ecology study guide
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/44
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
45 Terms
1
New cards
Give the levels of organization from biggest to smallest.
organism → any individual living thing \n population → a group of the same species living together \n community → a group of organisms living in a given area \n ecosystem → includes all biotic and abiotic factors in a given area \n biome →major regional or global community; characterized by specific climate conditions & plant communities \n biosphere → the world
2
New cards
Explain the difference between biotic and abiotic factors. Give an example of each.
biotic: living things that play key roles in an ecosystem
abiotic: nonliving things that determine which living things can survive in a particular environment
abiotic: nonliving things that determine which living things can survive in a particular environment
3
New cards
What is a keystone species? Provide an example.
holds an ecosystem together. ex: beavers
4
New cards
The ultimate source of energy in most ecosystems comes from the \___.
sun
5
New cards
Describe the process of chemosynthesis. Where do most organisms live that utilize this type of process?
make their food from inorganic compounds. use this due to lack of sunlight
6
New cards
Explain the difference between a food chain and a food web.
food chain: the simplest way to look at energy flow in an ecosystem
food web: shows the complex networks of energy transfer. multiple food chains combined
food web: shows the complex networks of energy transfer. multiple food chains combined
7
New cards
Draw a basic food chain and label the primary producer, primary consumer, secondary consumer, and tertiary consumer.
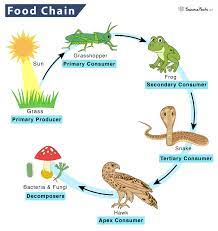
8
New cards
In your food chain that you drew for Question \#7, pretend that the primary consumer starts with 125,000 Joules of energy. How many Joules of energy do the other trophic levels in your food web have?
secondary consumer: 12,500 joules of energy. tertiary consumer: 1,250 joules of energy. apex consumer: 125 joules of energy.
9
New cards
Explain the differences between a generalist and a specialist. Provide examples of each.
generalist: consumers with a varying diet
specialist: consumers that feed on one specific organism or a small number of organisms
specialist: consumers that feed on one specific organism or a small number of organisms
10
New cards
What do the following organisms eat?
herbivore - eat plants
carnivore - eats the flesh of animals
omnivore - eats plants, animals, and fungi
detritivore - eat detritus
decomposer - eats dead/decaying organisms
carnivore - eats the flesh of animals
omnivore - eats plants, animals, and fungi
detritivore - eat detritus
decomposer - eats dead/decaying organisms
11
New cards
Diagram and label the 4 steps of the water cycle.
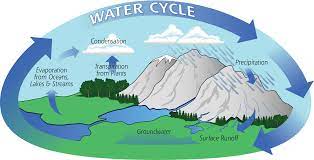
12
New cards
Briefly explain the carbon cycle.
nature's way of reusing carbon atoms, which travel from the atmosphere into organisms on the Earth and then back into the atmosphere over and over again
13
New cards
Explain the nitrogen cycle. Be sure to include the words ammonia, nitrate, nitrogen fixation, nitrogen gas, denitrification, and assimilation.
the nitrogen cycle is the process by which nitrogen is converted into different forms that can be used by living organisms. nitrogen fixation is the process by which nitrogen gas is converted into ammonia by bacteria. ammonia is then converted into nitrate by bacteria in a process called nitrification. plants can then assimilate the nitrate and use it to build proteins. when organisms die, decomposers break down the proteins and release ammonia back into the soil. denitrification is the process by which bacteria convert nitrate back into nitrogen gas, which is released into the atmosphere.
14
New cards
What organism is primarily responsible for nitrogen fixation? What else fixes nitrogen besides this organism (in other words, what other phenomena also fixes nitrogen)?
bacteria. decaying matter.
15
New cards
What organisms are primarily responsible for decomposition?
bacteria and fungi
16
New cards
Only about _% of energy gets transferred from one trophic level to the next in any ecosystem. The rest gets lost as _.
10%; waste
17
New cards
Explain the difference between a habitat and a niche. Provide an example of each for an organism of your choice.
habitat: describes the biotic and abiotic factors or the area; where does it live?
niche: describes the factors that an organism needs to survive; how does it live?
niche: describes the factors that an organism needs to survive; how does it live?
