Organismal Ecology
1/123
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
124 Terms
What is the study of the distribution and the abundance of organisms and their interactions with other organisms and their physical environment?
ecology
What are factors that are nonliving, including resources like temperature, climate, light, water availability, and topology?
abiotic factors

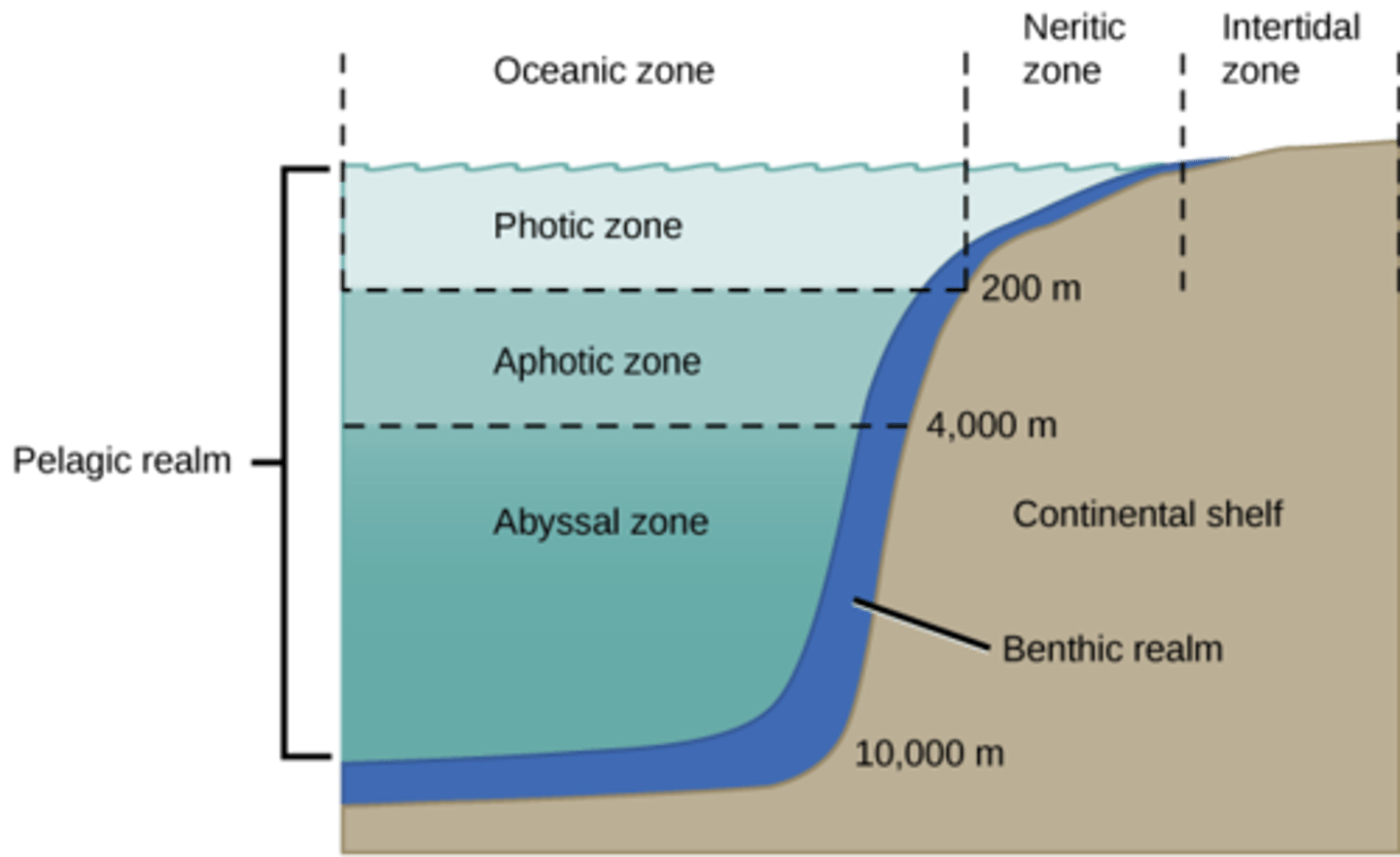
What is the zone in water has almost no light penetration?
aphotic zone
(Note: only animals and other heterotrophs exist here)
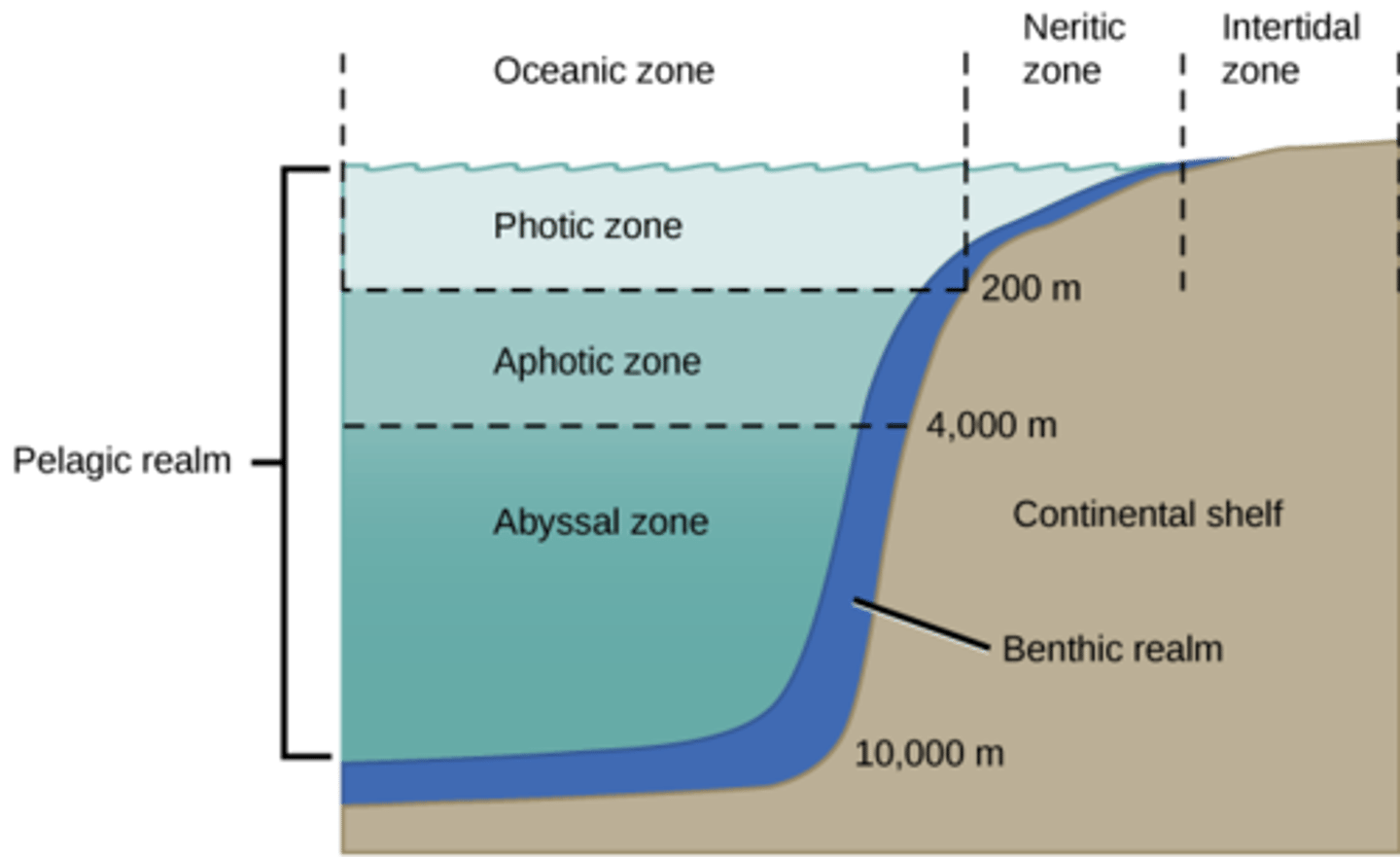
What is the zone in water where light penetrates?
photic zone
(Note: all aquatic photosynthesis occurs in this zone)
What are the factors that include all living things directly or indirectly influencing the life of the organism?
biotic factors
What factors are responsible for limiting the geographic distribution of species?
abiotic and biotic factors
What is a group of individuals of the same species living in the same area?
population
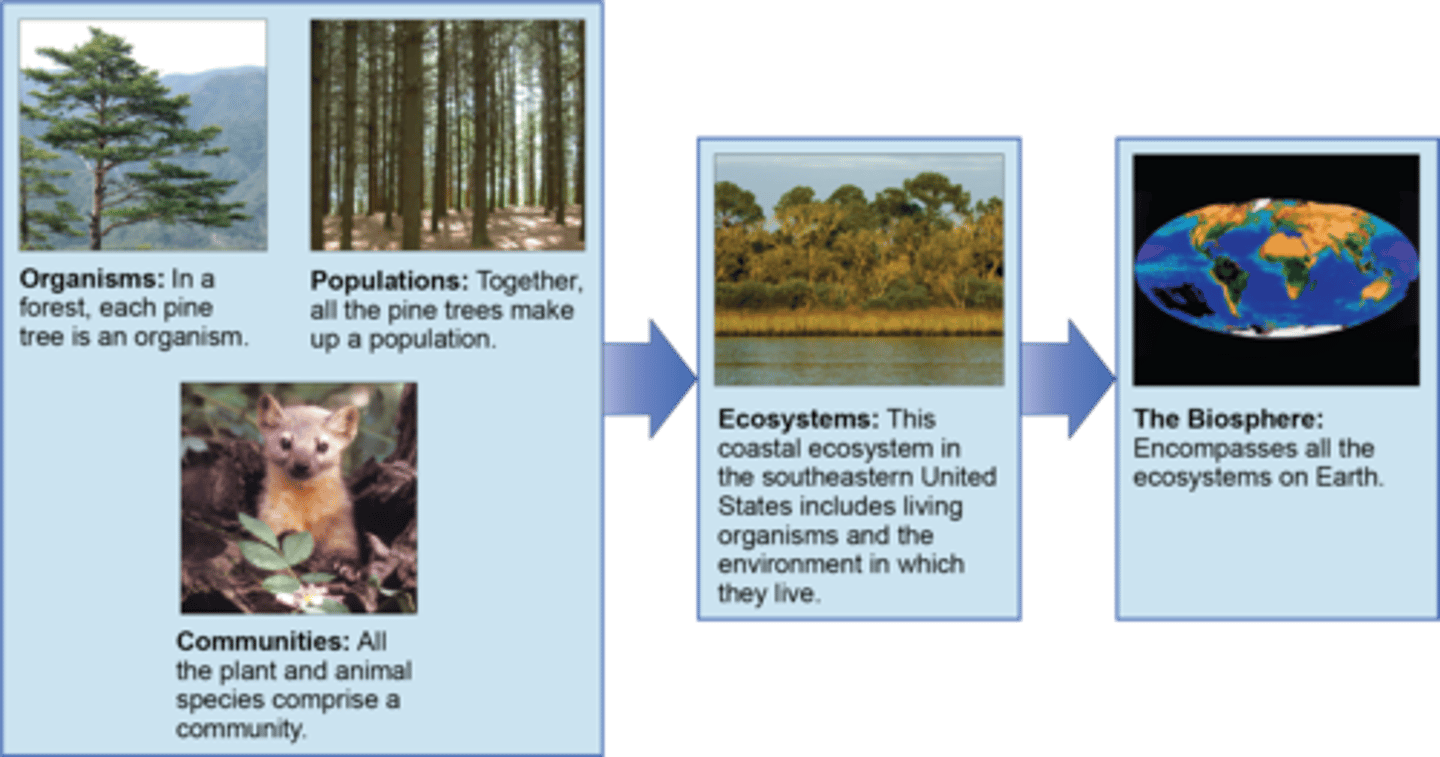
What is a group of populations living in the same area?
community
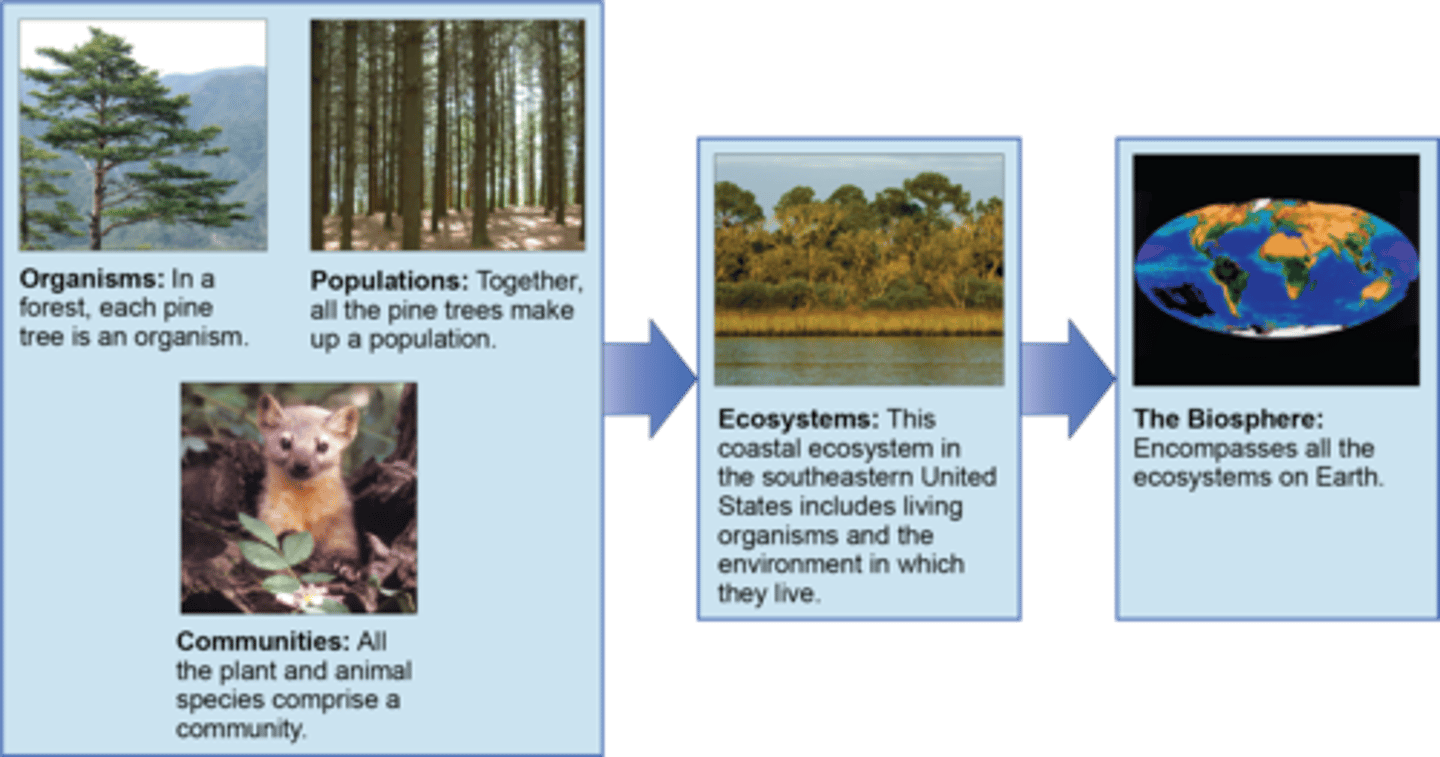
What organization describes interrelationships between organisms in a community and their physical environment?
ecosystem
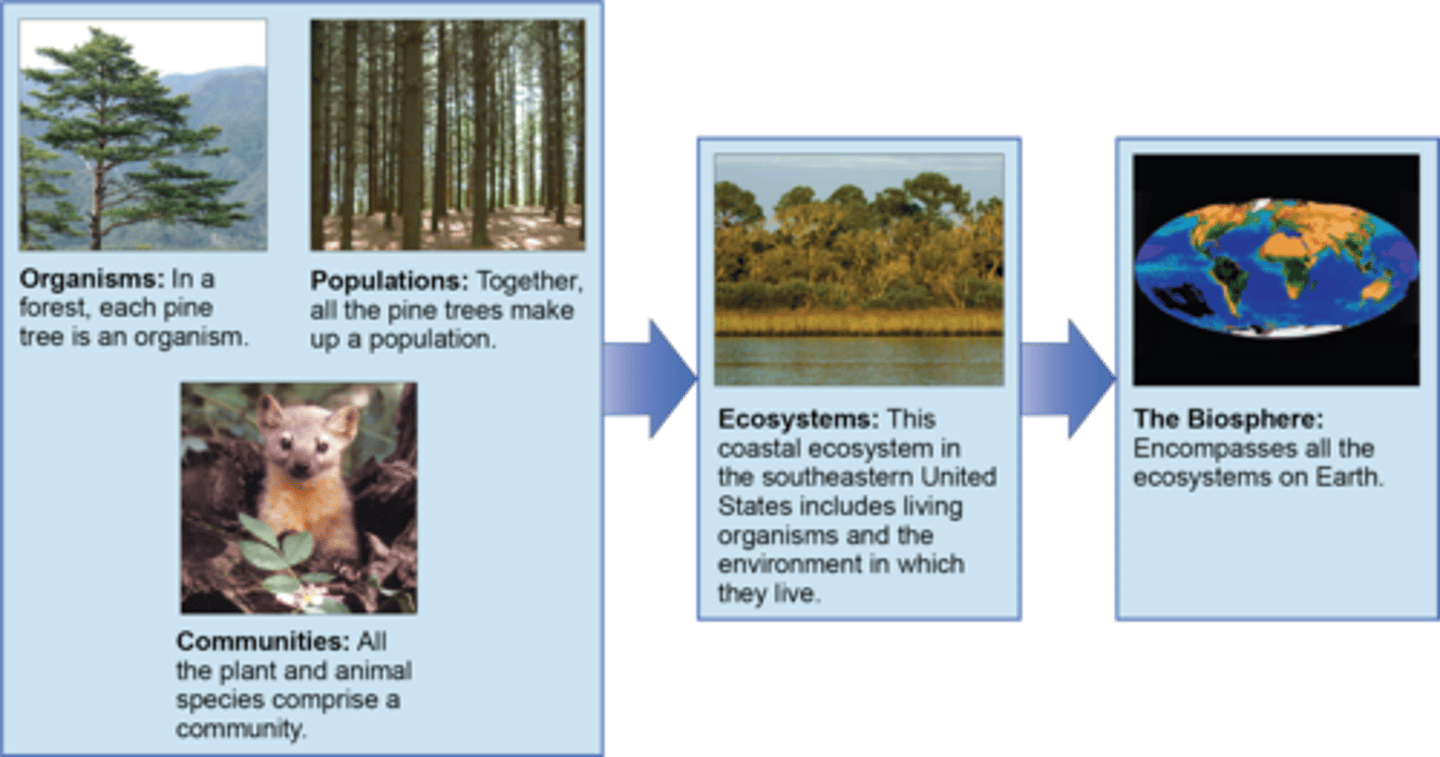
What is the combination of all the ecosystems of the earth?
biosphere
(Note: also includes atmosphere, hydrosphere, lithosphere, and geosphere)

What is a type of place where an organism usually lives?
habitat

What factors are present in a habitat?
1. other organisms
2. physical environment
3. chemical environment)
What occupation describes all the biotic and abiotic resources in the environment used by an organism?
niche

How many species can occupy the same niche?
only one
(Note: no two species can occupy the same niche indefinitely)
What is the study of the growth, abundance, and distribution of populations?
population ecology
What is the total number of individuals in a population (N)?
size

What is the total number of individuals per area or volume occupied?
density
What term describes how individuals in a population are distributed?
dispersion

