chemistry alevels - electrons, bonding and structure
1/79
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
80 Terms
another name for shells
energy levels
feature of shells
as the shell number increases so does the energy
define principle quantum number
the shell/energy level number
electron shell
a group of atomic orbitals with the same principle quantum number
sub shell
a group of orbitals of the same type within a shell
p - orbital
dumbell shape
1st shell
n and electrons
2
2(n2)
2nd shell
8
3rd shell
18
4th shell
32 electrons
define first ionisation energy
the energy required to remove one electron from each atom in one mole of gaseous atoms of an element to form one mole of gaseous 1+ ion
example of first ionisation energy
Mg (g) —> Mg+(g) +e-
Cl (g) —→ Cl+ (g) +e-
the trend in the ionization energy in the first 20 elements in a period
across a period the ionisation energy generally increases, due to the nuclear charge increasing, increasing the number of protons, resulting in a stronger attractions to the electrons on the outershell to the nucleus. therefore more energy is required for ionisation
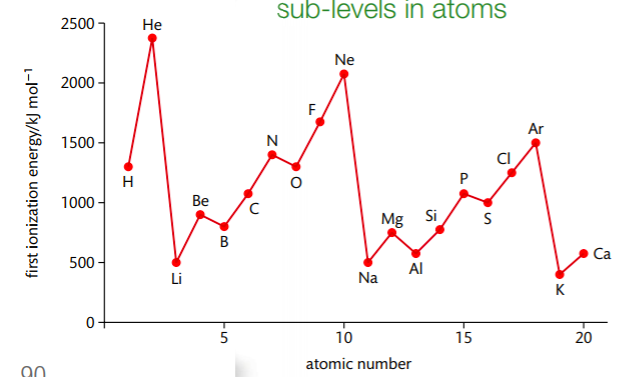
factors affecting ionisation energy
atomic radius
nuclear charge
electron shielding
atomic radius
the greater the distance between the nucleus and the outer electron - the weaker the attraction - smaller the ionisation energy
the smaller the distance between the nucleus and the outer electron -the stronger the attraction - higher the ionisation energy
nuclear charge
the more number of protons in the nucleus, the greater the attraction between the nucleus and the outer electron - the higher the ionisation energy
electron shielding
repulsion between the inner electrons and the outer electron is shielding - this reduces attraction between nucleus and outermost electron - reduces ionisation energy
s orbital - features
spherical in shape (not cirular or round)
all shells contain 1s orbital
max of 2 electrons (2×2)
p orbital - features
dumb bell shaped orbital
from shell 2, each shell has 3x p - orbitals
max of 6 electrons (3×2)
d orbitals - features
more complex shapes
3rd shell each has 5d orbitals
max of 10 electrons (5×2)
Hunds Rule
as orbitals have lots of different shapes boxes are used to represent them as easier
how much does these subshells hold s p d
2 6 10 electrons
electronic configuration order
1s 2s 2p 3s 3p 4s 3d 4p 4d
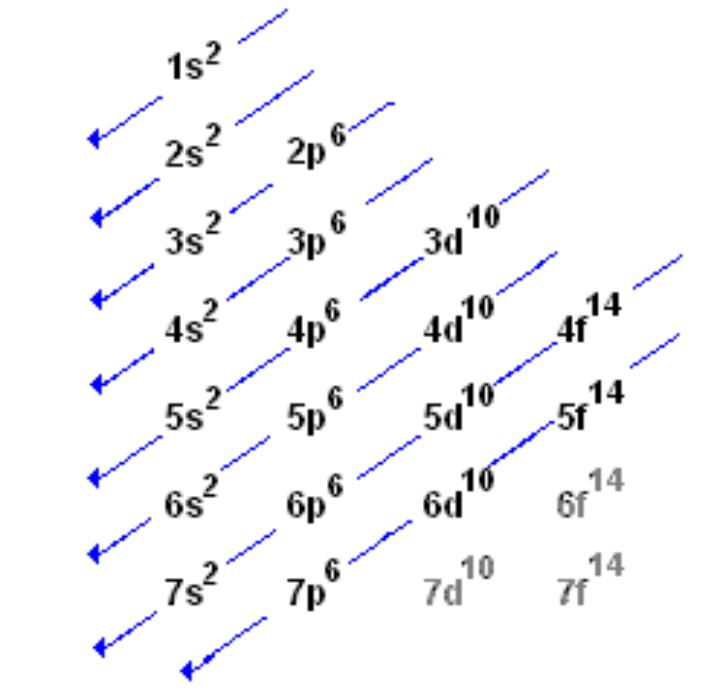
aufbau principle

short way to write the electronic configuration
F: (1s2)2s22p5 so is (He)2s22p5
USE NOBLE GASES AT THE BEGINNING THE NEAREST ONES
electronic configurations of Cl-
1s22s22p63s23p6
how many full orbitals are in atom of sulfur
7 - 2 electrons in each orbital as sulphur has 14 electrons
remember boxes
ionic bond
transfer of electrons between metals and non metals
the metals in an ionic bond
is oxidised so it loses electrons and becomes a positive ion
non metals in an ionic bond
is reduced so it gains electrons so becomes a negative ion
structure of ionic compound
electrostatic force that acts in all directions in an ionic bond
tightly packed structure called crystal
3D lattice
structure of alternating anions and cations
physical properties of ionic compound
do not melt or boil very easily because the electrostatic forces are very strong. as solids they are hard and brittle
forms a crystal lattice that results in release of energy, making the resulting salt more stable then before
properties of ionic compounds
when salts are dissolved in water, this breaks the ionic bond and allow the individual ions to move freely in water forming electrolyte
ionic bond energy - lattice energy - the energy required to seperate one mole ( a chemical quantity) of ions is an ionic compound into its gaseous ions.
