Closed later
Staging Pressure injuries
Stage 1: non-blanching redness
Stage 2: Partial skin loss, exposed DERMIS
Stage 3: full thickness loss, ADIPOSE TISSUE EXPOSED
Stage 4: full thickness and tissue loss BONE exposed
Unstageable: Covered in eschar or slough so cant see the bed
Deep tissue: unstagable, non blanchable purple discoularation
Lab Values associated with delayed wound healing
-Low platelets, Hgb, albumin
-Elevated WBC, glucose, bun and creatine
Skin cancer:
Malignant melanoma: existing mole that bleeds/changes shape
Basel Cell: most common, pearly white bump
Squamous cell: darker skin tones, firm red scaly patch
Left vs Right Heart Failure
Left: LUNGS-fluid backs up into the lungs, crackles, bloody sputum, orthopnea, signs of poor perfusion
Right: Fluid backs up in the BODY causing edema, weight gain, JVD, ascites
Cardiac output
Amount of blood that leaves the ventricles in one minute
Calculated by Stroke volume (volume of blood ejected each beat)x Heart rate
COMPENSATION: decreased stroke volume increased heart rate
Stroke volume- Detailed
Preload: amount in ventricle during diastole (stretch)
Afterload: resistance the ventricle has to overcome to push blood out (squeeze)
Contractility: force of contraction
Electrical conduction
SA node→atrial contraction→AV node→Bundle of His(along the septum)→Right/Left bundle branches→purjinkie fibers →ventricular contraction
Chest pain- respiratory vs heart vs musculoskeletal
Heart: pressure, sqeezing/burning sensation that is elevetated by rest. Spreads to neck and upper extremeties
Respiratory: sharp and stabbing, worse when you inhale. local and mostly unilateral worse when lying down
Musculoskeletal: Achy, sore, tender to touch. Local to ribs/muscles, hhurts with deep breaths and palpation
s4 vs s3
S3- from over filling ventricles, normal in younger than 30 active adults, HF in older
s4- non-compliant ventricles