What are the 3 types of dispersions?
1. clumped
2. uniform
3. random

What is the description of the abundance of individuals of each age?
age structure
What factor changes the shape of the age graph?
reproduction
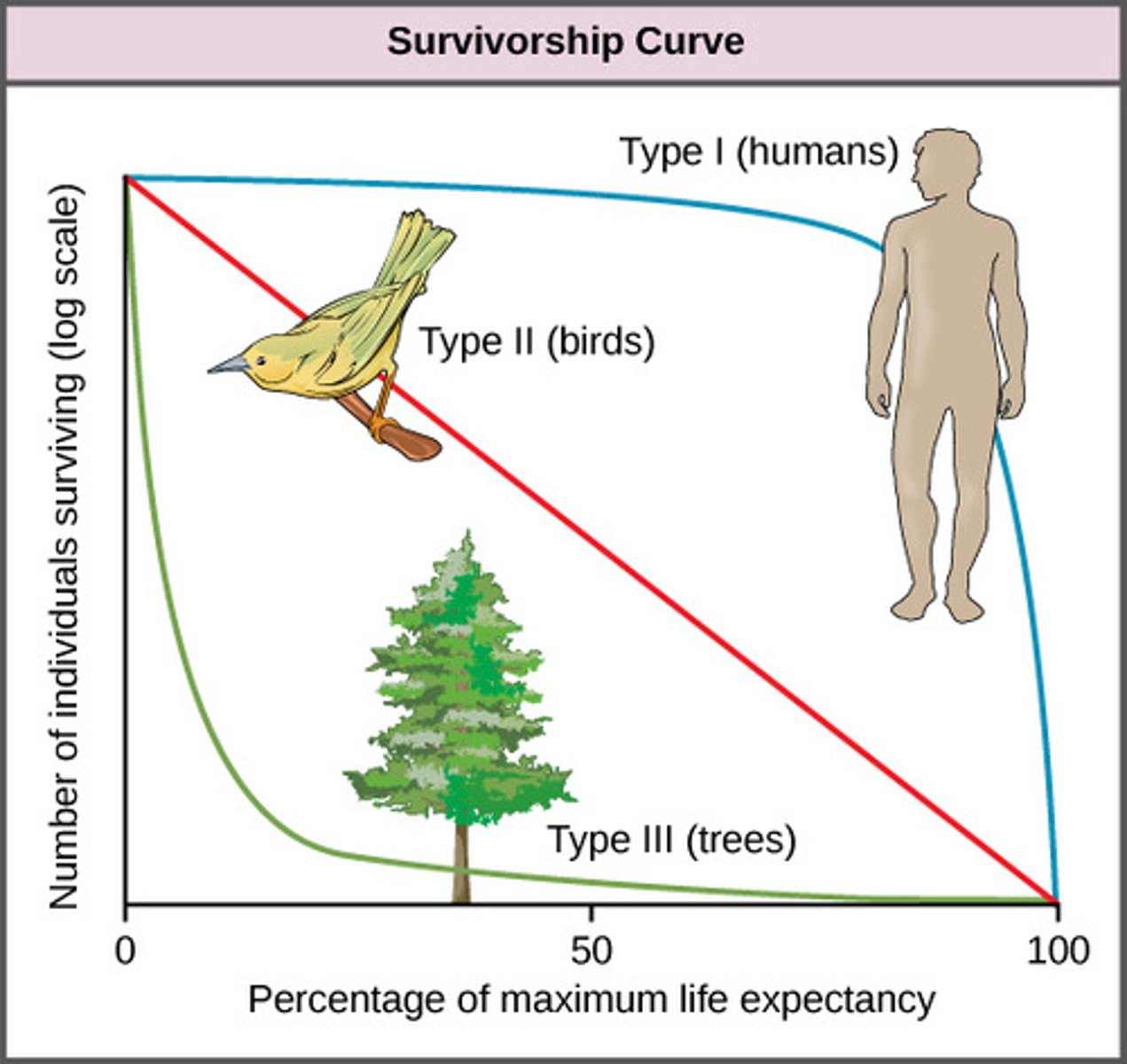
What representation demonstrates how the mortality of individuals in a species varies during their lifetimes?
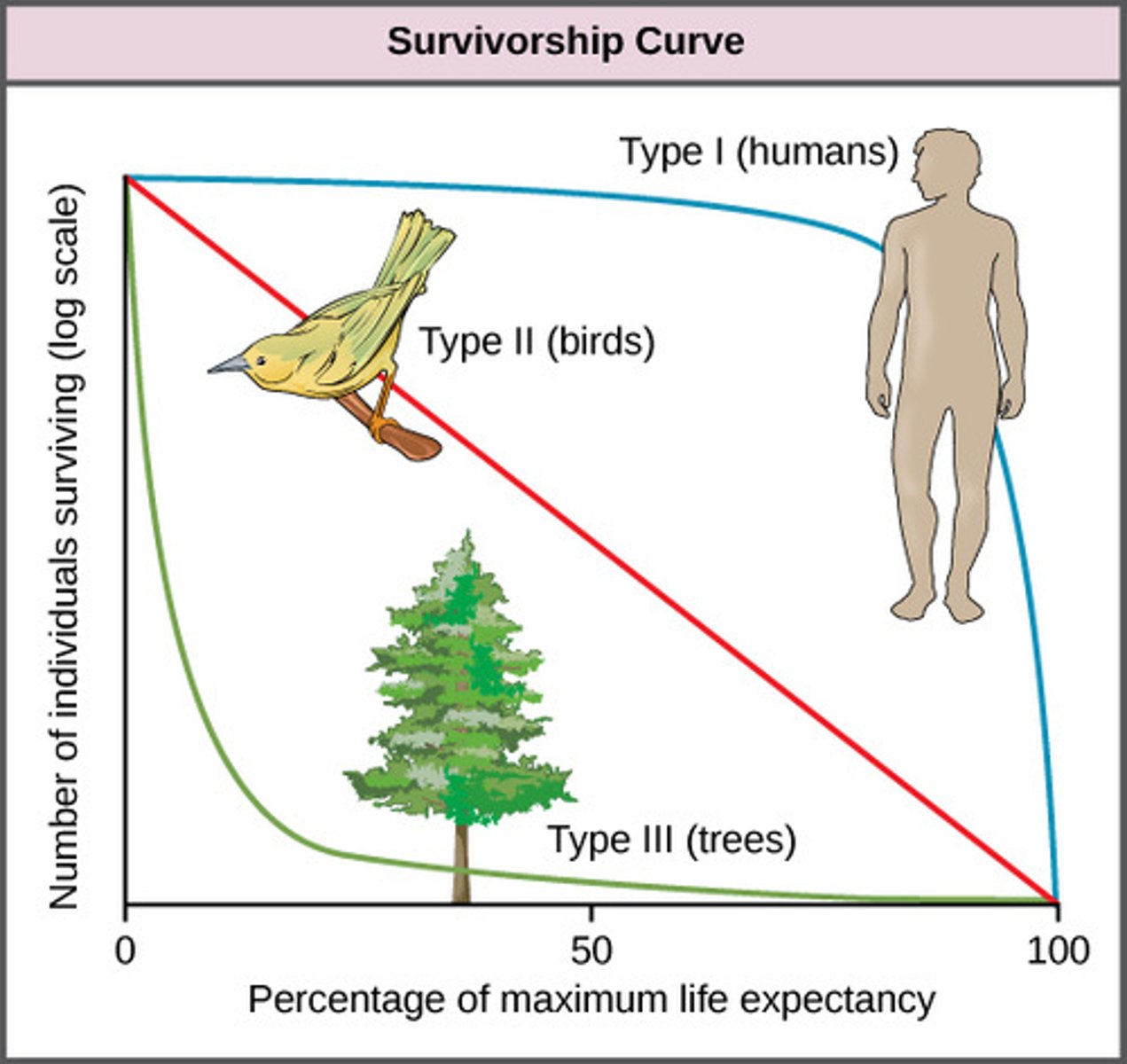
survivorship curve
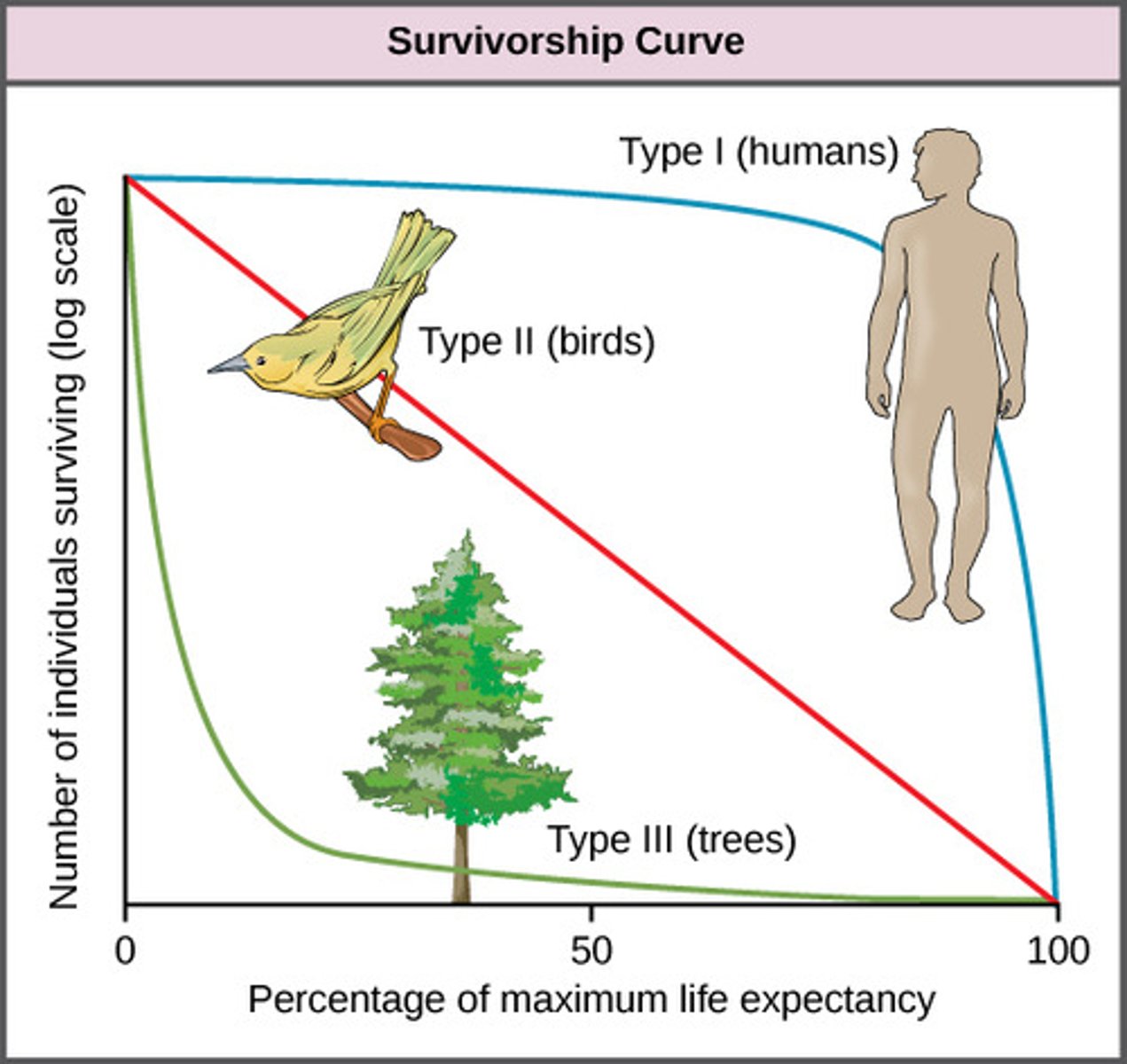
Which type of survivorship curve shows most individuals surviving to middle age but mortality increasing quickly in old age?
type I
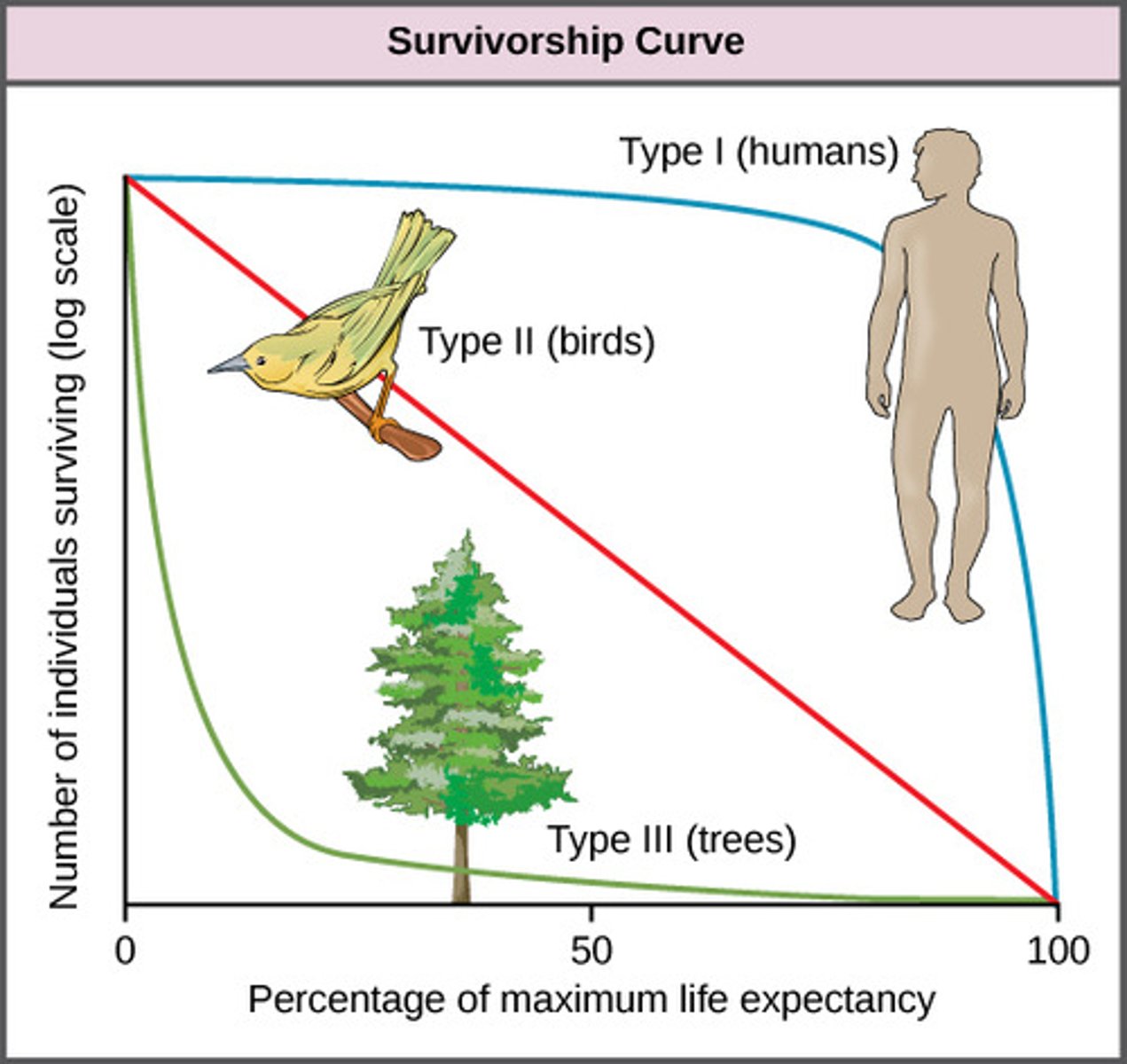
Which type of survivorship curve shows the probability of survival remaining constant and independent of age?
type II
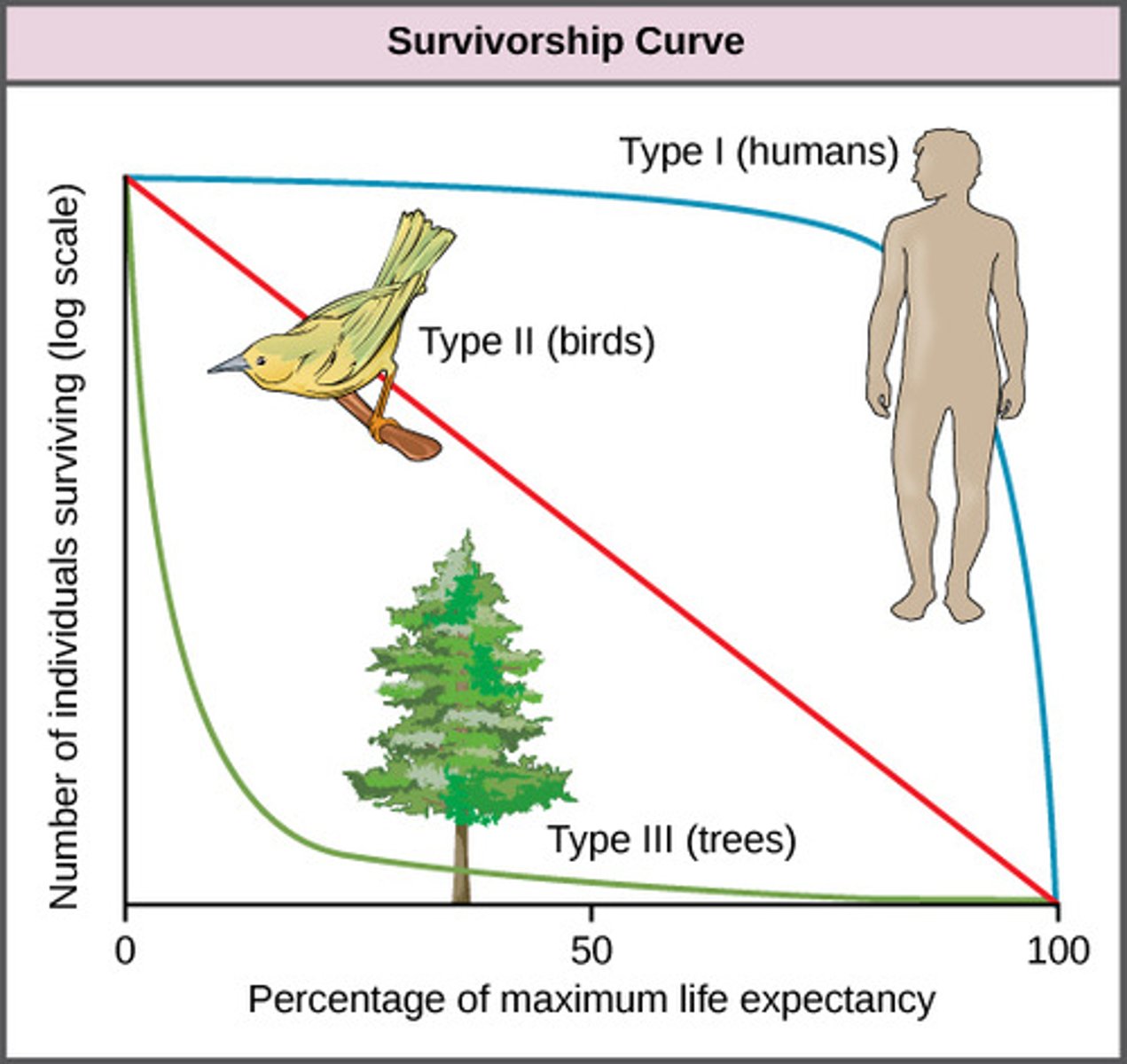
Which type of survivorship curve shows most individuals dying young, with a few surviving to reproductive age and beyond?
type III
What is the maximum growth rate of a population under ideal conditions (unlimited resources and no restrictions)?
biotic potential
What factors contribute to the biotic potential of a species?
1. age at reproductive maturity
2. clutch size (number of offspring produced at each reproduction)
3. frequency of reproduction
4. reproductive lifetime
5. survivorship of offspring that reach reproductive maturity
What is the maximum number of individuals of a population that can be sustained by a habitat?
carrying capacity (K)
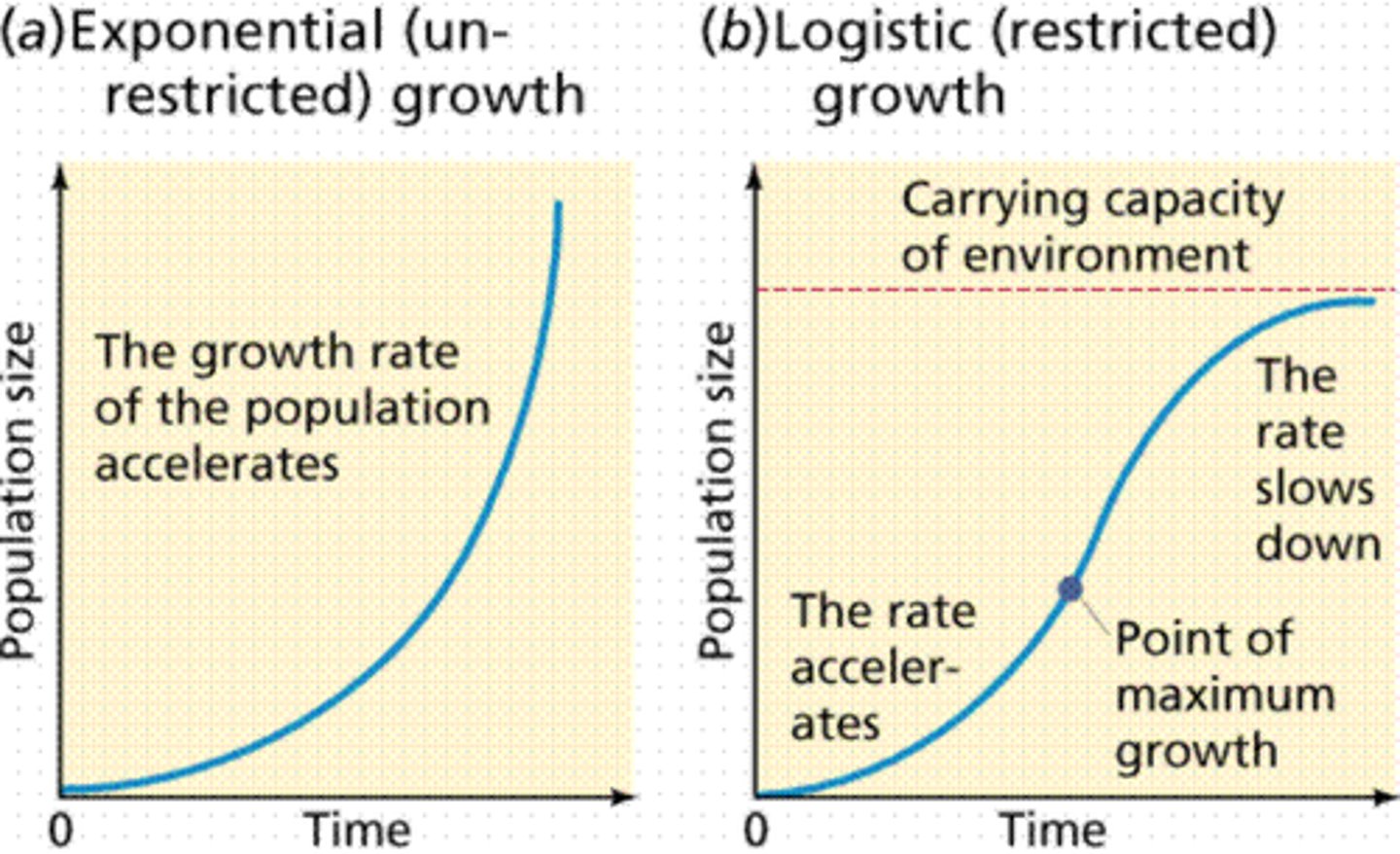
Which limiting factor becomes more intense as the population density increases?
density-dependent limiting factor
(Ex: competition, disease, parasites, predation, toxins)

