#1: the history of life on earth.
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
24 Terms
ecology
the study of the relationships between living organisms, including humans, and their physical environment
4.6 billion years
age of earth
nitrogen, nitrogen oxides, carbon dioxide, methane, ammonia, hydrogen, hydrogen sulfide
chemicals that created small organic molecules, leading to the evolution of life
RNA
ribonucleic acid; the nucleic acid that was probably the first genetic material
protobiont
collections of chemicals trapped within membranes
DNA
deoxyribonucleic acid; more stable repository for genetic information because it is double-stranded
prokaryote
single-celled organism with no nuclei
Archaean Eon
3.9 to 3.5 billion years ago, when prokaryotes entered the picture
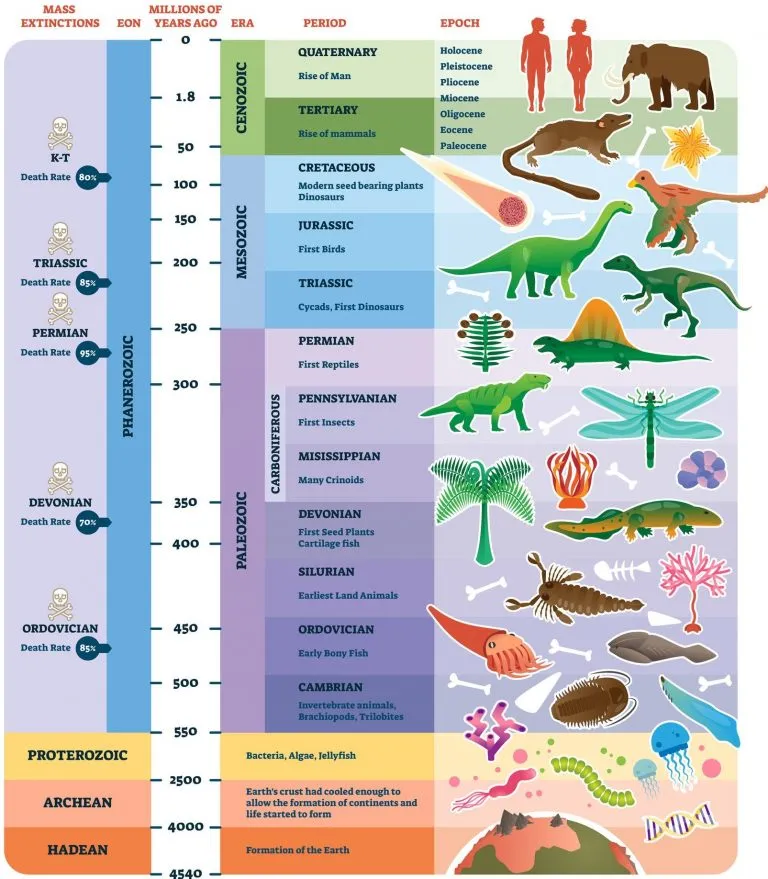
eons, eras, periods, epochs
divisions of time, from longest to shortest
cyanobacteria
a prokaryote that increased the amount of oxygen gas in the atmosphere through photosynthesis
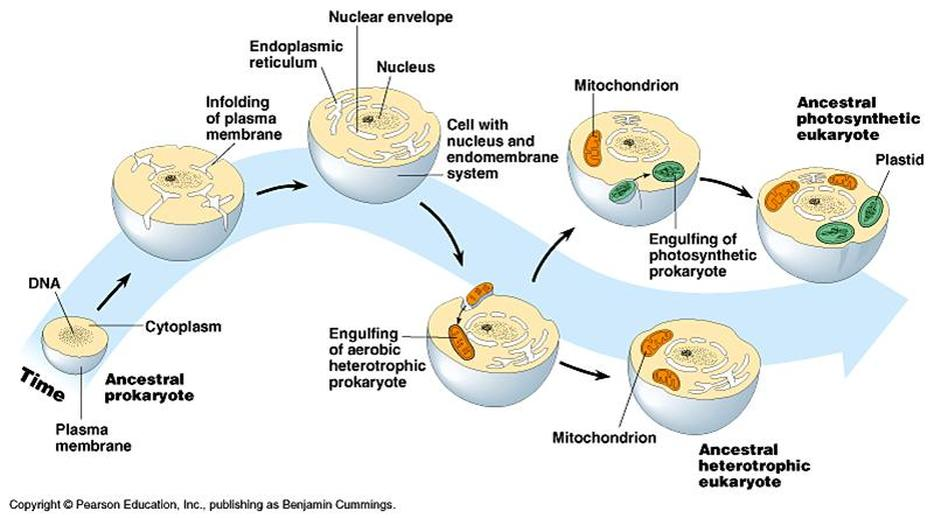
eukaryotes
debuted 2.1 billion years ago
endosymbiosis
one prokaryote parasitized another prokaryote, or maybe just ate it but forgot to digest it
Cambrian Explosion
535 million years ago; major biological golden age when the diversity of all animal life on earth exploded
Ordovician Period
500 million years ago; plants, animal, and fungi started colonising land, probably as a strategy for escaping predation
Devonian Period
365 million years ago; tetrapods and arthropods showed up on land
Carboniferous Period
359-299 million years ago; forests were so dense and widespread that they made all our fossil fuels (35% oxygen in the atmosphere instead of the normal 21%)
Permian Period
299-251 million years ago; all the land masses of the world joined to form one giant continent (Pangaea)
gymnosperms
first plants with seeds like modern pines, spruces, and firs
archosaur
ancestor of dinosaurs and modern birds
Permian-Triassic Extinction Event
252 million years ago; 96% of all marine species and 76% of terrestrial vertebrate species bought the farm and the only known mass extinction of insects (57% of all taxonomic families and 83% of all genera became extinct); most significant extinction event on the planet
niche
combination of living and non-living resources they use to survive
Jurassic Period
199-145 million years ago; huge herbivorous dinosaurs roamed the earth with smaller, carnivorous dinosaurs
co-evolution
reciprocal evolutionary change in a set of interacting populations over time resulting from the interactions between those populations
Cretaceous–Paleogene Extinction Event
KT Extinction; 66 million years ago; mass extinction of three-quarters of the plant and animal species