18
New cards
Explain the 2 outcomes of competitive exclusion. (HINT - I am not referring to death!)
1. niche partitioning: utilizes different resources based on competitive advantages
2. evolutionary response: divergent evolution leading to different physical features
19
New cards
What are ecological equivalents? Give an example.
species that occupy similar niches, but live in different geographic locations. ex: mantella frog in madagascar and the poison dart frog in south america
20
New cards
Explain the difference between intraspecific and interspecific competition. Provide examples of each.
intraspecific: between members of the same species. ex: two male deer competing for mates
interspecific: between members of the different species. ex: competition between lions and leopards that vie for similar prey
interspecific: between members of the different species. ex: competition between lions and leopards that vie for similar prey
21
New cards
Explain the 3 types of symbiosis and give examples of each.
1. mutualism: interaction where both (or many) organisms benefit. ex: an ant, butterfly caterpillar, and acacia tree in the american southwest
2. commensalism: one organism benefits, and the other isn't affected. ex: phoretic mites on a damsel fly
3. parasitism: one organism benefits and the other is harmed. ex: heartworms and humans
22
New cards
Diagram and label the 3 types of population distribution/dispersion.
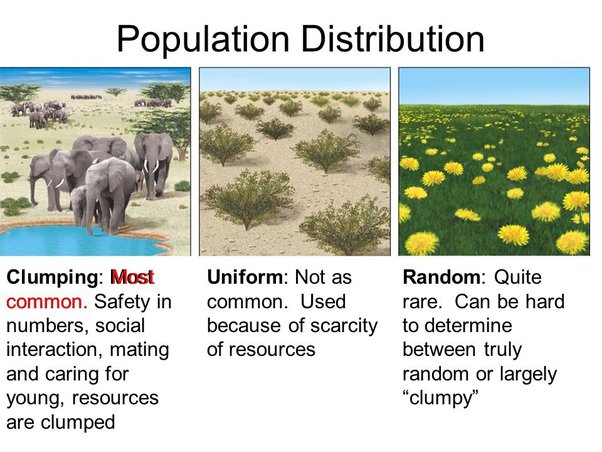
23
New cards
Diagram the 3 types of survivorship curves. Explain the reproductive strategies for organisms that exhibit each type and provide an example of an organism that exhibits each type of curve.
type 1: late loss, high survivorship throughout life; type 2: constant loss, independent of age; type 3: early loss, low mortality after maturity
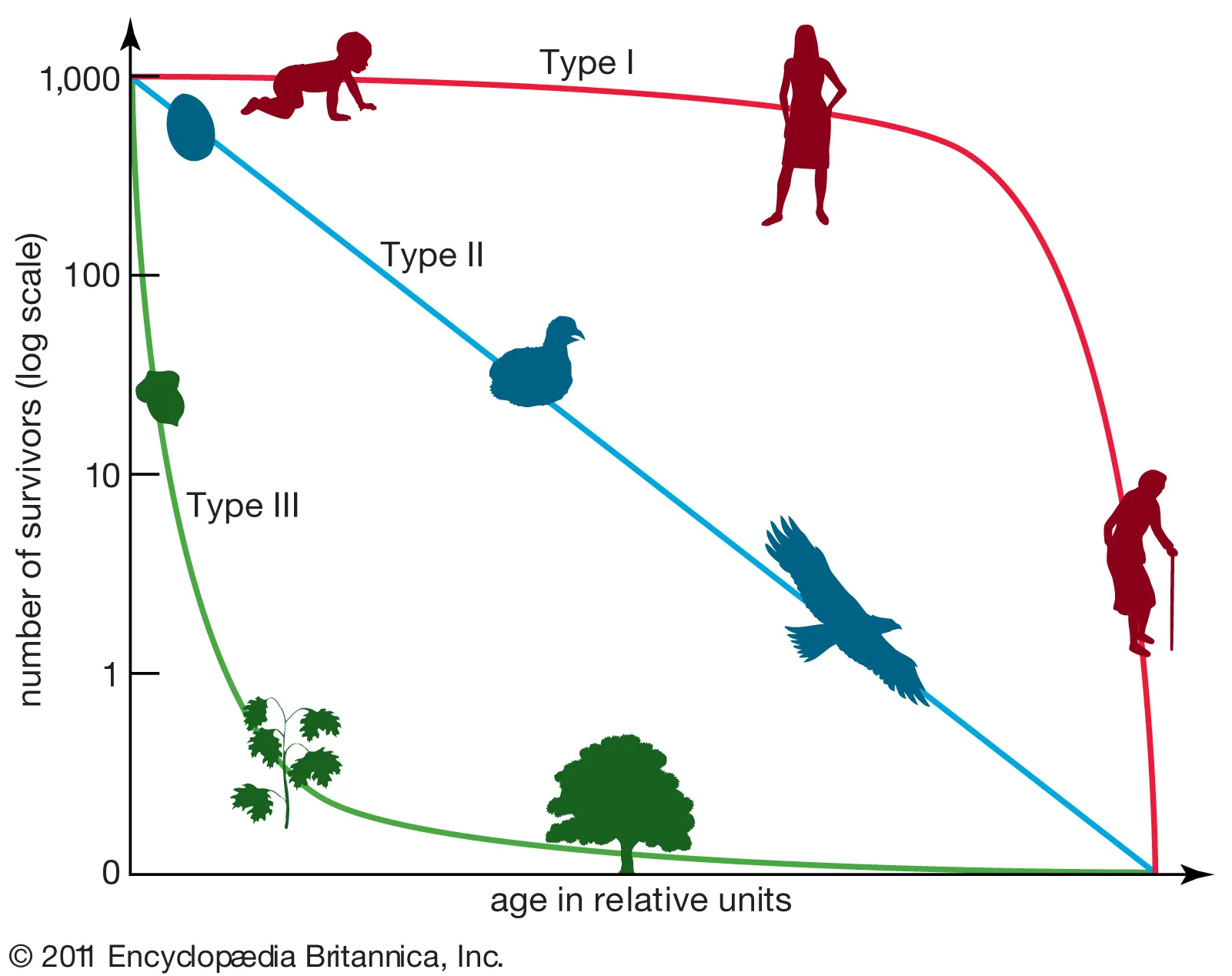