Which limiting factor occurs independently of the density of the population?
density-independent limiting factor
(Ex: natural disasters or big temp changes)

What are the elements that prevent a population from reaching its full biotic potential?
limiting factors
What is the formula for the growth rate of a population?
r = (births - deaths)/N = b - m
What is the expanded version of the formula for the growth rate of a population?
∆N/∆t = rN = births - deaths = bN - mN
What term describes when the reproductive rate (r) is at its maximum (biotic potential)?
intrinsic rate
What process occurs whenever the reproductive rate (r) is greater than zero?
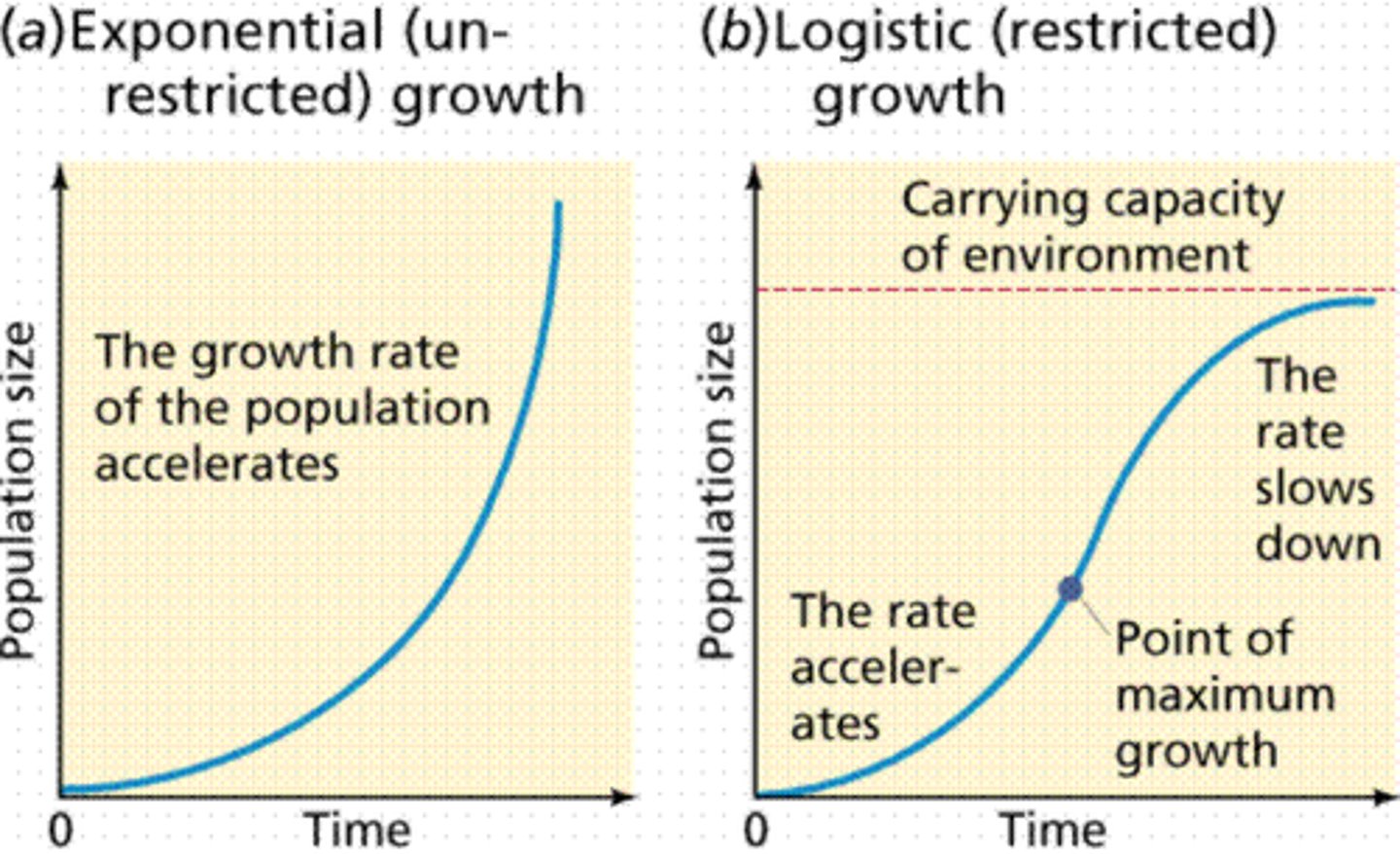
exponential growth
(Note this growth occurs when resources are unlimited)
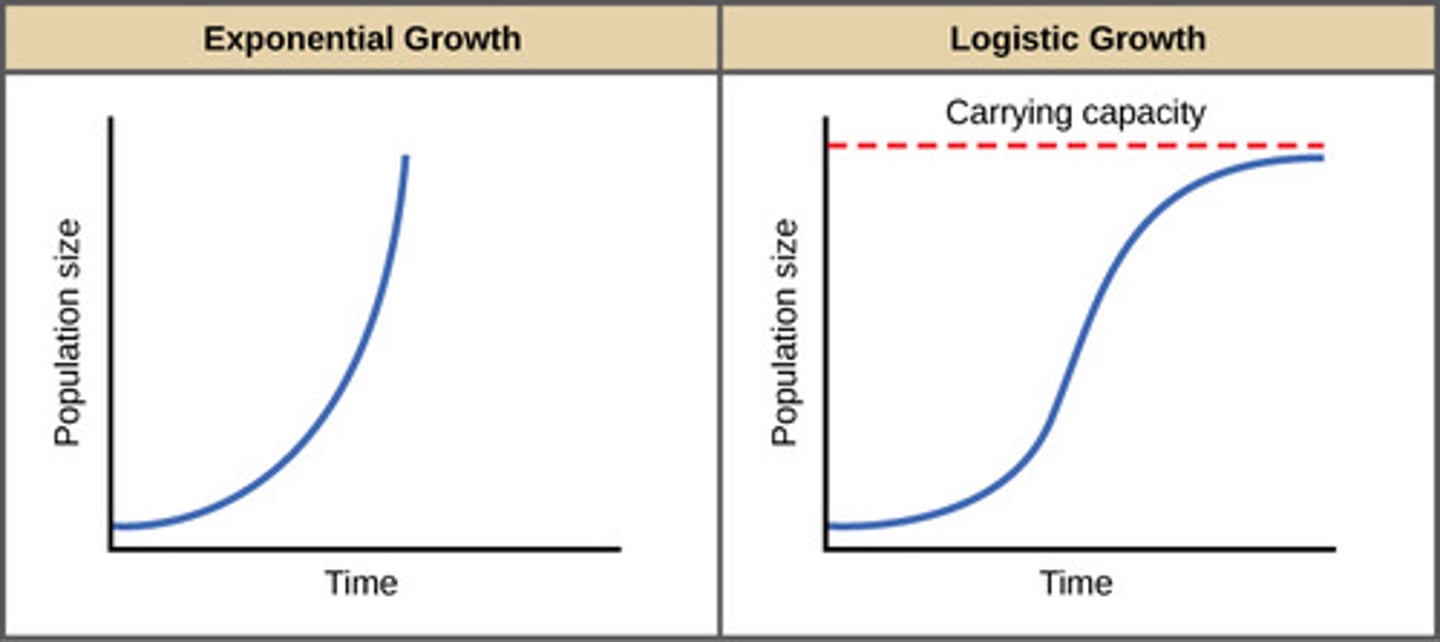
What shape of graph does exponential growth create?
j shaped curve
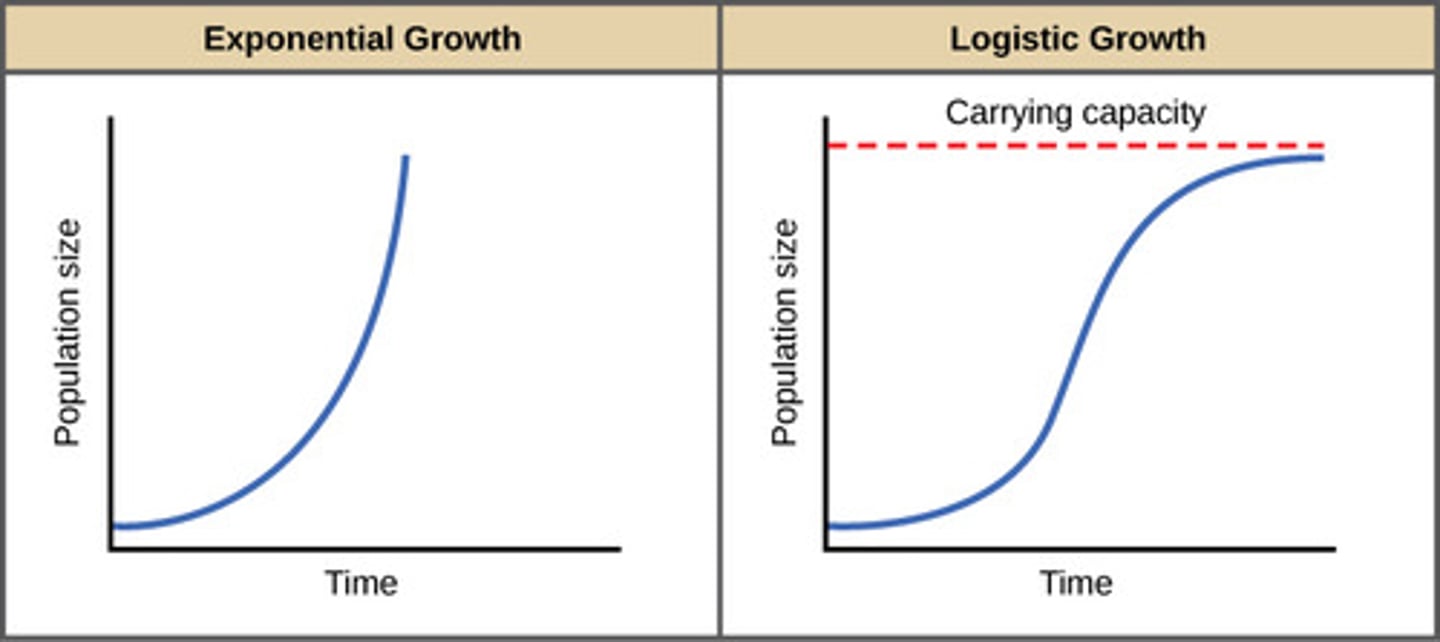
What process occurs when limiting factors restrict the size of the population to the carrying capacity of the habitat?
logistic growth

What is the equation for logistic growth?
ΔN /Δt = rN((K − N)/K)
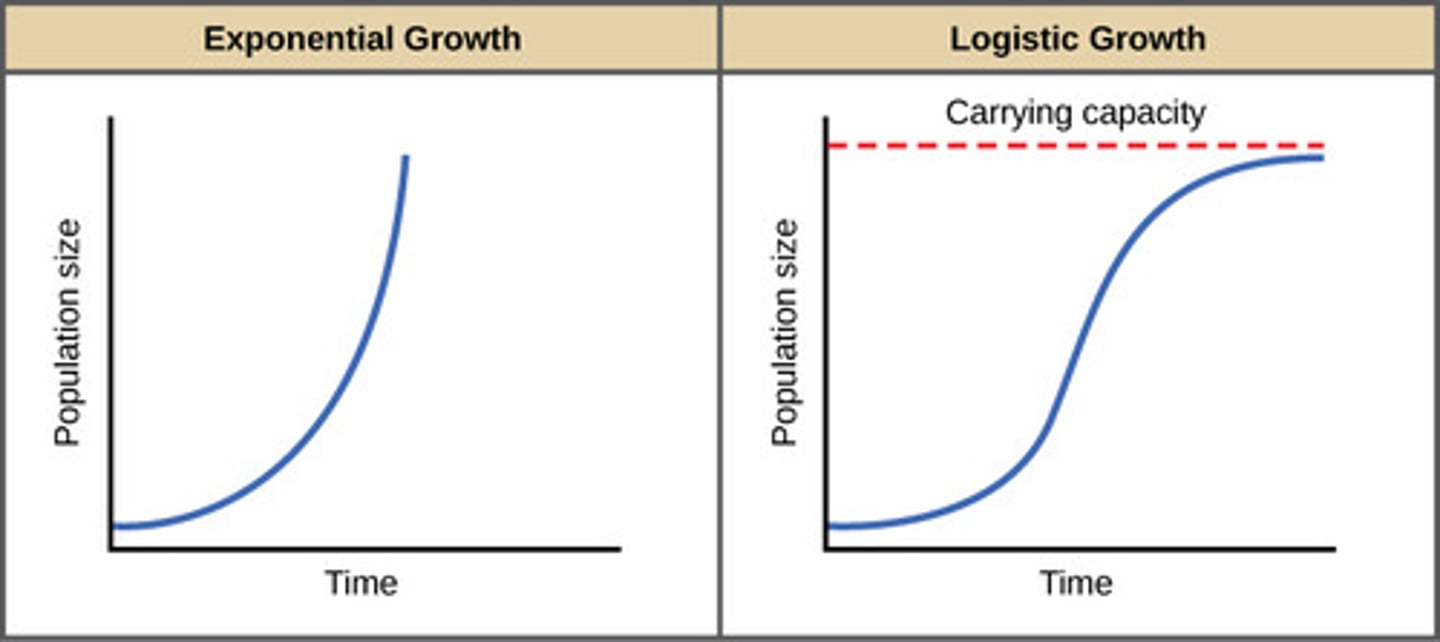
What value does the growth rate equal when the population size reaches the carrying capacity?
0
What shape of graph does logistic growth create?
s shaped curve
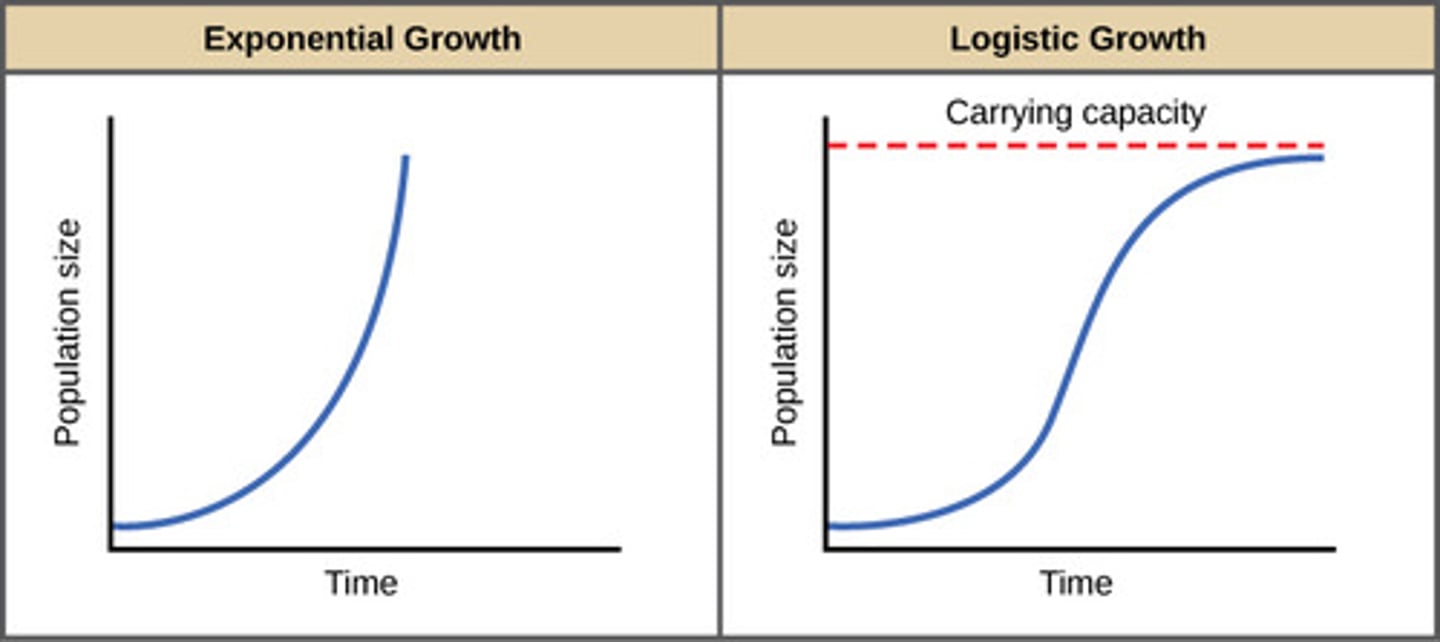
When does ZPG (zero population growth) occur?
birth and death rates are equal (r = 0)
What term describes a population size fluctuating in response to varying effects of limiting factors?
population cycle
(Note: may be caused by predator/prey relationships)
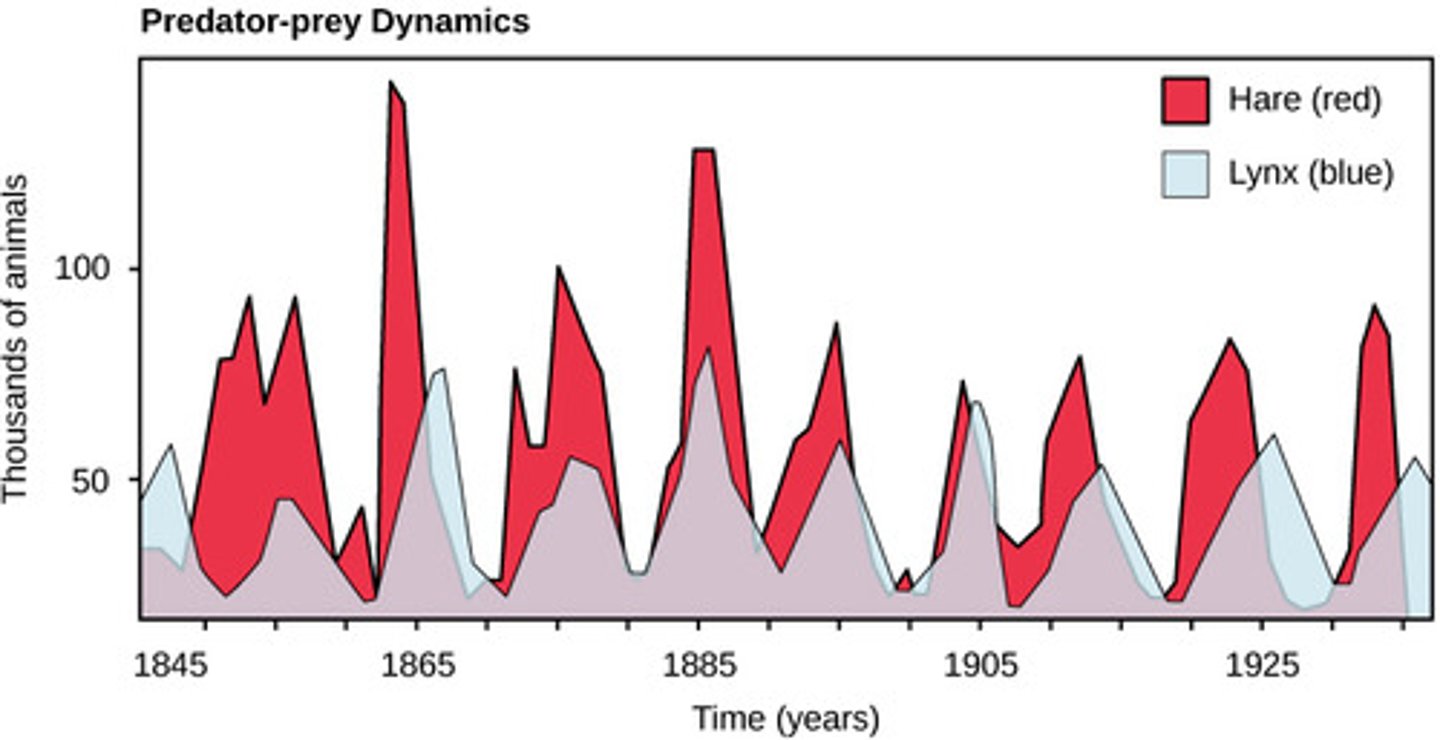
How do predator and prey population graphs relate?
they respond with delay to each other