Murmurs
Swishing noise from turbulent flow through valves
Systolic: between S1-s2, caused from mitral/tricuspid not closing all the way or aortic/pulm not opening all the way
Diastolic: S2-next S1, caused from mitral/tricuspid not opening all the way or aortdic and pulm not closing all the way.
Deep Vein Thrombosis and PE
Cause: A clot forms in one of the deep veins
Assessment: pitting edema, warm to the touch
Risk factor: Reduced mobility, Dehydration, Increased viscosity of the blood, Venous stasis
PVeinD vs PAD
VEINY: Voluptuous pulse, Edema, Irregular sores, NO sharp pain(dull), Yellow/brown ankles
PADC: Pain when walking, Absent pulses and hair loss/shiny skin, Dependent Rubor, Cool
P wave measurement
P wave: less than .12sec
PR interval:
0.12-0.20 sec
QRS complex:
0.06-0.12
Qt interval
0.36-0.44
ST segment
0.005-0.150
PR interval Duration meaning
Too long=Heart block, likely AV
too short: AV node is bypassed, fast HR
QRS duration meaning
To wide: heartbeat did not og in ATRIA
T wave evaluation
Inverted: repolarization altered: PE, PI etc
Flat: decreased repolar current, HYPOKALEMIA
Biphasic: ischemia
Tall: HYPERkalemia
SS of decreased cardiac output
Symptoms: Palpitations, anxiety, diaphoresis, SOB, syncope, weakness
Signs: LOC, hypotension, tachycardic, tachypnea, urine output, cool skin, pallor
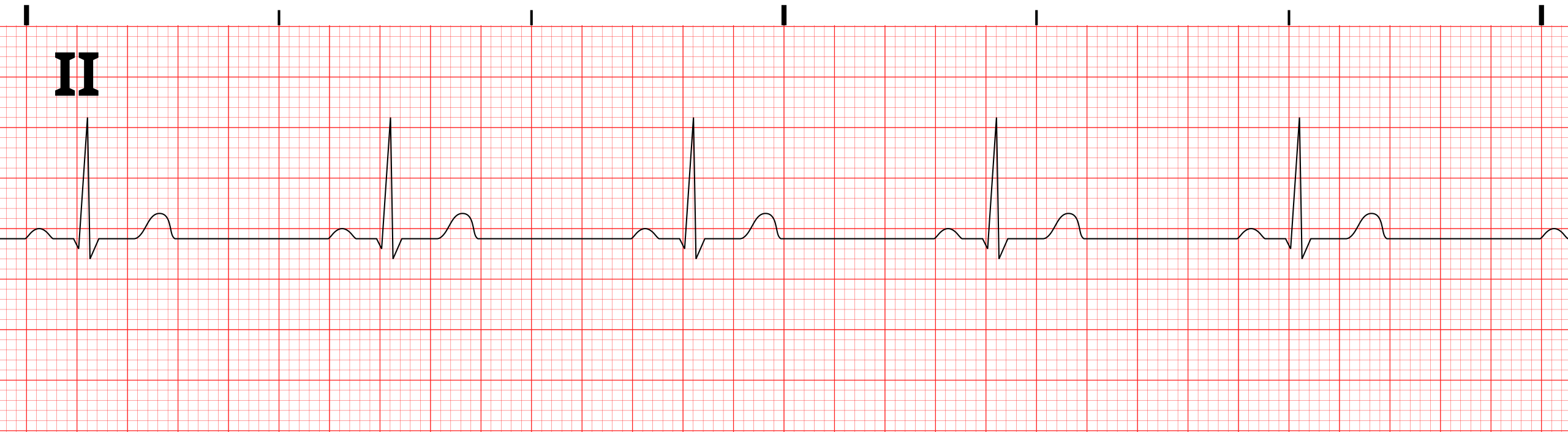
sinus brady cardia
CAUSE: hypoxia, hypothermia, well trained athlete
Symptoms: chest pain, hypotension, SOB, sweat
TX (only if symptoms); atropine
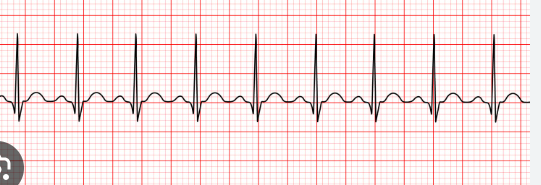
Sinus Tachycardia
CAUSE: fever, anemia, hypotension, PE< MI
TX: based on cause
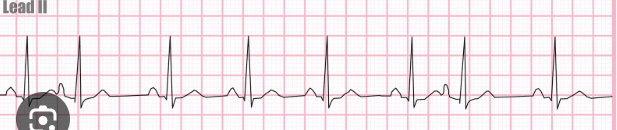
Premature atrial contraction
Cause: hypoxia, excessive stimulation, digitalis toxicity, CAD, infection
TX: common in older adults, don’t treat until symptomatic
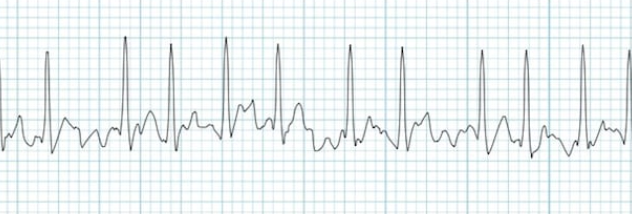
AFib
