IMED1003 - Cholesterol Absorption (1)
1/10
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
11 Terms
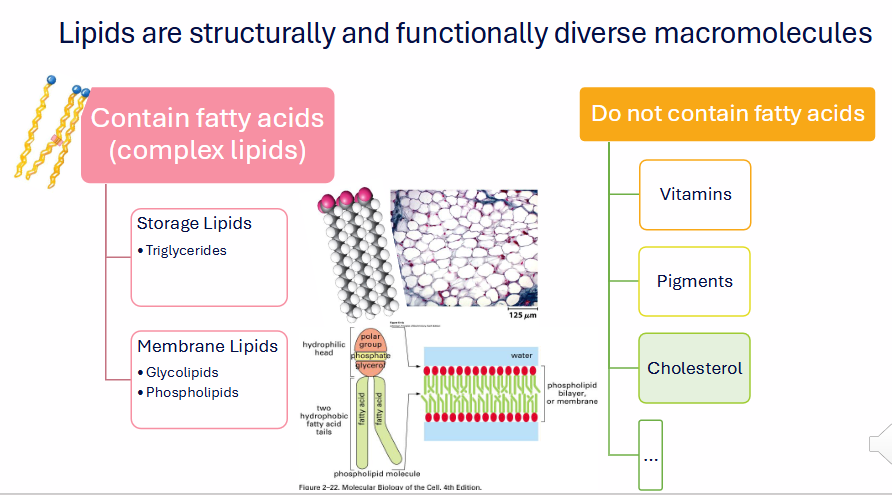
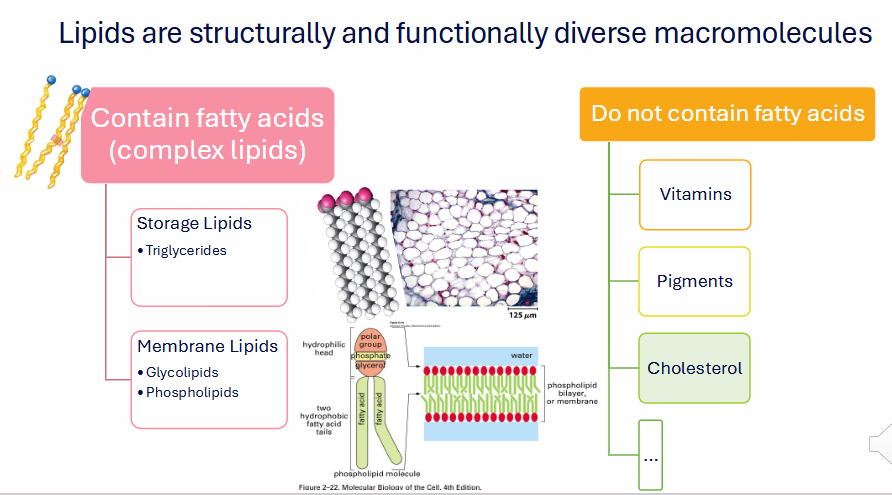
Lipids are structurally and functionally diverse macromolecules
COMPLEX FATTY ACIDS (COMPLEX LIPIDS)
- Storage Lipids: Triglycerides
- Membrane Lipids: Glycolipids and Phospholipids
DO NOT CONTAIN FATTY ACIDS:
- Vitamins
- Pigments
- Cholesterol
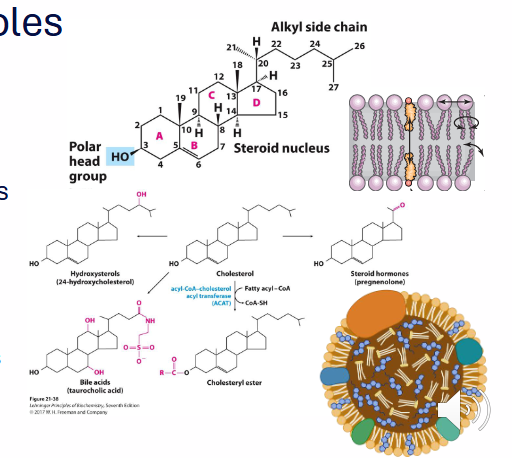
Cholesterol Structure
- sterol made by animals (including humans)
- membrane component
- production of other molecules (Vitamin D, steroid hormones, Bile Salts)
- Lipoprotein particles (mobilisation, transport of lipids in bloodstream)
DIAGRAM ON SLIDE 4
- its a molecule with a hydroxyl group (polar head) and steroid nucleus (made of 4 fused cyclohexane rings)
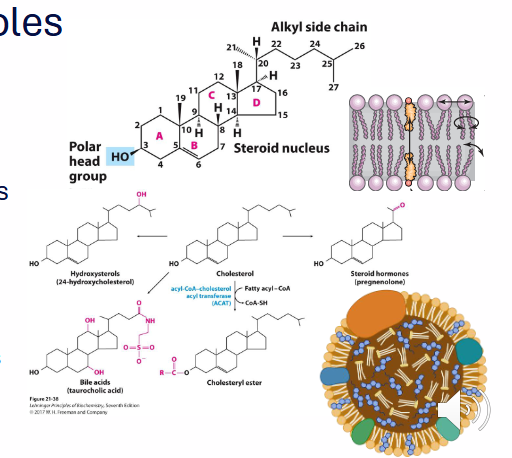
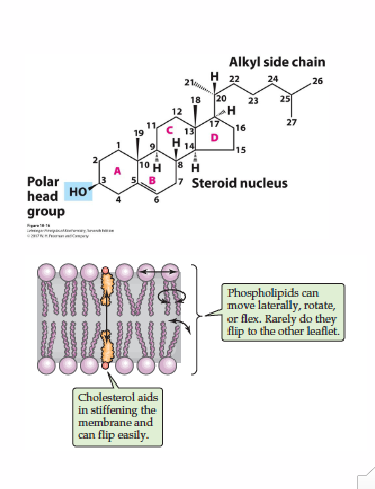
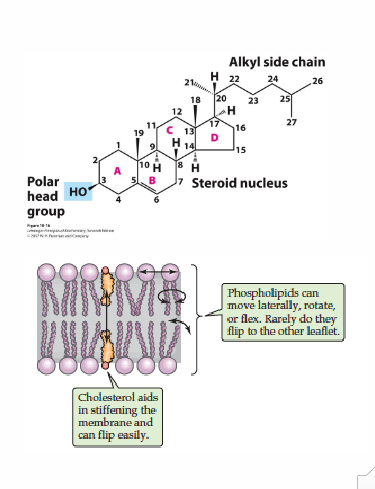
Major Role of Cholesterol - Membrane Component
- 85% of cholesterol in body is used as a membrane component