Which type of population involves members with low reproductive rates and longer maturation times, having a roughly constant size?
K-selected population
(Ex: humans)

What type of survivorship curve do most K-selected species display?
type I
(Note: because of strong parental care)
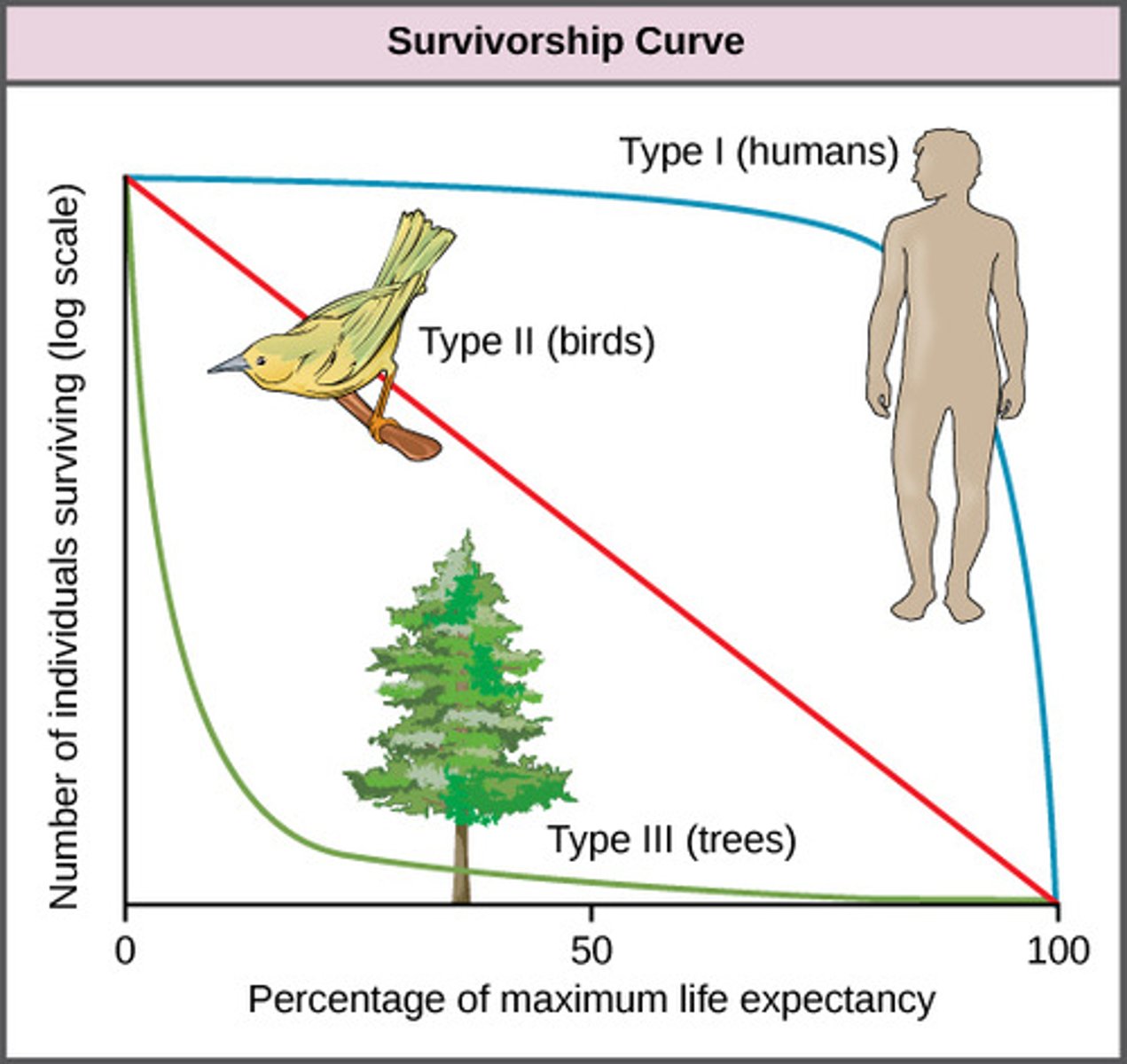
Which type of population involves members producing numerous offspring that are small and have fast maturation?
R-selected population
(Ex: bacteria)

In which environments are most R-selected populations found?
rapidly changing environments affected by density-independent factors

What type of survivorship curve do most R-selected species display?
type III survivorship curve
What are the 4 phases of microbial growth?
1. lag phase
2. exponential (log) phase
3. stationary phase
4. death phase
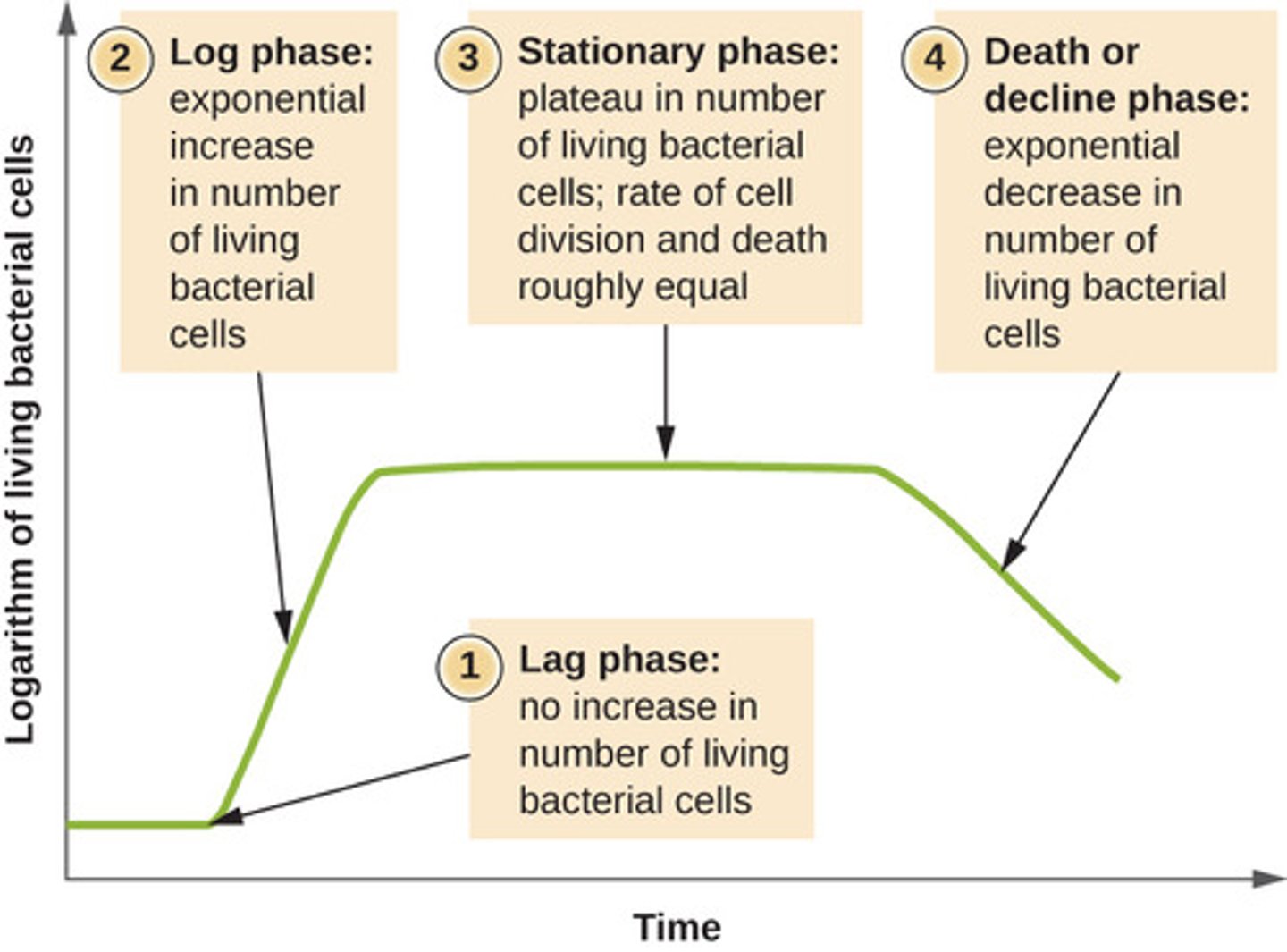
Which phase of microbial growth is characterized by bacteria adapting to growth conditions?
lag phase