CAUSE: cardiomyopathy, pericarditis, HTN, valve disease, CAD< Pulmonary disease
SS: Rapid ventricular rate= compensation, CLOTTING atria quivvering=blood pools=clots
LOOK FOR NO P WAVES AND IRREGULAR RHYTHM
TX: anticoagulantsss
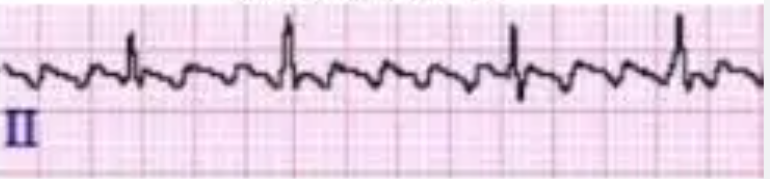
Atrial Flutter:
Cause: MI< severe mitral disease, Thyrotoxicosis, COPD, heart surgery
SS: SAW TOOTH, no p waves, no PR measurement, atrial pulse 250-300bm
TX: beta blockers, ca channel blockers, digoxin, Cardioversion if severe
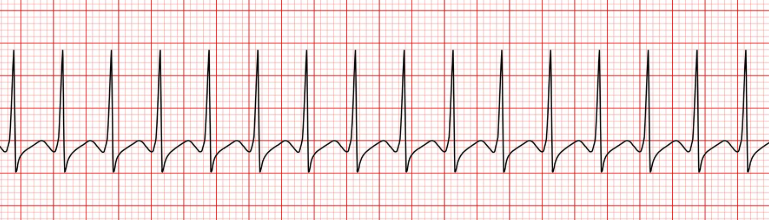
Supraventricular tachycardia
CAUSE: charge OG above the ventricles(Atria/av node)
TX: vagal stimulation, adenosene (pushed slowly) and cardioversion
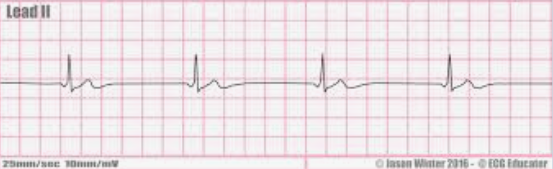
Junctional rhythm
CAUSE: charge within av node (40-60 bpm)
SS: Pwave absent or inverted
TX: symptoms, RED FLAG IF DROP IN BP/LOC
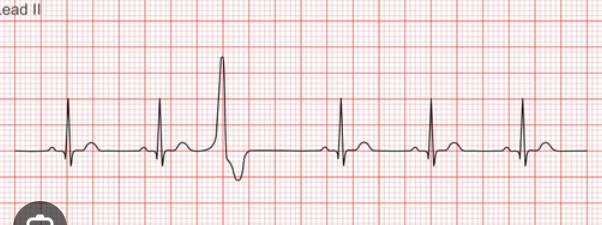
Premature ventricular Contraction
Cause: hypoxia, MI, electrolyte imbalance, EXCESSIVE STIMULANT (drug use/young people), HTN
SS: wide, early, and atypical qrs
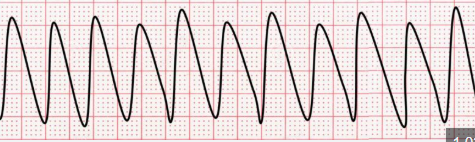
VTACH:
Ventricular rate greater than 120
CAUSE: hypovolemia, hypoxia, acidosis, hypokalemia, hypoglycemia, hypotermia, Cardiac tamponade, MI, PE
W pulse: amiodarone, electrolytes, cardioversion
W/O: CPR DEFIB AND EPINEPHRINE
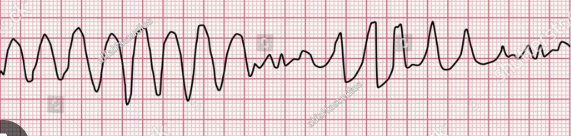
Torsade De Points
50% have symptoms
Cause: Hypomagnesemia, hypocalcemia, qt interval, anorexia
W/O pulse: CPR, Defib, Epinephrine=PREVENT WORSENING SYMTPOMS
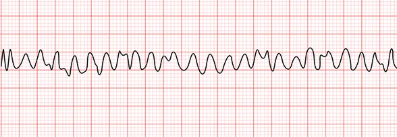
V-FIb
Cause: hypovolemia, hypoxia, hypo/hyperkalemia, hypothermia, MI, PE, cardiac tamponde
TX: Emergency, CPR defib

Pulseless electrical activity
WHY: electricity not strong enough to make a pulse or contraction
CAUSE: H&Ts (H-hypovolemia, hypoxia, hyper/hypokalemia, hypothermia) (T-tension pneuomothorax, cardiac tamponade, toxins, thrombosis)
TX: NO SHOCK, CPR