24
New cards
What 4 factors affect population size?
1. immigration
2. births
3. emigration
4. deaths
25
New cards
Diagram exponential and logistic growth. Make sure you include carrying capacity (K)!
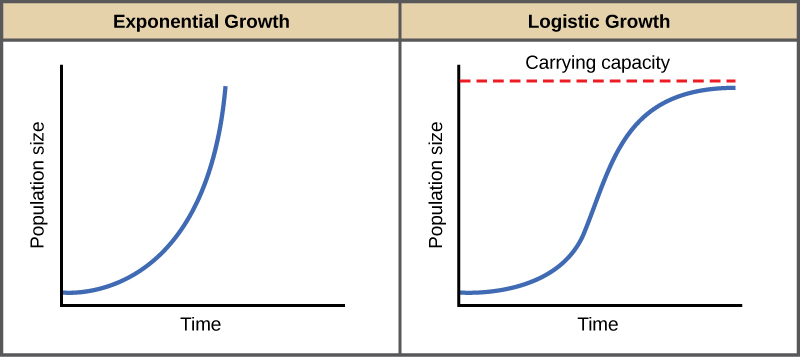
26
New cards
What is carrying capacity (K)?
the maximum \# of individuals an environment can hold
27
New cards
Explain the difference between a density-dependent limiting factor and a density-independent limiting factor. Provide examples of each.
density-dependent limiting factor: are affected by the number of individuals in a given area (competition, predation, parasitism, disease)
density-independent limiting factor: are aspects of the environment that can affect a population regardless of its size (unusual weather, natural disasters, human activities)
density-independent limiting factor: are aspects of the environment that can affect a population regardless of its size (unusual weather, natural disasters, human activities)
28
New cards
Explain the difference between primary and secondary succession and provide examples of each.
primary succession: establishment and development of an area that was previously uninhabited (takes longer). ex: cooled molten lava
secondary succession: the establishment of a damaged ecosystem in an area where the solid was left intact (less time needed). ex: forest fire
secondary succession: the establishment of a damaged ecosystem in an area where the solid was left intact (less time needed). ex: forest fire
29
New cards
What is a pioneer species? What organisms are the pioneer species of primary succession? What organisms are the pioneer species of secondary succession?
organisms that are the first to appear. primary succession: lichens or mosses; secondary succession: annual plants, grass, and perennials
30
New cards
What are the 4 systems of Earth?