Which phase of microbial growth is characterized by the exponential growth of the population
exponential (log) phase
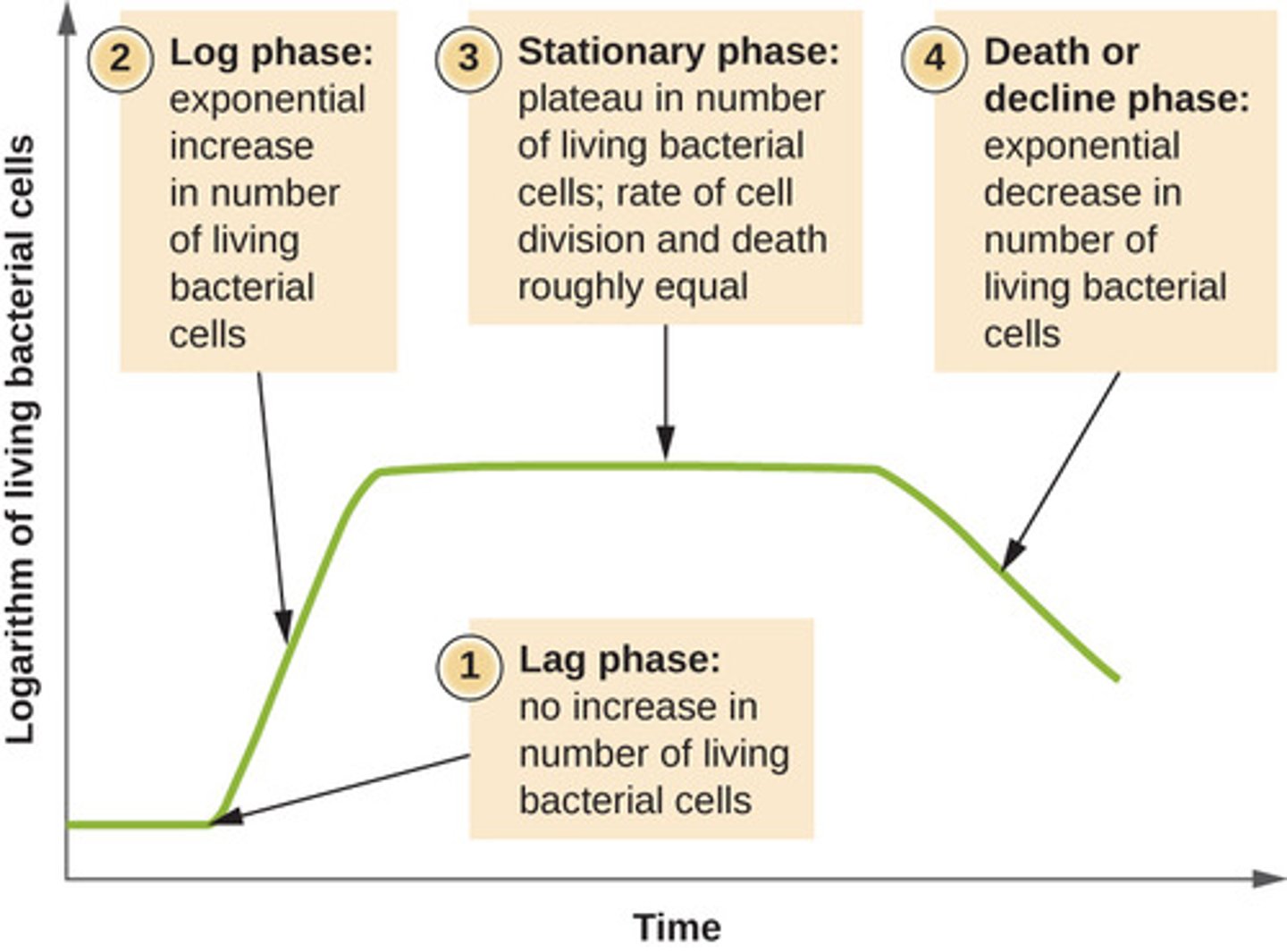
Which phase of microbial growth is characterized by the growth rate equaling the death rate due to growth-limiting factors?
stationary phase
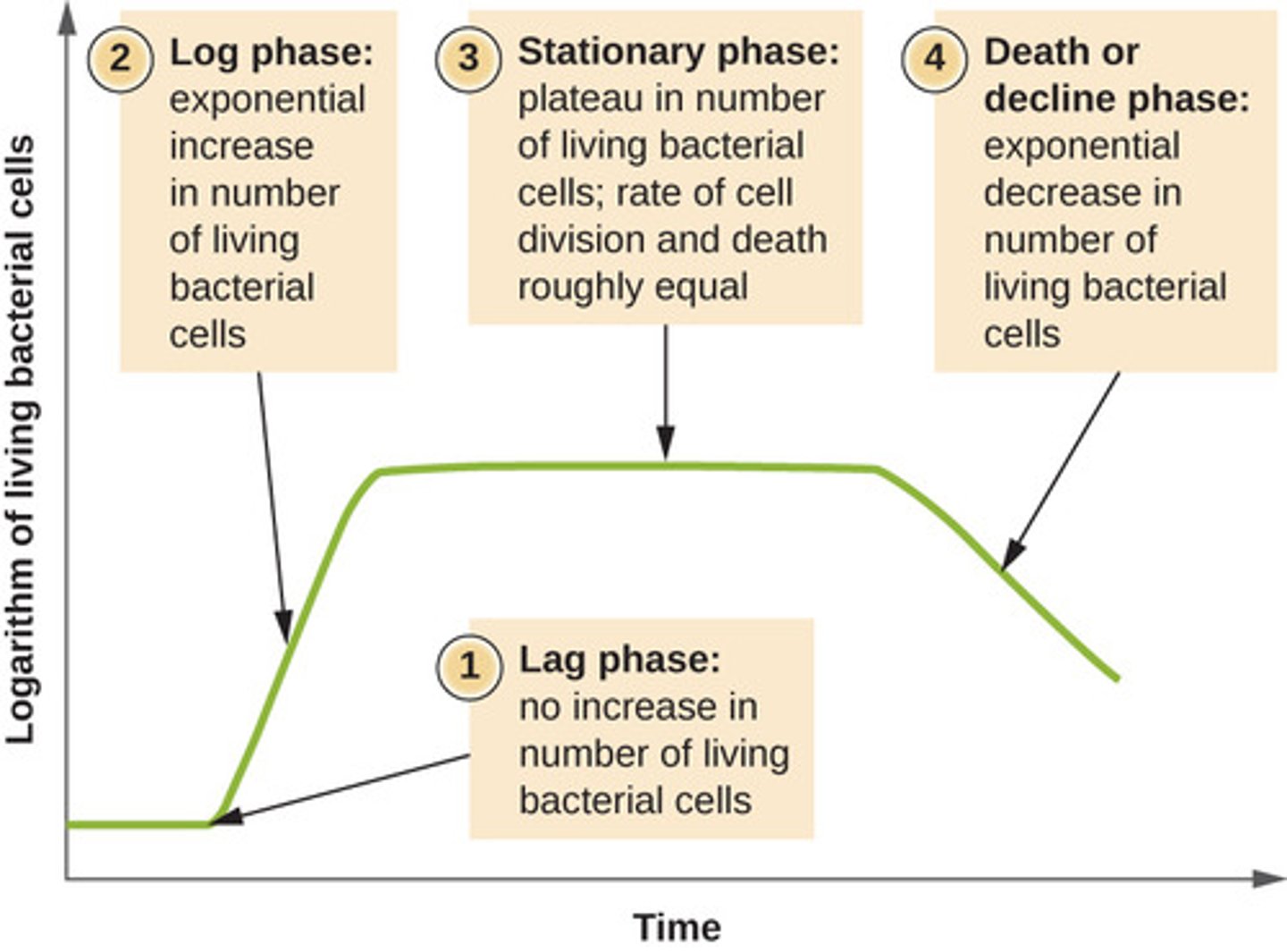
Which phase of microbial growth is characterized by the death of the population?
death phase
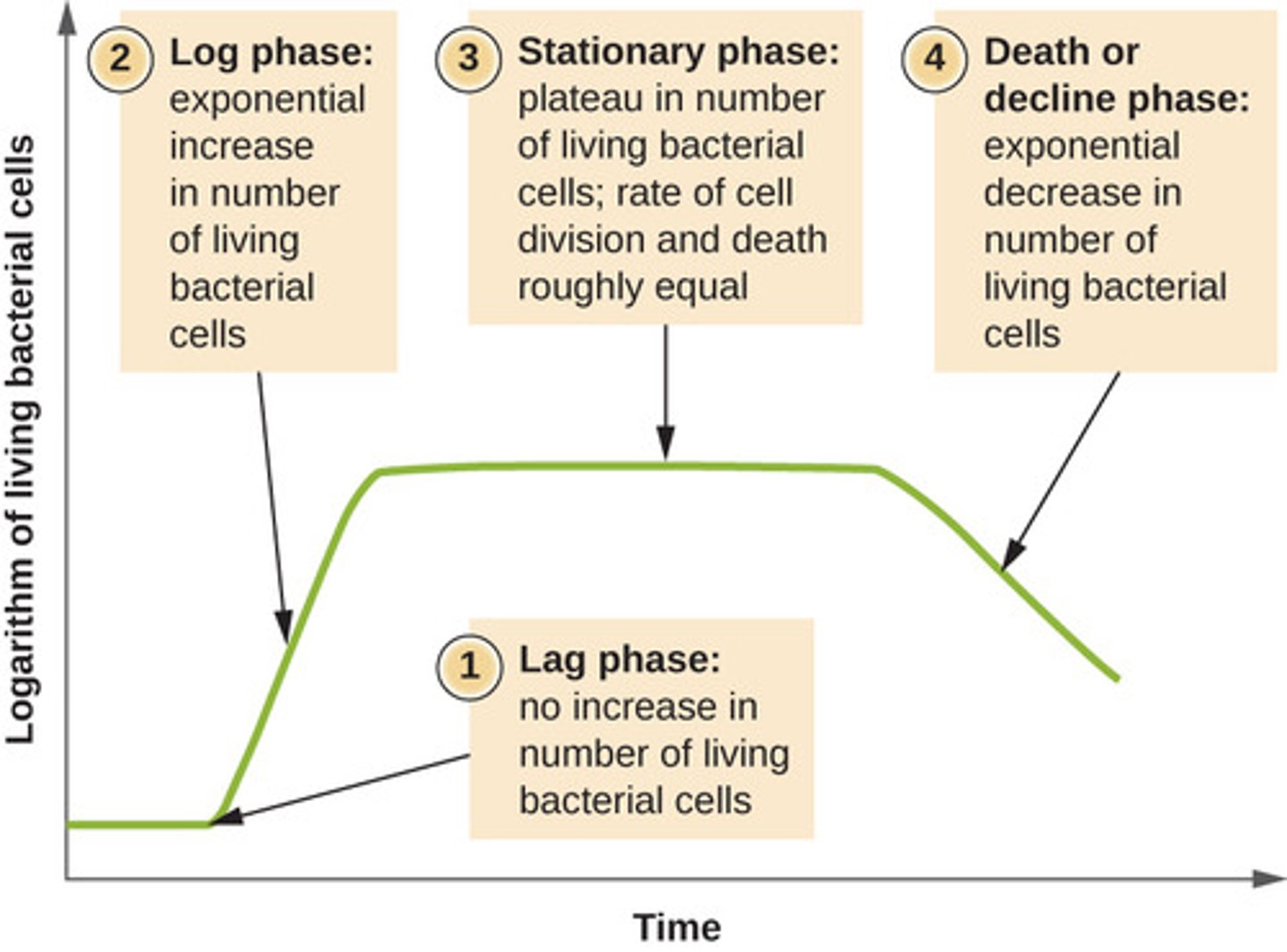
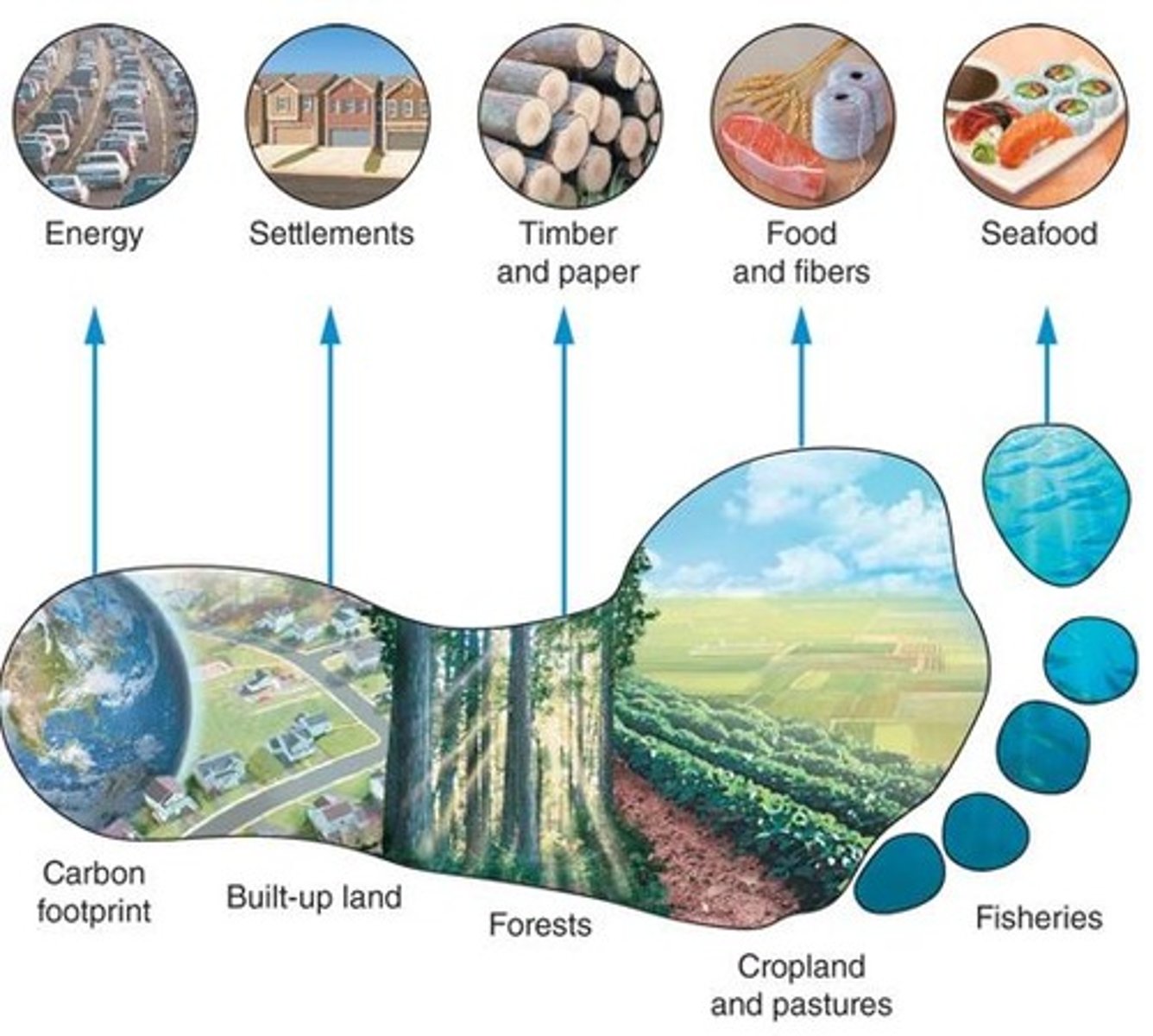
What is the aggregate land and water area necessary to produce all the resources to sustain a group and absorb all their wastes?
ecological footprint
What is the overall variety of organisms in a community?
species diversity

Which component of species variety describes the total number of different species present?
species richness
Which component of species variety describes the number of individuals of each species?
relative abundance
What index quantitatively measures the species diversity?
Shannon diversity index
Which relative value of the Shannon diversity index indicates a more diverse community?
high
Higher diversity communities are often more resistant to which types of species?
invasive
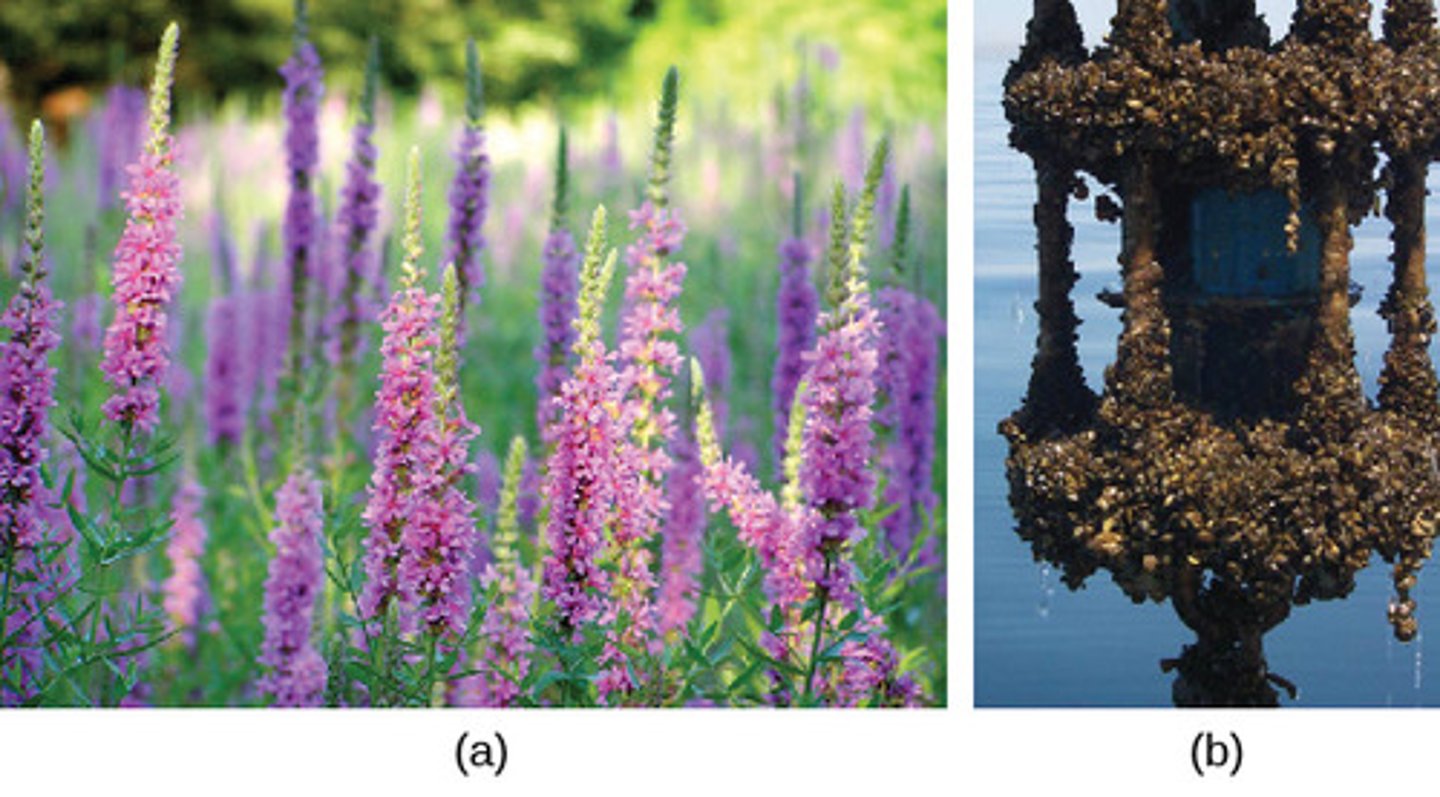