the lattice energy is affected by
the size of the ions - smaller the ions in bonds, the greater the lattice
the charge on the ions - greater the charges in the bonds, the greater the lattice energy
sodium chloride, potassium chloride, magnesium chloride
rank them from the highest to lowest melting points with reasons
magnesium chloride - ionic radius is smaller so greater charge density so electrostatic force is stronger so more energy needed to overcome the force
sodium chloride
potassium chloride - 1 extra shell
charge density
charge ions / volume of ions
why does MgO have a much higher boiling point than NaCl
comparisons of cations
Na+ and Mg2+ ionic radius of Mg ion is smaller than Na+ ion and has a greater magnitude (+2 +1) Mg2+ ion forms a stronger electrostatic forces of attraction. chloride ions has 3 shells/energy, whereas oxide has 2. Cl- ion has larger ionic radius than oxide ion. Cl- have a lower magnitude of charge -1 in comparison to -2. MgO forms strongest electrostatic forces of attraction.
if energy taken in to break lattice it is an
endothermic reaction
solubility
two processes - ionic lattice must be broken down and water molecules must attract and surround the ions
covalent bond
covalent bonding the attraction is localised, this means that it acts solely between the shared pair of electrons and nuclei of the two bonding atoms
dative covalent bond is also known as
coordinate bonds
define dative covalent bond
higher electronegativity means that the bond is
polar
define polarity
difference in electronegativity between elements
define dipole
consists of 2 equal but opposite charges or magnetic poles seperated by distance
dipole is often seen in
polar molecules with uneven charge distribution, leading to a positive and negative end
properties of covalent compounds
low melting ang boiling point - the bonds themselves are strong but the forces between the molecules are weak called the intermoleculare forces, so they are easy to break and disrupt
poor conductors of electricity - doesnt contain charged ions
soft and flexible - if compounds crystalline not the case
non polar covalent compounds dissolves poorly in water - water is polar so the rule for dissolving is like dissolves like —> polar and polar. non polar and non polar
define electronegativity
a measure of the tendency of an atom to attract a bonding pair of electrons in a covalent bond
greater electronegativity means
it attracts electrons towards it
factors affecting electronegativity
atomic charge
distance from the nucleus
electron shielding
what is pauling scale
measures electronegativity of atoms
the electronegativity across a period…
increases as the atomic radius decreases, meaning that there is an increase in nuclear attraction and in nuclear charge
the electronegativity down a group …
decreases, this is because the atomic radius increases - number of energy levels - meaning that there is a less of a nuclear charge
which elements have high electronegativity
group 7s, nitrogen oxygen
when the bonding pairs are unequally shared between to atoms this is due to
the difference in electronegativity (polar molecule bond) this sets up a permanent dipole
define permanent dipole
a dipole in a covalent bond that does not change
in a non polar bond the
bonded electron pair is shared equally between the bonded atoms
bond will be non polar when
the bonded atoms are the same or if they have the same or similar electronegativity
non polar bonds will form
pure covalent bonds
non polar solvent example
hexane
polar bonds are
bonded electron pairs shared unequally between the bonded atoms, contains different electronegativities and different bonded atoms
polar bonds forms
polar covalent bonds
example hydrogen chloride
hydrogen has an electronegativity of 2.1 and chlorine has an electronegativity of 3.0. chloride is more electronegative than hydrogen, this mean it has a greater attraction for the bonded pair of electrons than hydrogen.