1. biosphere: part of the earth where life exists
2. hydrosphere: all water, ice, and water vapor on earth
3. atmosphere: air on earth's solid and liquid surface
4. geosphere: geologic features of the earth
31
New cards
Explain the difference between climate and microclimate.
climate: long-term pattern of weather conditions in a region (forest)
microclimate: climate of a small specific place within a larger area (hole in a decaying log in the forest)
microclimate: climate of a small specific place within a larger area (hole in a decaying log in the forest)
32
New cards
Diagram the 3 climate zones of Earth.
1. polar: northern & southern reaches of the earth
2. temperate: broad areas between the polar & tropical zones
3. tropical: surrounds the equator
33
New cards
What are the 3 main influences of climate?
1. sunlight → surface is heated unevenly due to curvature of the earth (diff. temps.)
2. air/water movement → air & water is heated; causes movements (water currents & wind fronts)
3. landmasses → areas surrounded by land have larger changes in temp. during the seasons, not so much when closer to bodies of water; mountains moist side & dry side due to rain
34
New cards
What are some concerns about human population growth?
we don't know the carrying capacity for humans on earth, we will run out of resources
35
New cards
Explain the difference between renewable and nonrenewable resources. Provide examples of each.
renewable: resources that can be replenished faster than they are used
nonrenewable: resources that are used faster than they form
nonrenewable: resources that are used faster than they form
36
New cards
Provide some examples of pollutants.
undesirable factors that are added to air, water, or soil. affect air, water, and soil quality
37
New cards
What is smog? What is acid rain?
smog: pollution that is caused by the interaction of sunlight with fossil fuel emissions
acid rain: occurs when chemicals fuel emissions enter the water cycle and drop the pH of the rainwater
acid rain: occurs when chemicals fuel emissions enter the water cycle and drop the pH of the rainwater
38
New cards
Explain the greenhouse effect. Why is it beneficial to us? What are the 3 main greenhouse gasses?
some light gets trapped in the greenhouse gases. these gasses act like a blanket that keeps earth at a stable temperature.
1. carbon dioxide
2. water vapor
3. methane
1. carbon dioxide
2. water vapor
3. methane
39
New cards
What is global warming?
increase of heat being trapped and increasing the average temperature of our planet
40
New cards
What are the impacts that the hole in our ozone layer has on our planet and the organisms living here?
increased uv radiation levels. increases in certain types of skin cancers, eye cataracts, and immune deficiency disorders
41
New cards
What are indicator species? Provide an example.
an organism whose presence, absence, or abundance reflects a specific environmental condition. ex: lichen and mayflies
42
New cards
Explain the process of biomagnification. Use DDT as your example.
occurs when a pollutant moves up a food chain and accumulates in higher concentrations in the bodies of predators. DDT: bald eagles were poisoned with DDT when they ate the contaminated fish, eggs had thin shells and failed to hatch
43
New cards
What are the 2 main threats to biodiversity? Explain them.
1. habitat fragmentation: occurs when a barrier is formed that prevents an organism from accessing its home range (bc of humans)
2. introduced species: organisms that are brought to an ecosystem as a result of human action (causes damages to the ecosystem due to lack of predators)
44
New cards
What are some ways that we can conserve to help protect our environment?
sustainable development: natural resources are used and managed in a way that meets current and future needs
umbrella species: organisms that are placed under protection, others are positively impacted also
umbrella species: organisms that are placed under protection, others are positively impacted also
45
New cards
What has the government done to help protect our environment?
EPA was created in 1970 to increase awareness of our environment and to conserve the resources that we have. natural parks and endangered species act