- interacts with fatty acids in phospholipid membrane
- decreases membrane fluidity, permeability
- component of subcellular membranes (nucleus, mitochondria, endoplasmic reticulum, golgi apparatus, lysosome, vesicles)
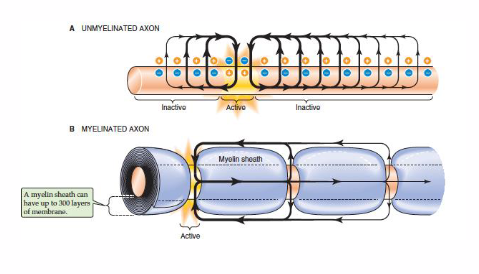
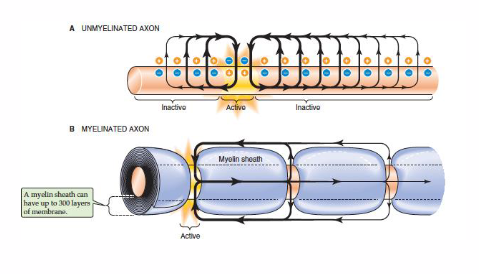
Myelin sheath is rich in cholesterol
- Composition: 40% in cholesterol
- Decreased membrane permeability (whcih is good because we want the impulse to jump)
- role as insulation of axons facilitates efficient signalling in neurons
- Brain: tissue containing most cholesterol
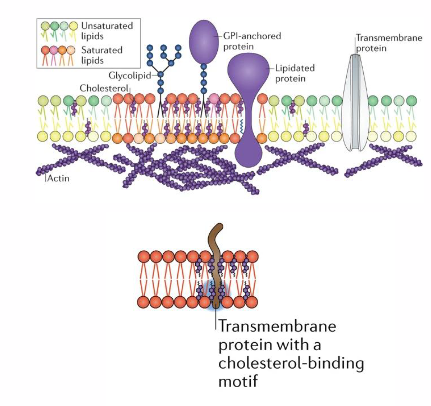
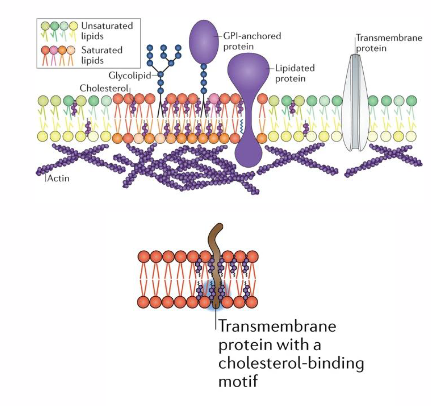
Cholesterol facilitates membrane function, including cell signalling
- molecules within membrane are organised into functional "microdomains"
- Lipid rafts: regions of increased stability due to composition of lipids (these are the microdomains)
Cholesterol:
- enhances membrane stability: increased packing and order
- binds to specific proteins: organising the membrane
- important for cell signalling
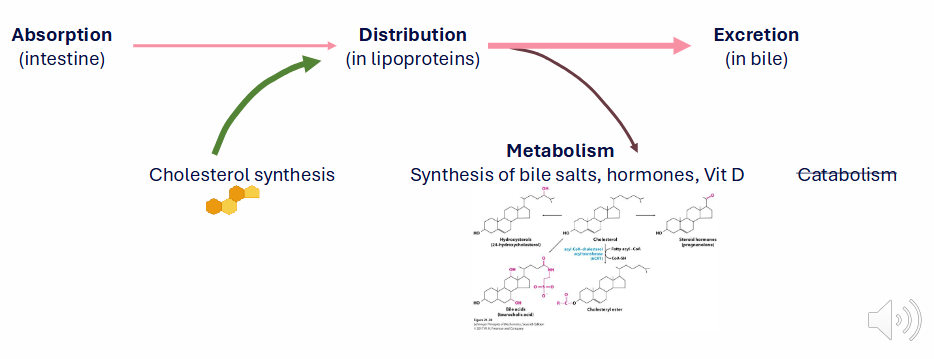