water is polar
OH bonds have a permanent dipole these act in different directions but not opposing each other
carbon dioxide is non polar
the CO double bond has a permanent dipole and the 2 dipoles acts in opposite directions cancelling each other out having an overall dipole of 0
shapes of molecules: solid line
bond in the plane of the paper
shapes of molecules: solid wedge
the bond is coming out of the plane of the paper
shapes of molecules: dotted wedge
goes into the plane of the paper
there is in repulsion in this order
bonded pair bonded pair
bonded pair lone pair
lone pair lone pair
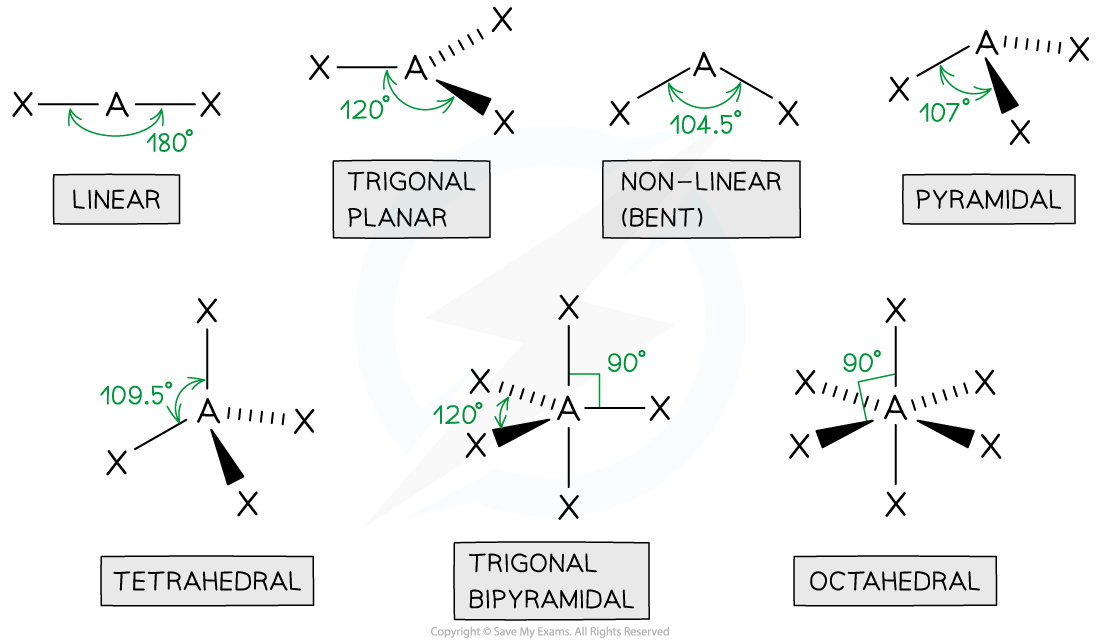
tetrahedral
4 bonded pairs
bond angle of 109.5
centre atom with 4 connected
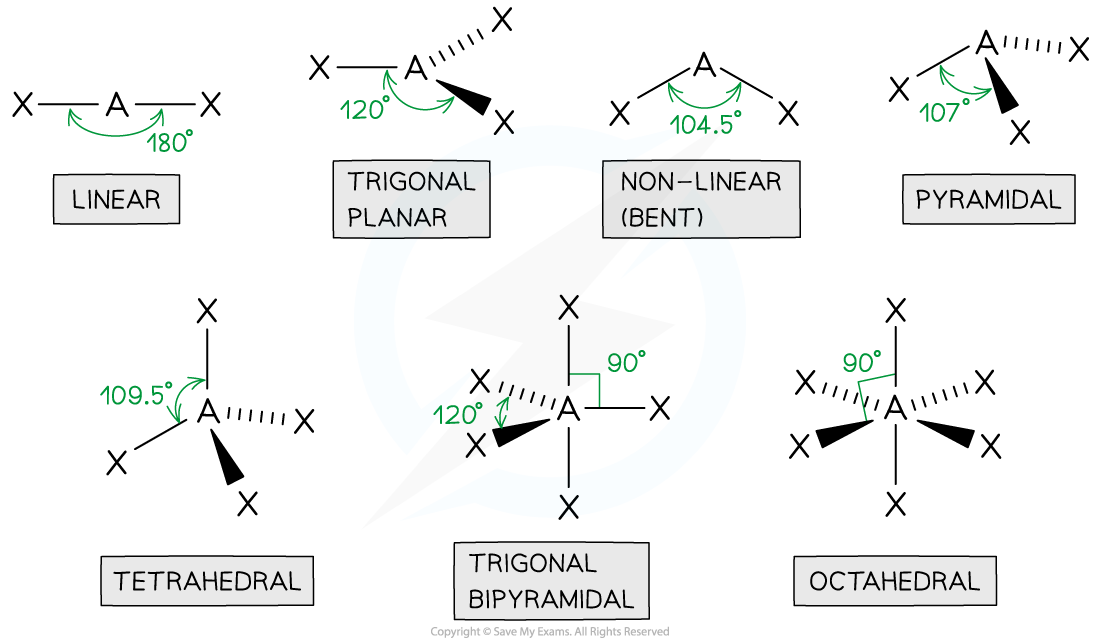
pyramidal
3 bonded pair
1 lone pair
bond angle is 107
1 in the centre with 3 other atoms
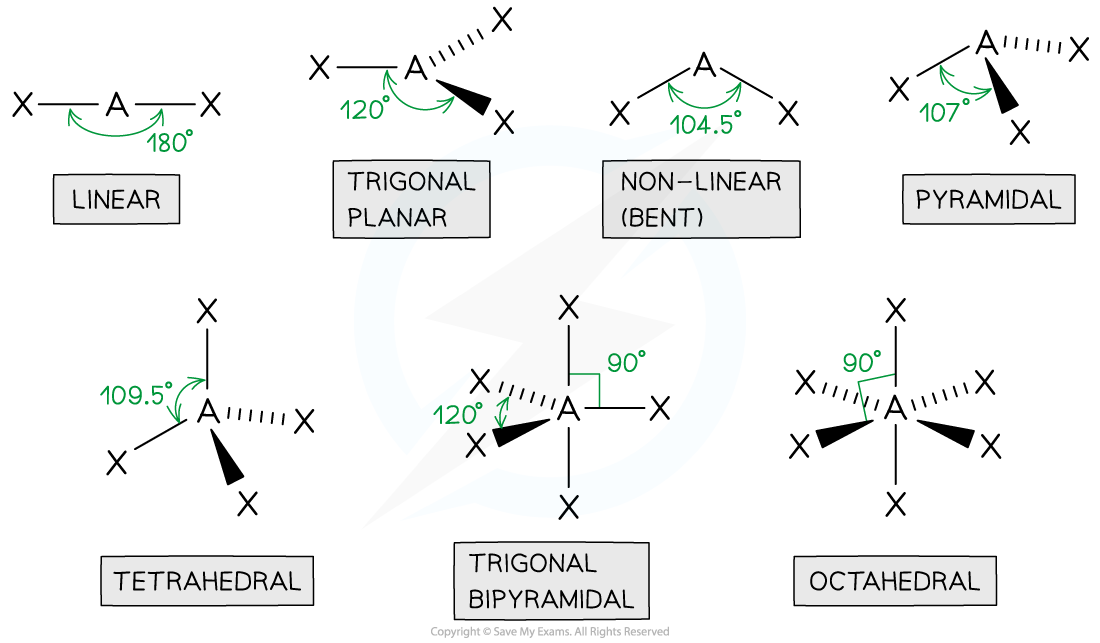
non linear
2 bond pairs
2 lone pairs