Community diversity is affected by what factors?
biogeographical factors
What component of species variety generally declines along a latitudinal gradient from the tropics to the poles?
species richness
(Note: due to evolutionary history and climate)
What method measures the evaporation of water from soil and plants and is a function of solar radiation, temperature, and water availability?
evapotranspiration
In terrestrial communities, what specific factors correlate with diversity and can be measured via evapotranspiration?
sunlight and precipitation
In which areas is evapotranspiration highest?
hot areas with abundant rainfall
How does species richness relate to a community's geographic size?
directly related
How is the relation of species richness to the geographic size described graphically?
species-area curve
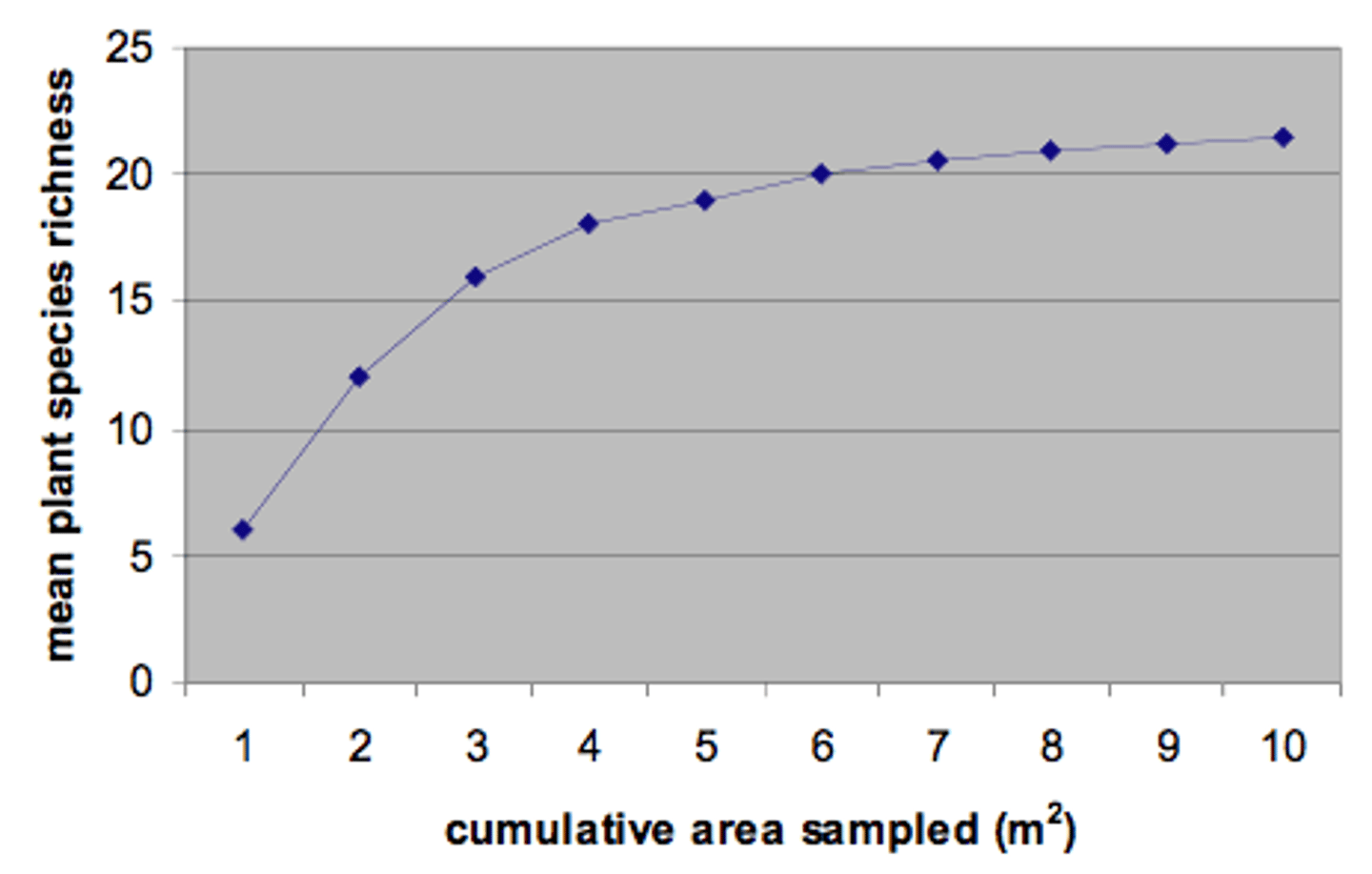
What component of species variety is dependent upon island size and distance from mainland for island habitats?
species richness
When is species richness equilibrium reached?
when new immigrations are balanced by extinctions
What study is concerned with the interaction of populations, such as interspecific competition?
community ecology
What principle involves the exclusion of a species when it competes with another species for the exact same resource?
competitive exclusion principle (Gause's Principle)
(Note: no two species can sustain coexistence if they occupy the same niche
What process occurs when two species occupy the same niche but pursue slightly different resources?
resource partitioning
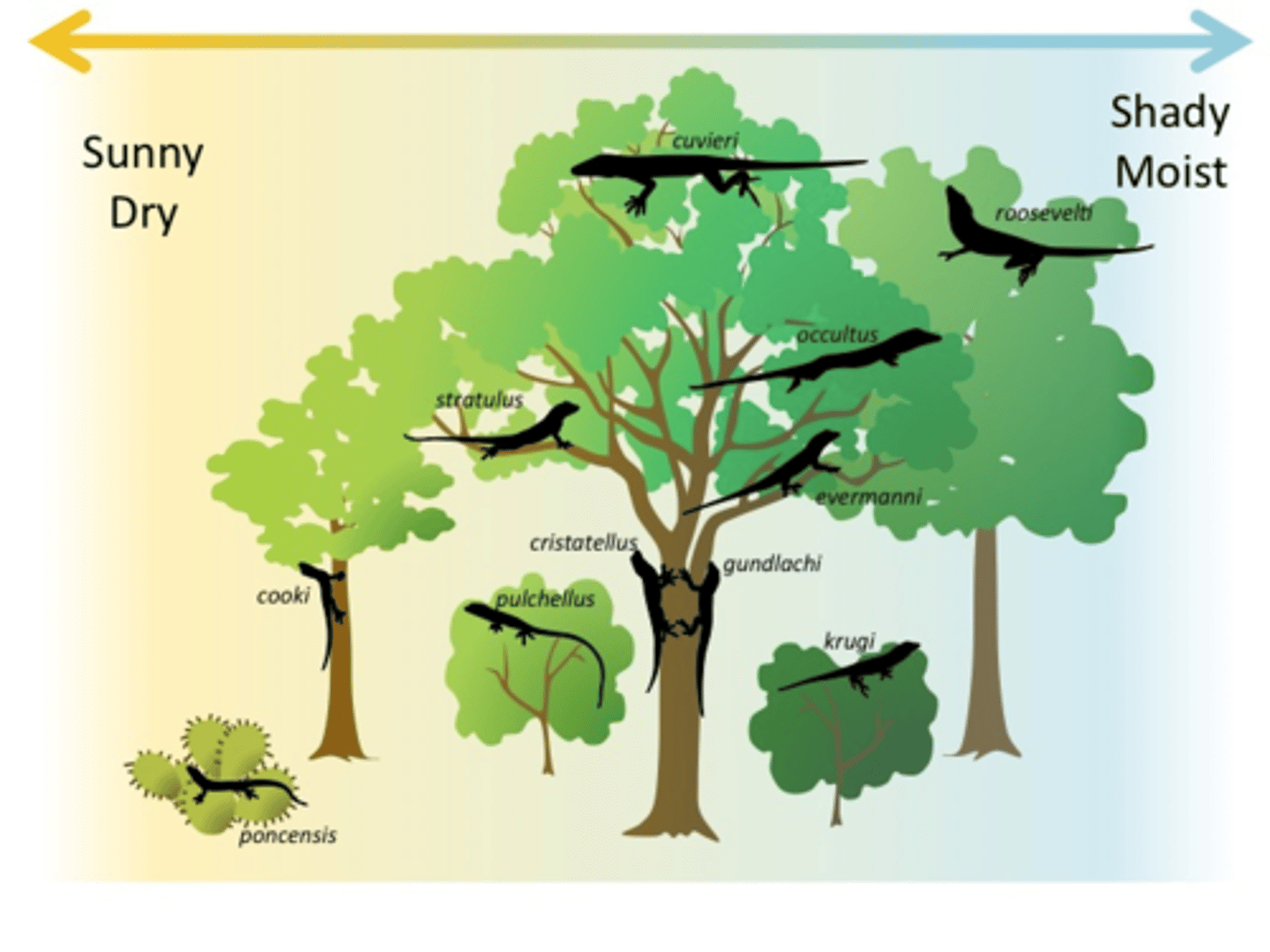
What function does resource partitioning have in a population?
minimize competition, maximize success
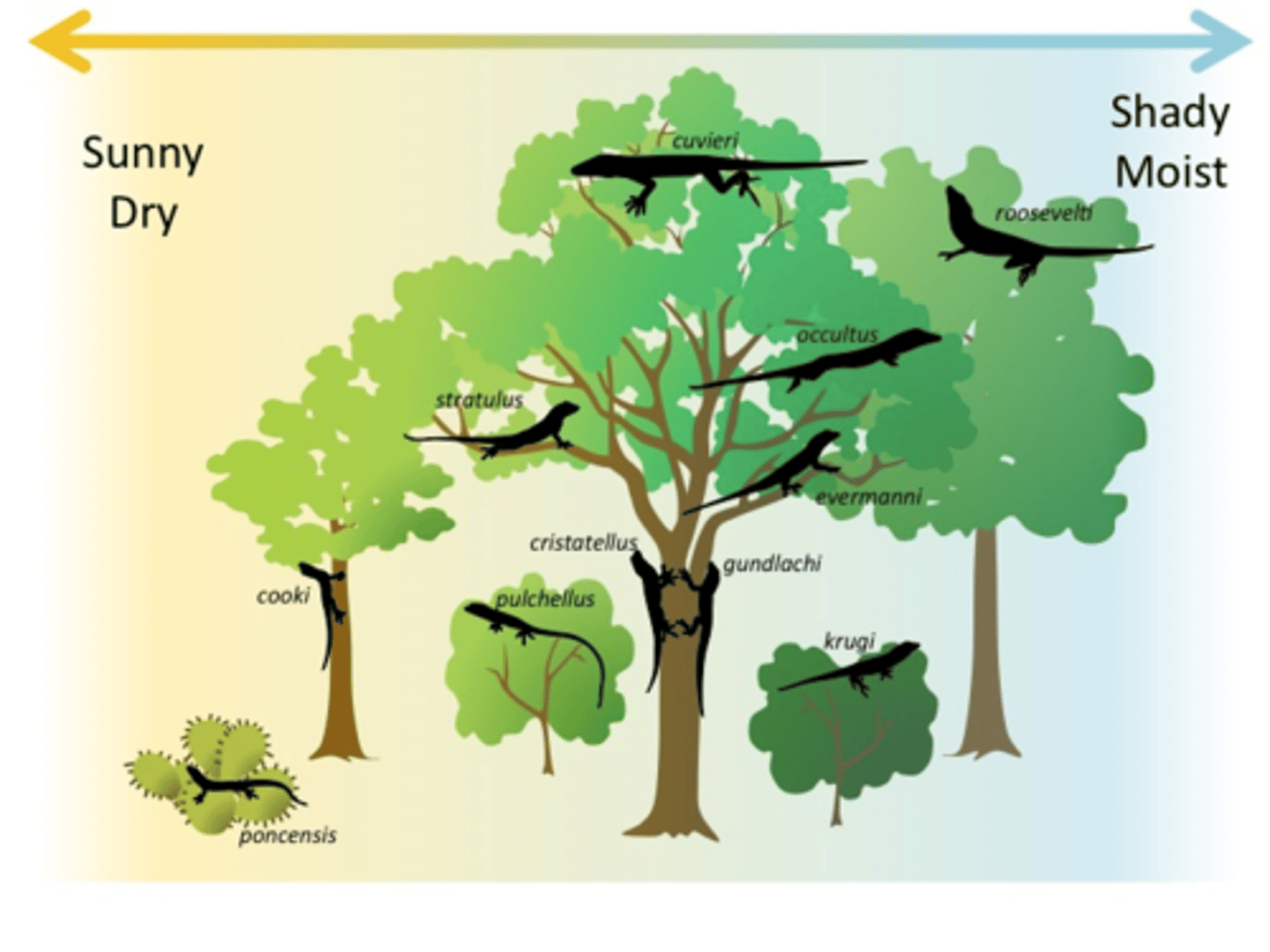
What shift occurs as a result of resource partitioning, where certain traits allow for more success in obtaining resources in their partitions?
character displacement (niche shift)
(Note: reduces competition and increases the divergence of features)
What is the niche that an organism occupies in the absence of competing species?
fundamental niche
(Note: potential area of survival)
What is the niche that a species actually lives in due to factors such as competitors?
realized niche
(Note: try not to overlap)
What form of community interaction involves a predator and prey?
predation
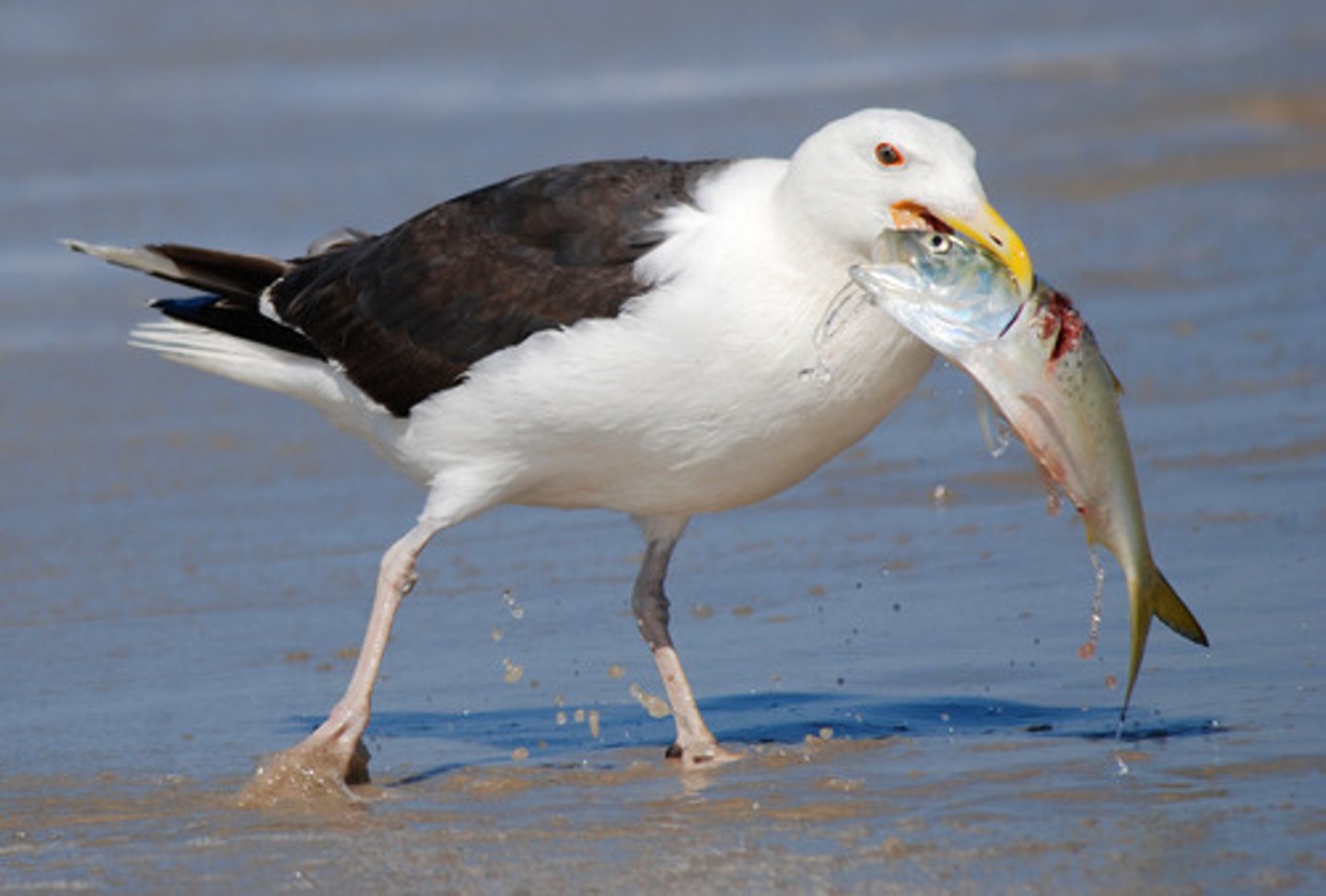

What is any animal that totally or partly consumes a plant or another animal?
predator
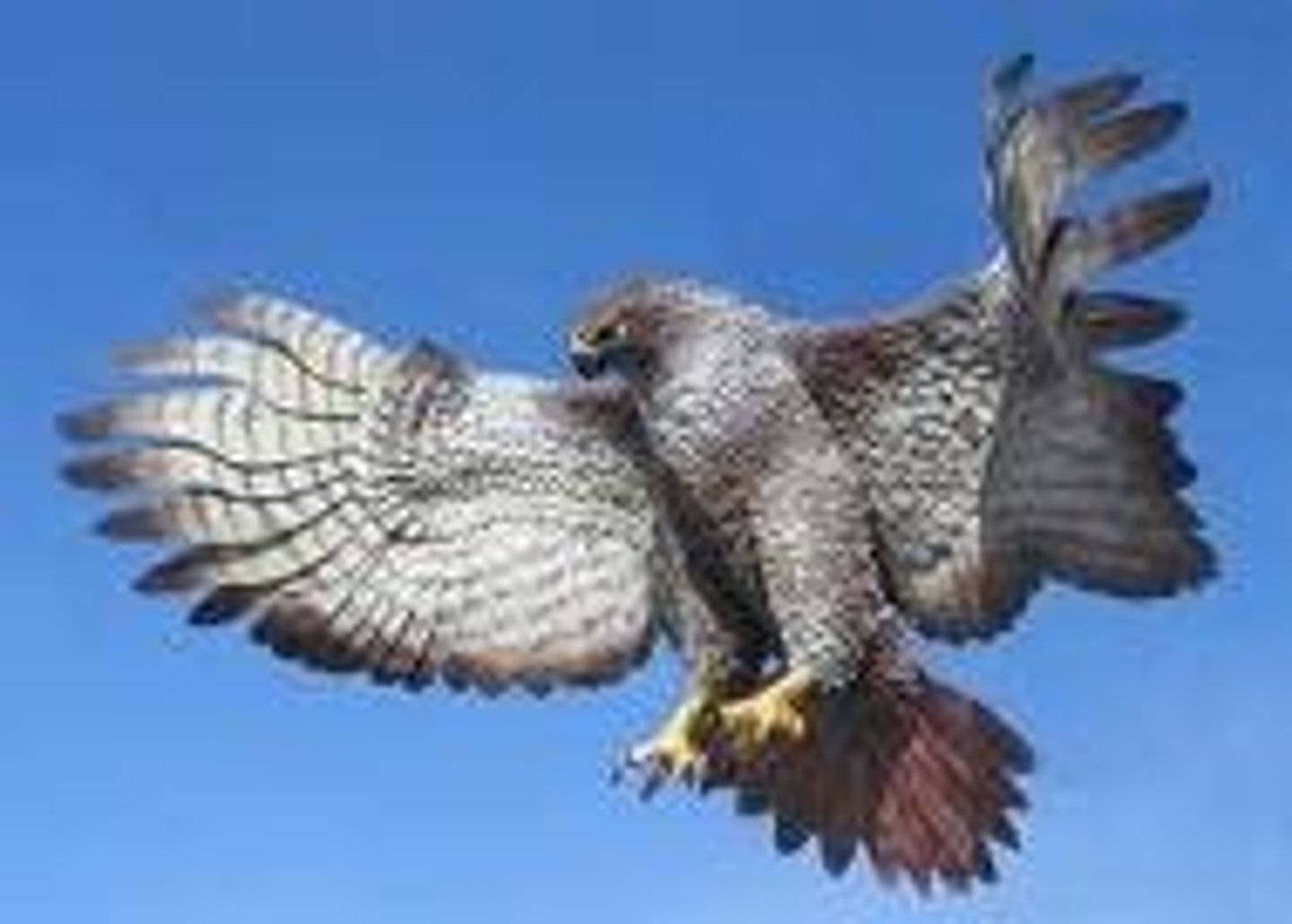

What is an animal that kills and eats another animal?
true predator

What is an organism that spends most of its life living on a host and obtaining nourishment by feeding off the host's tissues?
parasite
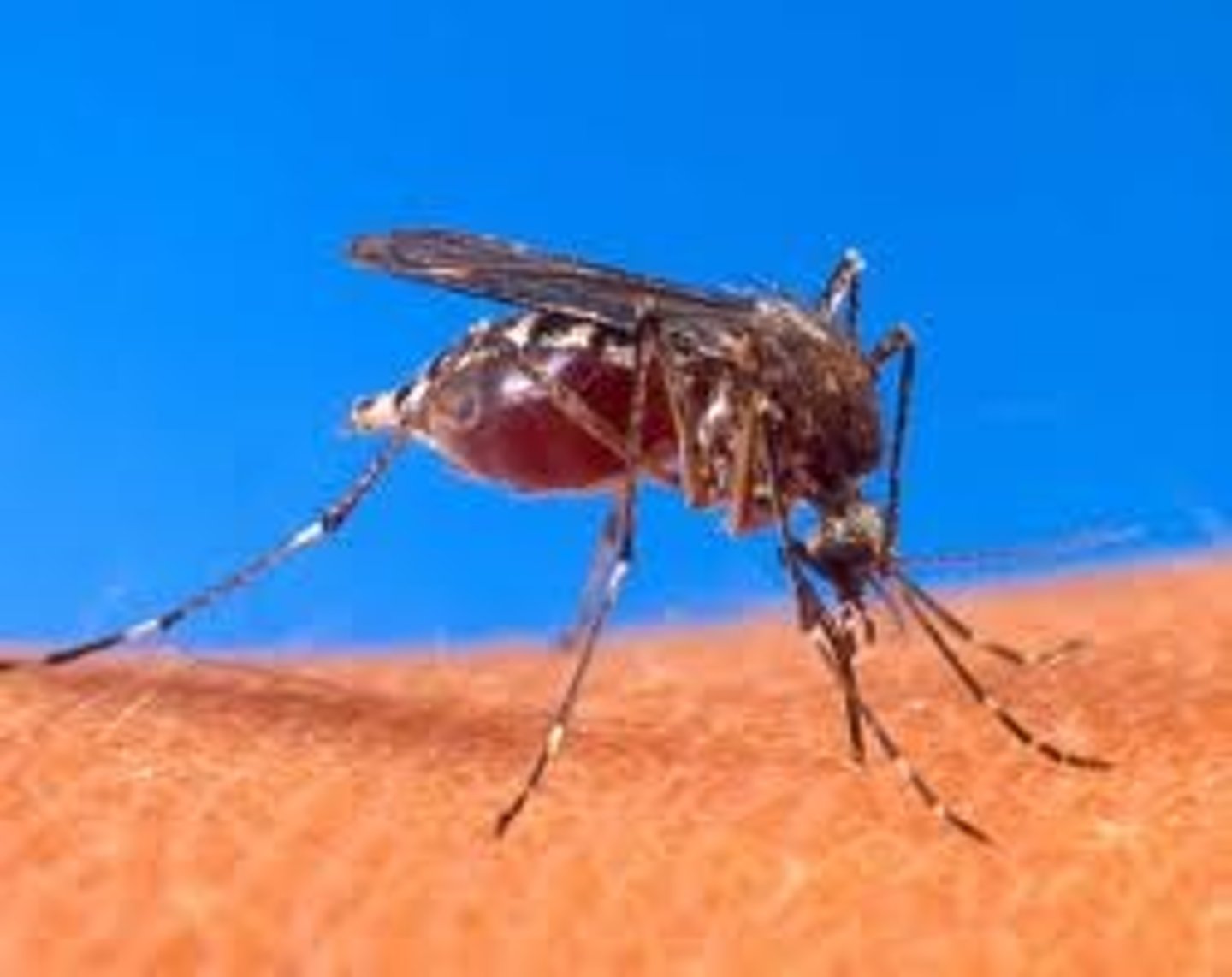

The host of a parasite usually does not die until the parasite completes at least how many life cycle?
at least one life cycle
What is an insect that lays its eggs on a host (insect or spider)?
parasitoid
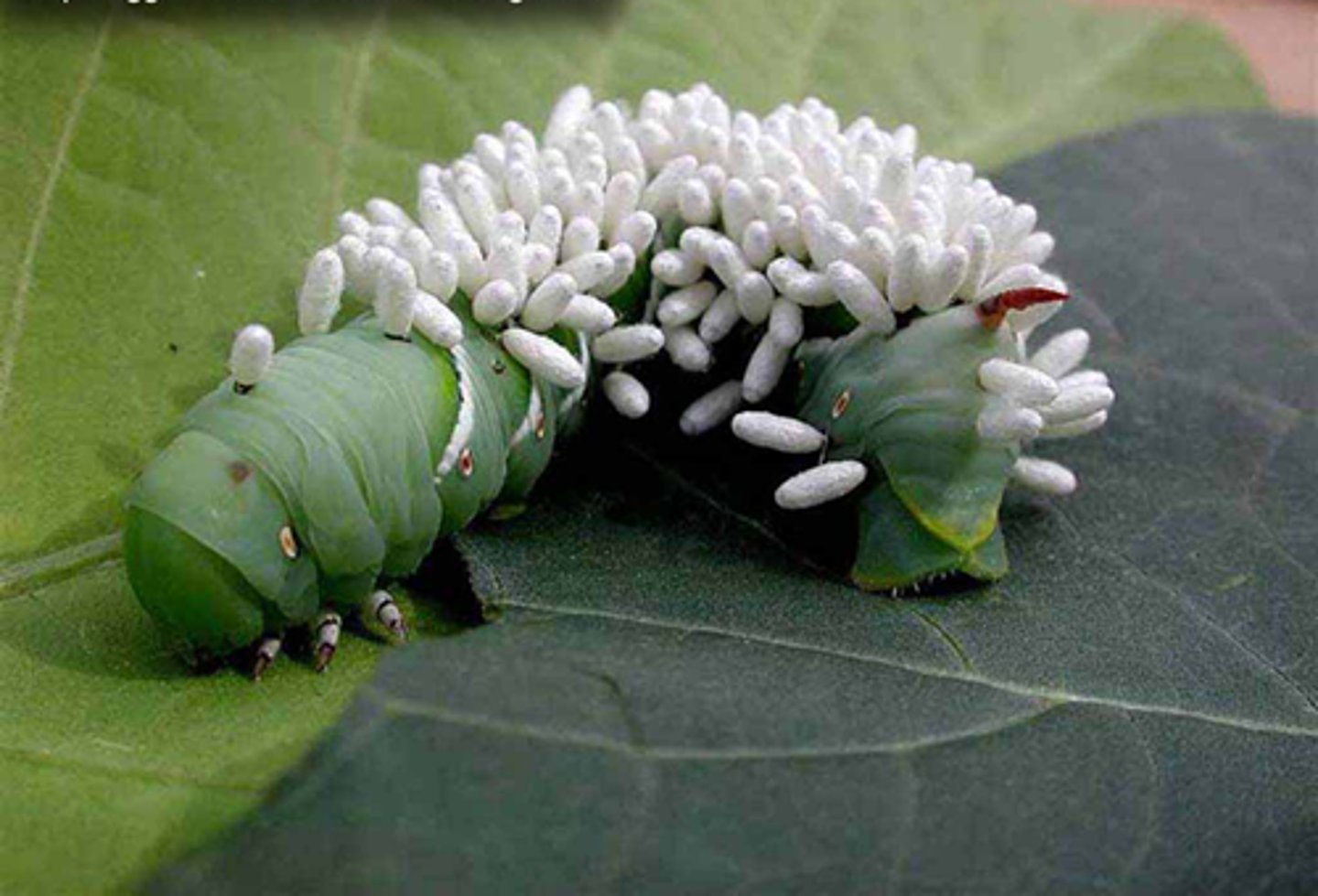