Cholesterol Homeostasis
SOURCES:
- dietary (minor)
- synthesis (major)
HYDROPHOBIC: requires lipoproteins for transport in bloodstream. excess of some plasma lipoproteins causes cardiovascular disease
EXCESS CHOLESTEROL IS EXCRETED:
- humans can not catabolise
- homeostasis requires regulation of sources, utilisation and excretion
Cholesterol ADME
DIAGRAM ON SLIDE 10
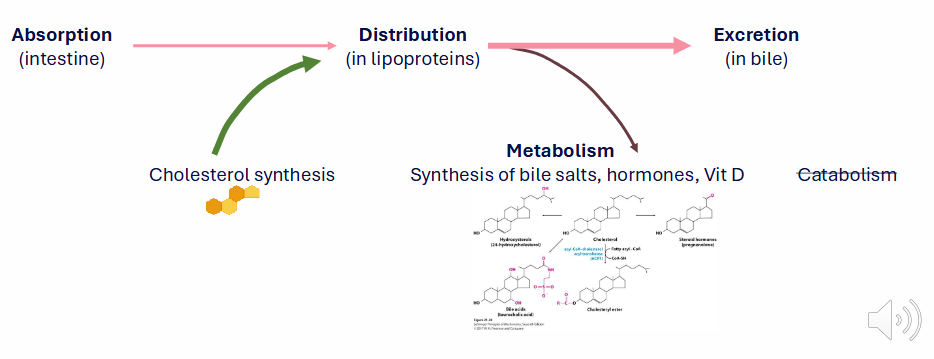
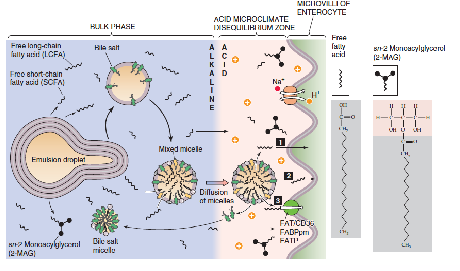
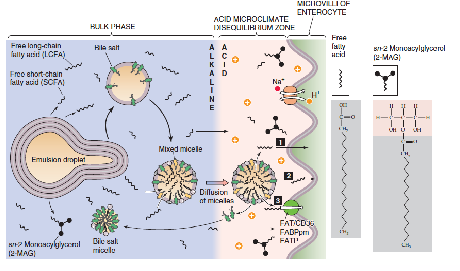
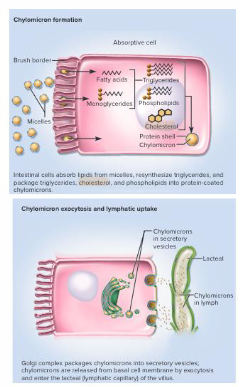
Absorption of dietary fats requires bile salts
- dietary fats are emulsified by bile acids in the small intestine
- Enterocytes: absorptive cells of small intestine
- in general cholesterol exists in the non-esterified form (unless you eat a lof of animal livers)
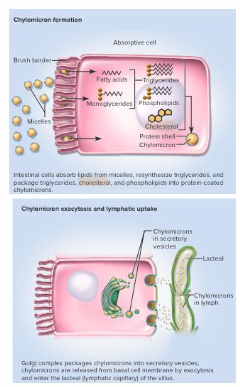
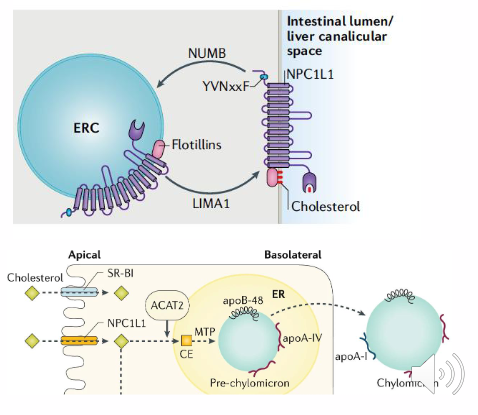
Enterocytes absorb dietary cholesterol
- Absorb cholesterol, secrete lipoproteins
- absorb cholesterol from micelles
- esterify cholesterol (CE)
- secrete cholesterol in lipoproteins
- Lipoproteins transported in CE in bloodstream