bond angle of 104.5
1 centre atom with 2 joined
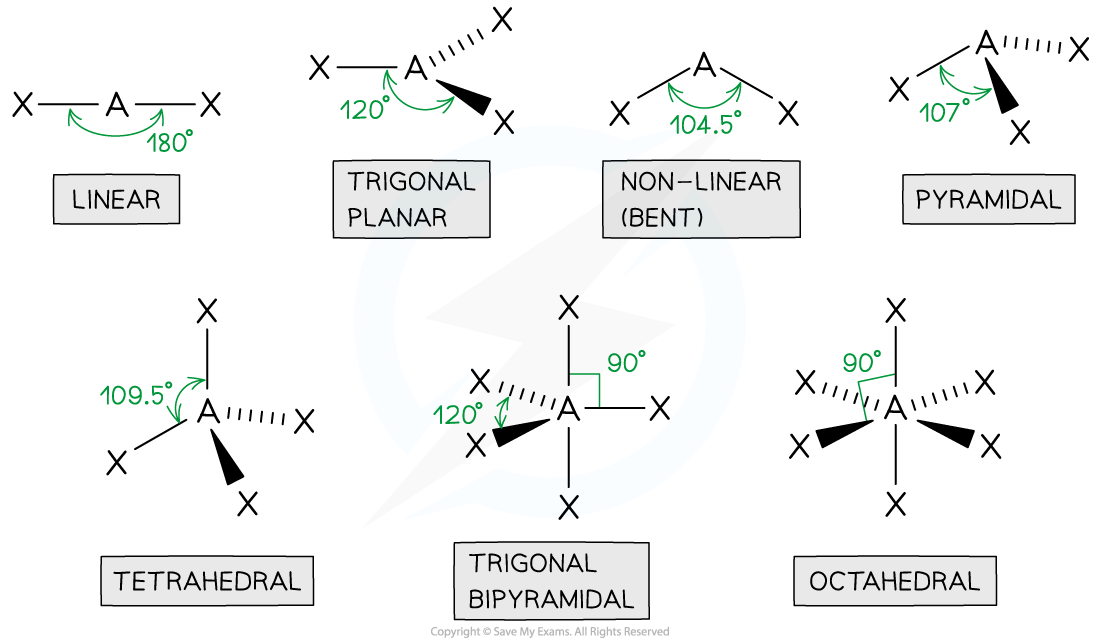
linear
2 bonded pairs
bond angle of 180
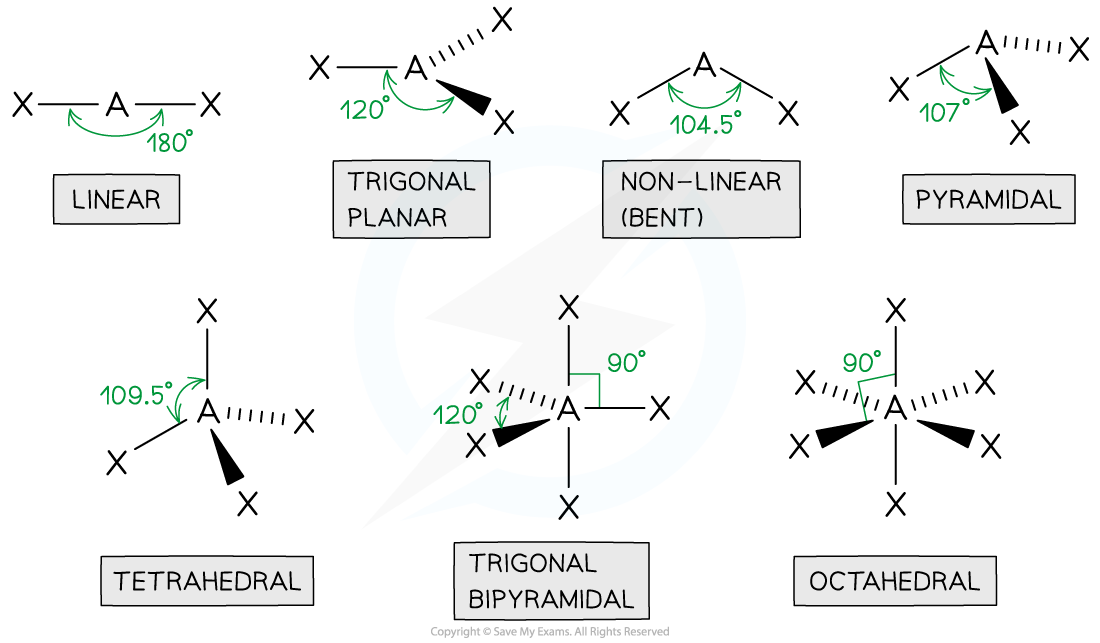
trigonal planar
3 bonded pairs
bond angle of 120
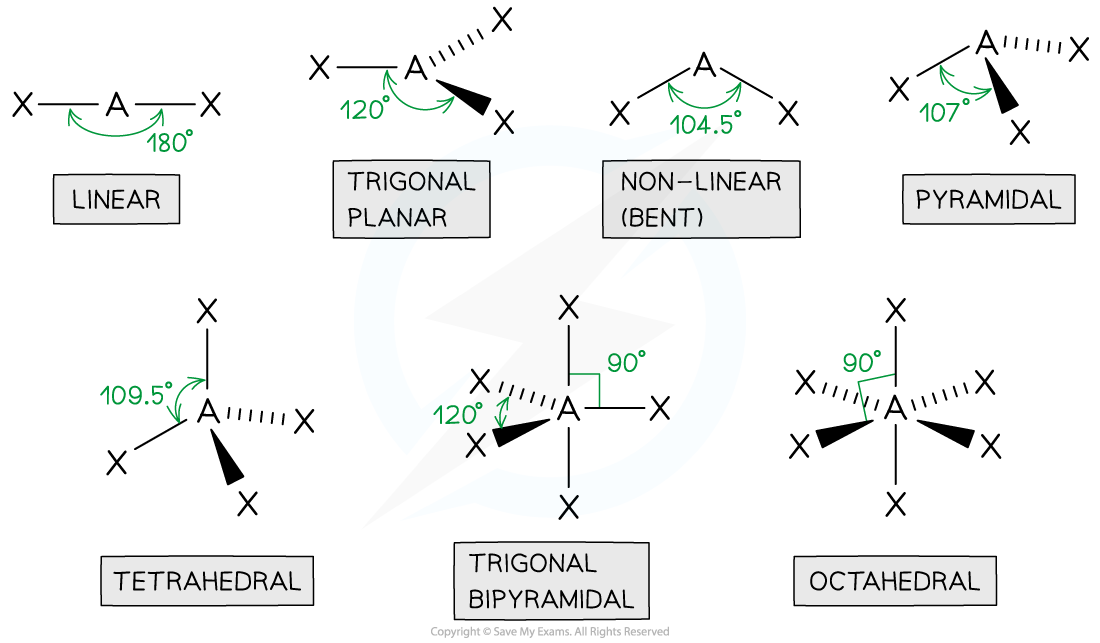
octahedral
5 bonded pairs
bond angle of 90
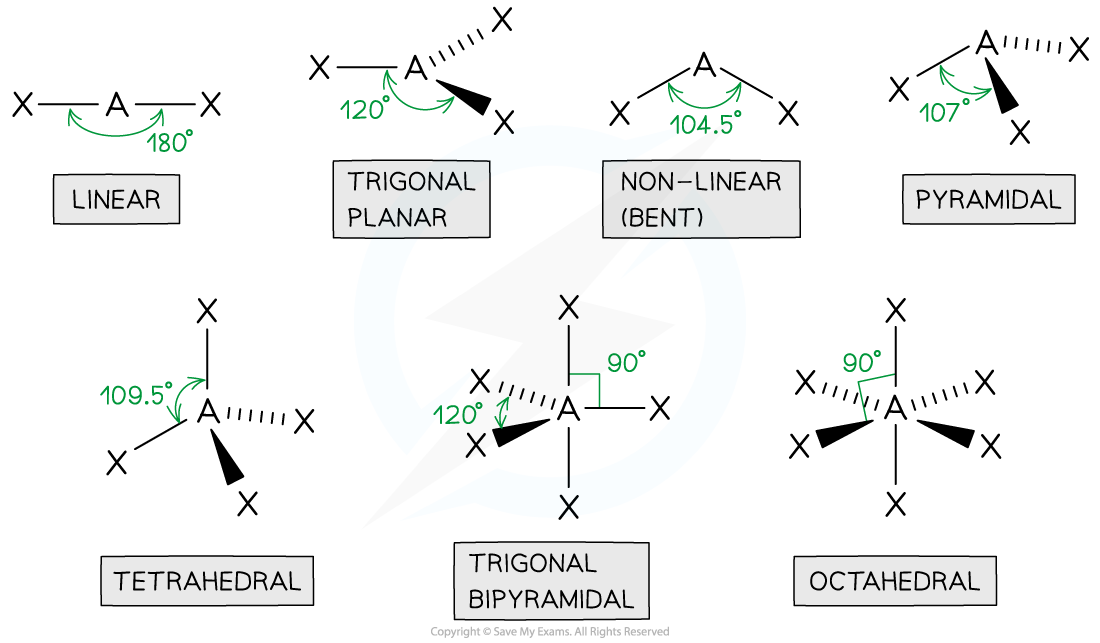
electron repulsion theory
predicts the arrangement of electron pairs around the central atom of unfamiliar molecules and ions
shape of molecules: electron pairs
the greater the number of electron pairs the smaller the bond angle as there is more repulsion
lone pairs repels more strongly than bonded paits
electrons pairs tends to repel each other as far as possible
intermolecular forces
in between
3 types of intermoleculare forces
induced dipole dipole interaction (weakest)
permanent dipole dipole interaction
hydrogen bonding (strongest)
induced dipole dipole interactions