After the eggs of a parasitoid hatch? how do the larvae obtain nourishment?
consuming the host's tissues
(Note: host eventually dies after larvae complete development)
What is an animal that eats plants?
herbivore

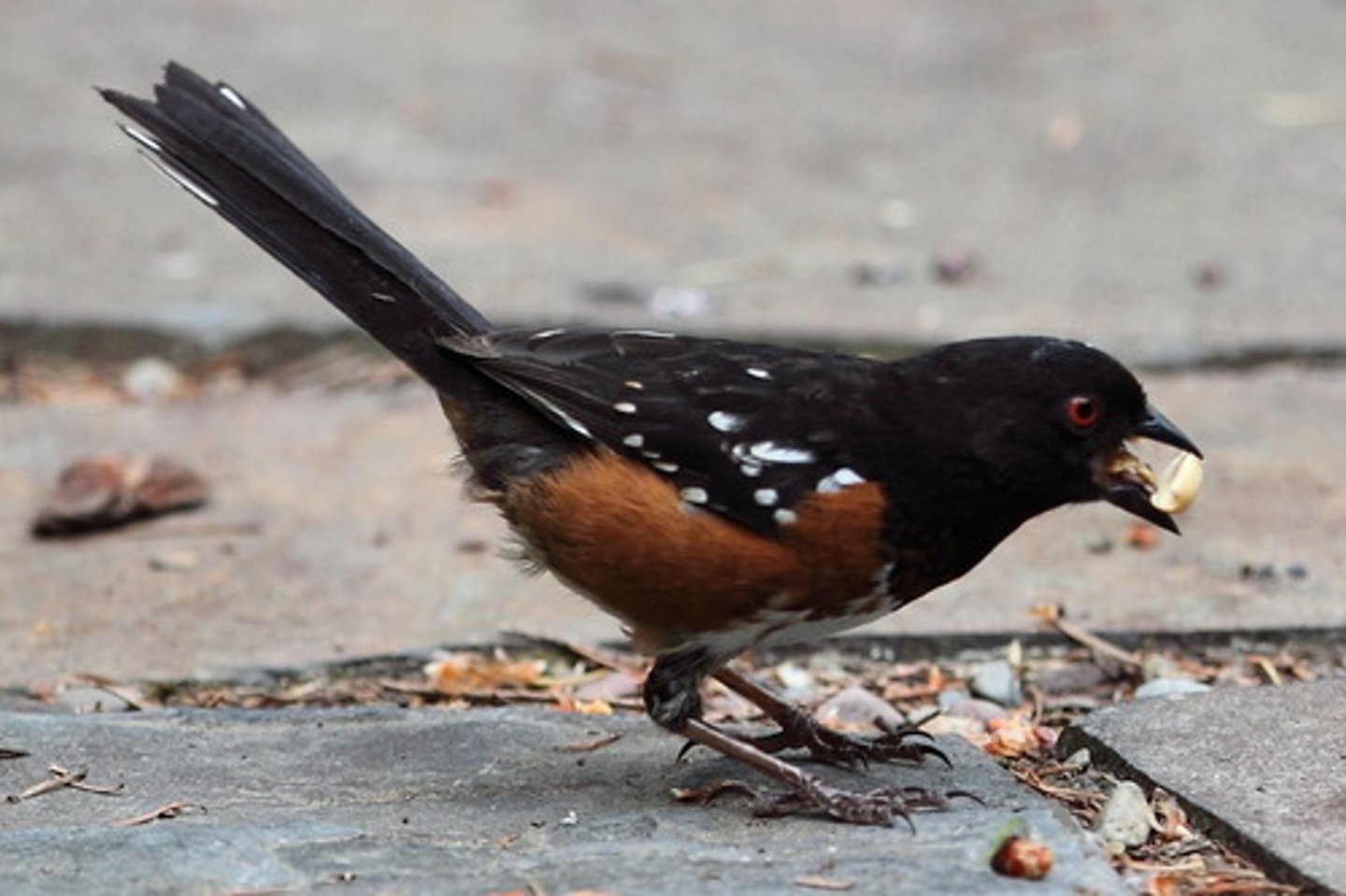
What are animals that eat seeds and act like predators because they totally consume the organism?
granivores

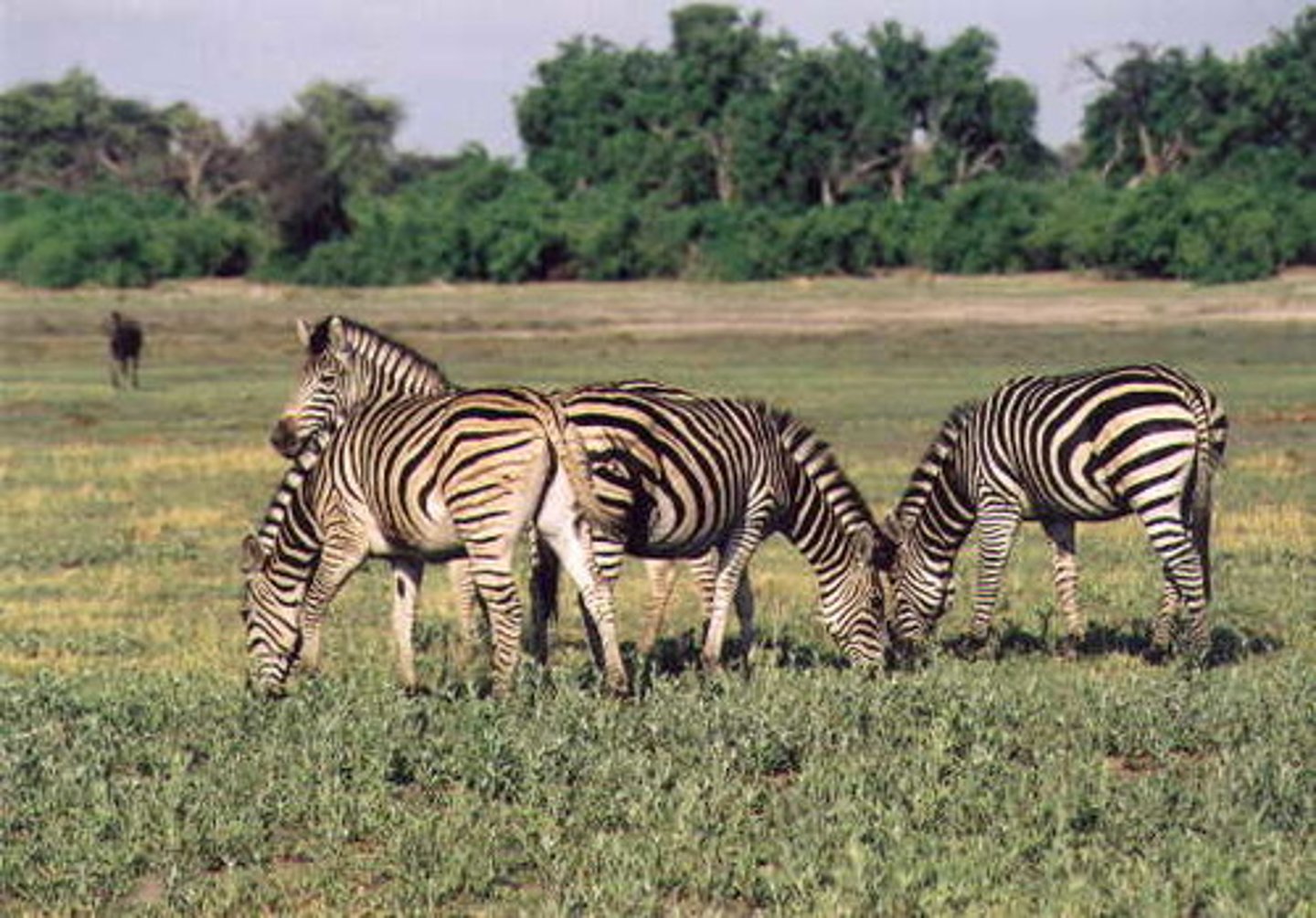
What are animals that eat grasses?
grazers
(Note: only eat part of the plant)

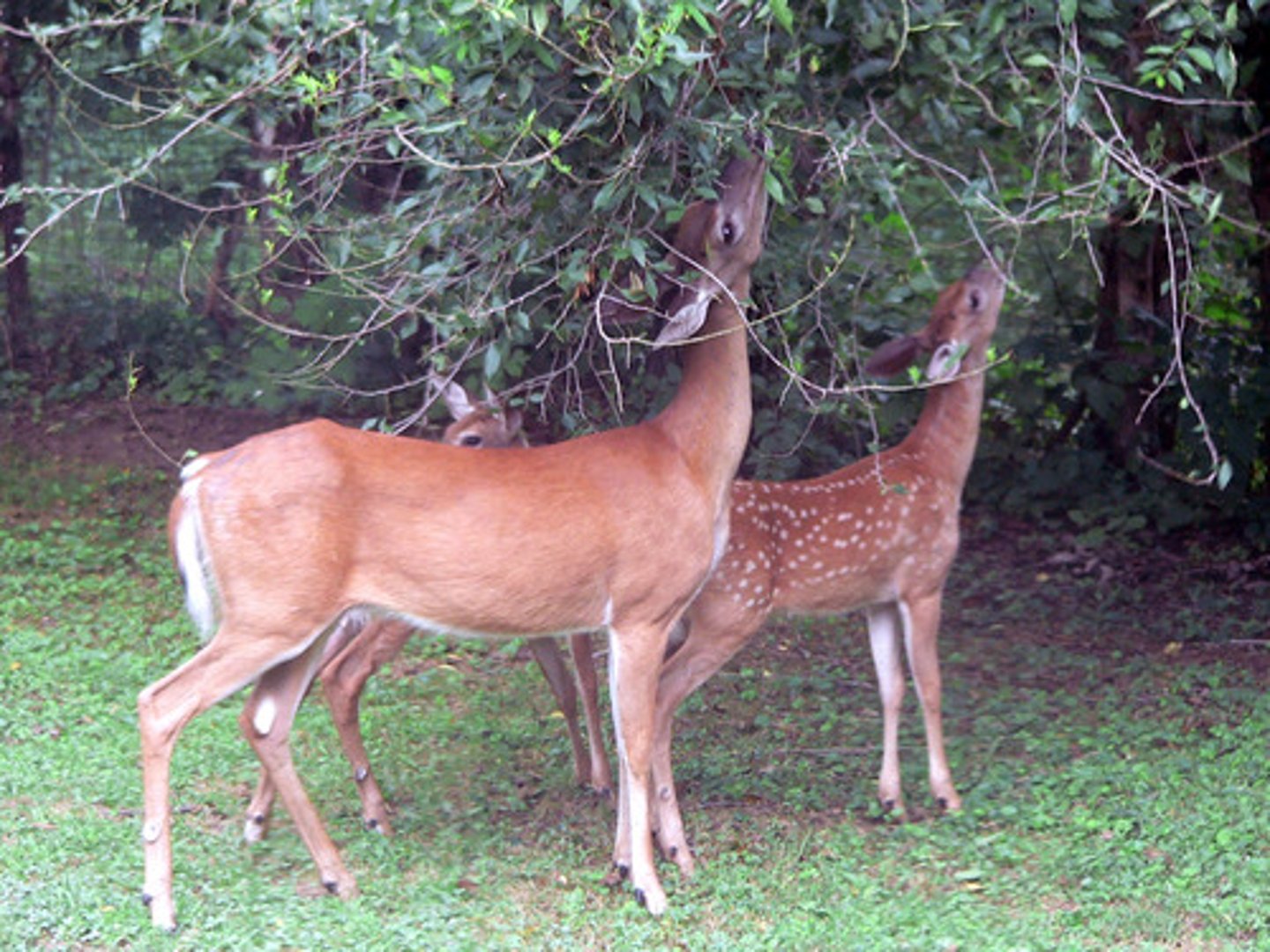
What are animals that eat leaves?
browsers
(Note: only eat part of the plant)

What is an intimate, often permanent association between two organisms?
symbiosis
(Note: may or may not be beneficial)
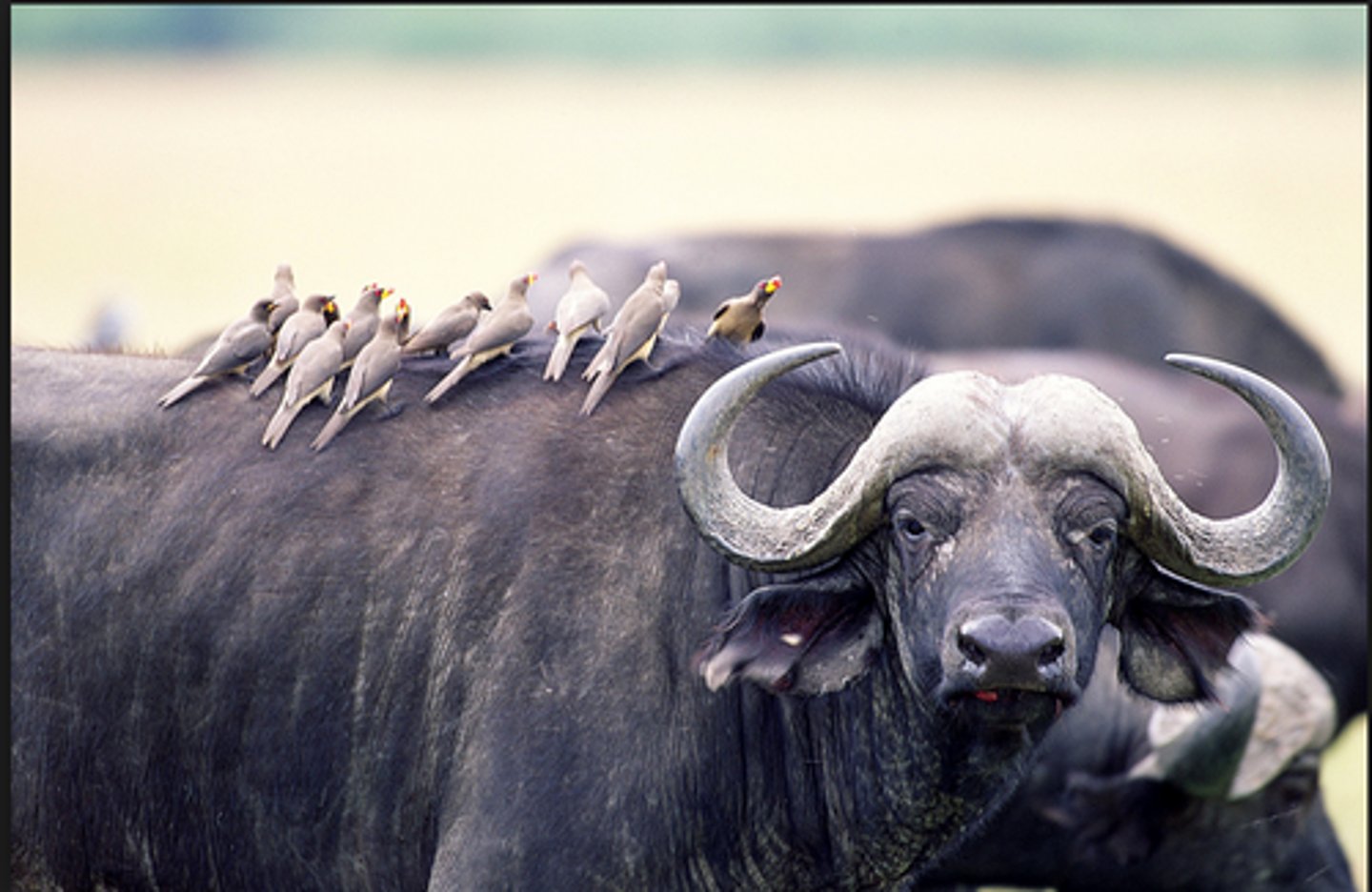

Which symbiotic relationship occurs when one organism benefits while the other is unaffected?
commensalism
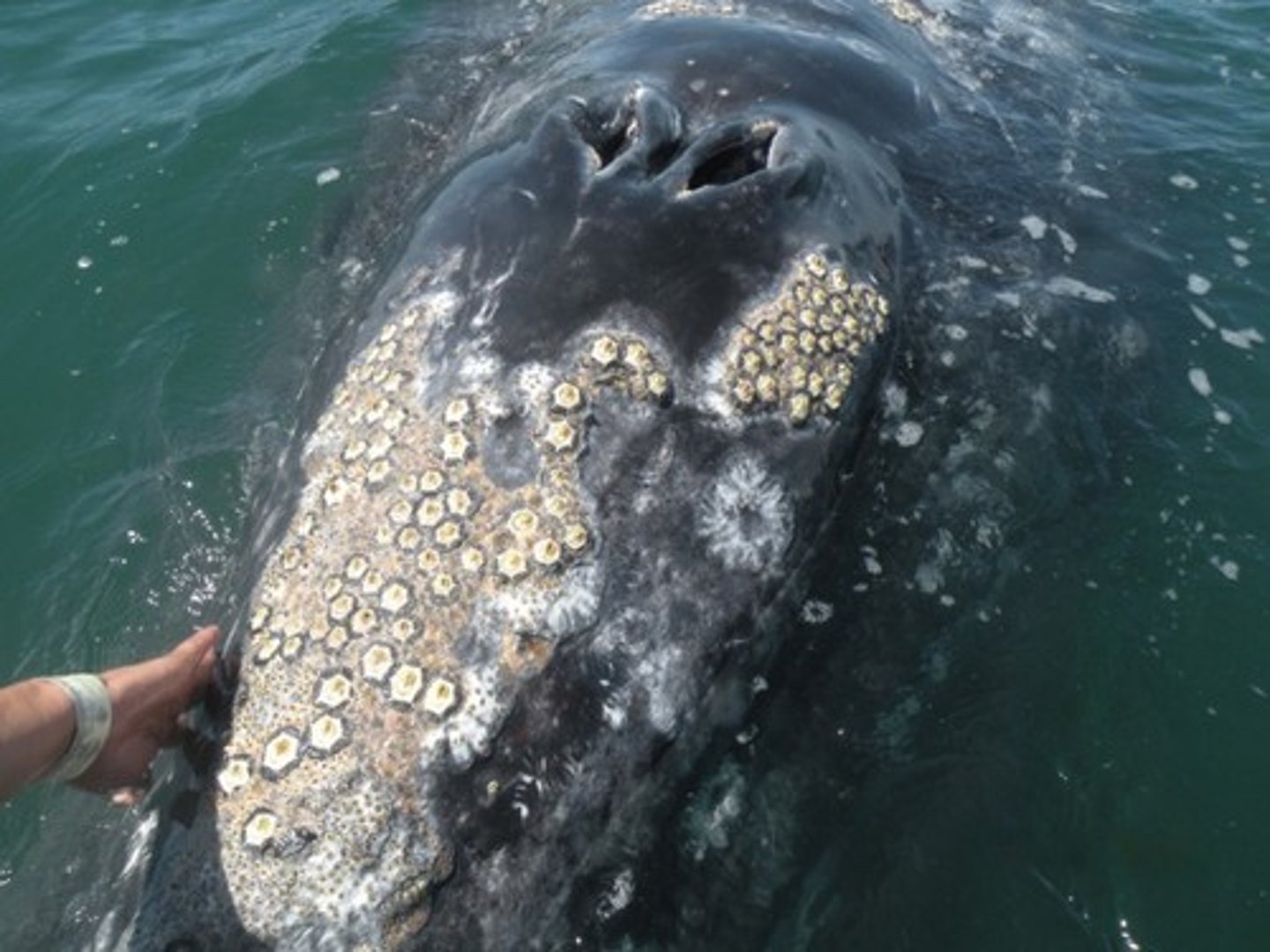