- excrete free cholesterol, other sterols, into gut
- enterocytes absorb them on the apical side and secrete packaged cholesterol on the basolateral side to be taken up by lympathic system
- this cholesterol ester (CE) is packaged in a chylomicron
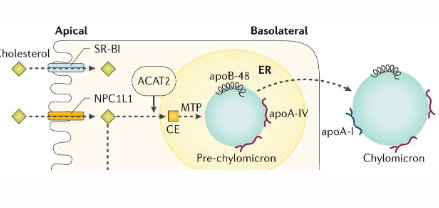
Enterocytes - Mechanism of Absorption
NIEMANN-PICK TYPE C1-LIKE 1 receptor (NPC1L1):
- Apical side
- Binds cholesterol in intestinal lumen
Acyl-CoA cholesterol acyltransferase (ACAT):
- esterifies cholesterol to cholesteryl esters (CE)
Secretes CE in chylomicrons:
- chylomicrons comprised of lipids, proteins
- constructed in ER
- requires microsomal triglyceride transfer protein (MTP)
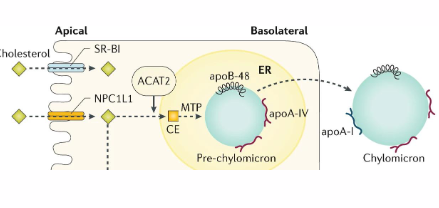
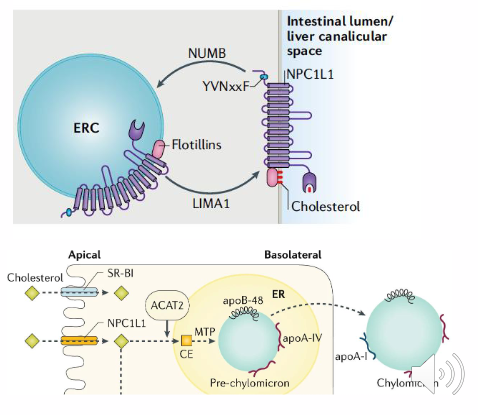
Enterocytes - Regulation of Absorption
NPC1L1 RECEPTOR:
- imports cholesterol via endocytosis
- activated by low cholesterol
- inactivated by high cellular cholesterol
ACAT:
- esterified cholesterol for construction of CM
- activated by high cholesterol
- promotes storage of excess cholesterol in cell (lipid droplets)