Which symbiotic relationship occurs when both organisms benefit?
mutualism

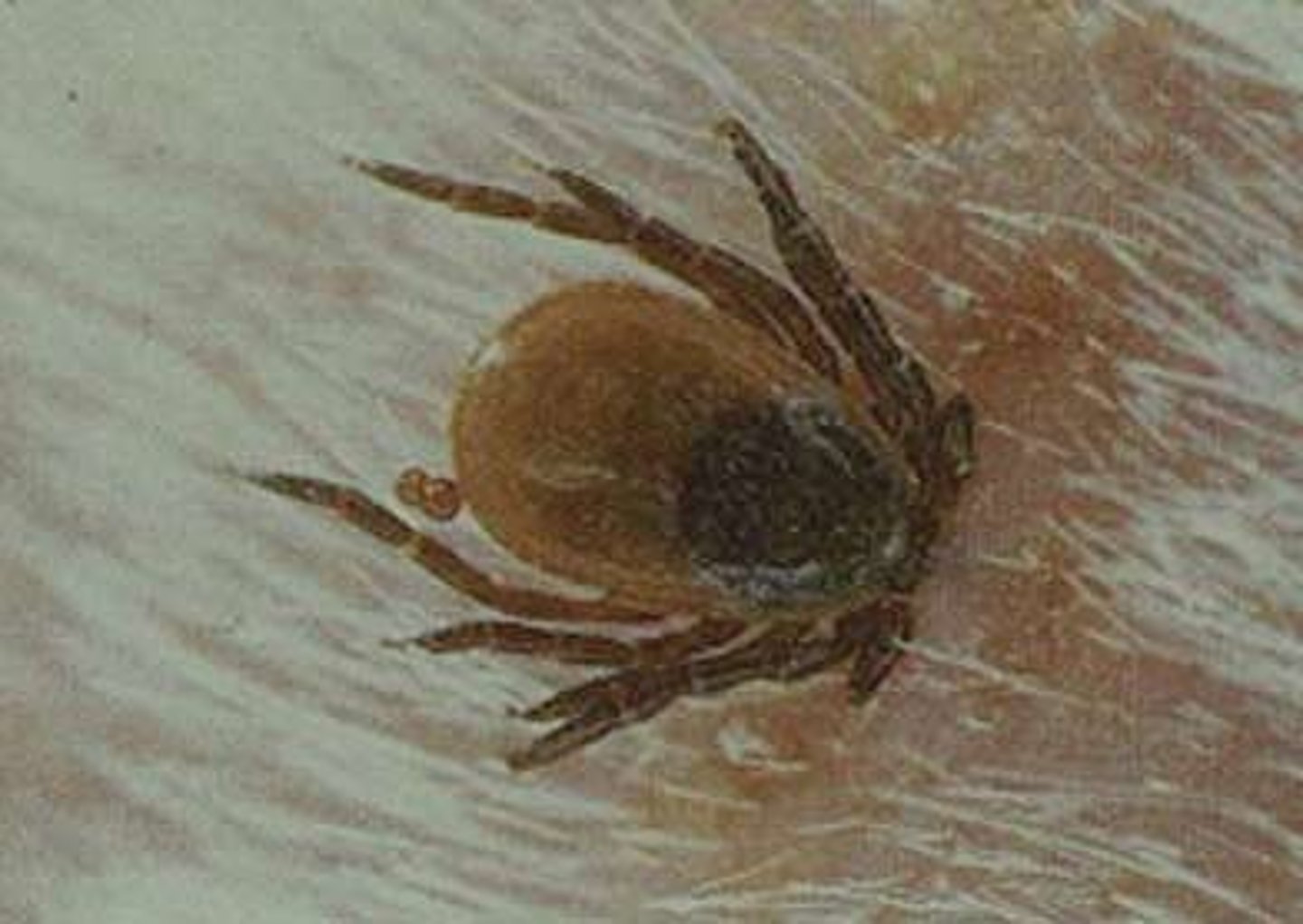
Which symbiotic relationship occurs when one organism benefits at the expense of its host?
parasitism

Which species relationship occurs when one has a positive effect on another species without necessarily living in direct and intimate contact?
facilitation
What process occurs when protists and fungi decompose dead organic matter externally and absorb the nutrients?
saprophytism

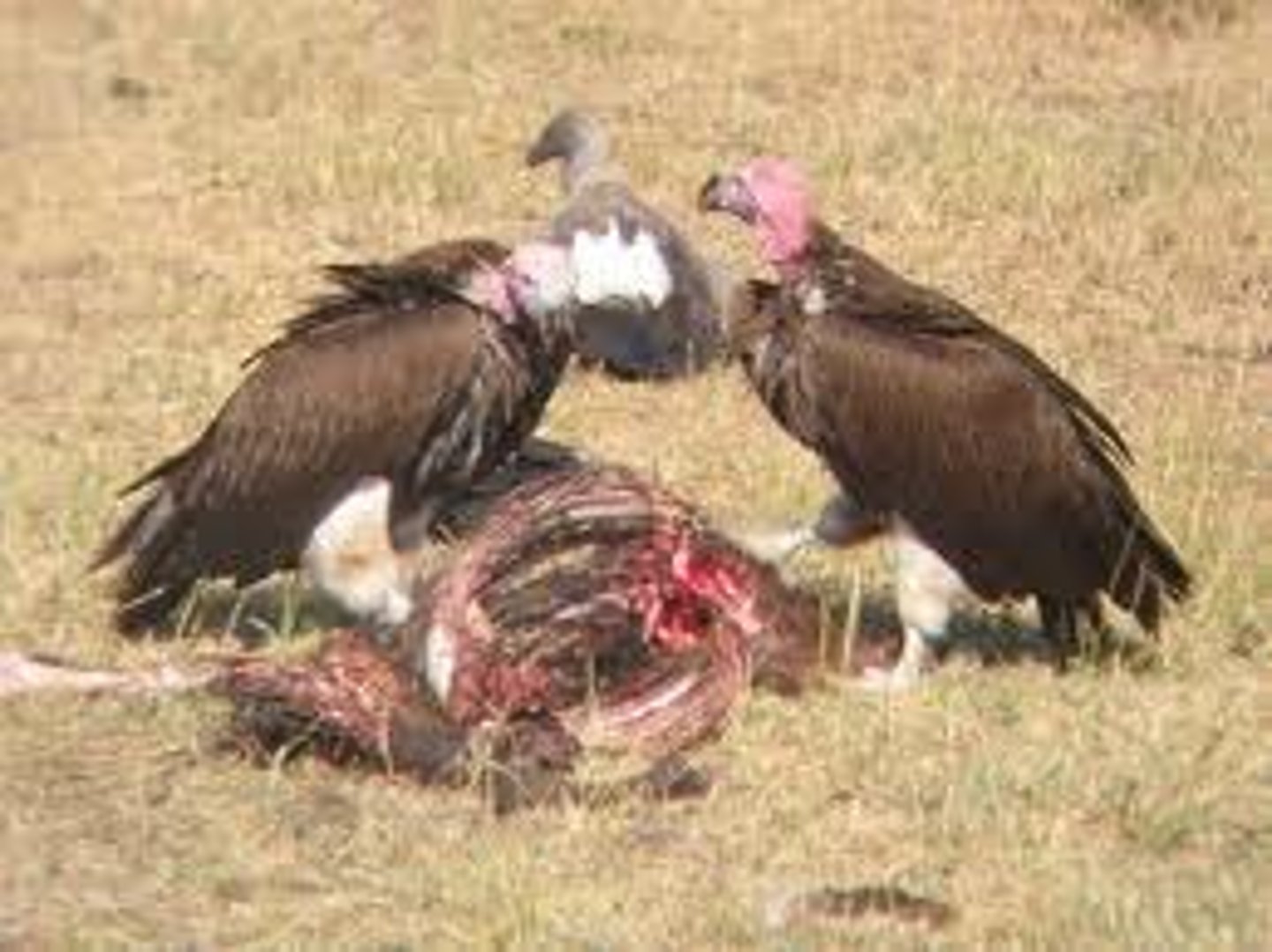
What are animals that consume dead animals directly?
scavengers
(Ex: vultures, hyenas, some bacteria)

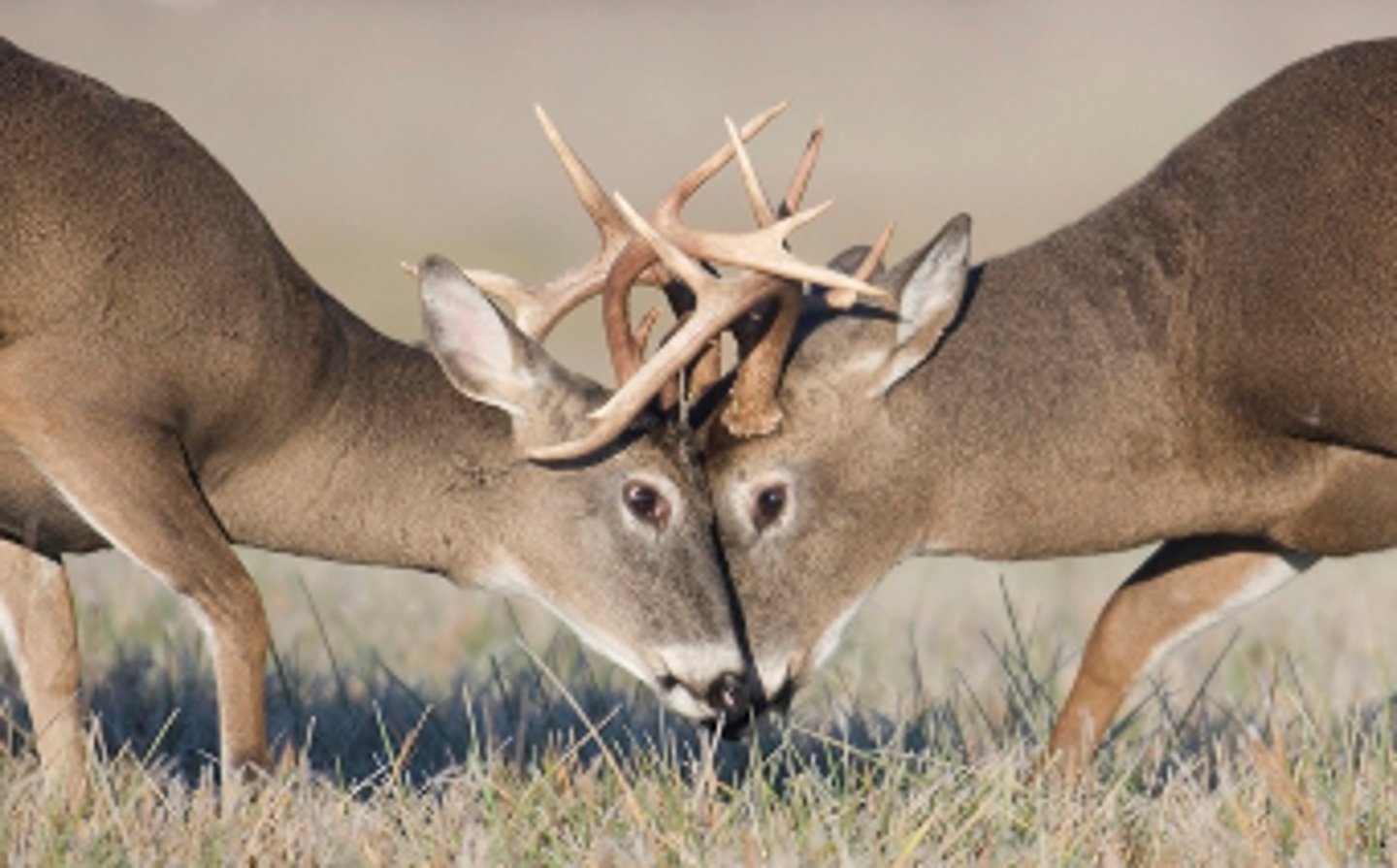
What is the competition between members of the same species?
intraspecific interactions

By which forces are intraspecific interactions influenced?
disruptive and cohesive forces
Which forces involve competition?
disruptive forces
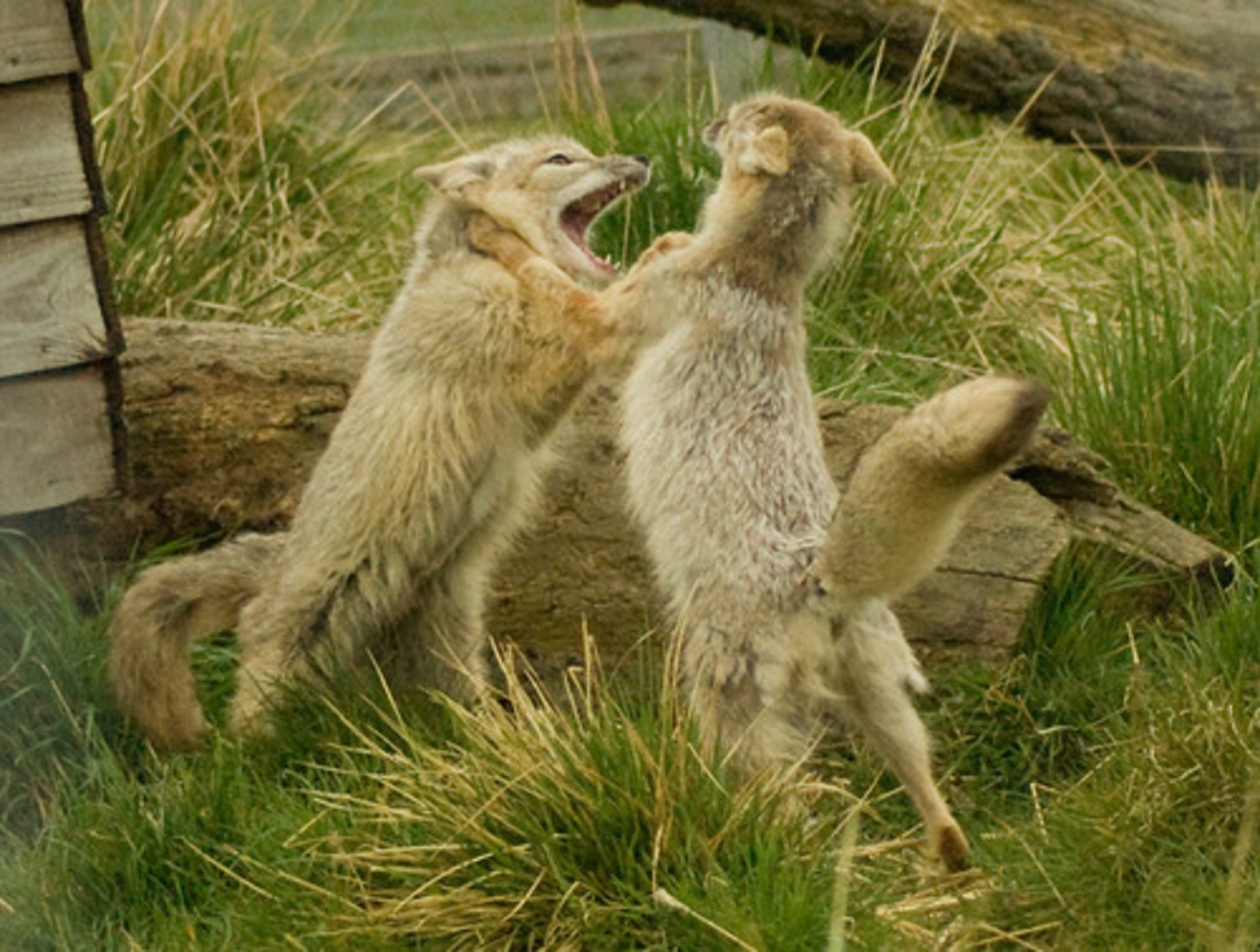

Which forces involve reproduction and protection from predators and weather?
cohesive forces
What is the competition between members of different species, and is ultimately negative because both are competing against each other for resources?
interspecific competition
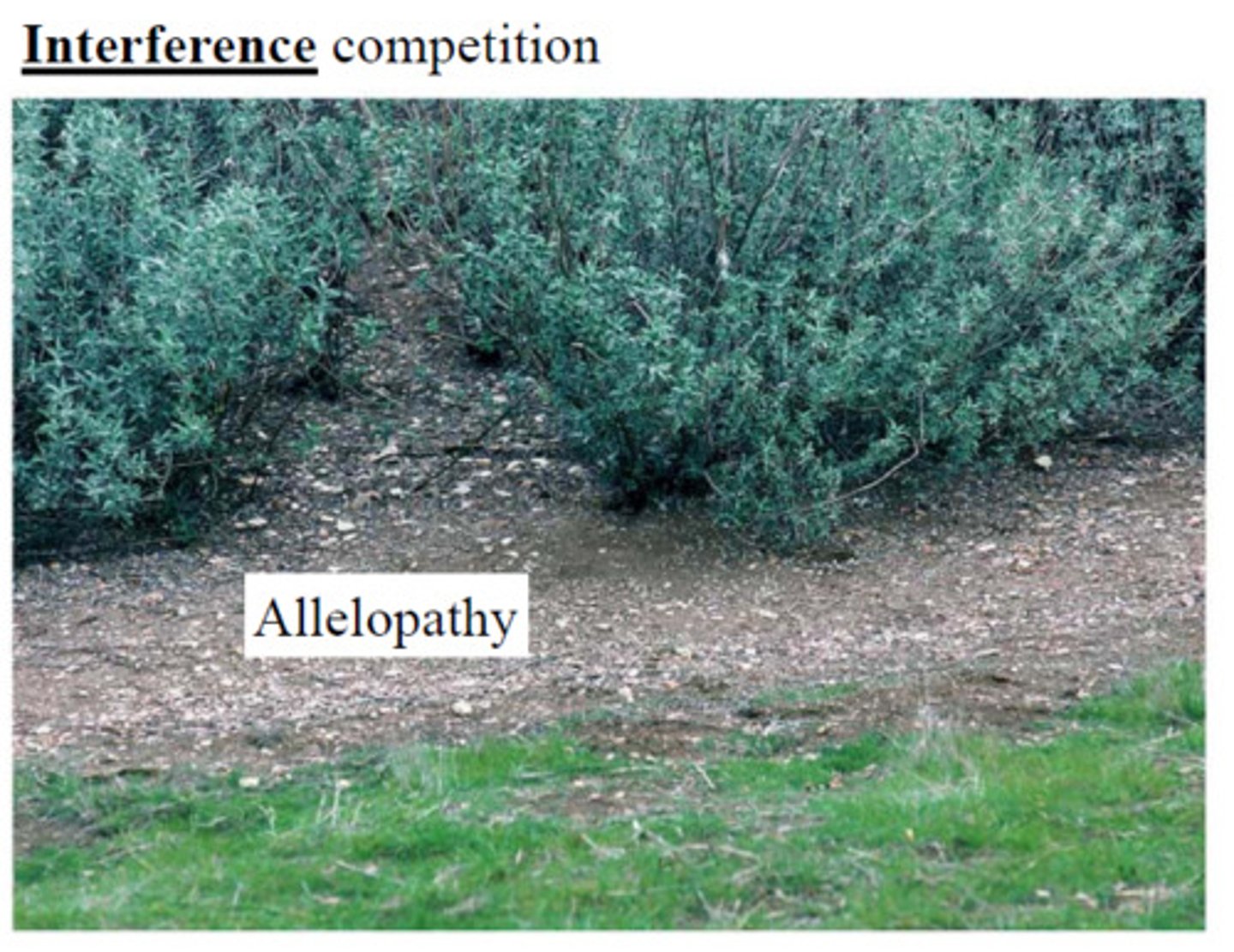
What is the production of biochemicals by an organism to influence the growth/survival/reproduction of other organisms?
allelopathy
